3.1. Model Improvement: Temperature Effect on Fire Spreading
It has been known that the higher the altitude, the lower the temperature, and the higher the humidity or moisture content of the ground vegetation cover, suggesting that the altitude of the forest can affect the fire spreading velocity.
The moisture content could affect the initial fire spread speed. Zhang et al. studied the relationship of water content and initial fire spread velocity, which can be given as:
where
(%) is the moisture content of the combustibles,
(m/min) is the initial spread speed.
Li et al. studied the relationship of the moisture content of ground cover and average temperature, which is:
where H(%) is water content, and T(°C) is the average temperature.
Therefore, by using the equation of temperature effect on moisture and how the moisture affects the initial fire spread speed, we calculated the relationship between the temperature (which is affected by altitude) and the forest fire spreading, which is
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
Assuming the initial temperatures of 10, 20, 30, and 40, the temperature at different altitudes for each different initial temperature was shown in
Table 3.
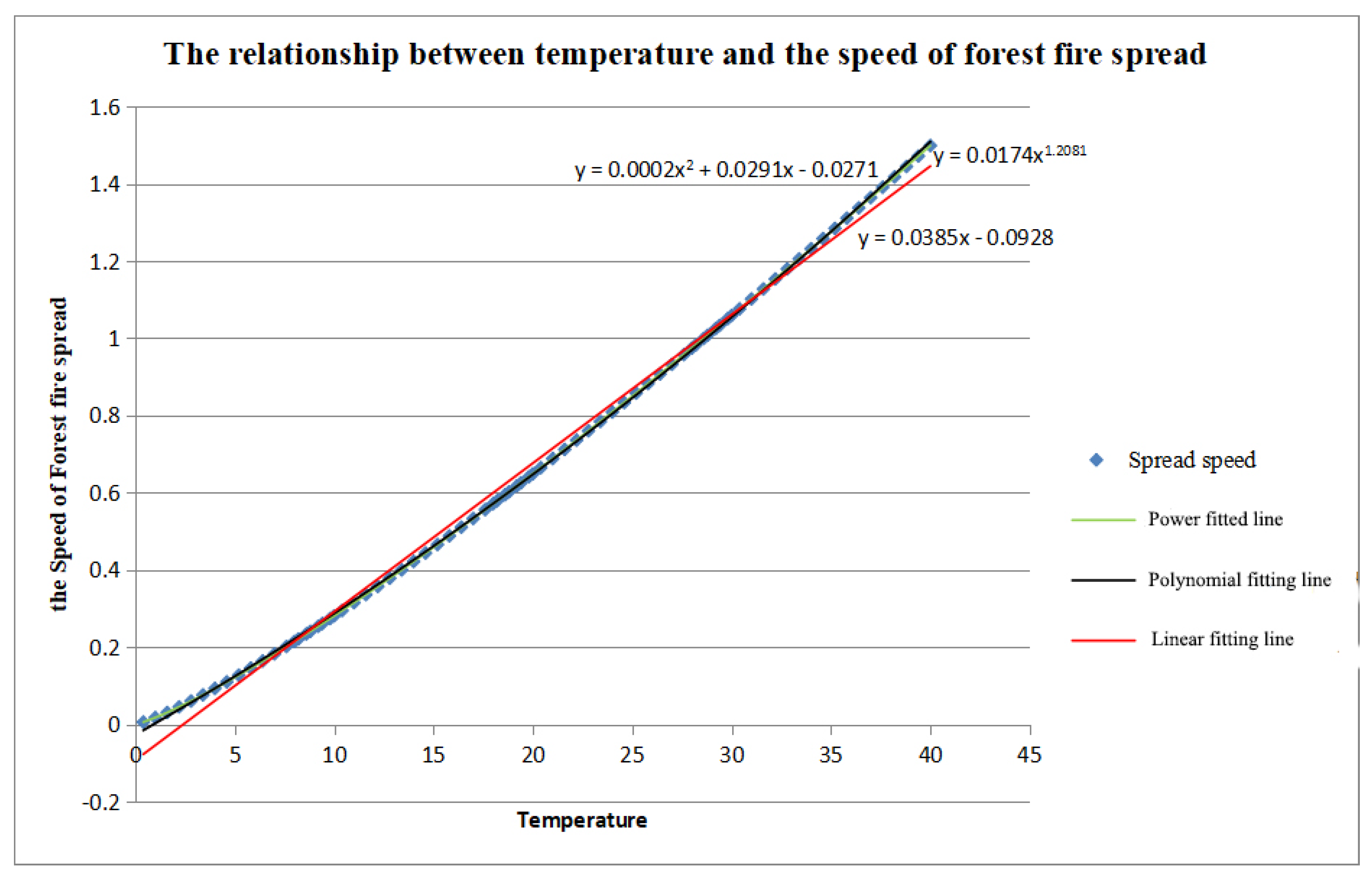
The relationship of the fire spread speed and temperature can be expressed as a linear equation:
where y is the fire spread speed and x is the temperature. Because the temperature decreases 0.6°C for each 100m of elevation increase as shown in
Table 3, the fire spread speed decreases 0.0231 m/min.
Assuming an initial temperature of 25°C and a spread speed of 0.870 m/min, the speed decreases by 2.7% for every 100 meters of elevation. The rate of decrease in fire spread speed at different initial temperatures is calculated as shown in
Table 4.
It can be seen from
Table 4 that the higher the initial temperature, the slower the reduction of fire spreading. And the improved fire spreading model is shown as follows:
where R is the estimated fire spread speed, R
0 is the initial spread rate, K
s is the combustible material type correction factor,
is the wind correction factor,
is the slope correction factor,
is the elevation correction factor, m is moisture content of combustibles, v is the wind speed,
is the angle between wind direction and uphill direction, w is slope,
is rate of decrease in fire spread speed with elevation, h is the elevation.
