Submitted:
21 August 2024
Posted:
21 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
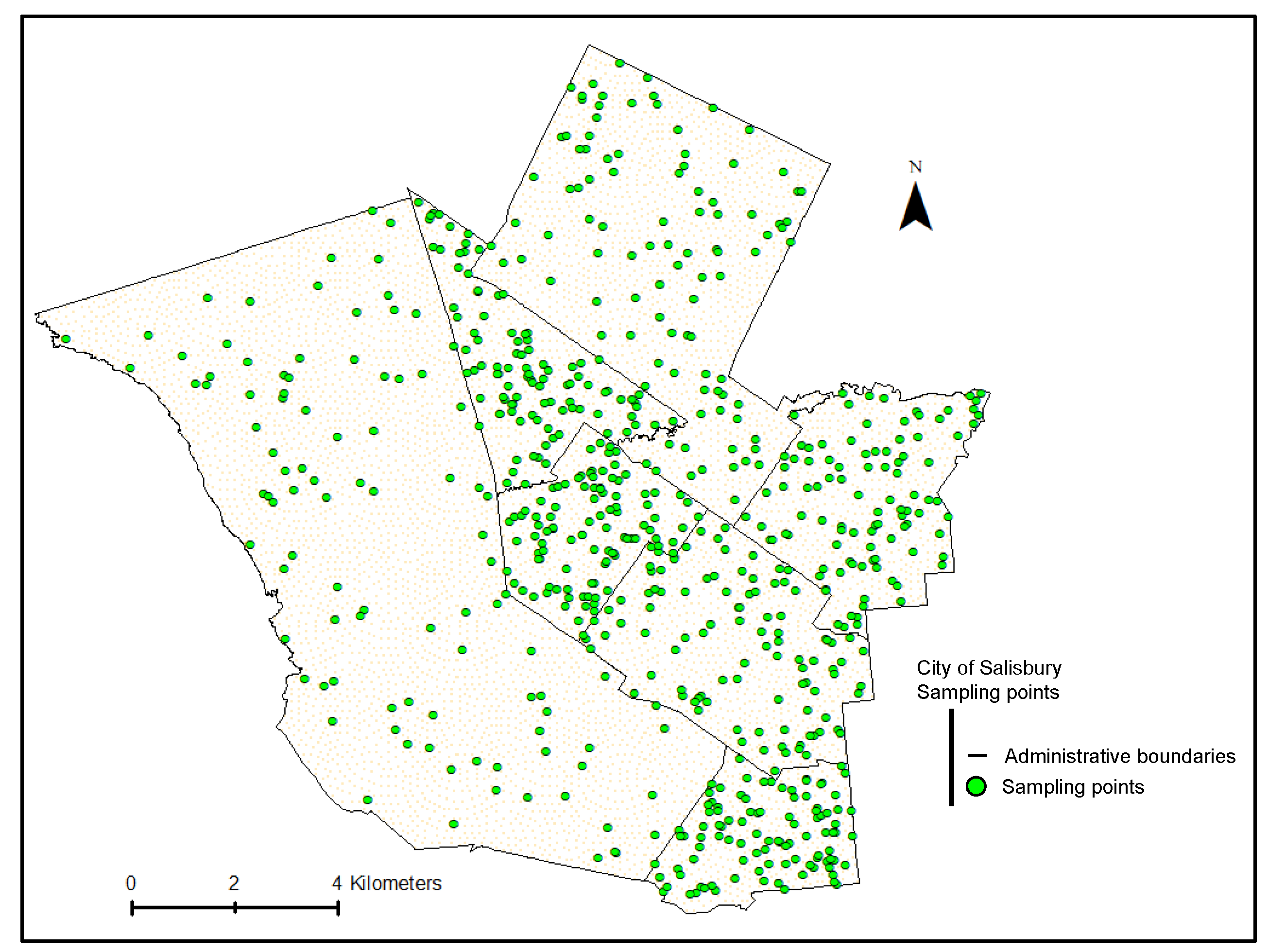
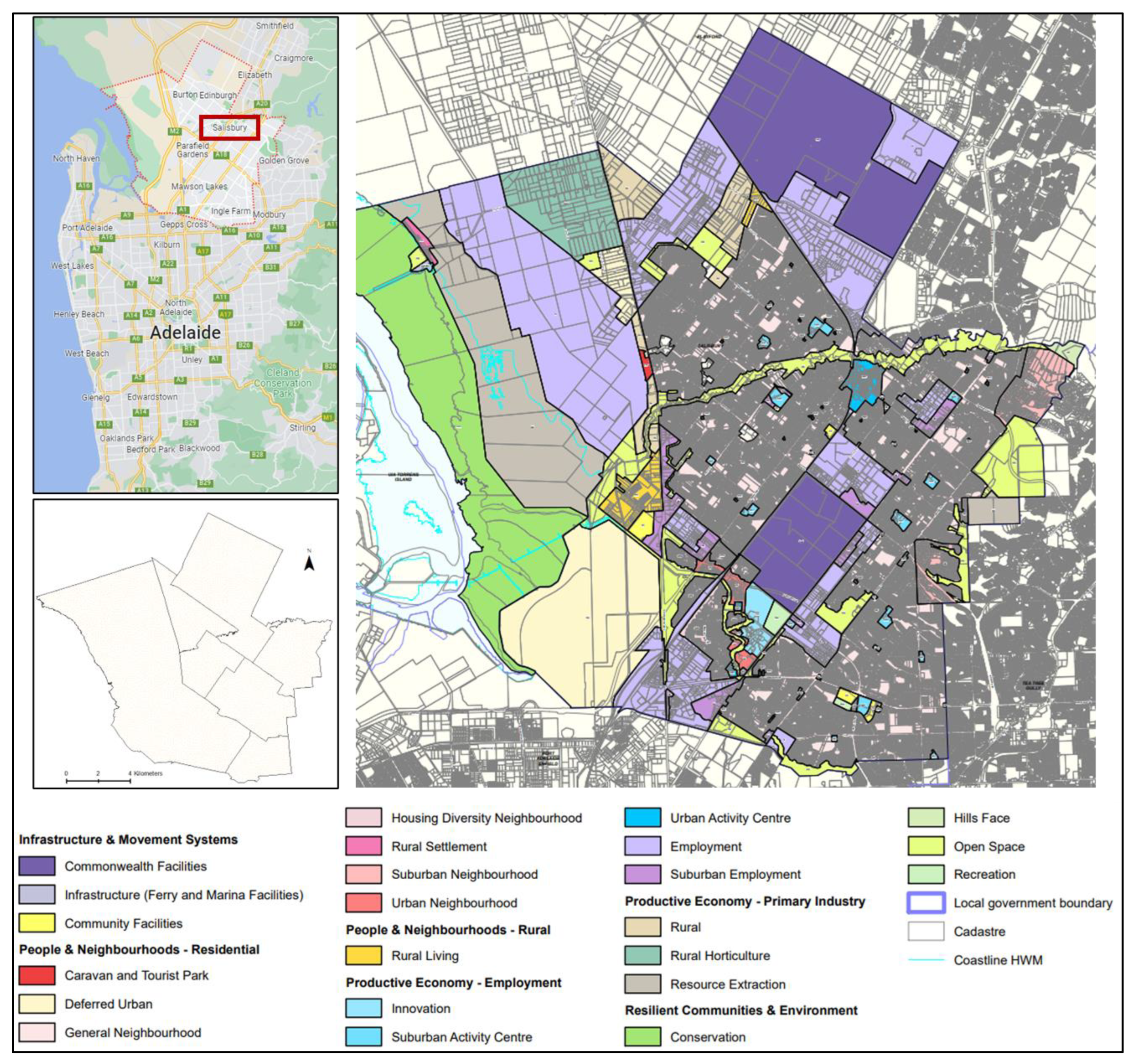
2.1. Study Area
2.2. Data Collection
- a.
