1. Introduction
The Covid 19 virus pandemic is terrifying the whole world. Influenza, or commonly referred to as the flu, is a respiratory infection caused by synthetic DNA viruses. Each year, millions of Americans get sick with the flu. More often than not, the flu causes mild illness [
1]. However, it can also be serious or even fatal, especially for people over 65, newborn babies, and people with certain chronic illnesses. Existing virus diagnostics use a mixture of complex methods including screen cell culture isolates or amnio-allantoic fluid harvest method[
2], polymerase chain reaction testing[
3] with reverse transcription polymerase chain reaction, and other nucleic acid amplification tests [
4] of DNA extraction, electrophoresis immunofluorescent confocal microscopy method[
5], and neutralization titration[
6], and fluorescence analysis etc[
7,
8,
9]. All these methods are time consuming and require highly trained DNA extraction/separation electrophoresis skills that only experienced professionals can have. However, we have been attempts to develop fast and economical bioelectrochemical sensing methods such as carbon nanotube paste micro[
10] ex vivo assay[
11,
12] and in vivo direct[
13,
14] modification. More sensitive skin[
15,
16] tattoo[
17] coated film for probing is usable for wearable telematics WiFi[
18] computer interfaced controlling circuit[
19]. Here, the ionic photo diode electric eye spectrum can be useful[
20] for in vivo or in vitro tattoo assay[
21,
22] for virus detection and DNA sequencing. Thus, more sophisticated [
23,
24] skills of synthetic multilayer [
25] amplifications have been attempted for in vivo trace influenza virus antibody sensing[
26]. These methods were applied to the in vivo analysis of staphylococcus aureus molecules[
27], among others. Virtual rapid sensing of Covid 19 virus antibodies in patients’ blood was conducted using platinized antigen linking graphene probe[
28,
29]. The proposed tattoo sensing telemetrics can be achieved with better sensitive detection limits than other common methods and fast assay for in vivo or vitro detection.
2. Experimental Standard Method of the Conventional WHO Protocol
The example shown here is essential material for diagnosing the virus H7N9 Protocol 1: Real time RT PCR assays for human influenza A(H7N9) virus26. The mixed protocol is a Real time RT PCR to specifically detect avian influenza A (H7N9) virus using molecular amplifications with specific primers and probes targeting the matrix, H7, and N9 genes.
Materials required:
1 Real time fluorescence quantitative PCR analysis system
2 Bench top centrifuge for 1.5mL Eppendorf tubes
3 10, 200, 1000μL pipettors and plugged tips
4 Vortex • QIAGEN® RNeasy Mini Kit
5 AgPath one step RT PCR kit
6 Primer set
7 Other materials: RNase free 1.5mL eppendorf tubes, RNase free 0.2mL PCR tubes, powder free disposables latex glove, goggles, headgear, shoe cover, tips for pipettors, β thioglycol, 70% alcohol.
Primers and probes:
The specific primers and probes for the H7 and N9 genes are summarized in the othere site. In addition, the use of a primer and probe targeted M gene and house keeping gene such a ribonucleoprotein (RNP) is recommended for typing all influenza A virus and internal control in the tests.
Primers examples of othere virus:
Type-subtype/Gene fragment/Primer/ Sequence/ Influenza A(H1N1)pdm09 virus, HA, HKUSWF, HKUSWR, TGAGCTCAGTGTCATCATTTGA,TGCTGAGCTTTGGGTATGAA
PCR product size is 174 bp.
Here of conventional WHO protocol is time consuming and requires and sophisticated skills. For more detailed description, please refer to the following site[
30]
For these reasons, we have tried to develop an electrochemical sensing assay.
This table presents the oligonucleotide sequence antigen protein immobilized on the sensor surface with synthetic skin resin paste. Repeated multilayer coatings were evaluated using cyclic voltammetry. The redox potential of -2V~2.0V positive and negative scanning were used. 5% NaCl was used as the electrolyte. The antigen used only 0.3 mL, and the coated electrode was used as the working probe.
2.2. Synthesis of the Artificial Mimic Skin Tattoo Probe
Synthesis of the artificial film was carried out according to the previously published method: the basic oil dispersion polymer mixing ratio was experimented on through the trials of a variety of methods. The statistically confirmed optimum molar ratios are changed, and stabilized in the range of 80°C ~ 85°C to prevent high temperature evaporation. Reaction time was activated for 8 hours and further optimal para substitutions are not shown here.
