Submitted:
25 August 2024
Posted:
27 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
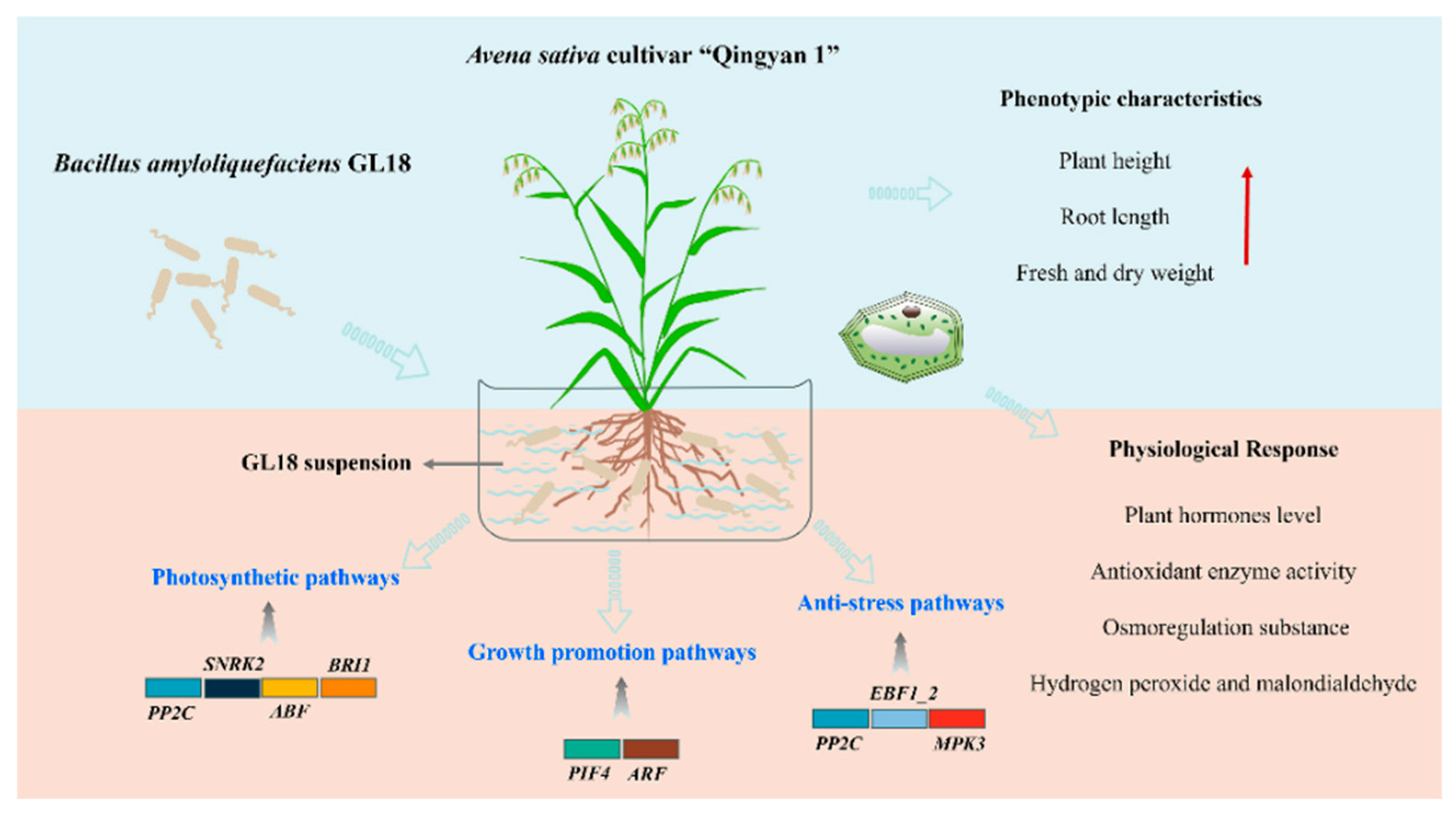
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
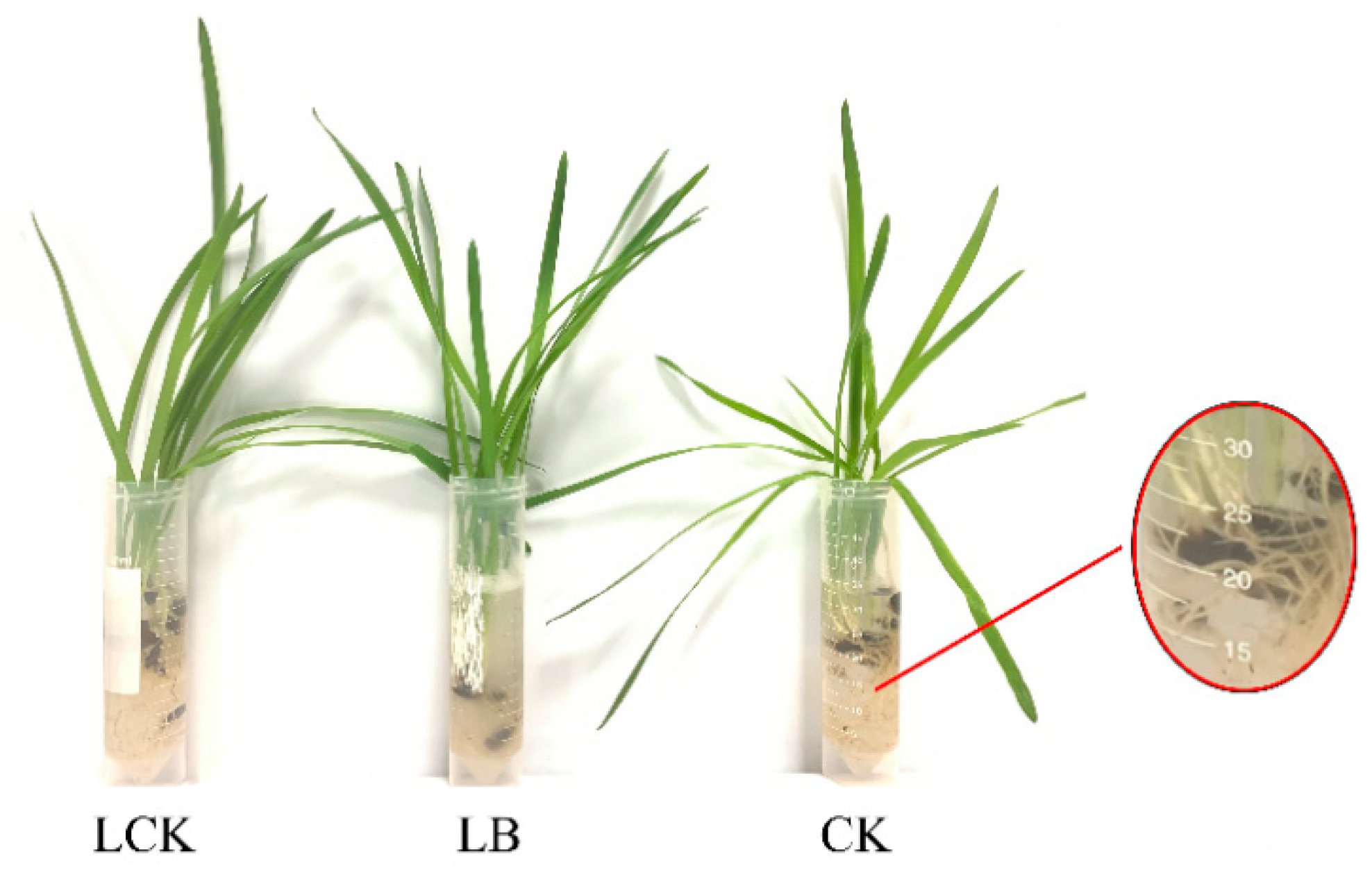
2.1. Bacterial Strain and Plant Material
2.2. Medium and Soil
2.3. GL18 Bacteria Suspension
2.4. Interaction between ‘Qingyan 1’ Root and GL18 Bacterial Suspension
