Submitted:
19 August 2024
Posted:
20 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methodology
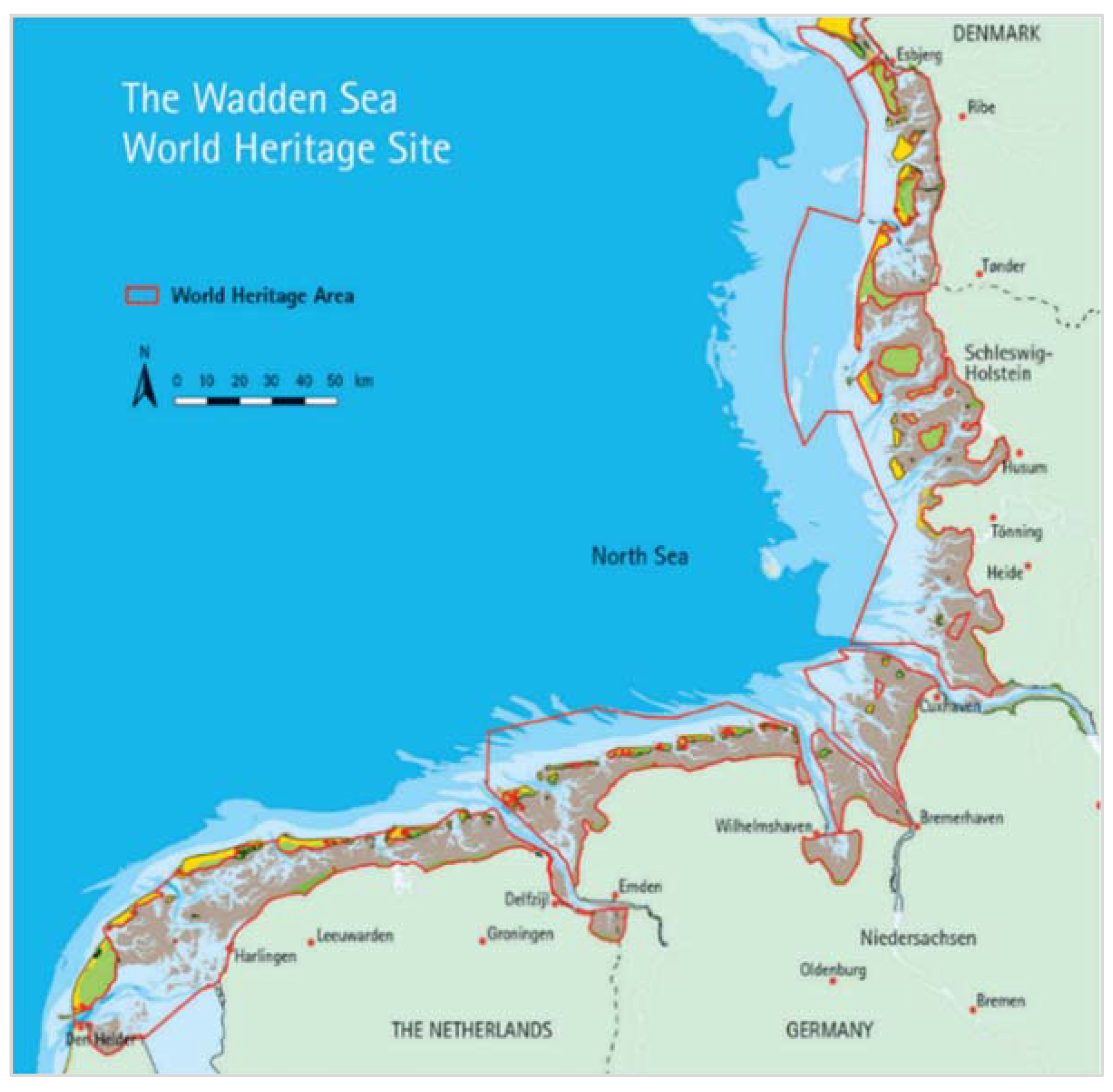
3. Salt Marshes in the Wadden Sea
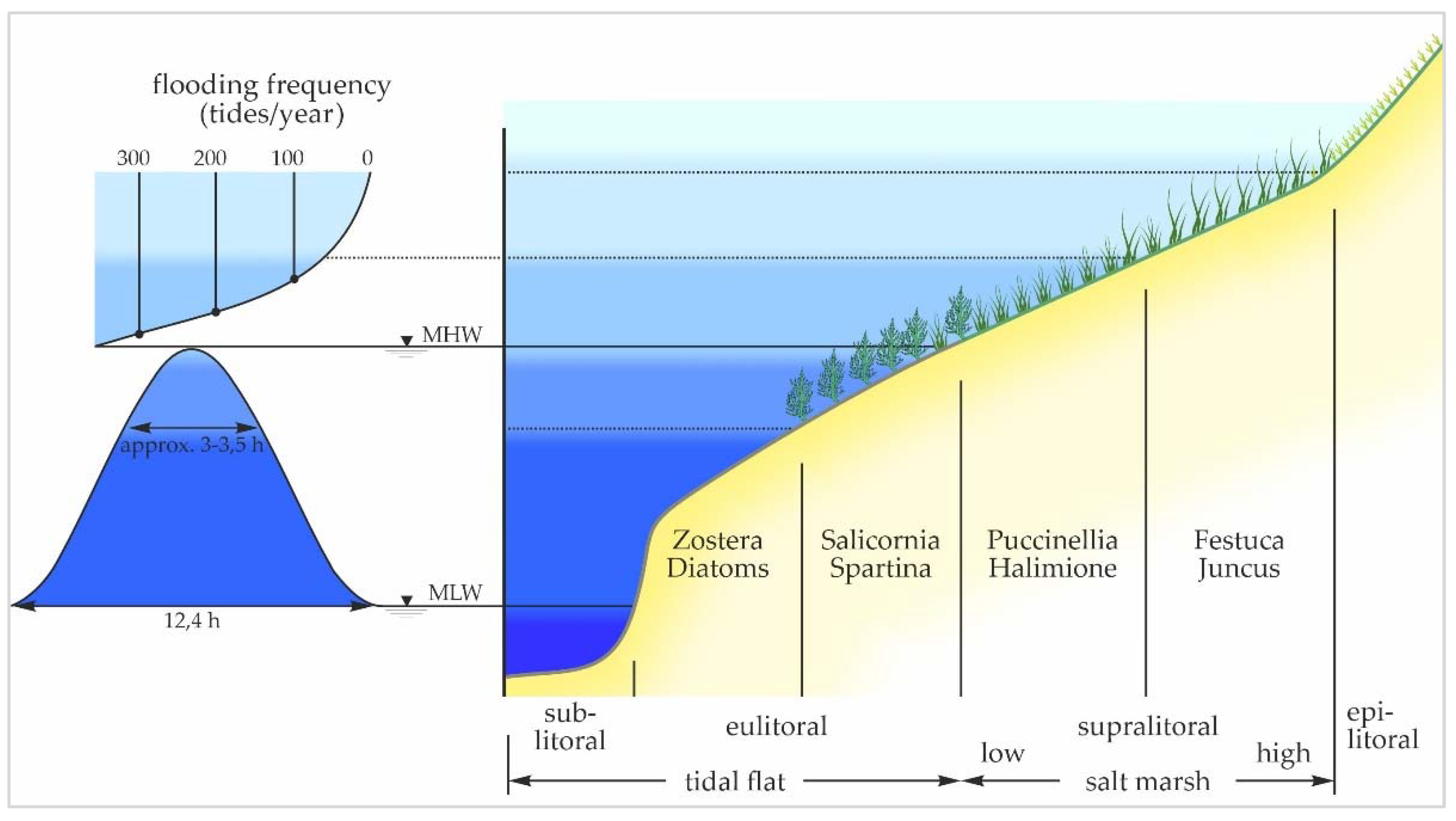
3.2. Salt Marshes
3.3. Biogeomorphological Processes
3.3.1. Sedimentation Processes
3.3.2. Erosion Processes
3.3.3. Drainage System
3.4. Salt Marsh Management
3.4.1. Influence of Management on Sedimentation Processes
3.4.2. Influence of Management on Erosion Processes
3.4.3. Influence of Management on Drainage System
3.5. Impact of Climate Change
4. Hydrodynamic Processes
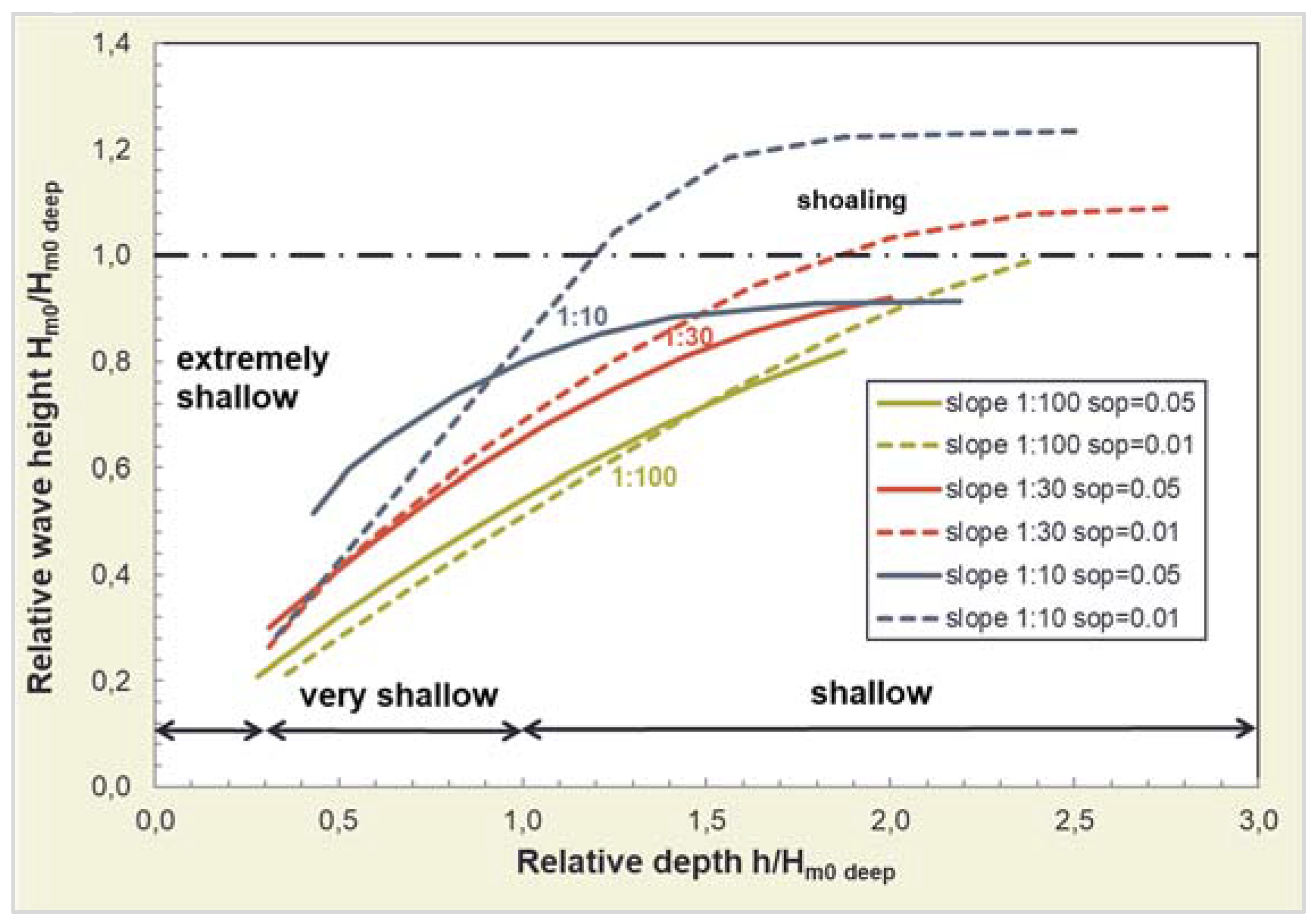
4.1. Effects on Wave Climate
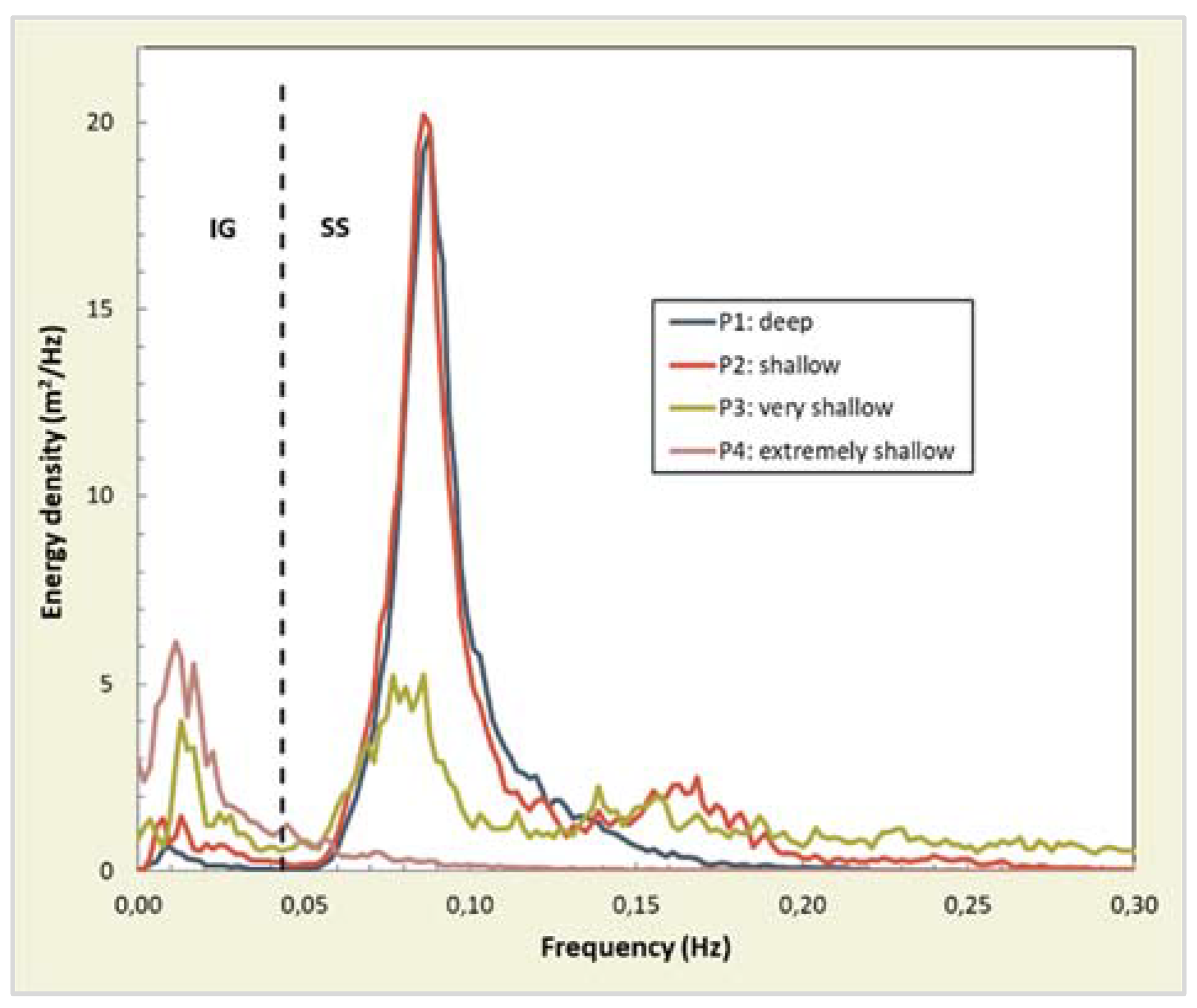
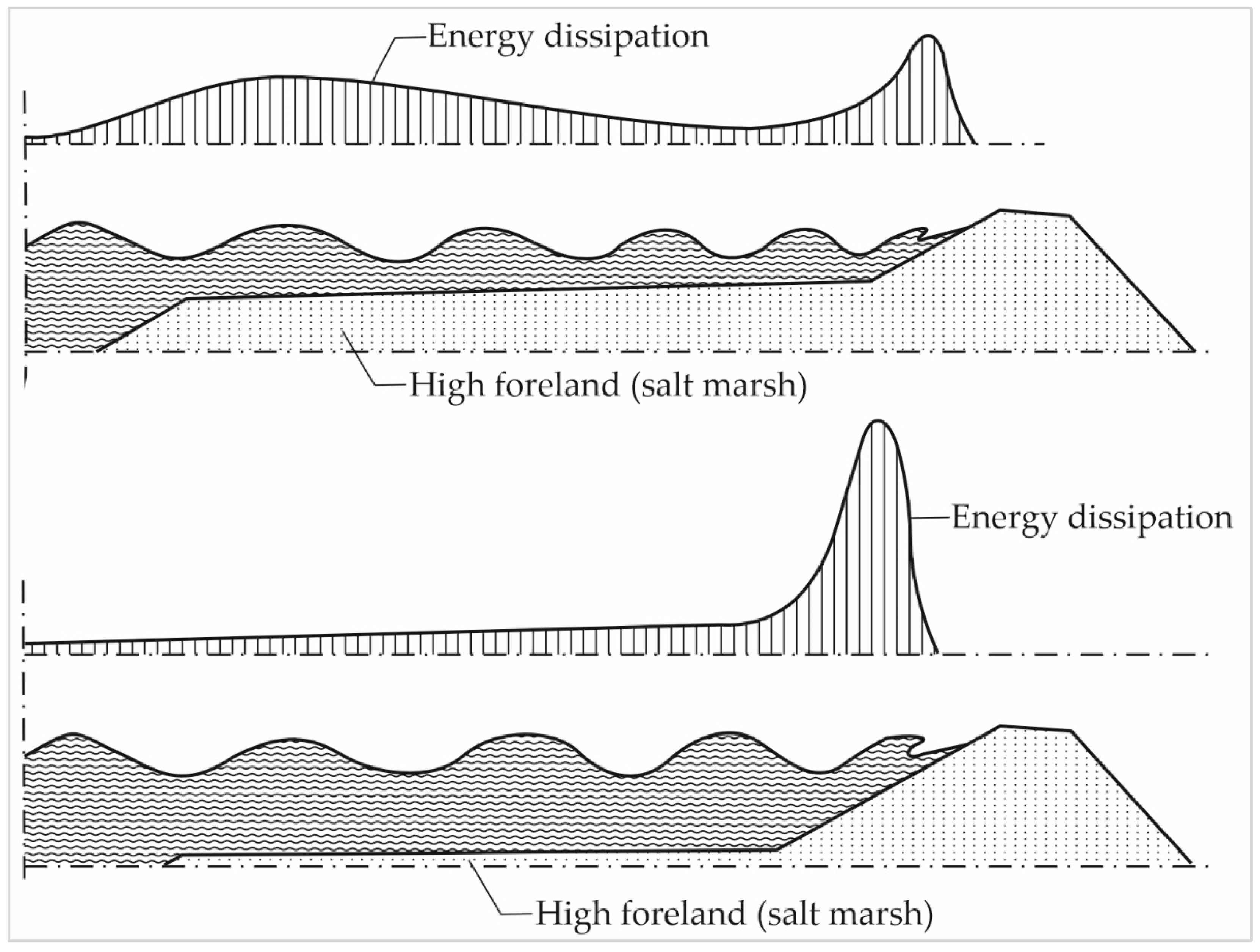
4.1.1. Wave Attenuation by Salt Marshes