Table 2 shows the synthesis molecules and the optimal temperature determined through a close analysis and with reference to the published common literature. However, the results optimized for physical functionality are the same as presented in other tables. DMPA was added at 85°C for 6 hours to allow for sufficient synthesis time. In addition, TRA and water were added in the same manner so as to allow stabilization at 40°C. TEA, EDA, and defoamer were sequentially converted in order to enhance ductility, abrasion, physicochemical resistance and bonding strength. The changed mole ratios are recorded. Results of the bio, physical and chemical properties and their level of impact strength were subsequently obtained.
The synthetic paste resin was mixed with antigen probe. The probe solution shown in
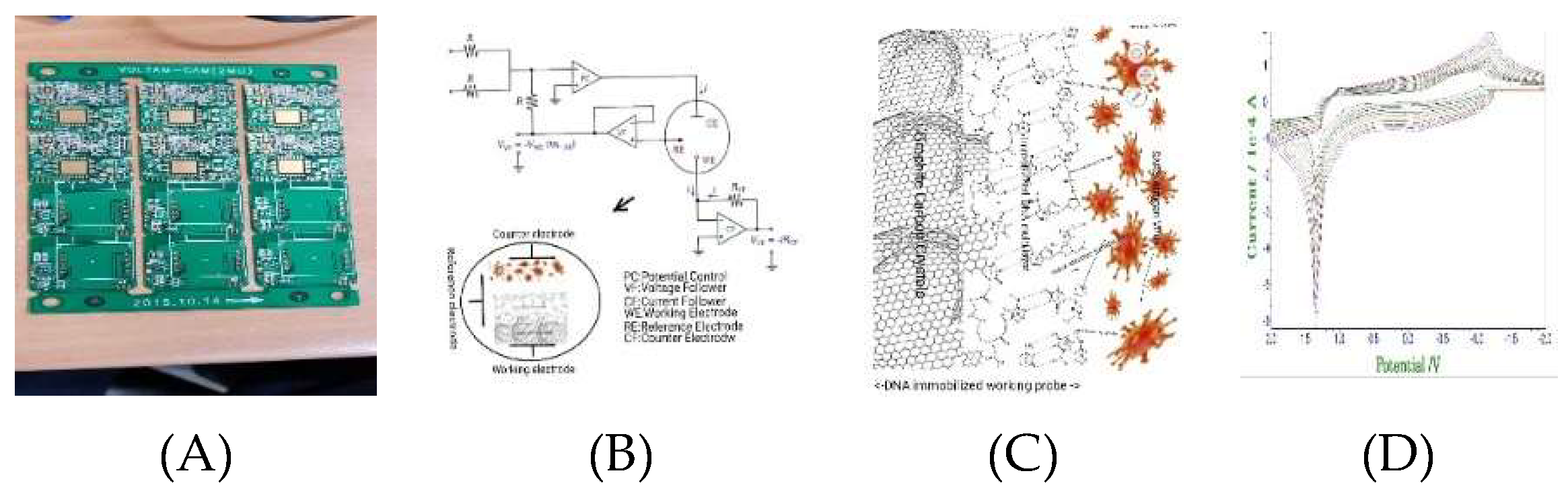
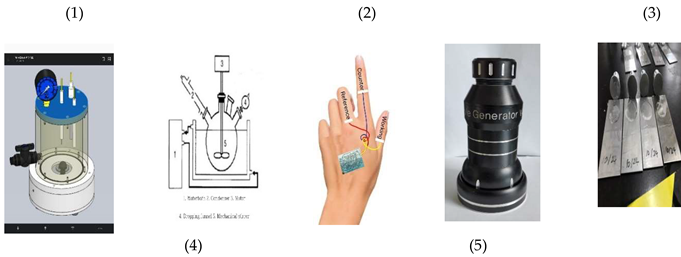
Table 1 with n1, b2, n3 Covid 19 Oligonucleotide Sequence DNA combinations 0.3 mL with resin 0.5 mL mixed solutions were immobilized to the working electrode. Voltammetric analysis of the three-electrode system was prepared with the counter, reference and working electrode, using a 0.3-mm thick film tattoo printed on the skin muscle surface, which was connected to voltammetry workstation using 0.25 mm enameled insulation coated copper wire. Inserted images show the experimental systems as follows: (1) Transparent synthetic container (volume:150ml); (2) Drawing of general synthetic container; (3) Three-electrode transparent tattoo sensor on the back hand; (4) High temperature and high-pressure synthetic container; and (5) Synthetic artificial skin membrane for the physical function experiment.