2.5‘. Qingyan 1’ Root for Transcriptome Sequencing
2.6. Transcriptome Data Analysis
2.7. Expression of Growth-Related Genes in Plants by Real-Time Quantitative PCR Analysis
3. Results
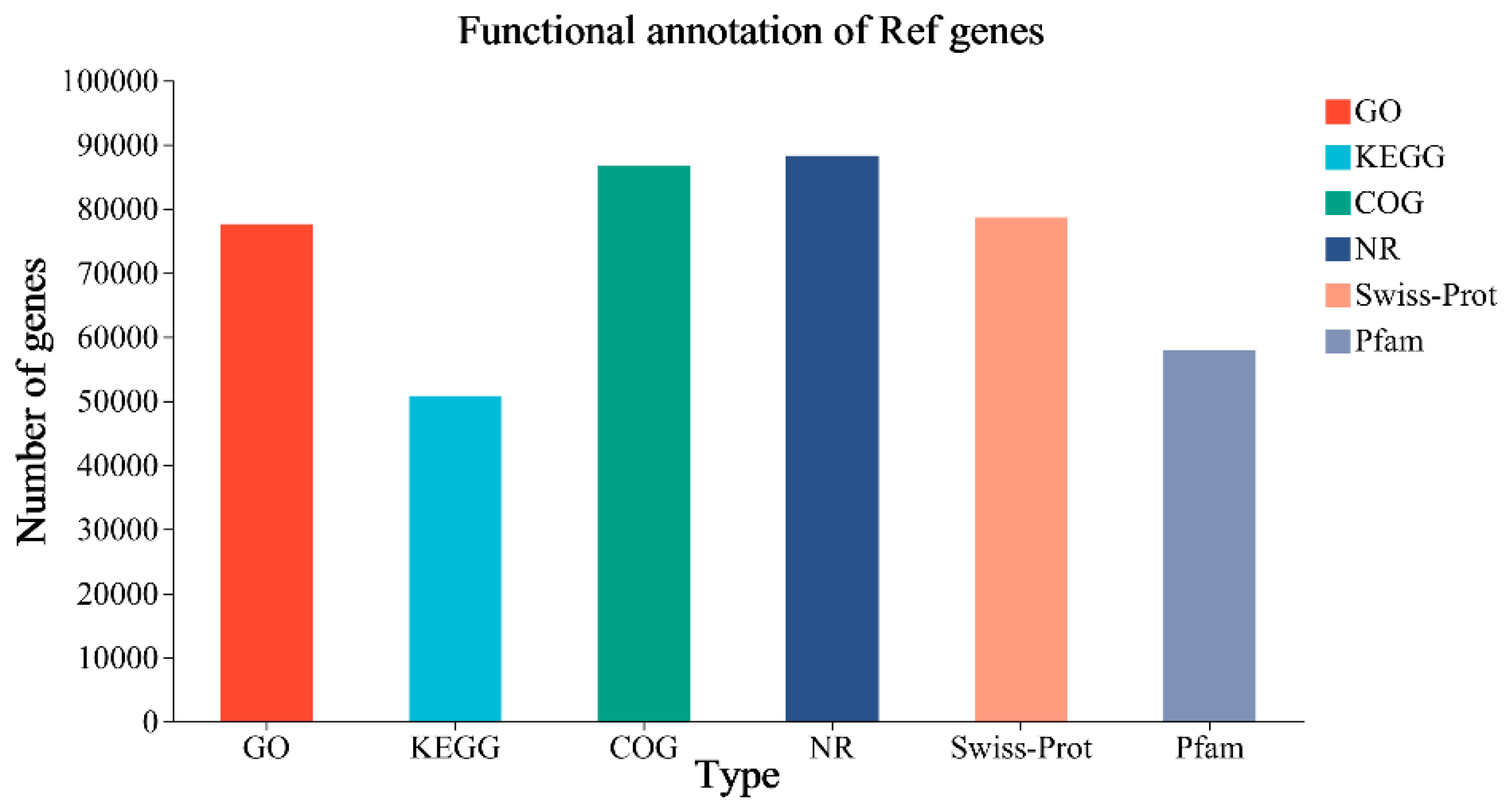
3.1. Sequencing Data Statistics and Evaluation
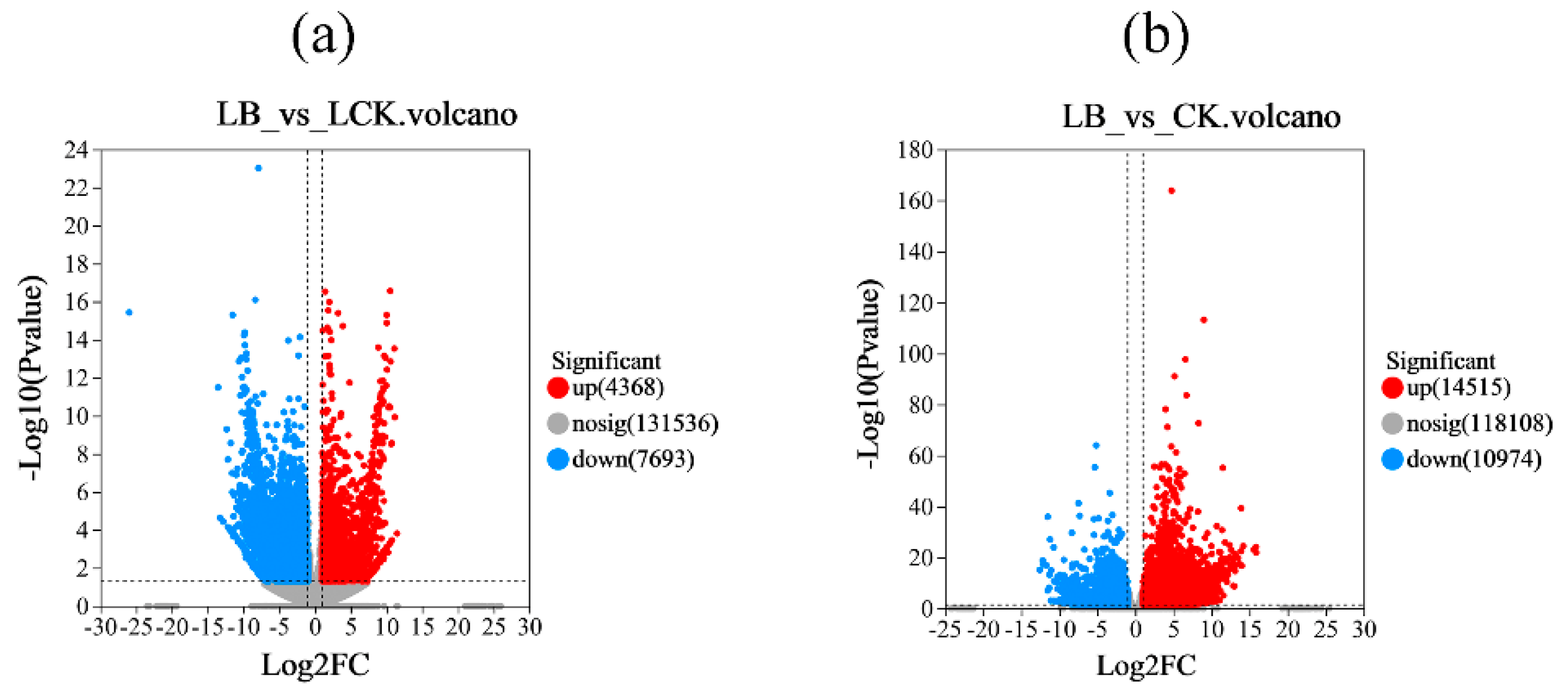
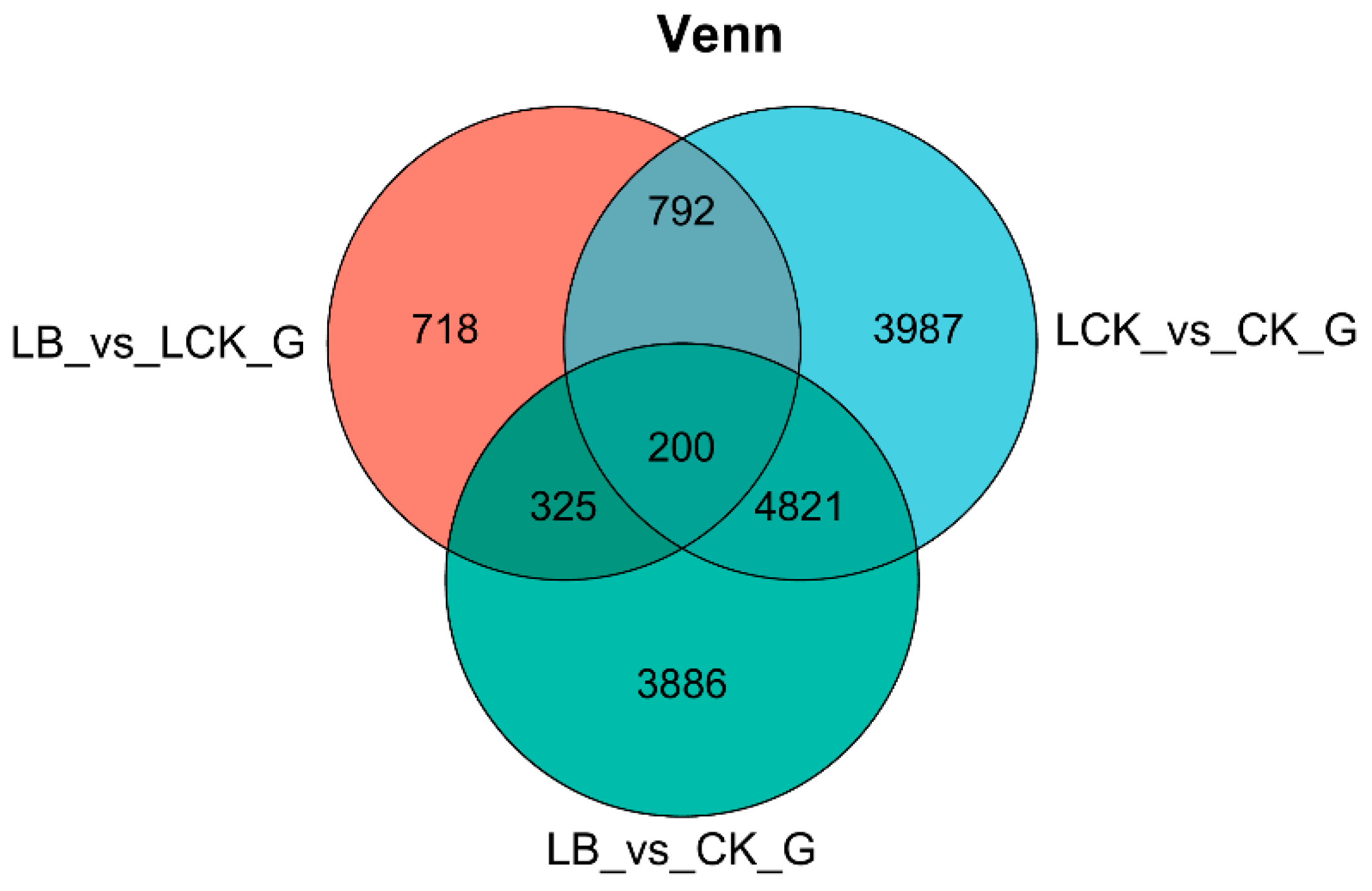