4.1.2. Influence of Salt Marsh Geometry on Wave Attenuation
4.1.3. Influence of Vegetation on Salt Marshes on Wave Attenuation
4.2. Limiting Impacts of Dike Breach
5. Management of Salt-Marshes in the Wadden Sea
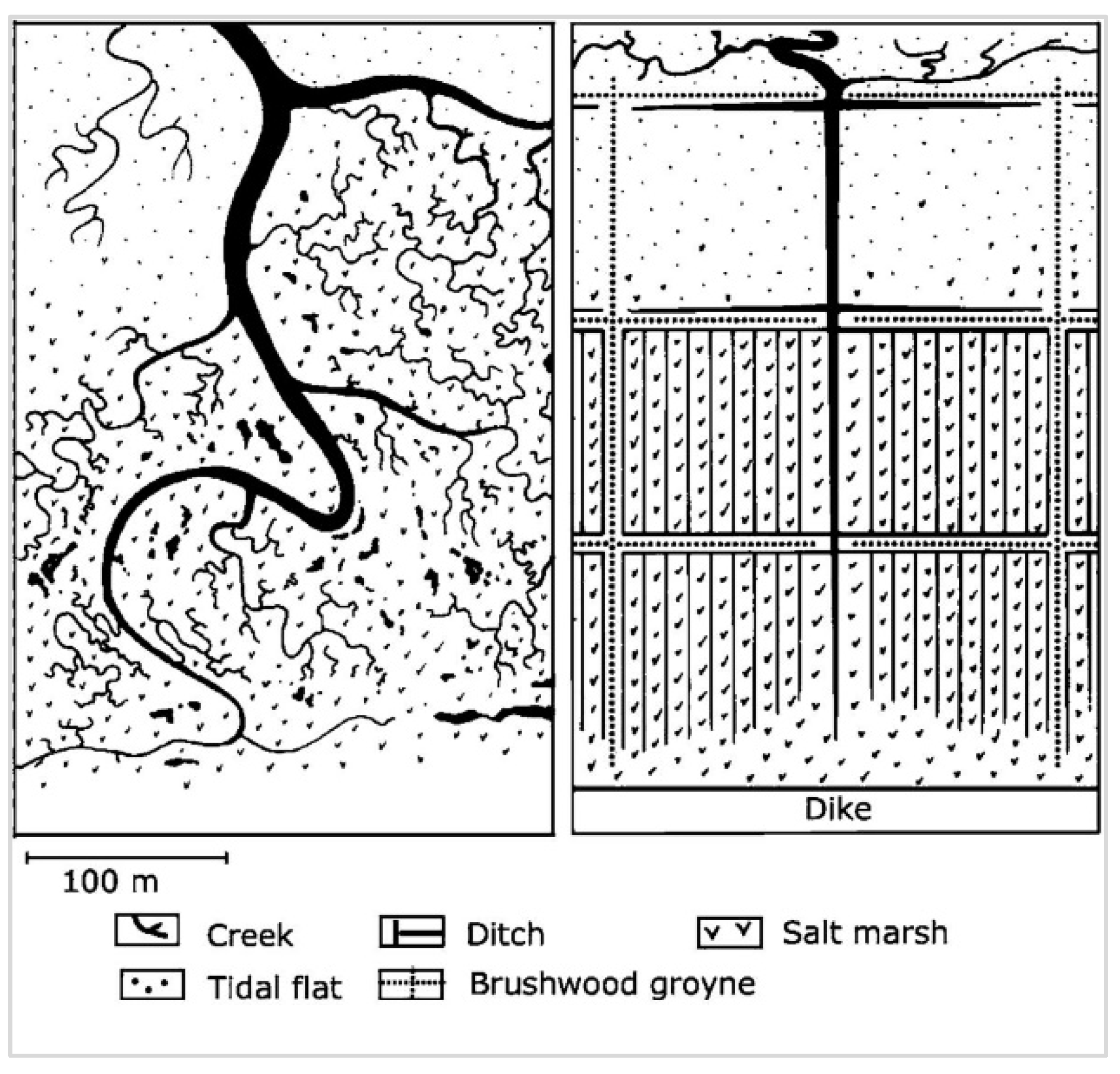
5.1. Salt Marsh Types and Development Goals
"NATURALLY DEVELOPING SALT MARSHES have a drainage system of irregular, winding gullies, a zonation of subtypes reaching from a pioneer zone up to higher saltmarshes and in most cases transition to dunes, and - in the course of time - formations of salt marsh cliffs between older parts on the one side and pioneer zones on the bordering tidal flats on the other. Natural salt marshes can be found on the islands on the landside of dune areas and, in some places, along the mainland coast."
