Introduction
The Bank Sector are one of the largest Economics services in Jordan, The Jordanian commercial banking sector recorded a remarkable growth in its most important financial indicators for the year 2021 The Jordanian economy witnessed a growth of 2.2% during the year 2021 compared to the year 2020. As for the inflation rate, it reached 35.1% in the year 2021, While the unemployment rate rose to 1.24%, foreign direct investment during the first three quarters of 2021 amounted to about 269 million dinars. A decrease of 5.32% compared to the same period in 2020, while workers’ remittances increased by 0.1% during 2021 compared to in 2020, it will reach approximately 412.2 billion dinars.
If we refer to the available annual reports of Central Bank of Jordan over a year (2015–2019) and examine it, we can conclude as for the Jordanian economy, it has faced many challenges and risks, the most important is the turbulent political situation in neighboring countries. Despite this, a moderate growth rate of the gross domestic product was achieved in 2016 by 2.1%, but it is less than the previously estimated rate of 3.2%, and International Monetary Fund estimates indicate an improvement in 2017 and 2018, it reached 2.3%F and 2.5%, respectively.
Also GDP grew the real total increased by 2.0% during 2019 compared to 1.9% in 2018. the overall financial position of the central government in its performance within a year, the general budget included an improvement in 2018, where the overall fiscal deficit of the general budget decreased to 727.6 million dinars (2.4% of the gross domestic product (Total), compared to a deficit of 747.9 One million dinars (2.6% of output) during 2017.
Jordan has experienced sluggish economic growth, continued fiscal deficits, and increased public debt in the last few years. Despite these challenges, Jordan is still attempting to increase economic growth through several measures. Growth and employment opportunities can be created in Jordan if Jordan focuses on promising sectors. One of the most important pillars of the Jordanian economy and state is the banking sector. Earnings are used for a variety of purposes, including contractual obligations (e.g., debt covenants), asset valuations and executive remuneration and bonus plans (e.g., equity compensation). In this way, accounting data provide relevant information and are used by a wide range of stakeholders. (vakilifard, Mortazavi 2016). Earnings management affects the quality of earnings by masking the underlying economic transactions. In the absence of effective control mechanisms, management has the opportunity to manipulate earnings with the goal of meeting certain targets (Healy and Elections, 1999).
Business strategy typology settings have never been examined in terms of EM preferences. (Martinez and Ferreira, 2019) based on Brazilian companies suggest “findings in the USA may not be generalizable to Brazil, Russia, India, or China (i.e., the BRICs).” We examine whether business strategies with prospector (defender) typologies have lower (higher) EM preferences.
Earnings measurement refers to the process of quantifying the financial performance of a business entity over a specific period. It involves determining the net income or profit earned by the entity during that period. Earnings measurement is a fundamental aspect of financial reporting and is essential for various stakeholders, including investors, creditors, and regulators, to assess the entity’s financial health and performance.
Similarly, earning management arises from agency problems. Among the literature on earnings management, agency theory is often cited as a prominent explanation. As Jensen and Mackling (1976) point out, there is a conflict of interest between managers and shareholders when management seeks to maximize its own utility over that of shareholders. As a result of this conflict, agency costs are incurred. (Elkalla, 2017)
Bhandia (2012) explains that in order to maximize their interests or maintain their position, they must Agents are willing to present shareholders with a good picture of the firm’s financial position (Elkalla, 2017).
“Earnings management occurs when managers use judgment in financial reporting and in structuring transactions to alter financial reports either to mislead some stakeholders about the underlying economic performance of the company or to influence contractual outcomes that depend on reported accounting numbers.” (Healy and Wahlen, 1999)
Earnings Management Techniques (Elkalla, 2017)
Management of Earnings Can Be Divided into Three Broad Categories
- -
Management of earnings based on accruals by changing estimates and accounting methods
- -
A policy is Managing cash flow directly through real activities-based earnings management
- -
Incidences Management of earnings based on classification shifting, such as shifting
Components of Earning Managements
The components of earnings measurement encompass various elements that collectively determine the financial performance and profitability of a business entity. These components include:
Revenue Recognition, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), Gross Profit, Operating Expenses, Operating Profit (or Loss), Other Income and Expenses, Earnings Before Interest and Taxes (EBIT), Interest Expenses, Earnings Before Tax (EBT), Income Tax Expense, Net Income, Earnings Per Share (EPS).
Contributions
The several contributions to the existing body of knowledge when it examines the impact of earnings management practices on the performance of the banking commercial sector in Jordan.
