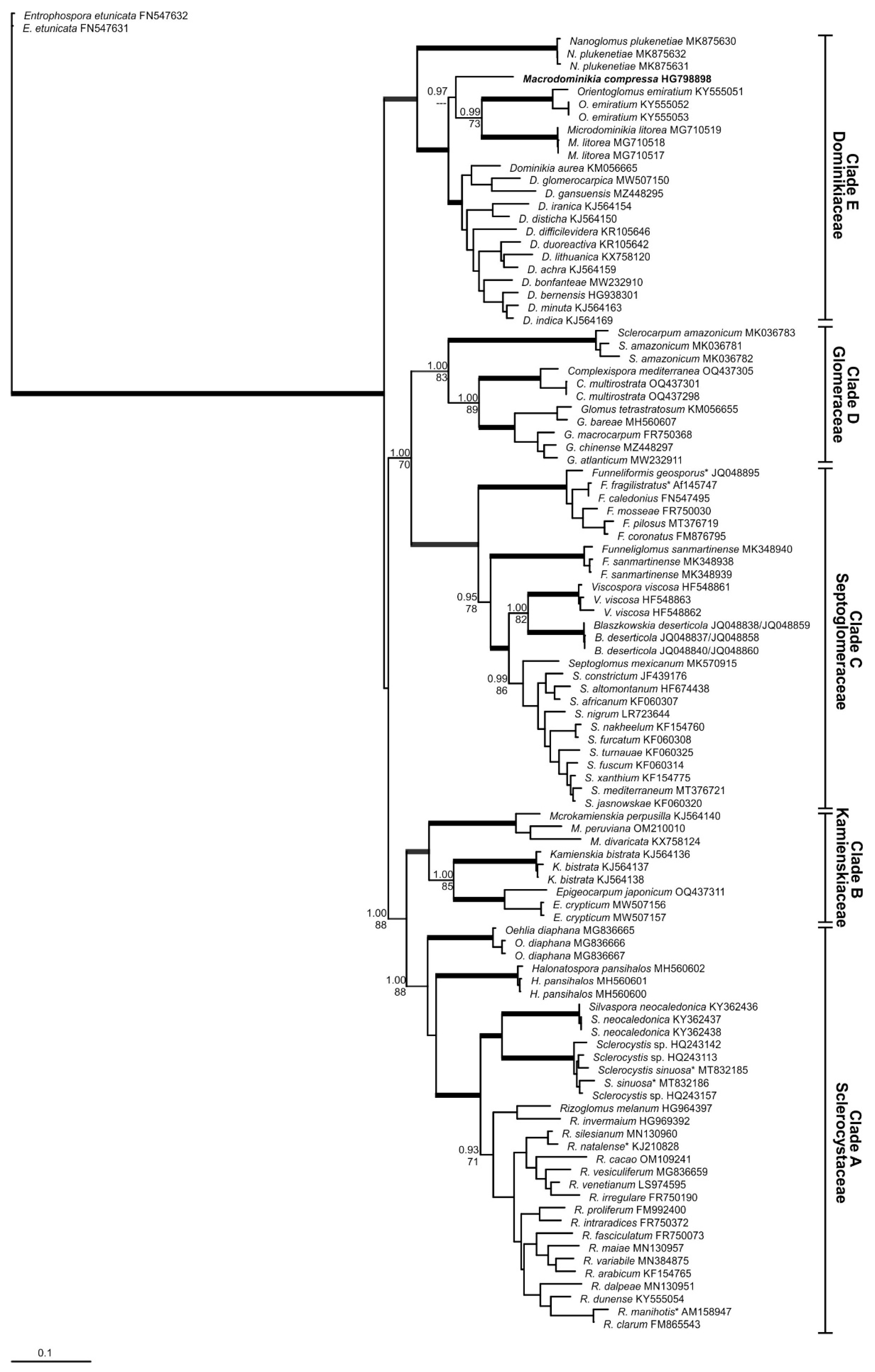
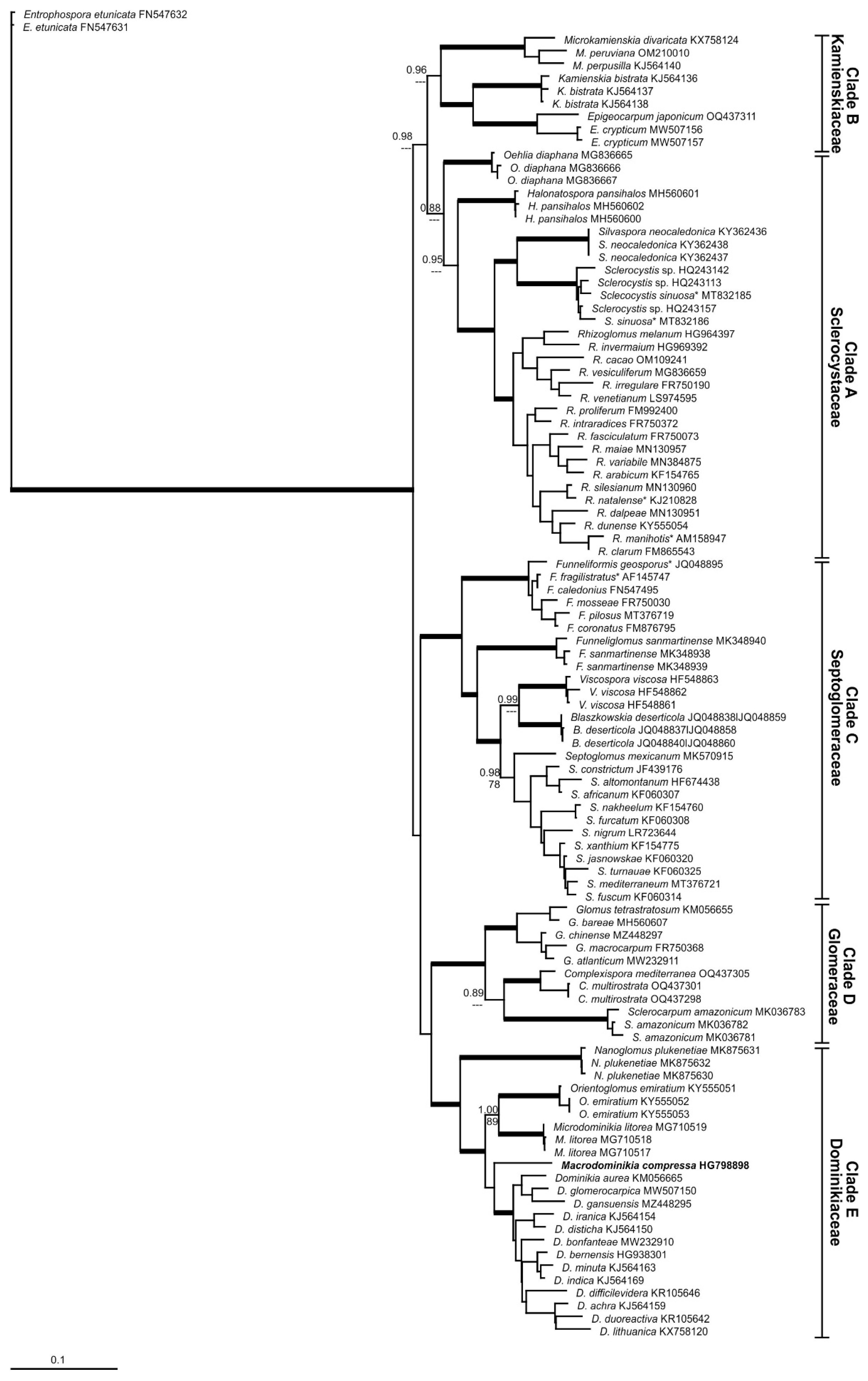
3.2. Taxonomy
Glomerales J.B. Morton and Benny, emend. Błaszk., B.T. Goto, and Magurno, Mycotaxon 37: 473. 1990.
MycoBank MB 90425
Description: Spores formed in soils or in roots, terminally on or intercalary in hyphae, either singly, in loose spore clusters, or in multiple-spored loose to compact sporocarps, when compact spores are randomly distributed or organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Compact sporocarps with or without peridium, and with or without intrasporocarpic hyphal gleba. Spores with one mono-to-multiple layered wall. Wall of the subtending hyphae (SH) conspicuously continuous and concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color than the spore wall; SH funnel-shaped, cylindrical or constricted; straight, curved or flared; pore at spore base open, or closed by a bridging, straight or curved septum or by introverted wall thickening, or SH closed at some distance from the spore base by a septum or plug-like structure forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type family: Glomeraceae Piroz. & Dalpé
