1. Introduction
The discharge into the environment of industrial effluents containing heavy metals without proper treatment is the main source of environmental pollution with this type of pollutants [
1]. The large volumes of effluents generated daily from various industrial activities (such as: metallurgy and coating industry, fertilizers manufacturing, paints industry, electronic components manufacturing, etc.) [
2,
3], the variable content of heavy metals, the non-adaptation of the operating conditions of the treatment processes, and last but not the least, the permissible legislation on environmental quality, and the main reasons why large amounts of heavy metals still reach the environment and affects the quality of many ecosystems. The negative effects on the ecosystems are much more serious if these effluents contain toxic heavy metals (such as Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions), which once reach the environment, even in low concentrations, affect the health of living organisms (including humans) for long periods of time [
4,
5]. Most of time, such toxic heavy metals have an essential role in industrial activities (so they cannot be avoided in production processes), but due to their persistency they accumulate in the environmental components (water, soil) and significantly affect the quality of food chain and implicitly the human health [
5,
6].
Under these conditions, to preserve the quality of the environment, two approaches must be considered. The first is related to environmental legislation, which must become increasingly restrictive and uniform. The increasingly character of environmental quality regulations will allow the historical pollution of water and soil to be avoided, and the uniformity of these regulations will ensure a climate of fair competition between industrial operators in different regions of the world [
7,
8]. The second approach is related to the companies that generate such industrial effluents. Such economic operators must use efficient technologies to treat the wastewater, and these technologies should allow, as far as possible, the recovery of heavy metals and their reuse in other production cycles. Of course, the cost of applying such technologies is a major criterion that must be taken into account. Therefore, finding an effective method for the removal and recovery of toxic heavy metals is still an open research topic, even though numerous studies are presented in the literature [
8,
9,
10,
11].
Various methods, such as precipitation, coagulation, flocculation, ion exchange, membrane filtration, biosorption, etc. [
12,
13,
14,
15], have been frequently tested in the literature for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous media, and some of them are still used on a large scale. Among them, biosorption is considered one of the most feasible methods for heavy metal removal because it is a non-destructive method, simple and easy to operate, can be used in a variety of experimental conditions, has high efficiency and low cost [
15,
16]. In addition, it allows the valorization of a large number of agricultural and industrial wastes by using them as biosorbents in heavy metal removal processes [
17,
18].
However, to date, biosorption is quite little used in industrial practice. One of the reasons why the applicability of biosorption on an industrial scale is so low is the difficulty of findings an effective biosorbent that is available in large quantities and has a low cost of preparation. Although most natural materials (such as zeolites, clay, peat, etc.) [
19,
20], and agricultural waste (cereal straw, leaves, husks, chaff, etc.) [
21,
22], meet the conditions of availability and low cost, their use as biosorbents is limited because all these materials already have some established uses that have proven their practical and economic efficiency. For example, zeolites and clays are used in the manufacturing of building materials [
20], while most agricultural waste are often used in animal husbandry [
21]. In addition, the use of agricultural waste for the removal of metal ions from wastewater leads, in most cases, to an increase in the chemical oxygen demand (CCO, mg O
2/L) of the treated effluent (secondary pollution), due to the easily soluble organic compounds that are released during the biosorption process [
22,
23].
A particular category of agricultural waste is the biomass waste obtained from the extraction of oils for the production of biofuels. The growing demand for biofuels has lead to the growth and use increasing amounts of oilseed crops (such as soybean, rapeseeds, mustard, corn, etc.) [
23,
24], for this purpose. After oil extraction (usually with organic solvents), the biomass wastes have no other uses and are therefore suitable for biosorption processes. Such biomass wastes have a low cost of preparation (since their washing, drying and grinding is already done before the extraction stage) and a high efficiency in metal ions removal processes (due to the large specific surface area, which is a consequence of breaking the cell walls in the extraction stage) [
25,
26]. Also, the danger of secondary pollution of the treated effluent is minimal, since the most of organic compounds from biomass composition are removal in the extraction step. Unfortunately, these biomass wastes also have a major drawback. To be able to keep them for a longer period of time, special conditions of humidity (constant) and temperature (low) are necessary to prevent fermentation of the polysaccharides in their composition.
This inconvenient can be eliminated if biomass wastes obtained from oil extraction is immediately subjected to a pyrolysis process at a moderate temperature (400 – 600 °C) and in a limited oxygen atmosphere. Biochar obtained from pyrolysis retains all the previous advantages (high specific surface area, high biosorption capacity for heavy metals, reasonable preparation costs, etc.) [
27,
28], and in addition, has high stability over time and significantly reduces the volume of biomass wastes [
29]. Moreover, due to traces of organic solvents (from the extraction stage), the amount of thermal energy generated by pyrolysis is higher than in the case of raw biomass, which contributes to the reductions of preparation costs.
In this study, soybean biomass (SB), soybean waste biomass obtained from oil extraction (SBW) and biochar obtained from soybean waste pyrolysis (BC-SBW) were used as biosorbents for the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions, in batch systems. In addition to testing the performance of these biosorbents in the biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions (in laboratory solutions), their use in wastewater treatment (using real wastewater samples) was also examined. The evaluation of the biosorptive performance of each biosorbent will allow the selection of the most suitable biosorbent for industrial applications. All these aspects highlight the possibility of a circular approach for the use of soybean biomass in the removal processes of toxic heavy metals.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials and Reagents
Soybean seeds were purchased from a local farm (Iaşi, Romania). After washing (several times with distilled water) and drying (in air at room temperature), they were ground and sieved, representing raw soybean biomass (SB) for the experimental studies. About 200 g of SB were packed into cartridges and subjected to the oil extraction step (Soxhlet extractor, n-hexane, 70 °C, 8 hours). After the extraction was finished, the residual biomass was dried again (in air, 70 °C) to remove traces of organic solvent, thereby obtaining soybean waste biomass (SBW). SBW samples (accurately weighed) were pyrolyzed in an oven at 550 °C and in limited oxygen atmosphere for 4 hours. After cooling, the obtained biochar samples were washed (with distilled water) and dried (in air at room temperature). In this way BC-SBW was obtained. All biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW) were stored in desiccators at constant humidity until used for experimental studies.
Stock solutions of metal ions (10-2 mol M(II)/L; M(II) – Pb(II) and Cd(II)) were obtained by dissolving lead nitrate and cadmium nitrate (purchased from Chemical Company, Iaşi, Romania) in distilled water. These solutions were used to obtain all working solutions, by diluting with distilled water. 10-2 mol/L HNO3 and NaOH solutions were used to adjust the pH of the working solutions to the desired value.
Wastewater samples were obtained from a local metal coating company. They were sampled directly from the wash tank of the pieces after coating. Such wastewater samples have a low content of organic compounds and inorganic salts, and were considered suitable for testing the practical applicability of biosorbents. After sampling, the wastewater samples were filtered (to remove solid impurities) and kept in a refrigerator (4 °C) until use in experimental studies (maxim 48 hours).