Conceptual Contributions
Advancing Agency Theory: The research examines how earnings management practices in the banking commercial sector align with or misalign with the interests of shareholders and managers. The study sheds light on bank performance’s impact on earnings manipulation. Study contributes to stakeholder theory by exploring how earnings management practices affect various stakeholders in the commercial banking sector. It can inform employees, customers, regulators, and society at large about earnings manipulation. Enhancing Institutional Theory: This research contributes to institutional theory by providing insights into how the regulatory environment and institutional factors influence earnings management practices in the commercial banking sector. Insights into institutional context and earnings management practices can be gained.
Empirical Contributions
In Jordan, the research can provide empirical evidence on earnings management practices in the commercial banking sector. This can help quantify the impact of bank strategies and techniques on financial performance. By examining the relationship between earnings management practices and bank performance, the study can contribute to understanding the factors that influence financial stability, profitability, and risk management.
To use the research to provide practical recommendations for reducing earnings management practices in the commercial banking sector by strengthening regulatory frameworks and corporate governance mechanisms. Reporting practices can be improved by providing insight into potential earnings management risks. The results of this study may help investors understand how earnings management practices affect commercial bank performance. This includes the associated risks as well.
Objective of Study
- -
Assessment of Earnings Management Practices
- -
Performance Metrics Analysis:
- -
Evaluate key performance indicators within the banking sector, including return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), and net interest margin (NIM), in light of earnings management practices.
Literature Review
A comprehensive review of existing literature will provide the theoretical foundations for this study. This section will explore global perspectives on earnings management within the commercial banking sector, with a specific focus on studies relevant to the Jordanian financial context. Theoretical frameworks, empirical findings, and regulatory considerations will be synthesized to guide the empirical analysis.
An interesting topic in financial research is an impact of earnings management practices on performing the Jordanian banking sector (Mersin, & Ben Othman, 2016). A firm’s earnings management involves manipulating financial statements to portray a certain level of performance or financial position in order to meet analysts’ expectations, influence stock prices, or receive regulatory benefits (Menisci, & Menicucci, 2020). Investors, regulators, and policymakers must understand how earnings management practices affect the banking sector.
Earnings management practices in banks may be motivated by specific factors. Among these motivations are meeting capital adequacy requirements, signaling financial stability to stakeholders, avoiding regulatory scrutiny (Kanagaretnam, & Wang, 2015) managing market expectations, and maintaining access to funding. Regulations governing banks, market rivalry, and the political and economic climate can all have an impact on earnings management techniques in the banking industry (Alghamdi & Ali, 2012).
Regarding the effect of profits management techniques on Jordanian bank performance, the literature offers conflicting findings (Al-Haddad, & Whittington, 2019). Research indicates a favorable association between bank performance and earnings management, implying that banks might deliberately manipulate earnings to strengthen their financial standing and draw in investors. However, research indicates that over-managing earnings might distort financial statements and impair long-term success (Jian, 2003).
Corporate governance systems have the potential to impact earnings management practices in banks, alongside board independence, audit quality, and ownership structure (Flayyih & Mohammed, 2018). Effective corporate governance can discourage profits management and encourage accountability and transparency. Examining the connection between company governance and earnings management can provide light on how well governance structures mitigate earnings management strategies (El Diri, & Alhadab, 2020).
A range of empirical approaches are employed in the literature to investigate the effects of earnings management practices on bank performance in Jordan (Alhadab & Al-Own, 2017). Among these approaches are panel data analysis, case studies, regression analysis, and event studies. The individual research topic, data accessibility, and study objectives all have a role in selecting the best research method (Denscombe, 2017).
The article discusses the various earnings management practices employed by banks, the motivations behind them, and their implications for bank performance (Barghathi, 2017). Furthermore, the review discusses how the regulatory environment and corporate governance mechanisms influence earnings management behavior. This review provides a foundation for further research by synthesizing the existing literature and contributes to the understanding of earnings management and bank performance in Jordan (Almarayeh, & Aibar-Guzmán, 2022).
The study of ElHawary, E. Hassouna, D., (2022) suggest that earnings management strategies can negatively impact financial reporting quality and dependability (Alzoubi, 2018), particularly in developing nations. As a result of the study’s findings, business managers could be prevented from using earnings management strategies by reducing the company’s financial leverage (Iatridis, & Kadorinis, 2009). Consequently, investors will feel more confident, and profits and share value of the company will increase. In addition to firm size, age, financial leverage, and survival, stakeholders should also take these factors into account. The COVID-19 pandemic issue is especially relevant now, since it may increase the firm’s financial leverage and result in earning management tactics that enhance the company’s reputation and public image (Khanchel, & Lassoued, 2022). These consequences are not yet evident in the 2019 financial statements. In the financial reports for 2020, a pandemic outbreak of this magnitude is shown to have a significant financial impact. Businesses are expected to be directed toward voluntary disclosure procedures by Egyptian regulatory bodies. Information availability has created a new era of motivation, and they play a crucial role (Elfeky,2017). Therefore, instead of using the audit quality variable used in this study, it can be suggested that future research look at other countries and take into account other firm characteristics or attributes and other corporate governance variables, such as cultural dimensions, which may have a greater impact on earnings management. It may be possible to uncover additional variables influencing earnings management tactics by analyzing Egypt’s banking and financial sectors (Bassiouny, 2016). With the COVID-19 pandemic a major issue for Egypt in the wake of the 2011 revolution, it is important to examine how it has affected earnings management and the quality of financial reporting. Financial reporting could be adversely affected by these two crises and managerial manipulation could increase (Habib, & Islam, 2013).