"FORELAND SALT MARSHES are salt marshes which have developed or which development has accelerated through active human interference […]. They are mainly situated in places where natural developments would not have led to salt marsh formation."
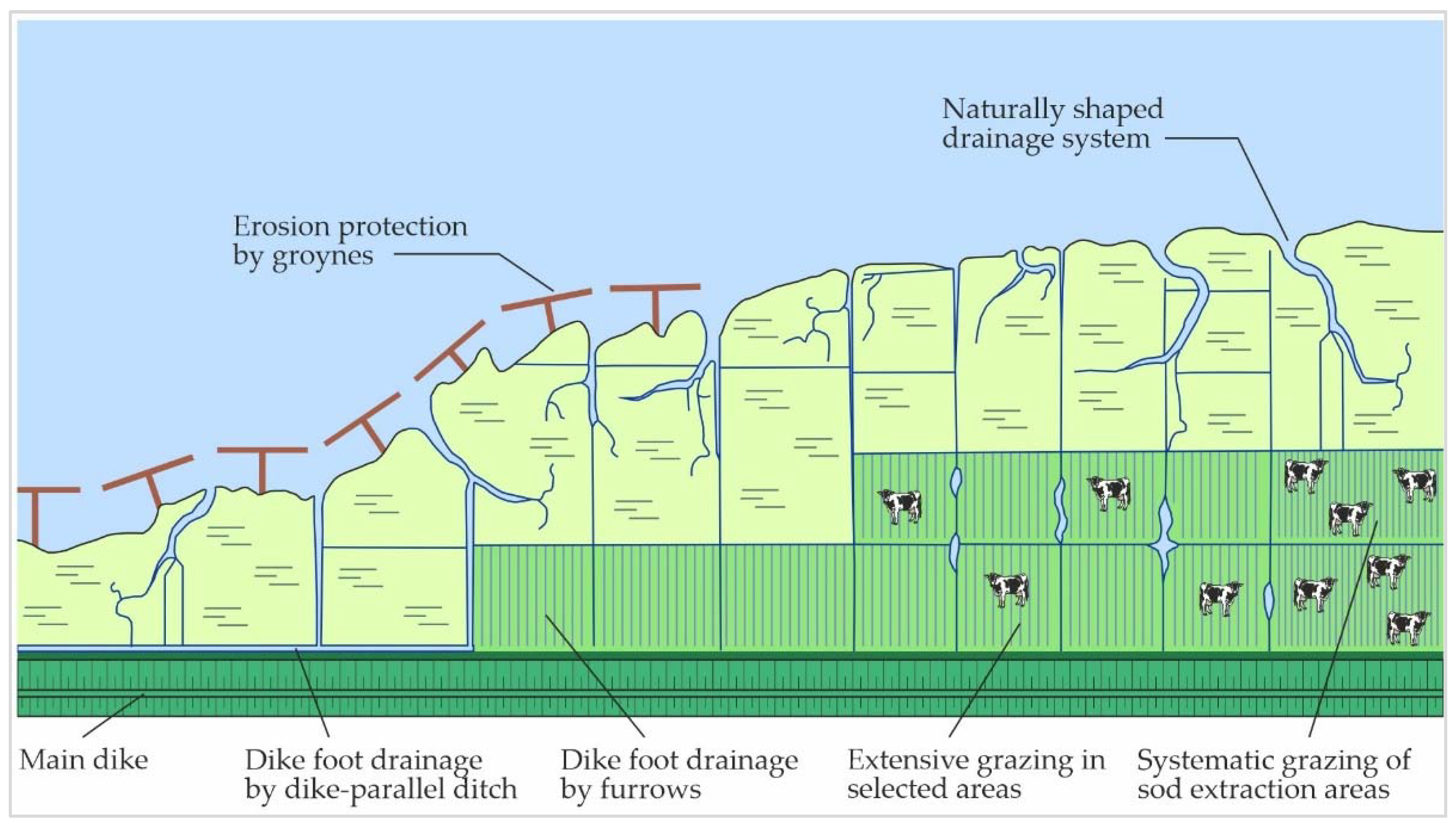
5.2. Management Techniques
5.2.1. Sediment Nourishment
5.2.2. Groynes
5.2.3. Drainage System
5.2.4. Vegetation Establishment
5.2.5. Topography Adaption
5.2.6. Grazing
5.3. Monitoring
5.3.1. Geomorphology
5.3.2. Vegetation
5.4. Nature-Based Solutions
6. Adaptation of salt marshes to effects of climate change and consequences for coastal flood and erosion risk management
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- CWSS. Wadden sea plan 2010: Eleventh Trilateral Governmental Conference on the Protection of the Wadden Sea, Common Wadden Sea Secretariat, Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2010. Available online: https://www.waddensea-worldheritage.org/de/2010-wadden-sea-plan (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- CWSS. Introduction. In Wadden Sea Quality Status Report Last updated 01.03.2018; Kloepper, S., Baptist, M.J., Bostelmann, A., Busch, J.A., Buschbaum, C., Gutow, L., Janssen, G.M., Jensen, K., Jørgensen, H.P., Jong, F. de, Lüerßen, G., Schwarzer, K., Strempel, R., Thieltges, D., Ed.; Wilhelmshaven, Germany.
- UNESCO. Wadden Sea. Available online: https://whc.unesco.org/en/list/1314/ (accessed on 30 May 2024).
- Erchinger, H.F. Dünen, Watt und Salzwiesen: Ostfrieslands Naturlandschaften ; Schutz und Erhaltung von Küste und Inseln, Tier- und Pflanzenwelt; Soltau-Kurier: Norden, Germany, 1985, ISBN 3922365558.
- Pott, R. Farbatlas Nordseeküste und Nordseeinseln: Ausgewählte Beispiele aus der südlichen Nordsee in geobotanischer Sicht; Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germany, 1995; ISBN 978-3800133505. [Google Scholar]
- Leuschner, C.; Ellenberg, H. Salt Marshes and Inland Saline Habitats. In Ecology of Central European Non-Forest Vegetation: Coastal to Alpine, Natural to Man-Made Habitats; Leuschner, C., Ellenberg, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017; pp. 3–61. ISBN 978-3-319-43046-1. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, I.; Spencer, T. Wave dissipation over macro-tidal saltmarshes: Effects of marsh edge typology and vegetation change. Journal of Coastal Research 2002, 36, 506–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EurOtop. Manual on wave overtopping of sea defences and related structures. An overtopping manual largely based on European research, but for worldwide application., 2018. Available online: www.overtopping-manual.com (accessed on 16 July 2024).
- Erchinger, H.F. Küstenschutz durch Vorlandgewinnung, Deichbau und Deicherhaltung in Ostfriesland. Die Küste 1970, 19, 125–185. [Google Scholar]
- Shepard, C.C.; Crain, C.M.; Beck, M. The protective role of coastal marshes: a systematic review and meta-analysis. PLoS One 2011, 6, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, J.L.A. Status and prospects of nature-based solutions for coastal flood and erosion risk management in the Federal State of Schleswig–Holstein, Germany. J Coast Conserv 2024, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MELUND. Generalplan Küstenschutz des Landes Schleswig-Holstein: Fortschreibung 2022; Schleswig-Holstein. Der echte Norden, Kiel, Germany, 2022.
- Thorenz, F. Coastal Flood Defence and Coastal Protection along the North Sea Coast of Niedersachsen. Die Küste 2008, 74 ICCE, 158–169. [Google Scholar]
- Thorenz, F. Die Klimaanpassungsstrategie im Niedersächsischen Küstenschutz. In Transformationsprozesse im Wasserbau. HTG Kongress, Bremen, Germany, 01 Nov - 03 Nov; Hafentechnische Gesellschaft, Ed., 2023; pp 102–110.
- Probst, B. Deichvorlandbewirtschaftung im Wandel der Zeit. Die Küste 1996, 47–60.
- Erchinger, H.F. Landgewinnung und Lahnungsbau im Wattgebiet. Die Küste 1971, 21, 102–108. [Google Scholar]
- Esselink, P.; Duin, W.E. van; Bunje, J.; Cremer, J.; Folmer, E.O.; Frikke, J.; Glahn, M.; Groot, A.V. de; Hecker, N.; Hellwig, U.; et al. Salt marshes. In Wadden Sea Quality Status Report Last updated 01.03.2018; Kloepper, S., Baptist, M.J., Bostelmann, A., Busch, J.A., Buschbaum, C., Gutow, L., Janssen, G.M., Jensen, K., Jørgensen, H.P., Jong, F. de, Lüerßen, G., Schwarzer, K., Strempel, R., Thieltges, D., Ed.; Wilhelmshaven, Germany.
- Thorenz, F. Die Entwicklung des Küstenschutzes an der Nordseeküste. In Jahrbuch der Hafentechnischen Gesellschaft; Schifffahrtsverlag Hansa, Ed.; Schifffahrts-Verl. Hansa, 2014: Hamburg, Germany, 2014; pp 135–155, ISBN 9783877001387.
- Niedersächsisches Deichgesetz, 2004.
- NLWKN. Generalplan Küstenschutz Niedersachsen/ Bremen: Festland, Norden, Germany, 2007.
- Brahms, A. Anfangs-Gründe der Deich- und Wasser-Baukunst; Tapper: Leer, Germany, 1754/1757.
- Thorenz, F.; Carstens, R. Foreland Management in Lower Saxony. Die Küste 2004, 154–161.
- Hofstede, J.L.A. Integrated management of artificially created salt marshes in the Wadden Sea of Schleswig-Holstein, Germany. Wetlands Ecology and Management 2003, 11, 183–194. [Google Scholar]
- Moraes, R.P.L.; Reguero, B.G.; Mazarrasa, I.; Ricker, M.; Juanes, J.A. Nature-Based Solutions in Coastal and Estuarine Areas of Europe. Front. Environ. Sci. 2022, 10, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siegersma, T.R.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Horstman, E.M.; Borsje, B.W. Modelling pioneer vegetation establishment at constructed salt marshes from seasons to decades, Twente, Netherlands, 2022. Available online: https://essay.utwente.nl/89488/1/Siegersma_MA_ET.pdf (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Jordan, P.; Fröhle, P. Bridging the gap between coastal engineering and nature conservation? J Coast Conserv 2022, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesenbeeck, B.K. van; Mulder, J.P.M.; Marchand, M.; Reed, D.J.; Vries, M.B. de; Vriend, H.J. de; Herman, P.M.J. Damming deltas: A practice of the past? Towards nature-based flood defenses. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2014, 140, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T.J.; Belzen, J. van; Balke, T.; Zhu, Z.; Airoldi, L.; Blight, A.J.; Davies, A.J.; Galvan, C.; Hawkins, S.J.; Hoggart, S.P.; et al. Identifying knowledge gaps hampering application of intertidal habitats in coastal protection: Opportunities & steps to take. Coastal Engineering 2014, 87, 147–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Diaz, B.; van der Wal, D. van der; Kaptein, L.; Martinez-Garcia, P.; Lashley, C.H.; Jong, K. de; Nieuwenhuis, J.W.; Govers, L.L.; Olff, H.; Bouma, T.J. Using salt marshes for coastal protection: Effective but hard to get where needed most. Journal of Applied Ecology 2023, 60, 1286–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coldewey, H.-G.; Erchinger, H.F. Deichvorland: Seine Entwicklung zwischen Ems und Jade und die Untersuchungen im Forschungsvorhaben Erosionsfestigkeit von Hellern: KFKI-Projekt 33. Die Küste 1992, 54, 169–187. [Google Scholar]
- Erchinger, H.F.; Coldewey, H.-G.; Meyer, C. Interdisziplinäre Erforschung des Deichvorlandes im Forschungsvorhaben Erosionsfestigkeit von Hellern - KFKI-Projekt 33. Die Küste 1996, 58, 1–45. [Google Scholar]
- Timmerman, A.; Haasnoot, M.; Middelkoop, H.; Bouma, T.J.; McEvoy, S. Ecological consequences of sea level rise and flood protection strategies in shallow coastal systems: A quick-scan barcoding approach. Ocean & Coastal Management 2021, 210, 105674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, J.L.A.; Matelski, B.; Stock, M. Schleswig-Holsteins Klima-Anpassungsstrategie für das Wattenmeer 2100 2019, 87, 19–38. [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, J.L.A.; Becherer, J.; Burchard, H. Morphologische Projektionen für zwei Tidesysteme im Wattenmeer von Schleswig-Holstein: SH-TREND 2019, 87, 115–131. [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; D'Alpaos, A.; Morris, J.T.; Mudd, S.M.; Temmerman, S. Limits on the adaptability of coastal marshes to rising sea level. Geophysical Research Letters 2010, 37, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- CPSL. Coastal Protection and Sea Level Rise: Solutions for sustainable coastal protection in the Wadden Sea region; Wadden Sea Ecosystem No. 21, Trilateral Working Group on Coastal Protection and Sea Level Rise, Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2005. Available online: https://www.waddensea-worldheritage.org/sites/default/files/2005_Ecosystem21_cpsl.pdf (accessed on 25 July 2024).