2.2. Biosorption/Desorption Experiments and Data Analysis
Two series of biosorption experiments were performed, in batch and mono-component systems. In the first series, laboratory solutions were used and the biosorption studies were carried out in 100 mL conical flasks, varying the initial concentration of metal ions (32 – 288 mg Pb(II)/L and 14 – 323 mg Cd(II)/L) and the contact time (5 – 180 min). In the case of experiments carried out in laboratory solutions using SB as biosorbent, the influence of pH (1.09 – 6.50), the amount of biosorbent (4.0 – 40.0 g/L) and temperature (5, 20 and 50 °C) on biosorption efficiency was also examined, in order to establish the optimal conditions. In the second series, wastewater samples were used as background, in which the initial concentration of metal ions (Pb(II) and Cd(II)) was adjusted at 35 mg/L for Pb(II) and 15 mg/L for Cd(II), and the other parameters to the optimal values (pH = 5.4, biosorbent dose = 4.0 g/L, contact time = 180 min, room temperature (25 ± 1°C)).
All solutions were intermittently stirred for a certain period of time, filtered (on quantitative filter paper) for phases separation, and analyzed. The concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions in the filtrated solutions was determined by Atomic Absorption Spectrometry (AAS NovaA400 spectrometer, in acetylene/air flame, at characteristic wavelength), and the obtained values were used to calculate the biosorption capacity (q, mg/g) and the removal percent (R, %), according to the equations:
where:
c0 and
c are initial and equilibrium concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions in solution (mg/L),
V is volume of solution used in the biosorption experiments (25 mL), and
m is the mass of biosorbent (g).
Experiments were performed in triplicate, at room temperature (22 ± 1 °C), and in all cases the means values of the measurements were used for graphical representations and tables.
The kinetic and isotherm data were analyzed using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order kinetic models [
30,
31], and Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models [
32,
33], whose mathematical equations are:
where:
q is biosorption capacity (mg/g),
c is equilibrium concentration of heavy metal ions in solution (mg/L),
qe,
qt are the biosorption capacities at equilibrium and at time t (mg/g),
k1 is the rate constant of pseudo-first order model (1/min),
k2 is the rate constant of pseudo-second order model (g/mg min),
qmax is the maximum biosorption capacity (mg/g),
KL is Langmuir constant (L/g),
n is heterogeneity factor,
KF is Freundlich constant (L/g).
The recovery of retained Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions on the three biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW) was achieved by treating 0.1 g of each biosorbent loaded with each metal ion with 10 mL of 10
-1 mol/L HNO
3 solution. After 180 min of intermittent stirring, the solutions were filtered and the concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions was determined by AAS spectrometry as described above. The heavy metal ions recovery efficiency (Recovery, %) was calculated based on the relation:
where:
cd is the concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions in aqueous solution (mg/L);
qe is the biosorption capacity (mg/g) for each metal ion and each biosorbent and
m is the mass of biosorbent used in recovery experiments (g).
2.3. Analytical Methods
The following methods were used to characterize the biosorbents: (i) FTIR spectrometry (Bio-Rad Spectrometer, 400–4000 cm-1 domain, resolution of 4 cm-1, KBr pellet technique, ACD/Spec Manager software) – which allows the identification of superficial functional groups, and (ii) SEM microscopy (SEM/EDAX Hitach S3000N, 20 kV) – which was used to analyze the surface morphology of the biosorbents and obtaining elemental mapping images.
The quality indicators of wastewater samples (pH, TSM, CCO-Cr and CBO
5), before and after biosorption, were determined by standard methods [
34], and the obtained values were compared with the maximum permissible limits according with the Romanian legislation (NTPA 002/2005) [
35].
3. Results and Discussion
As mentioned in the previous section, SBW was obtained from SB after oil extraction, while BC-SBW was prepared by pyrolysis of SBW under aforementioned conditions. The experimental results showed that after the extraction step, 43.18 % oil was extracted from SB, while the pyrolysis yield was 79.38 %. These encouraging results highlight, on the one hand, the usefulness of SB in obtaining oil for the biofuels production and the significant reduction of biomass waste through pyrolysis, and on the other hand, they show that both SBW and BC-SBW have significant structural changes, which can be exploited in biosorption processes.
3.1. Characterization of SB, SBW and BC-SBW Biosorbents
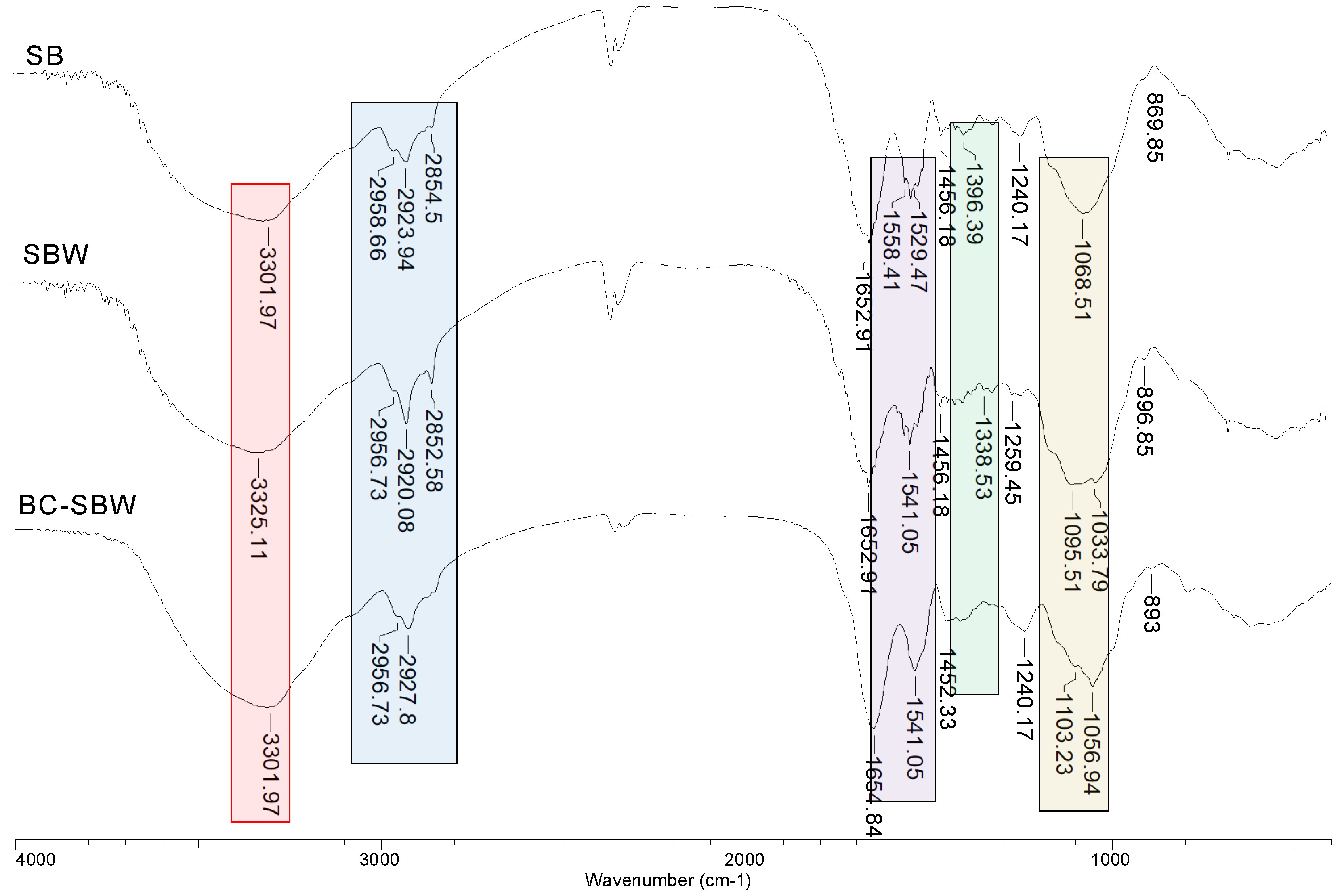
To highlight these changes in the structure of SB, SBW and BC-SBW, FTIR spectra (
Figure 1), SEM images and oxygen mapping images were recorded (
Figure 2). Oxygen was chosen for the mapping images, because most of the functional groups important for the retention of heavy metal ions contain this element, and its presence on the surface of biosorbents is an indication of their efficiency.