- Satellite maps
- b.
- Meteorological data
- c.
- Aerial photographs
2.3. Data Analysis
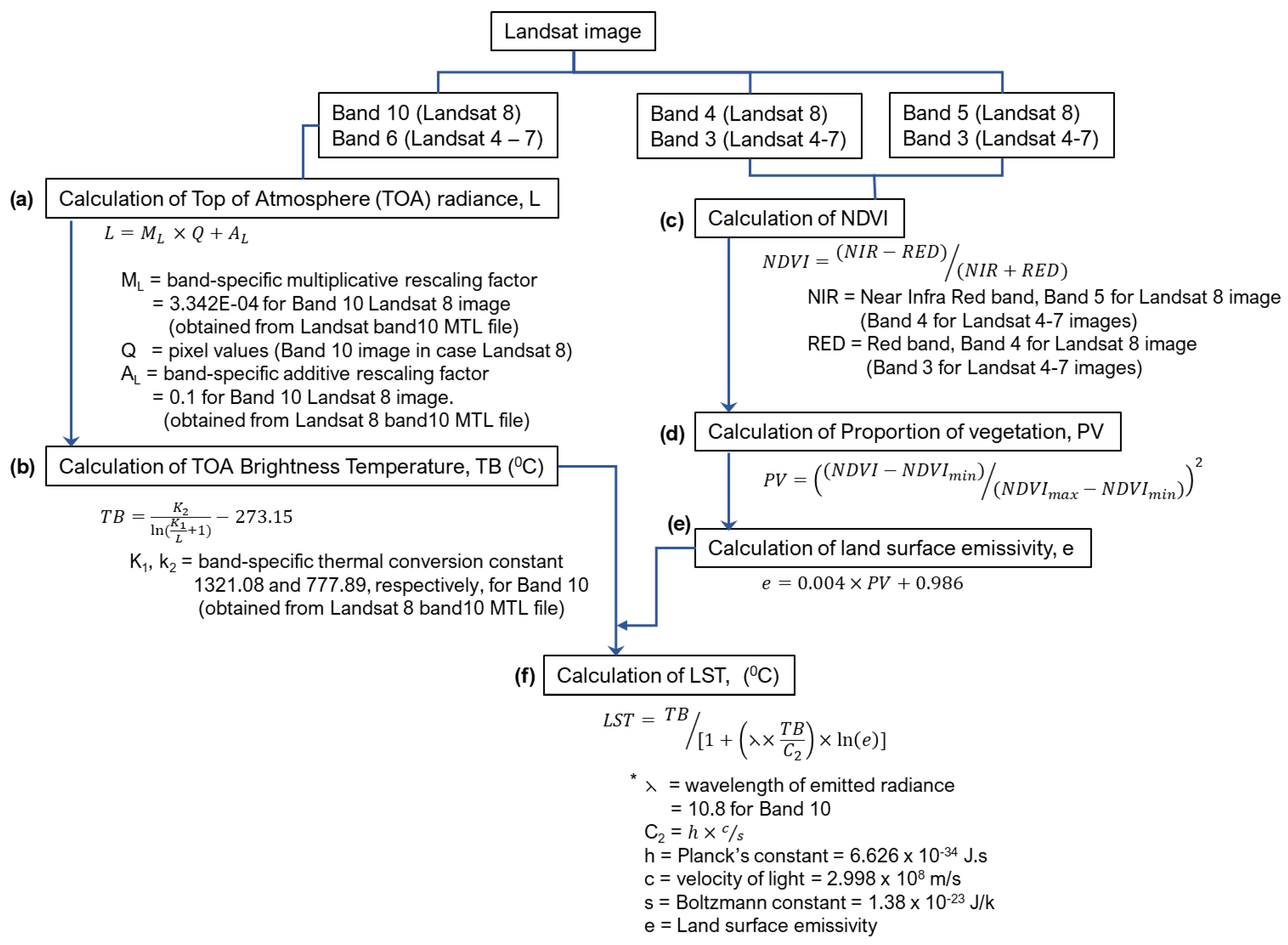
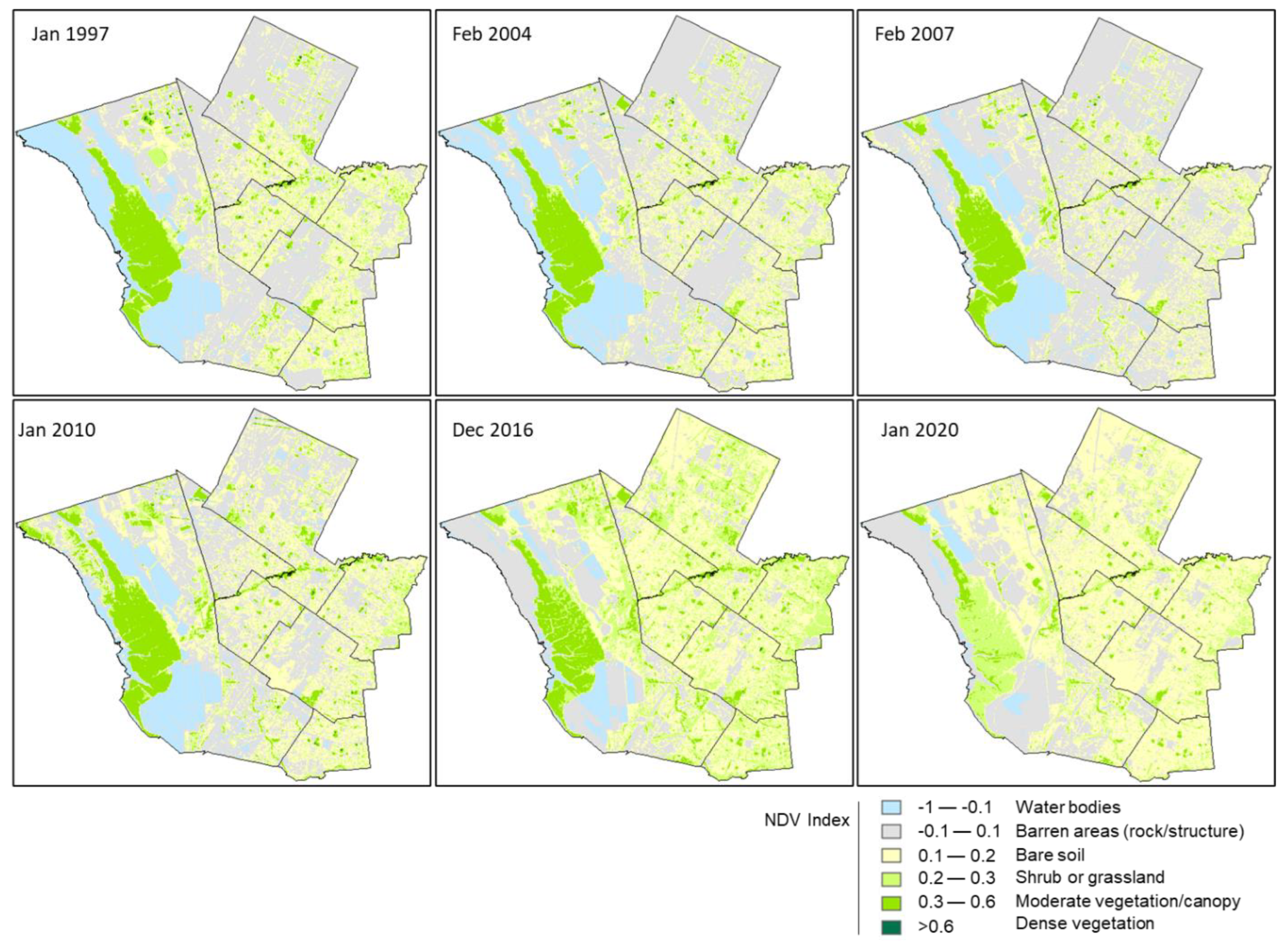
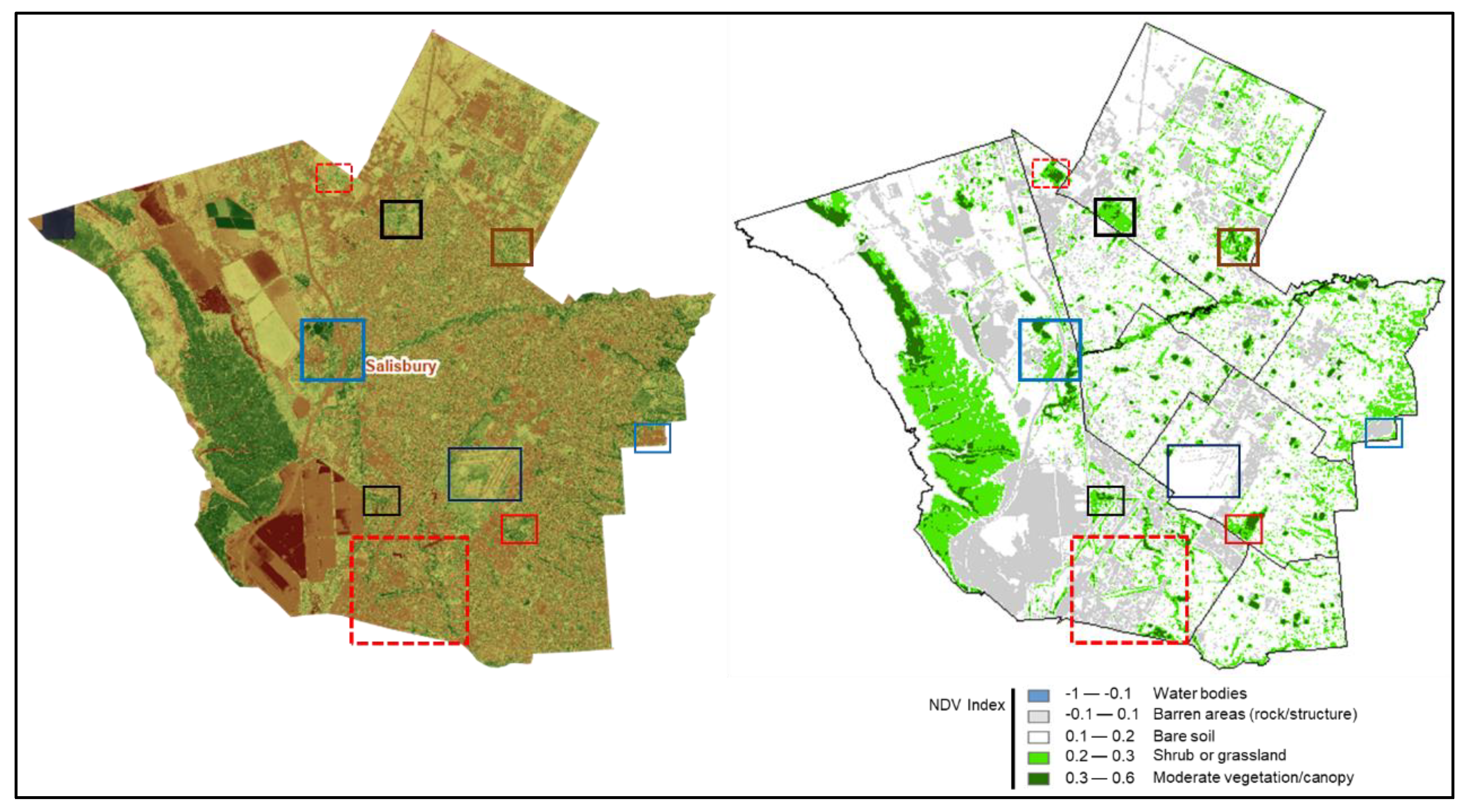
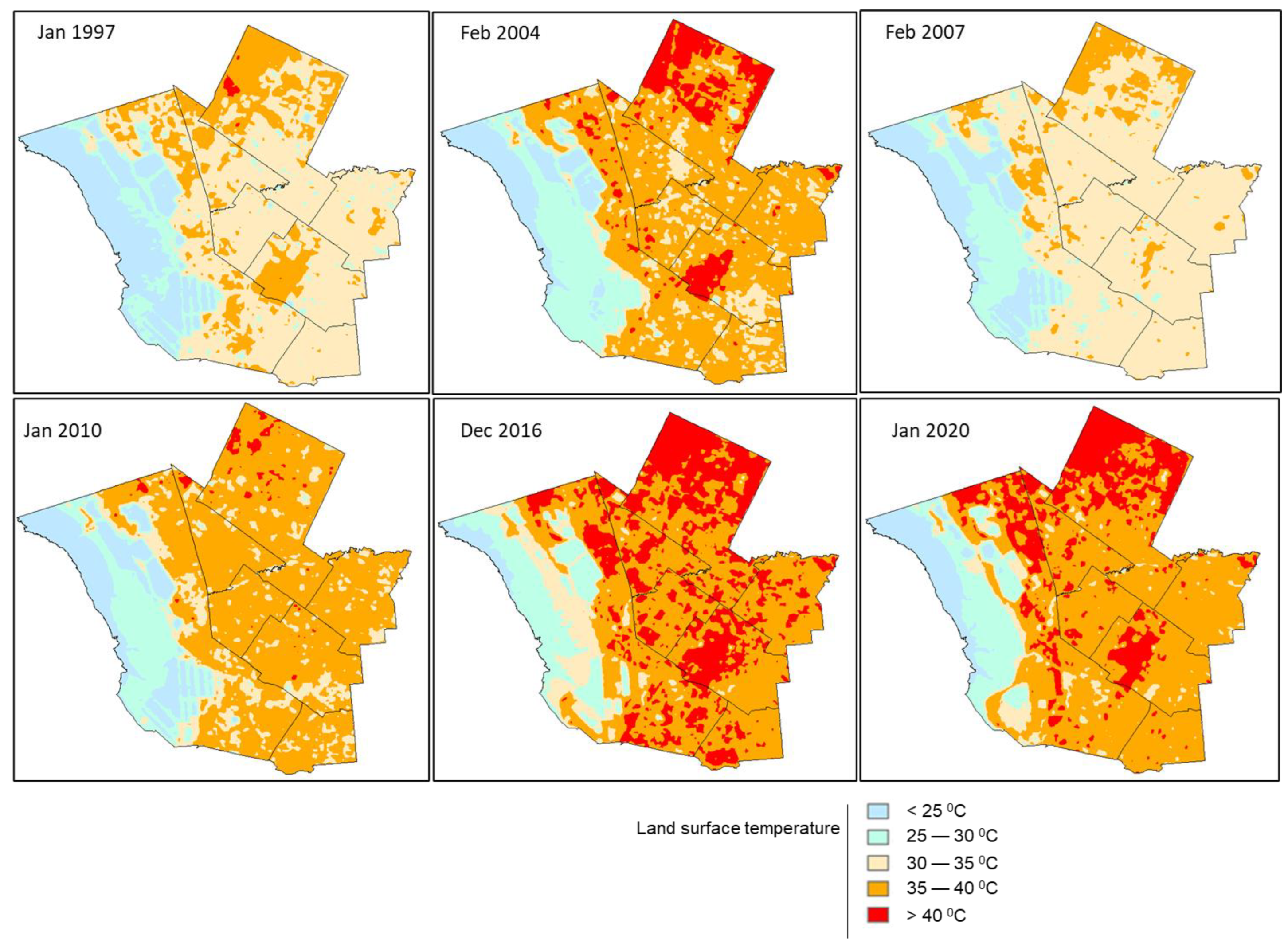
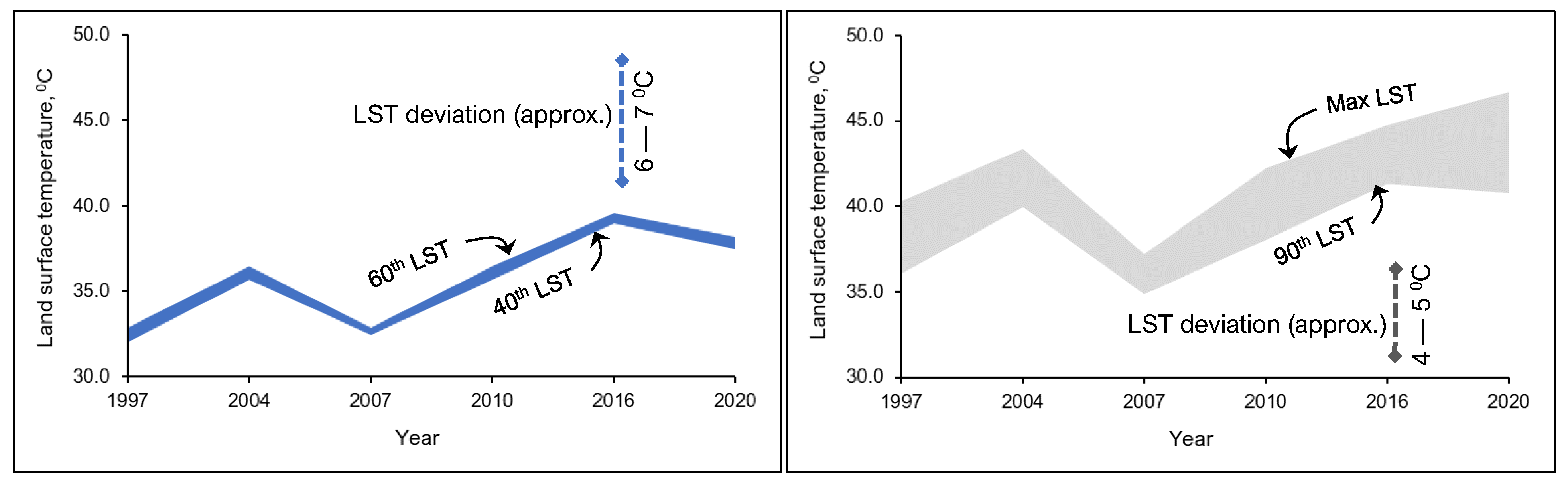
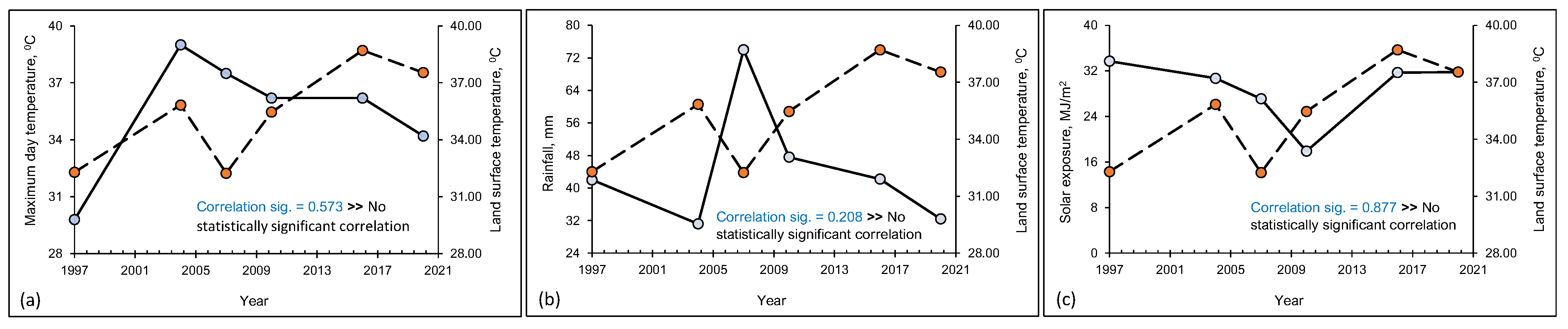
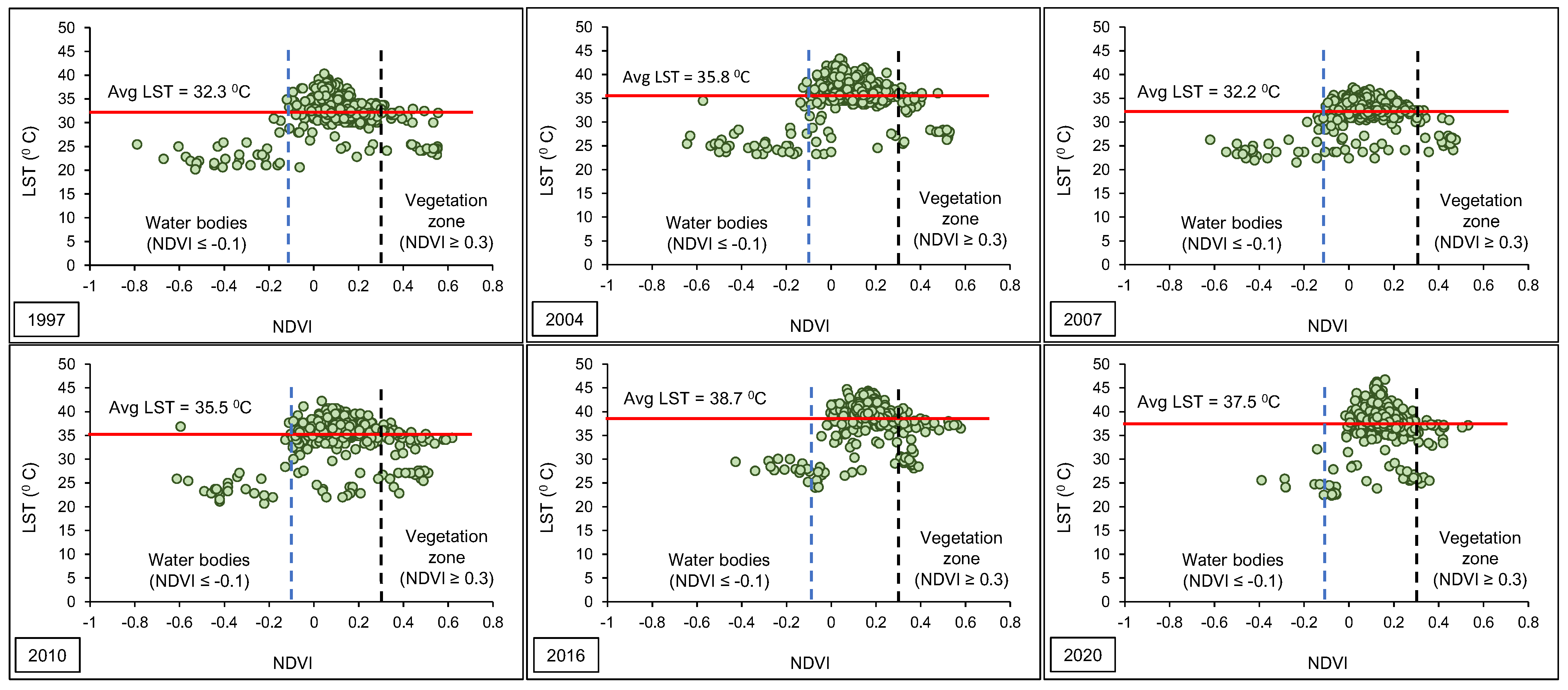
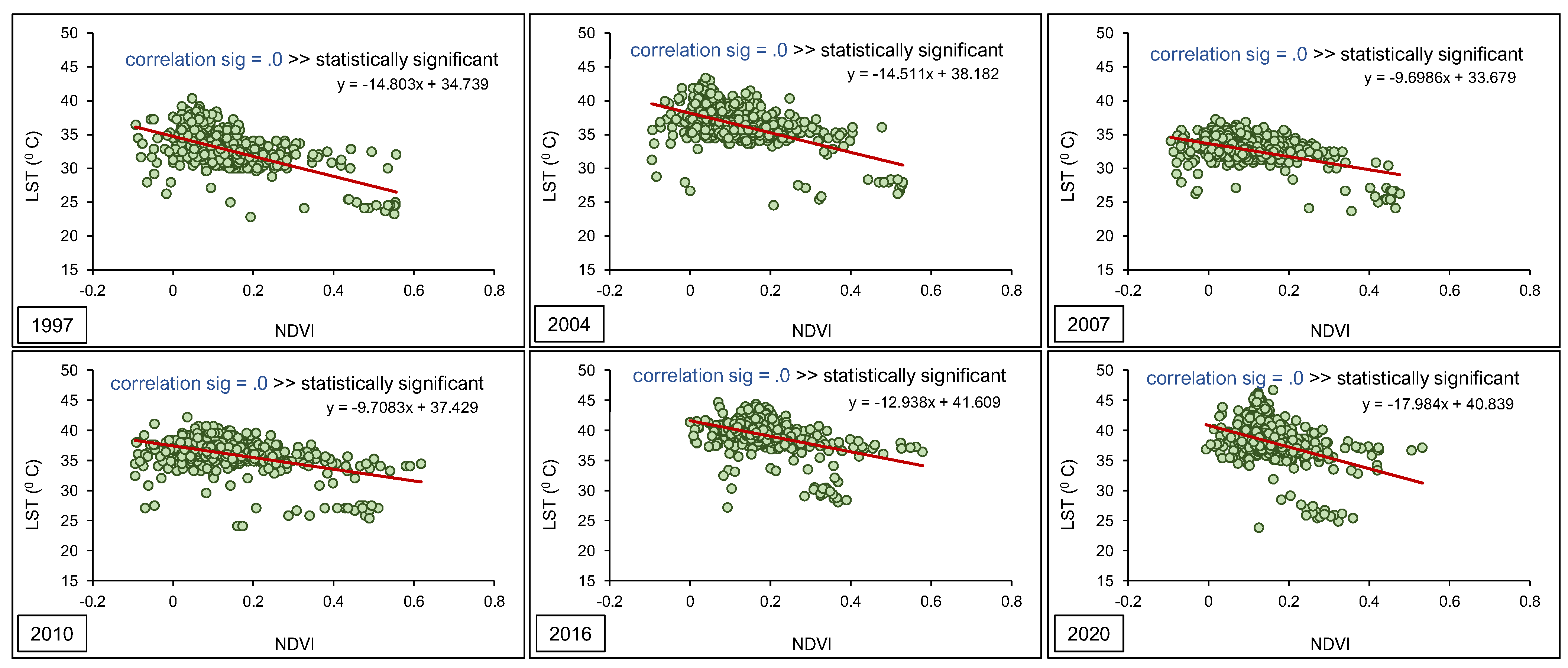
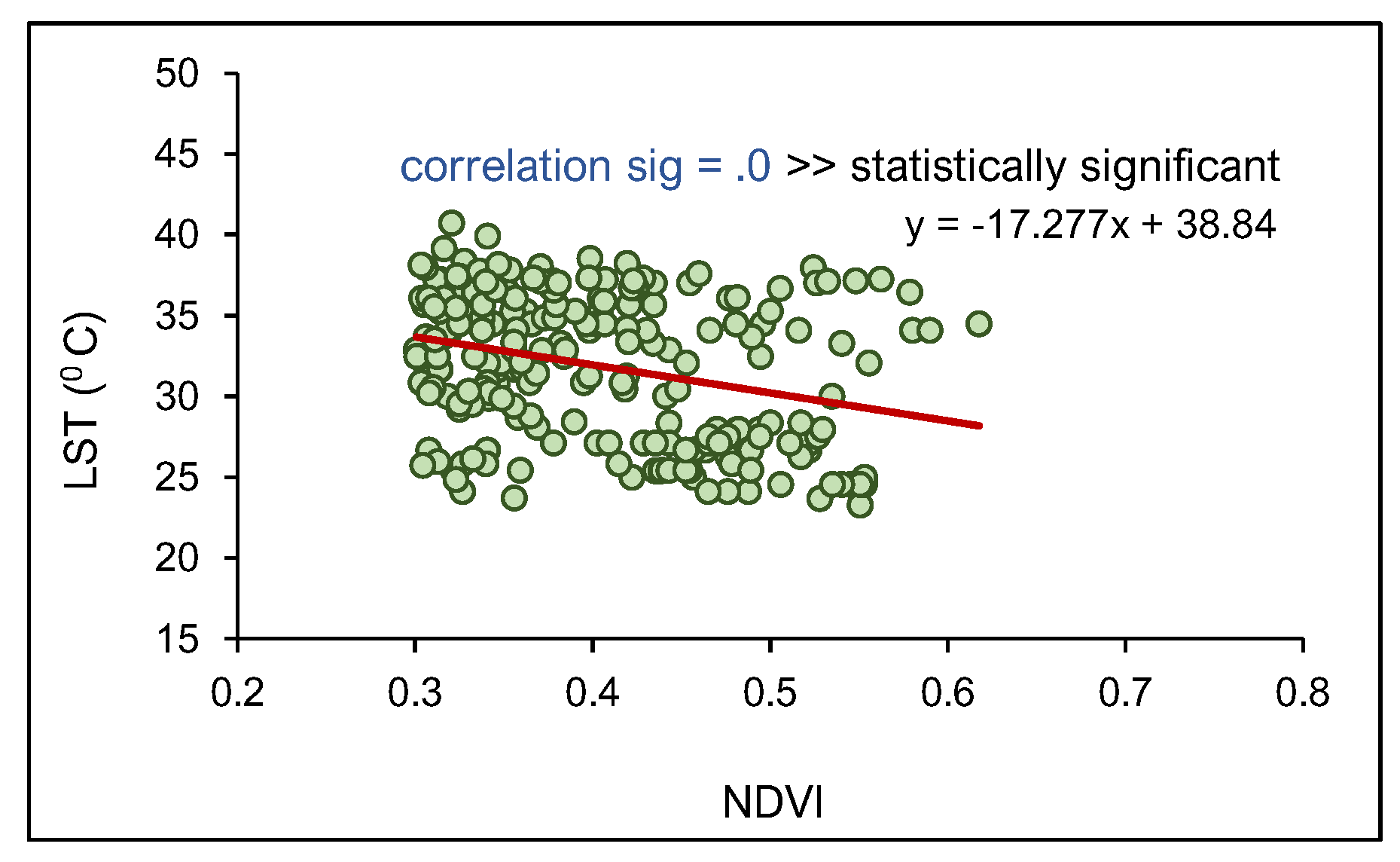
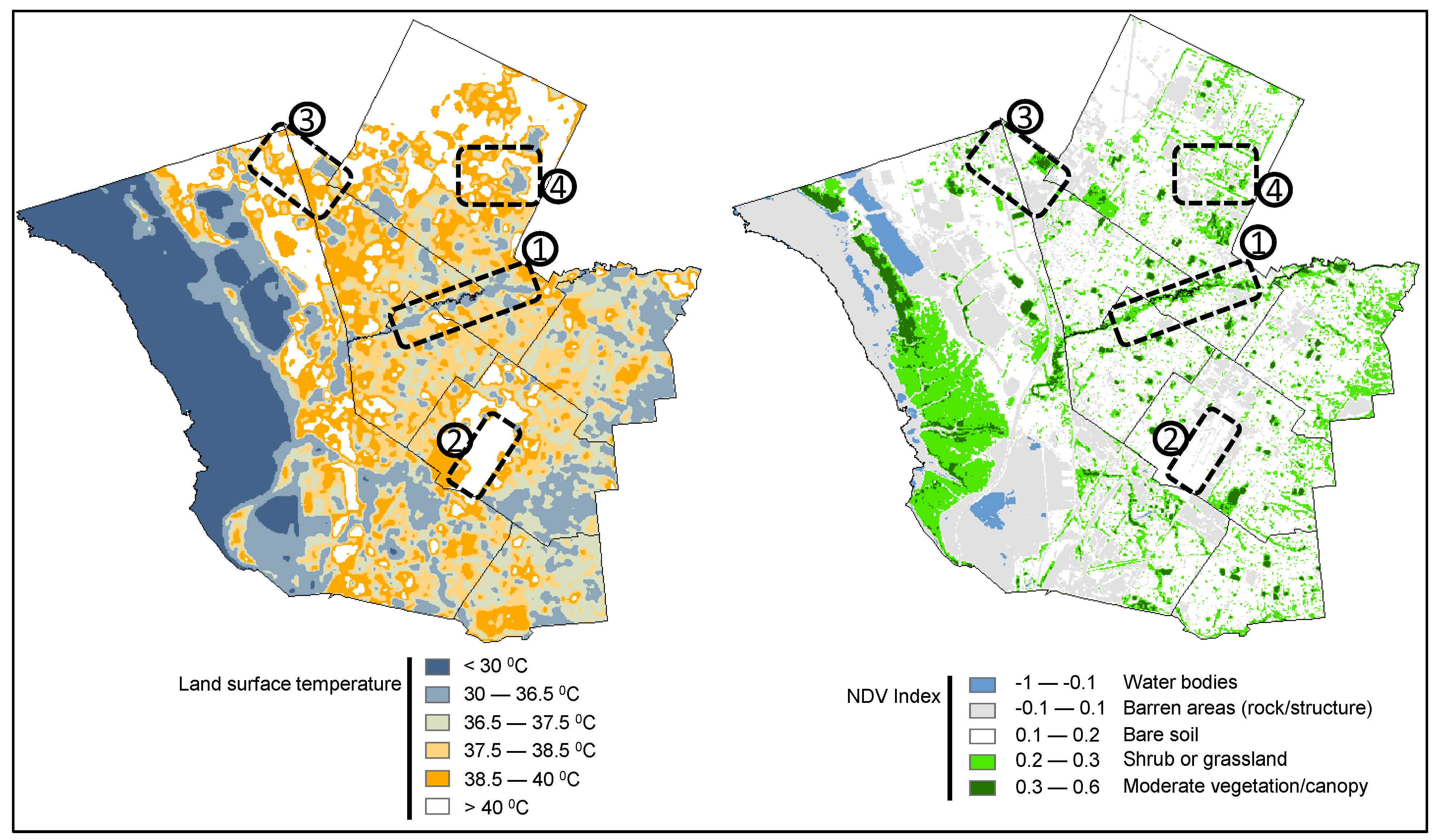
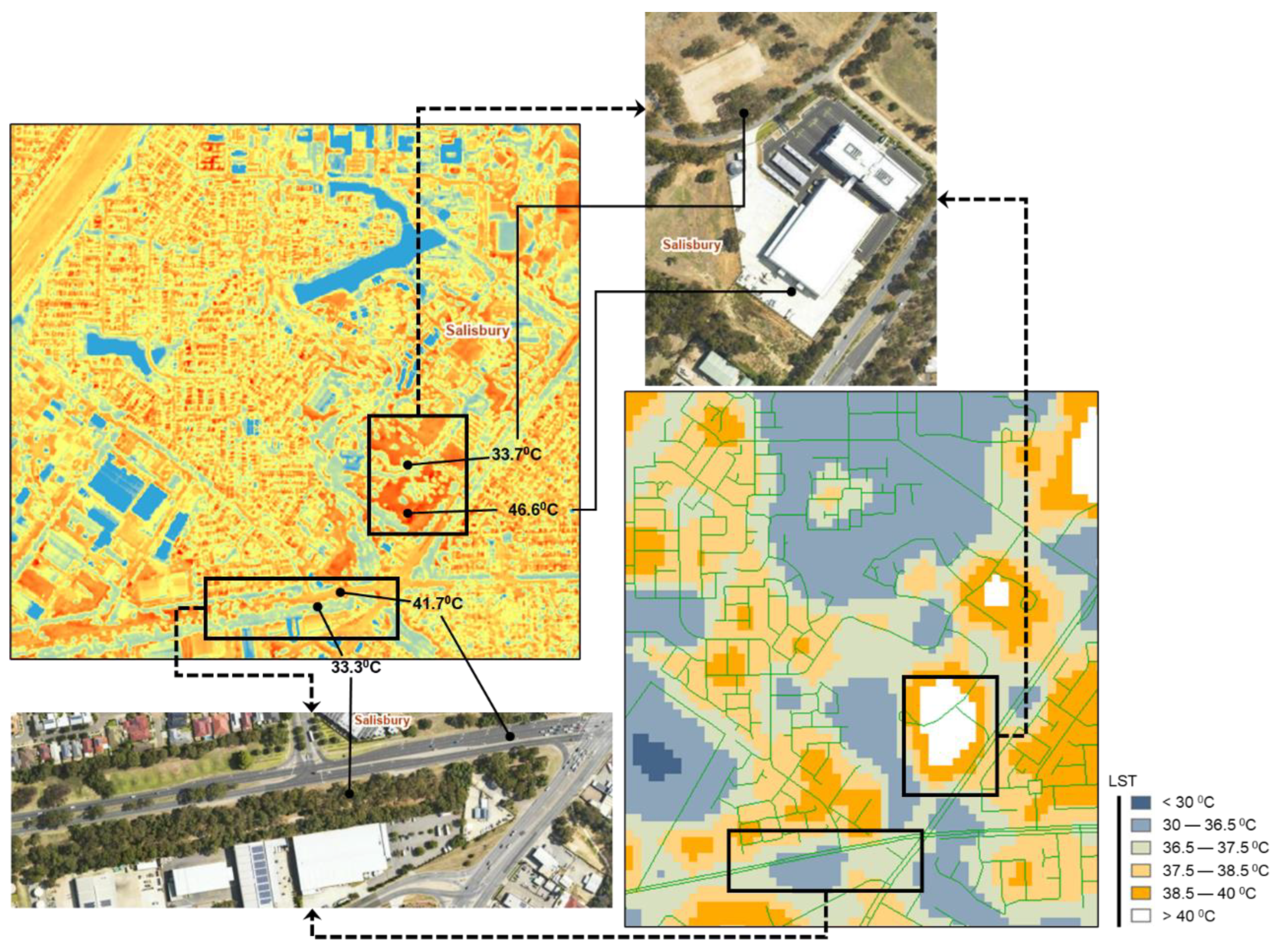
3. Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Yang, L.; Qian, F.; Song, D.-X.; Zheng, K.-J. Research on Urban Heat-Island Effect. Procedia Engineering 2016, 169, 11–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rashid, N.; Alam, J.A.M.M.; Chowdhury, M.A.; Islam, S.L.U. Impact of landuse change and urbanization on urban heat island effect in Narayanganj city, Bangladesh: A remote sensing-based estimation. Environmental Challenges 2022, 8, 100571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; He, X.; Yan, F.; Yu, L.; Bu, K.; Yang, J.; Chang, L.; Zhang, S. Mapping the Influence of Land Use/Land Cover Changes on the Urban Heat Island Effect—A Case Study of Changchun, China. Sustainability 2017, 9, 312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buo, I.; Sagris, V.; Burdun, I.; Uuemaa, E. Estimating the expansion of urban areas and urban heat islands (UHI) in Ghana: a case study. Natural Hazards 2021, 105, 1299–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jadraque Gago, E.; Etxebarria Berrizbeitia, S.; Pacheco Torres, R.; Muneer, T. Effect of Land Use/Cover Changes on Urban Cool Island Phenomenon in Seville, Spain. Energies 2020, 13, 3040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, P.S.-H.; Park, J. An Effect of Urban Forest on Urban Thermal Environment in Seoul, South Korea, Based on Landsat Imagery Analysis. Forests 2020, 11, 630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Kim, D.; Kim, G. Examining the Relationship between Land Use/Land Cover (LULC) and Land Surface Temperature (LST) Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI) Models: A Case Study of Seoul, South Korea. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2022, 19, 15926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Peng, F.; Zou, B. Spatiotemporal influences of land use/cover changes on the heat island effect in rapid urbanization area. Frontiers of Earth Science 2019, 13, 614–627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, S.; Wang, K.; Yang, S.; Li, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Fu, Y.; Liu, X.; Run, Y.; Chubwa, O.G.; et al. Warming Effort and Energy Budget Difference of Various Human Land Use Intensity: Case Study of Beijing, China. Land 2020, 9, 280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Huang, J.; Yang, X.; Fang, C.; Liang, Y. Quantifying the seasonal contribution of coupling urban land use types on Urban Heat Island using Land Contribution Index: A case study in Wuhan, China. Sustainable Cities and Society 2019, 44, 666–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, H.; Zhao, X.; Chen, F.; Wu, L. Using land use change trajectories to quantify the effects of urbanization on urban heat island. Advances in Space Research 2014, 53, 463–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, L.; Sun, S.; Song, C.; Li, J.; Xu, W.; Xu, Y. Understanding the spatiotemporal pattern of the urban heat island footprint in the context of urbanization, a case study in Beijing, China. Applied Geography 2021, 133, 102496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, B.; Fu, D.; Atkinson, P.M.; Zhang, X. Response of urban heat island to future urban expansion over the Beijing–Tianjin–Hebei metropolitan area. Applied Geography 2016, 70, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chun, B.; Guldmann, J.-M. Impact of greening on the urban heat island: Seasonal variations and mitigation strategies. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems 2018, 71, 165–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, Q.; Wu, Z.; Tan, J. The relationship between land surface temperature and land use/land cover in Guangzhou, China. Environmental Earth Sciences 2012, 65, 1687–1694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Zhang, S.W. ANALYSIS ON THE RELATIONSHIP BETWEEN THE PATTERN OF GREEN SPACES AND LAND SURFACE TEMPERATURE BASED ON NORMALIZED DIFFERENCE VEGETATION INDEX: A CASE STUDY IN CHANGCHUN CITY, CHINA. Fresenius Environ. Bull. 2015, 24, 2444–2451. [Google Scholar]
- Yue, W.; Xu, J.; Tan, W.; Xu, L. The relationship between land surface temperature and NDVI with remote sensing: application to Shanghai Landsat 7 ETM+ data. International Journal of Remote Sensing 2007, 28, 3205–3226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamali Maskooni, E.; Hashemi, H.; Berndtsson, R.; Daneshkar Arasteh, P.; Kazemi, M. Impact of spatiotemporal land-use and land-cover changes on surface urban heat islands in a semiarid region using Landsat data. International Journal of Digital Earth 2021, 14, 250–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, C.; Myint, S.W.; Kaplan, S.; Middel, A.; Zheng, B.; Rahman, A.; Huang, H.-P.; Brazel, A.; Blumberg, D.G. Understanding the Impact of Urbanization on Surface Urban Heat Islands—A Longitudinal Analysis of the Oasis Effect in Subtropical Desert Cities. Remote Sensing 2017, 9, 672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, Y.; Guldmann, J.-M.; Liu, D. Impacts of tree and building shades on the urban heat island: Combining remote sensing, 3D digital city and spatial regression approaches. Computers, Environment and Urban Systems 2021, 88, 101655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arshad, S.; Ahmad, S.R.; Abbas, S.; Asharf, A.; Siddiqui, N.A.; Islam, Z.u. Quantifying the contribution of diminishing green spaces and urban sprawl to urban heat island effect in a rapidly urbanizing metropolitan city of Pakistan. Land Use Policy 2022, 113, 105874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dissanayake, D.; Morimoto, T.; Ranagalage, M.; Murayama, Y. Land-Use/Land-Cover