Other families: Septoglomeraceae Oehl et al., Sclerocystaceae Oehl et al., Dominikiaceae G.A. Silva et al., Kamienskiaceae G.A. Silva et al.
Type genus: Glomus Tul. & C. Tul.
Other genera: Sclerocarpum B.T. Goto et al., Complexispora Błaszk. et al., Simiglomus Sieverd. et al., Blaszkowskia G.A. Silva & Oehl, Septoglomus Sieverd. et al., Funneliformis C. Walker & A. Schüssler, Funneliglomus Corazon-Guivin et al., Viscospora Sieverd. et al., Rhizoglomus Sieverd. et al., Oehlia Błaszk. et al., Sclerocystis Berk. & Broome, Halonatospora Błaszk. et al., Kamienskia et al. Błaszk. et al., Microkamienskia G.A. Silva et al., Dominikia Błaszk. et al., Macrodominikia Oehl et al., Microdominikia Oehl et al., Nanoglomus Corazon-
Guivin et al., Orientoglomus G.A. Silva et al., Epigeocarpum Błaszk., et al., Silvaspora Błaszk., et al., Parvocarpum Magurno.
Glomeraceae Piroz. & Dalpé emend. Oehl, G.A. Silva & Sieverd., Symbiosis 7: 19. 1989.
