Submitted:
25 August 2024
Posted:
27 August 2024
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
I. Introduction
1. Background
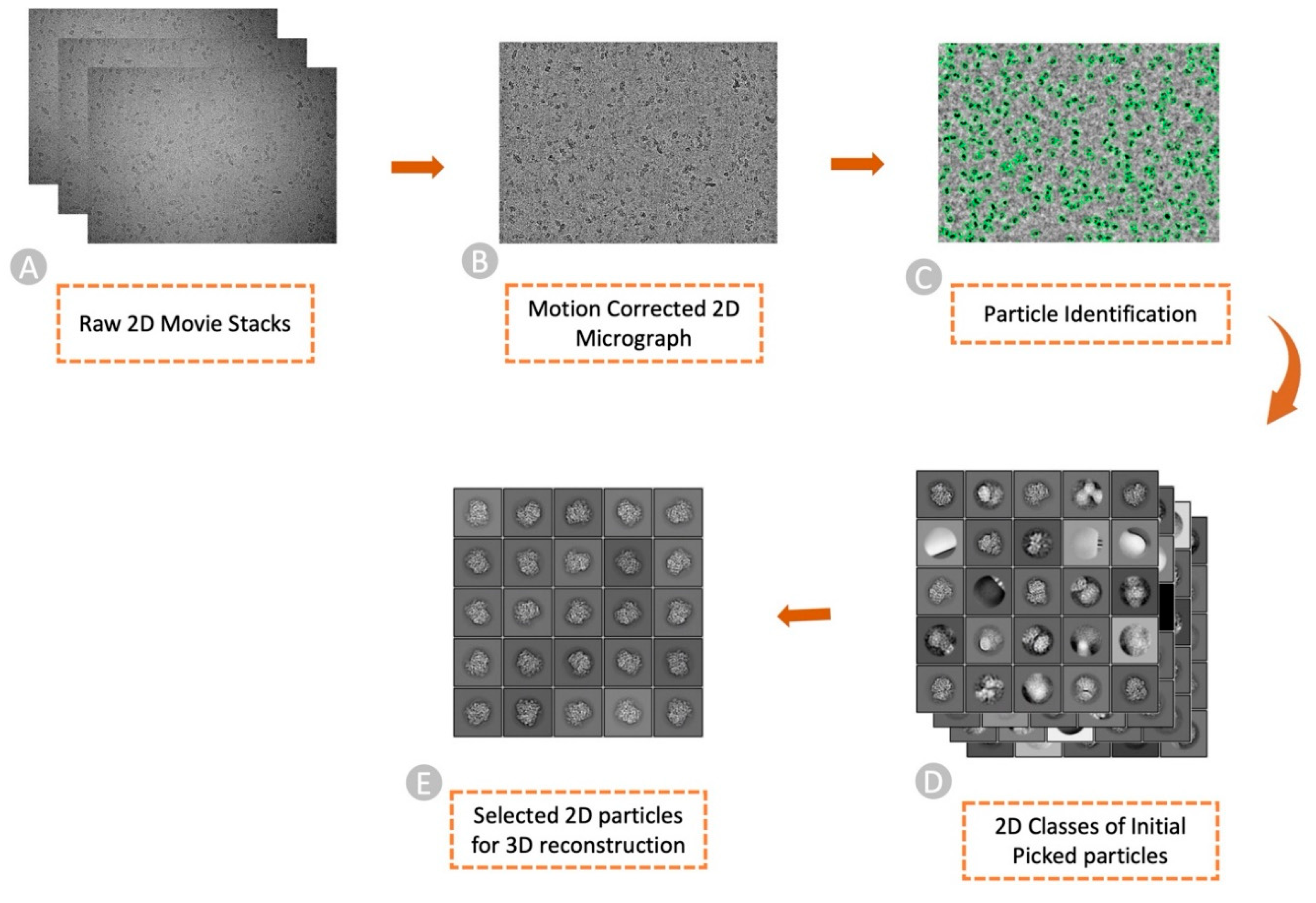
2. What Is Cryo-EM Particle Picking?
3. The Challenges in Particle Picking and the Resources to Tackle Them
II. Emergence of AI in Particle Picking
1. Classical Particle Picking Methods
| SN | Method | Techniques | Train/Test Data | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Mallick et al.’s method [14] | Adaboost Learning Algorithm | Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) [18] | 2004 |
| 2 | gEMpicker [15] | Roseman’s NCC Matching Algorithm | Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) | 2013 |
| 3 | Langlois et al.’s method [16] | Principal Component Analysis (PCA) and Otsu’s Algorithm | VA-ATPase from T. Thermophilus HB8 And 70S Ribosome from E. Coli, | 2014 |
| 4 | APPLE picker [17] | Support Vector Machine | Β-Galactosidase, T20S Proteasome, 70S Ribosome, and Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) | 2018 |
| 5 | SuperCryoEMPicker [19] | Super-Clustering Approach | 80S Ribosome and Beta-Galactosidase Datasets | 2019 |
| 6 | AutoCryoPicker [20] | Unsupervised Clustering | Apoferritin Dataset [21] and Keyhole Limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) Dataset | 2019 |
| 7 | Li et al. [22] | Segmentation-Aware Synergy Framework | EMPIAR-10028, EMPIAR-10097, and EMPIAR-10333 | 2022 |
2. Advanced Deep Learning Methods
| SN | Approach | Techniques | Train/Test Data | Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | DeepPicker [23] | Deep Learning (using Cross-Molecule Training Strategy) | y-secretase, spliceosome, TRPV1, b-galactosidase, N- ethylmaleimide sensitive factor complex | 2016 |
| 2 | DeepEM [24] | Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) | 800 manually selected particle images from the keyhole limpet Hemocyanin (KLH) dataset | 2017 |
| 3 | Xiao et al.’s method [26] | Region-based Convolutional Network (R-CNN) | Gammas, Spliceosome, Trpv1 | 2017 |