Changes and Their Impact on Surface Urban Heat Islands: Case Study of Kandy City, Sri Lanka. Climate 2019, 7, 99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, S.; Prior, J.; McGregor, G.; Shi, X.; Kinney, P. Urban heat: an increasing threat to global health. BMJ 2021, 375, n2467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piracha, A.; Chaudhary, M.T. Urban Air Pollution, Urban Heat Island and Human Health: A Review of the Literature. Sustainability 2022, 14, 9234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Singh, S.; Mall, R.K. Chapter 17 - Urban ecology and human health: implications of urban heat island, air pollution and climate change nexus. In Urban Ecology, Verma, P., Singh, P., Singh, R., Raghubanshi, A.S., Eds. Elsevier: 2020; pp. 317-334. [CrossRef]
- Conti, S.; Masocco, M.; Meli, P.; Minelli, G.; Palummeri, E.; Solimini, R.; Toccaceli, V.; Vichi, M. General and specific mortality among the elderly during the 2003 heat wave in Genoa (Italy). Environmental Research 2007, 103, 267–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, J.Y.; Shi, Y.; Lau, K.K.L.; Ng, E.Y.Y.; Ren, C.; Goggins, W.B. Urban heat island effect-related mortality under extreme heat and non-extreme heat scenarios: A 2010–2019 case study in Hong Kong. Science of The Total Environment 2023, 858, 159791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheridan, S.C.; Lee, C.C.; Allen, M.J. The Mortality Response to Absolute and Relative Temperature Extremes. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2019, 16, 1493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Xiang, Z.; Wang, W.; Chang, W.; Wang, Y. Impacts of strengthened warming by urban heat island on carbon sequestration of urban ecosystems in a subtropical city of China. Urban Ecosystems 2021, 24, 1165–1177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corumluoglu, O.; Asri, I. The effect of urban heat island on Izmir’s city ecosystem and climate. Environmental Science and Pollution Research 2015, 22, 