As can be seen from
Figure 1, hydroxyl (3301-3325 cm
-1), saturated and aromatic hydrocarbon chains (2852-2958 cm
-1), carbonyl (1652-1654 cm
-1) and ether (1068-1103 cm
-1) groups are present on the surface of the studied biosorbents, regardless of their nature. However, the transformation of SB in SBW and then in BC-SBW causes some changes in the FTIR spectra. Thus, after extraction step and respectively pyrolysis step, the most important changes in the FRIT spectra are (
Figure 1):
(i) a rearrangement of the saturated hydrocarbon radicals takes place. Simplification of the shape of the absorption bands at 2852-2958 cm-1 and 1529-1558 cm-1 (in SB spectrum) corresponding to the symmetric and asymmetric vibration of the C–H bonds, support this rearrangement.
(ii) some of the organic esters are removal by extraction or degraded following pyrolysis. This causes the band at 1396 cm-1 attributed to the C=O bond from acetyl or esters in the SB spectrum, to decrease in intensity in the SBW spectrum, or event disappear in the BC-SBW spectrum.
(iii) modification of the conformation of polysaccharides, since the band at 1068 cm-1, characteristic of C–O–C bonds in polysaccharides (in the SB spectrum) splits in the SBW and BC-SBW spectra.
All these observations show that the extraction and pyrolysis steps cause important changes in the structure of raw SB and that the materials obtained after these steps (SBW and BC-SBW) still have enough functional groups on their surface to be used as biosorbents.
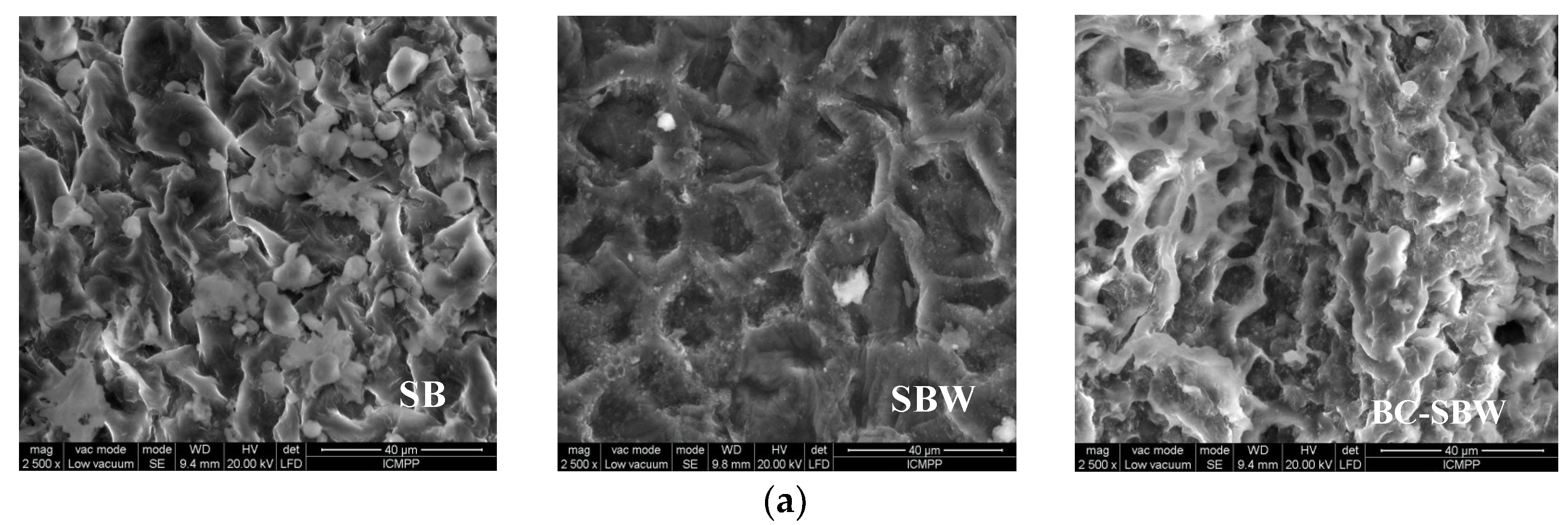
The changes caused by the extraction and pyrolysis steps in the surface morphology of SB can also be observed from the SEM images (
Figure 2a). After the extraction step, SBW surface becomes much more heterogeneous with deep wrinkles and cracks. These characteristics are further accentuated by the pyrolysis step (BC-SBW).
Therefore, SBW and BC-SBW are expected to have a higher surface area than raw SB, and thus to be more effective in the biosorption processes. In addition, the relatively homogenous distribution of O-donor functions groups on their surface (
Figure 2b), is another important argument for the used of SBW and BC-SBW as biosorbents in the retention processes of metal ions from aqueous media.