MycoBank 82026
Emended description: Spores formed in soil and sometimes in roots, terminally on or intercalary in hyphae, either singly, in loose spore clusters, or in multiple-spored loose to compact sporocarps, when compact, then spores are randomly distributed, but not organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Compact sporocarps with or without peridium, and with or without intrasporocarpic hyphal gleba. Spores with one (mono-)bi-to-multiple layered wall. SH wall conspicuously continuous and concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color than the spore wall; SH cylindrical or slightly funnel-shaped or slightly constricted; straight, curved or flared; pore at spore base open, or closed at spore base by a straight or curved septum or by introverted wall thickening, or at some distance from the spore base by a bridging septum arising from the SH wall; forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type genus: Glomus Tul. & C. Tul.
Other genera: Sclerocarpum B.T. Goto et al., Simiglomus Sieverd. et al., Complexispora Błaszk. et al.
Glomus Tul. & C. Tul., Giorn. Bot. Ital., Anno 1, 2(7–8): 63. 1845.
MycoBank 20244
Emended description: Spores formed singly within soil or sometimes roots, in disorganized, multiple-spored loose spore clusters or in compact sporocarps; compact, but not radially organized around a central hyphal plexus, without or with peridium, spores are either in sporocarp, or organized. Spores with a mono-to-multiple layered wall. SH wall conspicuously continuous and concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color than the spore wall. Spore pore closure often by introverted wall thickening, sometimes supported by a short bridging septum, rarely open. Forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Glomus macrocarpum Tul & C. Tul., Giorn. Bot. Ital., Anno 1, 2(7–8): 63. 1845.
MycoBank MB 240247
≡ Endogone macrocarpa (Tul. & C. Tul.) Tul. & C. Tul., Fungi Hypog.: 182. 1851.
MycoBank MB 218537
≡ Endogone guttulata E. Fisch., Ber. Schweiz. Bot. Ges. 32: 13. 1923.
≡ Endogone nuda Petch., Ann. R. Bot. Gdns Peradeniya 9: 322. 1925.
≡ Endogone pampaloniana Bacc., Nuovo Giorn. Bot. Ital., n.s. 10: 90. 1903.
≡ Paurocotylis fulva var. zelandica Cooke, Grevillea 8: 59. 1879.
Simiglomus Sieverd., G.A. Silva & Oehl, Mycotaxon 116: 104. 2011.
MycoBank MB 518435
Description: Spores formed in soil or in roots, terminally on or intercalary in hyphae, in small to multiple-spored loose clusters, randomly distributed, but not organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Loose sporocarps generally without peridium, and without intrasporocarpic hyphal gleba. Spores with one mono-to-multiple layered wall. SH wall conspicuously continuous and concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color than the spore wall; SH cylindrical or slightly to rarely slightly funnel-shaped or constricted; straight, curved or flared; pore open at spore base, but often in some distance by one to multiple bridging, straight to curved, septum, not supported by introverted wall thickening; forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Simiglomus hoi (S.M. Berch & Trappe) G.A. Silva, Oehl & Sieverd.
MycoBank MB 518461
Basionym: Glomus hoi S.M. Berch & Trappe, Mycologia 77: 654. 1985.
Sclerocarpum B.T. Goto, Błaszk., Niezgoda, Kozłowska & Jobim, Mycol. Progr. 18(3): 375. 2019.
MycoBank MB 828316
Description: Producing spores in scleroid, epigeous and sub-hypogeous, light- to dark-colored unorganized sporocarps, very hard to break, with a peridium and a gleba comprising hyphae and glomoid glomerospores (= spores) with a single SH; spores hyaline; globose to subglobose; small, < 100 μm diam; frequently ovoid; Spore wall composed a few smooth layers, of which one layer laminate and much thicker than the outermost layer, forming the spore surface. SH funnel-shaped with a wall continuous with the spore wall; pore narrow, open or occluded by thickening of the SH wall, or (rarely) occluded by a straight or slightly invaginated septum continuous with some innermost laminae of spore wall layer 2; septum, positioned at the spore base.
Type species: Sclerocarpum amazonicum B.T. Goto, Błaszk., Niezgoda, Kozłowska & Jobim, Mycol. Progr. 18: 377. 2019.
MycoBank MB 828317
Specific morphological observation on Sclerocarpum
Especially
Sclerocarpum shows well-defined, outstanding morphological characteristics of their hard sporocarps, their spores, which are exclusively formed within these sporocarps and of their funnel-shaped subtending hyphae including a pronounced wall-thickening at the spore base at the point of pore closure. Three
Glomus species described in the past, clearly combine with all these characteristics. These are
G. convolutum,
G. pellucidum and
G. segmentatum [
31,
32,
33]. Consequently, these species are hereafter transferred to the genus
Sclerocarpum.
Sclerocarpum convolutum (Gerd. & Trappe) Oehl, Sieverd. & G.A. Silva, comb. nov.
MycoBank MB 855472
Basionym: Glomus convolutum Gerd. & Trappe, Mycol. Mem. 5: 42. 1974. Mycological Memoirs 5: 42. 1974.
