1. Introduction
Lectins, which are representative glycan-binding proteins, exhibit a diverse range of structural families and glycan-binding properties across various organisms [
1]. They are potentially involved in a plethora of biological roles, which include defense, stress response, cell adhesion and growth regulation [
2,
3,
4]. According to the UniLectin structural database [
5], approximately one-quarter of the lectins discovered to date bind to galactose, indicating that many non-reducing terminal galactoses in glycans are targets for lectin binding.
Sponges (phylum Porifera), the most early-branching group of animals, first appeared during the Ediacaran period, in the Neoproterozoic era [
6]. They are sessile invertebrates living in a broad range of aquatic environments, from intertidal coastal waters to the deep sea, with about 5,000 described species [
7]. Consistently with their ancient origins deeply rooted at the stem of animal phylogeny, sponges possess lectins belonging to different families, such as galectins [
8,
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17], C-type lectin [
18], bacterial fucose-binding lectin [
19], and tachylectins [
20].
The genus
Chondrilla (order Chondrosida) includes more than 16 extant marine species, and its members are characterized by collagen-rich tissues [
21]. Different types of lectins have been previously discovered in several species of this genus. For example, a homotetrameric galectin has been purified from
Chondrilla caribensis, a species that inhabits the Gulf of Mexico and the South Atlantic Ocean. This galectin exhibits anti-microbial, anti-biofilm, and leishmanicidal activities [
10,
11].
In this study, we report the purification of a novel galectin from a different species of
Chondrilla living in the Pacific Ocean, i.e.,
Chondrilla australiensis. Although hRTL was evolutionarily related to other galectins, it displayed some peculiar features, which most notably included an N-terminal extension that, according to combined N-terminal sequencing by Edman degradation and the analysis of RNA-sequencing data. It likely serves as a signal peptide for secretion. Furthermore, hRTL exclusively displayed binding affinity towards the Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF)-antigen (Galβ1-3GalNAc) [
22,
23] and type-1 LacNAc (Galβ1-3GlcNAc). Notably, the TF-antigen is a characteristic oncogenic oligosaccharide in digestive carcinoma cells [
24,
25]. We show that administering hRTL to cells expressing TF-antigens induces cell death, accompanied by the activation of MAP kinases related to apoptosis.
2. Results
2.1. Tetrameric Structure of β-Galactoside-Binding Lectins (hRTL) Purified from C. australiensis
The crude extract from
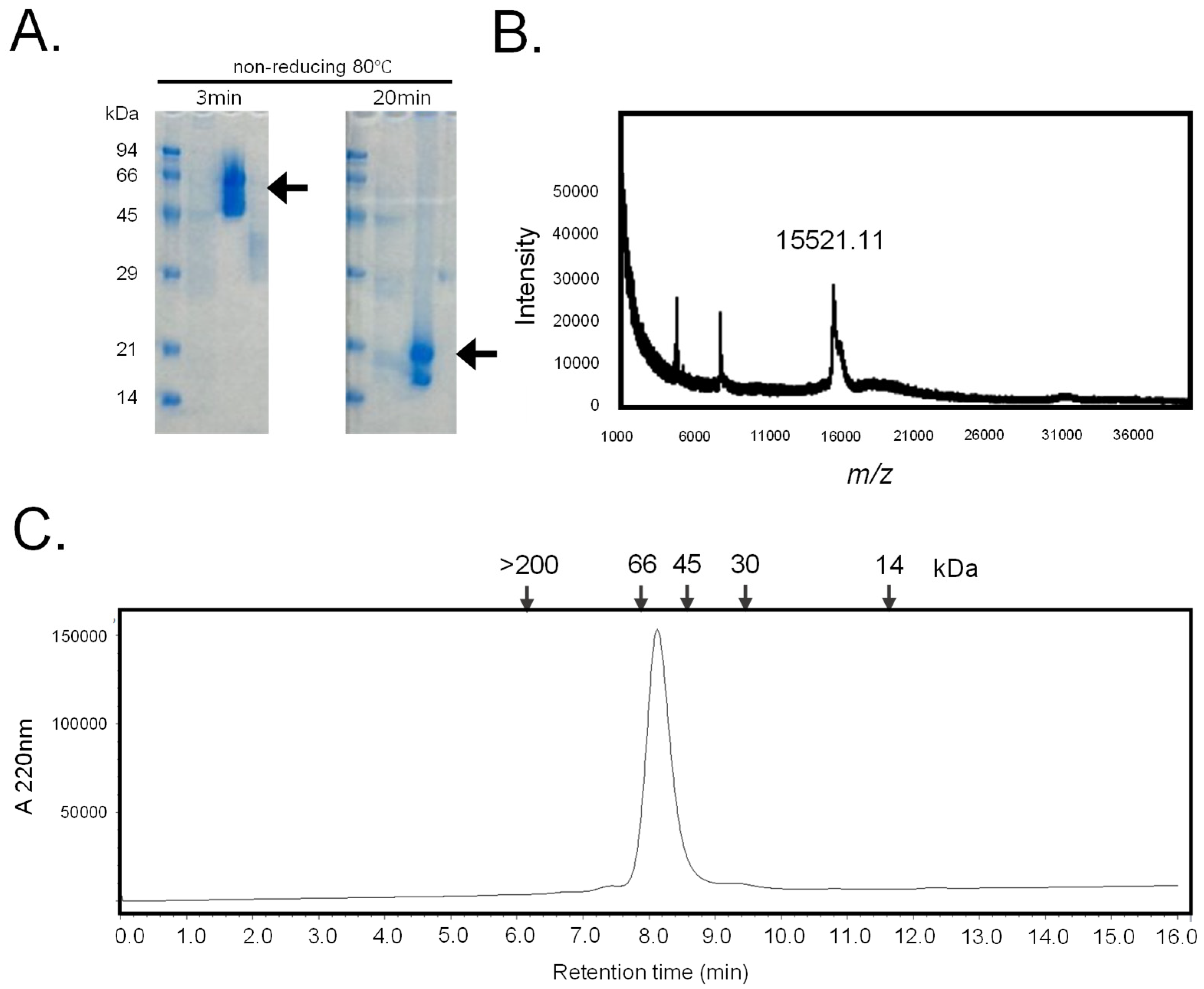
Chondrilla australiensis exhibited intense hemagglutinating activity, inhibited by the presence of β-galactosides, such as lactose. This crude supernatant was applied to a lactosyl-agarose column. After washing the column with a 50 mM sodium bicarbonate-containing saline buffer, the column-binding lectin was eluted using a 50 mM lactose-containing buffer. SDS-PAGE analysis revealed that the lectin had a molecular mass of 18 kDa under heated and short-heated conditions, and of 66 kDa under non-reducing conditions, respectively (
Figure 1A). The molecular mass of the polypeptide chain was determined by mass spectrometry to be 15,521.11 Da (
Figure 1B). Analysis by high-performance liquid chromatography coupled with a gel permeation column indicated a molecular mass of 60 kDa (
Figure 1C). Altogether, these results indicate that the β-galactoside-binding lectin from the sponge
C. australiensis has a tetrameric structure, with non-covalently bonded subunits of 15 kDa. This molecule was named hRTL (C
hondrilla aust
raliensis
tetramer
lectin).
12.8 mg of hRTL was purified from 200 g of fresh sponge (
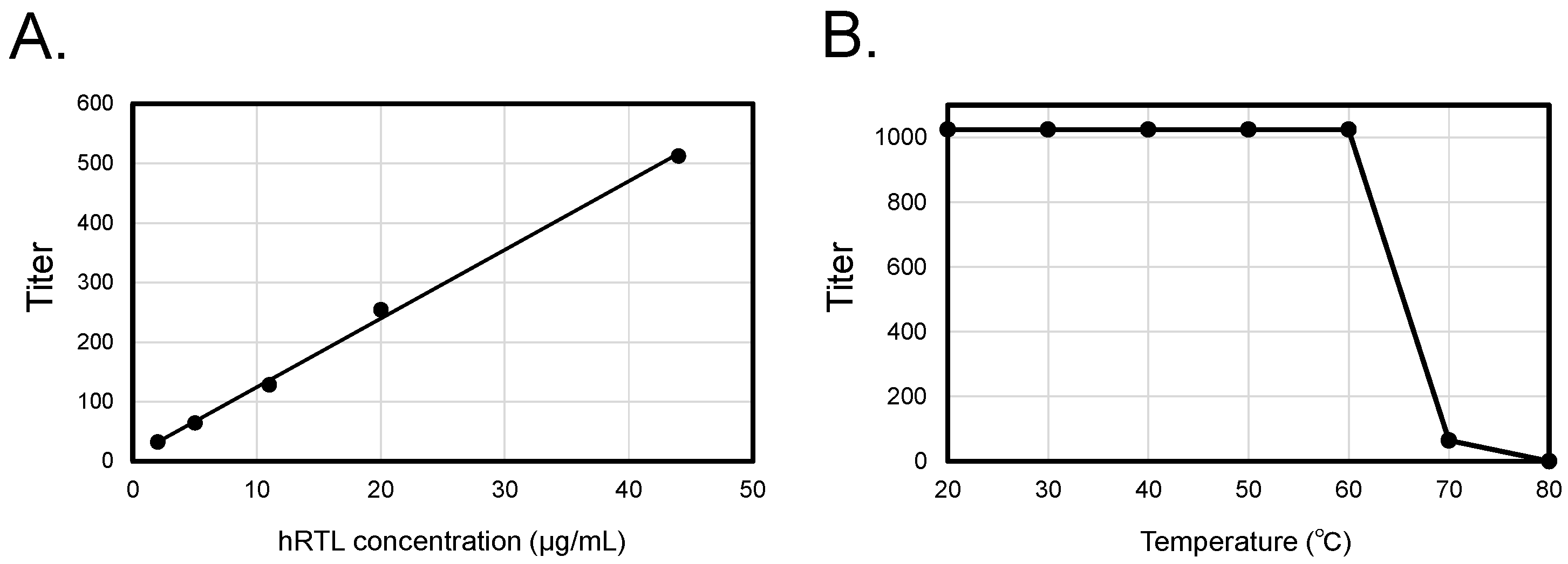
Table 1). This lectin could be repeatedly extracted from the precipitate of the sponge after the initial extraction. At low concentrations (< 50μg/mL), the hemagglutination activity increased proportionally with the lectin concentration (
Figure 2A and
Supplementary Figure S3). hRTL exhibited high thermotolerance (
Figure 2B), with thermal stability similar to CCL [
10].
The sugar-binding specificity of hRTL is summarized in
Table 2. Type-3 β-galactoside, such as TF-antigen (Galβ1-3GalNAc), was the most potent inhibitor of hemagglutination by hRTL (1.6 mM), though type-2 β-galactosides, such as lactose (Galβ1-4Glc) were also well recognized by the lectin (3.2 mM). However, hemagglutination was less inhibited by α-galactoside, such as melibiose (Galα1-6Glc) (50 mM). D-galactose and N-acetyl D-galactosamine moderately inhibited hemagglutination, whereas N-acetyl D-glucosamine and D-mannose did not lead to any inhibition. Porcine stomach mucin and fetuin strongly inhibited the hemagglutination of hRTL, whereas bovine submaxillary mucin was much less effective.