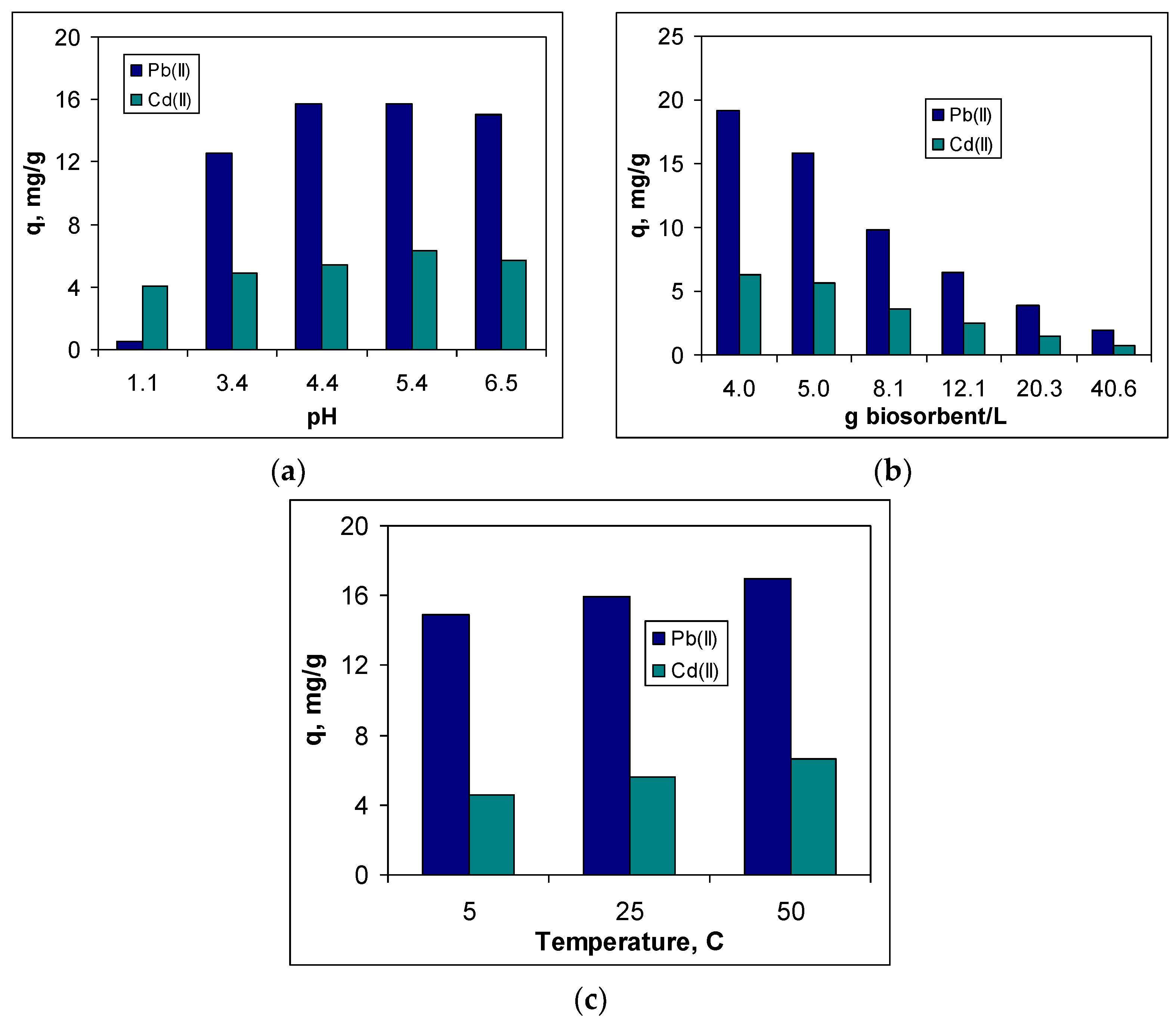
3.2. Establishing Optimal Biosorption Conditions
As mentioned in
Section 2.2, the optimal conditions (pH, biosorbent dose and temperature) were determined for both metal ions (Pb(II) and Cd(II)) using only SB as biosorbent. The values established as optimal for the retention of metal ions on SB were also used for the other two biosorbents (SBW and BC-SBW). The obtained results are illustrated in
Figure 3.
As expected, pH significantly influences the efficiency of the biosorption processes, for both studied metal ions. The highest values of the biosorption capacity are obtained at pH = 5.4 (
Figure 3a), when over 94 % of Pb(II) ions and 69 % of Cd(II) ions are removed from the aqueous solution. This increase in biosorption capacity with the pH increase is mainly determined by the increase of the dissociation degree of the functional groups of the biosorbent, which become negative and can interact with positively charged metal ions [
23,
36]. In addition, at this pH, the precipitation of metal ions is avoided, and their removal is done only by biosorption. Experimental measurements of pH after the completion of the biosorption processes show that regardless of the nature of metal ion or the biosorbent, the value of this parameter is not higher than 6.1 (
Table 1). Therefore, a pH value of 5.4 can be considered optimal for the biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions, and this value was used in all other experiments.
The influence of biosorbent dose on the biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions on SB is illustrated in
Figure 3b. The increase of the biosorbent dose from 4.0 to 40.0 g/L leads to a decrease in the biosorption capacity by 90 % for Pb(II) ions and by 88 % for Cd(II) ions. This accentuated decrease in the biosorption capacity of the two ions is a consequence of the agglomeration of the biomass particles, which occurs at high values of the biosorbent dose [
22,
23].
When the amount of biosorbent is high, biomass particles easily come into contact with each other, which causes the physical interactions (most often hydrogen bonds) to occur between superficial functional groups [
22,
36]. Therefore, at low concentrations of metal ions (when the driving force of the biosorption process is less pronounced), these functional groups become unavailable for further interactions. On the other hand, increasing the biosorbent dose by 10 times (from 4.0 to 40.0 g/L) causes an increase in the removal percent of at most 10 % (from 91.63 to 94.98 % for Pb(II) ions, and from 58.71 to 66.48 % for Cd(II) ions, respectively). Under these conditions, the biosorbent dose considered optimal for the biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions on SB, was selected as 4.0 g/L.
As can be seen from
Figure 3c, the influence of temperature on the biosorption efficiency of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions on SB is insignificant. Increasing the temperature from 5 to 50 °C leads to an increase in the biosorption capacity of only 8 % for Pb(II) ions (from 14.93 to 16.22 mg/g) and 11 % for Cd(II) ions (from 4.56 to 5.06 mg/g). Therefore, room temperature (25 ± 1 °C) can be considered the optimal temperature, since the costs required maintaining a high temperature are not justified by the increase by a few percents of the efficiency of the studied biosorption processes.
Based on the experimental results presented in this section, it was established that the biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions on SB occurs with maximum efficiency when: pH = 5.4, biosorbent dose = 4.0 g/L and at room temperature (25 ± 1 °C). As was mentioned initially, these experimental conditions are considered optimal, and were also used in the case of the other two biosorbents (SBW and BC-SBW).