Also Boachie, C., et al., (2022) investigate the relationship between earnings management and financial performance of firms in Anglophone sub-Saharan African Countries in a dynamic framework. The study shows how this relationship is moderated by aggregate disclosure and best-practice corporate governance quality metrics. The findings indicate that earnings management’s performance effects persist even after controlling for dynamic endogeneity, simultaneity, and unobserved time-invariant heterogeneity inherent in the earnings management and performance relationship. Again, the results support the prediction of agency theory regarding the efficient monitoring effect of adherence to best-practice internal governance systems in constraining firms’ earnings management practices and subsequently enhancing firms’ performance. Moreover, the study’s findings regarding the positive effect of earnings management on performance, which suggests efficiency motives behind earnings management practices in Africa, demonstrate that the African context is uniquely different from other emerging markets that report opportunistic motives. Concerning the moderating role, our study reveals that the positive effect of earnings management on the financial performance of firms tends to be stronger in the presence of corporate governance quality.
According to Al-Shahadah, A., et al., (2022) analyze the relationship between profitability measures and earnings management in Jordanian commercial banks. In his study The Earnings Management in Jordanian Banks: Do Profitability Measures Matter? The quantitative methodology was used to collect the research data from the financial statements of (35) Jordanian commercial banks from (2013 to 2019). The results of the study reveal that there is a negative and significant relationship between Return on Equity (ROE) and earnings management, and a positive and not significant relationship between Return on Deposits (ROD) and earnings management. It’s also documented that there is a positive and significant association between each Return on Investment (ROI), Earnings Per Share (EPS), and earnings management.
Alrjoub, A., (2021), in his study examines the impact of financial performance on earnings management practice behavior at the Jordanian public shareholding financial companies listed in the Amman stock exchange. The research findings proved the practice of earnings management behavior by several sectors at a different level. They found a statistically significant correlation between the financial performance variables and the response of earnings management practice at the public shareholding financial companies. The study also confirmed that Jordanian public shareholding financial companies had practiced earnings management during the study period, with a percentage of companies that practice earnings management is less than the rate of not practicing it.
According to Donald (2002), management practices affect earnings management methods at Kuwaiti public shareholding companies, and management practices affect earnings management methods (acquisitions, the misuse of relative importance, accounting estimates, and revenue recognition). The study also sought to identify differences between the covered categories’ views of the companies’ earnings management practices. Companies’ management practices earnings management methods, and earnings management practices have a statistically significant effect on earnings, as well as differences between views about earnings management practices. By examining the nature of earnings management processes, their indicators, methods used to practice them, and their implications, Shaheen (2011) examined the extent of earnings management practice and the resulting risks in the Palestinian banking environment. According to this study, bank management practices earnings management practices significantly and unevenly between banks during the study period (2005-2009), and management is unaware of the risks associated with these practices.
Theoretical Background
The impact of earnings management practices on the performance of the Jordanian commercial banking sector can be analyzed from a variety of theoretical perspectives: In organizations, conflicts of interest can arise between shareholders (principals) and managers (agents) (Young, & Jiang, 2008). The banking industry uses earnings management practices to align managers’ interests with shareholders’ in order to manipulate reported earnings. A bank’s long-term performance and stability may be adversely affected by excessive earnings management practices (Achleitner, & Siciliano, 2014), which may diverge from economic performance reported.
The concept of information asymmetry refers to the situation where one party has more or better information than the other party. Earnings management practices may be used by banks to present a more favorable financial performance (Hoang, & Phung, 2019), potentially misleading stakeholders, including investors and regulators. Creating information asymmetry can impact the assessment of a bank’s financial health and performance (Limpaphayom, & Polwitoon, 2004).
A stakeholder theory emphasizes the need to consider the interests of various stakeholders, such as shareholders (Tullberg,2013). employees, customers, and society at large. It is possible for earnings management practices to affect different stakeholders in different ways. A distorted financial report may cause long-term stakeholders, such as customers and regulators (Armstrong, & Weber, 2010)., to suffer due to the potential risks associated with short-term earnings manipulation.