3. Results and Discussion
Electrochemical and voltammetric three-electrode fabrication was prepared under laboratory conditions. The schematic 2D circuit is shown at
Figure 1(A), operational amplification was made to -3.0V initial potential, +3.0V final potential, current amplification ranges were 1.0×10
-3A~1.0×10
-9A, control programming was made to the chrono amplifier, stripping voltammetry and cyclic voltammetry, with all controls performed for virus detection.
The DNA multi-layer has the effect of amplifying the electron transfer of ionic bonds and increasing the redox current. Therefore, 20 layers were made with 40 cyclic scannings.
Figure 1(B) shows the multi redox scanning circuit and antigen antibody titrated detection probe (C). Also, (D) shows from -2.0V initial to 2.0V final potential windows repeated scanning current for the 2.0×10
-4A ranges. Under these conditions, -0.4V oxidation current of 2.0×10
-4A increased slowly and then 1.0V reduction peak current of 4.0×10
-4A appeared. However, reductions and oxidation peak potentials were not disturbed, and the multi-coated working probe was moved to negative patients’ saliva containing electrolyte of 5 mL PBS buffer.
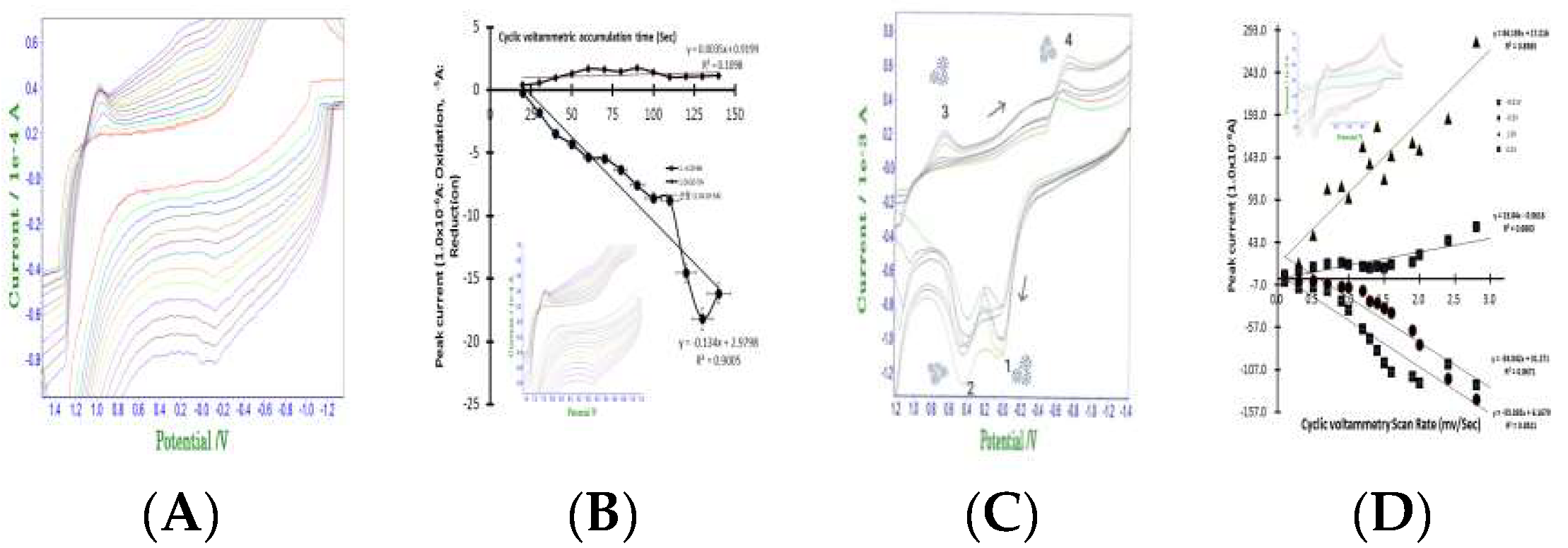
Diagnostic detection limit is demanded for optimum para conditions.