MycoBank MB 314590
Sclerocarpum segmentatum (Trappe, Spooner & Ivory) Oehl, Sieverd. & G.A. Silva, comb. nov.
MycoBank MB 855473
Basionym: Glomus segmentatum Trappe, Spooner & Ivory, Trans. Br. Mycol. Soc. 73: 362. 1979.
MycoBank MB 314610
Sclerocarpum pellucidum (McGee & Pattinson) Oehl, Sieverd. & G.A. Silva, comb. nov.
MycoBank MB 855474
Basionym: Glomus pellucidum McGee & Pattinson, Austral. Syst. Bot. 15: 120. 2002.
MycoBank MB 374910
Complexispora Błaszk., B.T. Goto, Niezgoda & Magurno, Mycol. Progr. 22(5, no. 34): 7. 2023.
MycoBank MB 847607
Description: Producing hypogeous glomoid spores singly and in clusters. Spores four to six layers, of which two consist of tightly adherent sublayers (laminae). SH cylindrical to funnel-shaped, concolorous with the spore wall layer, with a wall composed of layers continuous with all spore wall layers, except for the innermost layer. Pore closed by a septum continuous with the innermost spore wall layer, occasionally also by a septum connecting the inner surfaces of the main structural laminate spore wall layer. Forming mycorrhiza with vesicles and arbuscules staining dark in Trypan blue.
Type species: Complexispora multistratosa Błaszk., B.T. Goto, Niezgoda & Magurno, Mycol. Progr. 22(5, no. 34): 6. 2023.
MycoBank MB 847608
Septoglomeraceae Oehl, G.A. Silva, Sieverd. fam. nov.
Mycobank MB 855466
Description: Spores formed in soil and sometimes in roots, terminally on or intercalary in hyphae, either singly, in loose spore clusters or sporocarps. Compact sporocarps with or without peridium, without intrasporocarpic hyphal gleba. Spores with one mono-to-multiple layered wall. SH wall conspicuously continuous and concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color than the spore wall; SH pronounced funnel-shaped, slightly funnel-shaped, cylindrical or constricted, rarely inflated; straight, curved or flared; forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type genus: Septoglomus Sieverd. et al.
Other genera: Funneliformis C. Walker & A. Schüssler, Funneliglomus Corazon-Guivin et al., Viscospora Sieverd. et al., Blaszkowskia G.A. Silva & Oehl
Type species: Septoglomus constrictum (Trappe) Sieverd.
Septoglomus Sieverd., G.A. Silva & Oehl, Mycotaxon 116: 105. 2011.
MycoBank MB 518436
Emended description: Spores formed in soil and sometimes in roots, terminally on or intercalary in hyphae, either singly, in loose spore clusters. Spores with one mono-to-multiple layered wall. SH wall conspicuously continuous and concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color than the spore wall; SH constricted to cylindrical, rarely slightly funnel-shaped, or inflated in some distance to the spore base; straight, curved or flared; pore closed by a broad, pronounced septum or a plug at spore base or in some distance from spore; forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Septoglomus constrictum (Trappe) Sieverd., G.A. Silva & Oehl. Mycotaxon 116: 105. 2011.
MycoBank MB 518462
Basionym: Glomus constrictum Trappe, Mycotaxon 6: 361. 1977.
MycoBank MB 314589
≡ Funneliformis constrictus (Trappe) C. Walker & A. Schüssler, The Glomeromycota – a species list: 14. 2010.
MycoBank MB 542904
Blaszkowskia G.A. Silva & Oehl, Mycol. Progr. 22(11, no. 74): 5. 2023.
MycoBank MB 847414
Description: Spores light yellow to yellow brown to dark brown or dark red brown, generally 20–200 μm, with > 1 spore wall layer; SH funnel-shaped, rarely constricted, thick-walled; spore pores might be open at the spore base, but often closed by one to several thin septa within SH at some distance from the spore base. SH thicker-walled than mycelium hyphae and pigmented over long distances and within the whole spore clusters, including intraradical spore formations (> 100 μm).
Type species: Blaszkowskia deserticola (Trappe, Bloss & J.A. Menge) Oehl & G.A. Silva. Mycol. Progress 22 (11, no. 74): 5. 2023.
MycoBank MB 847415
Basionym: Glomus deserticola Trappe, Bloss & J.A. Menge, Mycotaxon 20: 123. 1984.
MycoBank MB 106847
≡ Septoglomus deserticola (Trappe, Bloss & J.A. Menge) G.A. Silva, Oehl & Sieverd. Mycotaxon 116: 106. 2011.
MycoBank MB 518463
Funneliglomus Corazon-Guivin, G.A. Silva & Oehl, Sydowia 71: 19. 2019.