3.3. Evaluation of Biosorption Performances
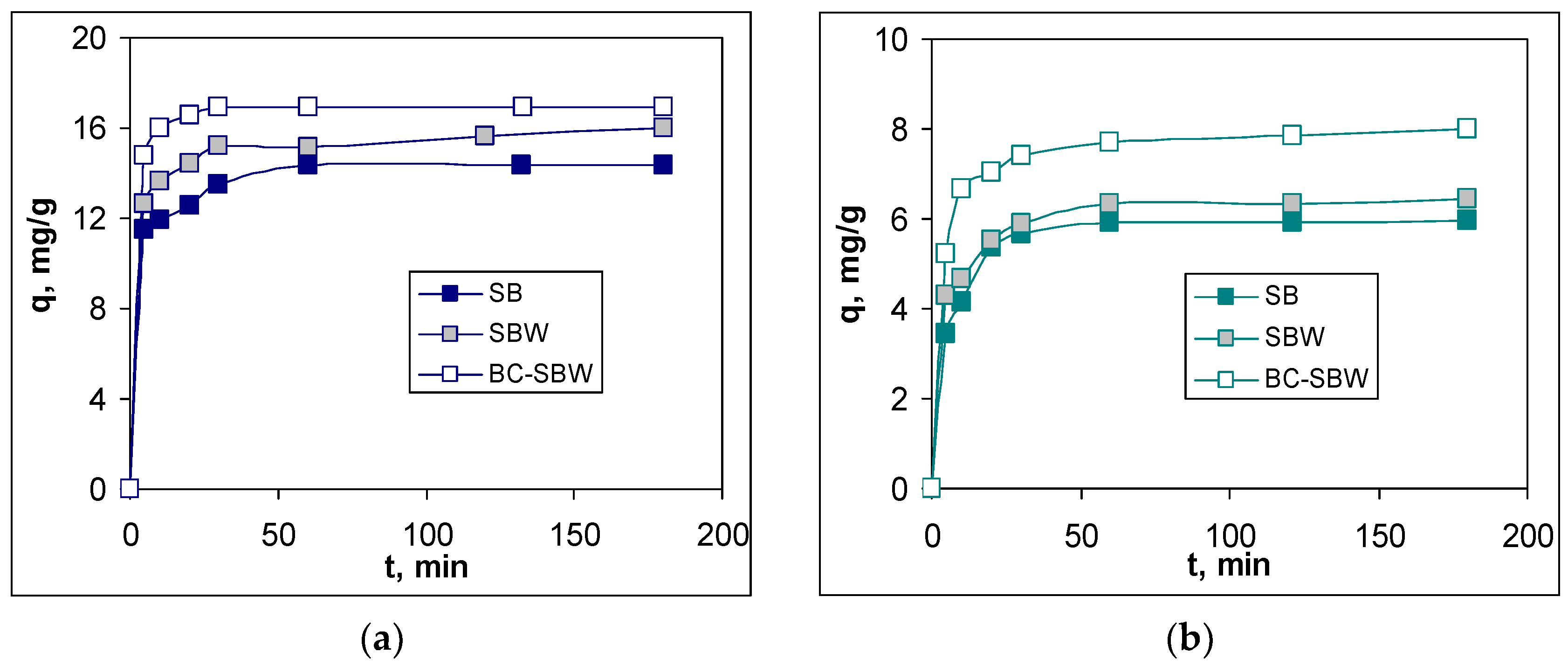
To evaluate the efficiency of the three biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW) in retaining Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution, the biosorption studies were carried out at different values of contact time and initial concentration of metal ions, under optimal conditions (previously established). The experimental results are presented in
Figure 4 and
Figure 5.
Regardless of the nature of the biosorbent or the heavy metal ion, increasing the contact time leads to an increase in the biosorption capacity (
Figure 3). This increase is accentuated in the first 30 min, when the number of free functional groups available to interact with metal ions is high, and much slower after 60 min, when the biosorption processes reach equilibrium (the variation of q is a maximum of 3 %). From the analysis of these experimental data, two aspects can be highlighted. The first is related to the fact that, regardless of the nature of the biosorbent, the biosorption processes proceed similarly, and the time required to reach the equilibrium state is practically the same (60 min). This observation suggest that at this (relative low) concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ion, all biosorbents have sufficient superficial functional groups that can participate in biosorption processes. The second aspect considers that for both heavy metal ions, the highest biosorption capacity values are obtained for BC-SBW, followed by SBW and then SB. This variation in q values (
Figure 4) shows that another important factor in the efficiency of the biosorption process is the morphology of the biosorbent surface.
The breaking of cell walls (In the case of SBW) and the thermal degradation of organic matter (In the case of BC-SBW) increase the number of functional groups available for interactions with metal ions, and this leads to an improvement in the efficiency of biosorption processes (
Table 2).
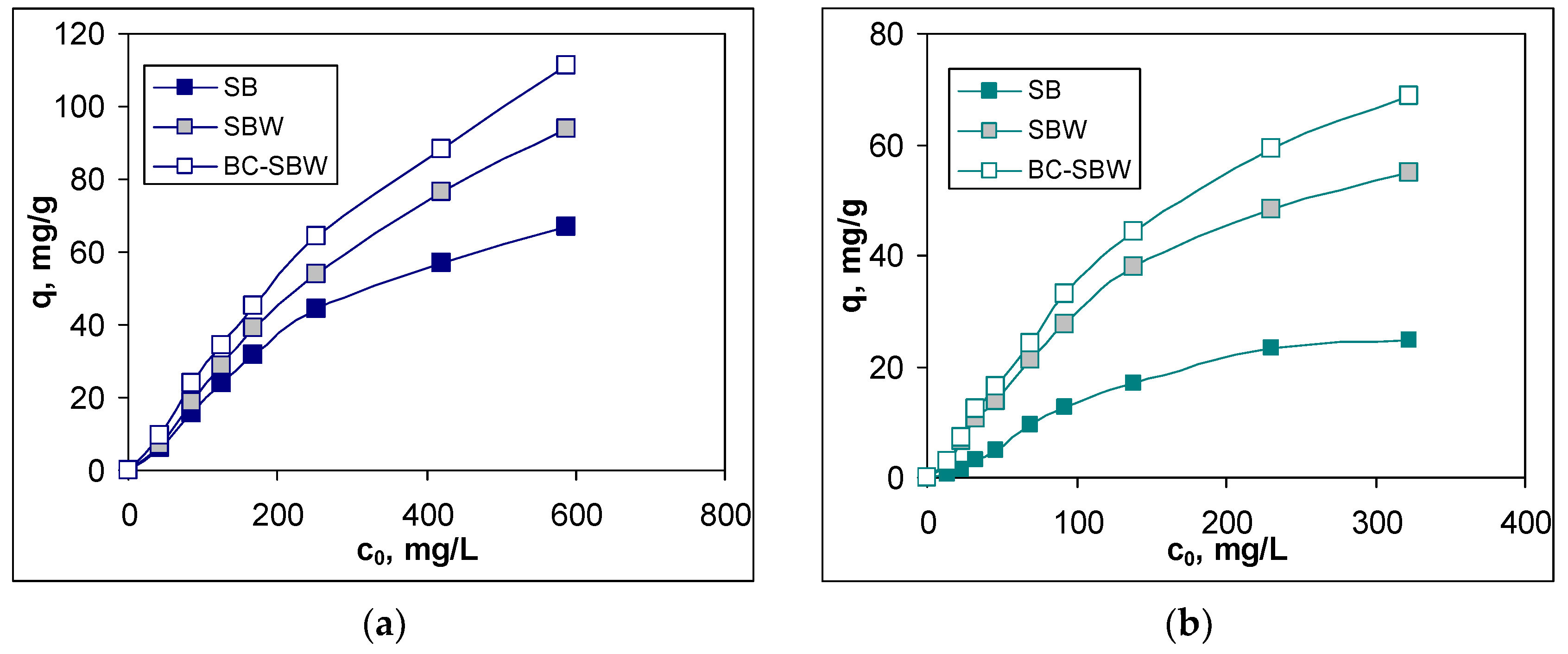
However, it should be noted that these results were obtained for relatively low concentrations of metal ions (see
Figure 4). Therefore, to evaluate the performance of the studies biosorption processes, it is very important to examine the influence of the initial concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution. The experimental results obtained in this case are illustrated in
Figure 5.