2.2. Characterization of the Primary Sequence of hRTL
Using an automated gas-phase protein sequencer for Edman degradation, we identified the N-terminal amino acid sequence of hRTL either as DYIEFES (the major sequence) and EYVEVES (the minor sequence) (
Supplementary Figure S1). These results indicate that the N-terminus of the lectins was not blocked. The determination of the N-terminal end of the lectin sequence was paired with the analysis of the de novo transcriptome assembly of
C. australiensis, which we report for the first time in this work, with the aim to identify the transcript encoding the full-length hRTL protein. Overall, RNA-sequecning, carried out on an Illumina platform, led to the generation of over 3.0E7 high-quality raw paired-end reads (
Supplementary Figure S2A,B), which were deposited in a public repository (NCBI BioProject: PRJNA1144512) and assembled to 152,299 unigenes. Overall, both the high quality of the reads and the completeness of the transcriptome assembly (BUSCO scores indicated the presence 92.2% complete, 1.7% fragmented and 6.1% missing conserved metazoan single-copy orthologs) supported the reliability of this resource as a database for sequence homology searches in this species.
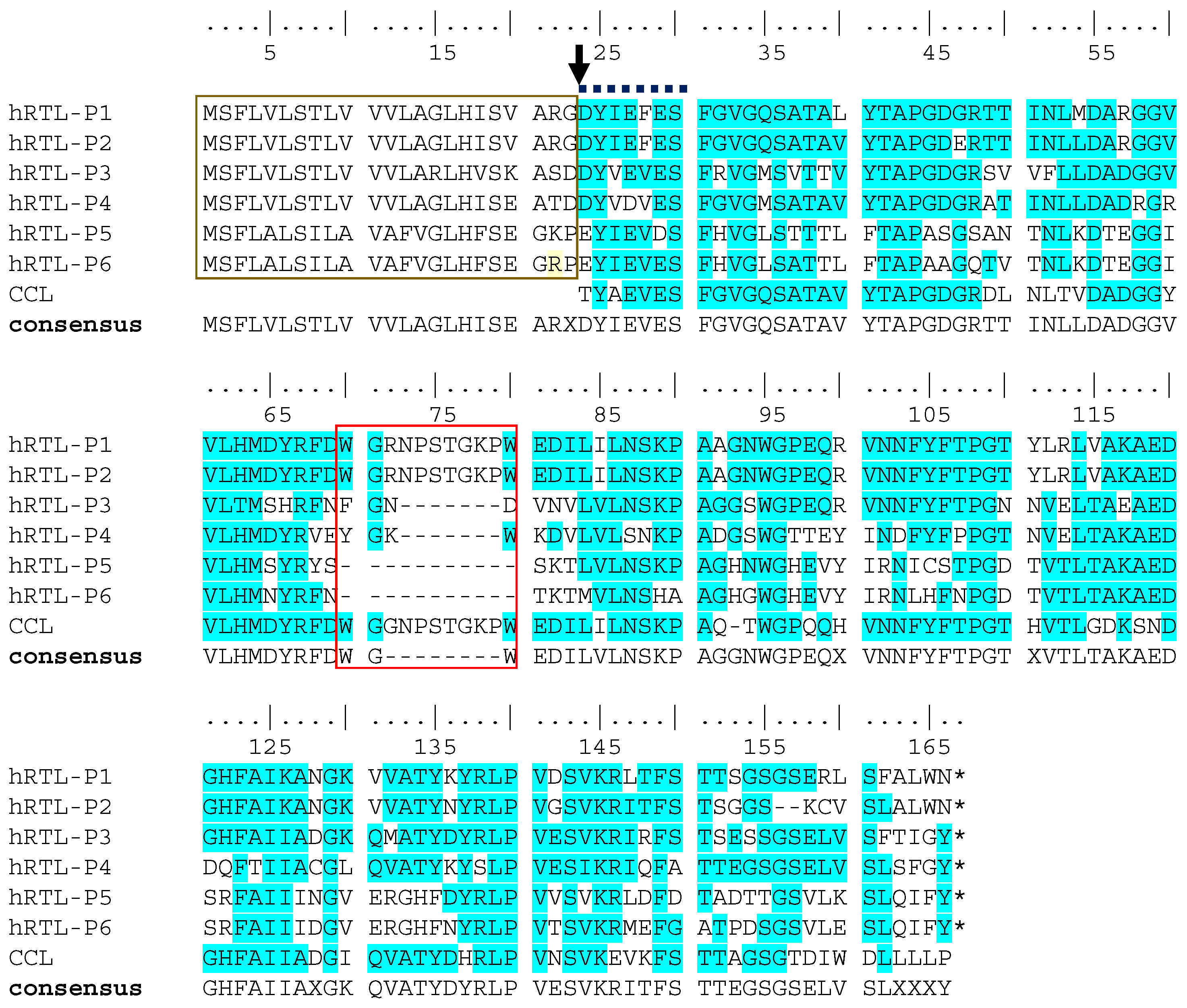
A tBLASTn search allowed to identify the complete protein sequence of two candidate hRTL precursor sequences, termed hRTL-P1 and hRTL-P2, confirming the correctness of the major sequence determined by Edman degradation. The inspection of the complete precursors identified the presence of 23 additional amino acid residues located at the N-terminal end, before the N-terminal residue detected by Edman degradation (
Figure 3). In addition, sequence homology searches allowed the recovery of four additional complete sequences related to hRTL (named hRTL_P3 to hRTL_P6). These sequences had high pairwise primary sequence homology and a similar length (
Figure 3), and they were also closely related to the CCL galectin, previously purified from another sponge species belonging to the same genera,
C. caribensis (
Figure 3, CCL). Like hRTL-P1 and hRTL-P2, also the other four galectin sequences of
C. australiensis displayed 23 amino acids located before the N-terminus determined by Edman degradation (
Figure 3, gold box).
By omitting these 23 amino acids, the calculated molecular masses of hRTL_P1 and P2 (15,526.23 and 15,534.87) would be well-matched with the molecular mass measured by mass spectrometry of hRTL, i.e., 15,521.11 (
Figure 1C), emerging as the best candidates to fit the hRTL lectin sequence purified from sponge extracts. Interestingly, compared with the other four hRTLs, these two proteins also displayed the presence of a 10-amino-long insertion, which was shared with CCL (
Figure 3, red box).
Overall, hRTL-P1, hRTL-P2, and CCL shared seven highly conserved amino acids that are important for carbohydrate binding in most galectins, as exemplified by their conservation also in human galectin-1 (
Figure 4, yellow highlight). Interestingly, the inserted sequence that distinguishes these lectins from the other hRTLs of
Chondrilla (Trp47-Trp57) corresponds to an insertion also compared to human galectin-1 (
Figure 4, red box).
2.3. hRTLs Are Targeted to the Secretory Pathway Due to the Presence of a Signal Peptide
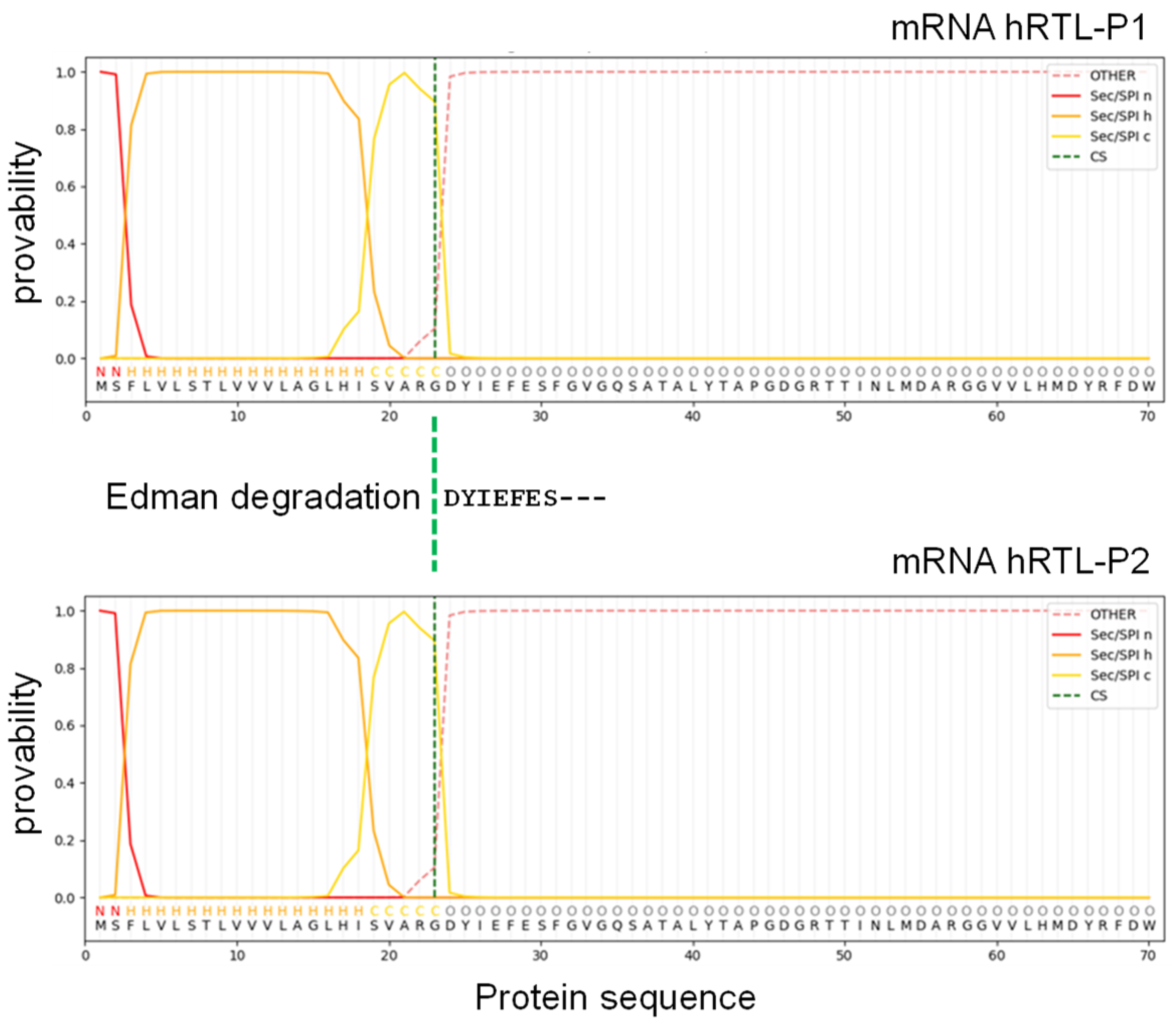
The SignalP algorithm predicted with high confidence that the 23 amino acids long extension located at the N-terminal end of the protein sequences of hRTL-P1 and hRTL-P2 were signal peptides used to target the proteins to the secretory pathway and proteolytically cleaved-off during protein maturation. The predicted cleavage site (Gly22) identified by SignalP corresponded precisely to the N-terminal amino acid of the purified mature hRTL (Asp23) detected by Edman degradation (
Figure 5). The other four
C. australiensis galectins, hRTL-P3 to -P6 sequences also shared the presence of signal peptides (
Supplementary Figure S3).