3.3. Prediction of RS Enabled Fire Spreading
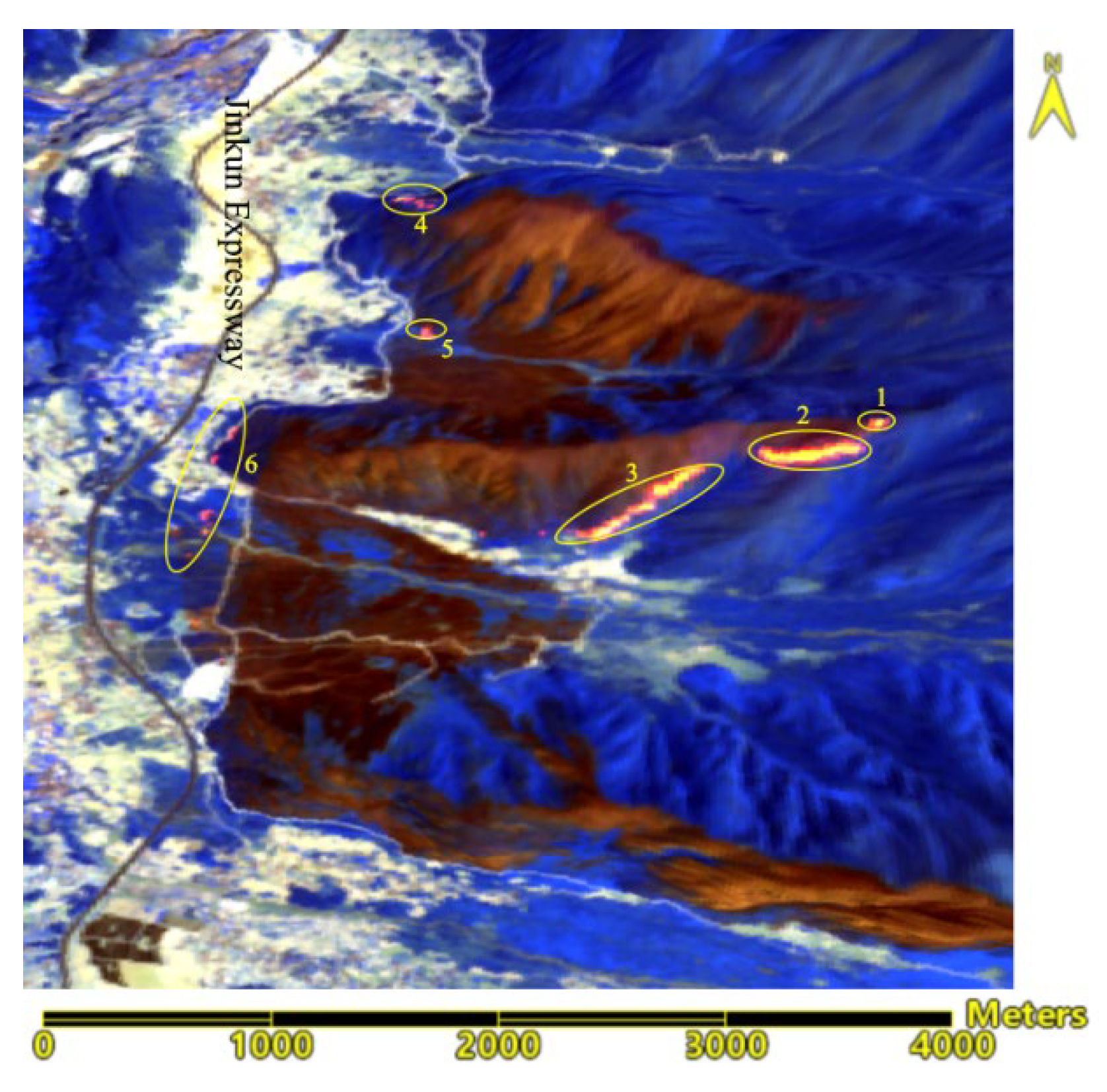
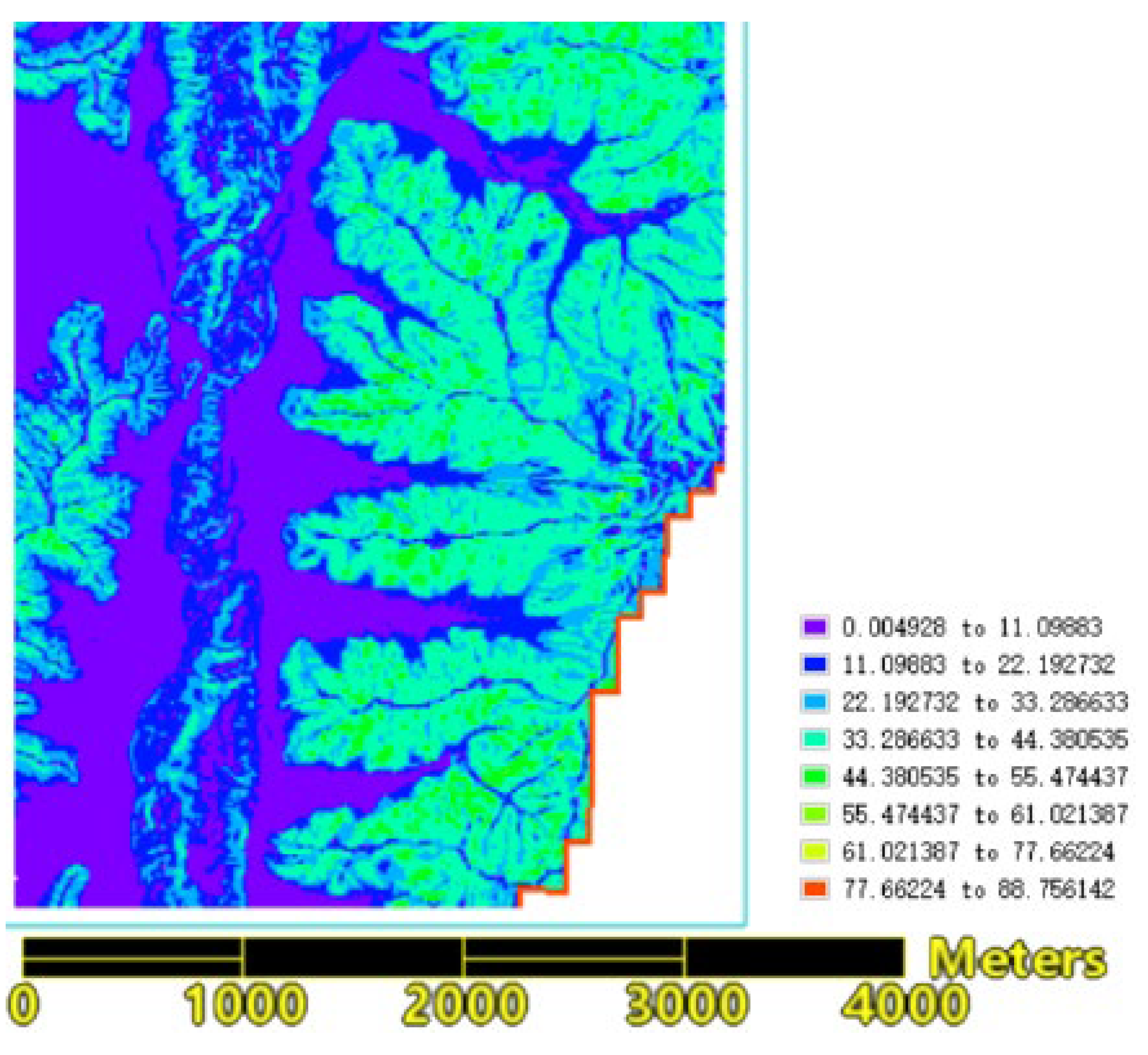
Slope and aspect of terrain are key factors affecting the speed of wildfire spread. Typically, fires spread slower downhill and faster uphill. The steeper the slope, the easier it is for water to run off, making the combustibles drier and indirectly accelerating the spread of the fire. This also affects the moisture content of the combustibles: sunlit slopes receive more sunlight, making the combustibles less moist and more flammable; conversely, the combustibles on shaded slopes retain more moist, making them less flammable. Therefore, based on the three-dimensional visualization of the fire scene (
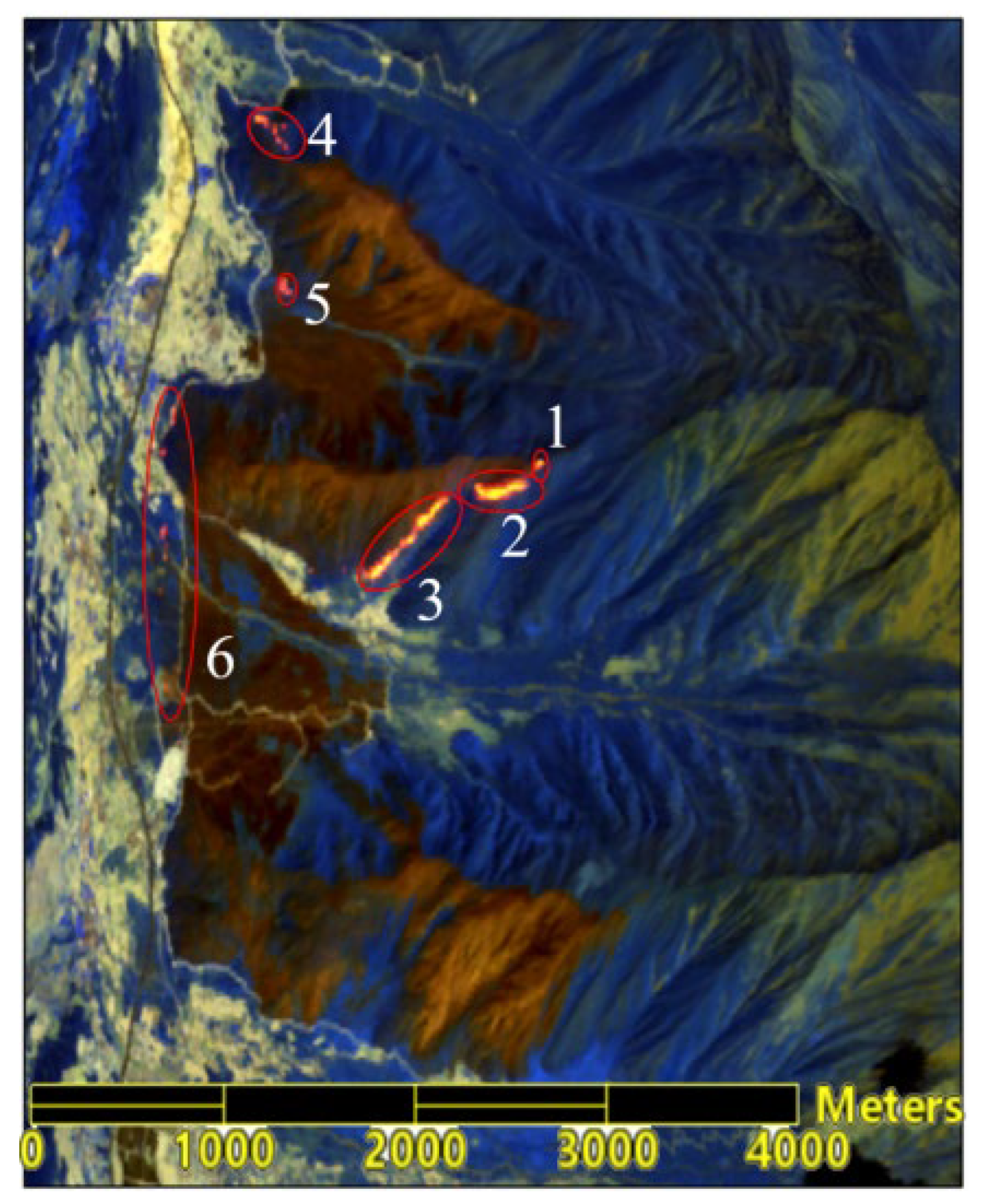
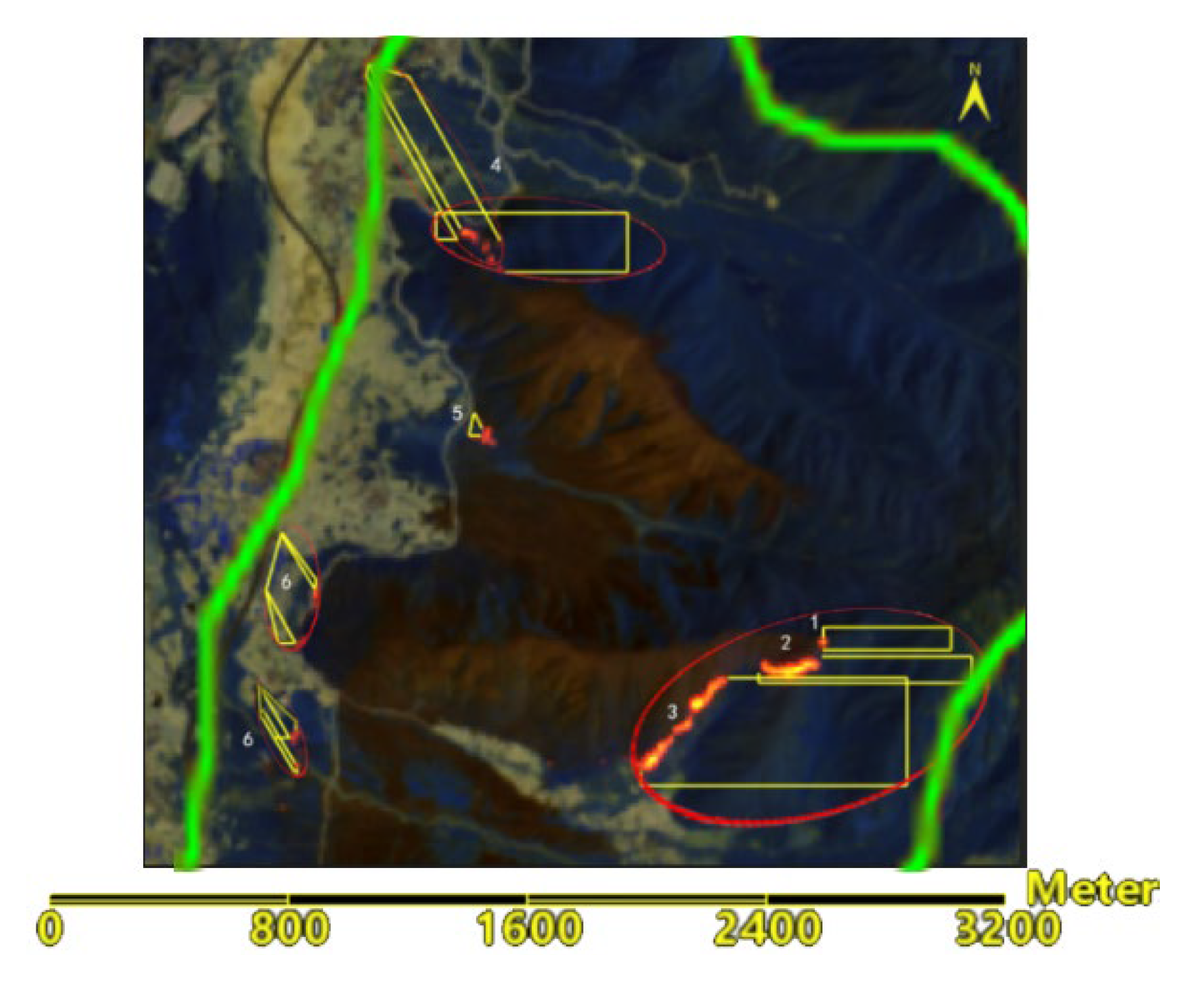
Figure 7), the positions of different fire lines on uphill, downhill, left level slopes, right level slopes, as well as the wind direction, were determined. Targeted fire speed simulations for each direction were also conducted.
As shown in
Figure 7, the north wind direction coincides with the direction of the left level slope and the east wind (which is negative) coincides with the downhill direction. The actual wind direction is from the northwest. Because burned areas generally do not reignite and form a barrier, they are not included in predictions for fire spread speeds. On the eastern line, sectors 1, 2, and 3 have intense fires and are located on uphill terrain with steep slopes, leading to faster spread speeds. Therefore, the fire spread speeds for uphill, left level slope, and right level slope at the top of the fire line of sector 1 are predicted, while for fire line of sectors 2 and 3, the spread speeds for uphill and right level slope directions are predicted. For fire line of sector 4, which is at the base of the mountain with a relatively low terrain slope, the fire spread speed for uphill, left level slope, downhill, and wind direction is predicted. Other fire spread predictions include downhill and wind direction for sectors 5, and downhill, left level slope, right level slope, and wind direction for sector 6.