3.2. Statistics of Differentially Expressed Genes
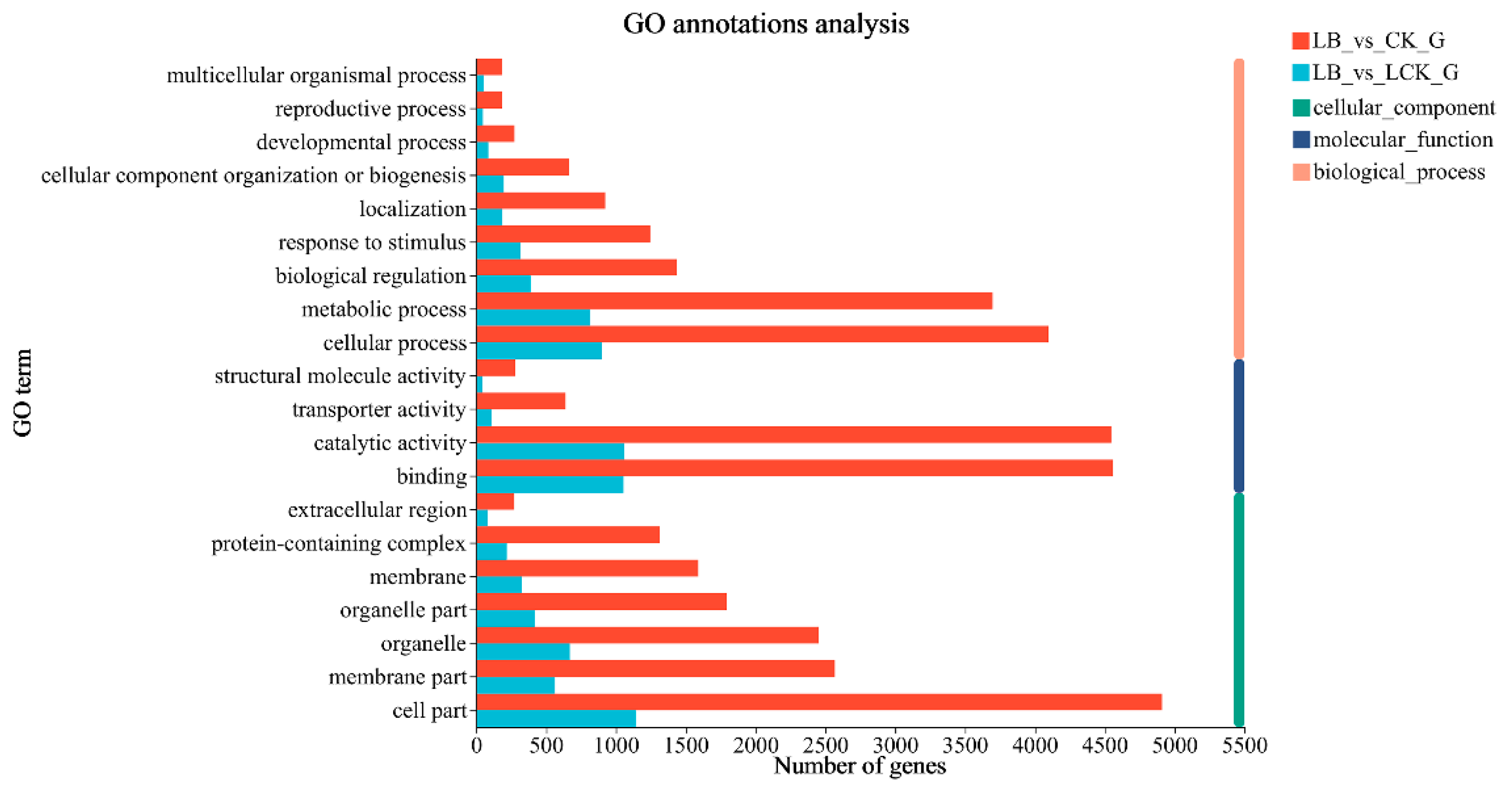
3.3. Annotation Analysis of GO Function of Differentially Expressed Genes
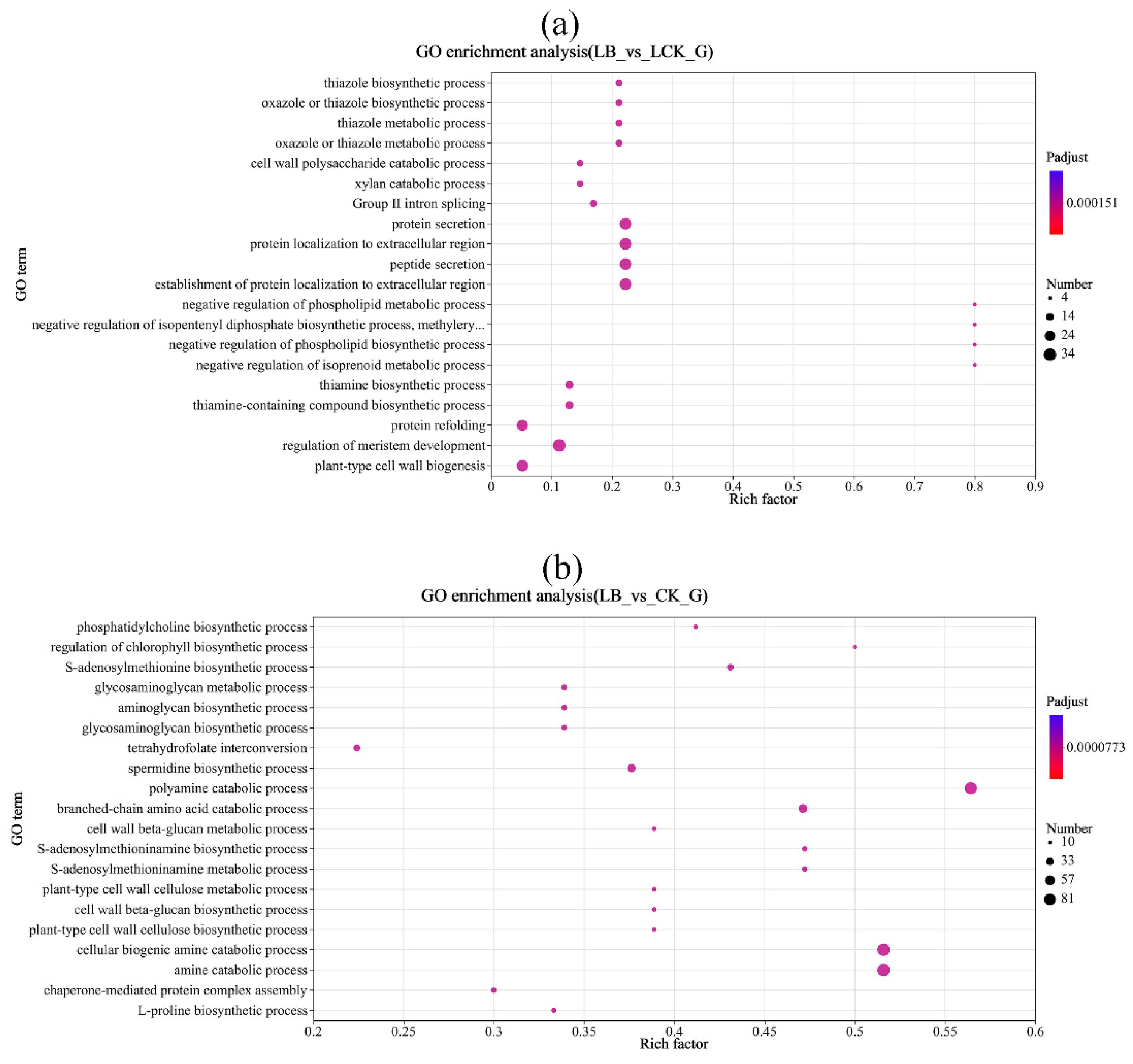
3.4. GO Enrichment Analysis
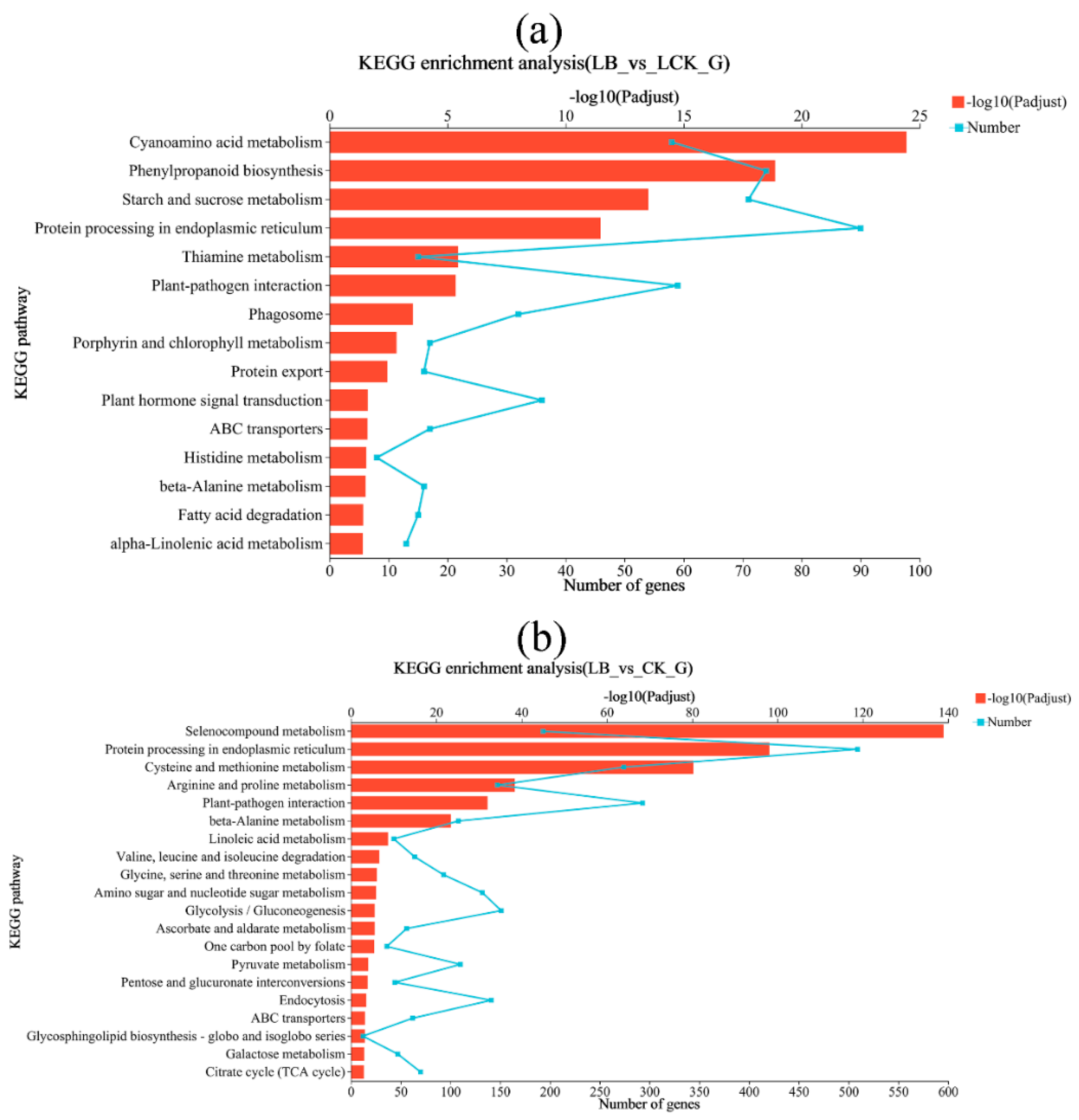
3.5. KEGG Enrichment Analysis of Differentially Expressed Genes
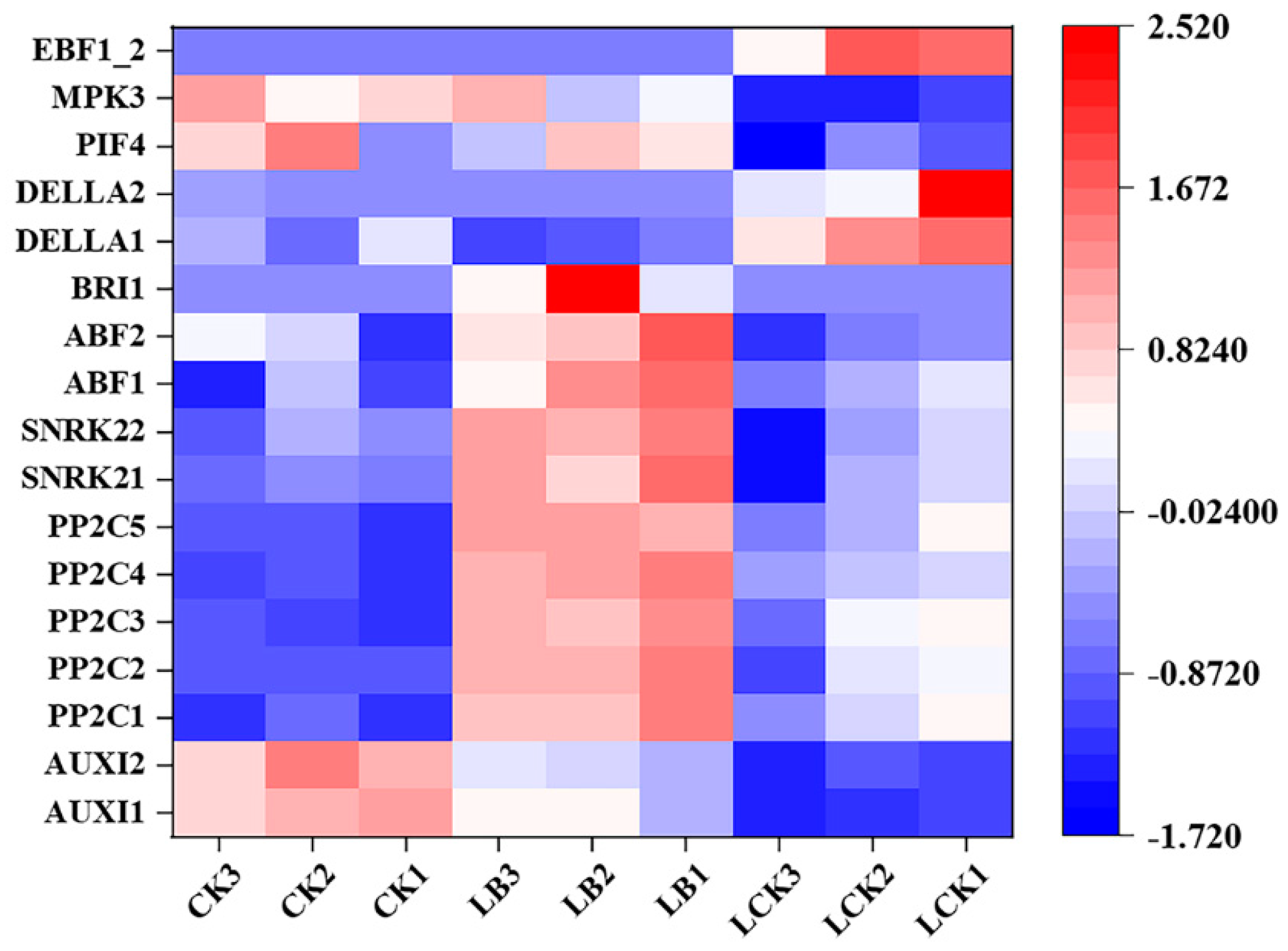