2.4. The Type-1 (Galβ1-3) Preferable Glycan-Binding Properties of hRTL
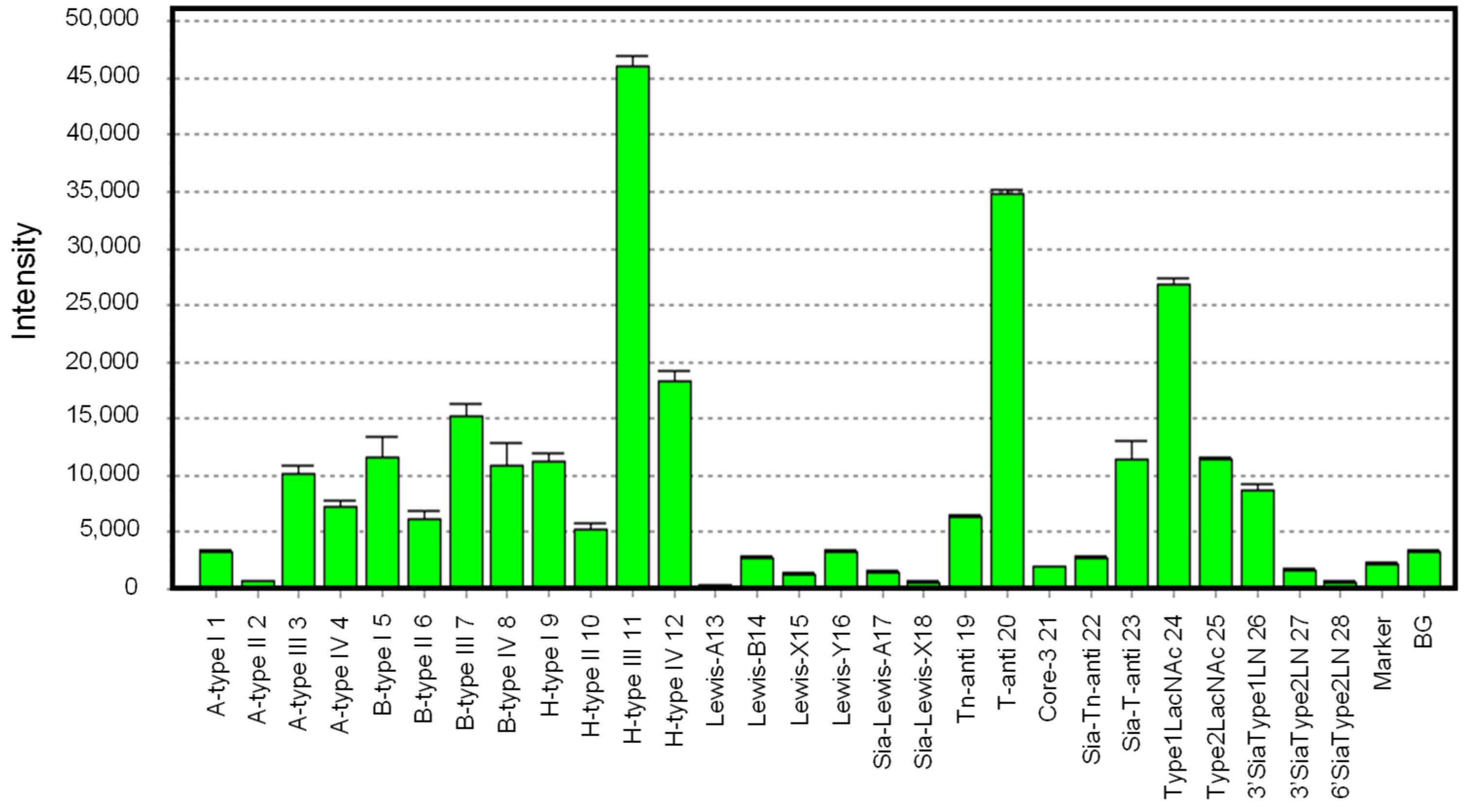
The glycan-binding profile of hRTL was determined by array analysis using 28 glycans (
Supplementary Table S1), as shown in
Figure 6. hRTL preferably bound to oligosaccharides of blood type H-glycans, especially those of type-3 (Fucα1-2Galβ1-3GalNAcα1-R) (
11). The lectin could also bind to those of type-4 (Fucα1-2Galβ1-3GalNAcβ1-) (
12), displaying a much lower affinity for the type-1 (Fucα1-2Galβ1-3GlcNAcβ1-) (
9) and type-2 (Fucα1-2Galβ1-4GlcNAcβ1-) (
10) glycans. However, the connection of other monosaccharides to the C-3 position of the non-reducing terminal Gal of type-3 (Galβ1-3GalNAcα1-) glycans, such as in the case of blood type A type-3 (GalNAcα1-3[Fucα1-2]Galβ1-3GalNAcα1-) (
3) and blood type B type-3 (Galα1-3[Fucα1-2]Galβ1-3GalNAcα1-) (
7), led to a significantly lower binding by the lectin.
hRTL displayed a remarkable binding to the Thomsen-Friedenreich (TF)-antigen (Galβ1-3GalNAc) (
20), which is known as a cancer-specific glycan associated with mucin. Similar to the case of the type-3 A and B blood group glycans mentioned above, the binding of the lectin to Sialyl-TF (Siacα2-3Galβ1-3GalNAc) (
23) was highly reduced. Compared to the strong binding to the TF-antigen, hRTL was only poorly bound to Tn (GalNAc) (
21) and sialyl-Tn (Siacα2-3GalNAc) (
22) antigens, which are also common cancer-specific mucin-associated glycans. This property was consistent with hRTL and was not strongly inhibited by GalNAc compared with Gal (
Table 2). Furthermore, the lectin displayed a moderate recognition ability towards type-1 LacNAc (Galβ1-3GlcNAc) (
24), which was higher than the one towards type-2 Lac-NAc (Galβ1-4GlcNAc) (
25). This property was also consistent with the stronger binding displayed against type-1 (
1,
5,
9), compared with type-2 (
2,
6,
10) glycans associated with the ABO(H) blood groups (
1-
12).
Regarding type-1 LacNAc, the binding of hRTL to Lea, where Fuc is bound to the C4 position of GlcNAc (13), and Leb, where Fuc is bound to the C3 position of Gal (14), was significantly reduced, similar to the binding reduction observed for Lex (15) and Ley (16), which are composed of type-2 LacNAc. This property was consistent with the fact that the binding of hRTL reduced sialyl type-1 LacNAc (26) compared to type-1 LacNAc. The binding of hRTL to α2-3sialyl type-2 LacNAc (27) had even low-er affinity than α2-3sialyl type-1 LacNAc. The complete abolishment of the binding to α2-6 sialylated Gal (28) by hRTL. In summary, among all teste glycans, hRTL preferentially recognized Galβ1-3GalNAc.
2.5. The Cytotoxic Activity of hRTL via TF-Antigen
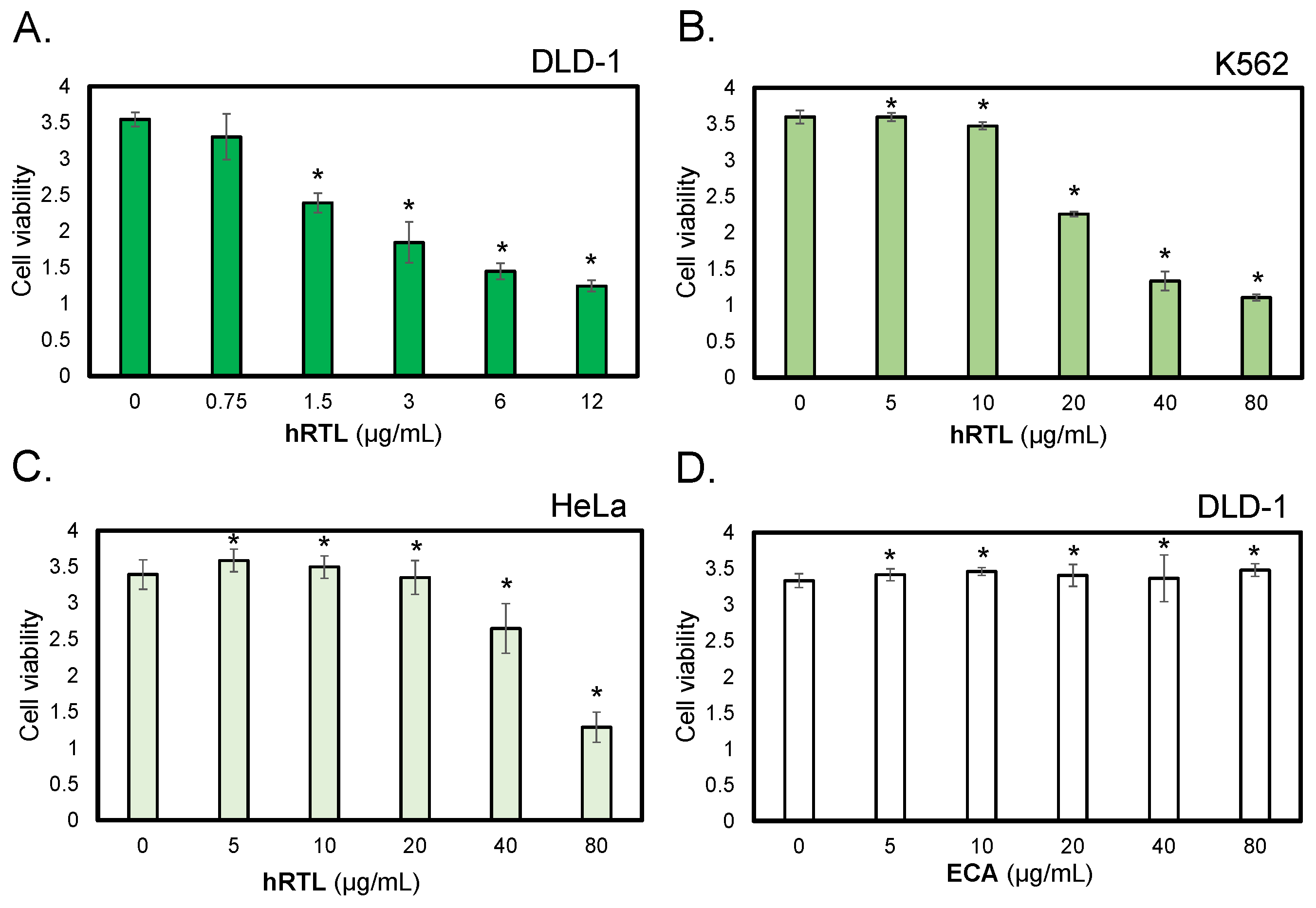
We investigated the cytotoxicity of hRTL against human cancer cell lines, such as DLD-1 colorectal carcinoma cells, K562 leukemia cells, and HeLa ovarian cancer cells. Cells (10
5/mL) were incubated with various concentrations of hRTL (0.75 - 80μg/mL ) for 48 h, and cell viability and the proportion of living cells were determined by WST-8 assay. Cell growth suppression was observed after adding hRTL at various concentrations, depending on the tested cell line (Figure 8A–C). In particular, the lectin strongly reduced the growth of the colorectal carcinoma DLD-1 cells at low concentrations, leading to a significant effect at 0.75 μg/mL (
Figure 7A). On the other hand, another LacNAc-binding lectin, ECA (
Erythrina cristagalli lectin), which was used in this case as a negative control, did not affect the DLD-1 cells even at much higher concentrations, up to 80 μg/mL (
Figure 8D).