Increasing the initial concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions (
Figure 5) enhances the probability of interactions between the metal ions and the functional groups of the biosorbents and, consequently, the values of the biosorption capacities increase, through the studied concentration range. Such a variation of the biosorption capacity as a function of the initial concentration is frequently encountered in the biosorption processes of metal ions, and indicates that the increase in the metal ion concentration, the driving force of the biosorption process also increases [
37,
38].
However, analyzing the results illustrated in
Figure 5, it can be seen that the biosorption capacity depends on the nature of the biosorbent, and this is evident at high initial concentrations of metal ions. For both metal ions, the highest values of this parameter are obtained in the case of BC-SBW, followed by SBW and then SB. This suggests that BC-SBW can be considered a much more efficient biosorbent for the retention of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions, compared to SBW and SB. Moreover, BC-SBW has high efficiency event at high initial concentration of metal ions (
Table 3), which highlight the possibility of its use for industrial wastewater treatment. At low initial concentrations, BC-SBW allows quantitative removal of metal ions (over 99 % for Pb(II) ions and about 90 % for Cd(II) ions), while the other biosorbents (SBW and SB) require two or more biosorption steps to effectively remove Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions from aqueous solution (
Figure 5 and
Table 3).
To highlight the biosorptive performances of the three biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW), the kinetic and equilibrium data were modelled using the pseudo-first and pseudo-second order models, and the Langmuir and Freundlich isotherm models. The parameters of each model were calculated from the slope and intercept of the characteristic linear plots (data not shown) and are summarized in
Table 4.
As can be seen from
Table 4, regardless of the nature of the metal ion (Pb(II) or Cd(II)) or the biosorbent (SB, SBW or BC-SBW), the experimental results are best described by the pseudo-second order kinetic model and the Langmuir model. This means that the biosorption of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions on the studied biosorbents occurs until the formation of a complete monolayer on the out-surface of the biosorbent [
39] and that in the retention process the metal ions need two functional groups to bind to the biosorbent surface [
40]. These observations confirm once again that the performances of SB, SBW and BC-SBW biosorbents depend on both the number and nature of superficial functional groups and the morphology of the biosorbent surface, and have important consequences on the design of the biosorbent preparation methodology. This in the case of SB, special attention must be paid to the choice of an appropriate grinding degree of soybean seeds. It is well known that the more advanced the biomass crushing, the higher the specific surface area of the biosorbent [
23]. In the case of SBW, in addition to the grinding degree of soybean, the optimal conditions for oil extraction must be also considered. A high efficiency of the extraction step leads to the effective breaking of the cell walls of the biomass particles and therefore to an increase in the specific surface area of the SBW biosorbent. In the case of BC-SBW, an optimal value of the pyrolysis temperature must be also taken into account.
This temperature must be chosen in such a way as to allow the thermal decomposition of the organic matter (which determines the obtaining of a heterogeneous surface), but also to ensure the presence of as many functional groups as possible (which will represent the binding centers for the metal ions in the aqueous solution). These considerations were the basis for choosing the temperature of 550 °C for SBW pyrolysis.
3.4. Evaluation of the Practical Applicability of Biosorbents
The first step in testing the practical applicability if a biosorbent is to examine it in desorption studies. Since the metal ions retained in this study (Pb(II) and Cd(II)) are ions with high toxic potential, the main purpose of the desorption studies is to determine the percent of heavy metal ions that pass into the aqueous solution (% Recovery) after treating the loaded-biosorbents with an adequate desorption agent. In this study, 10 mL of HNO
3 (10
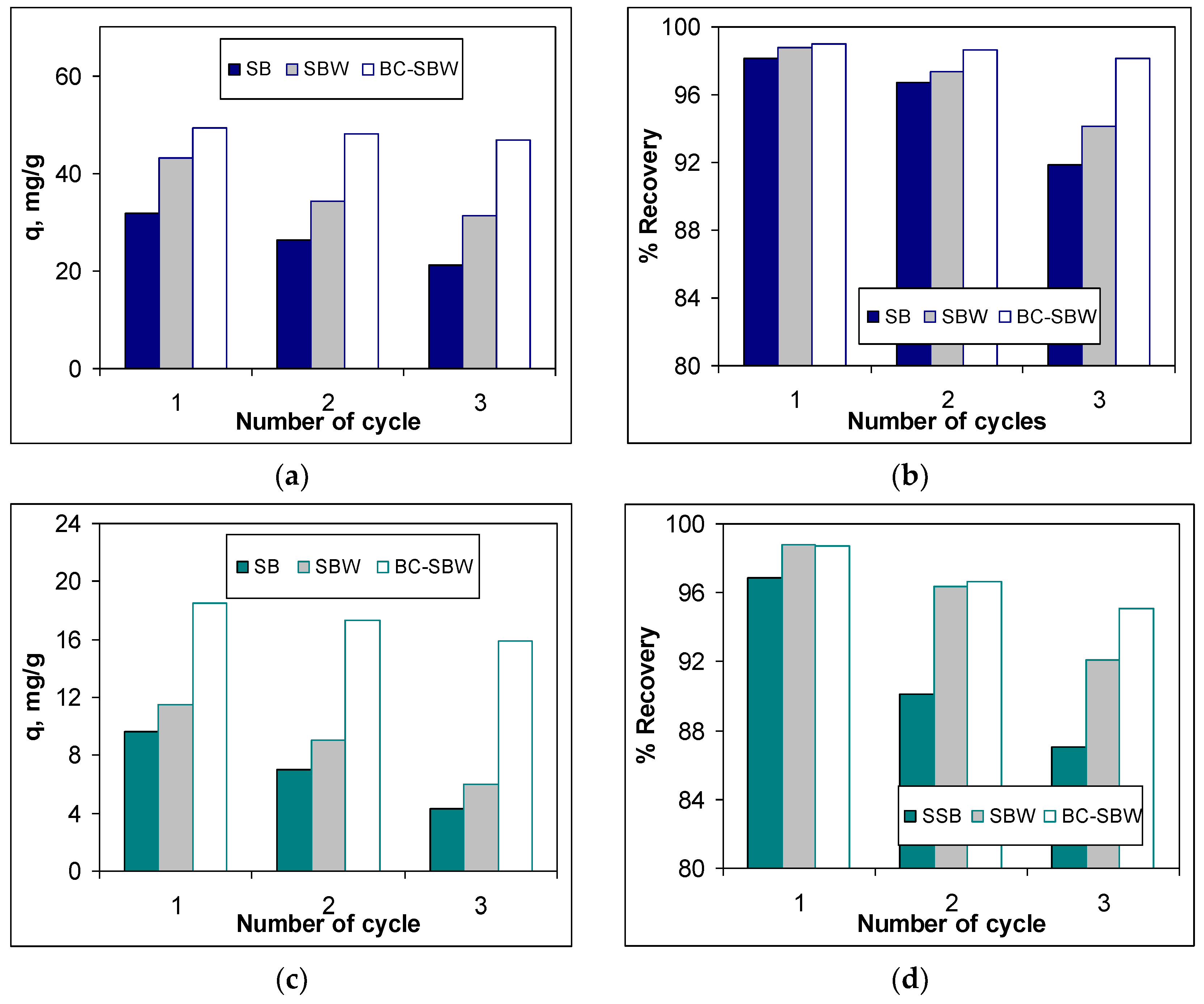
-1 mol/L) was used for desorption, because mineral acids ensure quantitative desorption of metal ions (even at small volumes of acid solution), and strongly acid media preserves metal ions in the form of free ions and can thus be reintroduced into the technological circuit. The experimental results obtained in the case of three biosorption/desorption cycles for each of the studied biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW), both in the case of Pb(II) ions and in the case of Cd(II) ions, are presented in
Figure 6.
