Submitted:
20 August 2024
Posted:
22 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Screened Studies Selected for Systematic Review
2.2. Quality Assurance
2.3. b Comparability between Studies
2.3. c Biomarkers Studied Only in Animal Models
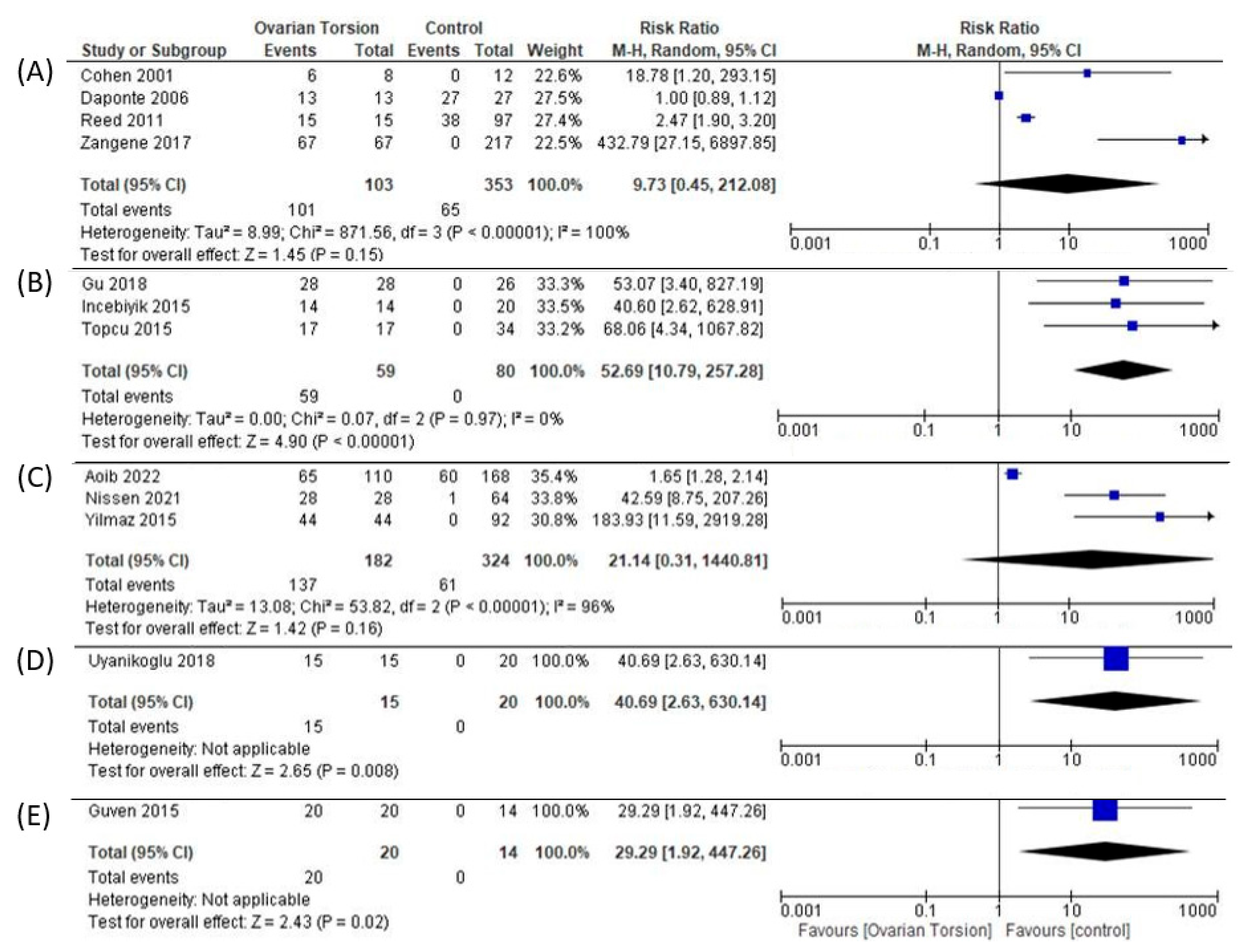
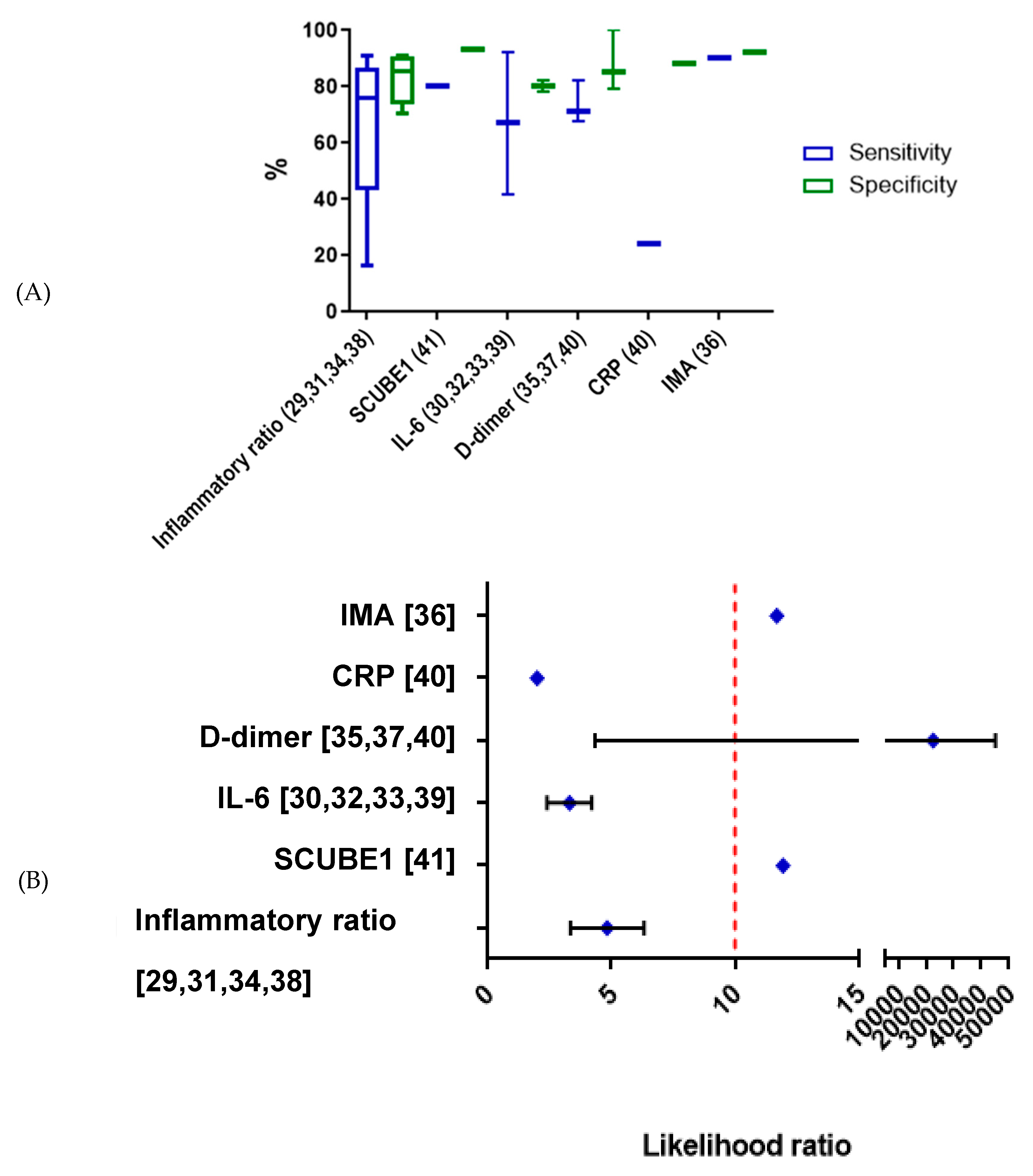
2.3. d Biomarkers of OT Studied in Human Subjects
2.3. c Biomarkers Studied in Humans and Animal Models
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Systematic review
4.2. Bias Quality Assessment
4.3. Data Extraction
4.4. Meta-Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| AT | adnexal torsion | HSP70 | Heat Shock Protein 70 |
| AU | Absorbance Units | s- or pls-DD | Serum or plasma D-dimer |
| CRP | c-reactive protein | PLR | platelet to lymphocyte ratio |
| FRAP | Ferric Reducing Ability of Plasma | PRISMA | Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses |
| GSH | Glutathione | PROSPERO | International prospective register of systematic reviews |
| IL-6 | interleukin-6 | PTX3 | pentraxin-3 |
| IMA | Ischaemia Modified Albumin | SCUBE 1 | Signal peptide, CUB domain and EGF like domain containing 1 |
| LR | likelihood ratio | SOD | superoxide dismutase |
| MDA | Malondialdehyde | TAS | Total Antioxidant Status |
| NLR | neutrophil to lymphocyte ratio | TOS | Total Oxidant Status |
| NOS | Newcastle Ottawa Scale | US | ultrasound |
| OSI | Oxidative Stress Index | VTE | venous thromboembolism |
| OT | ovarian torsion | WS | Whirlpool sign |
| PICO | Population Intervention Comparator Outcome |
References
- ACOG Committee Opinion No. Adnexal Torsion in Adolescents. Obstetrics and Gynecology 2019, 134, 435–436. [CrossRef]
- Guile, S.M., J. . Ovarian Torsion. StatPearls Publishing 2022.
- White, M.; Stella, J. Ovarian torsion: 10-year perspective. Emerg Med Australas 2005, 17, 231–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shetty, M. Acute Pelvic Pain: Role of Imaging in the Diagnosis and Management. Semin Ultrasound CT MR 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mahonski, S.; Hu, K.M. Female Nonobstetric Genitourinary Emergencies. Emerg Med Clin North Am 2019, 37, 771–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.; Hong, M.K.; Ding, D.C. A review of ovary torsion. Ci Ji Yi Xue Za Zhi 2017, 29, 143–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balachandren, N., Yasmin, E., Mavrelos, D., Saridogan, E. Does ovarian cystectomy pose a risk to ovarian reserve and fertility? The Obstetrician and Gynaecologist 2020, 23, 28–37.