Financial stability and effective risk management are closely related to the performance of the banking sector. In addition to distorting risk indicators and misrepresenting banks’ true financial position (Jones, & Aresu, 2020), earnings management practices can also influence risk management. Ultimately, this can increase the risk of financial crises or systemic risks in the banking sector.
Organizations are influenced by the norms, rules, and practices prevalent in their institutional environment, according to institutional theory (Gupta, & Gupta, N2021). Jordan’s regulatory framework, accounting standards, and corporate governance practices can influence the prevalence and effectiveness of earnings management practices in the banking sector. An institution’s institutional context should be considered when evaluating the impact of earnings management practices on bank performance (Lassoued, & Sassi, 2018).
These theoretical perspectives provide a foundation for understanding the relationship between earnings management practices and bank performance. However, empirical research is necessary to test and validate these theories in the specific context of Jordan’s banking sector (Alnsour, & Alshboul, 2023). In light of Jordan’s unique characteristics and its regulatory environment, empirical studies can provide a more concrete picture of the impact of earnings management practices on bank performance (Shen, & Chih, 2007).
The study of Salima, I., (2010) shows how entrenched leaders can hinder internal control mechanisms. These mechanisms include the board of directors and incentive compensation linked to stock market performance. By managing results, managers can maximize their wealth by intervening in the process of setting their remuneration.
According to the empirical analysis, the structure of the CEO remuneration contract affected discretionary accruals divided by total assets. The correlation between earnings management techniques and incentive ratios and stock option programs is strong and positive. This correlation disappears if we limit the analysis to observations made after the SOX Act (Sarbanes-Oxley) was passed. The SOX Act and the requirement for more thorough financial reporting have reduced the opportunistic acts of directors during the financial bubble (before the SOX law).
Research Method
Research conducted on the impact of earnings management practices on the performance of Jordan’s commercial banking sector typically employs quantitative methods. The researchers collect relevant financial data from the Jordanian commercial banking sector, including financial statements, annual reports, and other publicly available financial information. By using these data, bank financial performance can be analyzed and earnings management practices detected.
The descriptive analysis of financial data involves examining the characteristics and trends. A number of financial ratios can be calculated by researchers, including return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), net interest margin (NIM), non-performing loans (NPLs), and capital adequacy ratios. This report provides an overview of the banking sector’s performance as well as the ability to identify potential areas of concern.
Regression analysis is a crucial tool for analyzing the connection between bank performance and earnings management strategies. After adjusting for other pertinent variables, statistical methods can be used to calculate the effect of earnings management strategies on different financial performance metrics. The current study focus on five commercial banks in Jordan over the period (2015–2021): Jordan Ahli Bank, Cairo Amman Bank, Bank of Jordan, Housing Bank, Bank al-Eltihad, these banks are considered the largest five operating commercial bank in Jordan.
Hypotheses
From the results of previous related studies mentioned; the current study seeks to achieve the following hypothesis:
H1. There is is a significant relationship between Earning Management Practices and Performance in Jordanian Commercial Banks.
H2.
There is a significant relationship between Earning Management practices and debt ratios on assets (ROA) in Jordanian Commercial banks’ performance.
H3.
There is a significant relationship between Earning Management practices and Return on Investment (ROI) in Jordanian Commercial banks.
H4.
There is a significant correlation between Earning Management practice and Return on equity (ROE) in Jordanian Commercial Banks.
H5.
There is a significant relationship between Earning Management practices and Earnings per Share (EPS) in Jordanian Commercial Banks.
H6. There is significant relationship between Earning Management practice and Equity Ratio (ER) and and in Jordanian Commercial Banks
Conceptual Framework and Methodology
* Since the data is sourced from publicly available platforms and is already published, no additional permission is required to use it for research purposes”.
Practices used by companies to intentionally alter their reported earnings in order to meet specific financial targets are referred to as earnings management practices. Many accounting strategies, including accrual management, expense capitalization, timing revenue recognition, and reserve manipulation, are employed to either inflate or deflate reported results.
Financial Performance: Metrics used to evaluate a bank’s financial performance include return on assets (ROA), return on equity (ROE), net interest margin (NIM), nonperforming loans (NPLs), capital adequacy ratios, and further indicators of profitability, liquidity, and solvency. The market’s reaction to earnings management is measured using market performance measurements such as stock prices, market valuations, and market returns. However, Jordan is still striving to get over these challenges by putting in place a variety of measures designed to encourage economic growth. To promote growth, Jordan should focus on industries that create jobs and are growth-oriented.
One of the main pillars supporting Jordan’s economy and granting the government authority is the banking sector. The Jordanian Bank’s core economic policies state that it must maintain Jordan’s monetary stability, ensure the Jordanian dinar’s convertibility, achieve banking and financial stability, and foster steady economic growth.