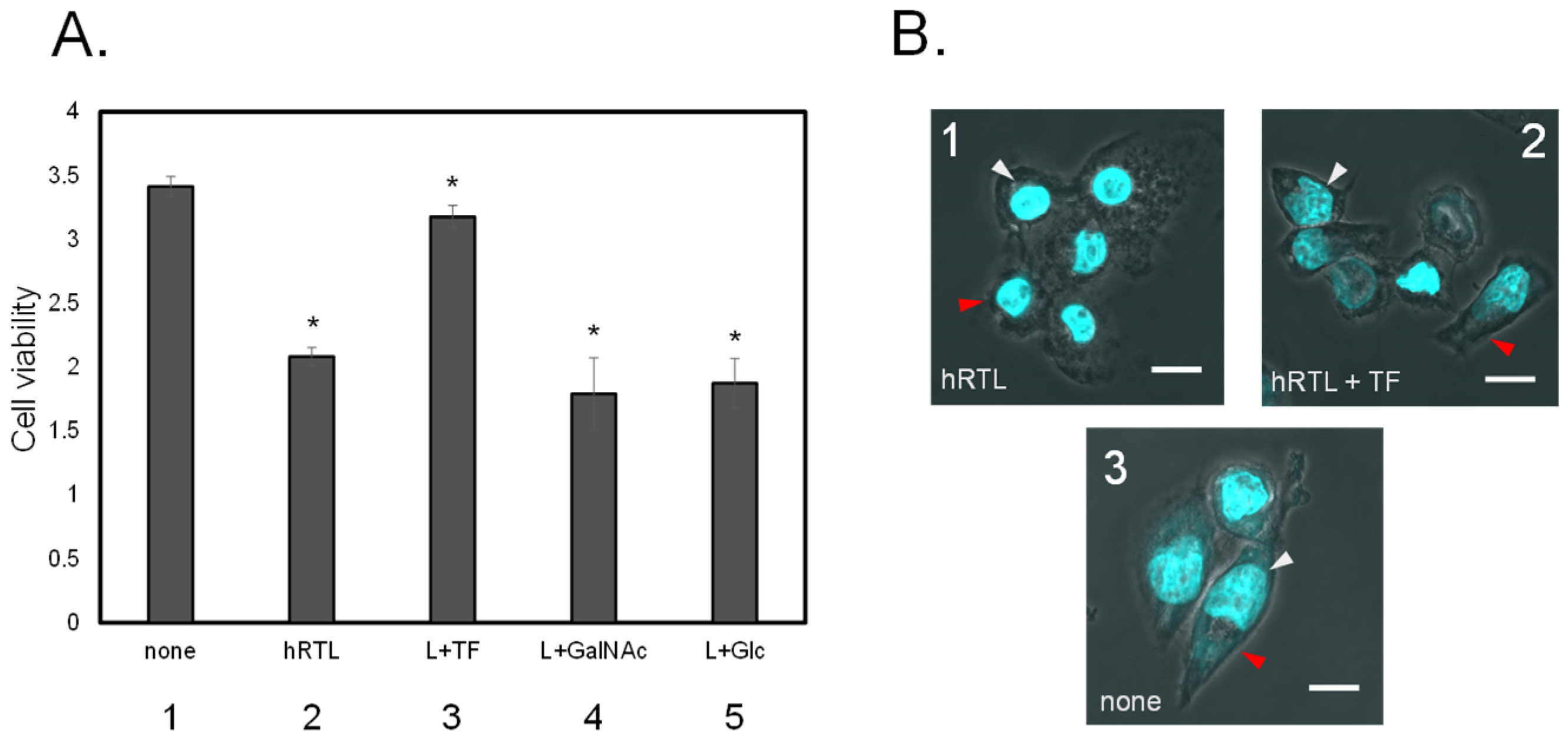
The co-presence of TF-antigen at twenty mM abrogated the cytotoxicity of hRTL (3μg/mL) against DLD-1 (
Figure 8A3), but this effect was not observed in the co-presence of GalNAc or Glc (
Figure 8A4 or 5). Prior to lectin administration, the shape of DLD-1 cells appeared to be elongated in the culture medium (
Figure 8B3). However, adding hRTL (3μg/mL) caused the cells to shrink (
Figure 8B1). This morphological change was rescued by adding ten mM of TF-antigen (
Figure 8B2).
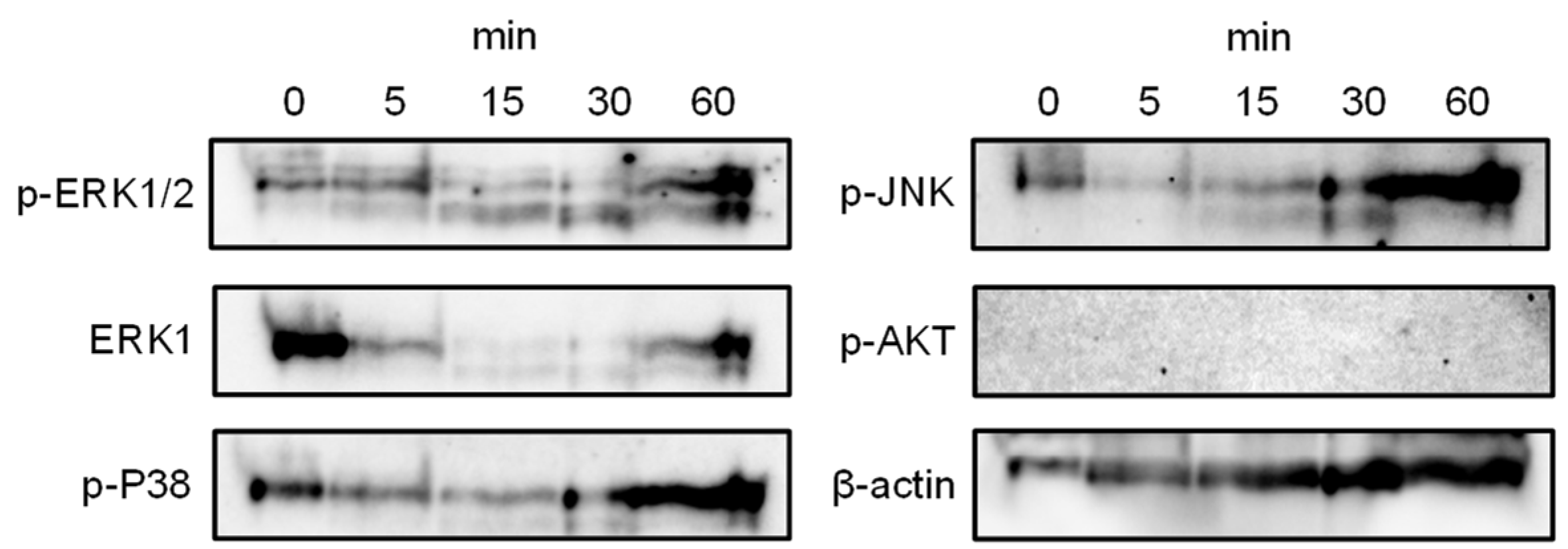
In DLD-1 cells, hRTL administration activated the MAPK signaling pathway, as highlighted by the time-dependent increased phosphorylation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK)1/2 in a manner, as shown by Western blotting (Figure 10, P-ERK1/2 vs. ERK1/2). The hRTL treatment also led to the phosphorylation of the p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and JNK (
Figure 9, P-p38 and p-JNK). These findings suggest that hRTL regulates cell physiological processes by regulating the activity of several key kinases part of the MAPK pathway, including MEK/ERK and p38.
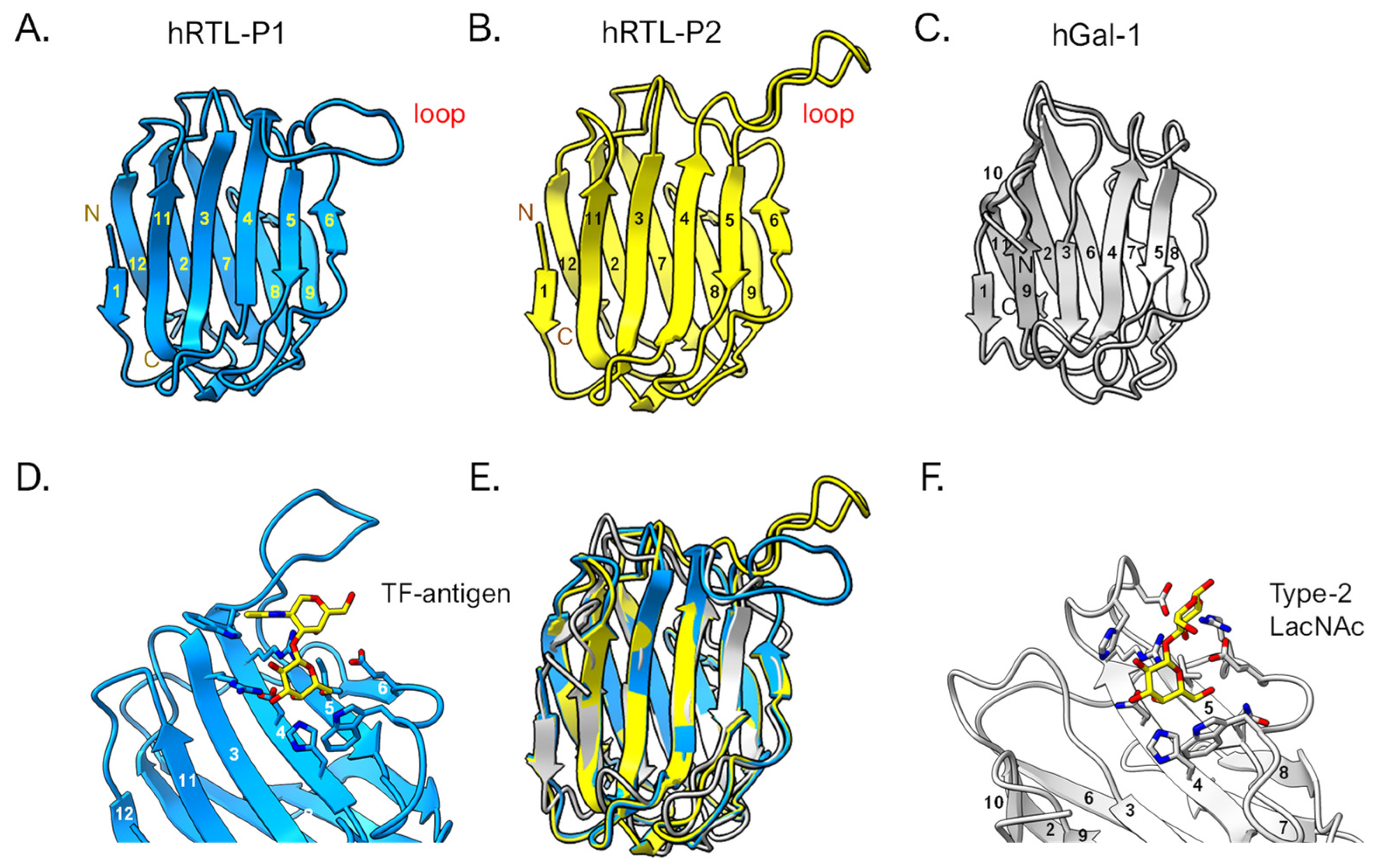
2.6. Prediction of the 3D Structure of hRTLs
The predicted 3-D structures of the hRTL-P1 and P2 were graphically represented with the ChimeraX software [
27] (
Figure 10). The tertiary structure of these sponge galectins was overall similar to that of human galectin-1 (
Figure 10A–C). However, when the structures were superimposed, hRTLs displayed an accessory loop (Trp47-Trp57), which was not present in hGal-1 (
Figure 10E). The loop appears to cover the binding site of the TF-antigen (
Figure 10D). The size of this loop is larger than the loop found in hGal-1, which covers type-2 LacNAc (
Figure 10F).
