Submitted:
23 August 2024
Posted:
26 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
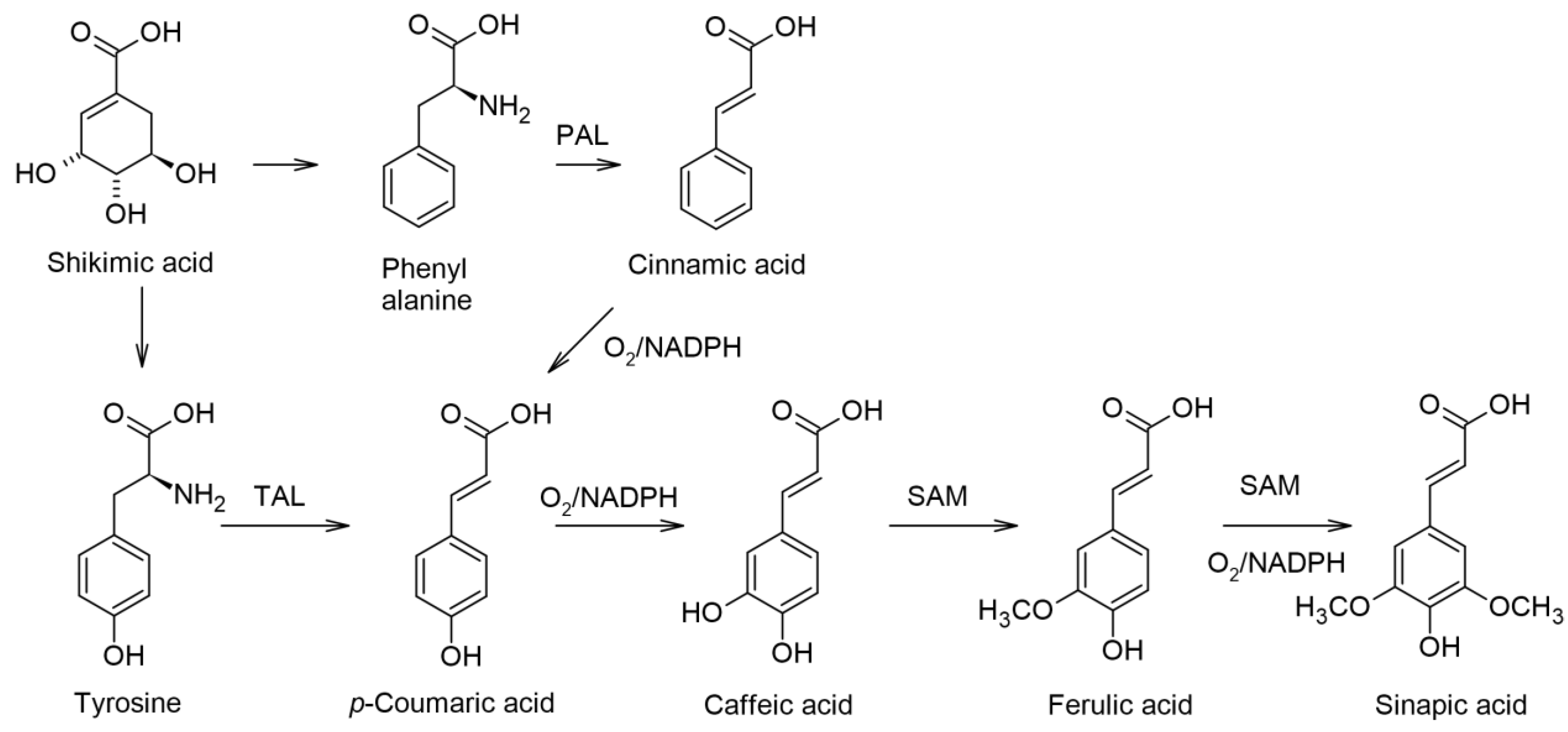
1. Introduction
2. The General Perspectives of Modified HCA Bioconjugates for various Applications -
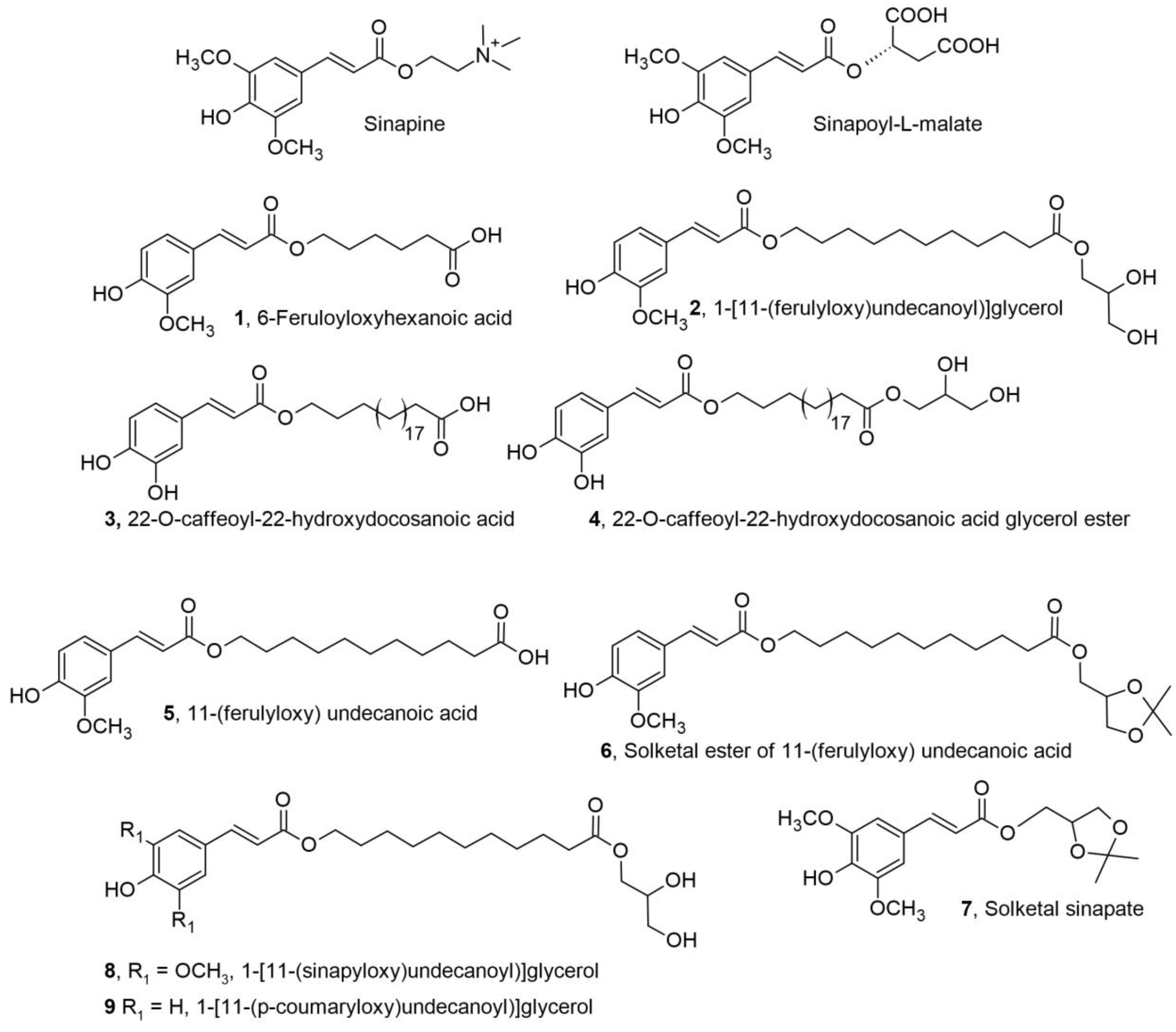
2.1. ω-Hydroxycinnamoyloxy Fatty Acids for Biomedical Applications
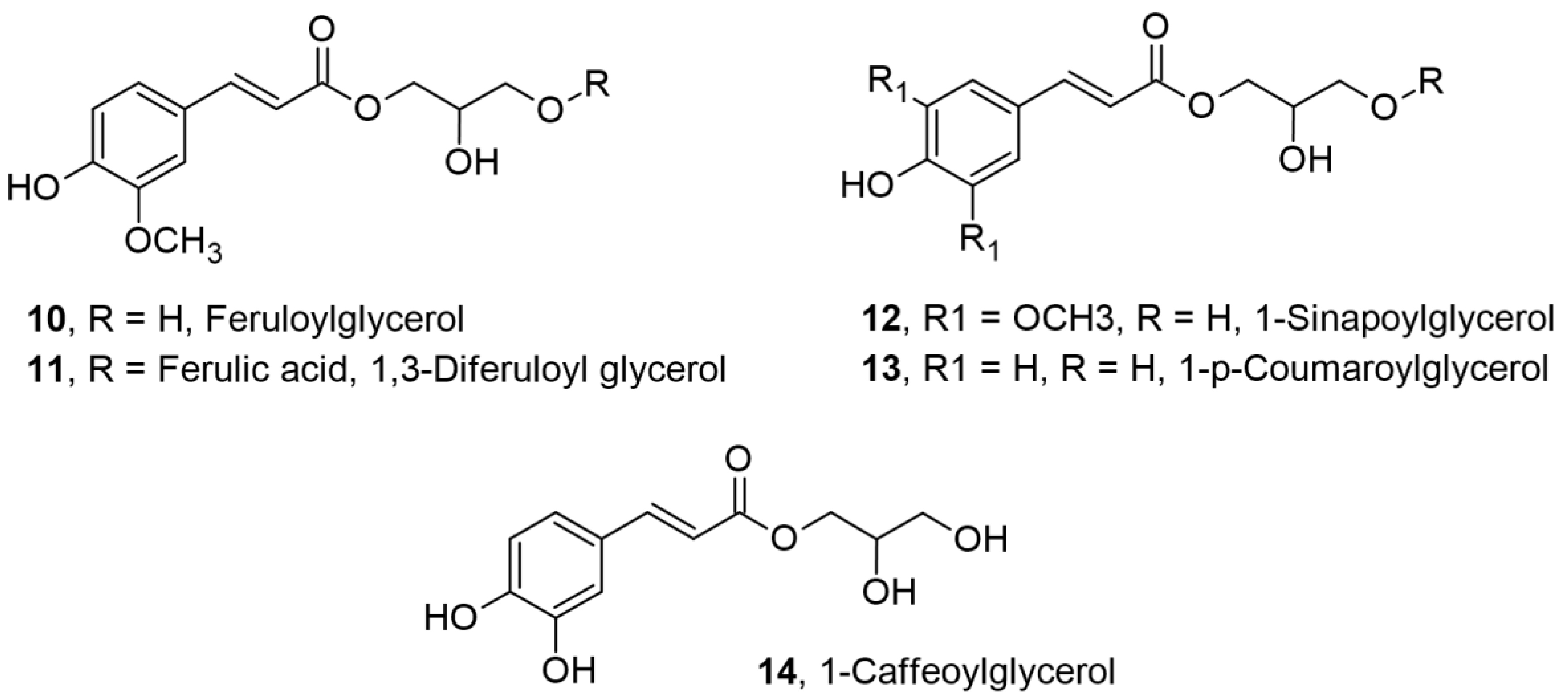
2.2. Mono and Di-Glyceryl Esters of Hydroxycinnamic Acids
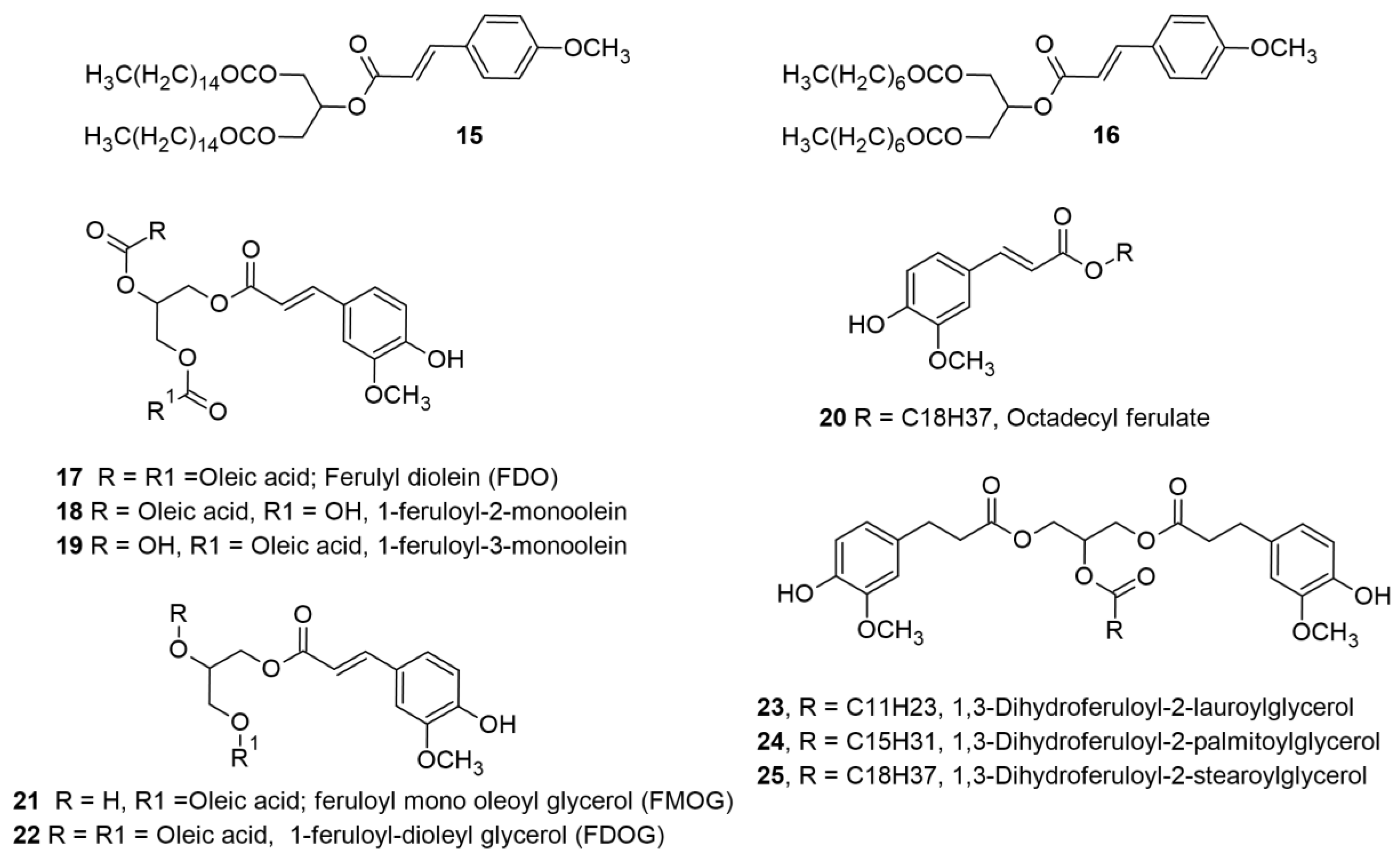
2.3. Lesquerella and Castor Oils-Based Phenolipids for Cosmetic and Other Applications
3. HCA-Polysaccharide-Based Polyols for Anti-UV and Cosmetic Applications
4. Polyethyleneglycol-Based HCA Conjugates in Food, BBB Transport, and Skin Applications
5. Encapsulation Approaches, and Modification of Biopolymeric Solid Supports for Hydroxycinnamate-Based Bioconjugates
5.1. Hydroxycinnamate-Cyclodextrin-Inclusion Complex-for Biological Applications
5.2. Nutraceutical Applications of HCA Polysaccharide Bioconjugates-
5.3. Cinnamates-Grafted Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNC) for UV Applications
6. Conclusions and Perspectives
CRediT authorship contribution statement
Funding-
Declaration of competing interests
Abbreviations
References
- Dewick, P.M. The Shikimate Pathway: Aromatic Amino Acids and Phenylpropanoids. In Medicinal Natural Products; 2009; pp. 121-158.