It can be seen in
Figure 6 that with the increase of the number of cycles, both the biosorption capacity (q, mg/g) and recovery percent (% Recovery) decrease, for all three biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW). However, the decrease in biosorption capacity (
Figure 6 a and c) is much more pronounced, and the largest differences between the first and the last cycle occurs in the case of SB (33.32 % for Pb(II) ions and 55.34 % for Cd(II) ions), followed by SBW (27.64 % for Pb(II) ions and 47.65 % for Cd(II) ions), and then BC-SBW (5.05 % for Pb(II) ions and 14.35 % for Cd(II) ions). The variation of recovery percent (% Recovery) during of the three biosorption/desorption cycles (
Figure 6 b and d) is much smaller, regardless of the nature of the metal ions of the biosorbent. This in the case of Pb(II) ions, the decrease in the recovery percent is 6.35 % in the case of SB, 4.69 % in the case of SBW and 0.91 % for BC-SBW, while for Cd(II) ions, the decrease in the recovery percent doest not exceed 10 % (10.15 % for SB, 6.72 % for SBW and 3.64 % for BC-SBW).
The analysis of these results shows that among the studied biosorbents, SB has the poorest biosorptive performance, because: (i) it has the lowest biosorption capacity, (ii) the biosorption capacity decreases the most when is used in several cycles, and (iii) the recovery percent of metal ions (by desorption) decrease significantly from cycle 1 to cycle 3. All these aspects drastically limit the practical utility of this biosorbent in the removal processes if metal ions from aqueous media. Unlike SB, BC-SBW has the best biosorptive performance. The much lower decrease in the biosorption capacity (up to 15 %) and the insignificant variation of the recovery percent of metal ions (up to 4 %), when is used in multiple biosorption/desorption cycles recommend the use of this biosorbent for practical applications.
To highlight the possibility of using these biosorbents in industrial decontamination processes, biosorption studies were performed for each biosorbent (SB, SBW and BC-SBW) and for both metal ions (Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions), using wastewater samples. In this case, the biosorption conditions were those established as optimal (pH = 5.4, biosorbent dose = 4.0 g/L, contact time = 180 min, temperature = 25 ± 1 °C), while the initial concentration of metal ions was adjusted to 35 mg/L for Pb(II) ions and 15 mg/L for Cd(II) ions (values similar with those encountered in industrial practice). The values of the quality indicators (pH, TSM, CCO-Cr and CBO
5) of the wastewater samples determined before and after the biosorption of each metal ion (Pb(II) and Cd(II)) on each biosorbent (SB, SBW and BC-SBW) are summarized in
Table 5.
Although none of the biosorbents decreases the concentration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions below the maximum permissible limit (
Table 5), it can be seen that the use of BC-SBW brings a number of advantages, compared to the other two biosorbents (SB and SBW). Thus, the pH of wastewater samples is greater than 6.5 (the lower limit imposed by the regulation), and therefore an additional neutralization step is no longer necessary after biosorption. This pH variation is a consequence of the high content of alkaline and alkaline-earth metals in the BC-SBW composition, which release hydroxyl groups (due to hydrolysis) [
41,
42], thus contributing to the increase in the value of this parameter. Furthermore, the value of the CCO-Cr indicator, which is a measure of the content of oxidizable organic compounds in the water sample, decrease significantly after using BC-SBW as a biosorbent. This shows that along with metal ions (Pb(II) and Cd(II), in this case), organic compounds are also retained/degraded on BC-SBW.
All these observations show that among the studied biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW), BC-SBW is the most suitable to be used in industrial wastewater treatment processes, and this recommendation can represent the starting point for the design a circular approach.