3. Discussion
The primary sequence of hRTLs, isolated from the Oceanian sponge
C. australiensis, displayed several exceptional features that are most likely linked by the proto-typical nature of a galectin family from a basal metazoan phylum. The mature protein sequence of hRTL is a rare example of a galectin with a free N-terminal end, in contrast to most galectins, which typically have this site acetylated. Interestingly, this characteristic is not shared by all sponge galectins, as other lectins in this family isolated from different sponge species have a blocked N-terminus [
14]. However, this same feature is shared by CCL, another galectin previously purified from a congeneric species [
10], demonstrating multiple occurrences of this unusual phenomenon in sponges.
Combining N-terminal amino acid determination using chemical identification by Edman degradation with the identification of the full-length protein precursor from transcriptomic data, we were able to detect the presence of six different hRTL sequences sharing high pairwise homology. All six hRTLs had an accessory 23 amino acids-long N-terminal sequence, which was predicted to serve as a signal peptide for secretion with high confidence by SignalP. Furthermore, the signal peptide cleavage site determined by computational prediction matched the N-terminal starting site determined by the Edman degradation (
Figure 5), providing a strong confirmation of in silico predictions and supporting the usefuleness of the combined multidisciplinary approach we used for the in-depth characterization of hRTL. The presence of a signal peptide is quite an unusual feature within the galectin family, since the overwhelming majority of its members lack are targeted to the extracellular environment through a non canonical secretory route, which does not require a N-terminal hybrophobic signal [
28]. Only a few exceptions of galetins bearing a signal peptide have been previously reported in Porifera (in a single lectin from the sponge
Geodia cydonium) and Nematoda (in six and eleven galectins from
Caenorhabditis elegans and
Strongyloides ratti, respectively) [
17,
29,
30], highlighting a similarity with the situation we have recently described for mytilectins, another lectin family that may or may not include a signal peptide for secretion in different phyla [
31].
The glycan array established that hRTL preferentially recognized type-3 and type-1 galactosides, such as TF-antigen and lacto N-biose, respectively, inducing cytotoxicity in gastric cancer cells, such as DLD-1, that express mucin-associated TF-antigen [
25]. The solid cytotoxic activity of hRTL might be influenced by its tetrameric configuration, compared to many proto-type galectins, which display dimeric configurations (
Figure 1B). We plan to bioengineer hRTL to transform it into a monomeric or dimeric form. The comparison between the activity of these different forms will clarify the relationship between cytotoxicity and the arrangement of the lectin in multimeric structures. Proto-type galectins have multi-functional features, such as the ability to induce signal transduction upon binding FGF receptor-1 associated glycans, leading to apoptosis, cell adhesion, and differentiation [
32].
Studying the relationships between galectin multimerization and the exerted cell regulative activities will pave the way to biotechnological applications for galectins. Besides the signal peptide, both hRTL-P1 and hRTL-P2 displayed an unusual insertion (Trp45-Trp55), which was not shared by most other functionally characterized galectins. Curiously, this insertion was only present in two of the six hRTLs of C. australiensis and CCL. The graphical representation of the 3D structure of the protein allowed to determine the structural organization of this region, which assumed a loop shape and covered the TF-antigen binding site of hRTL. We have now begun producing the Chondrilla galectins using biotechnological procedures for the crystal structure analysis. This will provide keys that the high-temperature resistance in the sponge galectin, its binding to TF antigen glycans, its anti-cancer cell activity mediated by the glycan, and the new secretion system of galectin by the signal sequence will be elucidated. Researches on galectins have a long history. However, research using sponge galectins to elucidate new knowledge about galectins through structural simulations and determination of their 3-D has only just started.
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Purification of β-D-Galactoside-Binding Lectin from C. australiensis
The marine sponge
Chondrilla australiensis was collected from the intertidal zone of Sagami Bay, Miura City, Kanagawa Prefecture, Japan. Based on national and local fishing regulations, no permits were required to collect the animals. The fresh sponges were maintained in an aquarium. They are cut into small pieces and homogenized. The purification methods of a
Halihcondria okadai lectin, HOL-30, applied the basic purification procedure [
16]. A single-edged razor minced two hundred grams (wet weight) of the sponge. Then, it was homogenized with ten volumes (w/v) of sodium bicarbonate in saline buffer (100 mM sodium bicarbonate containing 150 mM NaCl) containing ten mM of a protease inhibitor mixture (Fuji film Wako, Osaka, Japan). The homogenates were centrifuged at 14,720 ×g in 500-ml bottles for one hour at four °C with a Suprema 21 centrifuge equipped with an NA-18HS rotor (TOMY Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The supernatant was centrifuged again at 27,500 ×g for one hour at four °C, and the supernatant was applied to the affinity column of lactosyl-agarose (5 ml) (Sigma-Aldrich, USA). After passing through the crude extracts, the column was extensively washed with sodium bicarbonate-saline. The lectin was eluted with 50 mM lactose containing sodium bicarbonate-saline, and each 1 ml of elution was collected in tubes with a fraction collector (Model AC-5700, ATTO Co, Tokyo, Japan).
Lectin-eluted fractions were confirmed by SDS-PAGE [
33]. Each fraction is heated at 80°C for 5min or 20 min. The aliquots (10 μml) and the sample buffer (3 μml) were applied to each well of a mini-slab gel (c-PAGEL: 60 mm × 60 mm with 1 mm thickness; 15% polyacrylamide gel, ATTO Co, Tokyo, Japan). After electrophoresis, the gel was treated by CGP staining with 0.1% (w/v) Coomassie Brilliant Blue (CBB) G-250 in 40% polyvinyl pyrrolidone and 20% citrate acid [
34]. Protein concentrations were quantified using a micro-BCA protein assay kit (Thermo Fisher/ Pierce, MA, USA) based on the principle of bicinchoninic acid for colorimetric detection [
35,
36], using bovine serum albumin as standard by measuring A570 (reference: A600) with a microplate reader (model iMark; Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA).
4.2. Hemagglutinating Activity and the Sugar-Binding Property Analysis
Hemagglutination of lectin was performed in 96-well V-shaped plates as described previously [
37]. Twenty μL of 2-fold dilution of purified lectin in Tris buffered-saline (TBS) was mixed with 20 μL of a 1% suspension (with TBS; v/v) of trypsinized, glutaraldehyde-fixed rabbit red blood cells (RBC), TBS, and TBS with 0.01% Triton X-100. Plates were incubated for 1 hour at room temp, and the formation of a sheet (agglutination-positive) or dot (agglutination-negative) was observed and scored as lectin titer.
The saccharide solutions (200 mM, 20 μL) were serially diluted with TBS and added with 20 μL of each lectin solution (adjusted to hemagglutination units 16), Triton X-100 (0.01% final conc.), and RBC. Plates were incubated for 1 hour at room temp, and minimal inhibitory sugar concentration was determined.
4.3. Glycan-Binding Profiling of the Lectin
Glycan array analysis was performed by a system of Glycotechnica Co. Ltd (Yokohama, Japan). The lectin was fluorescence-labeled (λex/em 560/580 nm) using Cy3 labeling kit-NH
2 (Cytiva, Tokyo, Japan) per the manufacturer’s instructions. A total of 28 glycans were immobilized on wells of a microarray. Fluorescence-labeled lectins at concentrations ranging from 0 to 100 μg/mL were incubated overnight at four °C with shielding from light. The glycan-binding specificities were detected by a GlycoLyte2200 Model evanescent fluorescence scanner (Glycotechnica Co. Ltd, Yokohama, Japan) by modifications from the method of the previous report [
38,
39].
4.4. Molecular Mass Analysis
The purified lectin (5μg) was subjected to gel permeation chromatography (GPC) utilizing a Shodex KW 402.5-4F column (4.6 mm × 300 mm) connected to an HPLC pump LC-2000 (JASCO Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan). The lectins were dissolved in 50 mM sodium bicarbonate in saline, and the elution time of lectins from the column was detected by UV at an absorbance of 220 nm.
Mass spectrometry analysis Matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization-time of flight mass spectrometry (MALDI-TOF-MS) analysis was performed using an AXIMA confidence instrument (Shimadzu) in reflector mode. The purified lectin was co-crystallized with saturated sinapinic acid containing 0.1% trifluoroacetic acid as a matrix on a 384-well MALDI MS Sample Plate (TO-476R01). One hundred laser shots measured the MS spectrum [
40].
4.5. N-Terminal Amino Acid Sequence
The lectin’s N-terminal amino acid sequence was determined using an automated Edman degradation using a protein/peptide sequencer Procise 492HT (Applied Biosystems, Foster City, CA, USA) [
41].
4.6. RNA-Sequencing
The sponge tissue was cut into small pieces using razor blades to weigh 20 mg by cutting from the sponge (approximately 10 mm square) that adhered to the rock. The sampled tissue was homogenized in a vial with TRIzol (Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, USA). The total RNA, representing a pool of two individual sponges, was extracted following the manufacturer’s instructions. The quality and quantity of the extracted RNAs were assessed replicate of 500 ng and 100 ng of quantified samples was then pooled and subjected to next-generation sequencing (GENEWIZ, Azenta Life Sciences, Shinagawa, Tokyo Japan) on the Illumina Hiseq System in a 2×150-bp paired-end configuration for 1 lane. The same procedure was performed for 30-ng and 10-ng input samples.