- Loon-Steensma, J.M. van; Schelfhout, H.A. Green adaptation by innovative dike concepts along the Dutch Wadden Sea coast. Environmental Science & Policy 2014, 44, 108–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieuwhof, A.; Vos, P.C. New data from terp excavations on sea-level index points and salt marsh sedimentation rates in the eastern part of the Dutch Wadden Sea. Netherlands Journal of Geosciences 2018, 97, 31–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oost, A.P.; Colina A., A.; Esselink, P.; Wang, Z.B.; Kessel, T. van; Maren, B. van. Where mud matters: Towards a mud balance for the trilateral Wadden Sea Area: mud supply, transport and deposition. Report 2021-02, Leeuwarden, Netherlands, 2021.
- Reise, K.; Baptist, M.J.; Burbridge, P.; Dankers, N.; Fischer, L.; Flemming, B.; Oost, A.P.; Smit, C. The Wadden Sea - A universally outstanding tidal wetland; Wadden Sea Ecosystem No. 29, Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2010.
- Hayes, M.O. Barrier Island Morphology as a Function of Tidal and Wave Regime. In Barrier Islands from the Gulf of St. Lawrence to the Gulf of Mexico Hardcover, 1st ed.; Leatherman, S.P., Ed.; Academic Press Inc, 1979; pp 1–27, ISBN 978-0124402607.
- Alberts, H.C. The Wadden Sea: An Intertidal Ecosystem of Global Importance. Focus on Geography 2015, 58, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkema, K.S. Impact prognosis for salt marshes from subsidence by gas extraction in the Wadden Sea. Journal of Coastal Research 1997, 13, 1294–1304. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.B.; Elias, E.P.L.; van der Spek, A.J.; Lodder, Q.J. Sediment budget and morphological development of the Dutch Wadden Sea: impact of accelerated sea-level rise and subsidence until 2100. Netherlands Journal of Geosciences 2018, 97, 183–214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y.; Healy, T.; Augustinus, P.; Baba, M.; Bao, C.; Flemming, B.; Fortes, M.; Han, S.; Marone, E.; Mehta, A.; et al. Definition, properties, and classification of muddy coasts. In Muddy Coasts of the World: Processes, Deposits and Function: Proceedings in Marine Science, 4th ed.; Healy, T., Wang, Y., Healy, J.-A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, Netherlands, 2002; pp. 9–18. ISBN 9780444540119. [Google Scholar]
- Ecology of Central European Non-Forest Vegetation: Coastal to Alpine, Natural to Man-Made Habitats; Leuschner, C.; Ellenberg, H., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Germany, 2017, ISBN 978-3-319-43046-1.
- Niemeyer, H.D. Über den Seegang an einer inselgeschützten Wattküste: Technical Report, Norderney, Germany, 1983.
- Esselink, P.; Dijkema, K.S.; Reents, S.; Hageman, G. Vertical Accretion and Profile Changes in Abandoned Man-Made Tidal Marshes in the Dollard Estuary, the Netherlands. Journal of Coastal Research 1998, 14, 570–582. [Google Scholar]
- Flemming, B.; Chang, T.S.; Delafontaine, M.; Bartholomä, A. Distribution of individual mud fractions in a tidal basin of the East Frisian Wadden Sea (southern North Sea): affinities between sortable silts, aggregated particle suites, and calcium carbonate and organic matter contents. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 2024, 1–20. [CrossRef]
- Gesetz über den Nationalpark "Niedersächsisches Wattenmeer", 2001.
- Heydemann, B. Das Ökosystem "Küsten-Salzwiese" - ein Überblick. Faun.-ökol. Mitt. 1983, 5, 249–279. [Google Scholar]
- Hulskamp, R.; Luijendijk, A.; Maren, B. van; Moreno-Rodenas, A.; Calkoen, F.; Kras, E.; Lhermitte, S.; Aarninkhof, S. Global distribution and dynamics of muddy coasts. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mcowen, C.J.; Weatherdon, L.V.; van Bochove, J.-W.; Sullivan, E.; Blyth, S.; Zockler, C.; Stanwell-Smith, D.; Kingston, N.; Martin, C.S.; Spalding, M.; et al. A global map of saltmarshes. Biodivers. Data J. 2017, e11764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Landesamt für Natur und Umwelt des Landes Schleswig-Holstein. Programme zur langfristigen Erhaltung des Wattenmeeres - ProWatt: KFKI-Projekt: ProWatt., Laboe, Germany, 2002.
- Doody, J.P. Saltmarsh Conservation, Management and Restoration: Coastal Systems and Continental Margins, 12th ed.; Springer: Dordrecht, UK, 2008; ISBN 9781402057489. [Google Scholar]
- CPSL. Coastal Protection and Sea Level Rise: Final Report of the Trilateral Working Group on Coastal Protection and Sea Level Rise; Wadden Sea Ecosystem No. 13, Trilateral Working Group on Coastal Protection and Sea Level Rise (CPSL), Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2001.
- Chang, T.S.; Joerdel, O.; Flemming, B.W.; Bartholomä, A. The role of particle aggregation/disaggregation in muddy sediment dynamics and seasonal sediment turnover in a back-barrier tidal basin, East Frisian Wadden Sea, southern North Sea. Marine Geology 2006, 235, 49–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenz, N.; Lindhorst, S.; Arz, H.W. Determination and quantification of sedimentary processes in salt marshes using end-member modelling of grain-size data. The Depositional Record 2023, 9, 4–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duin, W.E. van; Dijkema, K.S.; Zegers, J. Veranderingen in bodemhoogte (opslibbing, erosie en inklink) in de Peazemerlannen: IBN-rapport 326; Instituut voor Bos- en Natuuronderzoek: Wageningen: Alterra, Netherlands, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- Brouns, J.J.W.M. The impact of sea level rise on the dutch coastal ecosystems: (NIOZ-rapport; No. 1988-8), (RIN-rapport; No. 88-60), Texel, Netherlands, 1988. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/387979 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Zhu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Bouma, T.J. Biomechanical properties of marsh vegetation in space and time: effects of salinity, inundation and seasonality. Ann. Bot. 2020, 125, 277–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pott, R. Die Pflanzengesellschaften Deutschlands, 2., überarb. und stark erw. Aufl.; Eugen Ulmer: Stuttgart, Germany, 1992; ISBN 3825280675. [Google Scholar]
- Granse, D.; Suchrow, S.; Jensen, K. Long-term invasion dynamics of Spartina increase vegetation diversity and geomorphological resistance of salt marshes against sea level rise. Biol Invasions 2021, 23, 871–883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reise, K. Coast of change: habitat loss and transformations in the Wadden Sea. Helgoland marine research 2005, 59, 9–21.
- Schuerch, M.; Dolch, T.; Reise, K.; Vafeidis, A.T. Unravelling interactions between salt marsh evolution and sedimentary processes in the Wadden Sea (southeastern North Sea). Progress in Physical Geography: Earth and Environment 2014, 38, 691–715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callaghan, D.P.; Bouma, T.J.; Klaassen, P.; van der Wal, D. van der; Stive, M.J.F.; Herman, P.M.J. Hydrodynamic forcing on salt-marsh development: Distinguishing the relative importance of waves and tidal flows. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2010, 89, 73–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peralta, G.; van Duren; Morris, E.P.; Bouma, T.J. Consequences of shoot density and stiffness for ecosystem engineering by benthic macrophytes in flow dominated areas: a hydrodynamic flume study. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2008, 368, 103–115. [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, S.; Bouma, T.J.; Govers, G.; Wang, Z.B.; Vries, M.B. de; Herman, P.M.J. Impact of vegetation on flow routing and sedimentation patterns: Three-dimensional modeling for a tidal marsh. J. Geophys. Res. 2005, 110, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bij de Vaate, I.; Brückner, M.Z.M.; Kleinhans, M.G.; Schwarz, C. On the Impact of Salt Marsh Pioneer Species-Assemblages on the Emergence of Intertidal Channel Networks. Water Resources Research 2020, 56, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwarz, C.; Gourgue, O.; Belzen, J. van; Zhu, Z.; Bouma, T.J.; Koppel, J. van de; Ruessink, G.; Claude, N.; Temmerman, S. Self-organization of a biogeomorphic landscape controlled by plant life-history traits. Nature Geosci 2018, 11, 672–677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bass, J.; Granse, D.; Hache, I.; Jensen, K.; Karius, V.; Minden, V.; Stock, M.; Suchrow, S.; Kleyer, M. Plant traits affect vertical accretion of salt marshes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2022, 276, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuik, V.; Borsje, B.W.; Jonkman, S.N. Salt marshes for flood risk reduction: Quantifying long-term effectiveness and life-cycle costs. Ocean & Coastal Management 2019, 171, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baaij, B.M.; Kooijman, J.; Limpens, J.; Marijnissen, R.J.C.; Loon-Steensma, J.M. van. Monitoring Impact of Salt-Marsh Vegetation Characteristics on Sedimentation: an Outlook for Nature-Based Flood Protection. Wetlands 2021, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppel, J. van de; van der Wal, D. van der; Bakker, J.P.; Herman, P.M.J. Self-organization and vegetation collapse in salt marsh ecosystems. Am. Nat. 2005, 165, E1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchrow, S.; Pohlmann, N.; Stock, M.; Jensen, K. Long-term surface elevation changes in German North Sea salt marshes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2012, 98, 71–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, J. Morphodynamics of Holocene salt marshes: a review sketch from the Atlantic and Southern North Sea coasts of Europe. Quaternary Science Reviews 2000, 19, 1155–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, T.J.; Svinth, S.; Pejrup, M. Temporal variation of accumulation rates on a natural salt marsh in the 20th century — The impact of sea level rise and increased inundation frequency. Marine Geology 2011, 279, 178–187. [Google Scholar]
- Best, Ü.S.N.; Wegen, M. van der; Dijkstra, J.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Borsje, B.W.; Roelvink, D.J. Do salt marshes survive sea level rise? Modelling wave action, morphodynamics and vegetation dynamics. Environmental Modelling & Software 2018, 109, 152–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heinrich, H. Teilprojekt Schwebstoffgehalt. In: Transport, Umsatz und Variabilität von Schad- und Nährstoffen in der Deutschen Bucht 1990 - 1992 (TUVAS) Abschlußbericht, 1993.
- Baptist, M.J.; Dankers, P.; Cleveringa, J.; Sittoni, L.; van Puijenbroek, M.E.B. van; Vries, B. de; Leuven, J.; Coumou, L.; Kramer, H.; Elschot, K. Salt marsh construction as a nature-based solution in an estuarine social-ecological system. Nature-Based Solutions 2021, 1, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kok, M.; Kroeze, C.; Loon-Steensma, J.M. van. The Sensitivity of a Dike-Marsh System to Sea-Level Rise—A Model-Based Exploration. JMSE 2020, 8, 42. [CrossRef]
- Michaelis, H. Langzeitstudie zur Entwicklung von Höhenlage, Sediment, Vegetation und Bodenfauna in Landgewinnungsfeldern: Untersuchungsbericht 02/08. Norderney, 2008.
- Bass, J. Biodiversity effects on dune and salt marsh biogeomorphology. PhD; Carl von Ossietzky Universität, Oldenburg.