- van Schijndel, J.; Canalle, L.A.; Molendijk, D.; Meuldijk, J. The green Knoevenagel condensation: solvent-free condensation of benzaldehydes. Green Chemistry Letters and Reviews 2017, 10, 404–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flourat, A.L.; Combes, J.; Bailly-Maitre-Grand, C.; Magnien, K.; Haudrechy, A.; Renault, J.-H.; Allais, F. Accessing p-Hydroxycinnamic Acids: Chemical Synthesis, Biomass Recovery, or Engineered Microbial Production? ChemSusChem 2021, 14, 118–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrot, C.; Peru, A.A.M.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Allais, F. Proline-Mediated Knoevenagel–Doebner Condensation in Ethanol: A Sustainable Access to p-Hydroxycinnamic Acids. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2019, 7, 9422–9427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domergue, F.; Kosma, D.K. Occurrence and Biosynthesis of Alkyl Hydroxycinnamates in Plant Lipid Barriers. Plants 2017, 6, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, J.C.J.M.D.S.; Edraki, N.; Kamat, S.P.; Khoshneviszadeh, M.; Kayani, Z.; Mirzaei, H.H.; Miri, R.; Erfani, N.; Nejati, M.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; et al. Long Chain Alkyl Esters of Hydroxycinnamic Acids as Promising Anticancer Agents: Selective Induction of Apoptosis in Cancer Cells. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2017, 65, 7228–7239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
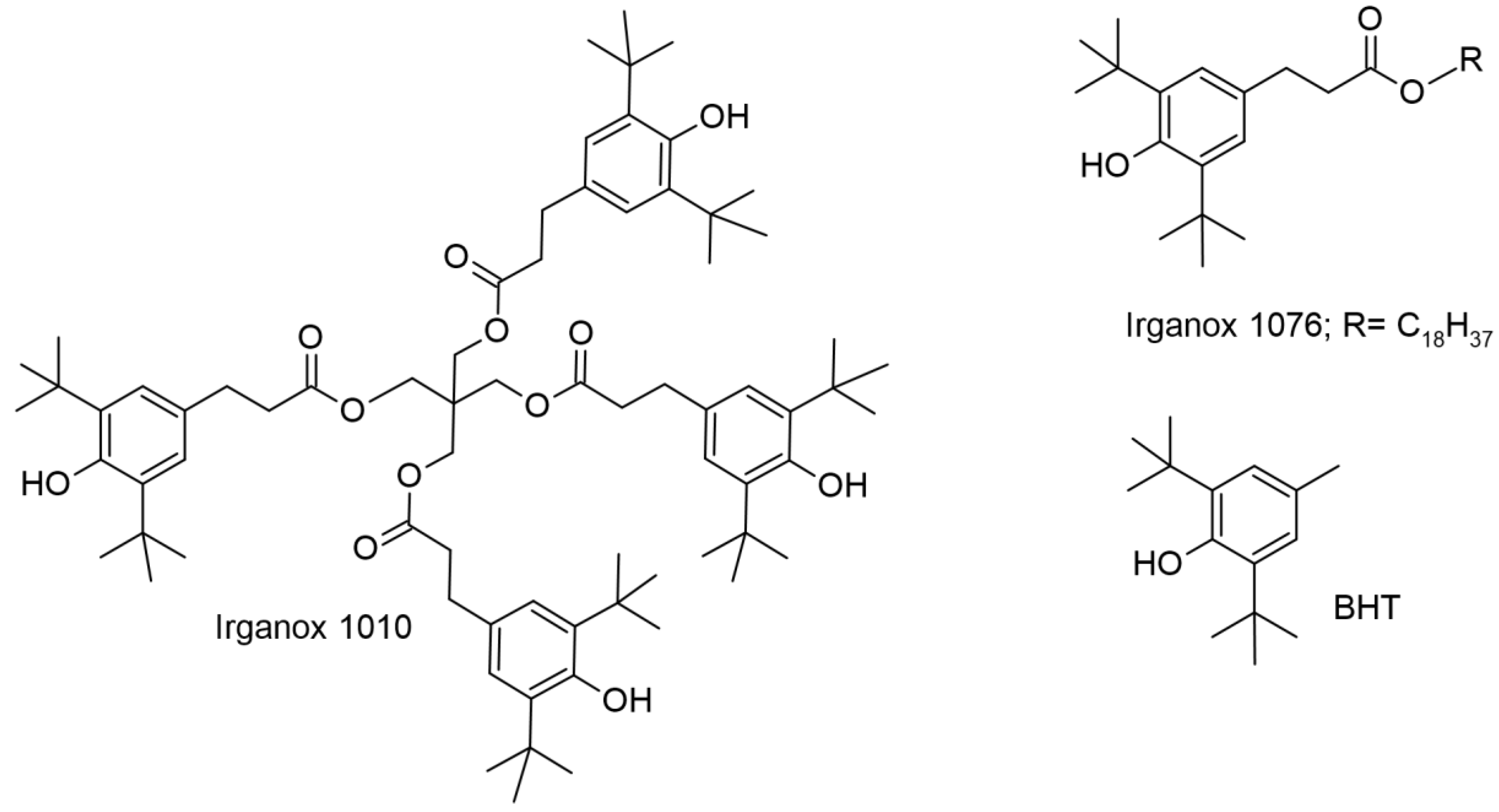
- Figueroa-Espinoza, M.C.; Bourlieu, C.; Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; Villeneuve, P. Lipophilized Antioxidants. In Encyclopedia of Food Chemistry; Melton, L., Shahidi, F., Varelis, P., Eds.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Michels, B.; Zwaka, H.; Bartels, R.; Lushchak, O.; Franke, K.; Endres, T.; Fendt, M.; Song, I.; Bakr, M.; Budragchaa, T.; et al. Memory enhancement by ferulic acid ester across species. Science Advances 2018, 4, eaat6994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, J.C.J.M.D.S.; Campos, V.R. Bench to any side- Pharmacology and applications of Natural and Synthetic Alkylated Hydroxy Cinnamates and Cinnamides. Submitted 2024, x, x. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, J.C.J.M.D.S.; Kamat, S.P.; Cavaleiro, J.A.S.; Gaspar, A.; Garrido, J.; Borges, F. Synthesis and antioxidant activity of long chain alkyl hydroxycinnamates. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2011, 46, 773–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abiola, T.T.; Auckloo, N.; Woolley, J.M.; Corre, C.; Poigny, S.; Stavros, V.G. Unravelling the Photoprotection Properties of Garden Cress Sprout Extract. Molecules 2021, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.P.T.; Stewart, J.D.; Ioannou, I.; Allais, F. Sinapic Acid and Sinapate Esters in Brassica: Innate Accumulation, Biosynthesis, Accessibility via Chemical Synthesis or Recovery From Biomass, and Biological Activities. Frontiers in Chemistry 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioux, B.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Alarcan, J.; Abiola, T.T.; Vink, M.J.A.; Woolley, J.M.; Peru, A.A.M.; Mention, M.M.; Brunissen, F.; Berden, G.; et al. An expeditive and green chemo-enzymatic route to diester sinapoyl-l-malate analogues: sustainable bioinspired and biosourced UV filters and molecular heaters. Chemical Science 2023, 14, 13962–13978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peyrot, C.; Mention, M.M.; Fournier, R.; Brunissen, F.; Couvreur, J.; Balaguer, P.; Allais, F. Expeditious and sustainable two-step synthesis of sinapoyl-l-malate and analogues: towards non-endocrine disruptive bio-based and water-soluble bioactive compounds. Green Chemistry 2020, 22, 6510–6518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mention, M.M.; Flourat, A.L.; Peyrot, C.; Allais, F. Biomimetic regioselective and high-yielding Cu(i)-catalyzed dimerization of sinapate esters in green solvent Cyrene™: towards sustainable antioxidant and anti-UV ingredients. Green Chemistry 2020, 22, 2077–2085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michels, B.; Franke, K.; Weiglein, A.; Sultani, H.; Gerber, B.; Wessjohann, L.A. Rewarding compounds identified from the medicinal plant Rhodiola rosea. Journal of Experimental Biology 2020, 223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; Zhou, J.; Wang, X.; Xie, X.