The quality of raw sequencing data was first assessed with FastQC v.0.12.0, which allowed the setting of the most appropriate trimming parameters for Trimmomatic v.0.40 [
42] to remove sequencing adapters, low-quality bases, and failed reads. High-quality trimmed reads were de novo assembled using Trinity v.3 [
43] with default parameters. Nearly perfect matches with the partial amino acid sequence obtained through Edman degradation were initially searched by selecting hits with tBLASTn matches, scoring an e-value lower than 0.05. Matching nucleotide sequences were subjected to virtual translation to protein with the Expasy translate tool [
44]. The resulting protein sequences were analyzed with SignalP v.6.0 [
45] to inspect the presence of a signal peptide. The transcriptome assembly quality was assessed with BUSCO v5.7.1 [
46] based on the set of conserved orthologous genes of the Metazoa lineage according to OrthoDB v.10 [
47].
4.7. Cell Viability and Cytotoxicity Assays
DLD-1 cells were maintained in RPMI 1640 supplemented with heat-inactivated FBS 10% (v/v), penicillin (100 IU/mL), and streptomycin (100 μg/mL) at 37 °C. Cytotoxic effects and cell growth following treatment with hRTL at concentrations ranging from 0 to 100 μg/mL were determined using Cell Counting Kit-8 containing WST-8 [
48]. Cells (2×104, in 90 μL solution) were seeded into 96-well flat-bottom plates and treated with ten μL lectin for 24 h at 37°C. To evaluate the glycan properties on cells, anti-MUC-1 pAb (100 μg/mL) was co-incubated with cells in addition to lectin for 24 hours and then applied to the assay system. To assay the effect on cell growth, each well was added with ten μL WST-8 solution and incubated for 4 hours at 37°C. Cell survival rate was determined by measuring A450 (reference: A600) with an iMark microplate reader.
4.8. 3-D Structure Prediction
The hRTL prediction models were generated using ColabFold [
49], a Google Colab-based implementation of AlphaFold2 [
50]. The docking of the TF-antigen to hRTL-P1 was performed using RosettaLigand on the Rosetta online server, Rosie [
51,
52,
53,
54]. The glycan docking position was selected based on the structures of known galectins, such as hGal-1. The output files were validated by comparing them with these known structures. The resulting predicted structures were visualized using ChimeraX [
27].
4.9. Statistical Analysis
Experiments were performed in triplicate, and results were presented as mean ± standard error (SE). Data were subjected to a one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) followed by Dunnett’s test using the SPSS Statistics software package, v. 10 (
www.ibm.com/products/spss-statistics). Differences with p< 0.05 were considered significant.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at:
Preprints.org, File S1: Raw data of primary structure analysis of hRTL by Edman degradation.; File S2: Plots and graphical representation of FASTQC per base sequence quality scores.; File S3: Signal peptide sequence prediction of hRTL-P3 to P6.; File S4: Twenty-eight glycan structures on the glycan array.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.Oz., R.H., and Y.F.; methodology, K. K. and M.G.; validation, M.G., K.H., T.K., N.M., F.H.; data and sample curation, M.G., Y.I., R.C., N.Ma., T.K., and N.M.; investigation, R.H., Y.F., T.H., Y.On., N.K., M.O., R.I., S.F., Y.N., S.Y., N.Mi., M.Y., D.A., S.R., I.H., S.M.A.K., Y.Og., Y.F., A.P., and Y.Oz.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.Oz.; writing—review and editing, M.G., N.M, S.P, B.P.C, A.P and Y.Oz.; visualization, M.G.; supervision, M.G.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported by the Assisted Joint Research Program (Exploration type) FY2024 of the J-GlycoNet cooperative network, accredited by the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology, MEXT, Japan, as a Joint Usage/Research Center. Yuki Fujii, Yukiko Ogawa, Tatsuya Kawasaki, and Yasuhiro Ozeki are supported by a research grant (24K06239, 24K15170, 23K10950, 23K06190) from JSPS. Marco Gerdol and Alberto Pallavicjni are supported by the Interconnected Nord-Est Innovation Ecosystem (iNEST) and received funding from the European Union Next-GenerationEU (PIANO NAZIONALE DI RIPRESA E RESILIENZA (PNRR) – MISSIONE 4 COMPONENTE 2, INVESTIMENTO 1.5 – D.D. 1058 23/06/2022, ECS00000043. Yasuhiro Ozeki is supported by the Yokohama Trial Grant for Research and Development YT2024-1050 from the City of Yokohama.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
All hRTL protein sequences are available in
File S1.
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge Mei Ikeda, Chisato Tsuda, Suzuna Yoshimo, Shinya Hatajima, Namiho Matsuzaki, and Keita Yamamoto at Yokohama City University for their experimental contributions to the purification, thermotolerance, and hemagglutination activities of lectins in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. This work is supported by the Yokohama City University Research Clerkship program FY2024-2021.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Taylor, M.E.; Drickamer, K.; Imberty, A.; van Kooyk, Y.; Schnaar, R.L.; Etzler, M.E.; Varki, A. Chapter 28, Discovery and Classification of Glycan-Binding Proteins: Varki, A.; Cummings, R.D.; Esko, J.D.; Stanley, P.; Hart, G.W.; Aebi, M.; Mohnen, D.; Kinoshita, T.; Packer, N.H.; Prestegard, J.H.; Schnaar, R.L.; Seeberger, P.H. ed. Essentials of Glycobiology 4th ed. Cold Spring Harbor (NY): Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press; 2022.
- Islam, M.K.; Khan, M.; Gidwani, K.; Witwer, K.W.; Lamminmäki, U.; Leivo, J. Lectins as potential tools for cancer biomarker discovery from extracellular vesicles. Biomark. Res. 2023, 11, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmmed, M.K.; Bhowmik, S.; Giteru, S.G.; Zilani, M.N.H.; Adadi., P.; Islam, S.S.; Kanwugu, O.N.; Haq, M.; Ahmmed, F.; Ng, C.C.W.; Chan, Y.S.; Asadujjaman, M.; Chan, G.H.H.; Naude, R.; Bekhit, A.E.A.; Ng, T.B.; Wong, J.H. An update of lectins from marine organisms: Characterization, extraction methodology, and potential biofunctional applications. Mar. Drugs 2022, 20, 430. [CrossRef]
- Marothia, D.; Kaur, N.; Jhamat, C.; Sharma, I.; Pati, P.K. Plant lectins: Classical molecules with emerging roles in stress tolerance. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 244, 125272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bonnardel, F.; Perez, S.; Lisacek, F.; Imberty, A. Structural database for lectins and the UniLectin web platform. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2132, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wood, R.A.; Grotzinger, J.P.; Dickson, J.A. Proterozoic modular biomineralized metazoan from the Nama Group, Namibia. Science 2002, 296, 2383–2386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, K.J.; Butterfield, N.J. Origin of the Eumetazoa: testing ecological predictions of molecular clocks against the Proterozoic fossil record. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2005, 102, 9547–9552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gardères, J.; Bourguet-Kondracki, M.L.; Hamer, B.; Batel, R.; Schröder, H.C.; Müller, W.E. Porifera lectins: Diversity, physiological roles and biotechnological potential. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 5059–5101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duarte, J.A.; Oliveira Neto, J.E.; Torres, R.C.F.; Sousa, A.R.O.; Andrade, A.L.; Chaves, R.P.; Carneiro, R.; Vasconcelos, M.A.; Teixeira, C.S.; Teixeira, E.H.; Nagano, C.S.; Sampaio, A.H. Structural characterization of a galectin from the marine sponge Aplysina lactuca (ALL) with synergistic effects when associated with antibiotics against bacteria. Biochimie 2023, 214, 165–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sousa, A.R.O.; Andrade, F.R.N.; Chaves, R.P.; Sousa, B.L.; Lima, D.B.; Souza, R.O.D.S.; da Silva, C.G.L.; Teixeira, C.S.; Sampaio, A.H.; Nagano, C.S.; Carneiro, R.F. Structural characterization of a galectin isolated from the marine sponge Chondrilla caribensis with leishmanicidal potential. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Gen. Subj. 2021, 1865, 129992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, D.N.; Almeida, A.S.; Sousa, A.R.O.; Pereira, R.; Andrade, A.L.; Chaves, R.P.; Carneiro, R.F.; Vasconcelos, M.A.; Nascimento-Neto, L.G.D.; Pinheiro, U.; Videira, P.A.; Teixeira, E.H.; Nagano, C.S.; Sampaio, A.H. Antibacterial activity of a new lectin isolated from the marine sponge Chondrilla caribensis. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 109, 1292–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ueda, T.; Nakamura, Y.; Smith, C.M.; Copits, B.A.; Inoue, A.; Ojima, T.; Matsunaga, S.; Swanson, G.T.; Sakai, R. Isolation of novel prototype galectins from the marine ball sponge Cinachyrella sp. guided by their modulatory activity on mammalian glutamate-gated ion channels. Glycobiology. [CrossRef]
- Freymann, D.M.; Nakamura, Y.; Focia, P.J.; Sakai, R.; Swanson, G.T. Structure of a tetrameric galectin from Cinachyrella sp. (ball sponge). Acta Crystallogr. 2012; 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawsar, S.M.; Fujii, Y.; Matsumoto, R.; Ichikawa, T.; Tateno, H.; Hirabayashi, J.; Yasumitsu, H.; Dogasaki, C.; Hosono, M.; Nitta, K.; Hamako, J.; Matsui, T.; Ozeki, Y. Isolation, purification, characterization and glycan-binding profile of a D-galactoside specific lectin from the marine sponge, Halichondria okadai. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B Biochem. Mol. Biol. 2008, 150, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.C.; Boreiko, A.; Korzhev, M.; Tahir, M.N.; Tremel, W.; Eckert, C.; Ushijima, H.; Müller, I.M.; Müller, W.E. Co-expression and functional interaction of silicatein with galectin: matrix-guided formation of siliceous spicules in the marine demosponge Suberites domuncula. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 12001–12009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pfeifer, K.; Haasemann, M.; Gamulin, V.; Bretting, H.; Fahrenholz, F.; Müller, W.E. S-type lectins occur also in invertebrates: high conservation of the carbohydrate recognition domain in the lectin genes from the marine sponge Geodia cydonium. Glycobiology 1993, 3, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner-Hülsmann, C.; Bachinski, N.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Blumbach, B.; Steffen, R.; Pancer, Z.; Müller, WE. A galectin links the aggregation factor to cells in the sponge (Geodia cydonium) system. Glycobiology 1996, 6, 785–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gundacker, D.; Leys, SP.; Schröder, HC.; Müller, IM.; Müller, WE. Isolation and cloning of a C-type lectin from the hexactinellid sponge Aphrocallistes vastus: a putative aggregation factor. Glycobiology 2001, 11, 21–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Watari, H.; Kageyama, H.; Masubuchi, N.; Nakajima, H.; Onodera, K.; Focia, P.J.; Oshiro, T.; Matsui, T.; Kodera, Y.; Ogawa, T.; Yokoyama, T.; Hirayama, M.; Hori, K.; Freymann, D.M.; Imai, M.; Komatsu, N.; Araki, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Sakai, R. A marine sponge-derived lectin reveals hidden pathway for thrombopoietin receptor activation. Nat. Commun. 