MycoBank MB 829266
Description: Spores formed in soil or rarely in roots, terminally on or intercalary in hyphae, singly or in small clusters; the conspicuous SH is concolorous with spore wall color (or slightly lighter in color), SH is species-specific and funnel-shaped to slightly funnel-shaped, to rarely cylindrical or slightly constricted, or inflated in some distance to the spore base; straight, curved or flared. Pore regularly closed by a conspicuous septum that species-specifically may arise from the structural wall layer, from an additional adherent innermost, (semi-)flexible lamina, or from both but not by introverted wall thickening, which is lacking. Forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Funneliglomus sanmartinense Corazon-Guivin, G.A. Silva & Oehl. Sydowia 71: 21. 2019
MycoBank MB 829267 (Funneliglomus sanmartinensis), MycoBank MB 830216 (corrected to Funneliglomus sanmartinense by Mycobank after publication)
Funneliformis C. Walker & A. Schüssler, emend. Oehl, G.A. Silva & Sieverd., The
Glomeromycota – a species list with new families and genera: 13. 2010.
MycoBank MB 542894
Description: Spores formed within soil or rarely in roots, singly or sometimes in sporocarps with a few to several spores per sporocarp only; the conspicuous SH is concolorous with spore wall color (or slightly lighter in color), SH is species-specific and generally pronounced funnel-shaped to slightly funnel-shaped to rarely cylindrical. Wall differentiation and pigmentation may continue over long distances from the spore base (often > 50–250 μm), then mycelium may become hyaline. Pore regularly closed by a conspicuous septum that species-specifically arises from the structural wall layer, from an additional adherent innermost, (semi-)flexible lamina, or from both but not by introverted wall thickening, which is lacking. Forming typical vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhiza, with mycorrhizal structures that stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Funneliformis mosseae (T.H. Nicolson & Gerd.) C. Walker & A. Schüssler, The Glomeromycota – a species list with new families and genera: 13. 2010.
MycoBank MB 542895
Basionym: Endogone mosseae T.H. Nicolson & Gerd., Mycologia 60: 314. 1968.
MycoBank MB 330367
≡ Glomus mosseae (T.H. Nicolson & Gerd.) Gerd. & Trappe, Mycol. Mem. 5: 40. 1974.
MycoBank MB 314604
Viscospora Sieverd., Oehl & G.A. Silva, Mycotaxon 116: 108: 2011.
MycoBank MB 518439
Emended description: Spores hyaline to white or subhyaline, terminally or intercalary on pronounced funnel-shaped to slightly funnel-shaped to cylindrical or inflated subtending hyphae, hyaline, singly, or in loose clusters with up to 100 spores per cluster. Outer layer is evanescent, viscose, gathering large amounts of debris during degradation. SWL2 is persistent, unite to laminate, and might stain whitish yellow to yellowish, when exposed to Melzer's reagent. SH straight or recurved, sometimes folded to rarely flared. Regularly, one to several straight to curved septa are formed in the SH close to the spore base or in a distance of up to 10–100 μm to the spore base. The spore wall layers continue in the SH, with similar to slightly smaller thickness towards the mycelium hyphae.
Type species: Viscospora viscosa (T.H Nicolson) Sieverd., Oehl & G.A. Silva. Mycotaxon 116: 108. 2011.
MycoBank MB 518471
Basionym Glomus viscosum T.H. Nicolson, Mycol. Res. 99: 1502. 1995.
MycoBank MB 413125
≡ Septoglomus viscosum (T.H. Nicolson) C. Walker, D. Redecker, D. Stiller & A. Schüßler: Mycorrhiza 23: 524. 2013
MycoBank MB 550089
Sclerocystaceae Oehl, G.A. Silva, & Sieverd. fam. nov.
MycoBank MB 855467
Description: Spores formed in loose sporocarps, in clusters, or singly in soil, and frequently in roots. When formed in compact sporocarps, spores can be randomly distributed on SH of different length, or well-organized around a central plexus of hyphae. SH wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. SH cylindrical or seldom slightly funnel shaped at spore base. Pore at spore base open, or closed by a septum. Spore walls show rarely one, to generally two to three (and up to five) distinct layers, of which one or several of the outermost may separate when pressure is applied to spores. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae, whose fungal structures stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type genus: Sclerocystis Berk. & Broome
Other genera: Oehlia Błaszk. et al., Rhizoglomus Sieverd. et al., Halonatospora Błaszk. et al., Silvaspora Błaszk. et al., Parvocarpum Magurno
Sclerocystis Berk. & Broome, J. Linn. Soc., Bot. 14 (73 & 74): 137. 1873.
MycoBank MB20512
Emended description: Spores formed in compact sporocarps, in soils or roots, in cultures sometimes also singly or in loose clusters. When formed in compact sporocarps, then spores are regularly organized, arising radially around a central plexus of hyphae. SH wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. SH funnel-shaped to cylindrical at spore base. Pore at spore base regularly closed by a fine septum, which is formed within the small pore channel within the spore base. Spore walls show more than one, and generally two or rarely > two distinct layers. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae, whose fungal structures stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Sclerocystis coremioides Berk. & Broome, J. Linn. Soc., Bot. 14(no. 74): 137 (1873) [1875]
MycoBank MB 213141
≡ Glomus coremioides (Berk. & Broome) D. Redecker & J.B. Morton
MycoBank MB 464612
Rhizoglomus Sieverd., G.A. Silva & Oehl, Mycotaxon 129: 377. 2015.