- Stock, M. Patterns in surface elevation change across a temperate salt marsh platform in relation to sea-level rise. In Dynamische Küsten - Grundlagen, Zusammenhänge und Auswirkungen im Spiegel angewandter Küstenforschung; Karius, V.; Hadler, H.; Deicke, M.; Eynatten, H.v.; Brückner, H.; Vött, A. Ed.; Leibniz-Institut für Ostseeforschung Warnemünde, Rostock, Germany 2011; pp 33–48, ISBN 978-3-939206-00-2.
- Reef, R.; Schuerch, M.; Christie, E.K.; Möller, I.; Spencer, T. The effect of vegetation height and biomass on the sediment budget of a European saltmarsh. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2018, 202, 125–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijnen, H.J. van; Bakker, J.P. Long-term Surface Elevation Change in Salt Marshes: a Prediction of Marsh Response to Future Sea-Level Rise. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2001, 52, 381–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koppenaal, E.C.; Esselink, P.; Duin, W.E. van; Bakker, J.P. Temporal and Spatial Accretion Patterns and the Impact of Livestock Grazing in a Restored Coastal Salt Marsh. Estuaries and Coasts 2022, 45, 510–522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baptist, M.J.; Gerkema, T.; Prooijen, B.C. van; Maren, D.S. van; Regteren, M. van; Schulz, K.; Colosimo, I.; Vroom, J.; van Kessel, T.; Grasmeijer, B.; et al. Beneficial use of dredged sediment to enhance salt marsh development by applying a ‘Mud Motor’. Ecological Engineering 2019, 127, 312–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlenberg, E. Über die tatsächliche Leistung von Salicornia herbacea L. im Haushalt der Watten; Wiss. Meeresunters. Abt. Helgoland 1933, 19, 3. [Google Scholar]
- Schulze, D.; Rupprecht, F.; Nolte, S.; Jensen, K. Seasonal and spatial within-marsh differences of biophysical plant properties: implications for wave attenuation capacity of salt marshes. Aquat Sci 2019, 81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nolte, S.; Esselink, P.; Bakker, J.P.; Smit, C. Effects of livestock species and stocking density on accretion rates in grazed salt marshes. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2015, 152, 109–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T.J.; Belzen, J. van; Balke, T.; Dalen, J. van; Klaassen, P.; Hartog, A.M.; Callaghan, D.P.; Hu, Z.; Stive, M.J.F.; Temmerman, S.; et al. Short-term mudflat dynamics drive long-term cyclic salt marsh dynamics. Limnol. Oceanogr. 2016, 61, 2261–2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marin-Diaz, B.; Govers, L.L.; van der Wal, D. van der; Olff, H.; Bouma, T.J. The importance of marshes providing soil stabilization to resist fast-flow erosion in case of a dike breach. Ecol. Appl. 2022, 32, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spencer, T.; Möller, I.; Rupprecht, F.; Bouma, T.J.; Wesenbeeck, B.K. van; Kudella, M.; Paul, M.; Jensen, K.; Wolters, G.; Miranda-Lange, M.; et al. Salt marsh surface survives true-to-scale simulated storm surges *flume. Earth Surf Processes Landf 2016, 41, 543–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feagin, R.A.; Lozada-Bernard, S.M.; Ravens, T.M.; Möller, I.; Yeager, K.M.; Baird, A.H. Does vegetation prevent wave erosion of salt marsh edges? Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2009, 106, 10109–10113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Eerdt, M.M. Salt marsh cliff stability in the oosterschelde. Earth Surf Processes Landf 1985, 10, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; van der Wal, D. van der; Li, X.; Belzen, J. van; Herman, P.M.J.; Hu, Z.; Ge, Z.; Zhang, L.; Bouma, T.J. Zooming in and out: Scale dependence of extrinsic and intrinsic factors affecting salt marsh erosion. J. Geophys. Res. 2017, 122, 1455–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schoutens, K.; Heuner, M.; Minden, V.; Schulte Ostermann, T.S.; Silinski, A.; Belliard, J.-P.; Temmerman, S. How effective are tidal marshes as nature-based shoreline protection throughout seasons? Limnology & Oceanography 2019, 1–21.
- Paul, M.; Kerpen, N.B. Erosion protection by winter state of salt marsh vegetation. Journal of Ecohydraulics 2022, 7, 144–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, J.L.A. Systemanalyse der Salzwiesen im Wattenmeer von Schleswig-Holstein. Beiträge zur aktuellen Küstenforschung. Aspekte, Methoden, Perspektiven.; pp 53–64.
- Silinski, A.; Fransen, E.; Bouma, T.J.; Meire, P.; Temmerman, S. Unravelling the controls of lateral expansion and elevation change of pioneer tidal marshes. Geomorphology 2016, 274, 106–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Wal, D. van der; Wielemaker-Van den Dool, A.; Herman, P.M.J. Spatial patterns, rates and mechanisms of saltmarsh cycles (Westerschelde, The Netherlands). Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2008, 76, 357–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brooks, H.; Möller, I.; Carr, S.; Chirol, C.; Christie, E.; Evans, B.; Spencer, K.L.; Spencer, T.; Royse, K. Resistance of salt marsh substrates to near-instantaneous hydrodynamic forcing. Earth Surf Processes Landf 2021, 46, 67–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Smits, B.P.; Borsje, B.W.; Herman, P.M.J.; Dijkstra, J.T.; Bouma, T.J.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Modeling Decadal Salt Marsh Development: Variability of the Salt Marsh Edge Under Influence of Waves and Sediment Availability. Water Resources Research 2022, 58, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tánczos, I.C. Salt Marsh cycles, an achievement report, 2003.
- Fagherazzi, S.; Furbish, D.J. On the shape and widening of salt marsh creeks. J. Geophys. Res. 2001, 106, 991–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temmerman, S.; Bouma, T.J.; Koppel, J. van de; van der Wal, D. van der; Vries, M.B. de; Herman, P.M.J. Vegetation causes channel erosion in a tidal landscape. Geol 2007, 35, 631–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijsel, R.C. van de; Belzen, J. van; Bouma, T.J.; van der Wal, D. van der; Borsje, B.W.; Temmerman, S.; Cornacchia, L.; Gourgue, O.; Koppel, J. van de. Vegetation controls on channel network complexity in coastal wetlands. Nat. Commun. 2023, 14, 7158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hughes, Z.J. Tidal Channels on Tidal Flats and Marshes. In Principles of Tidal Sedimentology; Davis, R.A., Dalrymple, R.W., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 2012; pp. 269–300. ISBN 978-94-007-0122-9. [Google Scholar]
- Fagherazzi, S.; Kirwan, M.L.; Mudd, S.M.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Temmerman, S.; D'Alpaos, A.; Koppel, J. van de; Rybczyk, J.M.; Reyes, E.; Craft, C.; et al. Numerical models of salt marsh evolution: Ecological, geomorphic, and climatic factors. Reviews of Geophysics 2012, 50, 1–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, J.L.A.; Schirmacher, R. Vorlandmanagement in Schleswig-Holstein. Die Küste 1996, 58, 61–73. [Google Scholar]
- Lieberman, N. von; Schwarze, H.; Zimmermann, C. Ausführung und Wirkungsweise von Lahnungen. Die Küste 1998a, 60, 191–225.
- Reimers, H.-C.; Ricklefs, K.; Thomas, B.Schlußbericht - Teil 2: -Optimierung von Küstensicherungsarbeiten im Küstenvorfeld der Nordseeküste;: KFKI-Projekt 43-1; MTK 0564 Sedimentologie und Morphologie von Lahnungsfeldern, 1998.
- Loon-Steensma, J.M. van; Dobben, H.F. van; Slim, P.A.; Huiskes, H.P.J.; Dirkse, G.M. Does vegetation in restored salt marshes equal naturally developed vegetation? Applied Vegetation Science 2015, 18, 674–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.P.; Bos, D.; Vries, Y. de. To graze or not to graze, that is the question. Proceedings of the 10th International 2003, Groningen, Netherlands, 31. October - 3 November 2000; pp 67–88.
- Arens, S.; Götting, E. Untersuchungen zur ökologischen Entwicklung naturnaher Lahnungsfelder und ihrer Stellung im Naturhaushalt, Oldenburg, Germany.
- Bakker, J.P.; Schrama, M.; Esselink, P.; Daniels, P.; Bhola, N.; Nolte, S.; Vries, Y. de; Veeneklaas, R.M.; Stock, M. Long-Term Effects of Sheep Grazing in Various Densities on Marsh Properties and Vegetation Dynamics in Two Different Salt-Marsh Zones. Estuaries and Coasts 2020, 43, 298–315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neuhaus, R.; Stelter, T.; Kiehl, K. Sedimentation in salt marshes affected by grazing regime, topographical patterns and regional differences. Senckenbergiana maritima 1999, 29, 113–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schulze, D.; Jensen, K.; Nolte, S. Effects of small-scale patterns of vegetation structure on suspended sediment concentration and sediment deposition in a salt marsh. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2022, 278, 108125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elschot, K.; Baptist, M.J.; van Puijenbroek, M.E.B. van. Biocompacting livestock accelerate drowning of tidal salt marshes with sea level rise. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkema, K.S.; Bossinade, J.H.; Bergs, J. van den; Kroeze, T. Natuurtechnisch beheer van kwelderwerken in de Friese en Groninger Waddenzee : greppelonderhoud en overig grondwerk: Nota / Rijkswaterstaat, Directie Groningen; No. GRAN 1991-2002, RIN-rapport; No. 91/10, Groningen, Netherlands, 1991. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/387730 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Nolte, S.; Wanner, A.; Stock, M.; Jensen, K. Elymus athericus encroachment in Wadden Sea salt marshes is driven by surface elevation change. Applied Vegetation Science 2019, 22, 454–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klink, R. van; Nolte, S.; Mandema, F.S.; Lagendijk, D.G.; WallisDeVries, M.F.; Bakker, J.P.; Esselink, P.; Smit, C. Effects of grazing management on biodiversity across trophic levels–The importance of livestock species and stocking density in salt marshes. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2016, 235, 329–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.P. Ecology of salt marshes: 40 years of research in the Wadden Sea; Wadden Academy: Leeuwarden, Netherlands, 2014; ISBN 9789490289324. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Q.; Bakker, J.P.; Alberti, J.; Bakker, E.S.; Smit, C.; Olff, H. Long-term cross-scale comparison of grazing and mowing on plant diversity and community composition in a salt-marsh system. Journal of Ecology 2021, 109, 3737–3747. [Google Scholar]
- Erchinger, H.F.; Thorenz, F. Deichvorland und Sommerdeich als aktiver Küstenschutz. In Tausend Jahre Leben mit dem Wasser in Niedersachsen: Band II; Kramer, J., Erchinger, H.F., Schwark, G., Eds.; Rautenberg: Leer, Germany, 1999; pp. 253–259. ISBN 3792106167. [Google Scholar]
- Bergs, J. van den; Bouwsema, P.; Dijkema, K.S. Management of the mainland saltmarshes and accretion works in relation to coastal protection. In Proceedings of the Second Trilateral Working Conference on Saltmarsh Management in the Wadden Sea Region, Rømø, Denmark, 10-13 October 1989; Ovesen, C.H., Ed.; Ministry of the Environment, National Forest and Nature Agency: [Copenhagen], 1990; pp 85–96, ISBN 87-503-8701-4.