After incorporating the remote sensing data and temperature effects associated with different elevations, the prediction results are as follows:
In Fire Line 1 area, there are 15 adjacent pixels, with one outlier removed. The vegetation moisture content is below 0.01, with the minimum and maximum slope being 13.24°and 42.34°respectively. The maximum speed for uphill, left level slope, and right level slope is 11.782, 0.939, and 0.562 m/min respectively.
In Fire Line 2 area, there are 32 adjacent pixels, with one outlier removed. Five pixels have vegetation moisture content below 0.01, with the maximum reaching 1.008. Slopes are above 34.5°, with the maximum slope being 45.01°. The maximum fire spread speed for uphill and right level slope is 13.858 and 0.562 m/min, respectively.
In Fire Line 3 area, there are 55 adjacent pixels, with five outliers removed. Nineteen pixels have vegetation moisture content below 0.01, while the majority of the remaining pixels are around 0.5, with the highest value reaching 0.911. The minimum slope is 15.500°and the maximum slope is 46.544°. The maximum fire spread speed for uphill and right level slope speed is 16.527 and 0.562 m/min, respectively.
In Fire Line 4 area, there are 26 adjacent pixels, with nine pixels having a moisture content below 0.01, and the rest between 0.483 and 0.987. Slopes are above 33°, with the maximum slope being 41.770°. The maximum speed for uphill, left level slope, downhill, and wind direction is 11.254, 0.939, 1.702, and 17.319 m/min, respectively.
In Fire Line 5 area, there are 9 adjacent pixels, with moisture content between 0.5 and 0.6. The slopes range from 11.984° to 12.550°. The maximum downhill speed is 1.061 m/min and the maximum wind direction speed is 1.587 m/min.
In Fire Line 6 area, there are 47 adjacent pixels, with one outlier removed. Ten pixels have vegetation moisture content below 0.01, the rest between 0.415 and 0.733. Slopes are below 28°, with the minimum slope being 1.024°. The maximum fire spread speed for downhill, left level slope, right level slope, wind direction is 1.378, 0.939, 0.562, and 5.669 m/min, respectively.