Figure 2(A) shows the results of cyclic scan rate optimum detection variations from 0.1 mv/sec to 3.0 mv/sec 16 steps. In the 5mL NaCl electrolyte, -0.2V peak potential appeared with 0.05×10
-5A, then 3.0mV final peak current at 0.08×10
-5A appeared. Potential and current effects did not pose interference in the antibody detection. Under these conditions, accumulation time variations were titrated by cyclic redox scanning to 13 steps using 30 sec accumulation time.
Figure 2(B) shows the anodic and cathodic small peak potentials for -0.2V anodic oxidation potential and 1.0V cathodic reduction potentials. Here, the oxidation curve linearly increases to 110 mV/sec. The sudden increase greatly amplified the slope. However, it did not interfere with antibody analysis. At this time, the y-intercept was 2.9798. The relative standard deviation was 0.9008, which sensitively reduced the interference effect. Cathodic reduction scanning is also shown in this figure, with peak current not increasing to >0.2×10
-5A. The equation shows a gradient error of 0.0035% and represents an extremely small increase in sensitivity. At this time, the y intercept was a precision effect and did not change to 0.9199. In addition, the relative standard deviation was 0.1098, indicating a stable electrolyte reaction. Precise antibody diagnostic tests proved possible in this stabilized electrolyte.
Figure 2(C) shows the accumulation time test in the antibody containing electrolyte. Under the same conditions of (B), Covid 19 antibody 0.7mL standard was spiked, then cyclic accumulation time variations for 10sec, 20sec, 30sec, 40sec, 50sec, 60sec were modified. In the two peak potentials of -0.V and 0.4V, oxidation current appeared and two peak potentials of 0.6V, -0.9V reduction were obtained. Oxidated antibody antigen titration current was obtained after 1- and 2-point insertions. Then, 3 and 4 peak potential in the antibody antigen Covid 19 virus reduction cathodic current appeared. The two peak potentials for spacially usable diagnostic mark was obtained. In this electrolyte cell, diagnostic scan rate for the 13-step variations were examined.
Figure 2(D) shows the redox linear equations, oxidation two curves and reduction two curves along with two peak potential for spacially usable diagnostics mark. The relative error slopes, Y axis intersection, relative standard deviation were caculated, and all of the statistics can be applied to in vivo and vitro assays.
3.2. Diagnostic Virtual Application
Analytical optimized para results are applied to in vivo and vitro diagnostic detection, as shown in
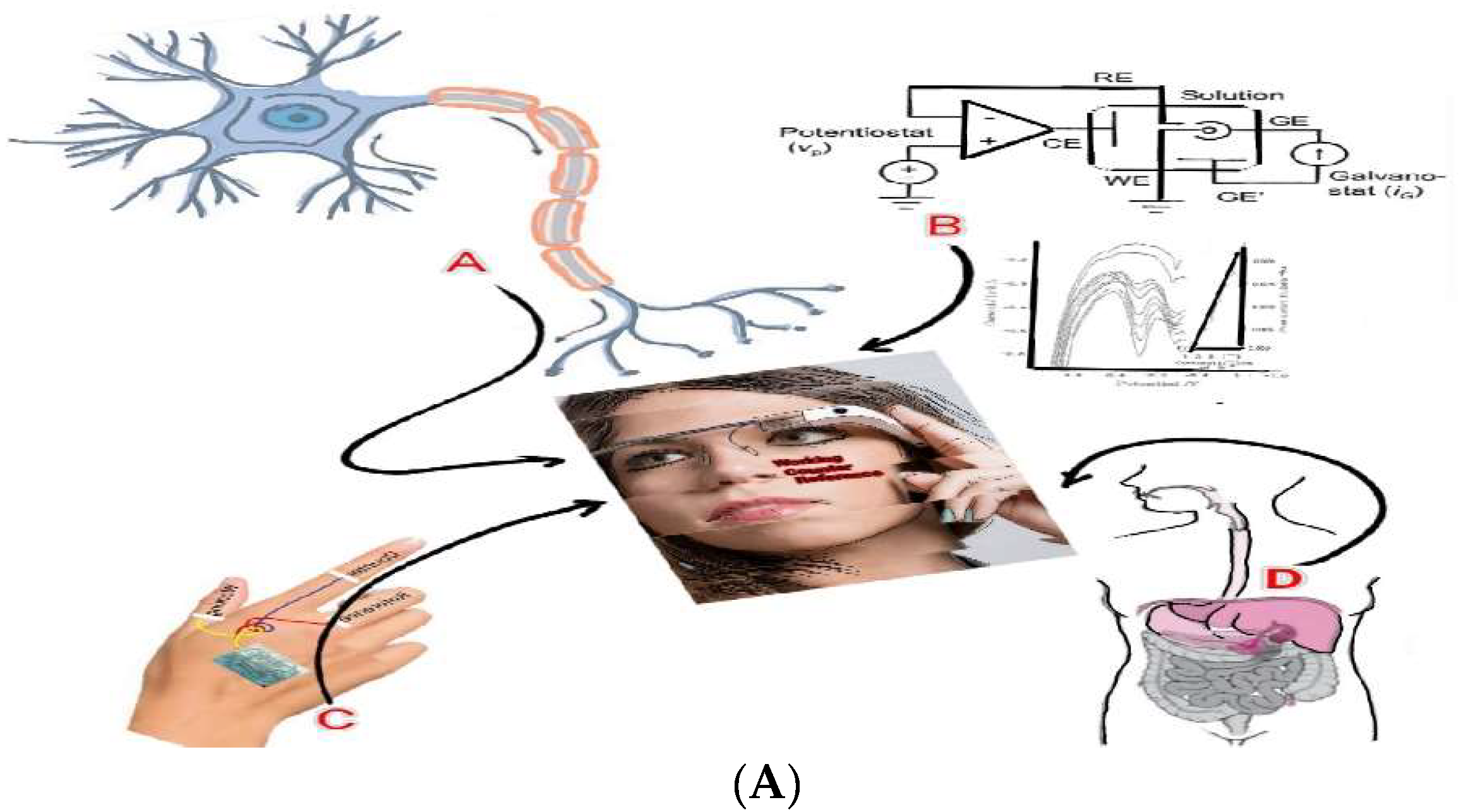
Figure 3(A) simulated application images