In order to achieve these goals, the Central Bank of Jordan works on a number of projects, such as maintaining and managing Jordan’s foreign exchange and gold reserves, selecting the appropriate exchange rate strategy for the nation’s economy, and developing and implementing monetary policy using an integrated system of tools. The Jordanian Central Bank regulates credit in the nation’s economy in addition to issuing coins and banknotes in order to support financial stability, monetary stability, and general economic growth.
Because it oversees and monitors banks, the Central Bank protects the accuracy of bank financial statements and upholds the interests of shareholders and depositors in compliance with corporate governance laws and regulations. In accordance with relevant rules and regulations, financial institutions must also be closely monitored and subject to supervision in order to preserve the integrity of their financial position. The Central Bank also manages and expands the nation’s payment infrastructure to ensure safe and efficient clearing, settlement, and payment systems.
Earnings management strategies can have a negative impact on the reliability and caliber of financial reporting. It has to use the earning management approach that Jordanian listed firms that aren’t financial have used in the past. The empirical analysis showed that the form of CEO compensation contracts affects discretionary accruals split by total assets, a measure of the intensity of earnings management.For this review, we utilize the four evidences that Healy and Wahl [1999] suggest. Standard setters are interested in information that could help them choose how much leeway to grant management when it comes to financial reporting, according to the literature on earnings management.
Discussions
This study evaluates all regression assumptions prior to performing the regression analysis to ensure there will be no significant errors. In order to determine whether outliers have a significant influence on the study model Cook’s Distance values were calculated for all cases with more than one area, according to Tabachnick and Fidel (2007).
According to this inquiry, the highest Cook’s Distance value is 0.111. As this study contains no outliers, the statistical analysis validates the outlier assumption.
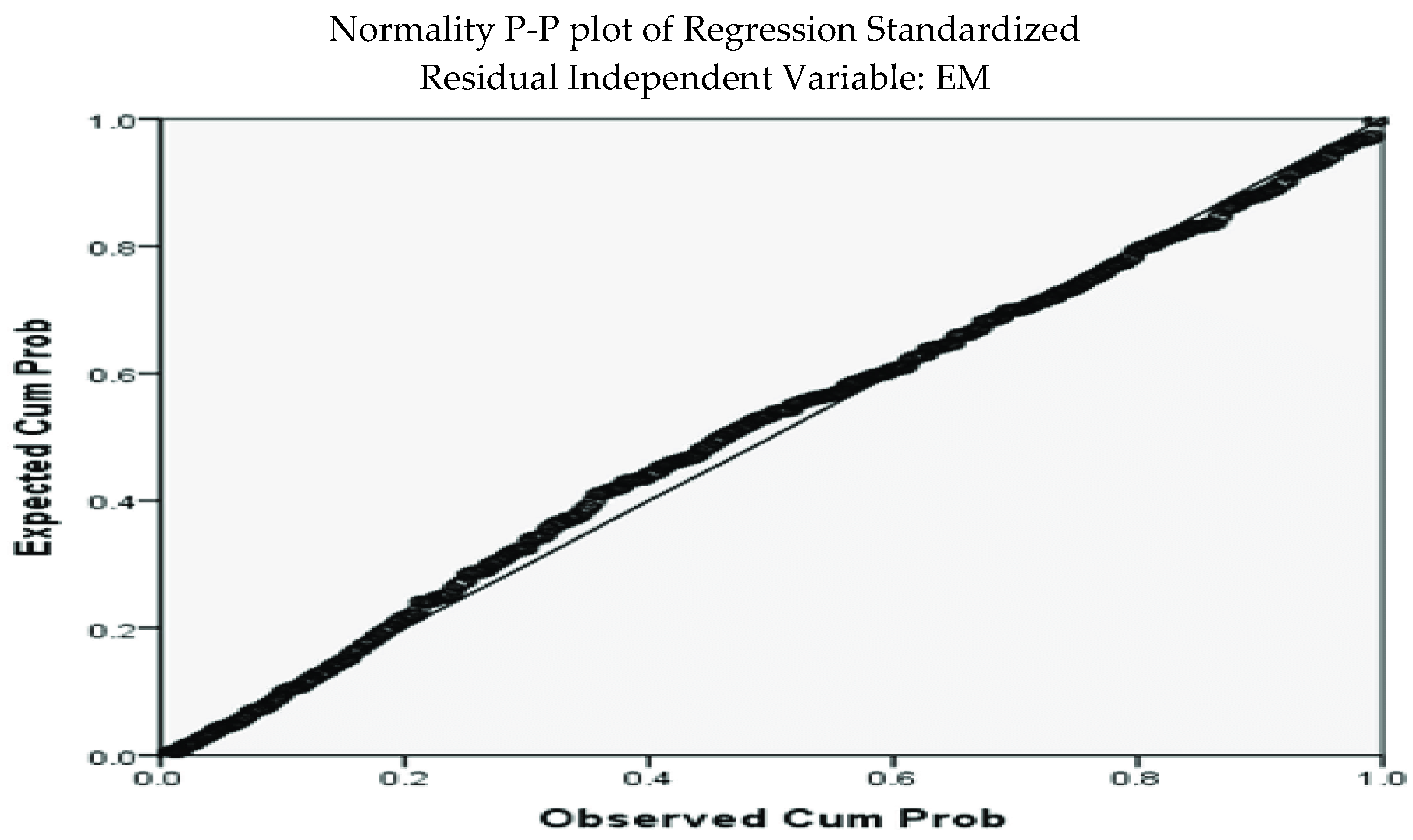
The next step is to examine normalcy. The normally distributed residual, as described by Anderson, and Latham (2010), is used in our investigation to assess the validity of hypotheses. Based on the test results, we could determine the skewness and kurtosis ratios. Kurtosis and skewness should be less than 10 and 3, respectively, according to (Kline, 1998). Based on the data shown in
Table 1, it is believed that they are reasonably normal. There is no value outside the allowable range for skewness kurtosis. The assumption of normalcy is thus maintained.
The main aim of examining linearity assumption is to check the linear relationship between independent and dependent variables in the research model, the independent and dependent variables in the study model must be linearly related. In addition, since regression analysis relies on linear associations, correlation is a strict problem (Hair et al., 2010). suggest comparing the standard deviations of the dependent variable with the residuals (
Figure 1) to assess the linearity assumption is not clear, which means no vio-lation of the linearity assumption.
A Pearson correlation in
