Submitted:
20 August 2024
Posted:
21 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
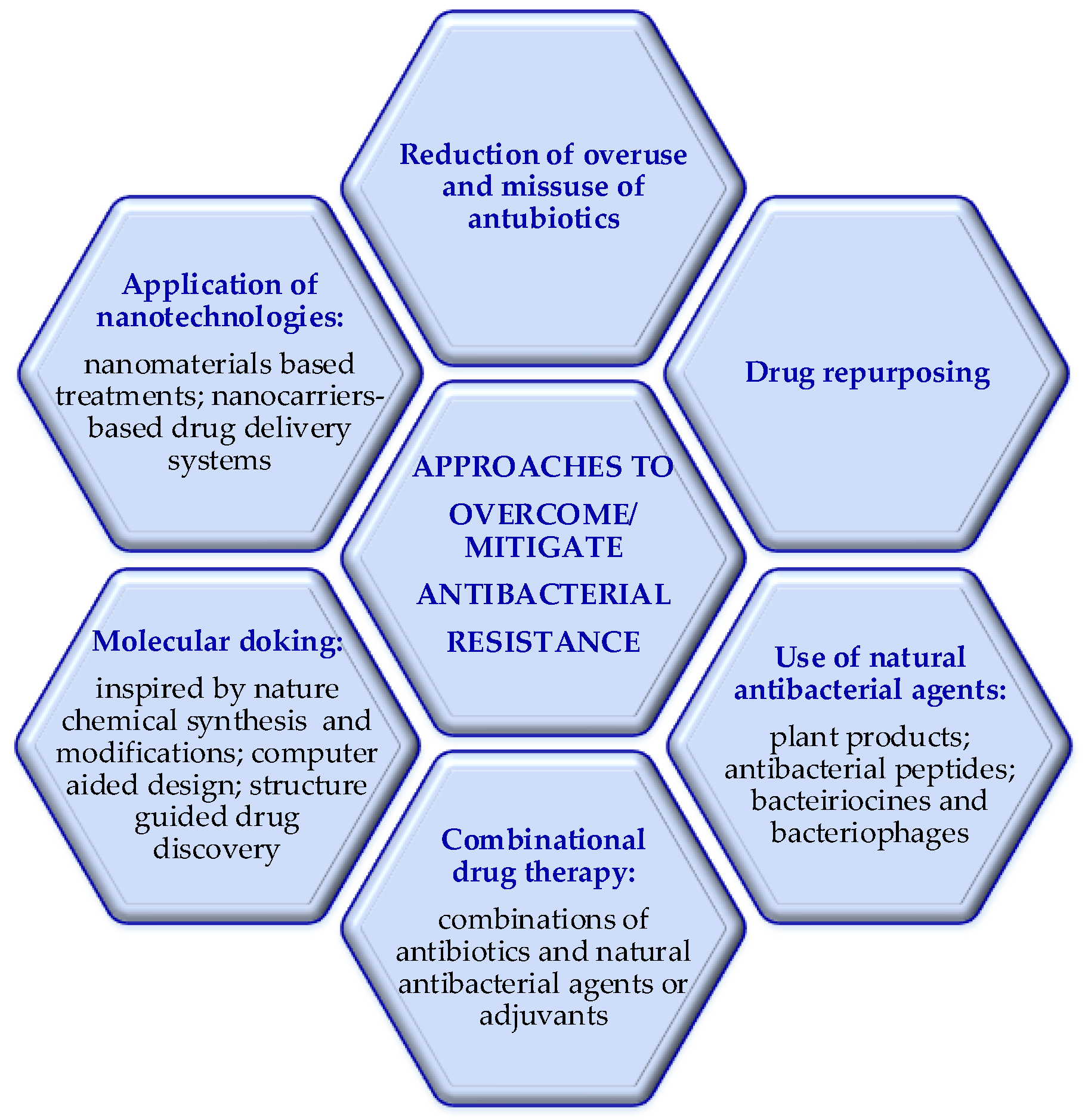
2. Approaches to Avoid/Mitigate the Bacterial Resistance
2.1. Use of Natural Antibacterial Agents: Plant Products, Antibacterial Peptides, Bacteriocines and Bacteriophages
2.2. Combination Drug Therapy
2.3. Nanotechnologies
2.4. Molecular Docking Inspired by Nature
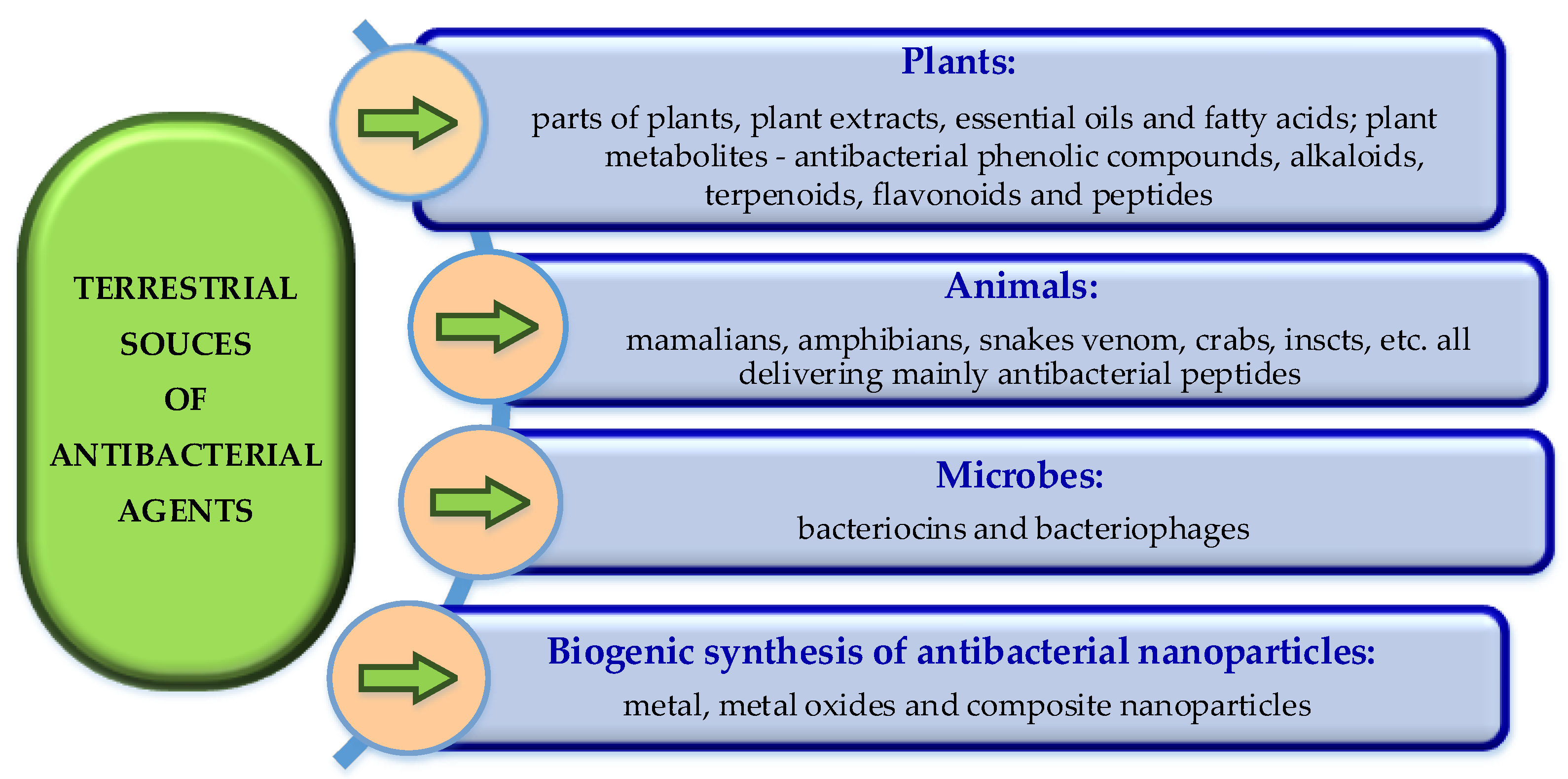
3. Terrestrial Sources of Antibacterial Agents
3.1. Plant-Derived Antibacterial Products
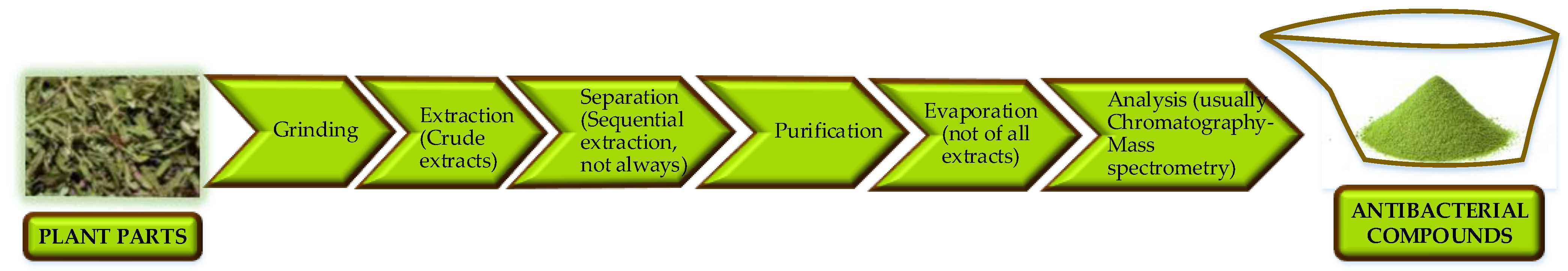
3.1.1. Antibacterial Plant Extracts
3.1.2. Essential Oils and Fatty Acids
3.1.3. Propolis and Honey
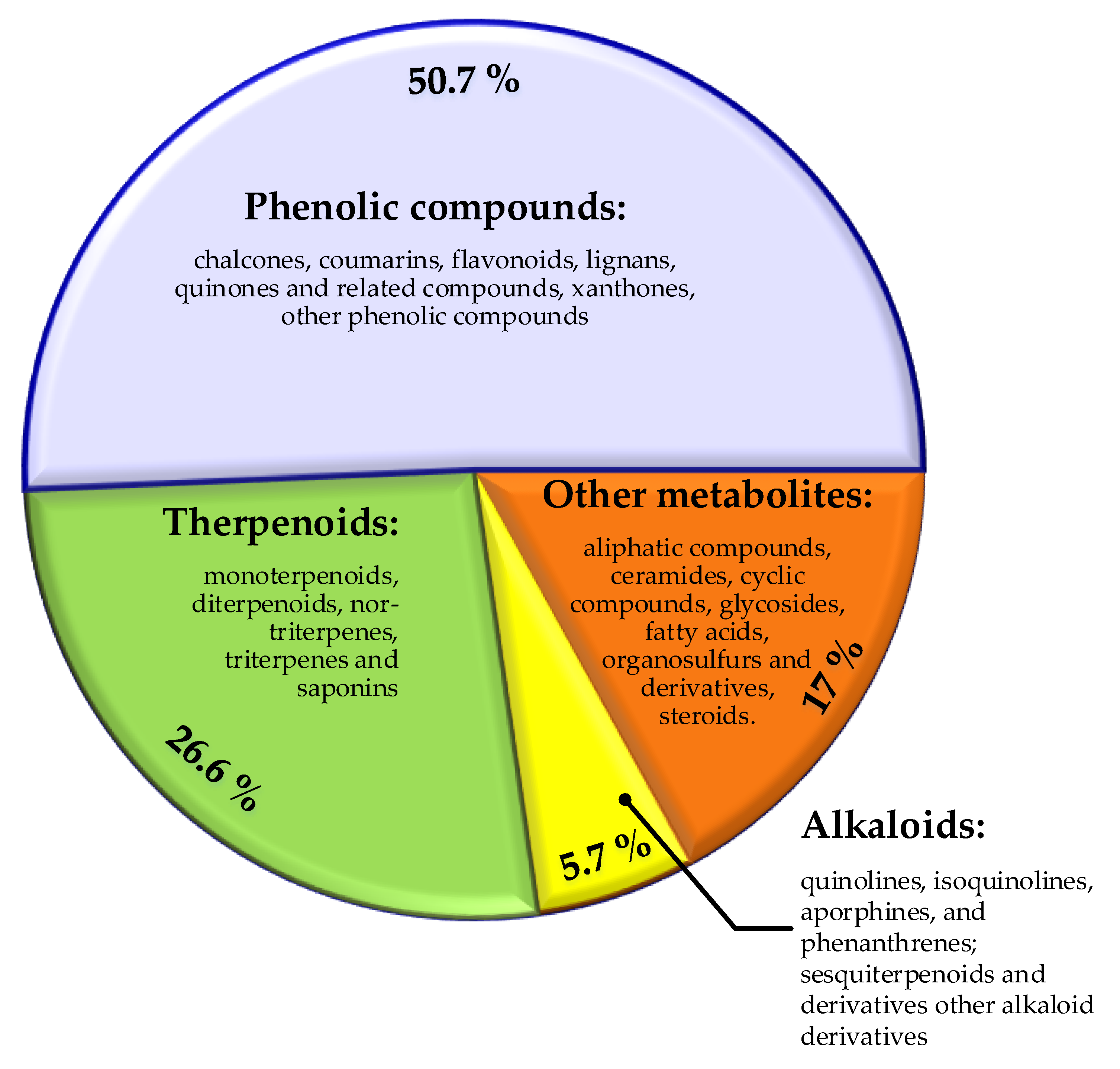
3.1.4. Plants-Derived Antibacterial Compounds
3.1.4.1. Phenolic Compounds
3.1.4.2. Alkaloids
3.1.4.3. Terpenoids
3.1.4.4. Other Compounds
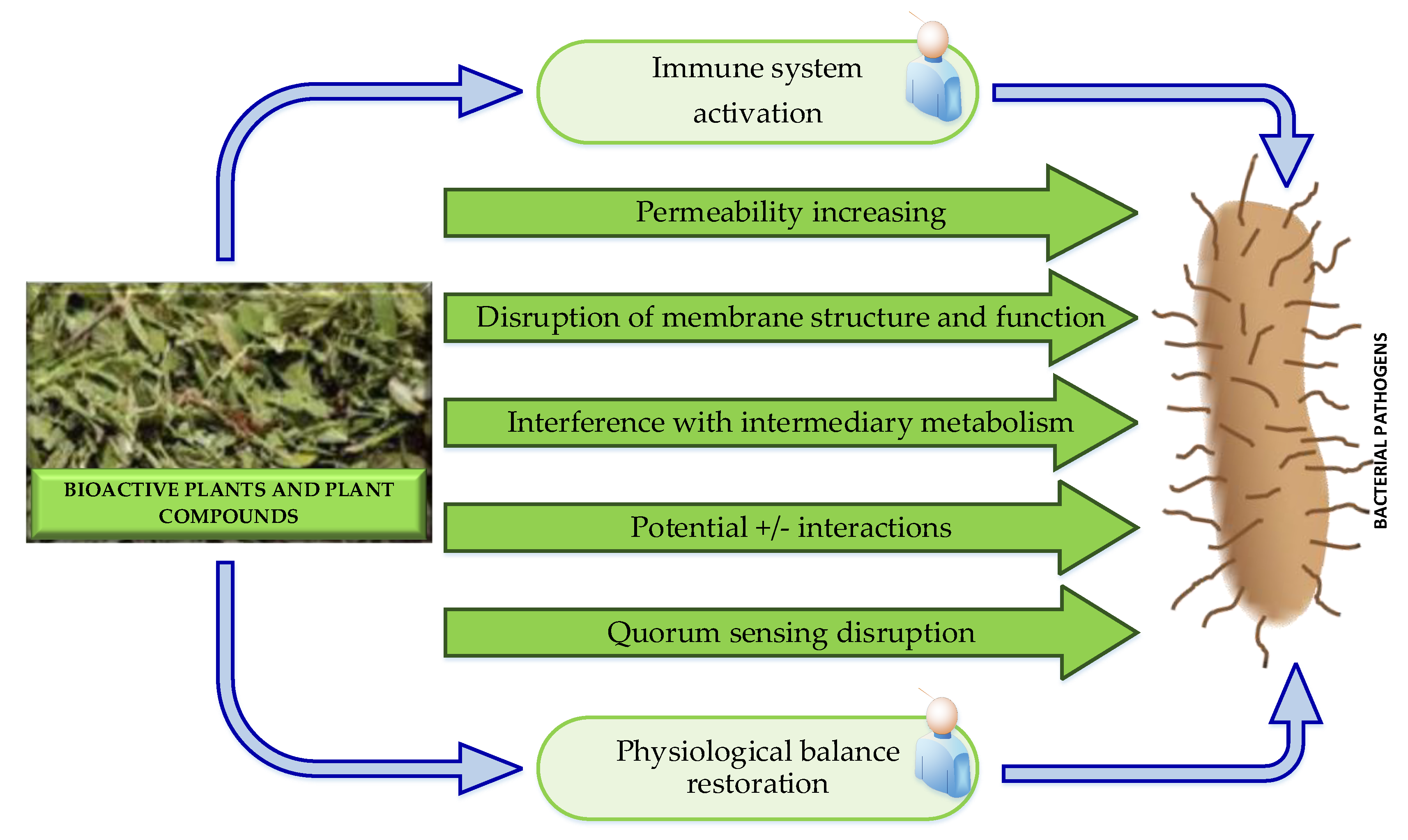
3.1.4.5. Possible Antibacterial Modes of Action of Plant-Derived Antibacterial Agents
3.2. Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Terrestrial Biota
3.2.1. Plant Antibacterial Peptides
3.2.2. Animal Origin Antibacterial Peptides
3.2.2.1. Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Mammalians
3.2.2.2. Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Amphibians
3.2.2.3. Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Snake Venom
3.2.2.4. Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Crabs
3.2.2.5. Antibacterial Peptides Derived from Insects and Others
3.2.3. Antibacterial Agents Produced by Microbes
3.2.3.1. Bacteriophages
3.2.3.2. Bacteriocines
3.2.4. Approaches to Address Shortcomings of Natural Antibacterial Peptides
3.2.4.1. Nanodelivery systems
3.2.4.2. Modified and Synthetic Analogues of Antibacterial Peptides Inspired by Nature
4. Biogenic Synthesized Metal, Metal Oxide and Composite Nanoparticles
4.1. Biosynthesized Silver Nanoparticles
4.2. Biosynthesized Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles
4.3. Biosynthesized Coper Nanoparticles
4.4. Biosynthesized Iron Oxide Nanoparticels
4.5. Biosynthesized Selenium Nanoparticles
4.6. Others
5. Concluding Remarks
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ye, L.; Zhang, J.; Xiao, W.; Liu, S. Efficacy and Mechanism of Actions of Natural Antimicrobial Drugs. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2020, 216, 107671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murray, C.J.L.; Ikuta, K.S.; Sharara, F.; Swetschinski, L.; Aguilar, G.R.; Gray, A.; Han, C.; Bisignano, C.; Rao, P.; Wool, E.; et al. Global Burden of Bacterial Antimicrobial Resistance in 2019: A Systematic Analysis. The Lancet 2022, 399, 629–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maarten van Dongen. AMR Insights in 2023 in a Bird’s Eye View; AMR Insights: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2024; p. 18. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization 10 Threats to Global Health in 2018. Available online: https://medium.com/who/10-threats-to-global-health-in-2018-232daf0bbef3 (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Health Promotion Board Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://hpb.gov.sg/healthy-living/preventive-health/antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- Li, W.; Separovic, F.; O’Brien-Simpson, N.M.; Wade, J.D. Chemically Modified and Conjugated Antimicrobial Peptides against Superbugs. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 4932–4973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulingam, T.; Parumasivam, T.; Gazzali, A.M.; Sulaiman, A.M.; Chee, J.Y.; Lakshmanan, M.; Chin, C.F.; Sudesh, K. Antimicrobial Resistance: Prevalence, Economic Burden, Mechanisms of Resistance and Strategies to Overcome. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2022, 170, 106103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jonas, O.B.; Irwin, A.; Berthe, F.C.J.; Le Gall, F.G.; Marquez, P. Drug-Resistant Infections : A Threat to Our Economic Future (Vol. 2) : Final Report. Available online: https://documents.worldbank.org/en/publication/documents-reports/documentdetail/323311493396993758/final-report (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- World Health Organization. World Health Statistics 2021: Monitoring Health for the SDGs, Sustainable Development Goals; World Health Organization: location, 2021; p. 136. [Google Scholar]
- World Health Organization. WHO Bacterial Priority Pathogens List, 2024 Bacterial Pathogens of Public Health Importance to Guide Research, Development and Strategies to Prevent and Control Antimicrobial Resistance; World Health Organization: location, 2024; p. 72. [Google Scholar]
- Qadri, H.; Shah, A.H.; Mir, M. Novel Strategies to Combat the Emerging Drug Resistance in Human Pathogenic Microbes. Current Drug Targets 2021, 22, 1424–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Symochko, L.; Demyanyuk, O.; Symochko, V.; Grulova, D.; Fejer, J.; Mariychuk, R. The Spreading of Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria in Terrestrial Ecosystems and the Formation of Soil Resistome. Land 2023, 12, 769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Theuretzbacher, U.; Bush, K.; Harbarth, S.; Paul, M.; Rex, J.H.; Tacconelli, E.; Thwaites, G.E. Critical Analysis of Antibacterial Agents in Clinical Development. Nat Rev Microbiol 2020, 18, 286–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abushaheen, M.A.; Muzaheed; Fatani, A.J.; Alosaimi, M.; Mansy, W.; George, M.; Acharya, S.; Rathod, S.; Divakar, D.D.; Jhugroo, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Resistance, Mechanisms and Its Clinical Significance. Disease-a-Month 2020, 66, 100971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancuso, G.; Midiri, A.; Gerace, E.; Biondo, C. Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance: The Most Critical Pathogens. Pathogens 2021, 10, 1310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, T.M.; Chakraborty, A.J.; Khusro, A.; Zidan, B.R.M.; Mitra, S.; Emran, T.B.; Dhama, K.; Ripon, M.K.H.; Gajdács, M.; Sahibzada, M.U.K.; et al. Antibiotic Resistance in Microbes: History, Mechanisms, Therapeutic Strategies and Future Prospects. Journal of Infection and Public Health 2021, 14, 1750–1766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bösch, A.; Macha, M.E.; Ren, Q.; Kohler, P.; Qi, W.; Babouee Flury, B. Resistance Development in Escherichia Coli to Delafloxacin at pHs 6.0 and 7.3 Compared to Ciprofloxacin. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2023, 67, e01625-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
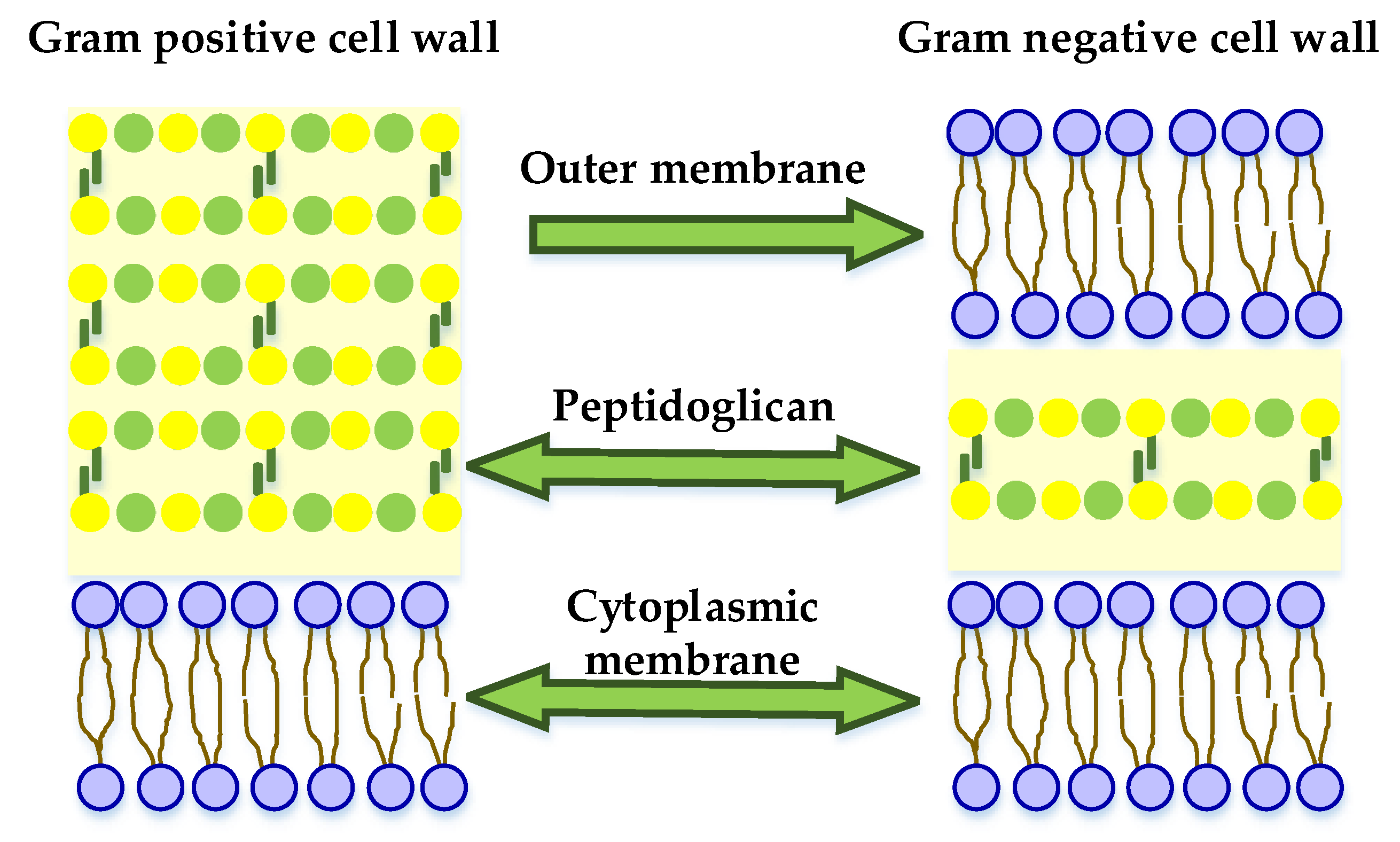
- Jubeh, B.; Breijyeh, Z.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Positive Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents and Overcoming Approaches. Molecules 2020, 25, 2888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of Gram-Negative Bacteria to Current Antibacterial Agents and Approaches to Resolve It. Molecules 2020, 25, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mir, M.A.; Aisha, S.; Qadri, H.; Jan, U.; Yousuf, A.; Jan, N. Chapter 2 - Evolution of Antimicrobial Drug Resistance in Human Pathogenic Bacteria. In Human Pathogenic Microbes; Developments in Microbiology; Mir, M.A., Ed.; Academic Press: lication, 2022; pp. 31–52. ISBN 978-0-323-96127-1. [Google Scholar]