3202–3211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, F.; Pang, H.; Guo, W. Impact of the urban heat island on residents’ energy consumption: a case study of Qingdao. IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science 2018, 121, 032026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Zhuang, Z.; Yang, F.; Yu, Y.; Xie, X. Urban morphology on heat island and building energy consumption. Procedia Engineering 2017, 205, 2401–2406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhou, Y.; Yu, S.; Jia, G.; Li, H.; Li, W. Urban heat island impacts on building energy consumption: A review of approaches and findings. Energy 2019, 174, 407–419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abuzar, M.; McAllister, A.; Whitfield, D.; Sheffield, K. Remotely-Sensed Surface Temperature and Vegetation Status for the Assessment of Decadal Change in the Irrigated Land Cover of North-Central Victoria, Australia. LAND 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Xu, G.; Coops, N.C.; Ciais, P.; Myneni, R.B. Satellite-observed changes in terrestrial vegetation growth trends across the Asia-Pacific region associated with land cover and climate from 1982 to 2011. International Journal of Digital Earth 2016, 9, 1055–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narisma, G.T.; Pitman, A.J. The Impact of 200 Years of Land Cover Change on the Australian Near-Surface Climate. Journal of Hydrometeorology 2003, 4, 424–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Deng, Q.; Zhou, Z.; Ren, Z.; Shan, X. Influence of land cover change on spatio-temporal distribution of urban heat island —a case in Wuhan main urban area. Sustainable Cities and Society 2022, 79, 103715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teimouri, R.; Ghorbani, R.; Karbasi, P.; Sharifi, E. Investigation of land use changes using the landscape ecology approach in Maragheh City, Iran. Journal of Environmental Studies and Sciences, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Zhang, Y. Urban Heat Island Analysis Using the