- Hartmann, K.; Stock, M. Long-term change in habitat and vegetation in an ungrazed, estuarine salt marsh: Man-made foreland compared to young marsh development. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2019, 227, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reents, S.; Dijkema, K.S.; Bergs, J. van den; Bossinade, J.; Vlas, J. de. Drainage systems in the Netherlands foreland salt marshes and natural creek systems. Marine Biodiversity 1999, 29, 125–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, N. von; Matheja, A.; Schwarze, H. Optimierung von Küstensicherungsarbeiten im Küstenvorfeld der Nordseeküste: Wellenuntersuchungen in Modell-Lahnungen. KFKI-Projekt: Küstensicherungsarbeiten, Hannover, Germany, 1998b. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11970/110384 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Duin, W.E. van; Dijkema, K.S.; Bos, D. Cyclisch beheer kwelderwerken Friesland: A&W-rapport, no. 887, Texel, Netherlands, 2007. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/121052 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Bunje, J.; Zwoch, I. Lebensräume im Wandel Flächenbilanz von Salzwiesen und Dünen im niedersächsischen Wattenmeer zwischen den Jahren 1966 und 1997: eine Luftbildauswertung, 1st ed.; NLPV "Niedersächsisches Wattenmeer": Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkema, K.S.; Bossinade, J.H.; Bouwsema, P.; Glopper, R.J. de. Salt Marshes in the Netherlands Wadden Sea: Rising High-Tide Levels and Accretion Enhancement. In Expected Effects of Climatic Change on Marine Coastal Ecosystems, 1st ed.; Beukema, J.J., Wolff, W.J., Brouns, J.J.W.M., Eds.; Springer: Dordrecht, Netherlands, 1990; pp. 173–188. ISBN 978-94-010-7397-4. [Google Scholar]
- Nevermann, H.; AghaKouchak, A.; Shokri, N. Sea level rise implications on future inland migration of coastal wetlands. Global Ecology and Conservation 2023, 43, e02421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schuerch, M.; Vafeidis, A.; Slawig, T.; Temmerman, S. Modeling the influence of changing storm patterns on the ability of a salt marsh to keep pace with sea level rise. J. Geophys. Res. 2013, 118, 84–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borsje, B.W.; Best, U.; Wegen, M. van der; Dijkstra, J. Modelling sea level rise impact on salt marsh/mangrove-mudflat morphodynamics. In NCK-Days - KIM, Den Helder, Netherlands, 15 Mar 2017 - 17 Mar 2017, 2007; Abstract.
- Dobben, H.F. van; Groot, A.V. de; Bakker, J.P. Salt Marsh Accretion With and Without Deep Soil Subsidence as a Proxy for Sea-Level Rise. Estuaries and Coasts 2022, 45, 1562–1582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dijkema, K.S.; Duin, W.E. van; Meesters, H.W.G.; Zuur, A.F.; Ieno, E.N.; Smith, G.M. Sea level change and salt marshes in the Wadden Sea: A time series analysis. In Analysing Ecological Data, 1st ed.; Zuur, A.F., Ieno, E.N., Eds.; Springer: New York, U.S, 2007; pp. 601–614. ISBN 978-0-387-45967-7. [Google Scholar]
- Schuerch, M.; Rapaglia, J.; Liebetrau, V.; Vafeidis, A.; Reise, K. Salt Marsh Accretion and Storm Tide Variation: an Example from a Barrier Island in the North Sea. Estuaries and Coasts 2012, 35, 486–500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suchrow, S. Modelling spatial and temporal patterns of surface elevation and vegetation in German North Sea salt marshes. PhD thesis; Universität Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany 2014.
- Duarte, B.; Carreiras, J.; Caçador, I. Climate Change Impacts on Salt Marsh Blue Carbon, Nitrogen and Phosphorous Stocks and Ecosystem Services. Applied Sciences 2021, 11, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koop-Jakobsen, K.; Dolch, T. Future climate conditions alter biomass of salt marsh plants in the Wadden Sea. Mar. Biodivers. 2023, 53, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Vuik, V.; Visser, P.J.; Soens, T.; Wesenbeeck, B.K. van; Koppel, J. van de; Jonkman, S.N.; Temmerman, S.; Bouma, T.J. Historic storms and the hidden value of coastal wetlands for nature-based flood defence. Nat Sustain 2020, 3, 853–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Borsje, B.W.; Belzen, J. van; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Wang, H.; Peng, Y.; Yuan, L.; Dominicis, M. de; Wolf, J.; Temmerman, S.; et al. Mechanistic Modeling of Marsh Seedling Establishment Provides a Positive Outlook for Coastal Wetland Restoration Under Global Climate Change. Geophysical Research Letters 2021, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hache, I.; Karius, V.; von Eynatten, H. Suspended particulate matter for sediment accumulation on inundated anthropogenic marshland in the southern North Sea – Potential, thresholds and limitations. Continental Shelf Research 2020, 207, 104214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hofstede, J.L.A.; Becherer, J.; Burchard, H. Are Wadden Sea tidal systems with a higher tidal range more resilient against sea level rise? J Coast Conserv 2018, 22, 71–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kirwan, M.L.; Temmerman, S.; Skeehan, E.E.; Guntenspergen, G.R.; Fagherazzi, S. Overestimation of marsh vulnerability to sea level rise. Nat. Clim. Chang. 2016, 6, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simas, T.; Nunes, J.; Ferreira, J. Effects of global climate change on coastal salt marshes. Ecological Modelling 2001, 139, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuik, V.; Jonkman, S.N.; Borsje, B.W.; Suzuki, T. Nature-based flood protection: The efficiency of vegetated foreshores for reducing wave loads on coastal dikes. In 18th Physics of Estuaries and Coastal Seas Conference, Scheveningen, the Netherlands, 09 October - 14 October; Zitman, T., Ed., 2016; pp 42–56.
- Borsje, B.W.; Vries, S. de; Janssen, S.K.H. Building with Nature as Coastal Protection Strategy in the Netherlands. In Living shorelines: The science and management of nature-based coastal protection, 1st ed.; Bilkovic, D.M., Mitchell, M.M., La Peyre, M.M., Toft, M. K., et al., Eds.; CRC Press (Taylor & Francis): Boca Raton, USA, 2017; ISBN 9781498740029. [Google Scholar]
- EAK. Empfehlungen für die Ausführung von Küstenschutzwerken durch den Ausschuss für Küstenschutzwerke der Deutschen Gesellschaft für Geotechnik e.V. und der Hafenbautechnischen Gesellschaft e.V.: EAK 2002. Die Küste 2020, 1–589.
- Vuik, V.; Jonkman, S.N. Wave attenuation by salt marsh vegetation. In 18th Physics of Estuaries and Coastal Seas Conference, Scheveningen, Netherlands, 09 October - 14 October; Zitman, T., Ed., 2016.
- Keimer, K.; Schürenkamp, D.; Miescke, F.; Kosmalla, V.; Lojek, O.; Goseberg, N. Ecohydraulics of Surrogate Salt Marshes for Coastal Protection: Wave–Vegetation Interaction and Related Hydrodynamics on Vegetated Foreshores at Sea Dikes. J. Waterway, Port, Coastal, Ocean Eng. 2021, 147, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuik, V.; van Vuren, S.; Borsje, B.W.; Wesenbeeck, B.K. van; Jonkman, S.N. Assessing safety of nature-based flood defenses: Dealing with extremes and uncertainties. Coastal Engineering 2018, 139, 47–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorenz, F.; Lambrecht, H.-J.; Blum, H. Untersuchungen zur Überflutungsausbreitung im Fall von Deichbrüchen. Die Küste 2017, 85, 183–221. [Google Scholar]
- Führböter, A. Über Verweilzeiten und Wellenenergien bei Sturmfluten. In Jahrbuch der Hafenbautechnischen Gesellschaft; Schwab, R., Becker, W., Eds.; Springer: Berlin, Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; pp. 269–282. ISBN 978-3-662-11014-0. [Google Scholar]
- Möller, I.; Kudella, M.; Rupprecht, F.; Spencer, T.; Paul, M.; Wesenbeeck, B.K. van; Wolters, G.; Jensen, K.; Bouma, T.J.; Miranda-Lange, M.; et al. Wave attenuation over coastal salt marshes under storm surge conditions. Nature Geosci 2014, 7, 727–731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loon-Steensma, J.M. van. Salt marshes for flood protection: Long-term adaptation by combining functions in flood defences. PhD thesis; Wageningen University: Wageningen, Netherlands, 2014, ISBN 9789462570993.
- Mai, S.; Lieberman, N. von. Effectiveness of forelands reducing the wave load on dikes. In Proceedings of the 2nd German-Chinese Joint Seminar on Recent Developments in Coastal Engineering, Tawain, 13. Sept - 15. Sept, 1999; pp 293–306.
- Niemeyer, H.D.; Kaiser, R. Hydrodynamische Wirksamkeit von Lahnungen, Hellern und Sommerdeichen. Die Küste 2001, 64, 15–60. [Google Scholar]
- Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Borsje, B.W.; Vuik, V.; Bouma, T.J.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Field-based decadal wave attenuating capacity of combined tidal flats and salt marshes. Coastal Engineering 2020, 156, 103628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- The effect of foreland on wave climate changes; Wang, Z.; Grüne, J., Eds. Proc. of 3rd. Intern. Symp. on Ocean Wave Meas. and Analysis (WAVES'97), Virginia Beach, USA, November 1997, 1997.
- Loon-Steensma, J.M. van. Salt marshes to adapt the flood defences along the Dutch Wadden Sea coast. Mitig. Adapt. Strateg. Glob. Chang. 2015, 20, 929–948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Knutson, P.L.; Brochu, R.A.; Seelig, W.N.; Inskeep, M. Wave damping inSpartina alterniflora marshes. Wetlands 1982, 2, 87–104. [Google Scholar]
- Niedersächsisches Deichgesetz: Kommentar; Lüders, K.; Leis, G., Eds.; Verl. Wasser u. Boden Lindow: Hamburg, 1964.
- Anderson, M.E.; Smith, J.M. Wave attenuation by flexible, idealized salt marsh vegetation. Coastal Engineering 2014, 83, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouma, T.J.; Vries, M.B. de; Low, E.; Peralta, G.; Tánczos, I.C.; Koppel, J. van de; Herman, P.M.J. Trade-offs related to ecosystem engineering: a case study on stiffness of emerging macrophytes. Ecology 2005, 86, 2187–2199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, I. Quantifying saltmarsh vegetation and its effect on wave height dissipation: Results from a UK East coast saltmarsh. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2006, 69, 337–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maza, M.; Lara, J.L.; Losada, I.J. A paradigm shift in the quantification of wave energy attenuation due to saltmarshes based on their standing biomass. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castagno, K.A.; Ganju, N.K.; Beck, M.; Bowden, A.A.; Scyphers, S.B. How Much Marsh Restoration Is Enough to Deliver Wave Attenuation Coastal Protection Benefits? Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, F.; Möller, I.; Evans, B.; Spencer, T.; Jensen, K. Biophysical properties of salt marsh canopies — Quantifying plant stem flexibility and above ground biomass. Coastal Engineering 2015, 100, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keimer, K.; Kosmalla, V.; Prüter, I.; Lojek, O.; Prinz, M.; Schürenkamp, D.; Freund, H.; Goseberg, N. Proposing a novel classification of growth periods based on biomechanical properties and seasonal changes of Spartina anglica. Front. Mar. Sci. 2023, 10, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewageegana, V.H.; Bilskie, M.V.; Woodson, C.B.; Bledsoe, B.P. The effects of coastal marsh geometry and surge scales on water level attenuation. Ecological Engineering 2022, 185, 106813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markov, A.; Muller, M.; Baker, S.; Nistor, I.; Murphy, E.; Stolle, J.; Cornett, A. New insights on using scaled marsh plant surrogates for wave attenuation. Int. Conf. Coastal. Eng. 2023, 37, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Möller, I.; Spencer, T.; French, J.R.; Leggett, D.J.; Dixon, M. Wave Transformation Over Salt Marshes: A Field and Numerical Modelling Study from North Norfolk, England. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 1999, 49, 411–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vuik, V.; Suh Heo, H.Y.; Zhu, Z.; Borsje, B.W.; Jonkman, S.N. Stem breakage of salt marsh vegetation under wave forcing: A field and model study. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2018, 200, 41–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leuven, J.; Vries, B. de; Dankers, P.; van Puijenbroek, M.E.B. van; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Coumou, L.; Cleveringa, J.; Baptist, M.J.; Elschot, K. Kwelderontwikkeling als Nature-based Solution: Kennis en ervaring van de Proefkwelder Marconi, Delfzijl,Netherlands 2021. Available online: https://www.ecoshape.org/en/pilots/saltmarsh-development-marconi-delfzijl-9/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Hoven, K. van den; Belzen, J. van; Kleinhans, M.G.; Schot, D.M.J.; Merry, J.; Loon-Steensma, J.M. van; Bouma, T.J. How natural foreshores offer flood protection during dike breaches: An explorative flume study. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science 2023, 294, 108560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thorenz, F.; Blum, H.; Lambrecht, H.-J.; Schüttrumpf, H.; Fröhle, P. Relevance of Varying Coastal Defense Systems on Flooding and Damage of Coastal Areas.: From Sea to Shore – Meeting the Challenges of the Sea. In From Sea to Shore – Meeting the Challenges of the Sea, Conference Proceedings. Coasts, Marine Structures and Breakwaters 2013, Edinburgh, Scotland; Allsop, W., Burgess, K., Eds.; ICE Publishing: London, UK; pp 552–561, ISBN 978-0-7277-5975-7.