2022, 13, 7262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schröder, H.C.; Ushijima, H.; Krasko, A.; Gamulin, V.; Thakur, N.L.; Diehl-Seifert, B.; Müller, I.M.; Müller, W.E. Emergence and disappearance of an immune molecule, an antimicrobial lectin, in basal metazoa. A tachylectin-related protein in the sponge Suberites domuncula. J. Biol. Chem 2003, 278, 32810–32817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araújo, T.A.T.; de Souza, A.; Santana, A.F.; Braga, A.R.C.; Custódio, M.R.; Simões, F.R.; Araújo, G.M.; Miranda, A.; Alves, F.; Granito, R.N.; Yu, N.; Renno, A.C.M. Comparison of different methods for spongin-like collagen extraction from marine sponges (Chondrilla caribensis and Aplysina fulva): Physicochemical properties and in vitro biological analysis. Membranes 2021, 11, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarsia, S.; Grosso, A.S.; Trovão, F.; Jiménez-Barbero, J.; Carvalho, A.L.; Nativi, C.; Marcelo, F. Molecular recognition of a Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen mimetic targeting human Galectin-3. ChemMedChem. 2018, 13, 2030–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karsten, U.; Goletz, S. What controls the expression of the core-1 (Thomsen-Friedenreich) glycotope on tumor cells? Biochemistry (Mosc) 2015, 80, 801–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtenkov, O. Profiling of naturally occurring antibodies to the Thomsen-Friedenreich antigen in health and cancer: The diversity and clinical potential. Biomed. Res. Int. 2020, 2020, 9747040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Inamdar, S.R.; Savanur, M.A.; Eligar, S.M.; Chachadi, V.B.; Nagre, N.N.; Chen, C.; Barclays, M.; Ingle, A.; Mahajan, P.; Borges, A.; Shastry, P.; Kalraiya, R.D.; Swamy, B.M.; Rhodes, J.M.; Yu, L.G. The TF-antigen binding lectin from Sclerotium rolfsii inhibits growth of human colon cancer cells by inducing apoptosis in vitro and suppresses tumor growth in vivo. Glycobiology 2012, 22, 1227–1235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K. Complete amino acid sequence of a beta-galactoside-binding lectin from human placenta. J. Biochem. 1988, 104, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goddard, T.D.; Huang, C.C.; Meng, E.C.; Pettersen, E.F.; Couch, G.S.; Morris, J.H.; Ferrin, T.E. UCSF ChimeraX: Meeting modern challenges in visualization and analysis. Protein Science 2018, 27, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Popa, SJ.; Stewart, SE.; Moreau, K. Unconventional secretion of annexins and galectins. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 83, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemoto-Sasaki, Y.; Hayama, K.; Ohya, H.; Arata, Y.; Kaneko, M.K.; Saitou, N.; Hirabayashi, J.; Kasai, K. Caenorhabditis elegans galectins LEC-1-LEC-11: structural features and sugar-binding properties. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008, 1780, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ditgen, D.; Anandarajah, E.M.; Reinhardt, A.; Younis, A.E.; Witt, S.; Hansmann, J.; Lorenz, E.; García-Hernández, M.; Paclik, D.; Soblik, H.; Jolodar, A.; Seeberger, P.H.; Liebau, E.; Brattig, N.W. Comparative characterization of two galectins excreted-secreted from intestine-dwelling parasitic versus free-living females of the soil-transmitted nematode Strongyloides. Mol. Biochem. Parasitol. 2018, 225, 73–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerdol, M.; Nerelli, D.E.; Martelossi, N.; Ogawa, Y.; Fujii, Y.; Pallavicini, A.; Ozeki, Y. Taxonomic distribution and molecular evolution of mytilectins. Mar. Drugs. 2023, 21, 614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Żukowska, D.; Chorążewska, A.; Ciura, K.; Gędaj, A.; Kalka, M.; Poźniak, M.; Porębska, N.; Opaliński, Ł. The diverse dependence of galectin-1 and -8 on multivalency for the modulation of FGFR1 endocytosis. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laemmli, U.K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 1970, 227, 680–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yasumitsu, H.; Ozeki, Y.; Kawsar, S.M.; Toda, T.; Kanaly, R. CGP stain: An inexpensive, odorless, rapid, sensitive, and in principle in vitro methylation-free Coomassie Brilliant Blue stain. Anal. Biochem. 2010, 406, 86–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiechelman, K.J.; Braun, R.D.; Fitzpatrick, J.D. Investigation of the bicinchoninic acid protein assay: identification of the groups responsible for color formation. Anal. Biochem. 1988, 175, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, P.K.; Krohn, R.I.; Hermanson, G.T.; Mallia, A.K.; Gartner, F.H.; Provenzano, M.D.; Fujimoto, E.K.; Goeke, N.M.; Olson, B.J.; Klenk, D.C. Measurement of protein using bicinchoninic acid. Anal. Biochem. 1985, 150, 76–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gourdine, J.P.; Cioci, G.; Miguet, L.; Unverzagt, C.; Silva, D.V.; Varrot, A.; Gautier, C.; Smith-Ravin, E.J.; Imberty, A. High affinity interaction between a bivalve C-type lectin and a biantennary complex-type N-glycan revealed by crystallography and microcalorimetry. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 30112–30120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuno, A.; Uchiyama, N.; Koseki-Kuno, S.; Ebe, Y.; Takashima, S.; Yamada, M.; Hirabayashi, J. Evanescent-field fluorescence-assisted lectin microarray: a new strategy for glycan profiling. Nat. Methods. 2005, 2, 851–856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hirabayashi, J.; Yamada, M.; Kuno, A.; Tateno, H. Lectin microarrays: concept, principle and applications. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2013, 42, 443–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyanishi, N.; Nishi, N.; Abe, H.; Kashio, Y.; Shinonaga, R.; Nakakita, S.; Sumiyoshi, W.; Yamauchi, A.; Nakamura, T.; Hirashima, M.; Hirabayashi, J. Carbohydrate-recognition domains of galectin-9 are involved in intermolecular interaction with galectin-9 itself and other members of the galectin family. Glycobiology 2007, 17, 423–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hewick, R.M.; Hunkapiller, M.W.; Hood, L.E.; Dreyer, W.J. A gas-liquid solid phase peptide and protein sequenator. J. Biol. Chem. 1981, 256, 7990–7997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: a flexible trimmer for Illumina sequence data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; Chen, Z.; Mauceli, E.; Hacohen, N.; Gnirke, A.; Rhind, N.; di Palma, F.; Birren, B.W.; Nusbaum, C.; Lindblad-Toh, K.; Friedman, N.; Regev, A. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasteiger, E.; Gattiker, A.; Hoogland, C.; Ivanyi, I.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. ExPASy: The proteomics server for in-depth protein knowledge and analysis. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 3784–3788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teufel, F.; Almagro Armenteros, J.J.; Johansen, A.R.; Gíslason, M.H.; Pihl, S.I.; Tsirigos, K.D.; Winther, O.; Brunak, S.; von Heijne, G.; Nielsen, H. SignalP 6.0 predicts all five types of signal peptides using protein language models. Nat. Biotechnol. 2022, 40, 1023–1025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manni, M.; Berkeley, M.R.; Seppey, M.; Simão, F.A.; Zdobnov, E.M. BUSCO Update: Novel and streamlined workflows along with broader and deeper phylogenetic coverage for scoring of eukaryotic, prokaryotic, and viral genomes. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2021, 38, 4647–4654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuznetsov, D.; Tegenfeldt, F.; Manni, M.; Seppey, M.; Berkeley, M.; Kriventseva, E.V.; Zdobnov, E.M. OrthoDB v11: annotation of orthologs in the widest sampling of organismal diversity. Nucleic. Acids Res. 2023, 51D, 445–451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ukeda, H.; Kawana, D.; Maeda, S.; Sawamura, M. Spectrophotometric assay for superoxide dismutase based on the reduction of highly water-soluble tetrazolium salts by xanthine-xanthine oxidase. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1999, 63, 485–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mirdita, M.; Schütze, K.; Moriwaki, Y.; Heo, L.; Ovchinnikov, S.; Steinegger, M. ColabFold: Making protein folding accessible to all. Nat. Methods 2022, 19, 679–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jumper, J.; Evans, R.; Pritzel, A.; Green, T.; Figurnov, M.; Ronneberger, O.; Tunyasuvunakool, K.; Bates, R.; Žídek, A.; Potapenko, A.; Bridgland, A.; Meyer, C.; Kohl, S.A.; Ballard, A.J; Cowie, A.; Romera-Paredes, B.; Nikolov, S.; Jain, R.; Adler, J.; Back, T.; Petersen, S.; Reiman, D.; Clancy, E.; Zielinski, M.; Steinegger, M.; Pacholska, M.; Berghammer, T.; Bodenstein, S.; Silver, D.; Vinyals, O.; Senior, A.W.; Kavukcuoglu, K.; Kohli, P.; Hassabis, D. Highly accurate protein structure prediction with AlphaFold. Nature 2021, 596, 583–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deluca, S.; Khar, K.; Meiler, J. Fully Flexible docking of medium sized ligand libraries with RosettaLigand. PLoS ONE, 2015, 10, e0132508. [CrossRef]
- Combs, S.A.; Deluca, S.L.; DeLuca, S.H.; Lemmon, G.H.; Nannemann, D.P. , Nguyen, E.D.; Willis, J.R.; Sheehan J.H.; Meiler J. Small-molecule ligand docking into comparative models with Rosetta. Nature Protocols 2013, 8, 1277–1298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kothiwale, S.; Mendenhall, J.L.; Meiler, J. BCL::Conf: small molecule conformational sampling using a knowledge based rotamer library. J. Cheminformatics 2015, 7, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyskov, S.; Chou, F.C.; Conchúir, S.Ó.; Der, B.S.; Drew, K.; Kuroda, D.; Xu, J.; Weitzner, B.D.; Renfrew, P.D.; Sripakdeevong, P.; Borgo, B.; Havranek, J.J.; Kuhlman, B.; Kortemme, T.; Bonneau, R.; Gray, J.J.; Das, R. Serverification of molecular modeling applications: The Rosetta Online Server that Includes Everyone (ROSIE). PLoS One 2013, 8, e63906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Purification of hRTL. A. The SDS-PAGE pattern obtained after 3 min and 20 min heating under non-reducing conditions. Numbers on the left indicate the molecular mass (kDa) of marker proteins. Arrows mark the positions of the lectins. B. Mass spectrometry of hRTL. The MALDI-TOF MS spectrum showed a molecular mass of 15,521.11 Da. One hundred laser shots measured the signal. C. The gel permeation chromatography pattern. The purified lectin was applied on a Shodex KW 402.5-4F column connected to an HPLC pump at a flow rate of 0.33 ml/min. Numbers in the upper part indicate the following standard molecular markers: blue dextran (>200 kDa); bovine serum albumin (66 kDa); ovalbumin (45 kDa); carbonic anhydrase (30 kDa); horse myoglobin (14 kDa). The absorbance was detected at 220 nm.