- Helmy, Y.A.; Taha-Abdelaziz, K.; Hawwas, H.A.E.-H.; Ghosh, S.; AlKafaas, S.S.; Moawad, M.M.M.; Saied, E.M.; Kassem, I.I.; Mawad, A.M.M. Antimicrobial Resistance and Recent Alternatives to Antibiotics for the Control of Bacterial Pathogens with an Emphasis on Foodborne Pathogens. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Browne, K.; Chakraborty, S.; Chen, R.; Willcox, M.D.; Black, D.S.; Walsh, W.R.; Kumar, N. A New Era of Antibiotics: The Clinical Potential of Antimicrobial Peptides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2020, 21, 7047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stan, D.; Enciu, A.-M.; Mateescu, A.L.; Ion, A.C.; Brezeanu, A.C.; Stan, D.; Tanase, C. Natural Compounds With Antimicrobial and Antiviral Effect and Nanocarriers Used for Their Transportation. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, M.S.; Paterson, D.L. Antibiotics in the Clinical Pipeline in October 2019. J Antibiot 2020, 73, 329–364. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vladkova, T.; Georgieva, N.; Staneva, A.; Gospodinova, D. Recent Progress in Antioxidant Active Substances from Marine Biota. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T.G.; Martinov, B.L.; Gospodinova, D.N. Anti-Biofilm Agents from Marine Biota. Journal of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy 2023, 58, 825–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T.G.; Staneva, A.D.; Avramova, I.A.; Ivanova, I.A.; Gospodinova, D.N. Fucoidan-Containing, Low-Adhesive Siloxane Coatings for Medical Applications: Inhibition of Bacterial Growth and Biofilm Development. Materials 2023, 16, 3651. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T.G.; Martinov, B.L.; Staneva, A.D.; Ivanova, I.A.; Gospodinova, D.N.; Albu-Kaya, M.G. Preparation and Antimicrobial Activity of Fucoidan Containing Collagen/(ZnTiO3/SiO2) Composites. Journal of Chemical Technology and Metallurgy 2023, 58, 654–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vladkova, T.G.; Monov, D.M.; Akuzov, D.T.; Ivanova, I.A.; Gospodinova, D. Comparative Study of the Marinobacter Hydrocarbonoclasticus Biofilm Formation on Antioxidants Containing Siloxane Composite Coatings. Materials 2022, 15, 4530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farha, M.A.; Brown, E.D. Drug Repurposing for Antimicrobial Discovery. Nat. Microbiol. 2019, 4, 565–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, M.; Chi, M.; Sun, X.; Xie, X.; Weir, M.D.; Oates, T.W.; Zhou, Y.; Wang, L.; Bai, Y.; Xu, H.H. Novel Nanomaterial-Based Antibacterial Photodynamic Therapies to Combat Oral Bacterial Biofilms and Infectious Diseases. IJN 2019, 14, 6937–6956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Imran, M.; Ahmad, M.N.; Dasgupta, A.; Rana, P.; Srinivas, N.; Chopra, S. Novel Approaches for the Treatment of Infections Due to Multidrug-Resistant Bacterial Pathogens. Future Medicinal Chemistry 2022, 14, 1133–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moo, C.-L.; Yang, S.-K.; Yusoff, K.; Ajat, M.; Thomas, W.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lim, S.-H.-E.; Lai, K.-S. Mechanisms of Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) and Alternative Approaches to Overcome AMR. Current Drug Discovery Technologies 2020, 17, 430–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ayaz, M.; Ullah, F.; Sadiq, A.; Ullah, F.; Ovais, M.; Ahmed, J.; Devkota, H.P. Synergistic Interactions of Phytochemicals with Antimicrobial Agents: Potential Strategy to Counteract Drug Resistance. Chemico-Biological Interactions 2019, 308, 294–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyers, M.; Wright, G.D. Drug Combinations: A Strategy to Extend the Life of Antibiotics in the 21st Century. Nat Rev Microbiol 2019, 17, 141–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zharkova, M.S.; Orlov, D.S.; Golubeva, O.Y.; Chakchir, O.B.; Eliseev, I.E.; Grinchuk, T.M.; Shamova, O.V. Application of Antimicrobial Peptides of the Innate Immune System in Combination With Conventional Antibiotics—A Novel Way to Combat Antibiotic Resistance? Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Douafer, H.; Andrieu, V.; Phanstiel, O.I.; Brunel, J.M. Antibiotic Adjuvants: Make Antibiotics Great Again! J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 8665–8681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.; Kumawat, M.; Nabi, B.; Kumar, M. Chapter 8 - Combinatorial Approach to Combat Drug Resistance in Human Pathogenic Bacteria. In Human Pathogenic Microbes; Developments in Microbiology; Mir, M.A., Ed.; Academic Press: location, 2022; pp. 187–206. ISBN 978-0-323-96127-1. [Google Scholar]
- León-Buitimea, A.; Garza-Cárdenas, C.R.; Garza-Cervantes, J.A.; Lerma-Escalera, J.A.; Morones-Ramírez, J.R. The Demand for New Antibiotics: Antimicrobial Peptides, Nanoparticles, and Combinatorial Therapies as Future Strategies in Antibacterial Agent Design. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moammeri, A.; Chegeni, M.M.; Sahrayi, H.; Ghafelehbashi, R.; Memarzadeh, F.; Mansouri, A.; Akbarzadeh, I.; Abtahi, M.S.; Hejabi, F.; Ren, Q. Current Advances in Niosomes Applications for Drug Delivery and Cancer Treatment. Materials Today Bio 2023, 23, 100837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huan, Y.; Kong, Q.; Mou, H.; Yi, H. Antimicrobial Peptides: Classification, Design, Application and Research Progress in Multiple Fields. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadri, H.; Haseeb Shah, A.; Mudasir Ahmad, S.; Alshehri, B.; Almilaibary, A.; Ahmad Mir, M. Natural Products and Their Semi-Synthetic Derivatives against Antimicrobial-Resistant Human Pathogenic Bacteria and Fungi. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2022, 29, 103376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrowsmith, C.H. Structure-Guided Drug Discovery: Back to the Future. Nat Struct Mol Biol 2024, 31, 395–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Süntar, I. Importance of Ethnopharmacological Studies in Drug Discovery: Role of Medicinal Plants. Phytochem Rev 2020, 19, 1199–1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malekian, A.; Esmaeeli Djavid, G.; Akbarzadeh, K.; Soltandallal, M.; Rassi, Y.; Rafinejad, J.; Rahimi Foroushani, A.; Farhoud, A.R.; Bakhtiary, R.; Totonchi, M. Efficacy of Maggot Therapy on Staphylococcus Aureus and Pseudomonas Aeruginosa in Diabetic Foot Ulcers: A Randomized Controlled Trial. Journal of Wound Ostomy & Continence Nursing 2019, 46, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porras, G.; Chassagne, F.; Lyles, J.T.; Marquez, L.; Dettweiler, M.; Salam, A.M.; Samarakoon, T.; Shabih, S.; Farrokhi, D.R.; Quave, C.L. Ethnobotany and the Role of Plant Natural Products in Antibiotic Drug Discovery. Chem. Rev. 2021, 121, 3495–3560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.-C.; Liu, F.; Zhu, K.; Shen, J.-Z. Natural Products That Target Virulence Factors in Antibiotic-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2019, 67, 13195–13211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Álvarez-Martínez, F.J.; Barrajón-Catalán, E.; Herranz-López, M.; Micol, V. Antibacterial Plant Compounds, Extracts and Essential Oils: An Updated Review on Their Effects and Putative Mechanisms of Action. Phytomedicine 2021, 90, 153626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farhadi, F.; Khameneh, B.; Iranshahi, M.; Iranshahy, M. Antibacterial Activity of Flavonoids and Their Structure–Activity Relationship: An Update Review. Phytotherapy Research 2019, 33, 13–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheikh, B.A.; Bhat, B.A.; Ahmad, Z.; Mir, M.A. Strategies Employed to Evade the Host Immune Response and the Mechanism of Drug Resistance in Mycobacterium Tuberculosis: In Search of Finding New Targets. Current Pharmaceutical Biotechnology 2022, 23, 1704–1720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayo-Muñoz, D.; Pinilla-Redondo, R.; Camara-Wilpert, S.; Birkholz, N.; Fineran, P.C. Inhibitors of Bacterial Immune Systems: Discovery, Mechanisms and Applications. Nat Rev Genet 2024, 25, 237–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vaishampayan, A.; Grohmann, E. Antimicrobials Functioning through ROS-Mediated Mechanisms: Current Insights. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Naqvi, S.A.R.; Nadeem, S.; Komal, S.; Naqvi, S.A.A.; Mubarik, M.S.; Qureshi, S.Y.; Ahmad, S.; Abbas, A.; Zahid, M.; Khan, N.-U.-H.; et al. Antioxidants: Natural Antibiotics. In Antioxidants; IntechOpen: location, 2019; ISBN 978-1-78923-920-1. [Google Scholar]