3.6. Analysis of GL18-Related Signal Transduction Pathways in ‘Qingyan 1’ Response
3.6.1. Tryptophan Metabolism
3.6.2. Carotenoid Biosynthesis
3.6.3. Brassinosteroid Biosynthesis
3.6.4. Diterpenoid Biosynthesis
3.6.5. Abscisic Acid-Mediated Stress Resistance Signal Transduction
3.6.6. Ethylene-Mediated Stress Resistance Signal Transduction
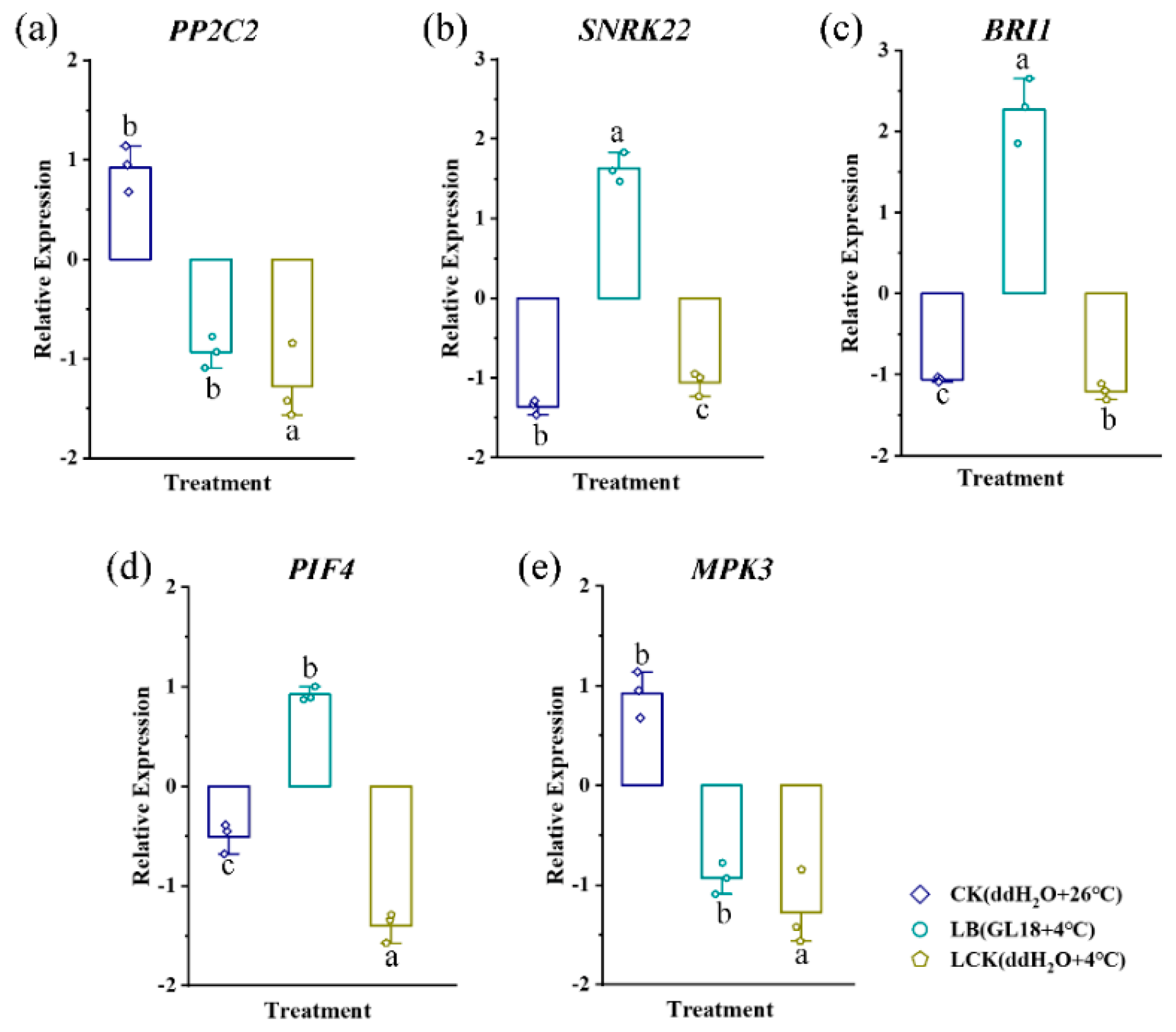
3.7. PCR Validation of GL18 on the Expression of Growth-Related Genes
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
6. Patents
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Pathak, M.R.; Teixeira da Silva, J.A.; Wani, S.H. Polyamines in response to abiotic stress tolerance through transgenic approaches. GM crops & food 2014, 5(2): 87-96. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Xiong, L., Shi, H.; et al. Plant abiotic stress response and nutrient use efficiency. Sci China Life Sci. 2020, 63(5):635-674. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, L.Y.; Li, Y.Y.; Wang, W.N.; et al. Research progress in the metabolomics for plants response to temperature stress. Journal of Shanxi Agricultural Sciences 2017,45(02):317-320.