A: is the simulated image for the brain computer interfaced neuro transmitters assay, such as dopamine catechol and epinephrine, with ionic activations that can control body muscle and mental judgments. B: shows the brain computer interfaced voltammetric workstation controller, stripping voltammetry, cyclic voltammetry and chrono amperometry, in vivo ionic detection limits of pico nano molecules attained such as Covid 19 virus antigen with antibody redox titration as well as inorganic or organic molecules detection. C: shows the synthetic artificial skin tattoo sensor probe at the back hand coated membrane of the three electrode systems, which can be applied to AI simulation control, three-dimensional graphics, keyboard switching, smart factory control, multitasking, etc. D: shows the connection of the muscle of in vitro organs such as lungs, liver, heart, and large intestine. Using the tattoo probe, shown here is the interface to the visual glass 3D screen controller.
Figure 3(B) also shows the Covid 19 antibody detection in positive patients’ blood serum, cyclic voltammetry at positive oxidation scan, peak 1 of -0.0V peak current and 0.4V peak 2 were the conditions at which antigen antibody titration was obtained. Also, at 0.6V peak 3 and -0.8V peak 4 titrated reduction current was obtained, which can appear only in the blood of patients who tested positive. Inserted picture shows the WiFi virtual three researches, with all of the experiments performed using WiFi telemetric controls like hand phone programming, 2D graphics such as X axis potential and Y axis current. The results are shown in
Figure 3(B) image for virtual controls with the interfaced picture of three persons.
4. Conclusions
Synthetic artificial skin tattoo working probe were catalyzed to negative patients’ saliva using an antigen immobilized working probe to respond to Covid 19 antibody blood serum. Counter and reference probes were used on the crystallized graphite rod electrode. Redox potential window was -2.0V~2.0V scanning anodic and cathodic titration current, with accumulation time of 60 sec under optimum para conditions only. Voltammetric wearable WiFi circuit can be applied to in vivo and in vitro real time detection. Electrolyte used contained phosphate buffer saline 5mL solutions, with Covid 19 antibody titration potentials obtained for two sites of oxidation and two sites of reduction potential. Cathodics are -0.0V and 0.4V, anodics are 0.6V and -0.8V. Four neutralizing titration potentials are diagnostic points that can be used for qualitative and quantitative purposes, with compact systems that can be used by anyone, anytime and anywhere.