- Novoa, M.; Friedman, J.; Mayrink, M. Ovarian torsion: can we save the ovary? Arch Gynecol Obstet 2021, 304, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gasparri, M.L.; Ruscito, I.; Braicu, E.I.; Sehouli, J.; Tramontano, L.; Costanzi, F.; De Marco, M.P.; Mueller, M.D.; Papadia, A.; Caserta, D.; et al. Biological Impact of Unilateral Oophorectomy: Does the Number of Ovaries Really Matter? Geburtshilfe Frauenheilkd 2021, 81, 331–338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, J.S.; Naoum, I.; Salem, N.; Perlitz, Y.; Izhaki, I. The impact of unilateral oophorectomy on ovarian reserve in assisted reproduction: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BJOG 2018, 125, 26–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akman, L.; Erbas, O.; Terek, M.C.; Aktug, H.; Taskiran, D.; Askar, N. The long pentraxin-3 is a useful marker for diagnosis of ovarian torsion: An experimental rat model. J Obstet Gynaecol 2016, 36, 399–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brierley, G.; Arshad, I.; Shakir, F.; Visvathanan, D.; Aramabage, K. Vascular injury during laparoscopic gynaecological surgery: a methodological approach for prevention and management. The Obstetrician and Gynaecologist 2020, 22, 191–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, W.H.; Broder, M.S.; Chang, E.; Feskanich, D.; Farquhar, C.; Liu, Z.; Shoupe, D.; Berek, J.S.; Hankinson, S.; Manson, J.E. Ovarian conservation at the time of hysterectomy and long-term health outcomes in the nurses’ health study. Obstet Gynecol 2009, 113, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jett, S.; Schelbaum, E.; Jang, G.; Boneu Yepez, C.; Dyke, J.P.; Pahlajani, S.; Diaz Brinton, R.; Mosconi, L. Ovarian steroid hormones: A long overlooked but critical contributor to brain aging and Alzheimer’s disease. Front Aging Neurosci 2022, 14, 948219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manolagas, S.C.; Kousteni, S. Perspective: nonreproductive sites of action of reproductive hormones. Endocrinology 2001, 142, 2200–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farland, L.V.; Rice, M.S.; Degnan, W.J., 3rd; Rexrode, K.M.; Manson, J.E.; Rimm, E.B.; Rich-Edwards, J.; Stewart, E.A.; Cohen Rassier, S.L.; Robinson, W.R.; et al. Hysterectomy With and Without Oophorectomy, Tubal