- Durand, G.A.; Raoult, D.; Dubourg, G. Antibiotic Discovery: History, Methods and Perspectives. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2019, 53, 371–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Franco, C.M.; Vázquez, B.I. Natural Compounds as Antimicrobial Agents. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miethke, M.; Pieroni, M.; Weber, T.; Brönstrup, M.; Hammann, P.; Halby, L.; Arimondo, P.B.; Glaser, P.; Aigle, B.; Bode, H.B.; et al. Towards the Sustainable Discovery and Development of New Antibiotics. Nat Rev Chem 2021, 5, 726–749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elmaidomy, A.H.; Shady, N.H.; Abdeljawad, K.M.; Elzamkan, M.B.; Helmy, H.H.; Tarshan, E.A.; Adly, A.N.; Hussien, Y.H.; Sayed, N.G.; Zayed, A.; et al. Antimicrobial Potentials of Natural Products against Multidrug Resistance Pathogens: A Comprehensive Review. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 29078–29102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, M.A.; Usman, M.; Qadri, H.; Aisha, S. Chapter 10 - Recent Trends in the Development of Bacterial and Fungal Vaccines. In Human Pathogenic Microbes; Developments in Microbiology; Mir, M.A., Ed.; Academic Press: location, 2022; pp. 233–259. ISBN 978-0-323-96127-1. [Google Scholar]
- Jabborova, D.; Davranov, K.; Egamberdieva, D. Antibacterial, Antifungal, and Antiviral Properties of Medical Plants. In Medically Important Plant Biomes: Source of Secondary Metabolites; Egamberdieva, D., Tiezzi, A., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 51–65. ISBN 9789811395666. [Google Scholar]
- Parham, S.; Kharazi, A.Z.; Bakhsheshi-Rad, H.R.; Nur, H.; Ismail, A.F.; Sharif, S.; RamaKrishna, S.; Berto, F. Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Antiviral Properties of Herbal Materials. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goodhealth Herbal Antimicrobials: Fighting Infections Naturally. Available online: https://goodhealth.co.nz/herbal-antibiotics-fighting-infections-naturally-2/ (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Gong, C. What Is the Most Effective Natural Antibiotic for Tooth Infections. Available online: https://europe.oclean.com/blogs/tips/what-is-the-strongest-natural-antibiotic-for-tooth-infection (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Adamczak, A.; Ożarowski, M.; Karpiński, T.M. Curcumin, a Natural Antimicrobial Agent with Strain-Specific Activity. Pharmaceuticals 2020, 13, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Huang, C.; Huang, H.; Zhao, Y.; Khan, M.R.U.; Zhao, H.; Huang, L. Antibacterial Mechanism of Curcumin: A Review. Chemistry & Biodiversity 2020, 17, e2000171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khaleghian, M.; Sahrayi, H.; Hafezi, Y.; Mirshafeeyan, M.; Moghaddam, Z.S.; Farasati Far, B.; Noorbazargan, H.; Mirzaie, A.; Ren, Q. In Silico Design and Mechanistic Study of Niosome-Encapsulated Curcumin against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khameneh, B.; Iranshahy, M.; Soheili, V.; Fazly Bazzaz, B.S. Review on Plant Antimicrobials: A Mechanistic Viewpoint. Antimicrobial Resistance & Infection Control 2019, 8, 118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorlenko, C.L.; Kiselev, H.Y.; Budanova, E.V.; Zamyatnin, A.A.; Ikryannikova, L.N. Plant Secondary Metabolites in the Battle of Drugs and Drug-Resistant Bacteria: New Heroes or Worse Clones of Antibiotics? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Ashmawy, I.M.; Aljohani, A.S.M.; Soliman, A.S. Studying the Bioactive Components and Phytochemicals of the Methanol Extract of Rhanterium Epapposum Oliv. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2024, 196, 2414–2424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manandhar, S.; Luitel, S.; Dahal, R.K. In Vitro Antimicrobial Activity of Some Medicinal Plants against Human Pathogenic Bacteria. Journal of Tropical Medicine 2019, 2019, 1895340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zofou, D.; Shu, G.L.; Foba-Tendo, J.; Tabouguia, M.O.; Assob, J.-C.N. In Vitro and In Vivo Anti-Salmonella Evaluation of Pectin Extracts and Hydrolysates from “Cas Mango” (Spondias Dulcis). Evidence-Based Complementary and Alternative Medicine 2019, 2019, 3578402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rasooly, R.; Molnar, A.; Choi, H.-Y.; Do, P.; Racicot, K.; Apostolidis, E. In-Vitro Inhibition of Staphylococcal Pathogenesis by Witch-Hazel and Green Tea Extracts. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portillo-Torres, L.A.; Bernardino-Nicanor, A.; Gómez-Aldapa, C.A.; González-Montiel, S.; Rangel-Vargas, E.; Villagómez-Ibarra, J.R.; González-Cruz, L.; Cortés-López, H.; Castro-Rosas, J. Hibiscus Acid and Chromatographic Fractions from Hibiscus Sabdariffa Calyces: Antimicrobial Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Pathogenic Bacteria. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faujdar, S.S.; Bisht, D.; Sharma, A. Antibacterial Potential of Neem (Azadirachta Indica) against Uropathogens Producing Beta-Lactamase Enzymes: A Clue to Future Antibacterial Agent? Biomedical and Biotechnology Research Journal (BBRJ) 2020, 4, 232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaczorová, D.; Karalija, E.; Dahija, S.; Bešta-Gajević, R.; Parić, A.; Ćavar Zeljković, S. Influence of Extraction Solvent on the Phenolic Profile and Bioactivity of Two Achillea Species. Molecules 2021, 26, 1601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajudin, N.J.; Ismail, I.N.A. Antimicrobial Activity of Kalanchoe Pinnata: A Review. Malaysian Journal of Science Health & Technology 2022, 8, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.; Musa, F.M.; Aliyu, F.; Adamu, A. Antibacterial Activity of Ethanol Leaf Extract of Sida Acuta Against Some Clinical Bacterial Isolates. Int. J. Life Sci. Biotechnol. 2022, 5, 572–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasution, A.K.; Wijaya, S.H.; Gao, P.; Islam, R.M.; Huang, M.; Ono, N.; Kanaya, S.; Altaf-Ul-Amin, M. Prediction of Potential Natural Antibiotics Plants Based on Jamu Formula Using Random Forest Classifier. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, A.G.; Silva, A.; Grosso, C.; Echave, J.; Chamorro, F.; Seyyedi-Mansour, S.; Donn, P.; Fraga-Corral, M.; Barroso, M.F.; Prieto, M.A. Antimicrobial Activity Screening of Camellia Japonica Flowers (Var. Carolyn Tuttle) for Potential Drug Development. Engineering Proceedings 2023, 56, 314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kavaz, D.; Faraj, R.E. Investigation of Composition, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial and Cytotoxic Characteristics from Juniperus Sabina and Ferula Communis Extracts. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 7193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Mannoubi, I. Impact of Different Solvents on Extraction Yield, Phenolic Composition, in Vitro Antioxidant and Antibacterial Activities of Deseeded Opuntia Stricta Fruit. J.Umm Al-Qura Univ. Appll. Sci. 2023, 9, 176–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltanian, S.; Sheikhbahaei, M.; Mirtadzadini, M.; Kalantari Khandani, B. Evaluation of Anticancer, Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties of Methanol Extract of Three Acantholimon Boiss. Species. Avicenna J Phytomed 2020, 10, 641–652. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Senhaji, S.; Lamchouri, F.; Toufik, H. Phytochemical Content, Antibacterial and Antioxidant Potential of Endemic Plant Anabasis Aretioïdes Coss. & Moq. (Chenopodiaceae). BioMed Research International 2020, 2020, 6152932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özcan, K. Antibacterial, Antioxidant and Enzyme Inhibition Activity Capacities of Doronicum Macrolepis (FREYN&SINT): An Endemic Plant from Turkey. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 2020, 28, 95–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhao, X.; Yang, F.; Wu, W.; Liu, Y.; Wang, L.; Wang, L.; Wang, Z. Enhanced Bioaccessibility in Vitro and Bioavailability of Ginkgo Biloba Extract Nanoparticles Prepared by Liquid Anti-Solvent Precipitation. International Journal of Food Science & Technology 2019, 54, 2266–2276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tariq, S.; Wani, S.; Rasool, W.; Shafi, K.; Bhat, M.A.; Prabhakar, A.; Shalla, A.H.; Rather, M.A. A Comprehensive Review of the Antibacterial, Antifungal and Antiviral Potential of Essential Oils and Their Chemical Constituents against Drug-Resistant Microbial Pathogens. Microbial Pathogenesis 2019, 134, 103580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wińska, K.; Mączka, W.; Łyczko, J.; Grabarczyk, M.; Czubaszek, A.; Szumny, A. Essential Oils as Antimicrobial Agents—Myth or Real Alternative? Molecules 2019, 24, 2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahizan, N.A.; Yang, S.-K.; Moo, C.-L.; Song, A.A.-L.; Chong, C.-M.; Chong, C.-W.; Abushelaibi, A.; Lim, S.-H.E.; Lai, K.-S. Terpene Derivatives as a Potential Agent against Antimicrobial Resistance (AMR) Pathogens. Molecules 2019, 24, 2631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdallah, E.M.; Alhatlani, B.Y.; de Paula Menezes, R.; Martins, C.H.G. Back to Nature: Medicinal Plants as Promising Sources for Antibacterial Drugs in the Post-Antibiotic Era. Plants 2023, 12, 3077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hovorková, P.; Laloučková, K.; Skřivanová, E. Determination of in Vitro Antibacterial Activity of Plant Oils Containing Medium-Chain Fatty Acids against Gram-Positive Pathogenic and Gut Commensal Bacteria. Czech Journal of Animal Science 2018, 63, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riski, D.G.; Maulana, R.G.R.; Permana, E.; Lestari, I.; Tarigan, I.L. Profile Analysis of Fatty Acids of Tengkawang (Shorea Sumatrana) Oil Using GC-MS and Antibacterial Activity. Indonesian Journal of Chemical Research 2020, 8, 114–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casillas-Vargas, G.; Ocasio-Malavé, C.; Medina, S.; Morales-Guzmán, C.; Del Valle, R.G.; Carballeira, N.M.; Sanabria-Ríos, D.J. Antibacterial Fatty Acids: An Update of Possible Mechanisms of Action and Implications in the Development of the next-Generation of Antibacterial Agents. Progress in Lipid Research 2021, 82, 101093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kannan, N.; Rao, A.S.; Nair, A. Microbial Production of Omega-3 Fatty Acids: An Overview. Journal of Applied Microbiology 2021, 131, 2114–2130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sidders, A.E.; Kedziora, K.M.; Arts, M.; Daniel, J.-M.; de Benedetti, S.; Beam, J.E.; Bui, D.T.; Parsons, J.B.; Schneider, T.; Rowe, S.E.; et al. Antibiotic-Induced Accumulation of Lipid II Synergizes with Antimicrobial Fatty Acids to Eradicate Bacterial Populations. eLife 2023, 12, e80246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almuhayawi, M.S. Propolis as a Novel Antibacterial Agent. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2020, 27, 3079–3086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mandal, M.D.; Mandal, S. Honey: Its Medicinal Property and Antibacterial Activity. Asian Pacific Journal of Tropical Biomedicine 2011, 1, 154–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Albaridi, N.A. Antibacterial Potency of Honey. International Journal of Microbiology 2019, 2019, 2464507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almasaudi, S. The Antibacterial Activities of Honey. Saudi Journal of Biological Sciences 2021, 28, 2188–2196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- University of Birmingham Honey and the Antibiotic Crisis. Available online: https://www.birmingham.ac.uk/alumni/giving/honey-and-the-antibiotic-crisis.aspx (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Zakir-Hussain, M. Scientists Turn to Honey in Their Urgent Search for Alternative Antibiotics. Available online: https://www.aol.com/scientists-turn-honey-urgent-search-103812541.html (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Ware, I.; Franke, K.; Frolov, A.; Bureiko, K.; Kysil, E.; Yahayu, M.; El Enshasy, H.A.; Wessjohann, L.A. Comparative Metabolite Analysis of Piper Sarmentosum Organs Approached by LC–MS-Based Metabolic Profiling. Nat. Prod. Bioprospect. 2024, 14, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mickymaray, S. Efficacy and Mechanism of Traditional Medicinal Plants and Bioactive Compounds against Clinically Important Pathogens. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gioia, S.D.; Hossain, M.N.; Conese, M. Biological Properties and Therapeutic Effects of Plant-Derived Nanovesicles. Open Medicine 2020, 15, 1096–1122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vestergaard, M.; Ingmer, H. Antibacterial and Antifungal Properties of Resveratrol. International Journal of Antimicrobial Agents 2019, 53, 716–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, J.I.; Ryu, J.; Jin, C.H.; Kim, D.-G.; Kim, J.M.; Seo, K.-S.; Kim, J.-B.; Kim, S.H.; Ahn, J.-W.; Kang, S.-Y.; et al. Phenolic Compounds in Extracts of Hibiscus Acetosella (Cranberry Hibiscus) and Their Antioxidant and Antibacterial Properties. Molecules 2020, 25, 4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Wu, J.; Li, Q.; Wang, J.; Mu, L.; Hui, L.; Li, M.; Xu, W.; Yang, H.; Wei, L. A Non-Bactericidal Cathelicidin Provides Prophylactic Efficacy against Bacterial Infection by Driving Phagocyte Influx. eLife 2022, 11, e72849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Cai, P.; Cheng, G.; Zhang, Y. A Brief Review of Phenolic Compounds Identified from Plants: Their Extraction, Analysis, and Biological Activity. Natural Product Communications 2022, 17, 1934578X211069721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Fan, L.; Pan, H.; Li, Y.; Zhao, X.; Qiu, Y.; Lu, Y. Identification and Characterization of a Novel Cathelicidin from Hydrophis Cyanocinctus with Antimicrobial and Anti-Inflammatory Activity. Molecules 2023, 28, 2082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, L.; Zhao, W.; Yang, Z.; Subbiah, V.; Suleria, H.A.R. Extraction and Characterization of Phenolic Compounds and Their Potential Antioxidant Activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2022, 29, 81112–81129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flavonoid. Wikipedia 2024.