Table 2 show that the highest level of correlation was 0.878 between return on equity and return on investment and return and between earnings per share and return on investment at 0.762. According to Tabachnick and Fidel (2010), multicollinearity occurs when independent variables are correlated by more than 0.7. In this study, the multicollinearity of the model is not problematic. Also, a multicollinearity probleme will happened if the correlation coeffeients exceed 0.9 which is not exist in this research.
Descriptive Statistics
Table 3 below shows a descriptive analysis of 24 observations of operating commercial banks in Jordan. There is an average value of 70% for the EM. That pertains to the impact of earnings management practices on Jordanian Commercial banks’ performance. According to
Table 3 below, which clarifies the dispersion of the study sample (24 banks), this research relies on descriptive statistics to interpret data.
Hypothesis and Model Testing
As shown in
Table 4 below, the research model is statistically significant based on the value of (F=11.623; Sig.000). The updated R2 of the research model was 0.585, which indicates that 58.5% of the benefits provided by Jordanian Commercial banks’ management strategies can be explained by the model. Accordingly, the study’s model’s variables have the best compensation, which explains some of the differences in profit management techniques. In order to accomplish the objectives of this investigation, research hypotheses were developed and made available in advance Also At 5%, return on assets (ROA) is positive as expected, but not statistically significant. The P value is 0.437 (t = 0.455, p = 0.437). Evidence suggests that ROA contributes positively to earnings management practices. Results are approved by earnings management, which does not directly relate to assets, This result has been supported by Tarawneh (2006) who document that the higher total deposits do not always mean that has better profitability performance.
According to a regression analysis as shown in
Table 5, ROI and earnings management are positively correlated (t = 1.921, P = 0.008). The results confirm the hypothesis that returns on investment (ROI) encourage business managers to employ earnings management strategies.
According to the third research hypothesis, earnings management techniques are positively and significantly impacted by return on equity (ROE). According to regression analysis (t = -5.724, P =.000), there is a statistically significant negative correlation. These findings contradict our assumptions, there is a positive relationship between earnings per share and profits per share (t = 3.461, P = .000).
Conclusion
The study’s particular objectives are to measure the impact of earning management on Jordanian banks’ debt to equity ratios and to review the literature that is currently available regarding the significance of return on assets (ROA), return on investment (ROI), and earnings per share (EPS). Quantitative methods were used to collect the study’s data. The result drawn from the examination of the hypotheses and the data extraction that followed showed a positive and statistically significant association between equity per share (EPS) and return on investment (ROI) with earnings management practices. This relationship is crucial since it gives stakeholders insight to take care about the bank’s actual performance level. Also the study show that there is a, weak correlation, between ROA and earnings management strategies.
Sample study consist of 24 active Jordanian banks for this investigation over (2015-2021) Larger domains, including businesses, can make use of and use this knowledge.