Ligation, and Risk of Cardiovascular Disease in the Nurses’ Health Study II. J Womens Health (Larchmt) 2023, 32, 747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassan, H.; Allen, I.; Sofianopoulou, E.; Walburga, Y.; Turnbull, C.; Eccles, D.M.; Tischkowitz, M.; Pharoah, P.; Antoniou, A.C. Long-term outcomes of hysterectomy with bilateral salpingo-oophorectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Am J Obstet Gynecol 2023. [CrossRef]
- Wells, G., Shea, B., O’Connell, D., Peterson, J., Welch, V., Losos, M., Tugwell, P. The Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) for Assessing the Quality of Nonrandomized Studies in Meta-Analysis. https://www.ohri.ca/programs/clinical_epidemiology/oxford.asp 2021.
- Karatas Gurgun, A.; Kaban, I.; Aka, N.; Mentese, A.; Aker, F.; Uras, A.R. The Role of Ischemia Modified Albumin and D-dimer as Early or Late Biochemical Markers in Ovarian Torsion. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2017, 43, 895–901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aran, T.; Guven, S.; Unsal, M.A.; Alver, A.; Mentese, A.; Yulug, E. Serum ischemia-modified albumin as a novel marker of ovarian torsion: an experimental study. Eur J Obstet Gynecol Reprod Biol 2010, 150, 72–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakacak, M.; Kostu, B.; Ercan, O.; Bostanci, M.S.; Kiran, G.; Aral, M.; Ciralik, H.; Serin, S. High-sensitivity C-reactive protein as a novel marker in early diagnosis of ovarian torsion: an experimental study. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2015, 291, 99–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cilgin, H.; Simsek, M.; Bal, R. Can adnexal torsion be predicted by measuring plasma heat shock protein 70 level? An experimental study. Arch Gynecol Obstet 2017, 296, 941–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunaydin, M.; Sipahi, M.; Kesicioglu, T.; Usta, M.; Tezcan, B.; Tokgoz, V.Y. The value of plasma SCUBE1 and oxidative stress parameters in the early diagnosis of acute ovarian torsion. Bratisl Lek Listy 2019, 120, 456–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakoc-Sokmensuer, L.; Hacivelioglu, S.; Demir, A.; Kose, M.; Kaymaz, F.F.; Cakir, D.U.; Bozdag, G. Histopathology of ipsilateral and contralateral ovaries and plasma interleukin 6 levels after unilateral ovarian torsion. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol 2016, 43, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kart, C.; Aran, T.; Guven, S.; Karahan, S.C.; Yulug, E. Acute increase in plasma D-dimer level in ovarian torsion: an experimental study. Hum Reprod 2011, 26, 564–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazăr, C., , Vozian, M., Pantea, V., Mișina, A., Tagadiuc, O. . Ischemia modified albumin in experimental ovarian torsion with and without controlled reperfusion. Revista Romana de Medicina de Laborator 2019, 27, 43–50. [CrossRef]
- Uzun, O.; Kaban, I.; Midi, A.; Uysal, H.; Boran, A.B.; Bacanakgil, B.H.; Tarbaghia, M. Diagnostic value of signal peptide-CUB-EGF domain-containing protein 1 as an early and late biochemical marker in the ovarian torsion rat model. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2018, 44, 1092–1099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yildirim, A.; Yildirim, S.; Topaloglu, N.; Tekin, M.; Kucuk, A.; Erdem, H.; Erbas, M.; Cakir, D.U. Correlation of ischemia-modified albumin levels and histopathologic findings in experimental ovarian torsion. Turk J Emerg Med 2016, 16, 8–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yilmaz, M.; Cimilli, G.; Saritemur, M.; Demircan, F.; Isaoglu, U.; Kisaoglu, A.; Emet, M. Diagnostic Accuracy of Neutrophil/Lymphocyte Ratio, Red Cell Distribution Width and Platelet Distribution Width in Ovarian Torsion. J Obstet Gynaecol 2016, 36, 218–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zangene, M.; Ashoori Barmchi, A.; Rezaei, M.; Veisi, F. The comparison between the serum level of interleukin-6 in women with acute ovarian torsion and other causes of lower abdominal pain. J Obstet Gynaecol 2017, 37, 223–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aiob, A.; Lowenstein, L.; Borik, I.; Naskovica, K.; Mikhail, S.M.; Odeh, M. The value of clinical symptoms, the neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio, and ultrasonographic features in predicting adnexal torsion: A case-control study. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 2023, 49, 289–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.B.; Wattiez, A.; Stockheim, D.; Seidman, D.S.; Lidor, A.L.; Mashiach, S.; Goldenberg, M. The accuracy of serum interleukin-6 and tumour necrosis factor as markers for ovarian torsion. Hum Reprod 2001, 16, 2195–2197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daponte, A.; Pournaras, S.; Hadjichristodoulou, C.; Lialios, G.; Kallitsaris, A.; Maniatis, A.N.; Messinis, I.E. Novel