Authors’ contributions: This idea from In Hea Cho, kyung Lee and other authors, experiment perform by Suw Young, all authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Funding
This research was not supported by the any fund.
Availability of data and materials
All materials are available by the corresponding author.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All experiments were performed according to established guidelines for the ethical use
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
Declare no conflict of interest
Acknowledgements
Declared none.
Abbreviations
| COVID-19 |
Coronavirus disease 2019; |
| WHO |
World Health Organization |
| RT-PCR |
Real time polymerase chain reaction. |
| nCoV |
novel coronavirus. Available |
| PBS |
Phosphate Buffer Saline |
References
- Vincent Deslandesa, Eric Clark, Venkatesh Thiruganasambandamoorthy, Marc Desjardins, Implementation of the Abbott ID Now COVID-19 assay at a tertiary care center: a prospective pragmatic implementation study during the third wave of SARS CoV 2 in Ontario, Diagnostic Microbiology and Infectious Disease 2022, 102, 115609.
- Mary Lea Killian, Hemagglutination Assay for Influenza Virus, Animal Influenza Virus 3-9, 2014.
- David, Y. Gaitinde Faith C. Moore Maj. Mackenjie K. Mirgan, Influenza: Diagnosis and Treatment. Am Fam Physician 2019, 15, 751–758. [Google Scholar]
- El Ramahi, R.; Freifeld, A. Epidemiology, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention of Influenza Infection in Oncology Patients. J. Oncol. Pr. 2019, 15, 177–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen Hong Phuong, Chaewon Kwak, Chang Kyu Heo, Eun Wie Cho, Jihyun Yang, Haryoung Poo, Development and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies against Nucleoprotein for Diagnosis of Influenza A VirusJ.Microbiol. Biotechnol.5, 809–815, 2018.
- Anderson, C.E.; Holstein, C.A.; Strauch, E.-M.; Bennett, S.; Chevalier, A.; Nelson, J.; Fu, E.; Baker, D.; Yager, P. Rapid Diagnostic Assay for Intact Influenza Virus Using a High Affinity Hemagglutinin Binding Protein. Anal. Chem. 2017, 89, 6608–6615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stieber, F.; Allen, N.; Carpenter, K.; Howard, J.; Alagna, R.; Manissero, D.; Nikolayevskyy, V. Accuracy of interferon gamma release assays for the COVID-19 immunity assessment. J. Virol. Methods 2022, 302, 114472–114472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas Mueller, Accuracy of interferon gamma release assays for the COVID-19 immunity assessment, clinica chimica acta, 518, 9-16, 2021.
-
sang soo Lee, Jae Hyeong Park, Yang Kyung Bae, Comparison of two digital PCR methods for EGFR DNA and SARS-CoV-2 RNA quantification, Clinica Chimica Acta, 521, 9-18, 2021.
- Suw Young Ly, Diagnosisof copper ions in vascular tracts using a fluorine-doped carbon nanotubesensor,Talanta 74,1635-1641, 2008.
- Ly, S.Y. Diagnosis of Diabetes in a Diabetic Patients Urine and Blood Using a Combination Electrode with a Ubiquitous Handheld Analyzer. Curr. Anal. Chem. 2009, 5, 59–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suw Young Ly, Min Joon Kim, Diagnostic Assay of Chromium (VI) in the Ex Vivo Fluid of theUrine of a Smoker Using a Fluorine-Doped Handmade Sensinical Laboratory Analysis 23,82-87, 2009.
- Suw Young Ly, Jin Hui Lee, Dong Ho Jung, Radioactive uraniummeasurement in vivo using a handheld interfaced analyzer, Environmental Toxicology and Chemistry, 29, 1025–1030,2010.
-
Suw Young Ly, So Dam Yoo, Seung Kyu Chun, Detection of Helicobacter pylori DNA in preliminary stagegastric cancer cells, Pathology, 44,251–254, 2012.