Author Contributions
Dr. Alhawtmeh has taken the overall responsibilities of the manuscript and he gave the idea of the issue to be investigated and therefore he has drafted the introduction part of manuscript and contributed methodology part and also run the statistical analysis, and the results Dr. Alleimoun edited the language of the overall manuscript and also contributed in qualitative data collection. Mr. Obeidat worked on literature Review section of the manuscript and took the responsibility of it.
Funding
No funding was received
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Conflicts of Interest
No potential conflict of interest was reported by the author(s).
References
- Achleitner, A. K. , Günther, N., Kaserer, C., & Siciliano, G. (2014). Real earnings management and accrual-based earnings management in family firms. European Accounting Review, 23(3), 431-461.
- Alhadab, M. M. , & Al-Own, B. (2017). Earnings management and banks performance: Evidence from Europe. International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Sciences, 7(4), 134-145.
- Al-Haddad, L. , & Whittington, M. (2019). The impact of corporate governance mechanisms on real and accrual earnings management practices: evidence from Jordan. Corporate Governance: The International Journal of Business in Society, 19(6), 1167-1186.
- Alghamdi, S. , & Ali, L. (2012). Investigation into earnings management practices and the role of corporate governance and external audit in emerging markets: Empirical evidence from Saudi Listed Companies, Doctoral Dissertation). Durham University.
- Almarayeh, T. , Abdullatif, M., & Aibar-Guzmán, B. (2022). The role of audit committees in mitigating earnings management: evidence from Jordan. Journal of Accounting in Emerging Economies, 12(5), 882-907.
- Alnsour, I. , Alghadi, M., Ahmad, A., Alibraheem, M., Altahat, S., Al-Smadi, R., & Alshboul, K. (2023). Islamic financial technology acceptance: An empirical study in Jordan. International Journal of Data and Network Science, 7(4), 1659-1668.
- Alrjoub, A. , Almomani, S., Al- Hosban, A., & Allahham, M., (2021), The Impact Of Financial Performance On Earnings Management Practice Behavior (An Empirical Study On Financial Companies In Jordan), Academy of Strategic Management Journal Volume 20, Special Issue 2.
- Al-shahadeh, A. , AlSarahen, D., & khudari, M., (2022), The Earnings Management in Jordanian Banks: Do Profitability Measures Matter? International Conference on Business and Technology, (487),. [CrossRef]
- Alzoubi, E. S. S. (2018). Audit quality, debt financing, and earnings management: Evidence from Jordan. Journal of International Accounting, Auditing and Taxation, 30, 69-84Choi, T.,H., (2006), Timeliness of Asset Write-offs, KDI School of Public Policy and Management, 6 (3), p.69.
- Armstrong, C. S. , Guay, W. R., & Weber, J. P. (2010). The role of information and financial reporting in corporate governance and debt contracting. Journal of accounting and economics, 50(2-3), 179-234.
- Boachie, C., & Mensah, E., (2022), The effect of earnings management on firm performance: The moderating role of corporate governance quality, International Review of Financial Analysis,V. 83, October 2022, 102270.
- Barghathi, Y. (2017). Stakeholders’ perceptions on earnings management motivations and techniques in Libyan commercial banks. Journal of Accounting and Management Information Systems, 16(3), 344-368.
- Bassiouny, S. W. (2016). The impact of firm characteristics on earnings management: an empirical study on the listed firms in Egypt. Journal of Business and Retail Management Research, 10(3).
- Denscombe, M. (2017). EBOOK: The good research guide: For small-scale social research projects. McGraw-Hill Education (UK).
- El Diri, M. , Lambrinoudakis, C., & Alhadab, M. (2020). Corporate governance and earnings management in concentrated markets. Journal of Business Research. 108, 291-306.
- Elfeky, M. I. (2017). The extent of voluntary disclosure and its determinants in emerging markets: Evidence from Egypt. The Journal of Finance and Data Science, 3(1-4), 45-59.
- ElHawary, E. , & Hassouna, D., (2022),” Earnings Management Determinants: A Study of Egyptian Listed Firm Characteristics Post the Egyptian Revolution Corporate Governance and Organizational Behavior Review / Volume 5, Issue 2.
- Elkalla, T. , (2017), An empirical investigation of earnings management in the MENA region (Doctoral dissertation, University of the West of England).
- Flayyih, H. H. , Ali, S. I., & Mohammed, Y. N. (2018). The Effect of Integration of Coroprate Governance Mechanisms and Audit Quality in Earning Management: An Empirical Analysis of Listed Banks in Iraqi Stock Exchange. International Journal of Engineering & Technology, 7(4.25), 337-344.
- Gupta, A. K., & Gupta, N. (2021). Environment practices mediating the environmental compliance and firm performance: An institutional theory perspective from emerging economies. Global Journal of Flexible Systems Management, 22, 157-178.