serum inflammatory markers in patients with adnexal mass who had surgery for ovarian torsion. Fertil Steril 2006, 85, 1469–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, A.; Ghimire, S.; Shrestha, A.; Pant, S.R.; Subedi, N.; Pant, P.R. Preoperative Neutrophil Lymphocyte Ratio in Prediction of Adnexal Mass Torsion. Obstet Gynecol Int 2023, 2023, 3585189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, X.; Yang, M.; Liu, Y.; Liu, F.; Liu, D.; Shi, F. The ultrasonic whirlpool sign combined with plasma d-dimer level in adnexal torsion. Eur J Radiol 2018, 109, 196–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guven, S.; Kart, C.; Guvendag Guven, E.S.; Cetin, E.C.; Mentese, A. Is the measurement of serum ischemia-modified albumin the best test to diagnose ovarian torsion? Gynecol Obstet Invest 2015, 79, 269–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Incebiyik, A.; Camuzcuoglu, A.; Hilali, N.G.; Vural, M.; Camuzcuoglu, H. Plasma D-dimer level in the diagnosis of adnexal torsion. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 2015, 28, 1073–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nissen, M.; Sander, V.; Rogge, P.; Alrefai, M.; Trobs, R.B. Neutrophil to Lymphocyte Ratio and Platelet to Lymphocyte Ratio Might Predict Pediatric Ovarian Torsion: A Single-Institution Experience and Review of the Literature. J Pediatr Adolesc Gynecol 2021, 34, 334–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reed, J.L.; Strait, R.T.; Kachelmeyer, A.M.; Byczkowski, T.L.; Ho, M.L.; Huppert, J.S. Biomarkers to distinguish surgical etiologies in females with lower quadrant abdominal pain. Acad Emerg Med 2011, 18, 686–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topcu, H.O.; Iskender, C.T.; Ceran, U.; Kaymak, O.; Timur, H.; Uygur, D.; Danisman, N. Evaluation of the Diagnostic Accuracy of Serum D-Dimer Levels in Pregnant Women with Adnexal Torsion. Diagnostics (Basel) 2015, 5, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uyanikoglu, H.; Hilali, N.G.; Yardimciel, M.; Koyuncu, I. A new biomarker for the early diagnosis of ovarian torsion: SCUBE-1. Clin Exp Reprod Med 2018, 45, 94–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamsrizi, P.; Gladstone, B.P.; Carrara, E.; Luise, D.; Cona, A.; Bovo, C.; Tacconelli, E. Variation of effect estimates in the analysis of mortality and length of hospital stay