- Harvard Health Publishing The Thinking on Flavonoids. Available online: https://www.health.harvard.edu/mind-and-mood/the-thinking-on-flavonoids (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Kozłowska, A.; Szostak-Węgierek, D. Flavonoids – Food Sources, Health Benefits, and Mechanisms Involved. In Bioactive Molecules in Food; Mérillon, J.-M., Ramawat, K.G., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2019; pp. 53–78. ISBN 978-3-319-78030-6. [Google Scholar]
- Mutha, R.E.; Tatiya, A.U.; Surana, S.J. Flavonoids as Natural Phenolic Compounds and Their Role in Therapeutics: An Overview. Future Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2021, 7, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doyle, A.A.; Stephens, J.C. A Review of Cinnamaldehyde and Its Derivatives as Antibacterial Agents. Fitoterapia 2019, 139, 104405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Wu, P.; Shen, F.; Ji, J.; Rakesh, K.P. Chalcone Derivatives and Their Antibacterial Activities: Current Development. Bioorganic Chemistry 2019, 91, 103133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dan, W.; Dai, J. Recent Developments of Chalcones as Potential Antibacterial Agents in Medicinal Chemistry. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 187, 111980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skarpalezos, D.; Detsi, A. Deep Eutectic Solvents as Extraction Media for Valuable Flavonoids from Natural Sources. Applied Sciences 2019, 9, 4169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez De Luna, S.L.; Ramírez-Garza, R.E.; Serna Saldívar, S.O. Environmentally Friendly Methods for Flavonoid Extraction from Plant Material: Impact of Their Operating Conditions on Yield and Antioxidant Properties. The Scientific World Journal 2020, 2020, 6792069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaves, J.O.; de Souza, M.C.; da Silva, L.C.; Lachos-Perez, D.; Torres-Mayanga, P.C.; Machado, A.P.d.F.; Forster-Carneiro, T.; Vázquez-Espinosa, M.; González-de-Peredo, A.V.; Barbero, G.F.; et al. Extraction of Flavonoids From Natural Sources Using Modern Techniques. Front. Chem. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurinjak Tušek, A.; Šamec, D.; Šalić, A. Modern Techniques for Flavonoid Extraction—To Optimize or Not to Optimize? Applied Sciences 2022, 12, 11865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Wu, J.; Qi, J.; Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Miao, Z.; Qiu, G.; Jia, W. Microwave-Assisted Extraction of Flavonoids from Phyllostachys Heterocycla Leaves: Optimization, Mechanism, and Antioxidant Activity in Vitro. BioResources 2021, 16, 8060–8081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Liu, Y.; Shan, C.; Yang, X.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, N.; Xu, L.; Song, W. Effects of Five Extraction Methods on Total Content, Composition, and Stability of Flavonoids in Jujube. Food Chemistry: X 2022, 14, 100287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vittaya, L.; Charoendat, U.; Ui-eng, J.; Leesakul, N. Effect of Extraction Solvents on Phenolic Compounds and Flavonoids from Pongame Oiltree (Derris Indica [Lamk.] Bennet) Aerial Parts and Their Growth Inhibition of Aquatic Pathogenic Bacteria. Agriculture and Natural Resources 2022, 56, 569–582. [Google Scholar]
- Simangunsong, S.N.; Lenny, S.; Marpaung, L. Isolation of Flavonoids Compounds from Akalifa (Acalypha Wilkesiana Muell. Arc.) Plant Leaves. Journal of Chemical Natural Resources 2023, 5, 40–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bribi, N. Pharmacological Activity of Alkaloids: A Review. 2018, 1.
- Lin, C.-J.; Chang, Y.-L.; Yang, Y.-L.; Chen, Y.-L. Natural Alkaloid Tryptanthrin Exhibits Novel Anticryptococcal Activity. Medical Mycology 2021, 59, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Han, J.; Feng, Y.; Guymer, G.; Forster, P.I.; Quinn, R.J. Antimicrobial Benzyltetrahydroisoquinoline-Derived Alkaloids from the Leaves of Doryphora Aromatica. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 676–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biva, I.J.; Ndi, C.P.; Semple, S.J.; Griesser, H.J. Antibacterial Performance of Terpenoids from the Australian Plant Eremophila Lucida. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, C.-Z.; Hu, B.-Y.; Liu, J.-W.; Cai, Y.; Chen, X.-C.; Qin, D.-P.; Cheng, Y.-X.; Zhang, Z.-D. Anti-Mycobacterium Tuberculosis Terpenoids from Resina Commiphora. Molecules 2019, 24, 1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hossain, S.; Urbi, Z.; Karuniawati, H.; Mohiuddin, R.B.; Moh Qrimida, A.; Allzrag, A.M.M.; Ming, L.C.; Pagano, E.; Capasso, R. Andrographis Paniculata (Burm. f.) Wall. Ex Nees: An Updated Review of Phytochemistry, Antimicrobial Pharmacology, and Clinical Safety and Efficacy. Life 2021, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pech-Puch, D.; Forero, A.M.; Fuentes-Monteverde, J.C.; Lasarte-Monterrubio, C.; Martinez-Guitian, M.; González-Salas, C.; Guillén-Hernández, S.; Villegas-Hernández, H.; Beceiro, A.; Griesinger, C.; et al. Antimicrobial Diterpene Alkaloids from an Agelas Citrina Sponge Collected in the Yucatán Peninsula. Marine Drugs 2022, 20, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyakoshi, M.; Tamura, Y.; Masuda, H.; Mizutani, K.; Tanaka, O.; Ikeda, T.; Ohtani, K.; Kasai, R.; Yamasaki, K. Antiyeast Steroidal Saponins from Yucca Schidigera (Mohave Yucca), a New Anti-Food-Deteriorating Agent. J. Nat. Prod. 2000, 63, 332–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussein, R.A.; El-Anssary, A.A.; Hussein, R.A.; El-Anssary, A.A. Plants. In Herbal Medicine; IntechOpen: location, 2018; ISBN 978-1-78984-783-3. [Google Scholar]
- Dev Kumar, G.; Mis Solval, K.; Mishra, A.; Macarisin, D. Antimicrobial Efficacy of Pelargonic Acid Micelles against Salmonella Varies by Surfactant, Serotype and Stress Response. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 10287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pacyga, K.; Pacyga, P.; Topola, E.; Viscardi, S.; Duda-Madej, A. Bioactive Compounds from Plant Origin as Natural Antimicrobial Agents for the Treatment of Wound Infections. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2024, 25, 2100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thapa, S.S.; Grove, A. Do Global Regulators Hold the Key to Production of Bacterial Secondary Metabolites? Antibiotics 2019, 8, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mahmood, N.; Nazir, R.; Khan, M.; Khaliq, A.; Adnan, M.; Ullah, M.; Yang, H. Antibacterial Activities, Phytochemical Screening and Metal Analysis of Medicinal Plants: Traditional Recipes Used against Diarrhea. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asif, F.; Zaman, S.U.; Arnab, M.K.H.; Hasan, M.; Islam, M.M. Antimicrobial Peptides as Therapeutics: Confronting Delivery Challenges to Optimize Efficacy. The Microbe 2024, 2, 100051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koehbach, J.; Craik, D.J. The Vast Structural Diversity of Antimicrobial Peptides. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2019, 40, 517–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin Hafeez, A.; Jiang, X.; Bergen, P.J.; Zhu, Y. Antimicrobial Peptides: An Update on Classifications and Databases. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 11691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chung, C.-R.; Liou, J.-T.; Wu, L.-C.; Horng, J.-T.; Lee, T.-Y. Multi-Label Classification and Features Investigation of Antimicrobial Peptides with Various Functional Classes. iScience 2023, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, H.; Dave, V.; Tyagi, E.; Prakash, A. Antimicrobial Peptides: A Novel and Natural Approach as Antibiofouling Mediator. Biologia 2024, 79, 2515–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mwangi, J.; Hao, X.; Lai, R.; Zhang, Z.-Y. Antimicrobial Peptides: New Hope in the War against Multidrug Resistance. zr 2019, 40, 488–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xuan, J.; Feng, W.; Wang, J.; Wang, R.; Zhang, B.; Bo, L.; Chen, Z.-S.; Yang, H.; Sun, L. Antimicrobial Peptides for Combating Drug-Resistant Bacterial Infections. Drug Resistance Updates 2023, 68, 100954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, L. Natural and Man-Made Cyclic Peptide-Based Antibiotics. Antibiotics 2023, 12, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakare, O.O.; Gokul, A.; Niekerk, L.-A.; Aina, O.; Abiona, A.; Barker, A.M.; Basson, G.; Nkomo, M.; Otomo, L.; Keyster, M.; et al. Recent Progress in the Characterization, Synthesis, Delivery Procedures, Treatment Strategies, and Precision of Antimicrobial Peptides. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 11864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.; Sun, L.; Huang, S.; Zhu, C.; Li, P.; He, J.; Mackey, V.; Coy, D.H.; He, Q. The Antimicrobial Peptides and Their Potential Clinical Applications. Am J Transl Res 2019, 11, 3919–3931. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.H.; Lu, T.K. Development and Challenges of Antimicrobial Peptides for Therapeutic Applications. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van der Does, A.M.; Hiemstra, P.S.; Mookherjee, N. Antimicrobial Host Defence Peptides: Immunomodulatory Functions and Translational Prospects. In Antimicrobial Peptides: Basics for Clinical Application; Matsuzaki, K., Ed.; Springer: Singapore, 2019; pp. 149–171. ISBN 9789811335884. [Google Scholar]
- Raheem, N.; Straus, S.K. Mechanisms of Action for Antimicrobial Peptides With Antibacterial and Antibiofilm Functions. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahlapuu, M.; Björn, C.; Ekblom, J. Antimicrobial Peptides as Therapeutic Agents: Opportunities and Challenges. Critical Reviews in Biotechnology 2020, 40, 978–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana, M.; Pushpanathan, M.; Santos, A.L.; Leanse, L.; Fernandez, M.; Ioannidis, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Apidianakis, Y.; Bradfute, S.; Ferguson, A.L.; et al. The Value of Antimicrobial Peptides in the Age of Resistance. The Lancet Infectious Diseases 2020, 20, e216–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Uddin, S.J.; Shilpi, J.A.; Nahar, L.; Sarker, S.D.; Göransson, U. Editorial: Natural Antimicrobial Peptides: Hope for New Antibiotic Lead Molecules. Front. Pharmacol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phazang, P.; Negi, N.P.; Raina, M.; Kumar, D. Plant Antimicrobial Peptides: Next-Generation Bioactive Molecules for Plant Protection. In Phyto-Microbiome in Stress Regulation; Kumar, M., Kumar, V., Prasad, R., Eds.; Springer: Singapore, 2020; pp. 281–293. ISBN 9789811525766. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, X.; Zhang, J.; Shen, J.; Cheng, B.; Bi, C.; Ma, Q. Branched-Chain Amino Acid Modulation of Lipid Metabolism, Gluconeogenesis, and Inflammation in a Finishing Pig Model: Targeting Leucine and Valine. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 10119–10134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zou, F.; Tan, C.; Shinali, T.S.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, L.; Han, Z.; Shang, N. Plant Antimicrobial Peptides: A Comprehensive Review of Their Classification, Production, Mode of Action, Functions, Applications, and Challenges. Food Funct. 2023, 14, 5492–5515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakare, O.O.; Gokul, A.; Fadaka, A.O.; Wu, R.; Niekerk, L.