MycoBank MB 803191
Description: Spores formed in loose sporocarps, in clusters, or singly, in soil and frequently also in roots. When formed in compact sporocarps, they are not organized around a central plexus of hyphae. SH wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. SH cylindrical or seldom slightly funnel shaped at spore base. Pore at spore base regularly open, rarely closed by a septum. Spore walls show more than one, and generally two to three (and up to five) distinct layers, of which one or several of the outermost may separate when pressure is applied to spores. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae, whose fungal structures stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Rhizoglomus intraradices (N.C. Schenck & G.S. Sm.) Sieverd., G.A. Silva & Oehl, Mycotaxon 129(2): 378 (2015) [2014]
MycoBank MB 803192
Basionym: Glomus intraradices N.C. Schenck & G.S. Sm., Mycologia 74: 78. 1982.
MycoBank MB 110704
≡ Rhizophagus intraradices (N.C. Schenck & G.S. Sm.) C. Walker & A. Schussler, The Glomeromycota: 19. 2010.
MycoBank MB 542910
Oehlia Błaszk., Kozłowska, Niezgoda, B.T. Goto & Dalpe, Nova Hedwigia 107: 507. 2018.
MycoBank MB 824689
Emended description: Spores formed in loose sporocarps, in clusters, or singly, in soil and frequently also in roots. When formed in compact sporocarps, they are not organized around a central plexus of hyphae. SH wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. SH cylindrical or seldom slightly funnel shaped at spore base. Pore at spore base regularly closed by a septum. Spore wall shows more than one, and generally two to three (and up to five) distinct layers. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae, whose fungal structures stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Oehlia diaphana (J.B.Morton & C.Walker) Błaszk., Kozłowska & Dalpe, Nova Hedwigia 107(3-4): 507 (2018)
MycoBank MB 824693
Basionym: Glomus diaphanum J.B.Morton & C.Walker. Mycotaxon 21: 433, 1984.
MycoBank MB 106161
Parvocarpum Magurno, MycoKeys 107: 283. 2024.
MycoBank MB 853558
Description: Producing glomoid spores mainly in small sporocarps, irregularly around a small central plexus of interwoven, intrasporocarpic hyphae, or singly in soils. SH generally short and cylindrical, often breaking at the spore base during sporocarp degradation. Pore closed by introverted wall thickening at the spore base, and additionally by a septum arising from the laminated wall layer and/or an additional flexible inner layer.
Type species: Parvocarpum badium (Oehl, Redecker & Sieverd.) Magurno, MycoKeys 107: 284. 2024
MycoBank MB 853560
Basionym: Glomus badium Oehl, D. Redecker & Sieverd., J. Appl. Bot. Food Qual. 79: 39. 2005.
MycoBank MB 341387
≡ Funneliformis badius (Oehl, D. Redecker & Sieverd.) C. Walker & A. Schüssler, The Glomeromycota – a species list: 13. 2010.
MycoBank MB 541897
Silvaspora Błaszk., Niezgoda, B.T. Goto, Crossay & Magurno, Frontiers in Microbiology 12 (no. 655910): 14. 2021.
MycoBank 838881
Description: Forming pigmented spores with 2-3 wall layers, of which only layer 1, forming the spore surface, is impermanent and hyaline to brightly colored. SH colored similarly to the spore wall, cylindrical, slightly funnel-shaped, or constricted at the spore base, with a pore occluded due to thickening of that SH wall layer continuous with the laminate spore wall layer, rarely slightly open. Forming mycorrhiza with arbuscules, vesicles, and hyphae staining dark in trypan blue.
Type species: Silvaspora neocaledonica (D. Redecker, Crossay & Cilia) Błaszk., Niezgoda, B.T. Goto, Crossay & Magurno, Frontiers in Microbiology 12(no. 655910): 14 (2021)
MycoBank MB 838882
≡ Rhizoglomus neocaledonicum (D. Redecker, Crossay & Cilia) Oehl, Turrini & Giovann.
MycoBank MB 827095
Basionym: Rhizophagus neocaledonicus D. Redecker, Crossay & Cilia, Mycological Progress 17: 739. 2018.
MycoBank MB 820537
Halonatospora Błaszk., Niezgoda, B.T. Goto & Kozłowska, Botany 96(11): 743. 2018.
MycoBank MB 826963
Description: Spores formed in loose clusters, or singly, in soil and frequently in roots. When formed in sporocarps, they are not organized around a central plexus of hyphae. SH wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. Outer spore wall layer strongly swells in PVLG, forming a halo with radiate columns. SH cylindrical or slightly flared, sometimes slightly constricted at spore base, straight or slightly curved. Pore open or closed by a septum at spore base. Spore wall shows more than one, and generally two to three (and up to five) distinct layers. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae, whose fungal structures stain blue to dark blue in trypan blue.