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, F.; Huang, W.; Wang, Z.; Xiao, W. A new ferulic acid ester from Rhodiola wallichiana var. cholaensis (Crassulaceae). Natural Product Research 2018, 32, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cong, Y.; Guo, J.-G.; Liu, J. Two New Chemical Constituents of Veratrum dahuricum (Turcz.) Loes. f. Helvetica Chimica Acta 2013, 96, 345–349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woo, M.H.; Nguyen, D.H.; Zhao, B.T.; Seo, U.M.; Nguyen, T.T.; Jun, D.Y.; Kim, Y.H. Echinochlorins A-C from the grains of Echinochloa utilis (Barnyard Millet) and their anti-inflammatory activity. Planta Medica 2015, 81, 81–PX66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, M.; Hussain, M.; Memon, H.; Zhou, W. Structure of pigment compositions and radical scavenging activity of naturally green-colored cotton fiber. Cellulose 2016, 23, 955–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fadilah, N.I.M.; Phang, S.J.; Kamaruzaman, N.; Salleh, A.; Zawani, M.; Sanyal, A.; Maarof, M.; Fauzi, M.B. Antioxidant Biomaterials in Cutaneous Wound Healing and Tissue Regeneration: A Critical Review. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonar, V.P.; Fois, B.; Distinto, S.; Maccioni, E.; Meleddu, R.; Cottiglia, F.; Acquas, E.; Kasture, S.; Floris, C.; Colombo, D.; et al. Ferulic Acid Esters and Withanolides: In Search of Withania somnifera GABAA Receptor Modulators. Journal of Natural Products 2019, 82, 1250–1257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maccioni, R.; Cottiglia, F.; Maccioni, E.; Talani, G.; Sanna, E.; Bassareo, V.; Kasture, S.B.; Acquas, E. The biologically active compound of Withania somnifera (L.) Dunal, docosanyl ferulate, is endowed with potent anxiolytic properties but devoid of typical benzodiazepine-like side effects. Journal of Psychopharmacology 2021, 35, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johny, J.; Kontham, V.; Veeragoni, D.; Misra, S.; Kaki, S.S. Bioorganic synthesis, characterization and evaluation of a natural phenolic lipid. Biotechnology Reports 2019, 24, e00375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrêa, I.; Faria, R.P.V.; Rodrigues, A.E. Continuous Valorization of Glycerol into Solketal: Recent Advances on Catalysts, Processes, and Industrial Perspectives. Sustainable Chemistry 2021, 2, 286–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peyrot, C.; Mention, M.M.; Brunissen, F.; Allais, F. Sinapic Acid Esters: Octinoxate Substitutes Combining Suitable UV Protection and Antioxidant Activity. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gandhi, B.; Juliya, J.; Dileep, V.; Uma Rajeswari, B.; Misra, S.; Kaki, S.S. Antioxidant and Biological Activities of Novel Structured Monoacylglycerol Derivatives with Phenolic Acids. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2021, 123, 2100055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunia-Krzyżak, A.; Słoczyńska, K.; Popiół, J.; Koczurkiewicz, P.; Marona, H.; Pękala, E. Cinnamic acid derivatives in cosmetics: current use and future prospects. International Journal of Cosmetic Science 2018, 40, 356–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monhaphol, T.; Albinsson, B.; Wanichwecharungruang, S.P. 2-Ethylhexyl-2,4,5-trimethoxycinnamate and di-(2-ethylhexyl)-2,4,5-trimethoxybenzalmalonate as novel UVA filters†. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2010, 59, 279–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zambrano, D.; Millán, D.; Guevara-Pulido, J. In silico design, synthesis and evaluation of a less toxic octinoxate alternative with suitable photoprotection properties. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2023, 180, 106332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taniguchi, H.; Nomura, E.; Tsuno, T.; Minami, S. Ferulic acid ester antioxidant/UV absorbent. 1995.
- Zhou, Y.; Lips, A.; Nanavaty, F.S.; Bartolone, J.B. Stabilization of ferulic acid in cosmetic compositions. 2001.
- Kaeswurm, J.A.H.; Scharinger, A.; Teipel, J.; Buchweitz, M. Absorption Coefficients of Phenolic Structures in Different Solvents Routinely Used for Experiments. Molecules 2021, 26, 4656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FerulanActive. https://www.gfn-selco.de/en/Productsearch/ferulan-active. Available online: https://www.gfn-selco.de/en/Productsearch/ferulan-active (accessed on 19 August 2022 2022).