-A.; Barker, A.M.; Keyster, M.; Klein, A. Plant Antimicrobial Peptides (PAMPs): Features, Applications, Production, Expression, and Challenges. Molecules 2022, 27, 3703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Hu, S.; Jian, W.; Xie, C.; Yang, X. Plant Antimicrobial Peptides: Structures, Functions, and Applications. Botanical Studies 2021, 62, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barashkova, A.S.; Rogozhin, E.A. Isolation of Antimicrobial Peptides from Different Plant Sources: Does a General Extraction Method Exist? Plant Methods 2020, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Brahim, R.; Ellouzi, H.; Fouzai, K.; Asses, N.; Neffati, M.; Sabatier, J.M.; Bulet, P.; Regaya, I. Optimized Chemical Extraction Methods of Antimicrobial Peptides from Roots and Leaves of Extremophilic Plants: Anthyllis Sericea and Astragalus Armatus Collected from the Tunisian Desert. Antibiotics 2022, 11, 1302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, A.M.; Azevedo, M.I.G.; Sousa, L.M.; Oliveira, N.S.; Andrade, C.R.; Freitas, C.D.T.; Souza, P.F.N. Plant Antimicrobial Peptides: An Overview about Classification, Toxicity and Clinical Applications. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2022, 214, 10–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Höng, K.; Austerlitz, T.; Bohlmann, T.; Bohlmann, H. The Thionin Family of Antimicrobial Peptides. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0254549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, K.; Yin, Y.; Liu, S.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, K.; Liang, Y.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, W.; Chao, H.; Li, M. Genome-Wide Identification and Functional Analysis of Oleosin Genes in Brassica Napus L. BMC Plant Biology 2019, 19, 294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.; Guo, Q.; Baten, A.; Mauleon, R.; Khatun, A.; Liu, L.; Barkla, B.J. Shotgun Proteomics of Brassica Rapa Seed Proteins Identifies Vicilin as a Major Seed Storage Protein in the Mature Seed. PLOS ONE 2021, 16, e0253384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afroz, M.; Akter, S.; Ahmed, A.; Rouf, R.; Shilpi, J.A.; Tiralongo, E.; Sarker, S.D.; Göransson, U.; Uddin, S.J. Ethnobotany and Antimicrobial Peptides From Plants of the Solanaceae Family: An Update and Future Prospects. Front. Pharmacol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mukherjee, P.K.; Kar, A.; Biswas, S.; Chaudhary, S.K.; Banerjee, S. Chapter 37 - Hyphenated Analytical Techniques for Validation of Herbal Medicine. In Evidence-Based Validation of Herbal Medicine (Second Edition); Mukherjee, P.K., Ed.; Elsevier: location, 2022; pp. 811–827. ISBN 978-0-323-85542-6. [Google Scholar]
- Parthasarathy, A.; Borrego, E.J.; Savka, M.A.; Dobson, R.C.J.; Hudson, A.O. Amino Acid–Derived Defense Metabolites from Plants: A Potential Source to Facilitate Novel Antimicrobial Development. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2021, 296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Slezina, M.P.; Odintsova, T.I. Plant Antimicrobial Peptides: Insights into Structure-Function Relationships for Practical Applications. Current Issues in Molecular Biology 2023, 45, 3674–3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moyer, T.B.; Allen, J.L.; Shaw, L.N.; Hicks, L.M. Multiple Classes of Antimicrobial Peptides in Amaranthus Tricolor Revealed by Prediction, Proteomics, and Mass Spectrometric Characterization. J. Nat. Prod. 2021, 84, 444–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jaiswal, M.; Singh, A.; Kumar, S. PTPAMP: Prediction Tool for Plant-Derived Antimicrobial Peptides. Amino Acids 2023, 55, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nazarian-Firouzabadi, F.; Torres, M.D.T.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C. Recombinant Production of Antimicrobial Peptides in Plants. Biotechnology Advances 2024, 71, 108296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mojsoska, B.; Jenssen, H. Peptides and Peptidomimetics for Antimicrobial Drug Design. Pharmaceuticals 2015, 8, 366–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Barros, E.; Gonçalves, R.M.; Cardoso, M.H.; Santos, N.C.; Franco, O.L.; Cândido, E.S. Snake Venom Cathelicidins as Natural Antimicrobial Peptides. Front. Pharmacol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.; Li, C.; Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Luo, Y.; Xia, X.; Song, Y.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, A.-M. Cathelicidin-DM Is an Antimicrobial Peptide from Duttaphrynus Melanostictus and Has Wound-Healing Therapeutic Potential. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 9301–9310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheenstra, M.R.; van Harten, R.M.; Veldhuizen, E.J.A.; Haagsman, H.P.; Coorens, M. Cathelicidins Modulate TLR-Activation and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klubthawee, N.; Adisakwattana, P.; Hanpithakpong, W.; Somsri, S.; Aunpad, R. A Novel, Rationally Designed, Hybrid Antimicrobial Peptide, Inspired by Cathelicidin and Aurein, Exhibits Membrane-Active Mechanisms against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 9117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, M.; Chen, R.; Zhang, J.; Chen, F.; Wang, K.-J. A Novel Antimicrobial Peptide Spampcin56–86 from Scylla Paramamosain Exerting Rapid Bactericidal and Anti-Biofilm Activity In Vitro and Anti-Infection In Vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 13316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galal-Khallaf, A.; Samir Aboali, E.; El-Sayed Hassab El-Nabi, S.; El-Tantawy, A.I.; Schott, E.J.; Mohammed-Geba, K. As Healthy as Invasive: Charybdis Natator Shell Extract Reveals Beneficial Metabolites with Promising Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Potentials. Front. Mar. Sci. 2024, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.; Shin, M.K.; Yoo, J.S.; Jang, W.; Sung, J.-S. Identifying Novel Antimicrobial Peptides from Venom Gland of Spider Pardosa Astrigera by Deep Multi-Task Learning. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elliott, A.G.; Huang, J.X.; Neve, S.; Zuegg, J.; Edwards, I.A.; Cain, A.K.; Boinett, C.J.; Barquist, L.; Lundberg, C.V.; Steen, J.; et al. An Amphipathic Peptide with Antibiotic Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Gram-Negative Bacteria. Nat Commun 2020, 11, 3184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fleming, A. On the Antibacterial Action of Cultures of a Penicillium, with Special Reference to Their Use in the Isolation of B. Influenzæ. Br J Exp Pathol 1929, 10, 226–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, S.; Tatsumura, Y. Alexander Fleming (1881–1955): Discoverer of Penicillin. smedj 2015, 56, 366–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, J.V.; Yilma, M.A.; Feliz, A.; Majid, M.T.; Maffetone, N.; Walker, J.R.; Kim, E.; Cho, H.J.; Reynolds, J.M.; Song, M.C.; et al. A Review of the Microbial Production of Bioactive Natural Products and Biologics. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moradali, M.F.; Rehm, B.H.A. Bacterial Biopolymers: From Pathogenesis to Advanced Materials. Nat Rev Microbiol 2020, 18, 195–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pérez-Ramos, A.; Madi-Moussa, D.; Coucheney, F.; Drider, D. Current Knowledge of the Mode of Action and Immunity Mechanisms of LAB-Bacteriocins. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Romero-Calle, D.; Guimarães Benevides, R.; Góes-Neto, A.; Billington, C. Bacteriophages as Alternatives to Antibiotics in Clinical Care. Antibiotics 2019, 8, 138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plumet, L.; Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Dunyach-Remy, C.; Kissa, K.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Costechareyre, D.; Molle, V. Bacteriophage Therapy for Staphylococcus Aureus Infections: A Review of Animal Models, Treatments, and Clinical Trials. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, M. Phage Therapy: Past, Present and Future. Available online: https://asm.org:443/Articles/2022/August/Phage-Therapy-Past,-Present-and-Future (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Parkinson, J. What’s Old Is New: Bacteriophage Is a Therapy That May Combat Antimicrobial Resistance. Available online: https://www.contagionlive.com/view/what-s-old-is-new-bacteriophage-is-a-therapy-that-may-combat-antimicrobial-resistance (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Ji, Y.; Cheng, M.; Zhai, S.; Xi, H.; Cai, R.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, H.; Wang, X.; Xue, Y.; Li, X.; et al. Preventive Effect of the Phage VB-SavM-JYL01 on Rabbit Necrotizing Pneumonia Caused by Staphylococcus Aureus. Veterinary Microbiology 2019, 229, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barylski, J.; Enault, F.; Dutilh, B.E.; Schuller, M.B.; Edwards, R.A.; Gillis, A.; Klumpp, J.; Knezevic, P.; Krupovic, M.; Kuhn, J.H.; et al. Analysis of Spounaviruses as a Case Study for the Overdue Reclassification of Tailed Phages. Systematic Biology 2020, 69, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Głowacka-Rutkowska, A.; Ulatowska, M.; Empel, J.; Kowalczyk, M.; Boreczek, J.; Łobocka, M. A Kayvirus Distant Homolog of Staphylococcal Virulence Determinants and VISA Biomarker Is a Phage Lytic Enzyme. Viruses 2020, 12, 292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Göller, P.C.; Elsener, T.; Lorgé, D.; Radulovic, N.; Bernardi, V.; Naumann, A.; Amri, N.; Khatchatourova, E.; Coutinho, F.H.; Loessner, M.J.; et al. Multi-Species Host Range of Staphylococcal Phages Isolated from Wastewater. Nat Commun 2021, 12, 6965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Łubowska, N.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Kosznik-Kwaśnicka, K.; Zauszkiewicz-Pawlak, A.; Węgrzyn, A.; Dołęgowska, B.; Piechowicz, L. Characterization of the Three New Kayviruses and Their Lytic Activity Against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. Microorganisms 2019, 7, 471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oduor, J.M.O.; Kadija, E.; Nyachieo, A.; Mureithi, M.W.; Skurnik, M. Bioprospecting Staphylococcus Phages with Therapeutic and Bio-Control Potential. Viruses 2020, 12, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kifelew, L.G.; Warner, M.S.; Morales, S.; Vaughan, L.; Woodman, R.; Fitridge, R.; Mitchell, J.G.; Speck, P. Efficacy of Phage Cocktail AB-SA01 Therapy in Diabetic Mouse Wound Infections Caused by Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus. BMC Microbiology 2020, 20, 204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fanaei Pirlar, R.; Wagemans, J.; Ponce Benavente, L.; Lavigne, R.; Trampuz, A.; Gonzalez Moreno, M. Novel Bacteriophage Specific against Staphylococcus Epidermidis and with Antibiofilm Activity. Viruses 2022, 14, 1340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Glonti, T.; Pirnay, J.-P. In Vitro Techniques and Measurements of Phage Characteristics That Are Important for Phage Therapy Success. Viruses 2022, 14, 1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaźmierczak, N.; Grygorcewicz, B.; Roszak, M.; Bochentyn, B.; Piechowicz, L. Comparative Assessment of Bacteriophage and Antibiotic Activity against Multidrug-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus Biofilms. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 1274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Podlesek, Z.; Žgur Bertok, D. The DNA Damage Inducible SOS Response Is a Key Player in the Generation of Bacterial Persister Cells and Population Wide Tolerance. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsaadi, S.E.; Lu, H.; Zhang, M.; Dykes, G.F.; Allison, H.E.; Horsburgh, M.J. Bacteriophages from Human Skin Infecting Coagulase-Negative Staphylococcus: Diversity, Novel Species and Host Resistance 2023, 2023.11.07.565964.