Type species: Halonatospora pansihalos (S.M. Berch & Koske) Błaszk., Niezgoda, B.T. Goto & Kozłowska, Can. J. Bot. 96(11): 743 (2018)
MycoBank MB 826964
Basionym: Glomus pansihalos S.M. Berch & Koske. Mycologia 78: 832, 1986.
MycoBank MB 358213
Kamienskiaceae G.A. Silva, Sieverd. & Oehl
MycoBank MB 855468
Description: Spores hypogeous and/or intraradical, produced in loose clusters to compact sporocarps, and never organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Spores hyaline, small, up to 50 μm diam. when globose. Spore wall with two permanent, smooth layers, of which one may stain in Melzer’s reagent. The structural laminate layer is layer 1 or 2. SH cylindrical to funnel-shaped with an open pore. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae staining dark in trypan blue.
Type genus: Kamienskia Błaszk. et al.,
Other genus: Microkamienskia Corazon-Guivin, G.A. Silva & Oehl, Epigeocarpum Błaszk., B.T. Goto, Jobim, Niezgoda & Marguno
Kamienskia Błaszk., Chwat & Kovács, Nova Hedwigia 100(1-2): 230. (2014) [2015].
MycoBank MB 808260
Emended description: Spores hypogeous and/or intraradical, produced in loose clusters to compact, but fast degrading sporocarps, but never organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Spores hyaline, small, up to 50 μm diam. when globose. Spore wall with two permanent, smooth layers. The structural laminate layer might be layer 1 or 2. SH regularly funnel-shaped with an open pore. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae staining dark in trypan blue.
Type species: Kamienskia bistrata (Błaszk., D. Redecker, Koegel, Symanczik, Oehl & Kovács) Błaszk., Chwat & Kovács, Nova Hedwigia 100(1-2): 230. (2014) [2015].
MycoBank MB 808261
Basionym: Glomus bistratum Błaszk., D. Redecker, Koegel, Symanczik, Oehl & Kovács, Botany 87: 267. 2009.
MycoBank MB 512540
Microkamienskia Corazon-Guivin, G.A. Silva & Oehl, Nova Hedwigia 109: 359. 2019.
MycoBank MB 830814
Description: Spores hypogeous and/or intraradical, produced in loose clusters to compact, but fast degrading sporocarps, but never organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Spores hyaline, small, up to 50 μm diam. when globose. Spore wall with two permanent, smooth layers, of which one may stain in Melzer’s reagent. The structural laminate layer might be layer 1 or 2. SH cylindrical to rarely slightly funnel-shaped with an open pore. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae staining dark in trypan blue.
Type species: Microkamienskia perpusilla (Błaszk. & Kovács) Corazon-Guivin, G.A. Silva & Oehl. Nova Hedwigia 109: 361. 2019.
MycoBank MB 830815
Basionym: Glomus perpusillum Błaszk. & Kovács. Mycologia 101: 249. 2009.
MycoBank MB 512346
≡ Kamienskia perpusilla (Błaszk. & Kovács) Błaszk., Chwat & Kovács. Nova Hedwigia 100: 231. 2015-
MycoBank MB 808264
Epigeocarpum Błaszk., B.T. Goto, Jobim, Niezgoda & Marguno, Frontiers in Microbiology 12 (no. 655910): 10. 2021.
MycoBank MB 838879
Description: Spores hyaline to light yellow, formed in compact, unorganized sporocarps. Spores have 2–3 wall layers, laminate layer usually transferring into a crown-like structure due to contracting in spores crushed in PVLG and PVLG + Melzer’s reagent. The channel connecting the lumen of the SH with the interior of spores is closed by a septum usually positioned at half the thickness of the laminate layer; SH funnel-shaped, SH lumen gradually narrowing in maturing spores due to internal thickening of the laminate wall layer.
Type species: Epigeocarpum crypticum Jobim, Błaszk., Niezgoda, Magurno & B.T. Goto, Frontiers Microbiol. 12(no. 655910): 14. 2021.
MycoBank MB 838880
Dominikiaceae G.A. Silva, Sieverd. & Oehl
MycoBank MB 855469
Description: Spores hypogeous and/or intraradical, produced in loose clusters to compact sporocarps, but never organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Spores hyaline to creamy or yellow to yellow brown; spore wall with one to regularly two, or > 2 layers. SH wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. Spore pore often closed at spore base by a thin bridging septum, sometimes supported by a certain degree of introverted wall thickening, rarely continuing in the SH for a short distance (2-10 μm). Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae staining dark in trypan blue.
Type genus: Dominikia Błaszk. et al.,
Other genera: Macrodominikia Oehl et al., Microdominikia Oehl et al., Nanoglomus Corazon-Guivin et al., Orientoglomus G.A. Silva et al.
Dominikia Błaszk., Chwat & Kovács, Nova Hedwigia 100(1-2): 228. (2014) [2015].