- Matsuo, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Kimura, Y.; Tsuchiyama, M.; Oh, T.; Sakamoto, T.; Adachi, S. Synthesis of glyceryl ferulate by immobilized ferulic acid esterase. Biotechnology Letters 2008, 30, 2151–2156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kikugawa, M.; Tsutsuki, H.; Ida, T.; Nakajima, H.; Ihara, H.; Sakamoto, T. Water-soluble ferulic acid derivatives improve amyloid-β-induced neuronal cell death and dysmnesia through inhibition of amyloid-β aggregation. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 2016, 80, 547–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsuchiyama, M.; Sakamoto, T.; Tanimori, S.; Murata, S.; Kawasaki, H. Enzymatic Synthesis of Hydroxycinnamic Acid Glycerol Esters Using Type A Feruloyl Esterase from Aspergillus niger. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry 2007, 71, 2606–2609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Compton, D.L.; Laszlo, J.A.; Evans, K.O. Antioxidant properties of feruloyl glycerol derivatives. Industrial Crops and Products 2012, 36, 217–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, D.L.; Appell, M.; Kenar, J.A.; Evans, K.O. Enzymatic Synthesis and Flash Chromatography Separation of 1,3-Diferuloyl-sn-Glycerol and 1-Feruloyl-sn-Glycerol. Methods and Protocols 2020, 3, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Evans, K.O.; Compton, D.L.; Laszlo, J.A.; Appell, M. Feruloyl glycerol and 1,3-diferuloyl glycerol antioxidant behavior in phospholipid vesicles. Chemistry and Physics of Lipids 2016, 195, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Chen, X.; Sun, S.; Xu, R. Enhancement of the hydrophilic feruloyl glycerol synthesis using A-35 as a catalyst and its functional characteristics. Food & Function 2021, 12, 9763–9772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, X.-Y.; Xu, Y.; Wu, J.-X.; Zhu, C.-T.; Zhang, D.-Y.; Wu, G.-H.; Wu, F.-A.; Wang, J. Enzymatic Synthesis and Antioxidant Activity of 1-Caffeoylglycerol Prepared from Alkyl Caffeates and Glycerol. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 2018, 95, 149–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eudes, A.; Mouille, M.; Robinson, D.S.; Benites, V.T.; Wang, G.; Roux, L.; Tsai, Y.-L.; Baidoo, E.E.K.; Chiu, T.-Y.; Heazlewood, J.L.; et al. Exploiting members of the BAHD acyltransferase family to synthesize multiple hydroxycinnamate and benzoate conjugates in yeast. Microbial Cell Factories 2016, 15, 198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Rong, Z.; Ying, X. Calculation of hydrophile–lipophile balance for polyethoxylated surfactants by group contribution method. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science 2006, 298, 441–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, Z.M.F.; Santos, E.P.d.; Rocha, J.F.d.; Dellamora-Ortiz, G.M.; Gonçalves, J.C.S. A new sunscreen of the cinnamate class: Synthesis and enzymatic hydrolysis evaluation of glyceryl esters of p-methoxycinnamic acid. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2005, 25, 67–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, D.L.; Laszlo, J.A.; Berhow, M.A. Lipase-catalyzed synthesis of ferulate esters. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 2000, 77, 513–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, J.A.; Smith, L.J.; Evans, K.O.; Compton, D.L. Phenol Esterase Activity of Porcine Skin. European Journal of Pharmaceutics and Biopharmaceutics 2015, 89, 175–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Totani, N.; Tateishi, S.; Takimoto, T.; Shinohara, R.; Sasaki, H. Ferulic Acid Esters and Weight-Loss Promoting Effects in Rats. Journal of Oleo Science 2012, 61, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laszlo, J.A.; Evans, K.O.; Vermillion, K.E.; Appell, M. Feruloyl Dioleoylglycerol Antioxidant Capacity in Phospholipid Vesicles. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry 2010, 58, 5842–5850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Villeneuve, P.; Bourlieu-Lacanal, C.; Durand, E.; Lecomte, J.; McClements, D.J.; Decker, E.A. Lipid oxidation in emulsions and bulk oils: a review of the importance of micelles. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition 2023, 63, 4687–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hollande, L.; Domenek, S.; Allais, F. Chemo-Enzymatic Synthesis of Renewable Sterically-Hindered Phenolic Antioxidants with Tunable Polarity from Lignocellulose and Vegetal Oil Components. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2018, 19, 3358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
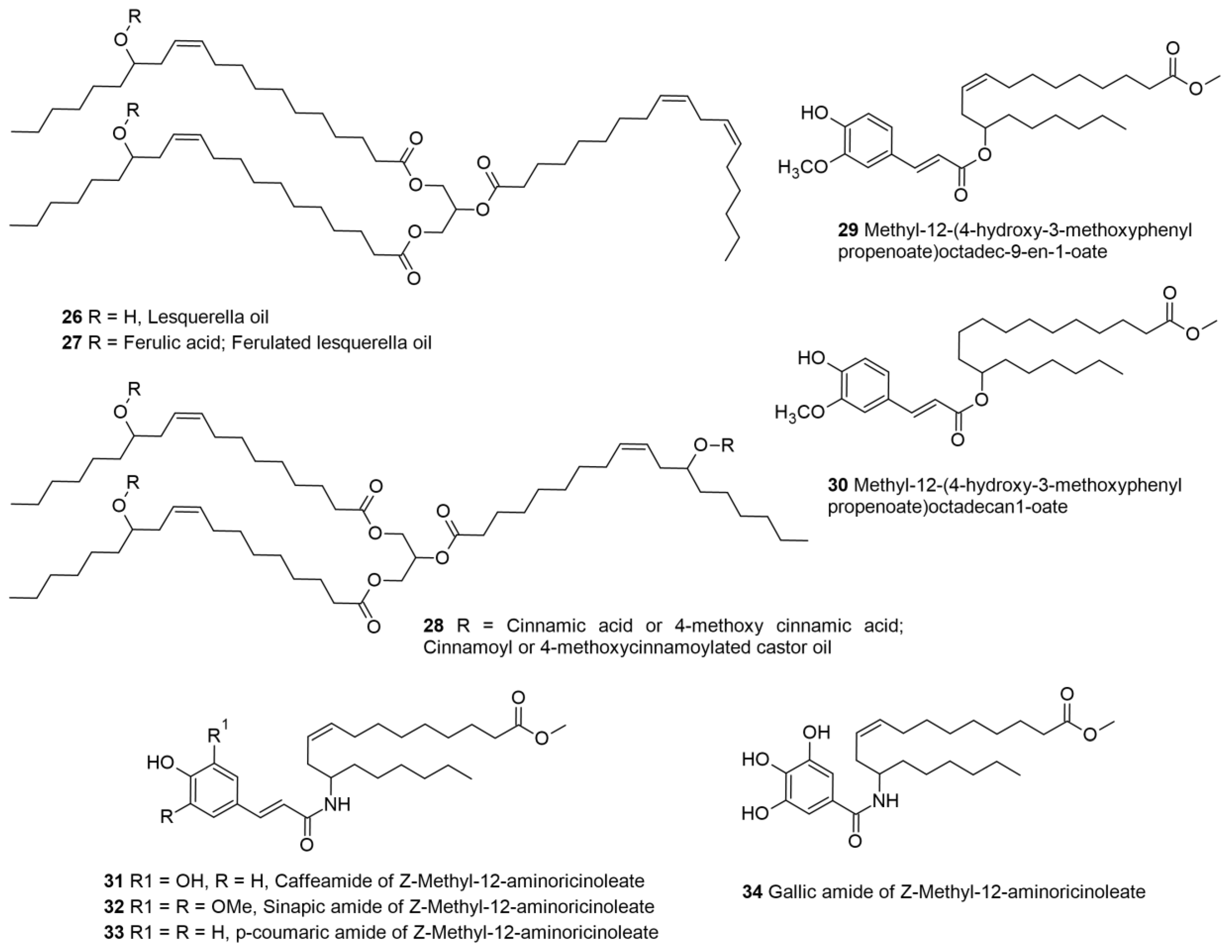
- Compton, D.L.; Laszlo, A.; Isbell, T.A. Cinnamoyl esters of lesquerella and castor oil: Novel sunscreen active ingredients. Journal of the American Oil Chemists' Society 2004, 81, 945–951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compton, D.L.; Laszlo, J.A.; Evans, K.O. Phenylpropanoid esters of lesquerella and castor oil. Industrial Crops and Products 2015, 63, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Zhu, S.; Bi, Y. Solvent-free enzymatic synthesis of feruloylated structured lipids by the transesterification of ethyl ferulate with castor oil. Food Chemistry 2014, 158, 292–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Chen, X.; Jiang, C. Enhanced synthesis of feruloylated acylglycerols by the lipase-catalyzed transesterification of glyceryl monoferulate with different acyl donors using ionic liquids as reaction solvents. Journal of Biotechnology 2018, 280, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Wang, P.; Zhu, S. Enzymatic incorporation of caffeoyl into castor oil to prepare the novel castor oil-based caffeoyl structured lipids. Journal of Biotechnology 2017, 249, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reddy, K.K.; Ravinder, T.; Kanjilal, S. Synthesis and evaluation of antioxidant and antifungal activities of novel ricinoleate-based lipoconjugates of phenolic acids. Food Chemistry 2012, 134, 2201–2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yarra, M.; Kaki, S.S.; Prasad, R.B.N.; Mallampalli, K.S.L.; Yedla, P.; Chityala, G.K. Synthesis of novel (Z)-methyl-12-aminooctadec-9-enoate-based phenolipids as potential antioxidants and chemotherapeutic agents. European Journal of Lipid Science and Technology 2016, 118, 622–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
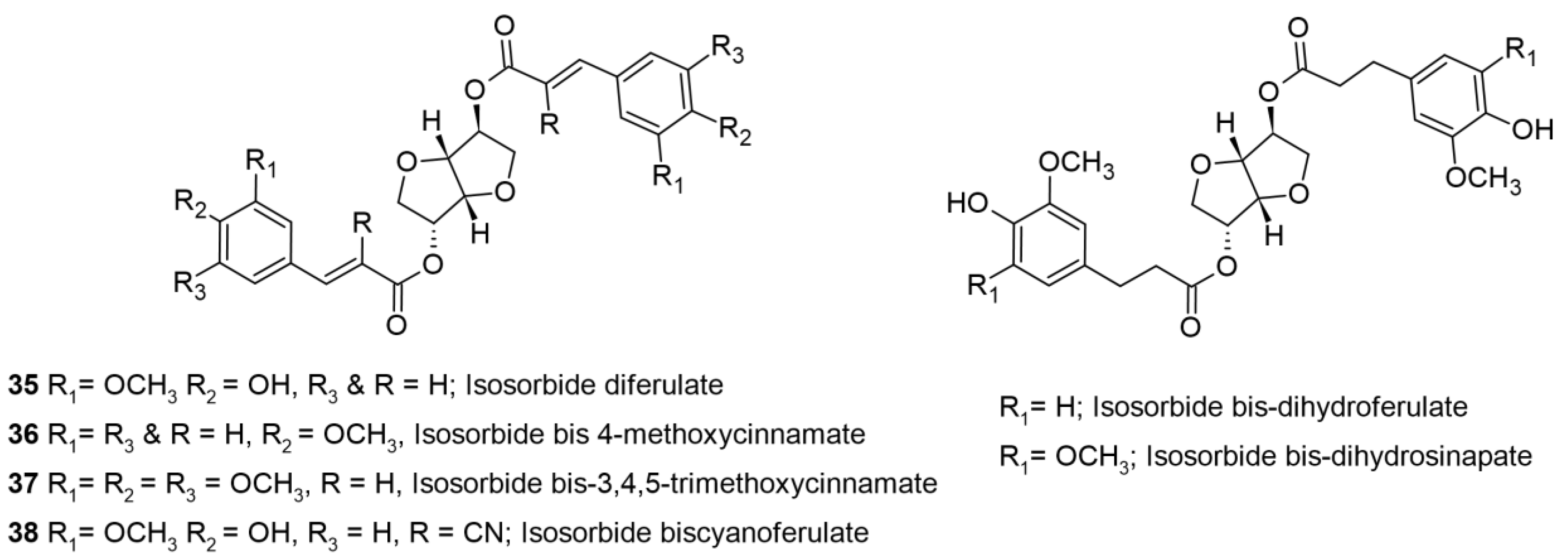
- Bonnin, I.; Mereau, R.; Tassaing, T.; De Oliveira Vigier, K. One-pot synthesis of isosorbide from cellulose or lignocellulosic biomass: a challenge? Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry 2020, 16, 1713–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxon, D.J.; Luke, A.M.; Sajjad, H.; Tolman, W.B.; Reineke, T.M. Next-generation polymers: Isosorbide as a renewable alternative. Progress in Polymer Science 2020, 101, 101196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- East, A.; Zhang, Y.; Jaffe, M. Ultraviolet absorber for cosmetics and polymeric materials. 2007.