Figure 1.
Purification of hRTL. A. The SDS-PAGE pattern obtained after 3 min and 20 min heating under non-reducing conditions. Numbers on the left indicate the molecular mass (kDa) of marker proteins. Arrows mark the positions of the lectins. B. Mass spectrometry of hRTL. The MALDI-TOF MS spectrum showed a molecular mass of 15,521.11 Da. One hundred laser shots measured the signal. C. The gel permeation chromatography pattern. The purified lectin was applied on a Shodex KW 402.5-4F column connected to an HPLC pump at a flow rate of 0.33 ml/min. Numbers in the upper part indicate the following standard molecular markers: blue dextran (>200 kDa); bovine serum albumin (66 kDa); ovalbumin (45 kDa); carbonic anhydrase (30 kDa); horse myoglobin (14 kDa). The absorbance was detected at 220 nm.
Figure 2.
Concentration-dependent enhancement and thermal stability of hRTL hemagglutination activity. Co-relationship between concentrations, hemagglutination (A), and thermotolerance (B) of hRTL.
Figure 2.
Concentration-dependent enhancement and thermal stability of hRTL hemagglutination activity. Co-relationship between concentrations, hemagglutination (A), and thermotolerance (B) of hRTL.
Figure 3.
Multiple sequence alignment of the six hRTLs identified in the
C. australiensis transcriptome. CCL indicates the lectin previously described in
C. calibensis [
10]. Two peculiar sequence features of hRTLs are marked with a gold box (the extension located upstream of the N-terminal end determined by Edman degradation) and a red box (the hRTL-P1, hRTL-P2, and CCL specific insertion). An arrow indicates the position of the N-terminal end of the mature protein determined by Edman degradation. A bold dashed line indicates the partial sequence determined by Edman degradation. Conserved amino acids in the multiple sequence alignment are highlighted with a blue background. The numbering of amino acids starts from the N-terminus at the top. Sequence gaps are indicated by dashes (-). X indicates the presence of any amino acid in the sequence consensus.
Figure 3.
Multiple sequence alignment of the six hRTLs identified in the
C. australiensis transcriptome. CCL indicates the lectin previously described in
C. calibensis [
10]. Two peculiar sequence features of hRTLs are marked with a gold box (the extension located upstream of the N-terminal end determined by Edman degradation) and a red box (the hRTL-P1, hRTL-P2, and CCL specific insertion). An arrow indicates the position of the N-terminal end of the mature protein determined by Edman degradation. A bold dashed line indicates the partial sequence determined by Edman degradation. Conserved amino acids in the multiple sequence alignment are highlighted with a blue background. The numbering of amino acids starts from the N-terminus at the top. Sequence gaps are indicated by dashes (-). X indicates the presence of any amino acid in the sequence consensus.
Figure 4.
Comparison among the primary sequences of hRTL-P1, P2, and the proto-type
C. caribensis galectin CCL represents the mature protein sequence only (i.e., after proteolytic cleavage of the signal peptide). Deduced conserved glycan-binding sites are marked in yellow compared to human galectin-1 (hGal-1) [
26].
Figure 4.
Comparison among the primary sequences of hRTL-P1, P2, and the proto-type
C. caribensis galectin CCL represents the mature protein sequence only (i.e., after proteolytic cleavage of the signal peptide). Deduced conserved glycan-binding sites are marked in yellow compared to human galectin-1 (hGal-1) [
26].
Figure 5.
Signal peptide sequence prediction of hRTL. The mRNA sequence was assigned to SignalP 6.0 software. N (red), H (orange), and C (yellow) mean N-region, H-region, and C-region of the signal sequence, respectively.
Figure 5.
Signal peptide sequence prediction of hRTL. The mRNA sequence was assigned to SignalP 6.0 software. N (red), H (orange), and C (yellow) mean N-region, H-region, and C-region of the signal sequence, respectively.
Figure 6.
Glycan-binding profile of hRTL. Cy3-labeled hRTL was subjected to glycan array analysis combining a glycan-conjugated array with 28 immobilized glycan structures and a surface plasmon resonance scanning detector (the numbering in the X-axis is the same as in
Supplementary Table S1). The evanescent-field fluorescence occurring by the binding between Cy3-hRTL and the glycans is represented as a net intensity (Y-axis of the graph). BG: background.
Figure 6.
Glycan-binding profile of hRTL. Cy3-labeled hRTL was subjected to glycan array analysis combining a glycan-conjugated array with 28 immobilized glycan structures and a surface plasmon resonance scanning detector (the numbering in the X-axis is the same as in
Supplementary Table S1). The evanescent-field fluorescence occurring by the binding between Cy3-hRTL and the glycans is represented as a net intensity (Y-axis of the graph). BG: background.
Figure 7.
The cytotoxic effects of hRTL against TF-antigen positive cells. The cytotoxic effects of lectins were evaluated on human colorectal carcinoma cells (DLD-1, panels A and D), human leukemic cells (K562, panel B), and human ovarian cancer cells (HeLa, panel C). Cells were treated with hRTL (A-C) or ECA (D: a negative control provided by a lectin that binds to type-1/2 LacNAc) at various concentrations (0-80 μg/mL) for 24 h, and cell viability was determined by WST-8 assay. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Magnification: x40. Scale bar: 10 μm. Data shown are mean ± SE (n= 3). *, p< 0.05.
Figure 7.
The cytotoxic effects of hRTL against TF-antigen positive cells. The cytotoxic effects of lectins were evaluated on human colorectal carcinoma cells (DLD-1, panels A and D), human leukemic cells (K562, panel B), and human ovarian cancer cells (HeLa, panel C). Cells were treated with hRTL (A-C) or ECA (D: a negative control provided by a lectin that binds to type-1/2 LacNAc) at various concentrations (0-80 μg/mL) for 24 h, and cell viability was determined by WST-8 assay. Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (blue). Magnification: x40. Scale bar: 10 μm. Data shown are mean ± SE (n= 3). *, p< 0.05.
Figure 8.
A. Inhibition of cytotoxic effect of 3 μg/mL hRTL on DLD-1. Without (1) or with (2) hRTL (10μg/mL). Co-presence of TF-antigen, GalNAc, or Glc (each 20 mM: 3-5). All data are reported as mean ± SE (n= 3). *p< 0.05. B. The morphological appearance of the cells in Presence (1 and 2) or absence (3) of the hRTL lectin. Panel 2 illustrates the simultaneous presence of 20 mM TF-antigen and hRTL (2). Cell shrinkage and extensions are indicated by red arrows, whereas nucleus condensation is shown with white-gray arrows, respectively. Magnification: x 40. Scale bar: 10 μm.
Figure 8.
A. Inhibition of cytotoxic effect of 3 μg/mL hRTL on DLD-1. Without (1) or with (2) hRTL (10μg/mL). Co-presence of TF-antigen, GalNAc, or Glc (each 20 mM: 3-5). All data are reported as mean ± SE (n= 3). *p< 0.05. B. The morphological appearance of the cells in Presence (1 and 2) or absence (3) of the hRTL lectin. Panel 2 illustrates the simultaneous presence of 20 mM TF-antigen and hRTL (2). Cell shrinkage and extensions are indicated by red arrows, whereas nucleus condensation is shown with white-gray arrows, respectively. Magnification: x 40. Scale bar: 10 μm.
Figure 9.
Phosphorylation of MAPKs by hRTL in DLD-1 cells. Cells (5×105) were treated with hRTL (10 μg/mL) for different periods (0-60 min). The phosphorylation of target kinases was evaluated by Western blotting of cell lysates. P-ERK1/2, P-p38, P-Jnk, and P-Akt: phosphorylated forms of ERK1/2, p38, Jnk, and Akt kinases, respectively.
Figure 9.
Phosphorylation of MAPKs by hRTL in DLD-1 cells. Cells (5×105) were treated with hRTL (10 μg/mL) for different periods (0-60 min). The phosphorylation of target kinases was evaluated by Western blotting of cell lysates. P-ERK1/2, P-p38, P-Jnk, and P-Akt: phosphorylated forms of ERK1/2, p38, Jnk, and Akt kinases, respectively.
Figure 10.
3D-structural prediction of hRTLs. hRTL-P1 (A) and hRTL-P2 (B). hGal-1 (human galectin-1) is also shown as a comparison (C). The binding between hRTL-P1, TF-antigen (D), and hGal-1 and LacNAc (F), respectively. A superimposed view among hRTL-P1, hRTL-P2, and hGal-1 (E). The loops found in the two Chondrilla galectins (upper right blue and yellow in panels A and B) were unique characteristics of these hRTLs.
Figure 10.
3D-structural prediction of hRTLs. hRTL-P1 (A) and hRTL-P2 (B). hGal-1 (human galectin-1) is also shown as a comparison (C). The binding between hRTL-P1, TF-antigen (D), and hGal-1 and LacNAc (F), respectively. A superimposed view among hRTL-P1, hRTL-P2, and hGal-1 (E). The loops found in the two Chondrilla galectins (upper right blue and yellow in panels A and B) were unique characteristics of these hRTLs.
Table 1.
Purification of hRTL from Chondrilla australiensis.
Table 1.
Purification of hRTL from Chondrilla australiensis.
| Fraction |
Titer
(HU) |
Volume (mL) |
Total
activitya |
Protein
conc. (mg mL-1) |
Protein
amount (mg) |
Specific
activityb |
Purification
ratio (fold)c |
Recovery of
activity (%)d
|
| Crude extract |
65,536 |
500 |
32,768,000 |
9.5 |
4,750 |
13.79 |
1 |
100 |
| Purified lectin |
262,144 |
80 |
20,971,520 |
0.86 |
68.8 |
3810.23 |
276 |
64 |
Table 2.
Saccharides and glycoprotein specificity of hRTLT a.
Table 2.
Saccharides and glycoprotein specificity of hRTLT a.
| Saccharides |
Minimum inhibitory concentration (mM) |
| TF-antigen |
1.6 |
| Lactose |
3.2 |
| Melibiose |
50 |
| Sucrose |
N.I.b
|
| D-galactose |
25 |
| D-GalNAc |
>50 |
| D-GlcNAc |
N.I. |
| D-mannose |
N.I. |
| Glycoproteins |
Minimum inhibitory concentration (mg/mL) |
| Fetuin |
0.125 |
| Porcine stomach mucin |
0.125 |
| Bovine submaxillary mucin |
N.I.c
|
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).