Given the limitations of time and spatial resolution associated with satellite RS images, the sudden nature of forest fires, and the accuracy of RS inversion parameters, the fire spread range one hour later is based on the statistical values of forest fire spread speed results in each direction mentioned above. The results are shown in
Table 7 and
Figure 10.
It is evident that the fire spread speed is the fastest in the uphill direction, resulting in the longest spread distance, while the spread distances on the left level slope and the right level slope are essentially the same. Note that fire line 6 area shows a greater spread distance in the wind direction.
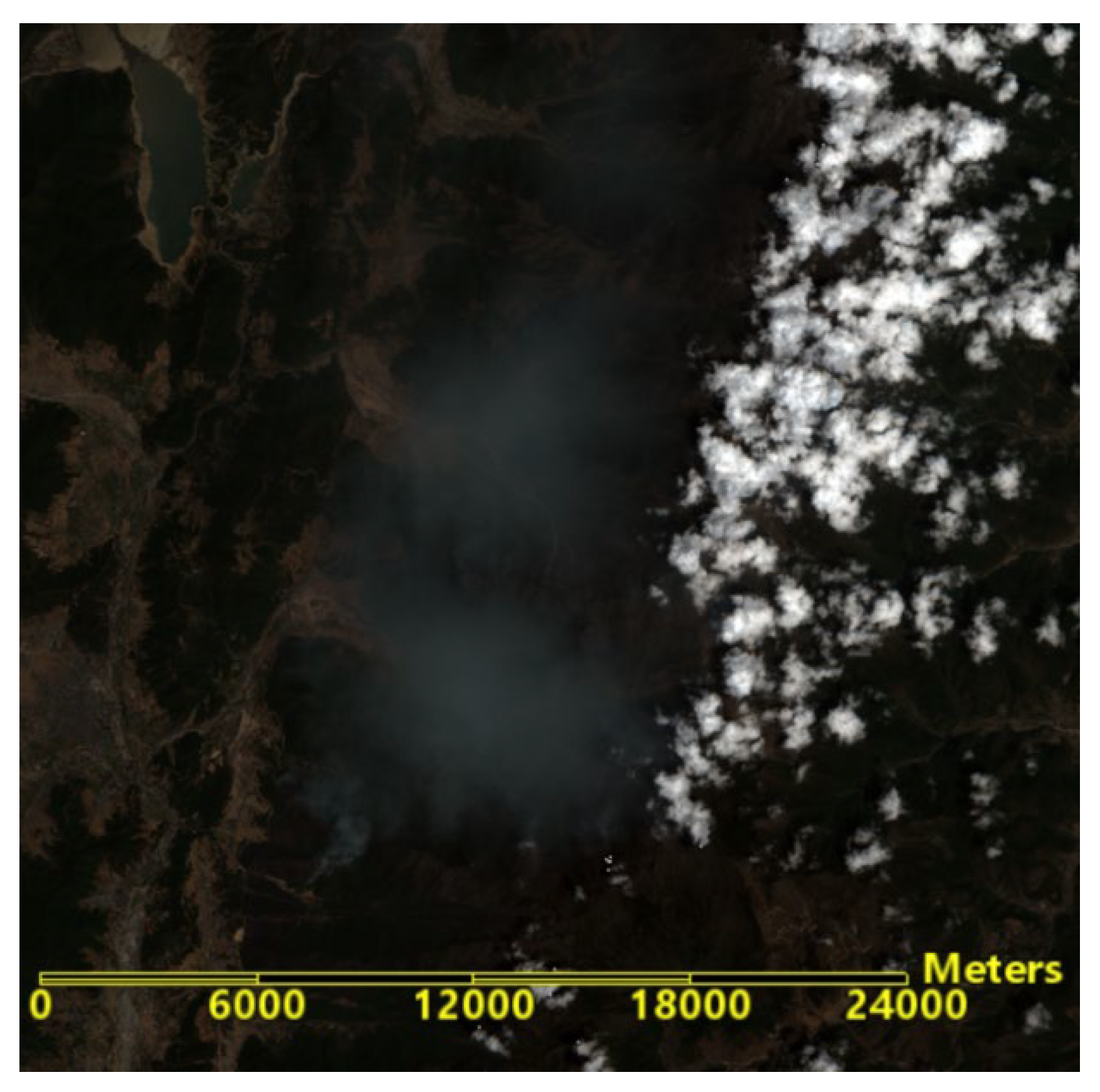
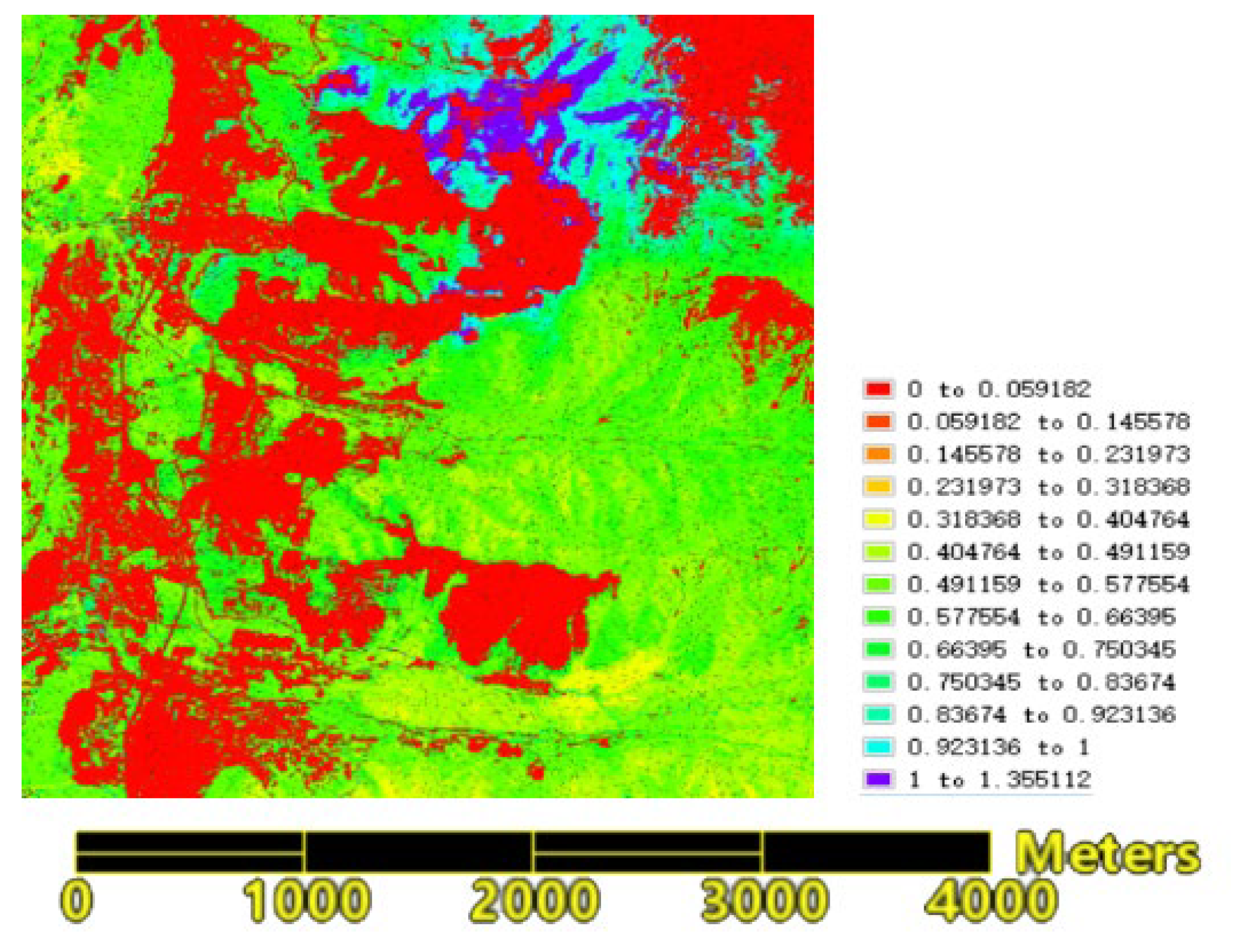
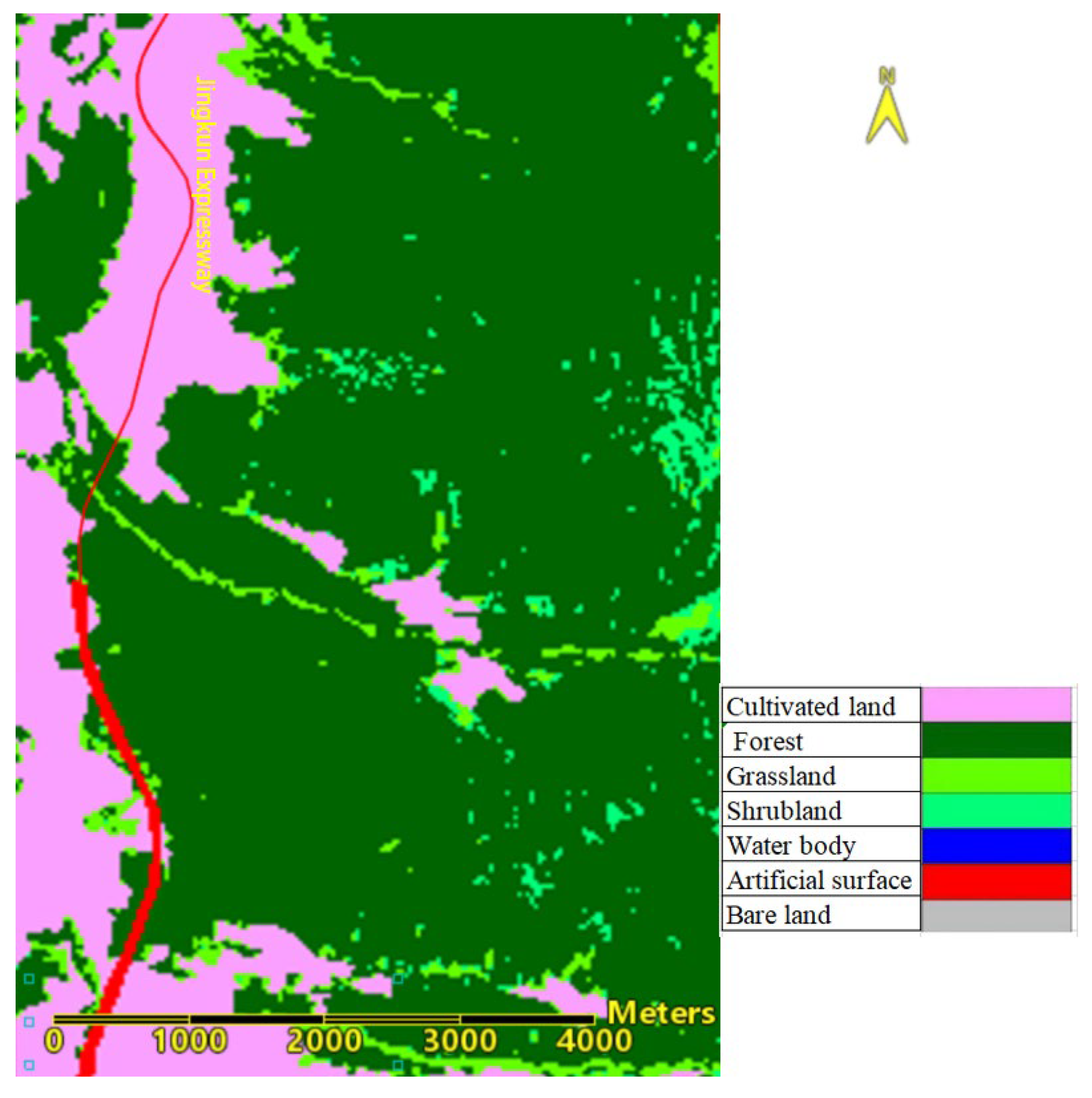
The RS enabled fire spread prediction can provide critical information for firefighters to effectively combat fires. In the case of Mianning fire, based on the land cover type map before the forest fire (from the National Basic Geographic Information Center) (as shown in