- Wang, H.; Zhao, J.; Lai, M.; et al. Differential gene expression analysis and physiological response characteristics of passion fruit (Passiflora edulis) buds under high-temperature stress. Peer J 2023, 11: e14839. [CrossRef]
- Akter, N.; Rafiqul Islam, M. Heat stress effects and management in wheat. A review. Agronomy for sustainable development 2017, 37: 1-17. [CrossRef]
- Megha, S.; Basu, U.; Kav, N.N.V. Regulation of low temperature stress in plants by microRNAs. Plant, Cell & Environment 2018, 41(1): 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.W.; Wang, S.; Gao, Y.; et al. Role of microRNAs in response to low temperature stress in plants. Plant Physiol. J 2019, 55: 117-124.
- He, J.S.; Liu, Z.P.; Yao, T.; et al. Analysis of the main constraints and restoration techniques of degraded grassland on the Tibetan Plateau. Science & Technology Review 2020,38(17):66-80.
- Sun, Y.; Guo, R.; Liu, H.C.; et al. Evolutionary game of overgrazing and grassland degradation governance in Qinghai-Tibet Plateau. Science & Technology for Development 2022,18(05):665-673.
- Liang, G.L.; Zhou, Q.P.; Geng, F.; et al. Karyotype analysis of Avena sativa L. ‘Qingyan No.1’. Acta Agrestia Sinica 2016,24(02):389-392.
- Liu, K.Q.; Liu, W.H.; Jia, Z.F.; et al. Effects of drought stress on yield and dry matter accumulation and distribution of Avena sativa cv. Qingyan No.1. Acta Prataculturae Sinica 2021,30(03):177-188.
- Chen, G.; Zhang, Z.H.; Hu, Z.Z. Herbage yield dynamics and solar energy conversion of annual cultivated grassland in Xining city. Acta Prataculturae Sinica 2003, (01):69-73.
- Mahajan, S.; Tuteja, N. Cold, salinity and drought stresses: an overview. Archives of biochemistry and biophysics 2005, 444(2): 139-158.
- Ongena, M.; Jacques, P. Bacillus lipopeptides: versatile weapons for plant disease biocontrol. Trends Microbiol. 2008, 16(3):115-25. [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Suresh, D. Plant growth-promoting rhizobacteria—alleviators of abiotic stresses in soil: a review. Pedosphere 2020, 30(1): 40-61.
- Rosier, A.; Medeiros, F.H.V.; Bais, H.P.; et al. Defining plant growth promoting rhizobacteria molecular and biochemical networks in beneficial plant-microbe interactions. Plant and Soil 2018, 428(1-2), 35–55. [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Hanif, A.; Farzand, A.; et al. Genetic screening and expression analysis of psychrophilic Bacillus spp. reveal their potential to alleviate cold stress and modulate phytohormones in Wheat. Microorganisms 2019, 7(9):337. [CrossRef]
- Zubair, M.; Farzand, A.; Mumtaz, F.; et al. Novel genetic dysregulations and oxidative damage in Fusarium graminearum induced by plant defense eliciting psychrophilic Bacillus atrophaeus TS1. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22(22):12094. [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Xie, Y.L.; Wu, X.H.; et al. Physiological response of Avena sativa to low-temperature stress is promoted by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens GL18 and its functional genes. Russian Journal of Plant Physiology 2022, 69:161.
- Xie, Y.L.; Ma, L.Z.; Xu, Z.W.; et al. Molecular identification of Bacillus strains isolated from extreme dry-sand environment in Qinghai Chaidamu region and its lipopeptide compound analysis. Microbiology China 2012,39(08):1079-1086.
- Yang, X.; Xie, Y.L.; Chen, L.; et al. Biological activity of grass growth-promoting and genome analysis of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DGL1 isolated from the rhizosphere of Nitraria tangutorum of sand soil in Qinghai Province. Acta Agrestia Sinica 2021, 29(8): 1637-1648.
- Ayaz, M.; Ali, Q.; Farzand, A.; et al. Nematicidal volatiles from Bacillus atrophaeus GBSC56 promote growth and stimulate induced systemic resistance in tomato against meloidogyne incognita. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22(9):5049. [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Pertea, G.; Trapnell, C.; et al. TopHat2: accurate alignment of transcriptomes in the presence of insertions, deletions and gene fusions. Genome biology 2013, 14(4): R36. [CrossRef]
- Love, M.I.; Huber, W.; Anders, S. Moderated estimation of fold change and dispersion for RNA-seq data with DESeq2. Genome biology 2014, 15(12): 550.