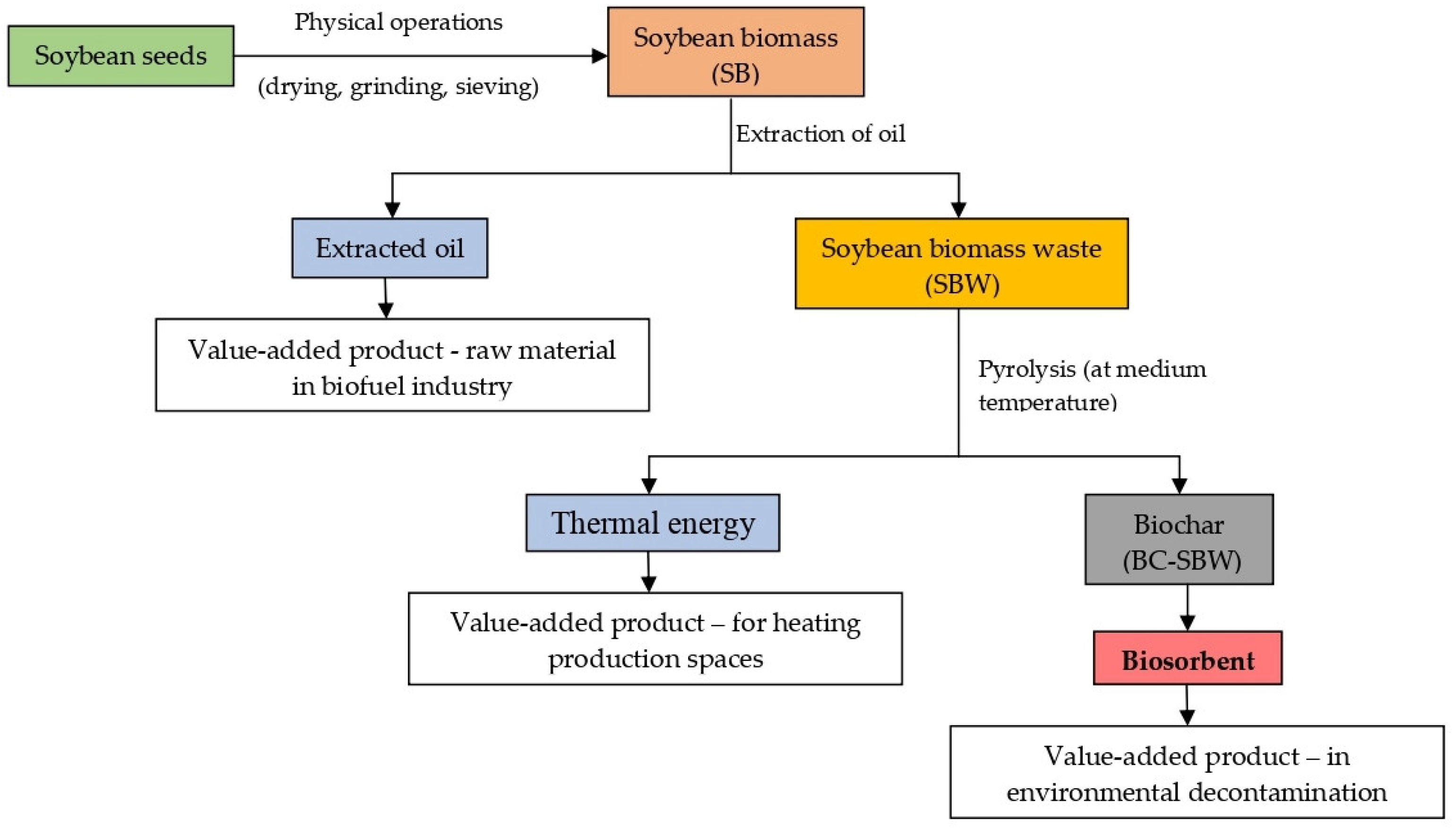
3.5. Circular Approach of Using Soybean Biomass in Environmental Decontamination
The use of soybean seeds as a raw material in various industrial sectors is well known, and they have led to a significant increase in the cultivation of this plant. If at first soybean was only used in the food industry and animal husbandry, in recent years, it has become a plant of industrial interest, due to its high oil content, which can be used in the biofuels production [
43]. But with the processing of soybean seed on a large scale, important amounts of biomass waste are generated, for which valorization solutions must be found. The solution most often proposed for the valorization of such waste biomass is their use as biosorbents for the removal of heavy metals from aqueous media [
44].
Unfortunately, the experimental results presented in this study showed that this solution has a number of disadvantages than can be easily minimized by converting biomass and biomass waste into biochar.
Figure 7 illustrates such a strategy that can be used to convert soybean waste into biochar, and that is in the line with the principles of the circular economy.
Thus, instead of using SB directly in biosorption processes (where it has a moderate efficiency and produces secondary pollution (an increase of the content of organic oxidizable compounds) of the treated effluents (see
Table 4 and
Table 5)), it is more appropriate to extract the oil from its composition and convert it into biomass waste (SBW). The obtained oil (oil extraction percent = 43.18 %) can be used in the biofuels production, covering an important part of SB processing costs. But although SBW has a higher efficiency in biosorption processes compared with SB (see
Table 4) and the secondary pollution of the treated effluents is significantly reduced (see
Table 5), it is difficult to store (due to traces of organic solvents or other extraction agents), especially in large quantities and for long period of time.
Permanent moisture and traces of organic solvents in the composition of SBW cause the initiation of undesirable fermentation processes, which can change the biosorptive performance of this waste biomass. Therefore, much more suitable is the conversion of SBW to biochar, by pyrolysis at moderate temperature (550 °C) and in limited oxygen atmosphere. The biosorbent obtained in this case (BC-SBW): (i) has a much improved biosorptive performance compared with SBW, at least for Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions (see
Table 4), (ii) allows the neutralization and reduction of secondary pollution (the content of organic oxidizable compounds decreases) of the treated effluents (see
Table 5), (iii) ensures a significant reduction in the volume of waste biomass (the pyrolysis percent being 79.38 %), and (iv) is much more stable and can be stored for long periods of time. In addition, thermal energy and pyrolysis gases can be captured and valorised to reduce the costs of biosorbent preparation.
Of course, this circular approach needs to be more detailed analyzed, both from economic point of view and from the point of view of environmental impact. Such an analysis will be the subject of a further study. However, it should be noted that, in addition to all technical advantages (described in detail in the previous sections), this approach can be implemented both on a pilot scale and on an industrial scale.
5. Conclusions
In this study, soybean biomass (SB), soybean waste biomass obtained from oil extraction (SBW) and biochar obtained from soybean waste pyrolysis (BC-SBW) were testes, in batch systems, as biosorbents form the removal of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions. Under optimal conditions (pH = 5.4, 4.0 g biosorbent/L, room temperature (25 ± 1 °C), contact time = 180 min), the biosorptive performance increase in the order: SB < SBW < BC-SBW for both Pb(II) ions (69.43 mg/g < 99.81 mg/g < 116.83 mg/g) and Cd(II) ions (25.63 mg/g < 36.12 mg/g < 49.10 mg/g), indicating that BC-SBW has the highest efficiency in removing these toxic heavy metals. Also, experiments on wastewater samples have shown that, in addition to significant reducing the content of Pb(II) and Cd(II) ions, BC-SBW also allows the neutralization and reduction of secondary pollution of the treated effluents, compared to the other biosorbents (SB and SBW). Quantitative evaluation of the biosorptive performances of the three biosorbents (SB, SBW and BC-SBW) shows that BC-SBW has a real chance of being used on an industrial scale for wastewater treatment. All these aspects allowed the development of a circular approach for the use of soybean biomass in the removal processes of toxic heavy metals. This approach minimizes the shortcomings of using biomass as a biosorbent and increase the chance of using these materials in industrial practice.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.B., D.I.F and A.A.C.; methodology, D.I.F. and A.A.C.; software, L.B.; validation, L.B., D.I.F. and I.G.C.; formal analysis, L.B, I.G.C, I.M. and I.A.; investigation, D.I.F., I.M. and G.N.; resources, L.B.; writing—original draft preparation, L.B. and D.I.F; writing—review and editing, L.B.; visualization, D.I.F.; supervision, L.B.; project administration, L.B. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.