in patients with infections caused by bacteria-producing extended-spectrum beta-lactamases: a systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ Open 2020, 10, e030266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee-Robichaud, H.; Thomas, K.; Morgan, J.; Nelson, R.L. Lactulose versus Polyethylene Glycol for Chronic Constipation. Cochrane Database Syst Rev 2010. [CrossRef]
- Rylander, M.N.; Feng, Y.; Bass, J.; Diller, K.R. Thermally induced injury and heat-shock protein expression in cells and tissues. Ann N Y Acad Sci 2005, 1066, 222–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porte, R.; Davoudian, S.; Asgari, F.; Parente, R.; Mantovani, A.; Garlanda, C.; Bottazzi, B. The Long Pentraxin PTX3 as a Humoral Innate Immunity Functional Player and Biomarker of Infections and Sepsis. Front Immunol 2019, 10, 794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohara, T.; Farhoudi, M.; Bang, O.Y.; Koga, M.; Demchuk, A.M. The emerging value of serum D-dimer measurement in the work-up and management of ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 2020, 15, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Favresse, J.; Lippi, G.; Roy, P.M.; Chatelain, B.; Jacqmin, H.; Ten Cate, H.; Mullier, F. D-dimer: Preanalytical, analytical, postanalytical variables, and clinical applications. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 2018, 55, 548–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lazăr, C., Vozian, M, Pantea, V, Mishina, A, Tagadiuc, O. . Ischemia modified albumin in experimental ovarian torsion with and without controlled reperfusion. In: Russian Open Medical Journal. 2019, 8. [CrossRef]
- Dugue, B.; Leppanen, E. Short-term variability in the concentration of serum interleukin-6 and its soluble receptor in subjectively healthy persons. Clin Chem Lab Med 1998, 36, 323–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, T.; Narazaki, M.; Kishimoto, T. IL-6 in inflammation, immunity, and disease. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol 2014, 6, a016295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumari, N.; Dwarakanath, B.S.; Das, A.; Bhatt, A.N. Role of interleukin-6 in cancer progression and therapeutic resistance. Tumour Biol 2016, 37, 11553–11572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grunau, G.L.; Harris, A.; Buckley, J.; Todd, N.J. Diagnosis of Ovarian Torsion: Is It Time to Forget About Doppler? J