Landsat TM Data and ASTER Data: A Case Study in Hong Kong. Remote Sensing 2011, 3, 1535–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yee, M.; Kaplan, J.O. Drivers of urban heat in Hong Kong over the past 116 years. Urban Climate 2022, 46, 101308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dihkan, M.; Karsli, F.; Guneroglu, A.; Guneroglu, N. Revisiting Urban Heat Island Effects in Coastal Regions: Mitigation Strategies for the Megacity of Istanbul. In Urban Heat Island (UHI) Mitigation: Hot and Humid Regions, Enteria, N., Santamouris, M., Eicker, U., Eds. Springer Singapore: Singapore, 2021; pp. 277-307. [CrossRef]
- CoS. About our City of Salisbury- quick facts. Availabe online: https://www.salisbury.sa.gov.au/council/about-our-city-of-salisbury/quick-facts (accessed on 26 April).
- GoogleMaps. Salisbury, South Australia. Availabe online: https://www.google.com/maps/place/Salisbury,+SA/@-34.8333696,138.6928723,11z/data=!4m6!3m5!1s0x6ab0b12e3cda0511:0x69869588a94a402a!8m2!3d-34.7602947!4d138.6188423!16zL20vMDZsM2Ri (accessed on 26 April).
- PlanSA. Development plan map. Availabe online: https://plan.sa.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0012/744978/Consultation_change_maps_-_Salisbury.pdf (accessed on 26 March).
- USGS. Landsat levels of processing. Availabe online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-levels-processing (accessed on 26 April).
- USGS. Earth explorer. Availabe online: https://earthexplorer.usgs.gov/ (accessed on 15 Jun).
- BOM. Climate data online. Availabe online: http://www.bom.gov.au/climate/data/index.shtml (accessed on 12 Jan).
- DEW. Urban heat mapping viewer. Availabe online: http://spatialwebapps.environment.sa.gov.au/urbanheat/?viewer=urbanheat&runWorkflow=StartupResilientEast (accessed on 12 June).
- USGS. Using the USGS Landsat level-1 data product. Availabe online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/using-usgs-landsat-level-1-data-product (accessed on 26 April).