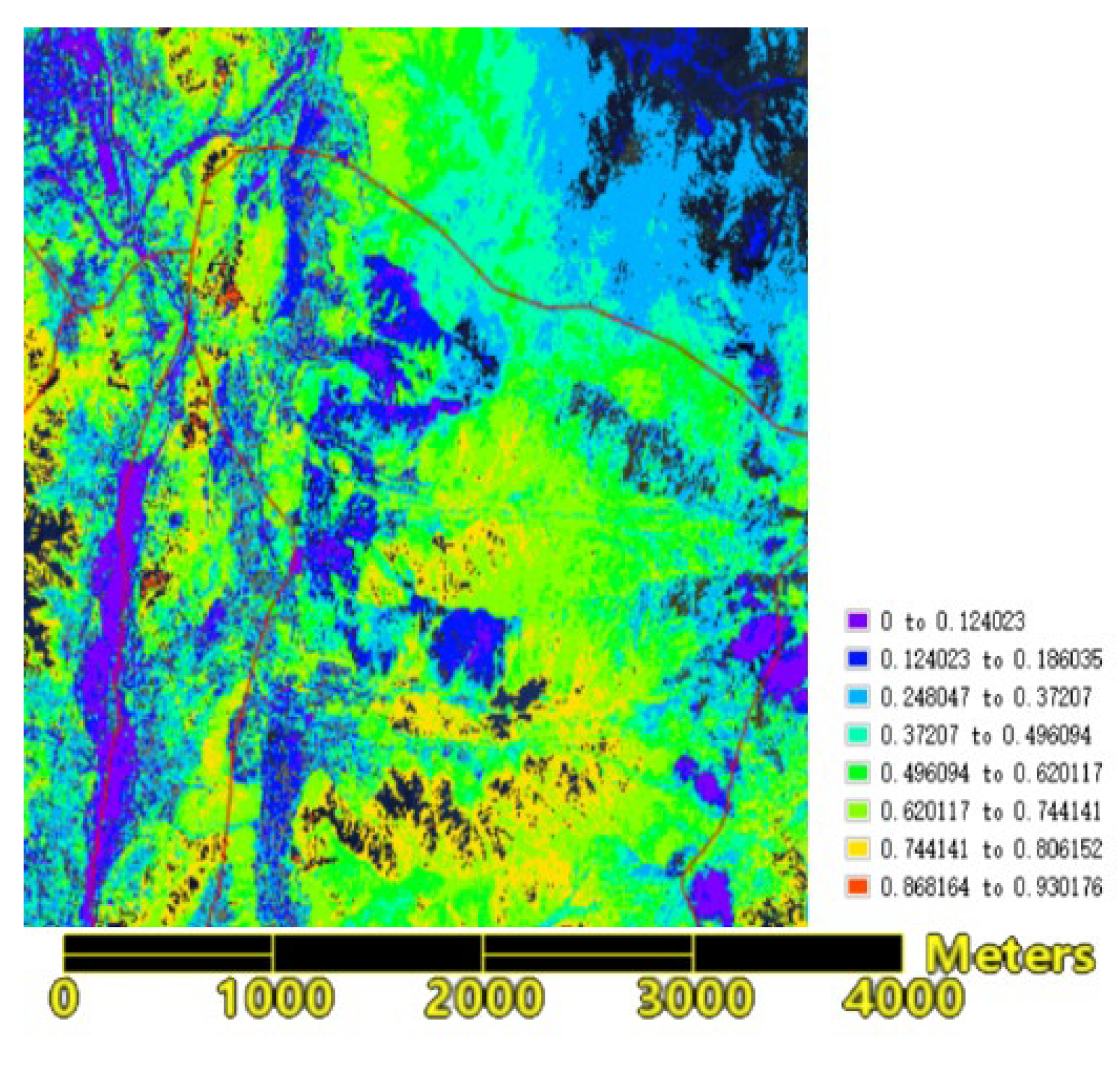
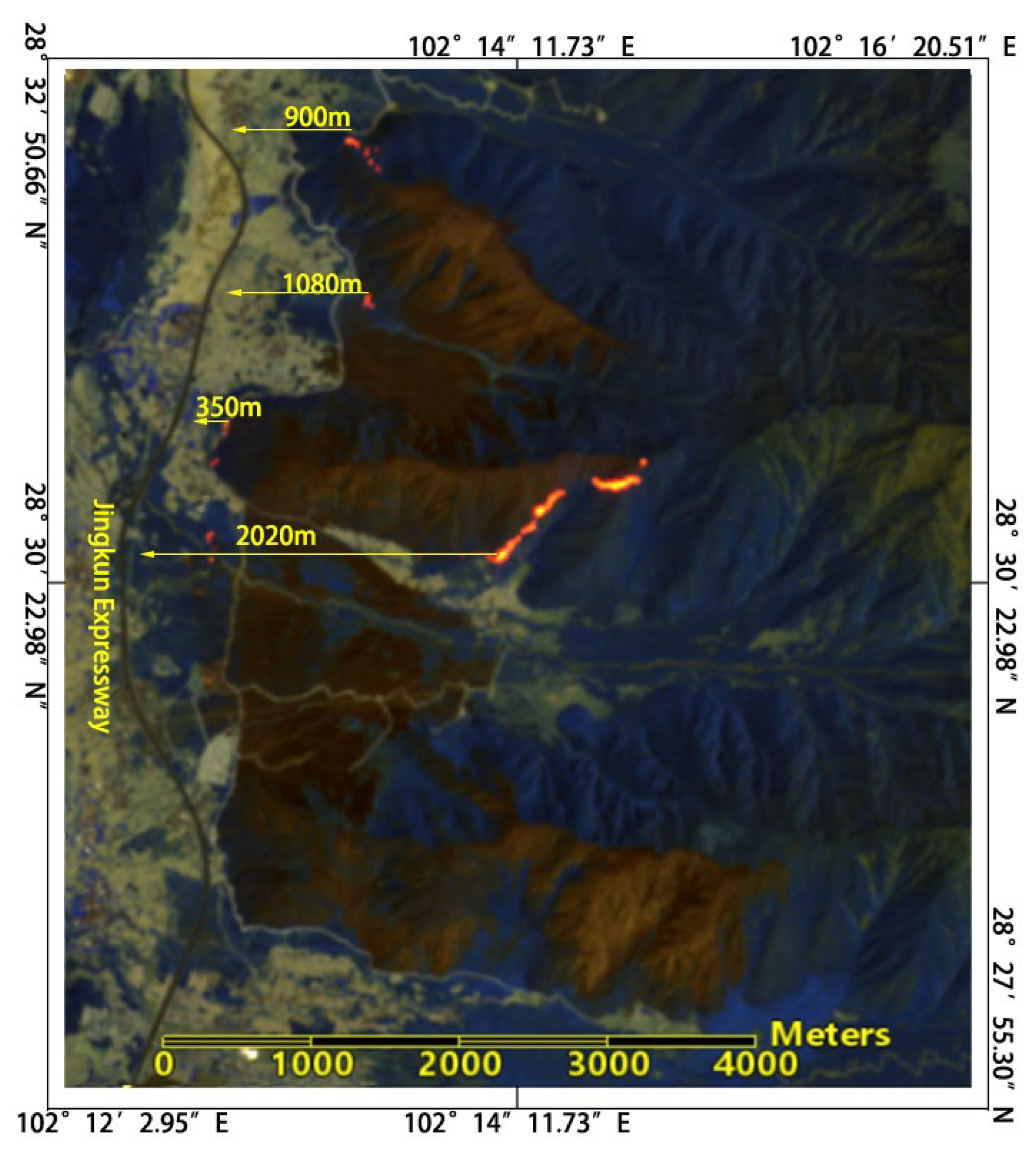
Figure 11) and high-resolution remote sensing imagery (Sentinel-2), the west side of the forest fire borders the Jingkun Expressway (as shown in
Figure 12), which is non-forested and forms a barrier. Typically, a forest fire will extinguish on its own upon encountering non-combustible materials unless spot fires occur (which would cause the fire to jump to other mountain tops). Therefore, based on the RS-enabled fire spread prediction, it is recommended that defense and firefighting efforts should concentrate on the eastern sectors 1, 2, and 3, as well as the northern and eastern areas of sector 4 on the western line.
3.4. Comparison of RS Enabled Fire Spread Prediction with Actual Mianning Fire
According to the hourly meteorological data for Mianning County on 2021-04-24 shown in
Table 2, between T4:00 and 5:00, the wind direction and speed changed from north at 1.44 m/s and east at -0.78 m/s to north at 1.48 m/s and east at -0.54 m/s, indicating relatively stable conditions. Based on the maximum spread distances in each direction shown in