Obstet Gynaecol Can 2018, 40, 871–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yaakov, O.; Ashwal, E.; Gemer, O.; Peled, Y.; Kapustian, V.; Namazov, A.; Eitan, R.; Krissi, H. Acute Adnexal Torsion: Is Immediate Surgical Intervention Associated with a Better Outcome? Gynecol Obstet Invest 2022, 87, 100–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linkins, L.A.; Takach Lapner, S. Review of D-dimer testing: Good, Bad, and Ugly. Int J Lab Hematol 2017, 39 Suppl 1, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Shamseer, L.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015 statement. Syst Rev 2015, 4, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shamseer, L.; Moher, D.; Clarke, M.; Ghersi, D.; Liberati, A.; Petticrew, M.; Shekelle, P.; Stewart, L.A.; Group, P.-P. Preferred reporting items for systematic review and meta-analysis protocols (PRISMA-P) 2015: elaboration and explanation. BMJ 2015, 350, g7647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wohlin, C. Guidelines for snowballing in systematic literature studies and a replication in software engineering. EASE ‘14: Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Evaluation and Assessment in Software Engineering 2014, 38, 1-10.
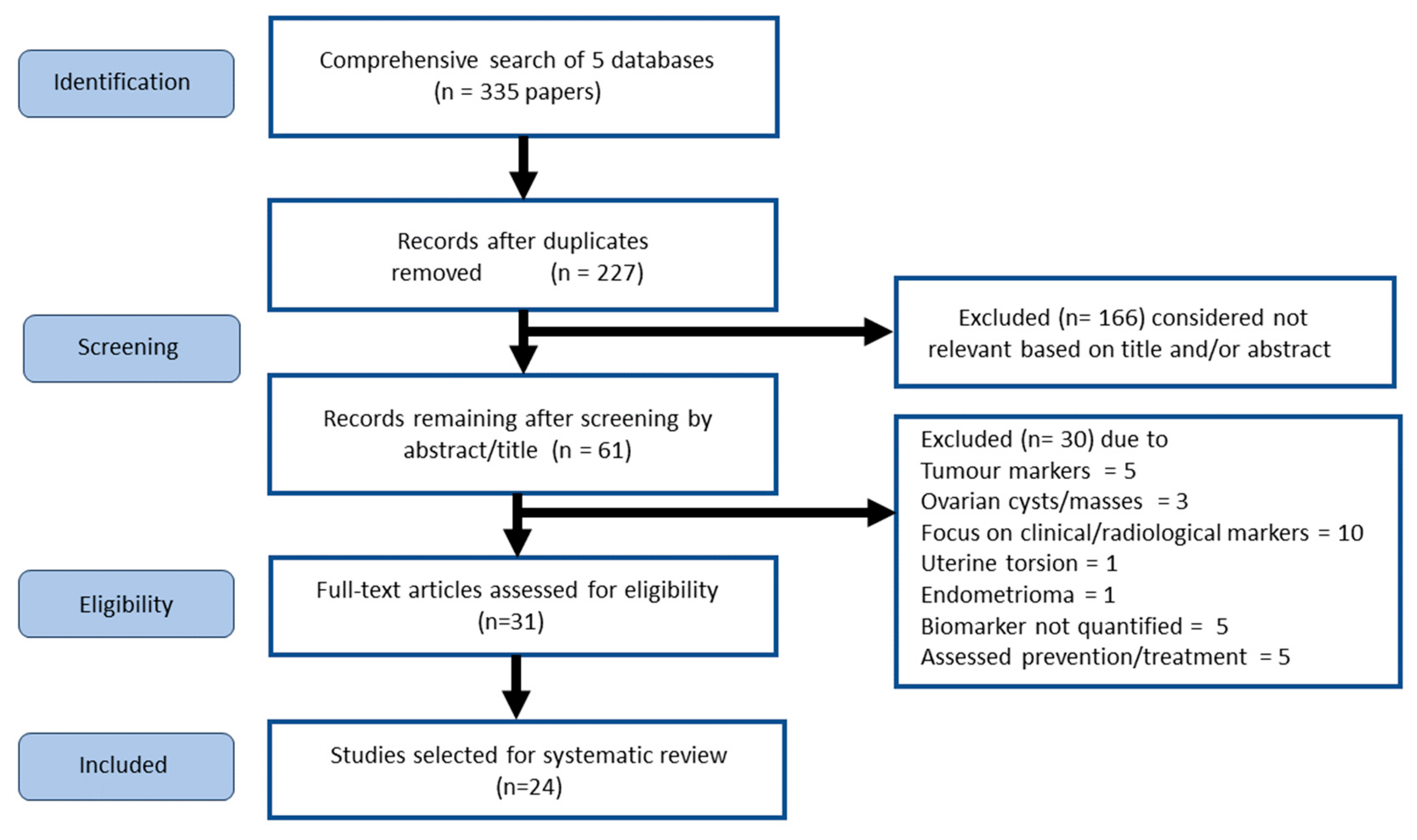
| Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|
| Primary literature sources: with reviews kept in until screening is completed to facilitate the benefits of reverse snowballing | Biomarkers are not directly quantified (qualitative biomarkers) |
| Humans and animal models | Cell lines |
| Patients diagnosed with OT | Disease other than OT |
| Quantitative biomarkers | Biomarkers for ovarian cancer |
| Have a quantified non-invasive blood biomarker expression which predicts OT | |
| All ages | |
| All geographical locations | |
| All publication dates |
| Paper | Selection | Comparability | Outcome | |
| Animal models | Akman et al., 2016 [11] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
| Aran et al., 2010 [20] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Bakacak et al., 2015 [21] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Çılgın et al., 2017 [22] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Gunaydin et al., 2019 [23] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Karakoc-Sokmenseur et al., 2016 [24] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Karatas Gurgun et al., 2017 [19] |
 