- Feng, X. Synthesis of corn-derived carbohydrate derivatives as effective multifunctional sunscreen, Masters Thesis, . New Jersey Institute of Technology, New Jersey, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Reano, A.F.; Chérubin, J.; Peru, A.M.M.; Wang, Q.; Clément, T.; Domenek, S.; Allais, F. Structure–Activity Relationships and Structural Design Optimization of a Series of p-Hydroxycinnamic Acids-Based Bis- and Trisphenols as Novel Sustainable Antiradical/Antioxidant Additives. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2015, 3, 3486–3496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
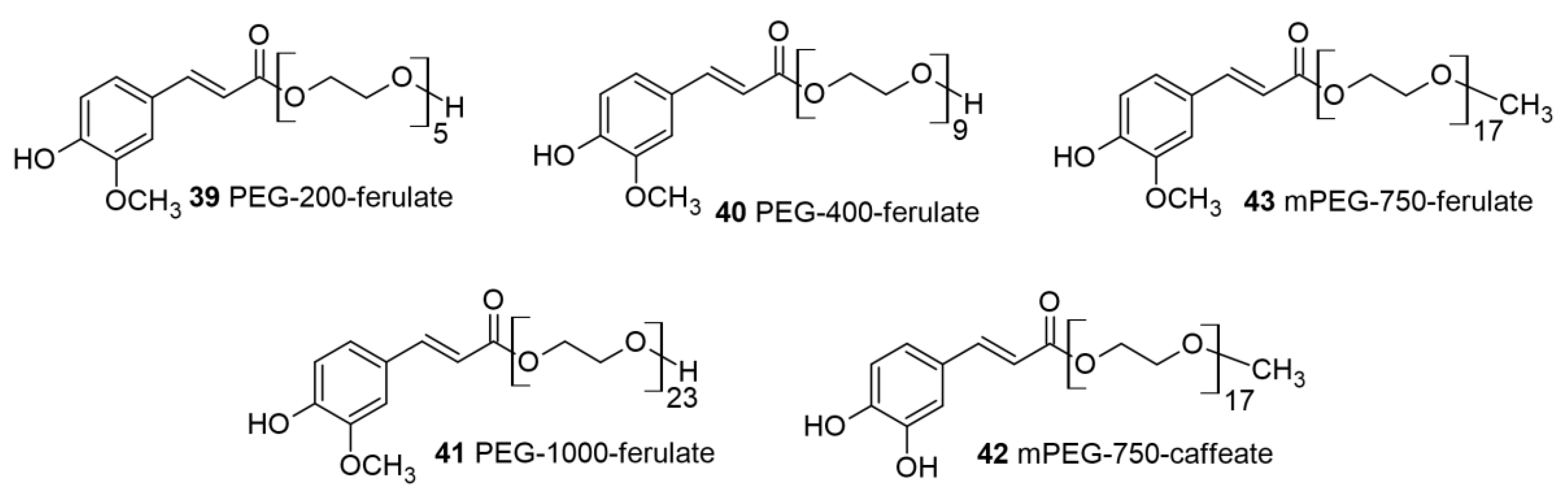
- Nicks, F.; Richel, A.; Dubrowski, T.; Wathelet, B.; Wathelet, J.-P.; Blecker, C.; Paquot, M. Effect of new synthetic PEGylated ferulic acids in comparison with ferulic acid and commercial surfactants on the properties of wheat flour dough and bread. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture 2013, 93, 2415–2420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Pinto, M.; Martins, C.; Gomes, M.J.; Sarmento, B.; Oliveira, P.J.; Remião, F.; Borges, F. Development of a PEGylated-Based Platform for Efficient Delivery of Dietary Antioxidants Across the Blood–Brain Barrier. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2018, 29, 1677–1689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sguizzato, M.; Mariani, P.; Ferrara, F.; Drechsler, M.; Hallan, S.S.; Huang, N.; Simelière, F.; Khunti, N.; Cortesi, R.; Marchetti, N.; et al. Nanoparticulate Gels for Cutaneous Administration of Caffeic Acid. Nanomaterials 2020, 10, 961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duceac, I.A.; Coseri, S. Biopolymers and their derivatives: Key components of advanced biomedical technologies. Biotechnology Advances 2022, 61, 108056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EMA. Background review for cyclodextrins used as excipients. 2014, EMA/CHMP/333892/2013.
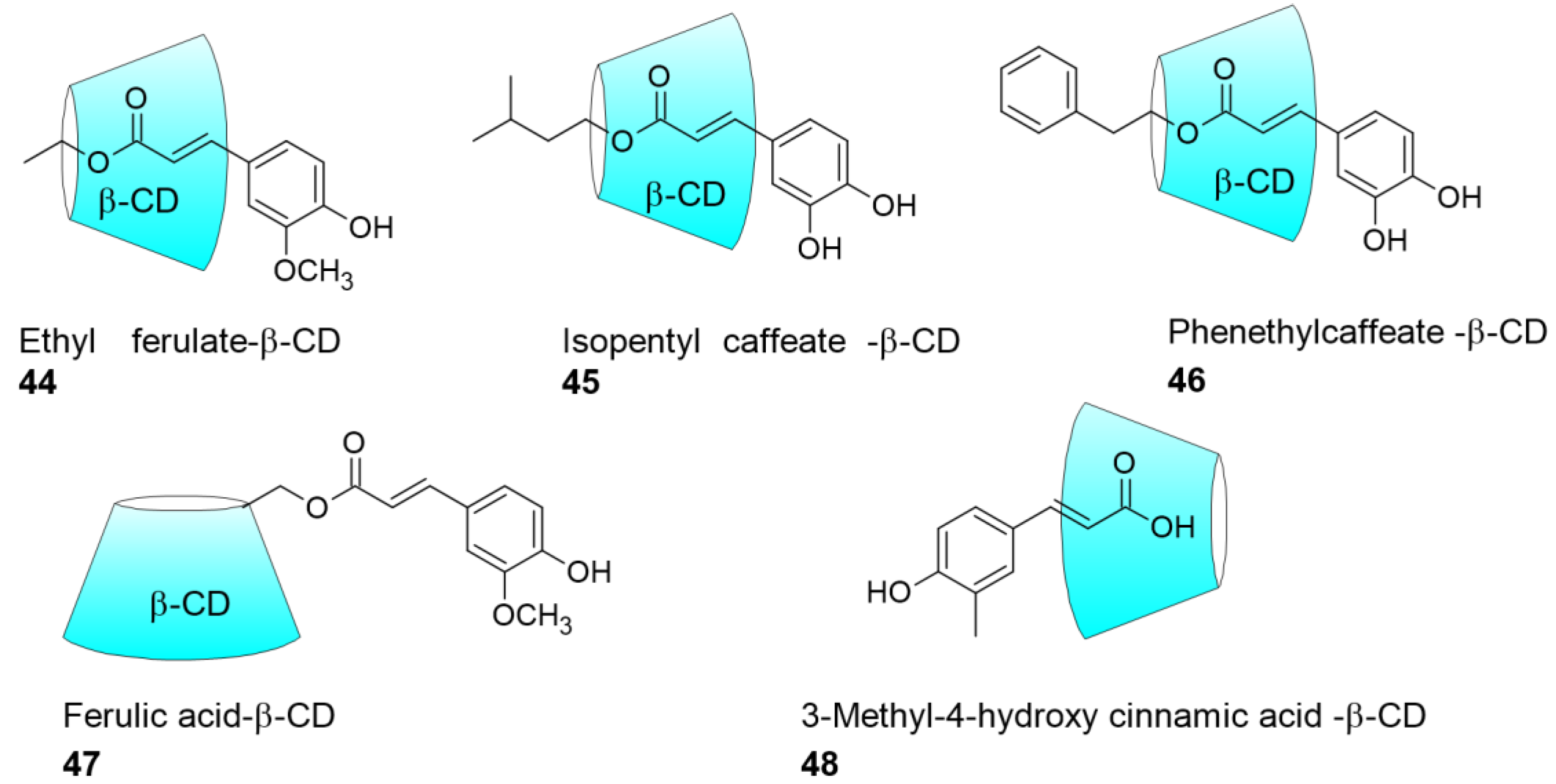
- Cunha, F.V.M.; do Nascimento Caldas Trindade, G.; da Silva Azevedo, P.S.; Coêlho, A.G.; Braz, E.M.; Pereira de Sousa Neto, B.; de Rezende, D.C.; de Sousa, D.P.; de Assis Oliveira, F.; Nunes, L.C.C. Ethyl ferulate/β-cyclodextrin inclusion complex inhibits edema formation. Materials Science and Engineering: C 2020, 115, 111057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marques, C.S.F.; Barreto, N.S.; Oliveira, S.S.C.d.; Santos, A.L.S.; Branquinha, M.H.; Sousa, D.P.d.; Castro, M.; Andrade, L.N.; Pereira, M.M.; Silva, C.F.d.; et al. β-Cyclodextrin/Isopentyl Caffeate Inclusion Complex: Synthesis, Characterization and Antileishmanial Activity. Molecules 2020, 25, 4181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garrido, E.M.P.J.; Cerqueira, A.S.; Chavarria, D.; Silva, T.; Borges, F.; Garrido, J.M.P.J. Microencapsulation of caffeic acid phenethyl ester and caffeic acid phenethyl amide by inclusion in hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin. Food Chemistry 2018, 254, 260–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, X.; Zhang, Z.; Shen, H.