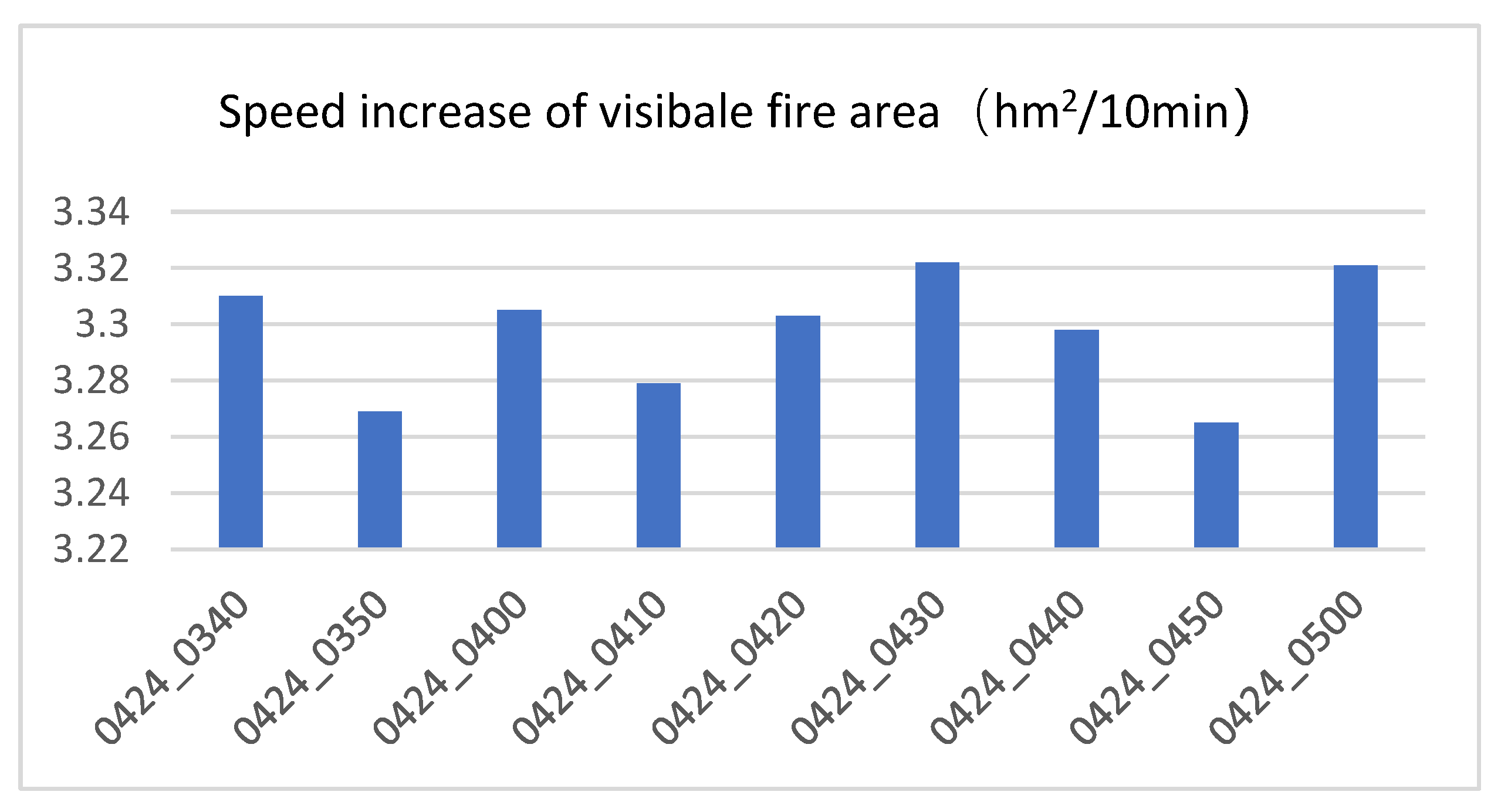
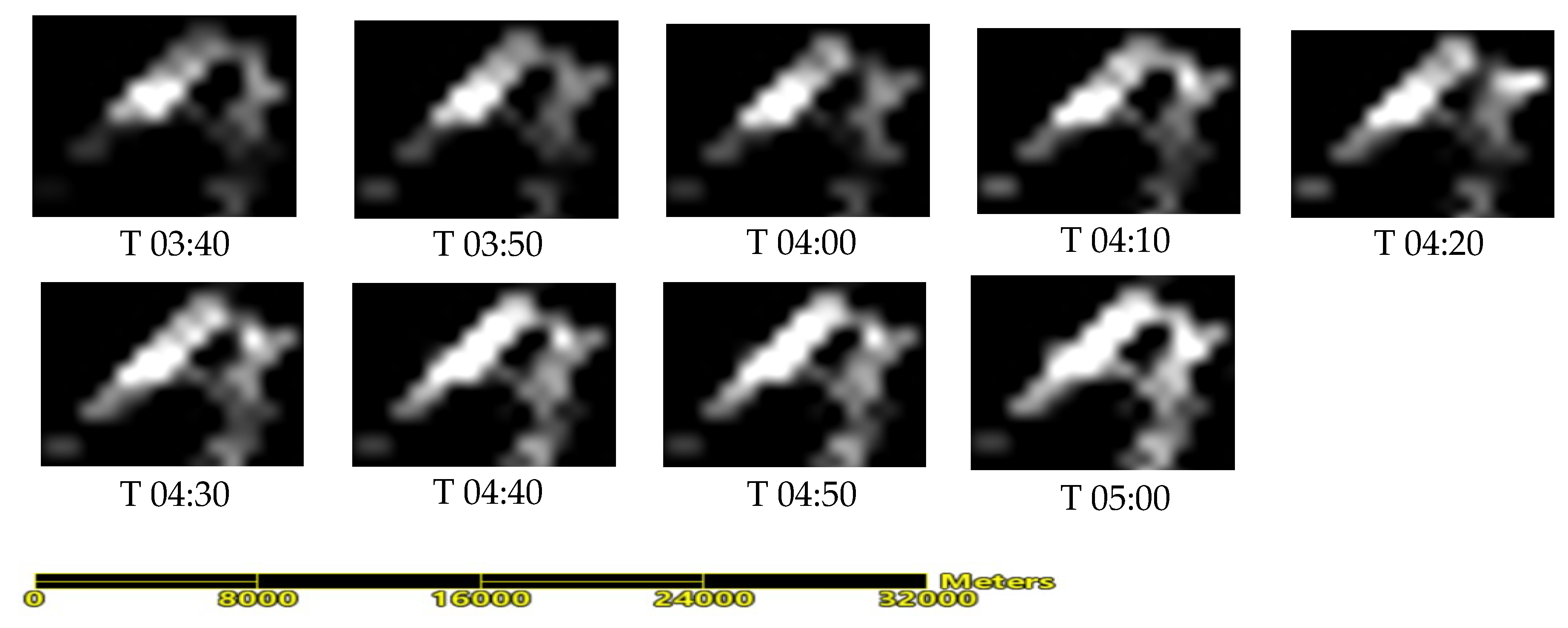
Table 7, the average increase in visible fire area was calculated to be 3.257 hm²(square hectare) per 10 minutes within one hour. Analysis of the dynamic changes in the visible fire area of the Mianning forest fire monitored by Himawari-8 satellite every 10 minutes from 2021-04-24 T03:40 to 2021-04-24 T05:00 (UTC) (
Figure 13) shows a significant increase in visible fire area, with an average increase rate of 3.297 hm² per 10 minutes. This rate can be considered consistent with the results simulated by the RS-enabled forest fire spread model. The small discrepancy may be likely due to the differences in spatial resolution between remote sensing images.
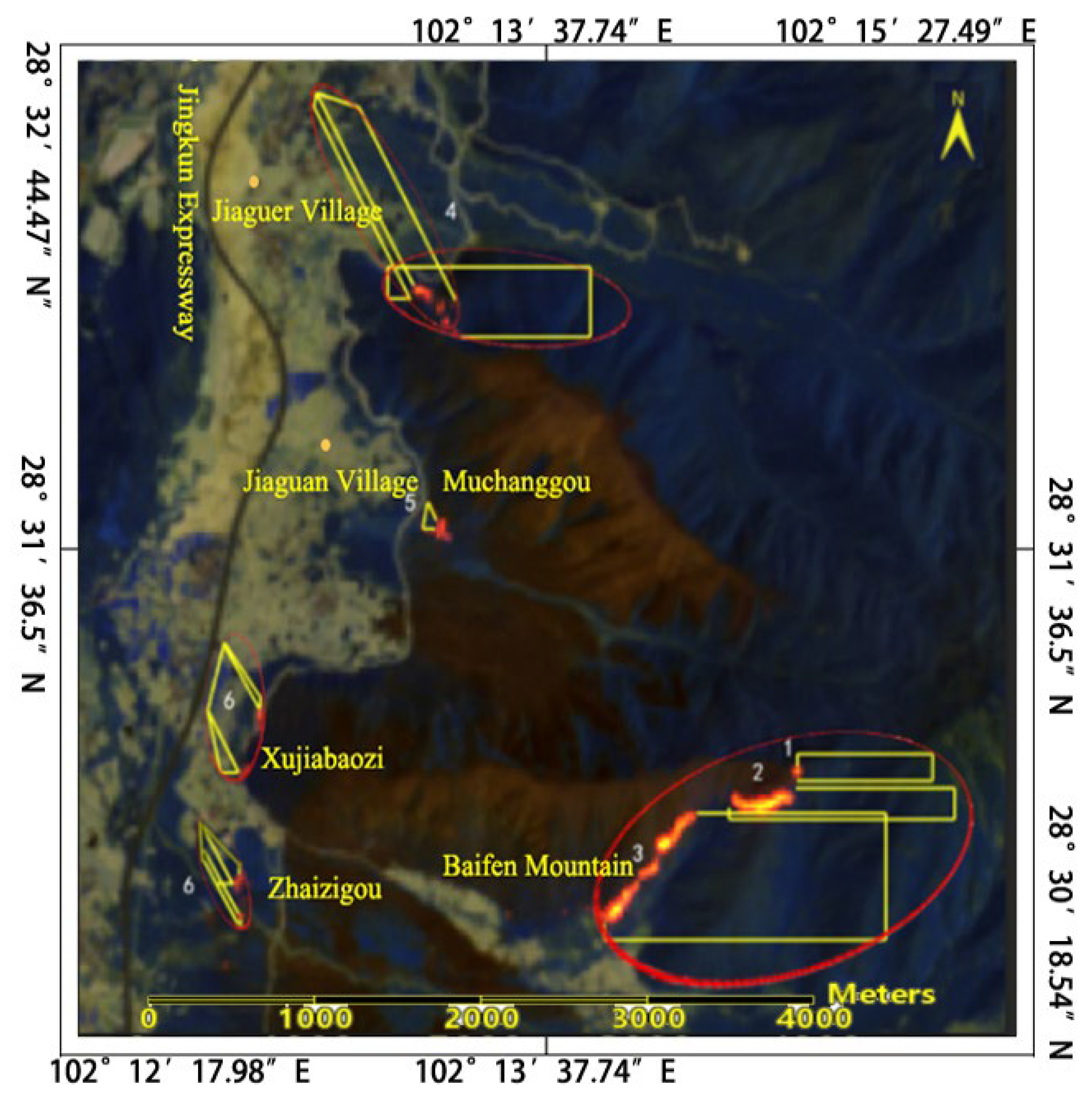
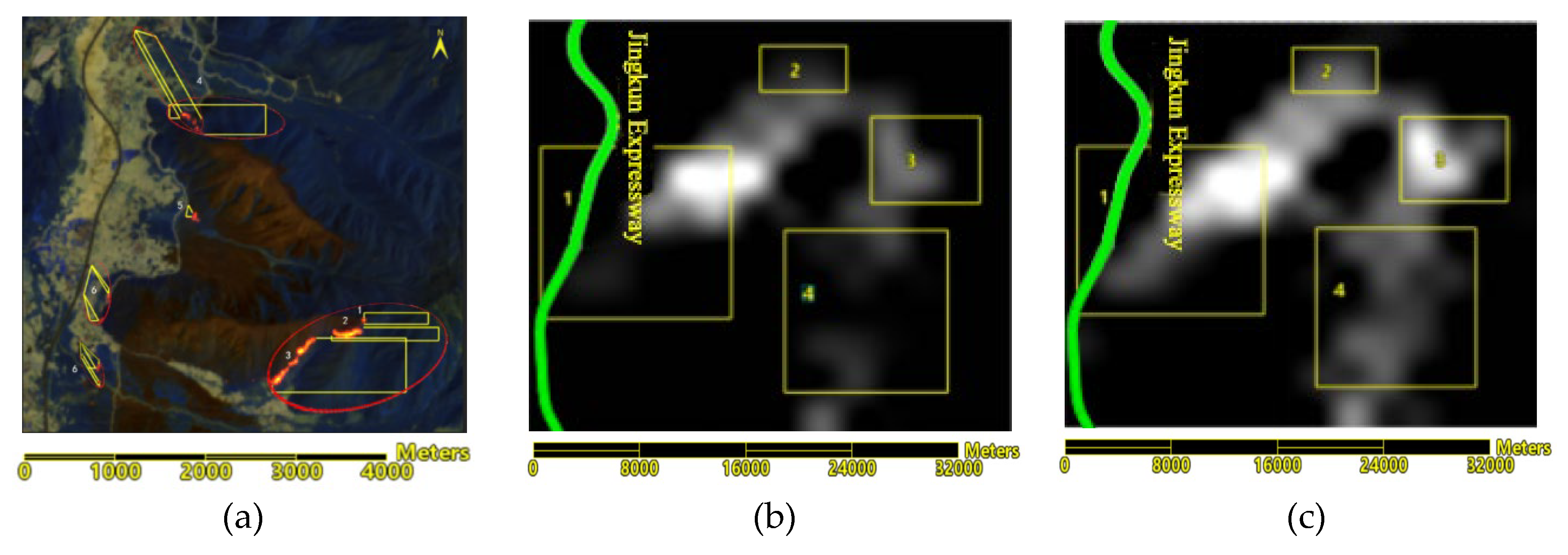
According to the analysis of the remote sensing imagery of fire spots from the Himawari-8 satellite on April 24 from 3:40 to 5:00 (