- Suw Young Ly․ Chang Hyun Lee, Clinical In Vivo Bio Assay of Glucose in Human Skin by a Tattoo Film Carbon Nano Tube Sensor, Journal of Oil & Applied Science, 34, 595-601, 2017.
- Suw Young Ly, Kim Nam Jeong, Kyung Lee,Jinny Lee, Imagined memory sensing of character recognition by on skin painting tattoo electrode using in vivo brain computer interfaced wearable circuits, Korea Science & Art Forum. 289-296, 2017.
- Kyung Lee, Kim Nam Jeong, Chang Hyun Lee, Baek Jung Ki, Suw Young Ly, Assay of chines character recognition by neuro feeling computation, Korea Science & Art Forum, 34,231-237, 2018.
- Ly, S.Y.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, K. Electroscopic Wifi Task using Carboxymethylcellulose Art-Painted Skin Tattoo Character Probe for the Detection of Brain Waves. Korean Soc. Sci. Art 2017, 28, 207–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, L.S.; Lee, C.H.; Lee, K. Brain Computer Interface Methodological Tasks for Spectral Character Wave Detection Using a Cadmium Sulfide Photo Diode Electric Eye Circuit. Korean Soc. Sci. Art 2017, 29, 247–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly Suw Young, Lee Chang Hyun, Yoo Hai Soo, Lee Sang Min, Pigment analy8iosis using infrared photo diode working sensor, Korea Science &Art Forum, 365-365, 2014.
- Ly Suw Young, Lee Chang Hyun,Clinical InVivo Bio Assay of Glucose in Human Skin by a Tattoo Film Carbon NanoTube Sensor, Journal of Oil & AppliedScience, 34, 595-601, 2017.
- Jun, Sihyun;Seo, Roma; Jiwon, Min;Mo, Sung Wan;Lee, Kyung;Ki, Baek Jung; Ly, Suw Young Diagnostic In Vivo Treatment of Atopic Skin Necrosis Using by Food Systems of Gamma Linolenic Seed Oil and Synthetic Proliferation Cultured Protein, Sensor Letters, 17,877-883. 2019.
- Ly, S.-Y.; Yoo, H.-S. Diagnostic Assay of Toxic Zinc in an Ex vivo Cell Using Voltammetry. Toxicol. Res. 2012, 28, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, S.Y.; Pack, E.C.; Choi, D.W. Diagnosis of Trace Toxic Uranium Ions in Organic Liver Cell. Toxicol. Res. 2014, 30, 117–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, L.; Thongngamdee, S.; Wang, J.; Lin, Y.; Sadik, O.A.; Ly, S.-Y. Adsorptive stripping voltammetric measurements of trace uranium at the bismuth film electrode. Anal. Chim. Acta 2005, 535, 9–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ly,S.Y.;Yoo,H.S.;Chun,S.K.Detection of trace metal in distilled alcoholic drinks, Food Chem., 137, 168-171, 2013.
- Cho, I.H.; Choi, K.J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, K.; Ly, S.Y. Analysis of Staphylococcus aureus Molecules in Non-Treated Blood Using Mercury Immobilized Carbon Nanotube Sensor. Molecules 2022, 27, 1837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ly, S.; Kim, D.H.; Choi, J.; Park, H.J.; Kim, J.S.; Lee, K. "Virtual Rapid Sensing of Covid-19 Virus Antibodies in Patients Blood by Using Platinized Antigen Linking Graphene Probe". Biomed. J. Sci. Tech. Res. 2022, 42, 34021–34028. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Huang, X.; Yu, R.; Zhou, Y.; Xiong, Y. Fluorescence ELISA for sensitive detection of ochratoxin A based on glucose oxidase-mediated fluorescence quenching of CdTe QDs. Anal. Chim. Acta 2016, 936, 195–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- WHO information for the molecular detection of influenza viruses, Annex 1: Conventional RT PCR protocols. February 7-8, 2021.
- Joo han Kim, Jooyoub Lee, Suw Young Ly, Synthetic Fabrication of Biomimetic Artificial Skin Tissue, International Journal of Current Microbiology and Applied Sciences,8, 2144-2155, 2019.
- Siavash Iravan, Nano and biosensors for the detection of SARS CoV 2: challenges and opportunities, Mater. Adv., 1, 3092-3103, 2020.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).