- Thorenz, F.; Lambrecht, H.-J. Relevance and management of dike forelands as a natural Element of an integrated coastal management. In Proceedings of the 9th Chinese-German Joint Symposium on Hydraulic & Ocean Engineering. CGJOINT 2018, National Cheng Kung University (NCKU), Tainan, Taiwan, Nov. 11-17, 2018.
- Mai, S.; Zimmermann, C. Importance of Forelands and Summer Dikes for Coastal Safety. In Proceedings of the 3rd Int. Conf. Port Development & Coastal Environment. PDCE, Varna, Bulgaria, 2003; 119 – 128.
- Wolters, M.; Garbutt, A.; Bakker, J.P. Salt-marsh restoration: evaluating the success of de-embankments in north-west Europe. Biological Conservation 2005, 123, 249–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Council Directive 92/43/EEC on the conservation of natural habitats and of wild fauna and flora, 1992.
- Landeswassergesetz Schleswig-Holstein, 2019.
- Adnitt, C. Saltmarsh management manual, 1st ed.; Environment Agency: Bristol, UK, 2007; ISBN 978-1-84432-714-0. [Google Scholar]
- Schulz, K.; Klingbeil, K.; Morys, C.; Gerkema, T. The Fate of Mud Nourishment in Response to Short-Term Wind Forcing. Estuaries and Coasts 2021, 44, 88–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillmann, S.; Blum, H.; Thorenz, F. National Analysis: Germany / Lower Saxony NLWKN, 2021. Available online: https://northsearegion.eu/media/10002/national-analysis_langeoog_nlwkn.pdf (accessed on 9 March 2020).
- NLWKN. Generalplan Küstenschutz Niedersachsen: Ostfriesische Inseln, 2010.
- Wilmink, R. Overall document: From flood prevention strategy to current practice nourishments. This document is a composition of six factsheets current practices from Belgium, the Netherlands, Lower Saxony, Schleswig Holstein, Denmark and Skåne (Sweden)., 2017. Available online: https://northsearegion.eu/building-with-nature/output-library/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Delta programme. Delta programme 2024: Now for the Future, The Hague, 2023. Available online: https://english.deltaprogramma.nl/delta-programme/documents/publications/2023/09/19/delta-programme-2024-english (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- International guidelines on natural and nature-based features for flood risk management; Bridges, T.S.; King, J.K.; Simm, J.D.; Beck, M.W.; Collins, G.; Mohan, R.K., Eds.; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, USA, 2021, ISBN 978-1-7325904-9-6.
- MELUR. Strategie für das Wattenmeer 2100, Kiel, Germany.
- VanZomeren, C.; Acevedo-Mackey, D. Maintaining salt marshes in the face of sea level rise — review of literature and techniques, Vicksburg, USA, 2019. Available online: https://hdl.handle.net/11681/33297 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Vries, B. de; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; van Puijenbroek, M.E.B. van; Coumou, L.; Baptist, M.J.; Cleveringa, J.; Dankers, P.; Elschot, K. Salt marsh pilot Marconi: Monitoring results, 2021. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/572943 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Groot, A.V. de; Duin, W.E. van. Best practices for creating new salt marshes in a saline estuarine setting, a literature study: IMARES Wageningen UR IMARES rapport C145/12 for EcoShape Building with Nature., 2013. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/248715 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Piercy, C.D.; Pontee, N.; Narayan, S.; Davis, J.; Meckley, T. Coastal Wetlands and Tidal Flats. In International guidelines on natural and nature-based features for flood risk management; Bridges, T.S., King, J.K., Simm, J.D., Beck, M.W., Collins, G., Mohan, R.K., Eds.; U.S. Army Engineer Research and Development Center: Vicksburg, MS, 2021; pp. 414–500. ISBN 978-1-7325904-9-6. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, J.L.A.; Stock, M. Climate change adaptation in the Schleswig-Holstein sector of the Wadden Sea: an integrated state governmental strategy. J Coast Conserv 2018, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groot, A.V. de; Wesenbeeck, B.K. van; Loon-Steensma, J.M. van. Stuurbaarheid van kwelders: IMARES Rapport C004/13, 2013.
- Fiege, M.; Hagmeier, H. Lahnungsbauwerke: Entwicklung, Ausführungsvarianten und Entwässerungssysteme. Diplomarbeit; Universität Hannover, Hannover, Germany, 1996.
- Weichbrodt, F. Coastal Groynes in Germany. Die Küste 2008, 74, 241–251. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkema, K.S.; Kers, A.; Duin, W.E. van. Salt marshes: applied long-term monitoring. In Proceedings of the 12th International Scientific Wadden Sea Symposium. Science for Nature Conservation - The Wadden Sea Ecosystem, Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 30 March - 3 April; Common Wadden Sea Secretariat, Ed., 2009; pp 35–40.
- Dijkema, K.S.; Bergs, J. van den; Bossinade, J.H.; Bouwsema, P.; Glopper, R.J. de; Meegen, van J. W. T. M. Effecten van rijzendammen op opslibbing en omvang van de vegetatiezones in de Friese en Groninger landaanwinningswerken. Rijksinstituut voor Natuurbeheer, Texel, RIN-rapport 88/66; Rijkswaterstaat, Directie Groningen, Netherlands, 1988.
- Jong, F. de; Bakker, J.F.; van Berkel, C.J.M.; Dankers, N. M. J. A.; Dahl, K.; Gätje, C.; Marencic, H.; Potel, P. Quality Status Report Wadden Sea; Common Wadden Sea Secretariat, Trilateral Monitoring and Assessment Group: Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, J.L.A.; Buss, T.; Eckhold, J.-P.; Mohr, A.; Jäger, B.; Strotmann, T.; Thorenz, F.; von Lieberman, N. Küstenschutzstrategien: Bericht einer FAK-Arbeitsgruppe. Die Küste 2009, 76, 1–74. [Google Scholar]
- Dijkema, K.S.; Nicolai, A.; Vlas, J. de; Smit, C.; Jongerius, H.; Nauta, H. Van Landaanwinning naar Kwelderwerken; Rijkswaterstaat: Texel, Leeuwarden, Netherlands, 2001; ISBN 9036935830. [Google Scholar]
- Stock, M.; Maier, M. Salzwiesenschutz im Nationalpark Wattenmeer. Vogelkdl. Ber. Niedersachs. 2016, 44, 131–156. [Google Scholar]
- Esselink, P.; Zijlstra, W.; Dijkema, K.S.; Diggelen, R. van. The effects of decreased management on plant-species distribution patterns in a salt marsh nature reserve in the Wadden Sea. Biological Conservation 2000, 93, 61–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wesenbeeck, B.K. van; Esselink, P.; Oost, A.P.; Duin, W.E. van; Veeneklaas, R.M.; Balke, T.; van Geer, P.; Calderon A. C.; Smale, A. Verjonging van half-natuurlijke kwelders en schorren. Rapport nr. 2014/OBN196-DK; Ontwikkeling en Beheer Natuurkwaliteit, Driebergen, Netherlands, 2014. Available online: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/283069226_Verjonging_van_half-natuurlijke_kwelders_en_schorren_Rapport_2014OBN196-DK (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Duin, W.E. van; Dijkema, K.S. Proef met de onderhoudsarme ontwatering in de kwelderwerken: "de Krekenproef"; evaluatie 1997-2002. Alterra-rapport; No. 634, Wageningen, Netherlands, 2003. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/39117 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Stock, M.; Kiehl, K.; Reinke, D. Salzwiesenschutz im schleswig-holsteinischen Wattenmeer: Grundlagen, Zielsetzung und bisherige Umsetzung. Heide, Germany, 1994.
- Dijkema, K.S.; Duin, W.E. van; Dijkman, E.M.; van Leeuw, P.W. Monitoring van kwelders in de Waddenzee: WOT IN serie, no. nr. 5, Wageningen, Netherlands, 2007. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/120746 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Dijkema, K.S.; Duin, W.E. van; Dijkman, E.M.; Nicolai, A.; Jongerius, H.; Keegstra, H.; Jongsma, J.J. Friese en Groninger kwelderwerken: Monitoring en beheer 1960-2010. WOt-rapport, no. 122, Wageningen, Netherlands, 2013. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/279715 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Planungsgruppe Grün. Ökologische Grundlagen und naturschutzfachliche Bewertung von Strategien zur Treibselreduzierung: Endbericht. Forschungsvorhaben, 2011.
- Steinigeweg, C.S.; Paul, M.; Kleyer, M.; Schröder, B. Conquering New Frontiers: The Effect of Vegetation Establishment and Environmental Interactions on the Expansion of Tidal Marsh Systems. Estuaries and Coasts 2023, 46, 1515–1535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huiskes, A.H.L.; Koutstaal, B.P.; Herman, P.M.J.; Beeftink, E. G.; Markusse, M. M.; De Munk, W. Seed Dispersal of Halophytes in Tidal Salt Marshes. Journal of Ecology 1995, 83, 559–567. [Google Scholar]
- Regteren, M. van; Colosimo, I.; Vries, P. de; van Puijenbroek, M.E.B. van; Freij, V.S.; Baptist, M.J.; Elschot, K. Limited seed retention during winter inhibits vegetation establishment in spring, affecting lateral marsh expansion capacity. Ecol. Evol. 2019, 9, 13294–13308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wohlenberg, E. Biologische Kulturmaßnahmen mit dem Queller (Salicornia herbacea L.) zur Landgewinnung im Wattenmeer. Westküste 1938, 1, 52–104. [Google Scholar]
- Houwing, E.-J.; Terwindt, J.H.J. Salt Marshes and sea level rise: marsh dynamics in relation to accretion processes and accretion enhancement techniques. Climate Change Research - Evaluation and Policy Implications, Proceedings of the International Climate Change Research Conference; Elsevier, 1995; pp 823–826, ISBN 9780444821430.
- Poppema, D.W.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Vries, M.B. de; Zhu, Z.; Borsje, B.W.; Hulscher, S.J.M.H. Experiment-supported modelling of salt marsh establishment. Ocean & Coastal Management 2019, 168, 238–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horstman, E.M.; Bouma, T.J.; Baptist, M.J.; van Puijenbroek, M.E.B. van; Borsje, B.W. Facilitating Salt Marsh Restoration: The Importance of Event-Based Bed Level Dynamics and Seasonal Trends in Bed Level Change. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 8, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oevelen, D. van; Bergh, E. van den; Ysebaert, T.; Meire, P. Literatuuronderzoek naar estuariene herstelmaatregelen: Rapporten van het instituut voor natuurbehoud nr. 4, 2000. Available online: https://edepot.wur.nl/79430 (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Bartholomä, A.; Bunje, J.; Dittmann, T. Bewertung der ökologischen Verträglichkeit von Pütten. Natur- und Umweltschutz 2013, 12, 61–75. [Google Scholar]
- Götting, E. Verzeichnis der Kleientnahmen im Deichvorland der niedersächsischen Festlandsküste; Dienstbericht Forschungsstelle Küste 17/2002, Norderney, Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2002.
- Bundesamt für Seeschifffahrt und Hydrogrpahie. Regenerierung von Materialentnahmestellen in Nord-und Ostsee, Hamburg, Germany: Bundesamt für Seeschifffahrt und Hydrogrpahie.
- Zeiler, M.; Figge, K.; Griewatsch, K.; Diesing, M.; Scharzer, K. Regenerierung von Materialentnahmestellen in Nord-und Ostsee. Die Küste 2004, 68, 67–98. [Google Scholar]
- Karle, M.; Bartholomä, A. Salt marsh sediments as natural resources for dike construction — sediment recycling in clay pits. Senckenbergiana maritima 2008, 38, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esselink, P.; Kok, M.; Kroeze, C.; Loon-Steensma, J.M. van. How natural processes contribute to flood protection - A sustainable adaptation scheme for a wide green dike. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 739, 139698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, F.; Reichert, G.; Merling, B.; Oltmanns, B. Renaturierung von Salzwiesen im Nationalpark Niedersächsisches Wattenmeer: Berichte aus dem Nationalpark und der Biosphärenregion Niedersächsisches Wattenmeer; Nationalparkverwaltung Niedersächsisches Wattenmeer: Wilhelmshaven, Germany, 2023.