- Habib, A. , & Hansen, J., (2009) Review of Earnings Management around Earnings Benchmarks, Journal of Accounting Literature.
- Habib, A. , Uddin Bhuiyan, B., & Islam, A. (2013). Financial distress, earnings management and market pricing of accruals during the global financial crisis. Managerial Finance, 39(2), 155-180.
- Hair, J.F. , Black, W.C., Babin, B.J. and Anderson, R.E. (2010) Multivariate Data Analysis. 7th Edition, Pearson, New York.
- Healy, P. M., & Wahlen, J. M. (1999). A review of the earnings management literature and its implications for standard setting. Accounting horizons, 13(4), 365-383.
- Herusetya, A., Sambuaga, E., & Sihombing, S., (2023) Business strategy typologies and the preference of earnings management practices: Evidence from Indonesian listed firms, Cogent Business & enragement, 10:1. [CrossRef]
- Hoang, K. M. T. , & Phung, T. A. (2019). The effect of financial leverage on real and accrual-based earnings management in Vietnamese firms. Economics & Sociology, 12(4), 299-333.
- Iatridis, G. , & Kadorinis, G. (2009). Earnings management and firm financial motives: A financial investigation of UK listed firms. International Review of Financial Analysis, 18(4), 164-173.
- Imen Fakhfakh Ben Salima (2010). “ Impact of Compensation Policies on Results Management”.
- Jian, M. (2003). Earnings management and tunneling through related party transactions: Evidence from Chinese corporate groups. Hong Kong University of Science and Technology (Hong Kong).
- Jones, M. J. , Melis, A., Gaia, S., & Aresu, S. (2020). Impression management and retrospective sense-making in corporate annual reports: Banks’ graphical reporting during the global financial crisis. International Journal of Business Communication, 57(4), 474-496.
- Kanagaretnam, K., Lobo, G. J., & Wang, C. (2015). Religiosity and earnings management: International evidence from the banking industry. Journal of Business Ethics, 132, 277-296.
- Khanchel, I. , & Lassoued, N. (2022). Is it hard to be different during the COVID-19 crisis? Investigating the relationship between corporate social responsibility and earnings management. International Journal of Ethics and Systems, https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/IJOES-05-2022-0102/full/htm.
- Kline, R.B. , (1998), Principles and practice of structural equation modeling. New York: Guilford Press.
- Lassoued, N. , Attia, M. B. R., & Sassi, H. (2018). Earnings management in islamic and conventional banks: Does ownership structure matter? Evidence from the MENA region. Journal of International Accounting, Auditing and Taxation, 30, 85-105.
- Limpaphayom, P. , & Polwitoon, S. (2004). Bank relationship and firm performance: evidence from Thailand before the Asian financial crisis. Journal of Business Finance & Accounting, 31(9-10), 1577-1600.
- Martinez, E. F., Rodrigues, A. E. A., Teixeira, L. N., Esposito, A. R., Cabrera, W. I. R., Demasi, A. P. D., & Passador-Santos, F. (2019). Histological evaluation of a new beta-tricalcium phosphate/hydroxyapatite/poly (1-lactide-co-caprolactone) composite biomaterial in the inflammatory process and repair of critical bone defects. Symmetry, 11(11), 1356.
- Menicucci, E. (2020). Earnings quality and earnings management, In: Earnings Quality. Palgrave Pivot, Cham. eBook Packages Economics and Finance, Economics and Finance (R0),. [CrossRef]
- Mersin, H., & Ben Othman, H. (2016). The impact of corporate governance mechanisms on earnings management in Islamic banks in the Middle East region. Journal of Islamic Accounting and Business Research, 7(4), 318-348.
- Shen, C. H. , & Chih, H. L. (2007). Earnings management and corporate governance in Asia’s emerging markets. Corporate Governance: An International Review, 15(5), 999-1021.
- Tarawneh, M. A. : Comparison of Financial Performance in the Banking Sector: Some Evidence from Omani Commercial Banks. International Research Journal of Finance and Economics, 3(3), 101-112. (2006).
- Tullberg, J. (2013). Stakeholder theory: Some revisionist suggestions. The Journal of Socio-Economics, 42, 127-135.
- Vakilifard, H. , & Mortazavi, M. S., (2016), The Impact of Financial Leverage on Accrual-Based and Real Earnings Management, International Journal of Academic Research in Accounting, Finance and Management Science.
- Young, M. N. , Peng, M. W., Ahlstrom, D., Bruton, G. D., & Jiang, Y. (2008). Corporate governance in emerging economies: A review of the principal–principal perspective. Journal of management studies, 45(1), 196-220.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).