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, G. Comparison of structures, physicochemical properties and in vitro bioactivity between ferulic acid-β-cyclodextrin conjugate and the corresponding inclusion complex. Food Research International 2019, 125, 108619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Yu, H.; Cai, Y.; Yuan, C.; Chen, S.; Ding, T.; Liu, D.; Hu, Y. Ferulic acid-β-cyclodextrin inclusion complexes: Application on the preservation of hairtail (Trichiurus lepturus). International Journal of Food Properties 2020, 23, 282–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikeda, N.; Inoue, Y.; Ogata, Y.; Murata, I.; Meiyan, X.; Takayama, J.; Sakamoto, T.; Okazaki, M.; Kanamoto, I. Improvement of the Solubility and Evaluation of the Physical Properties of an Inclusion Complex Formed by a New Ferulic Acid Derivative and γ-Cyclodextrin. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 12073–12080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kenar, J.A.; Compton, D.L.; Little, J.A.; Peterson, S.C. Formation of inclusion complexes between high amylose starch and octadecyl ferulate via steam jet cooking. Carbohydrate Polymers 2016, 140, 246–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Chen, G.; Ma, Y.; Wang, Y.; Chen, J. Construction of ferulic acid modified porous starch esters for improving the antioxidant capacity. RSC Advances 2022, 12, 4253–4262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Ma, Y.; Gao, X.; Chen, G.; Wang, Z. Probing the structure-antioxidant activity relationships of four cinnamic acids porous starch esters. Carbohydrate Polymers 2021, 256, 117428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ou, S.; Yang, A.L.A. A study on synthesis of starch ferulate and its biological properties. Food Chemistry 2001, 74, 91–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, J.; Mehta, V.; Kaur, G. Preparation, development and characterization of Leucaena leucocephala galactomannan (LLG) conjugated sinapic acid: A potential colon targeted prodrug. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules 2021, 178, 29–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, E.M.; Lee, H.; Jayabalan, R.; Suh, J.-W. Ferulic acid grafted self-assembled fructo-oligosaccharide micro particle for targeted delivery to colon. Carbohydrate Polymers 2020, 247, 116550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, T.; Zhong, Y.; Chen, Q.; Wu, L.; Ji, S.; Yang, B.; Zhang, Y.; Shen, J.; Lu, B. Modulating the digestibility of cassava starch by esterification with phenolic acids. Food Hydrocolloids 2022, 127, 107432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
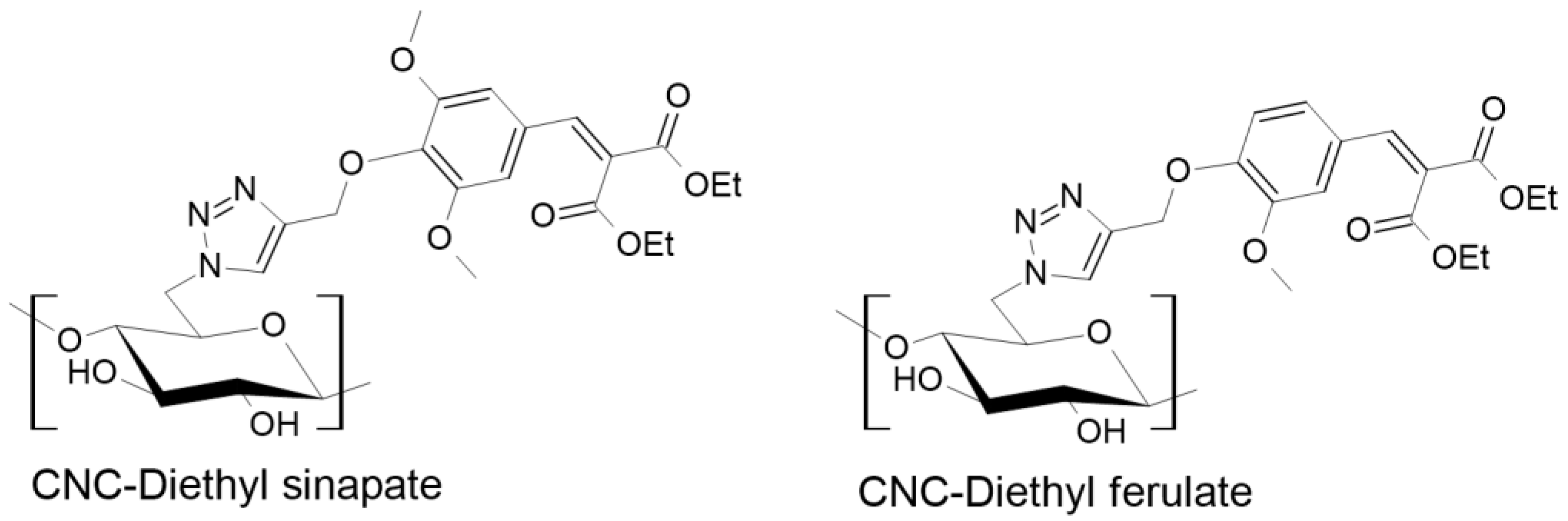
- Mendoza, D.J.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Browne, C.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Simon, G.P.; Garnier, G.; Allais, F. Grafting Nature-Inspired and Bio-Based Phenolic Esters onto Cellulose Nanocrystals Gives Biomaterials with Photostable Anti-UV Properties. ChemSusChem 2020, 13, 6552–6561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, D.J.; Maliha, M.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Browne, C.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Simon, G.P.; Allais, F.; Garnier, G. Diethyl sinapate-grafted cellulose nanocrystals as nature-inspired UV filters in cosmetic formulations. Materials Today Bio 2021, 12, 100126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mendoza, D.J.; Browne, C.; Raghuwanshi, V.S.; Mouterde, L.M.M.; Simon, G.P.; Allais, F.; Garnier, G. Phenolic Ester-Decorated Cellulose Nanocrystals as UV-Absorbing Nanoreinforcements in Polyvinyl Alcohol Films. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2021, 9, 6427–6437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