|
 
|
 
|
|
| Kart et al., 2011 [25] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Lazăr et al., 2019 [26] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Uzun et al., 2018 [27] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Yildirim et al., 2016 [28] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Yilmaz et al., 2015 [29] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Zangene et al., 2017 [30] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Clinical studies | Aiob et al., 2023 [31] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
| Cohen et al., 2001 [32] |
  
|
 
|
 
|
|
| Daponte et al., 2006 [33] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Ghimire et al., 2023 [34] |
  
|
 
|
 
|
|
| Gu et al., 2018 [35] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Guven et al., 2015 [36] |
  
|
 
|
 
|
|
| Incebiyik et al., 2015 [37] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Nissen et al., 2019 [38] |
  
|
 
|
 
|
|
| Reed et al., 2011 [39] |
  
|
 
|
 
|
|
| Topçu et al., 2015 [40] |
  
|
 
|
  
|
|
| Uyanikoglu et al., 2018 [41] |
   
|
 
|
  
|
| Article | Primary Data | P-value | Secondary Data | |||
| Aran et al., 2010 [20] |
Pre-operative IMA (AU) | Similar in both groups | Group 2 had increased follicular degeneration | |||
| Post-operative IMA (AU) | 0.05 | |||||
| Sham operation: 0.191 ± 0.034 | Torsion model: 0.277 ± 0.089 | |||||
| Akman et al., 2016 [11] |
Pentraxin-3 (PTX3) | Sham operation (ng/ml) | Torsion model (ng/ml) | |||
| Pre-operative levels (ng/ml) | 1.05 ± 0.20 | 1.09 ± 0.28 | >0.05 | Higher follicular degeneration in group | ||
| Post-operative levels (ng/ml) | 1.07 ± 0.22 | 2.13 ± 0.49 | 0.001 | |||
| Bakacak et al., 2015 [21] |
Sham operation | Torsion model | Higher follicular cell degeneration in group 2 | |||
| CRP levels | Pre-operative | 0.36±0.04 | 0.36±0.04 | 0.214 | ||
| (mg/l) | Post-operative | 0.39±0.06 | 0.91±0.18 | <0.001 | ||
| Çilgin et al., 2017 [22] |
Heat shock protein 70 (hsp-70; ng/ml) | No statistical difference between pre-operative levels (p= 0.966); P=0.001 for post-operative levels | ||||
| Torsion model (Group 1) |
Sham operation (Group 2) |
No operation (Group 3) |
||||
| Pre-operative | 1.19 (±0.13) | 1.18 (±0.78) | 1.15 (±0.49) | / | ||
| Post-operative |
1.75 (±0.25) | 1.16 (±0.99) |
1.19 (±0.11) |
Statistically significant difference between Group 1 and 2 (p=0.002), 1 and 3 p=0.002) but not 2 and 3 (p=0.561) | ||
| Gunaydin et al., 2019 [23] |
Control | Torsion | Increased vascular congestion and haemorrhage in the torsion group | |||
| SCUBE1 (ng/ml) | 1.83+0.16 | 1.82+0.18 | 0.987 | |||
| Superoxide dismutase (SOD)(U/ml) | 5.33+0.44 | 5.98+0.45 | 0.33 | |||
| malondialdehyde (MDA)(mmol/l) | 25.81+2.16 | 33.83+2.78 | 0.039 | |||
| Total antioxidant status (TAS; mmmol Trolox Evuiv/l) | 0.92+0.01 | 1.04+0.08 | 0.244 | |||
| Karakoc-Sokmensuer et al., 2016 [24] |
No change to mean plasma IL-6 (pg/ml) |
0.584 | Total tissue damage was similar across groups | |||
| Karatas Gurgun et al., 2017 [19] |
Sham operation | 4-hr torsion | 24-hr torsion | Increased follicular cell degeneration in the torsion groups | ||
| IMA (ng/ml) | 0.59+0.06 | 0.58 +0.1 | 0.71 +0.14 | 0.064 | ||
| DD (ng/ml) | 250.71+ 71.95 | 1740.20+913.94 | 474.36+222.4 | 0.001 | ||
| Kart et al., 2011 [25] |
DD (mg/l) | Sham operation | Torsion model | Greater follicular cell degeneration in group 2 | ||
| Pre-operative plasma levels | 0.5963+0.2047 | 0.6344+ 0.1348 | 0.815 | |||
| 2h after OT | 1.2267+0.3099 | 0.6213+0.2346 | 0.001 | |||
| Mean difference | +0.0250+0.2660 | +0.5922+0.3001 | 0.001 | |||
| IMA levels (μmol/l) | ||||||
| Lazăr et al., 2019 [26] |
Control | 402.370 ± 2.732 | 0.003 | |||
| Sham operation | 418.472 ± 1.854 | |||||
| 3h torsion | 478.359 ± 5.218 | <0.001 |
||||
| 3h torsion, 1hr simple reperfusion | 490.024 ± 3.376 | |||||
| 3h ischaemia, 1hr controlled reperfusion | 452.564 ± 3.096 | |||||
| 3h ischaemia, 24h simple reperfusion | 483.370 ± 1.550 | |||||
| 3h ischaemia, 24h-controlled reperfusion | 454.207 ± 0.878 | |||||
| Uzun et al., 2018 [27] |
Post-operative | Group 1. Sham operation | Group 2. Torsion model + ischaemia >8h | Group 3. Torsion model + ischaemia >24h | Group 1: 0.004 Group 2: 0.150 Group 3: 0.016 |
Increased follicular degeneration in the ischemic groups |
| SCUBE1 (ng/ml) | 51.12+17.04 | 71.83+20.53 | 132.85+51.18 | |||
| Yildirim et al., 2016 [28] |
Median post-operative IMA levels (ABSU) | Torsion group | Control group | 0.001 for the difference between groups |
No pathological change in the control group, but pathological change present in the OT group | |
| 921 (870.0-966.00) | 853 (783-869) | |||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