- Plumet, L.; Morsli, M.; Ahmad-Mansour, N.; Clavijo-Coppens, F.; Berry, L.; Sotto, A.; Lavigne, J.-P.; Costechareyre, D.; Molle, V. Isolation and Characterization of New Bacteriophages against Staphylococcal Clinical Isolates from Diabetic Foot Ulcers. Viruses 2023, 15, 2287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plotka, M.; Kapusta, M.; Dorawa, S.; Kaczorowska, A.-K.; Kaczorowski, T. Ts2631 Endolysin from the Extremophilic Thermus Scotoductus Bacteriophage vB_Tsc2631 as an Antimicrobial Agent against Gram-Negative Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Viruses 2019, 11, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, J.; Kim, S.W.; Kim, S.G.; Kang, J.W.; Jung, W.J.; Lee, S.B.; Lee, Y.M.; Giri, S.S.; Chi, C.; Park, S.C. The Characterization of a Novel Phage, pPa_SNUABM_DT01, Infecting Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. Microorganisms 2021, 9, 2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rice, C. Novel Bacteriophages and Their Derived Proteins for the Biocontrol of Proteus and Pseudomonas Biofilms. Doctoral Thesis, Queen’s University Belfast, Belfast, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Hylling, O.; Carstens, A.B.; Kot, W.; Hansen, M.; Neve, H.; Franz, C.M.A.P.; Johansen, A.; Ellegaard-Jensen, L.; Hansen, L.H. Two Novel Bacteriophage Genera from a Groundwater Reservoir Highlight Subsurface Environments as Underexplored Biotopes in Bacteriophage Ecology. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 11879. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sattar, S.; Bailie, M.; Yaqoob, A.; Khanum, S.; Fatima, K.; Altaf, A.U.R.B.; Ahmed, I.; Shah, S.T.A.; Munawar, J.; Zehra, Q.A.; et al. Characterization of Two Novel Lytic Bacteriophages Having Lysis Potential against MDR Avian Pathogenic Escherichia Coli Strains of Zoonotic Potential. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 10043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolas, M.; Trotereau, A.; Culot, A.; Moodley, A.; Atterbury, R.; Wagemans, J.; Lavigne, R.; Velge, P.; Schouler, C. Isolation and Characterization of a Novel Phage Collection against Avian-Pathogenic Escherichia Coli. Microbiology Spectrum 2023, 11, e04296-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nale, J.Y.; Chan, B.; Nnadi, N.E.; Cheng, J.K.J.; Matts, S.; Nezam-Abadi, N.; Turkington, C.J.R.; Charreton, L.M.; Bola, H.; Nazir, R.; et al. Novel Escherichia Coli-Infecting Bacteriophages Isolated from Uganda That Target Human Clinical Isolates. PHAGE 2023, 4, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parra, B.; Cockx, B.; Lutz, V.T.; Brøndsted, L.; Smets, B.F.; Dechesne, A. Isolation and Characterization of Novel Plasmid-Dependent Phages Infecting Bacteria Carrying Diverse Conjugative Plasmids. Microbiology Spectrum 2023, 12, e02537-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhandare, S.; Lawal, O.U.; Colavecchio, A.; Cadieux, B.; Zahirovich-Jovich, Y.; Zhong, Z.; Tompkins, E.; Amitrano, M.; Kukavica-Ibrulj, I.; Boyle, B.; et al. Genomic and Phenotypic Analysis of Salmonella Enterica Bacteriophages Identifies Two Novel Phage Species. Microorganisms 2024, 12, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakonieczna, A.; Rutyna, P.; Fedorowicz, M.; Kwiatek, M.; Mizak, L.; Łobocka, M. Three Novel Bacteriophages, J5a, F16Ba, and Z1a, Specific for Bacillus Anthracis, Define a New Clade of Historical Wbeta Phage Relatives. Viruses 2022, 14, 213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kabwe, M.; Brown, T.; Speirs, L.; Ku, H.; Leach, M.; Chan, H.T.; Petrovski, S.; Lock, P.; Tucci, J. Novel Bacteriophages Capable of Disrupting Biofilms From Clinical Strains of Aeromonas Hydrophila. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kallies, R.; Hu, D.; Abdulkadir, N.; Schloter, M.; Rocha, U. Identification of Huge Phages from Wastewater Metagenomes. Viruses 2023, 15, 2330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumariya, R.; Garsa, A.K.; Rajput, Y.S.; Sood, S.K.; Akhtar, N.; Patel, S. Bacteriocins: Classification, Synthesis, Mechanism of Action and Resistance Development in Food Spoilage Causing Bacteria. Microbial Pathogenesis 2019, 128, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simons, A.; Alhanout, K.; Duval, R.E. Bacteriocins, Antimicrobial Peptides from Bacterial Origin: Overview of Their Biology and Their Impact against Multidrug-Resistant Bacteria. Microorganisms 2020, 8, 639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meade, E.; Slattery, M.A.; Garvey, M. Bacteriocins, Potent Antimicrobial Peptides and the Fight against Multi Drug Resistant Species: Resistance Is Futile? Antibiotics 2020, 9, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yount, N.Y.; Weaver, D.C.; de Anda, J.; Lee, E.Y.; Lee, M.W.; Wong, G.C.L.; Yeaman, M.R. Discovery of Novel Type II Bacteriocins Using a New High-Dimensional Bioinformatic Algorithm. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljohani, A.B.; Al-Hejin, A.M.; Shori, A.B. Bacteriocins as Promising Antimicrobial Peptides, Definition, Classification, and Their Potential Applications in Cheeses. Food Sci. Technol 2023, 43, e118021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lei, S.; Zhao, R.; Sun, J.; Ran, J.; Ruan, X.; Zhu, Y. Partial Purification and Characterization of a Broad-Spectrum Bacteriocin Produced by a Lactobacillus Plantarum Zrx03 Isolated from Infant’s Feces. Food Science & Nutrition 2020, 8, 2214–2222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Golneshin, A.; Gor, M.-C.; Williamson, N.; Vezina, B.; Van, T.T.H.; May, B.K.; Smith, A.T. Discovery and Characterisation of Circular Bacteriocin Plantacyclin B21AG from Lactiplantibacillus Plantarum B21. Heliyon 2020, 6, e04715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, J.; Jin, W.; Abd El-Aty, A.M.; Baranenko, D.A.; Gou, X.; Zhang, H.; Geng, J.; Jiang, L.; Chen, D.; Yue, T. Isolation, Purification, and Structural Identification of a New Bacteriocin Made by Lactobacillus Plantarum Found in Conventional Kombucha. Food Control 2020, 110, 106923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.-H.; Xin, W.-G.; Yang, L.-Y.; Ying, J.-P.; Zhao, Z.-S.; Lin, L.-B.; Li, X.-Z.; Zhang, Q.-L. A Novel Bacteriocin against Staphylococcus Aureus from Lactobacillus Paracasei Isolated from Yunnan Traditional Fermented Yogurt: Purification, Antibacterial Characterization, and Antibiofilm Activity. Journal of Dairy Science 2022, 105, 2094–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thuy, T.T.D.; Lu, H.-F.; Bregente, C.J.B.; Huang, F.-C.A.; Tu, P.-C.; Kao, C.-Y. Characterization of the Broad-Spectrum Antibacterial Activity of Bacteriocin-like Inhibitory Substance-Producing Probiotics Isolated from Fermented Foods. BMC Microbiology 2024, 24, 85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Y.; Li, W.; Aweya, J.J.; Jin, R.; Lin, R.; Liang, D.; Weng, W.; Yang, S. Lacticaseibacillus Paracasei-Derived Antibacterial Peptide NGJ1D and Its Mechanism of Action Against Staphylococcus Aureus. Food Bioprocess Technol 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elnar, A.G.; Kim, G.-B. In Vitro and In Silico Characterization of N-Formylated Two-Peptide Bacteriocin from Enterococcus Faecalis CAUM157 with Anti-Listeria Activity. Probiotics & Antimicro. Prot. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, G.; Pan, C.; Xu, P.; Li, Y.; Wang, L.; Gong, B.; Li, X.; Huang, S. Purification and Characterization of a Novel Bacteriocin Produced by Enterococcus Faecalis CG-9 from Human Saliva. Biotechnology & Biotechnological Equipment 2020, 34, 1224–1233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, P.; Kaur, S.; Chadha, B.S.; Kaur, R.; Kaur, M.; Kaur, S. Anticancer and Antimicrobial Potential of Enterocin 12a from Enterococcus Faecium. BMC Microbiology 2021, 21, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newstead, L.L.; Varjonen, K.; Nuttall, T.; Paterson, G.K. Staphylococcal-Produced Bacteriocins and Antimicrobial Peptides: Their Potential as Alternative Treatments for Staphylococcus Aureus Infections. Antibiotics 2020, 9, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ovchinnikov, K.V.; Kranjec, C.; Thorstensen, T.; Carlsen, H.; Diep, D.B. Successful Development of Bacteriocins into Therapeutic Formulation for Treatment of MRSA Skin Infection in a Murine Model. Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 2020, 64, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sriragavi, G.; Sangeetha, M.; Santhakumar, M.; Lokesh, E.; Nithyalakshmi, M.; Saleel, C.A.; Balagurunathan, R. Exploring Antibacterial Properties of Bioactive Compounds Isolated from Streptomyces Sp. in Bamboo Rhizosphere Soil. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 36333–36343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mwangi, J.; Kamau, P.M.; Thuku, R.C.; Lai, R. Design Methods for Antimicrobial Peptides with Improved Performance. zr 2023, 44, 1095–1114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verma, S.; Pathak, R.K. Chapter 16 - Discovery and Optimization of Lead Molecules in Drug Designing. In Bioinformatics; Singh, D.B., Pathak, R.K., Eds.; Academic Press: location, 2022; ISBN 978-0-323-89775-4. [Google Scholar]
- Luong, H.X.; Thanh, T.T.; Tran, T.H. Antimicrobial Peptides – Advances in Development of Therapeutic Applications. Life Sciences 2020, 260, 118407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teixeira, M.C.; Carbone, C.; Sousa, M.C.; Espina, M.; Garcia, M.L.; Sanchez-Lopez, E.; Souto, E.B. Nanomedicines for the Delivery of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs). Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowers, A.; Wang, G.; Xing, M.; Li, B. Advances in Antimicrobial Peptide Discovery via Machine Learning and Delivery via Nanotechnology. Microorganisms 2023, 11, 1129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chauhan, M.K.; Bhatt, N. Bioavailability Enhancement of Polymyxin B With Novel Drug Delivery: Development and Optimization Using Quality-by-Design Approach. JPharmSci 2019, 108, 1521–1528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, B.H.; Gaynord, J.; Rowe, S.M.; Deingruber, T.; Spring, D.R. The Multifaceted Nature of Antimicrobial Peptides: Current Synthetic Chemistry Approaches and Future Directions. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2021, 50, 7820–7880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, M.; Qian, Y.; Xie, J.; Zhang, W.; Jiang, W.; Xiao, X.; Chen, S.; Dai, C.; Cong, Z.; Ji, Z.; et al. Poly(2-Oxazoline)-Based Functional Peptide Mimics: Eradicating MRSA Infections and Persisters While Alleviating Antimicrobial Resistance. Angewandte Chemie International Edition 2020, 59, 6412–6419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ouertani, A.; Mosbah, A.; Cherif, A.; Ouertani, A.; Mosbah, A.; Cherif, A. Anti-Microbial Peptides: The Importance of Structure-Function Analysis in the Design of New AMPs. In Insights on Antimicrobial Peptides; IntechOpen: location, 2022; ISBN 978-1-83969-714-2. [Google Scholar]
- Ajish, C.; Kumar, S.D.; Kim, E.Y.; Yang, S.; Shin, S.Y. A Short Novel Antimicrobial Peptide BP100-W with Antimicrobial, Antibiofilm and Anti-Inflammatory Activities Designed by Replacement with Tryptophan. Journal of Analytical Science and Technology 2022, 13, 46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiman, E.; Zattarin, E.; Aili, D.; Bengtsson, T.; Selegård, R.; Khalaf, H. Development of Novel Broad-Spectrum Antimicrobial Lipopeptides Derived from Plantaricin NC8 β. Sci Rep 2023, 13, 4104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaudhary, S.; Ali, Z.; Tehseen, M.; Haney, E.F.; Pantoja-Angles, A.; Alshehri, S.; Wang, T.; Clancy, G.J.; Ayach, M.; Hauser, C.; et al. Efficient in Planta Production of Amidated Antimicrobial Peptides That Are Active against Drug-Resistant ESKAPE Pathogens. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramazi, S.; Mohammadi, N.; Allahverdi, A.; Khalili, E.; Abdolmaleki, P. A Review on Antimicrobial Peptides Databases and the Computational Tools. Database 2022, 2022, baac011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cardoso, M.H.; Orozco, R.Q.; Rezende, S.B.; Rodrigues, G.; Oshiro, K.G.N.; Cândido, E.S.; Franco, O.L. Computer-Aided Design of Antimicrobial Peptides: Are We Generating Effective Drug Candidates? Front. Microbiol. 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boone, K.; Wisdom, C.; Camarda, K.; Spencer, P.; Tamerler, C. Combining Genetic Algorithm with Machine Learning Strategies for Designing Potent Antimicrobial Peptides. BMC Bioinformatics 2021, 22, 239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumancev, C.; Rosenhahn, A.; Hilpert, K. BioSAXS–an Emerging Method to Accelerate, Enrich and de-Risk Antimicrobial Drug Development. Front. Pharmacol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianxun; Yushan, B.Y.; Yinxue; Yisuo; Boxing; Wei; Huaxi. De Novo Design and Antibacterial Activity of α-Helical Antimicrobial Peptide YHX-1. 食品科学技术学报 2022, 40, 98–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mustafa, G.; Mehmood, R.; Mahrosh, H.S.; Mehmood, K.; Ahmed, S. Investigation of Plant Antimicrobial Peptides against Selected Pathogenic Bacterial Species Using a Peptide-Protein Docking Approach. BioMed Research International 2022, 2022, 1077814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-T.; Yang, L.-Y.; Lin, C.-Y.; Wang, C.-T.; Lai, C.-W.; Ko, C.-F.; Shih, Y.-H.; Chen, S.-H. Intelligent De Novo Design of Novel Antimicrobial Peptides against Antibiotic-Resistant Bacteria Strains. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2023, 24, 6788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szymczak, P.; Możejko, M.; Grzegorzek, T.; Jurczak, R.; Bauer, M.; Neubauer, D.; Sikora, K.; Michalski, M.; Sroka, J.; Setny, P.; et al. Discovering Highly Potent Antimicrobial Peptides with Deep Generative Model HydrAMP. Nat Commun 2023, 14, 1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedyalkova, M.; Paluch, A.S.; Vecini, D.P.; Lattuada, M. Progress and Future of the Computational Design of Antimicrobial Peptides (AMPs): Bio-Inspired Functional Molecules. Digital Discovery 2024, 3, 9–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilera-Puga, M. d. C.; Cancelarich, N.L.; Marani, M.M.; de la Fuente-Nunez, C.; Plisson, F. Accelerating the Discovery and Design of Antimicrobial Peptides with Artificial Intelligence. In Computational Drug Discovery and Design; Gore, M., Jagtap, U.B., Eds.; Springer US: New York, NY, 2024; pp. 329–352. ISBN 978-1-07-163441-7. [Google Scholar]
- Ogunsona, E.O.; Muthuraj, R.; Ojogbo, E.; Valerio, O.; Mekonnen, T.H. Engineered Nanomaterials for Antimicrobial Applications: A Review. Applied Materials Today 2020, 18, 100473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díez-Pascual, A.M. Recent Progress in Antimicrobial Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 2315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alavi, M.; Rai, M. Recent Advances in Antibacterial Applications of Metal Nanoparticles (MNPs) and Metal Nanocomposites (MNCs) against Multidrug-Resistant (MDR) Bacteria. Expert Review of Anti-infective Therapy 2019, 17, 419–428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karnwal, A.; Kumar, G.; Pant, G.; Hossain, K.; Ahmad, A.; Alshammari, M.B. Perspectives on Usage of Functional Nanomaterials in Antimicrobial Therapy for Antibiotic-Resistant Bacterial Infections. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 13492–13508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, S.; Nazam, N.; Rizvi, S.M.D.; Ahmad, K.; Baig, M.H.; Lee, E.J.; Choi, I. Mechanistic Insights into the Antimicrobial Actions of Metallic Nanoparticles and Their Implications for Multidrug Resistance. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Gautam, P.K.; Verma, A.; Singh, V.; Shivapriya, P.M.; Shivalkar, S.; Sahoo, A.K.; Samanta, S.K. Green Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles as Effective Alternatives to Treat Antibiotics Resistant Bacterial Infections: A Review. Biotechnology Reports 2020, 25, e00427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Nieto, C.; Losada-Garcia, N.; Prodan, D.; Furtos, G.; Palomo, J.M. Recent Advances on the Design and Applications of Antimicrobial Nanomaterials. Nanomaterials 2023, 13, 2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaghela, H.M.; Pathan, A.; SHAH, R. Biogenic Synthesis of Au, Pd and Pt Metal: Nanoparticles Using Various Plants and Its Medicinal Applications: A Review; ISBN 978-3-330-01803-7.