- USGS. Landsat Normalized Difference Vegetation Index. Availabe online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-normalized-difference-vegetation-index#:~:text=In%20Landsat%204%2D7%2C%20NDVI,Band%205%20%2B%20Band%204). (accessed on 26 April).
- USGS. Landsat collection 2 surface temperature. Availabe online: https://www.usgs.gov/landsat-missions/landsat-collection-2-surface-temperature (accessed on 26 Apri).
- Avdan, U.; Jovanovska, G. Algorithm for Automated Mapping of Land Surface Temperature Using LANDSAT 8 Satellite Data. Journal of Sensors 2016, 2016, 1480307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajib, M.Q.U.; Wang, T. Estimation of land surface temperature in an agricultural region of bangladesh from landsat 8: Intercomparison of four algorithms. Sensors (Basel) 2020, 20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahani, N. Assessment of spatio-temporal changes of land surface temperature (LST) in Kanchenjunga Biosphere Reserve (KBR), India using Landsat satellite image and single channel algorithm. Remote Sensing Applications: Society and Environment 2021, 24, 100659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- USGS. What are the band designations for the Landsat satellites? Availabe online: https://www.usgs.gov/faqs/what-are-band-designations-landsat-satellites (accessed on 26 April).
- NASA. Measuring vegetation (NDVI & EVI). Availabe online: https://earthobservatory.nasa.gov/features/MeasuringVegetation (accessed on 24 Feb).
- Garai, S.; Khatun, M.; Singh, R.; Sharma, J.; Pradhan, M.; Ranjan, A.; Rahaman, S.M.; Khan, M.L.; Tiwari, S. Assessing correlation between Rainfall, normalized difference Vegetation Index (NDVI) and land surface temperature (LST) in Eastern India. Safety in Extreme Environments 2022, 4, 119–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Chatterjee, S.; Weng, Y. 2 - Characterizing thermal fields and evaluating UHI effects. In Urban Heat Island Modeling for Tropical Climates, Khan, A., Chatterjee, S., Weng, Y., Eds. Elsevier: 2021; pp. 37-67. [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