- Conesa, A.; Götz, S.; García-Gómez, J.M.; et al. Blast2GO: a universal tool for annotation, visualization and analysis in functional genomics research. Bioinformatics 2005, 21(18): 3674-3676. [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Klopfenstein, D.; Pedersen, B.; et al. GOATOOLS: tools for gene ontology. Zenodo., 2015.
- Wang, J.L.; Liu, D.C.; Guo, X.L.; et al. Research advances in auxin biosynthesis. Chinese Bulletin of Botany 2012,47(03):292-301.
- Yue, J.; Hu, X.; Huang, J. Origin of plant auxin biosynthesis. Trends Plant Sci. 2014, 19(12):764-70.
- Tian, Q.Y.; Yue, Y.Z.; Shen, H.M.; et al. Research progress in the regulation of carotenoid metabolism in plant ornamental organ. Biotechnology Bulletin 2022,38(12):35-46.
- Auldridge, M.E.; McCarty, D.R.; Klee, H.J. Plant carotenoid cleavage oxygenases and their apocarotenoid products. Current Opinion in Plant Biology 2006, 9(3), 315-321. [CrossRef]
- Nolan, T.M.; Vukašinović, N.; Liu, D.; et al. Brassinosteroids: multidimensional regulators of plant growth, development, and stress responses. Plant Cell 2020, 32(2):295-318. [CrossRef]
- Abe, H.; Marumo, S. Advance of new plant hormone brassinosteroid. ChemInform 2002,33(42). [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Chen, M.; Chai, T.Y.; et al. Advances in structure-function relation of plant type Ⅲ polyketide synthases by site-directed mutagenesis. Chinese journal of biotechnology 2018,34(4).
- Thompson, A.J.; Jackson, A.C.; Symonds, R.C.; et al. Ectopic expression of a tomato 9-cis-epoxycarotenoid dioxygenase gene causes over-production of abscisic acid. The Plant Journal 2000, 23(3): 363-374.
- Pierik, R.; Tholen, D.; Poorter, H.; et al. The Janus face of ethylene: growth inhibition and stimulation. Trends Plant Sci. 2006, 11(4):176-83. [CrossRef]
- Gouda, S.; Kerry, R.G.; Das, G.; et al. Revitalization of plant growth promoting rhizobacteria for sustainable development in agriculture. Microbiological research 2018, 206: 131-140. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, P.; Irulappan, V.; Bagavathiannan, M.V.; et al. Impact of combined abiotic and biotic stresses on plant growth and avenues for crop improvement by exploiting physio-morphological traits. Frontiers in plant science 2017, 8: 537. [CrossRef]
- Luo, J.; Zhou, J.J.; Zhang, J.Z. Aux/IAA gene family in plants: molecular structure, regulation, and function. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19(1):259.
- Semeradova, H.; Montesinos, J.C.; Benkova, E. All roads lead to Auxin: post-translational regulation of Auxin transport by multiple hormonal pathways. Plant Commun. 2020, 22;1(3):100048. [CrossRef]
- Overvoorde, P.J.; Okushima, Y.; Alonso, J.M.; et al. Functional genomic analysis of the Auxin/Indole-3-Acetic acid gene family members in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant Cell 2005, 17(12):3282-300.
- Gan, D.; Zhuang, D.; Ding, F.; et al. Identification and expression analysis of primary auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in cucumber (Cucumis sativus). J Genet. 2013, 92(3):513-21. [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.; Kaur, N.; Garg, R.; et al. Structure and expression analysis of early auxin-responsive Aux/IAA gene family in rice (Oryza sativa). Funct Integr Genomics. 2006, 6(1):47-59. [CrossRef]
- Audran-Delalande, C.; Bassa, C.; Mila, I.; et al. Genome-wide identification, functional analysis and expression profiling of the Aux/IAA gene family in tomato. Plant Cell Physiol. 2012, 53(4):659-72. [CrossRef]
- Du, H.; Wu, N.; Chang, Y.; et al. Carotenoid deficiency impairs ABA and IAA biosynthesis and differentially affects drought and cold tolerance in rice. Plant Mol Biol. 2013, 83(4-5):475-88. [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Hu, Q.; Yan, J.; et al. ζ-Carotene isomerase suppresses tillering in rice through the coordinated biosynthesis of strigolactone and abscisic acid. Mol Plant. 2020, 13(12):1784-1801. [CrossRef]
- Lozano-Elena, F.; Caño-Delgado, A.I. Emerging roles of vascular brassinosteroid receptors of the BRI1-like family. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019, 51:105-113. [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Wang, Z.Y.; Li, J.; et al. Perception of brassinosteroids by the extracellular domain of the receptor kinase BRI1. Science 2000, 288(5475): 2360-2363. [CrossRef]
- Filo, J.; Wu, A.; Eliason, E.; et al. Gibberellin driven growth in elf3 mutants requires PIF4 and PIF5. Plant Signal Behav. 2015, 10(3): e992707.
- Chen, L.; Dodd, I.C.; Theobald, J.C.; et al. The rhizobacterium Variovorax paradoxus 5C-2, containing ACC deaminase, promotes growth and development of Arabidopsis thaliana via an ethylene-dependent pathway. Journal of experimental botany 2013, 64(6): 1565-1573. [CrossRef]
- Galland, M.; Gamet, L.; Varoquaux, F.; et al. The ethylene pathway contributes to root hair elongation induced by the beneficial bacteria Phyllobacterium brassicacearum STM196. Plant Science 2012, 190: 74-81. [CrossRef]
- Shi, Y.W.; Lou, K.; Li, C.; et al. Effects of endogenous Bacillus polymyxoides S-7 on photosynthesis, yield and quality of sugar beet. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2009, 20(03):597-602.
- Ferreira, S.; Hjernø, K.; Larsen, M.; et al. Proteome profiling of Populus euphratica Oliv. upon heat stress. Ann Bot. 2006, 98(2):361-77. [CrossRef]
- Chen, D.; Shao, Q.; Yin, L.; et al. Polyamine function in plants: metabolism, regulation on development, and roles in abiotic stress responses. Frontiers in plant science 2019, 9: 1945. [CrossRef]
- Pál, M.; Tajti, J.; Szalai, G.; et al. Interaction of polyamines, abscisic acid and proline under osmotic stress in the leaves of wheat plants. Sci Rep. 2018, 8: 12839. [CrossRef]
- Dong, C.J.; Li, L.; Cao, N.; et al. Roles of phenylalanine ammonia-lyase in low temperature tolerance in cucumber seedlings. Chinese Journal of Applied Ecology 2015,26(07):2041-2049.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