- Wellbrock, A.; Thyen, S.; Exo, K.-M. Ökologische Bedeutung einer wiederverlandenden Kleipütte für Brut- und Rastvögel im westlichen Jadebusen. Vogelkundliche Berichte aus Niedersachsen 2010, 41, 225–239. [Google Scholar]
- Metzing, D.; Gerlach, A.; Buchwald, R. Kapitel VIII: Auswirkungen von Kleientnahmen auf Flora und Vegetation der Salzwiesen. In Wiederverlandung einer Pütte: Forschungsergebnisse zu Chancen und Risiken von Kleientnahmen in Salzwiesen für den Deichbau; Oldenburgischer Deichband, Ed.; KomReGis Verlag, 2013: Oldenburg, Germany, 2013; pp 107–153, ISBN 9783938501351.
- Bakker, J.P.; Leeuw, J. de; Dijkema, K.S.; Leendertse, P.C.; Prins, H.H.T.; Rozema, J. Salt marshes along the coast of The Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 1993, 265, 73–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.P.; Bunjes, J.; Dijkema, K.S.; Frikke, J.; Hecker, N.; Kers, B.; Körber, P.; Kohlus, J.; Stock, M. Salt marshes. In Wadden Sea quality status report 2004; Essink, K., Dettmann, C., Farke, H., Laursen, K., Lüerßen, G., Marencic, H., Wiersinga, W., Eds.; Common Wadden Sea Secretariat Trilateral Monitoring and Assessment Group: Wilhelmshaven, Germany; pp 163–180.
- Nolte, S.; Esselink, P.; Smit, C.; Bakker, J.P. Herbivore species and density affect vegetation-structure patchiness in salt marshes. Agriculture, Ecosystems & Environment 2014, 185, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bockelmann, A.-C.; Bakker, J.P.; Neuhaus, R.; Lage, J. The relation between vegetation zonation, elevation and inundation frequency in a Wadden Sea salt marsh. Aquatic Botany 2002, 73, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Q.; Bakker, J.P.; Alberti, J.; Smit, C. Long-term management is needed for conserving plant diversity in a Wadden Sea salt marsh. Biodivers Conserv 2020, 29, 2329–2341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rupprecht, F.; Wanner, A.; Stock, M.; Jensen, K. Succession in salt marshes – large-scale and long-term patterns after abandonment of grazing and drainage. Applied Vegetation Science 2015, 18, 86–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andresen, H.; Bakker, J.P.; Brongers, M.; Heydemann, B.; Irmler, U. Long-term changes of salt marsh communities by cattle grazing 1990, 89, 137–148. [CrossRef]
- Bos, D. Grazing in coastal grasslands: Brent geese and facilitation by herbivory. PhD thesis, Groningen, Netherlands, 2002.
- Kleyer, M.; Feddersen, H.; Bockholt, R. Secondary succession on a high salt marsh at different grazing intensities. J Coast Conserv 2003, 9, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vlas, J. de; Mandema, F.; Nolte, S.; Klink, R. van; Esselink, P. Nature conservation of salt marshes: The influence of grazing on biodiversity. PUCCIMAR report, Olterterp, Netherlands, 2013.
- Nolte, S. Grazing as a nature-management tool: The effect of different livestock species and stocking densities on salt-marsh vegetation and accretion. PhD thesis. University of Groningen, Groningen, Netherlands 2014.
- Arcadis. Bouwsteen beheerplan kwelders Groninger noordkust en Dollard. Provincie Groningen, 2006.
- Marin-Diaz, B.; Govers, L.L.; van der Wal, D. van der; Olff, H.; Bouma, T.J. How grazing management can maximize erosion resistance of salt marshes. Journal of Applied Ecology 2021, 58, 1533–1544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiehl, K.; Eischeid, I.; Gettner, S.; Walter, J. Impact of different sheep grazing intensities on salt marsh vegetation in northern Germany. J Vegetation Science 1996, 7, 99–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosmalla, V.; Keimer, K.; Schürenkamp, D.; Lojek, O.; Goseberg, N. Erosion resistance of vegetation-covered soils: Impact of different grazing conditions in salt marshes and analysis of soil-vegetation interactions by the novel DiCoastar method. Ecological engineering : the journal of ecotechnology 2022, 181, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hijuelos, A.C.; Dijkstra, J.T.; Carruthers, T.J.B.; Heynert, K.; Reed, D.J.; Wesenbeeck, B.K. van. Linking management planning for coastal wetlands to potential future wave attenuation under a range of relative sea-level rise scenarios. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0216695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NLWKN. Vollzugshinweise zum Schutz der FFH-Lebensraumtypen sowie weiterer Biotoptypen mit landesweiter Bedeutung in Niedersachsen. – FFH-Lebensraumtypen und Biotoptypen mit Priorität für Erhaltungs- und Entwicklungsmaßnahmen: – Atlantische Salzwiesen. – Niedersächsische Strategie zum Arten- und Biotopschutz, Hannover, Germany, 2011.
- Nolte, S.; Koppenaal, E.C.; Esselink, P.; Dijkema, K.S.; Schuerch, M.; Groot, A.V. de; Bakker, J.P.; Temmerman, S. Measuring sedimentation in tidal marshes: a review on methods and their applicability in biogeomorphological studies. J Coast Conserv 2013, 17, 301–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedersen, J.; Bartholdy, J. Budgets for fine-grained sediment in the Danish Wadden Sea. Marine Geology 2006, 235, 101–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weitkamp, A. Untersuchungen zum Einsatz von Laserscanningverfahren beim Monitoring der Deichvorlandentwicklung. Diplomarbeit; Universität Hannover, Hannover, Germany 2001.
- Farris, A.S.; Defne, Z.; Ganju, N.K. Identifying Salt Marsh Shorelines from Remotely Sensed Elevation Data and Imagery. Remote Sensing 2019, 11, 1795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loon-Steensma, J.M. van; Decuyper, M.; Hu, Z. Salt-marsh erosion and restoration in relation to flood protection on the Wadden Sea barrier island Terschelling. J Coast Conserv 2014, 18, 415–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petersen, J.; Kers, B.; Stock, M. TMAP-Typology of coastal vegetation in the Wadden Sea Area; Wadden Sea Ecosystem, Wilhelmshaven, Germany.
- Routhier, M.; Moore, G.; Rock, B. Assessing Spectral Band, Elevation, and Collection Date Combinations for Classifying Salt Marsh Vegetation with Unoccupied Aerial Vehicle (UAV)-Acquired Imagery. Remote Sensing 2023, 15, 5076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Windle, A.E.; Staver, L.W.; Elmore, A.J.; Scherer, S.; Keller, S.; Malmgren, B.; Silsbe, G.M. Multi-temporal high-resolution marsh vegetation mapping using unoccupied aircraft system remote sensing and machine learning. Front. Remote Sens. 2023, 4, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Nature-based solutions to address global societal challenges; Cohen-Shacham, E.; Walters, G.; Janzen, C.; Maginnis, S., Eds.; IUCN International Union for Conservation of Nature: Gland, Switzerland, 2016, ISBN 9782831718125.
- United Nations. Scaling up wetland conservation, wise use and restoration to achieve the Sustainable Development Goals: Wetlands and the SDGs, 2018. Available online: https://www.ramsar.org/document/wetlands-sdgs (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Choya, R.M. Catalogue of Nature-Based Solutions for coastal protection; Universitat Politècnica de Catalunya, Barcelon, 2018.
- Markus-Michalczyk, H. Nature-Based Solutions for Flood Risk Reduction: North Sea Region, Flat Coasts and Estuaries. In SDGs in the European Region; Leal Filho, W., Dinis, M.A.P., Moggi, S., Price, E., Hope, A., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2022; pp. 1–23. ISBN 978-3-030-91261-1. [Google Scholar]
- Temmerman, S.; Horstman, E.M.; Krauss, K.W.; Mullarney, J.C.; Pelckmans, I.; Schoutens, K. Marshes and Mangroves as Nature-Based Coastal Storm Buffers. Ann. Rev. Mar. Sci. 2023, 15, 95–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nat, A. van der; Vellinga, P.; Leemans, R.; van Slobbe, E. Ranking coastal flood protection designs from engineered to nature-based. Ecological Engineering 2016, 87, 80–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoek, R.E. van den; Brugnach, M.; Hoekstra, A.Y. Shifting to ecological engineering in flood management: Introducing new uncertainties in the development of a Building with Nature pilot project. Environmental Science & Policy 2012, 22, 85–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Borsje, B.W.; Wang, C.; Wang, H.; van der Wal, D. van der; Zhu, Z.; Oteman, B.; Vuik, V.; Evans, B.; et al. Synchronized high-resolution bed-level change and biophysical data from 10 marsh–mudflat sites in northwestern Europe. Earth Syst. Sci. Data 2021, 13, 405–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loon-Steensma, J.M. van; Kok, M. Risk reduction by combining nature values with flood protection? In 3rd European Conference on Flood Risk Management, E3S Web of Conferences. FLOODrisk, Lyon, France, 17-21 October; EDP Sciences, Ed., 2016; pp 1–10, ISBN 9781510833609.
- Hofstede, J.L.A. Update of the Schleswig-Holstein State master plan for coastal flood defense and coastal protection with a focus on climate change adaptation. Die Küste 2022, 91, 1–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MvIM; MvEZ. Delta programme 2015. Working on the delta: The decision to keep the Netherlands safe and liveable, The Hague, 2014.
- Calderon, A.; Smale, A.J. Doelbereik innovative dijkconcepten DP Wadden, 2013.
- Smale, A. Kwelders en waterveiligheid, 2012. Available online: https://open.rijkswaterstaat.nl/open-overheid/onderzoeksrapporten/@119374/kwelders-waterveiligheid/ (accessed on 17 July 2024).
- Martens, M.; Müller, P., Gösele, C.; Jensen, K.; Schuchardt, B. Blue Carbon im Nationalpark Niedersächsisches Wattenmeer: Grundlagen für eine Prüfung und Bewertung möglicher Maßnahmen zur Förderung der Kohlenstofffixierung in Salzwiesen. Studie i.A. der Nationalparkverwaltung, 2021.
- Siegersma, T.R.; Willemsen, P.W.J.M.; Horstman, E.M.; Hu, Z.; Borsje, B.W. Protective structures as adaptive management strategy in Nature-based Solutions to mitigate sea level rise effects. Ecological Engineering 2023, 196, 1–25. [Google Scholar]
- Clausen, K.K.; Stjernholm, M.; Clausen, P. Grazing management can counteract the impacts of climate change-induced sea level rise on salt marsh-dependent waterbirds. Journal of Applied Ecology 2013, 50, 528–537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakker, J.P.; Esselink, P.; Dijkema, K.S.; Duin, W.E. van; Jong, D.J. de. Restoration of salt marshes in the Netherlands. Hydrobiologia 2002, 478, 29–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seiberling, S.; Stock, M. Renaturierung von Salzgrasländern bzw. Salzwiesen der Küsten. In Renaturierung von Ökosystemen in Mitteleuropa; Zerbe, S., Wiegleb, G., Eds.; Spektrum: Heidelberg, Germany, 2009; pp. 183–208. ISBN 978-3-8274-1901-9. [Google Scholar]
- Seiberling, S.; Schultz, R.; Müller-Motzfeld, G. Restoration of Salt Meadows at the Baltic Sea Coast: the De-Embankment Experiment at Karrendorf Meadows. In Terrestrial coastal ecosystems in Germany and climate change, 1st ed.; Mossakowski, S., Irmler, U., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2023; pp. 415–430. ISBN 9783031125386. [Google Scholar]
- Hofstede, J.L.A. On the feasibility of managed retreat in the Wadden Sea of Schleswig-Holstein. J Coast Conserv 2019, 23, 1069–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