Figure 14 and
Figure 15), the fire monitoring points progressed westward from Jiaguan Village and did not cross the Jingkun Expressway (102°12′38″E); it extended eastward from Baifen Mountain and northward from Dashuigou (as shown in rectangles 1, 2, 3, and 4 in
Figure 15), consistent with the trend observed in the forest fire spread model simulations.
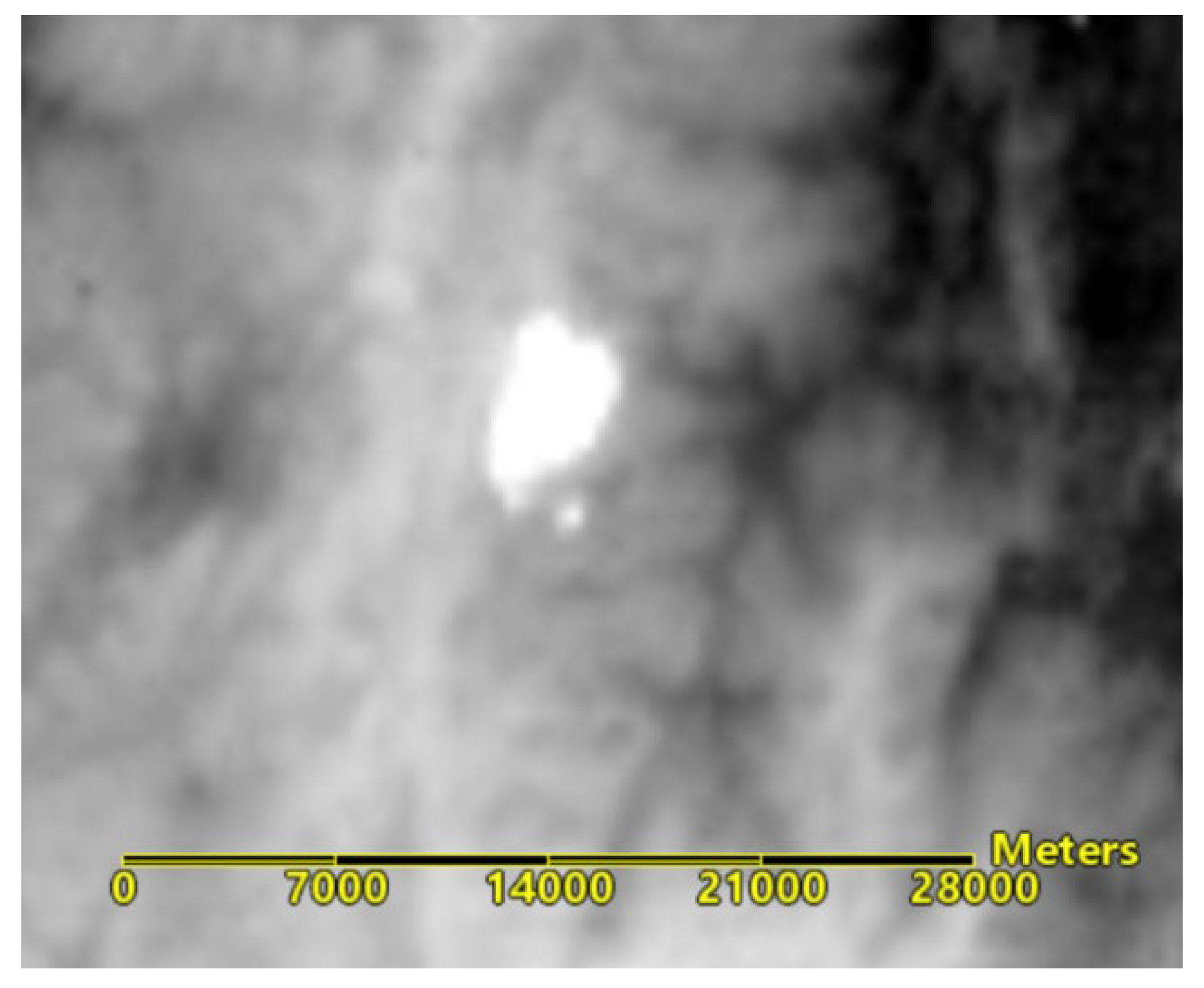
Using the mid-infrared image from Gaofen-4 IRS (GF4_IRS_E103.0_N29.3_20210424 _L1A0000374570), taken 58 minutes after the Sentinel-2 image at T03:45, the anomaly temperature perception in the forest fire area was studied to verify the results of the RS enabled forest fire spread. The Gaofen-4 data were collected at 04:43:42 on April 24, and the brightness temperatures derived from the mid-infrared band are shown in
Figure 16. Using the 20-meter resolution remote sensing image from Sentinel-2 as a base image, the Gaofen-4 infrared IRS image was geometrically corrected and precisely registered. The two images were overlaid with the Gaofen image on top, with the top image’s transparency being set to 50%, as shown in
Figure 17. Upon enlargement, the boundary of the anomaly temperature and the predicted forest fire spread area overlapped as shown in
Figure 18. The results clearly show that the predicted forest fire spread area (Regions 1-6) essentially aligns well with the brightness temperature anomaly boundary detected by the Gaofen-4 IRS image. The small discrepancies may have been caused by factors such as smoke from the fire, lower mid-infrared image resolution, and firefighting activities.
The deduced spread area is also consisitent with the results of Tang Y. et al.’s research [
31] and historical archives.
The above analysis shows that the predicted spread area of the model generally matches the actual spread results, demonstrating the accuracy and reliability of the RS enabled fore fire spread model for predicting the forest fire development, particularly in those fires occurring in the difficult-to-access areas.