- Kushwah, K.S.; Verma, D.K.; Kushwah, K.S.; Verma, D.K. Biological Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles from Different Plant Species. In 21st Century Nanostructured Materials - Physics, Chemistry, Classification, and Emerging Applications in Industry, Biomedicine, and Agriculture; IntechOpen: location, 2021; ISBN 978-1-80355-085-5. [Google Scholar]
- Rizki, I.N.; Klaypradit, W. Patmawati Utilization of Marine Organisms for the Green Synthesis of Silver and Gold Nanoparticles and Their Applications: A Review. Sustainable Chemistry and Pharmacy 2023, 31, 100888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardwaj, K.; Chopra, C.; Bhardwaj, P.; Dhanjal, D.S.; Singh, R.; Najda, A.; Cruz-Martins, N.; Singh, S.; Sharma, R.; Kuča, K.; et al. Biogenic Metallic Nanoparticles from Seed Extracts: Characteristics, Properties, and Applications. Journal of Nanomaterials 2022, 2022, 2271278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chauhan, A.; Anand, J.; Parkash, V.; Rai, N. Biogenic Synthesis: A Sustainable Approach for Nanoparticles Synthesis Mediated by Fungi. Inorganic and Nano-Metal Chemistry 2023, 53, 460–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nandhini, S.N.; Sisubalan, N.; Vijayan, A.; Karthikeyan, C.; Gnanaraj, M.; Gideon, D.A.M.; Jebastin, T.; Varaprasad, K.; Sadiku, R. Recent Advances in Green Synthesized Nanoparticles for Bactericidal and Wound Healing Applications. Heliyon 2023, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mayegowda, S.B.; Sarma, G.; Gadilingappa, M.N.; Alghamdi, S.; Aslam, A.; Refaat, B.; Almehmadi, M.; Allahyani, M.; Alsaiari, A.A.; Aljuaid, A.; et al. Green-Synthesized Nanoparticles and Their Therapeutic Applications: A Review. Green Processing and Synthesis 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhati, M. Biogenic Synthesis of Metallic Nanoparticles: Principles and Applications. Materials Today: Proceedings 2023, 81, 882–887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayasinghe, M.K.; Lee, C.Y.; Tran, T.T.T.; Tan, R.; Chew, S.M.; Yeo, B.Z.J.; Loh, W.X.; Pirisinu, M.; Le, M.T.N. The Role of in Silico Research in Developing Nanoparticle-Based Therapeutics. Front. Digit. Health 2022, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kailasa, S.K.; Park, T.-J.; Rohit, J.V.; Koduru, J.R. Chapter 14 - Antimicrobial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles. In Nanoparticles in Pharmacotherapy; Grumezescu, A.M., Ed.; William Andrew Publishing: location, 2019; ISBN 978-0-12-816504-1. [Google Scholar]
- Das, G.; Patra, J.K.; Debnath, T.; Ansari, A.; Shin, H.-S. Investigation of Antioxidant, Antibacterial, Antidiabetic, and Cytotoxicity Potential of Silver Nanoparticles Synthesized Using the Outer Peel Extract of Ananas Comosus (L.). PLOS ONE 2019, 14, e0220950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paladini, F.; Pollini, M. Antimicrobial Silver Nanoparticles for Wound Healing Application: Progress and Future Trends. Materials 2019, 12, 2540. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anees Ahmad, S.; Sachi Das, S.; Khatoon, A.; Tahir Ansari, M.; Afzal, M.; Saquib Hasnain, M.; Kumar Nayak, A. Bactericidal Activity of Silver Nanoparticles: A Mechanistic Review. Materials Science for Energy Technologies 2020, 3, 756–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamad, A.; Khashan, K.S.; Hadi, A. Silver Nanoparticles and Silver Ions as Potential Antibacterial Agents. J Inorg Organomet Polym 2020, 30, 4811–4828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruna, T.; Maldonado-Bravo, F.; Jara, P.; Caro, N. Silver Nanoparticles and Their Antibacterial Applications. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2021, 22, 7202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gupta, A.; Briffa, S.M.; Swingler, S.; Gibson, H.; Kannappan, V.; Adamus, G.; Kowalczuk, M.; Martin, C.; Radecka, I. Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Curcumin-Cyclodextrins Loaded into Bacterial Cellulose-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing Applications. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 1802–1811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, C.G.A.; Kumar, V.G.; Dhas, T.S.; Karthick, V.; Govindaraju, K.; Joselin, J.M.; Baalamurugan, J. Antibacterial Activity of Silver Nanoparticles (Biosynthesis): A Short Review on Recent Advances. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology 2020, 27, 101593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feroze, N.; Arshad, B.; Younas, M.; Afridi, M.I.; Saqib, S.; Ayaz, A. Fungal Mediated Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles and Evaluation of Antibacterial Activity. Microscopy Research and Technique 2020, 83, 72–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garibo, D.; Borbón-Nuñez, H.A.; de León, J.N.D.; García Mendoza, E.; Estrada, I.; Toledano-Magaña, Y.; Tiznado, H.; Ovalle-Marroquin, M.; Soto-Ramos, A.G.; Blanco, A.; et al. Green Synthesis of Silver Nanoparticles Using Lysiloma Acapulcensis Exhibit High-Antimicrobial Activity. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 12805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, M.; Noruzi, E.B.; Sheykhsaran, E.; Ebadi, B.; Kariminezhad, Z.; Molaparast, M.; Mehrabani, M.G.; Mehramouz, B.; Yousefi, M.; Ahmadi, R.; et al. Carbohydrate Polymer-Based Silver Nanocomposites: Recent Progress in the Antimicrobial Wound Dressings. Carbohydrate Polymers 2020, 231, 115696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barabadi, H.; Mojab, F.; Vahidi, H.; Marashi, B.; Talank, N.; Hosseini, O.; Saravanan, M. Green Synthesis, Characterization, Antibacterial and Biofilm Inhibitory Activity of Silver Nanoparticles Compared to Commercial Silver Nanoparticles. Inorganic Chemistry Communications 2021, 129, 108647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez-Rosas, S.L.; Delgado-Alvarado, E.; Sanchez-Vargas, L.O.; Herrera-May, A.L.; Peña-Juarez, M.G.; Gonzalez-Calderon, J.A. Green Route to Produce Silver Nanoparticles Using the Bioactive Flavonoid Quercetin as a Reducing Agent and Food Anti-Caking Agents as Stabilizers. Nanomaterials 2022, 12, 3545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chavan, R.R.; Bhutkar, M.A.; Bhinge, S.D. Design, Synthesis, and Optimization of Silver Nanoparticles Using an Artocarpus Heterophyllus Lam. Leaf Extract and Its Antibacterial Application. Nano Biomedicine and Engineering 2023, 15, 239–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahalingam, S.; Govindaraji, P.K.; Solomon, V.G.; Kesavan, H.; Neelan, Y.D.; Bakthavatchalam, S.; Kim, J.; Bakthavatchalam, P. Biogenic Synthesis and Characterization of Silver Nanoparticles: Evaluation of Their Larvicidal, Antibacterial, and Cytotoxic Activities. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 11923–11930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Said, A.; Abu-Elghait, M.; Atta, H.M.; Salem, S.S. Antibacterial Activity of Green Synthesized Silver Nanoparticles Using Lawsonia Inermis Against Common Pathogens from Urinary Tract Infection. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2024, 196, 85–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hani, U.; Kidwan, F.N.; Albarqi, L.A.; Al-qahtani, S.A.; AlHadi, R.M.; AlZaid, H.A.; Haider, N.; Ansari, M.A. Biogenic Silver Nanoparticle Synthesis Using Orange Peel Extract and Its Multifaceted Biomedical Application. Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 2024, 47, 1363–1375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Zahed, M.M.; Abou-Dobara, M.I.; El-Sayed, A.K.A.; Baka, Z.A.M. Ag/SiO2 Nanocomposite Mediated by Escherichia Coli D8 and Their Antimicrobial Potential. Nova Biotechnologica et Chimica 2022, 21, e1023–e1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naseer, M.; Aslam, U.; Khalid, B.; Chen, B. Green Route to Synthesize Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles Using Leaf Extracts of Cassia Fistula and Melia Azadarach and Their Antibacterial Potential. Sci Rep 2020, 10, 9055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gur, T.; Meydan, I.; Seckin, H.; Bekmezci, M.; Sen, F. Green Synthesis, Characterization and Bioactivity of Biogenic Zinc Oxide Nanoparticles. Environmental Research 2022, 204, 111897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veselova, V.O.; Plyuta, V.A.; Kostrov, A.N.; Vtyurina, D.N.; Abramov, V.O.; Abramova, A.V.; Voitov, Y.I.; Padiy, D.A.; Thu, V.T.H.; Hue, L.T.; et al. Long-Term Antimicrobial Performance of Textiles Coated with ZnO and TiO2 Nanoparticles in a Tropical Climate. Journal of Functional Biomaterials 2022, 13, 233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rasool, A.; Kiran, S.; Gulzar, T.; Abrar, S.; Ghaffar, A.; Shahid, M.; Nosheen, S.; Naz, S. Biogenic Synthesis and Characterization of ZnO Nanoparticles for Degradation of Synthetic Dyes: A Sustainable Environmental Cleaner Approach. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 398, 136616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandrasekaran, S.; Anbazhagan, V. Green Synthesis of ZnO and V-Doped ZnO Nanoparticles Using Vinca Rosea Plant Leaf for Biomedical Applications. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2024, 196, 50–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramasubbu, K.; Rajeswari, V.D. Green Synthesising ZnO Nanoparticle Using Sesbania Grandiflora and Their Evaluation of Anti-Diabetic Anti-Advanced Glycation End Products and Cytotoxic Effects. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 2024, 196, 2652–2672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajeshkumar, S.; Menon, S.; Venkat Kumar, S.; Tambuwala, M.M.; Bakshi, H.A.; Mehta, M.; Satija, S.; Gupta, G.; Chellappan, D.K.; Thangavelu, L.; et al. Antibacterial and Antioxidant Potential of Biosynthesized Copper Nanoparticles Mediated through Cissus Arnotiana Plant Extract. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 2019, 197, 111531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Losada-García, N.; Rodríguez-Otero, A.; Palomo, J.M. Tailorable Synthesis of Heterogeneous Enzyme–Copper Nanobiohybrids and Their Application in the Selective Oxidation of Benzene to Phenol. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2020, 10, 196–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naz, S.; Gul, A.; Zia, M.; Javed, R. Synthesis, Biomedical Applications, and Toxicity of CuO Nanoparticles. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2023, 107, 1039–1061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ortega-Nieto, C.; Losada-Garcia, N.; Pessela, B.C.; Domingo-Calap, P.; Palomo, J.M. Design and Synthesis of Copper Nanobiomaterials with Antimicrobial Properties. ACS Bio Med Chem Au 2023, 3, 349–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madubuonu, N.; Aisida, S.O.; Ali, A.; Ahmad, I.; Zhao, T.; Botha, S.; Maaza, M.; Ezema, F.I. Biosynthesis of Iron Oxide Nanoparticles via a Composite of Psidium Guavaja-Moringa Oleifera and Their Antibacterial and Photocatalytic Study. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology B: Biology 2019, 199, 111601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chellapa, L.R.; Shanmugam, R.; Indiran, M.A.; Samuel, S.R. Biogenic Nanoselenium Synthesis, Its Antimicrobial, Antioxidant Activity and Toxicity. Bioinspired, Biomimetic and Nanobiomaterials 2020, 9, 184–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lange, A.; Matuszewski, A.; Kutwin, M.; Ostrowska, A.; Jaworski, S. Farnesol and Selected Nanoparticles (Silver, Gold, Copper, and Zinc Oxide) as Effective Agents Against Biofilms Formed by Pathogenic Microorganisms. NSA 2024, 17, 107–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yılmaz, G.E.; Göktürk, I.; Ovezova, M.; Yılmaz, F.; Kılıç, S.; Denizli, A. Antimicrobial Nanomaterials: A Review. Hygiene 2023, 3, 269–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