MycoBank MB 808255
Emended description: Spores hypogeous and/or intraradical, produced in loose clusters to compact sporocarps but never organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Spores hyaline to creamy or yellow to yellow brown, small, up to 70 μm diam; spore wall with one to regularly two, or > 2 layers. SW wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. Spore pore often closed at spore base by a thin bridging septum, sometimes supported by a certain degree of introverted wall thickening, rarely continuing in the SH for a short distance. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae staining dark in trypan blue.
Type species: Dominikia minuta (Błaszk., Tadych & Madej) Błaszk., Chwat & Kovács, Nova Hedwigia 100: 230. (2014) [2015].
MycoBank MB 808256
Basionym: Glomus minutum Błaszk., Tadych & Madej. Mycotaxon 76: 189. 2000.
Macrodominikia Oehl, Sieverd. & G.A. Silva, gen. nov.
MycoBank 855470
Description: Spores hypogeous and/or intraradical, produced singly or in loose clusters to loose sporocarps but never organized around a central plexus of hyphae. Spores creamy to yellow to yellow brown, generally 70-110 μm diam; spore wall with one to regularly two, or > 2 layers. SH wall continuous with the spore wall, and for a certain distance concolorous with the spore wall, or slightly lighter in color. Spore pore often closed at spore base by a thin bridging septum, supported by a large degree of introverted wall thickening, continuing in the SH for 10-50 μm distance, forming an irregular, tortuous pore channel. Forming vesicular-arbuscular mycorrhizae staining dark in trypan blue.
Etymology: Macro-, -dominikia, referencing to the spores, which are larger than known hitherto for other genera in the Dominikiaceae
Type species: Macrodominikia compressa (Sieverd., Oehl, Palenz., Sánchez-Castro & G.A. Silva) Oehl, Siev. & G.A. Silva. comb. nov.
MycoBank MB 855471
Basionym: Glomus compressum Błaszk., Tadych & Mad Sieverd., Oehl, Palenz., Sánchez-Castro & G.A. Silva. Nova Hedwigia 99: 433. 2014.
MycoBank MB 807530
≡ Dominikia compressa (Sieverd., Oehl, Palenz., Sánchez-Castro & G.A. Silva) Oehl, Palenz., Sánchez-Castro & G.A. Silva. Nova Hedwigia. 101: 71. (2014) [2015]
MycoBank MB 809861
Microdominikia Oehl, Corazon-Guivin & G.A. Silva, Mycological Progress 18(12): 1400. 2019.
MycoBank MB 831098
Description: Spores formed singly or in clusters in soils or rarely in roots, terminally or intercalary on SH, globose to subglobose, generally hyaline to subhyaline, 10–45 μm in diameter, rarely egg-shaped or irregular, 25–50 × 20–35 μm, with a permanent outer spore wall layer. SH straight or recurved, usually funnel-shaped, more rarely cylindrical, rarely slightly constricted at the spore base. Spore pores open at the spore base, but closed within SH at some distance.
Type species: Microdominikia litorea (Błaszk. & Kozłowska) Oehl, Corazon-Guivin & G.A. Silva, Mycological Progress 18 (12): 1400 (2019)
MycoBank MB 831099
Basionym: Dominikia litorea Błaszk. & Kozłowska, Phytotaxa 338(3): 246 (2018)
MycoBank MB 823832
Nanoglomus Corazon-Guivin, G.A. Silva & Oehl, Mycological Progress 18(12): 1398. 2019.
MycoBank MB 831096
Description: Nanoglomus species differentiate small spores, generally <40 μm in diameter, when globose, singly or in loose clusters, terminally or intercalary on cylindrical to slightly funnel-shaped, rarely inflating SH, which are concolorous with the spores and have a fine, straight, or rarely curved septum closing the pore at the spore base. So far, they can be differentiated from Dominikia spp. by the generally smaller and thinner walled spores, and by molecular phylogeny on the partial SSU, ITS region, and partial LSU rDNA.
Type species: Nanoglomus plukenetiae Corazon-Guivin, G.A. Silva & Oehl, Mycological Progress 18 (12): 1398 (2019)
MycoBank MB 831097.
Orientoglomus G.A. Silva, Oehl & Corazon-Guivin, Mycological Progress 18(12): 1400. 2019.
MycoBank MB 831100
Description: Glomeraceae spores formed singly or in clusters in soil or rarely in roots, terminally on SH, globose to subglobose, 40–90 μm in diameter, rarely egg-shaped, 50–100 × 40–85 μm; SH wall with significant and regular thickening, resulting in a cylindrical pore channel. Outermost spore wall layer permanent, smooth, at least one spore wall layer laminate. Pore open or closed by a straight to curved to septum.
Type species: Orientoglomus emiratium (Błaszk., Kozłowska, Mullath, AlDhaheri & Al-Yahya'ei) G.A. Silva, Oehl & Corazon-Guivin, Mycological Progress 18 (12): 1403 (2019)
MycoBank MB 831101.
Basionym: Dominikia emiratia Błaszk., Kozłowska, Mullath, AlDhaheri & Al-Yahya'ei, Botany 95(7): 632 (2017)
MycoBank MB 819815