| 4 | Warp [31] | Convolutional ResNet Architecture | EMPIAR-10097, EMPIAR-10045, EMPIAR-10078, EMPIAR-10061, EMPIAR-10164, EMPIAR-10153 | 2019 |
| 5 | SPHIRE-crYOLO [30] | Deep Learning (Based on YOLO) | TcdA1 toxin subunit, Drosophila transient receptor channel NOMPC, human peroxiredoxin-3 (Prx3), simulated data of the canonical TRPC4 ion channel, and keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH) | 2019 |
| 6 | HydraPicker [29] | ResNet Architecture | Data from Warp [31] | 2019 |
| 7 | Pixer [27] | Deep Neural Network | beta-galactosidase, influenza hemagglutinin trimer, Plasmodium falciparum 80S ribosome, cyclic nucleotide-gated ion channel, and GroEl + TRPV1, KLH, bacteriophage MS2, and rabbit muscle aldolase | 2019 |
| 8 | Topaz [33] | Positive U learning CNN | EMPIAR-10025, EMPIAR-10096, EMPIAR-10028, EMPIAR-10261, EMPIAR-10234, and EMPIAR-10096 | 2019 |
| 9 | DeepCryoPicker [34] | Unsupervised Learning | Apoferritin, KLH, 80S ribosome, β-galactosidase | 2020 |
| 10 | McSweeney et al.’s method [35] | Convolutional Neural Networks | EMPIAR-10204, 10218, 10028, 10335, 10184, and 10059. | 2020 |
| 11 | DRPnet [36] | Double Convolutional Neural Network (CNN) Cascade | TRPV1 dataset (EMPIAR-10005) | 2021 |
| 12 | TransPicker [37] | End-to-End Transformer-based Architecture | EMPIAR-10093, EMPIAR-10017, EMPIAR-10028, EMPIAR-10096, EMPIAR-10406, and EMPIAR-10590 | 2021 |
| 13 | CASSPER [38] | Full Resolution Residual Network (FRRN) | TcdA1 (EMPIAR 10089), HCN1 (EMPIAR 10081), TRPV1 (EMPIAR 10005) and b-galactosidase (EMPIAR 10017) | 2021 |
| 14 | Urdnet [39] | U-Net based residual intensive neural network | 71 human 80S ribosomal micrographs, 30 HCN1 micrographs, 24 TcdA1 micrographs, and 16 KLH micrographs | 2022 |
| 15 | CryoSegNet [40] | U-Net + SAM Model | CryoPPP [2] | 2024 |
| 16 | CryoTransformer [41] | Transformer + ResNet Architecture | CryoPPP [2] | 2024 |
III. A Comparative Study of the AI-Based Cryo-EM Particle Picking Methods
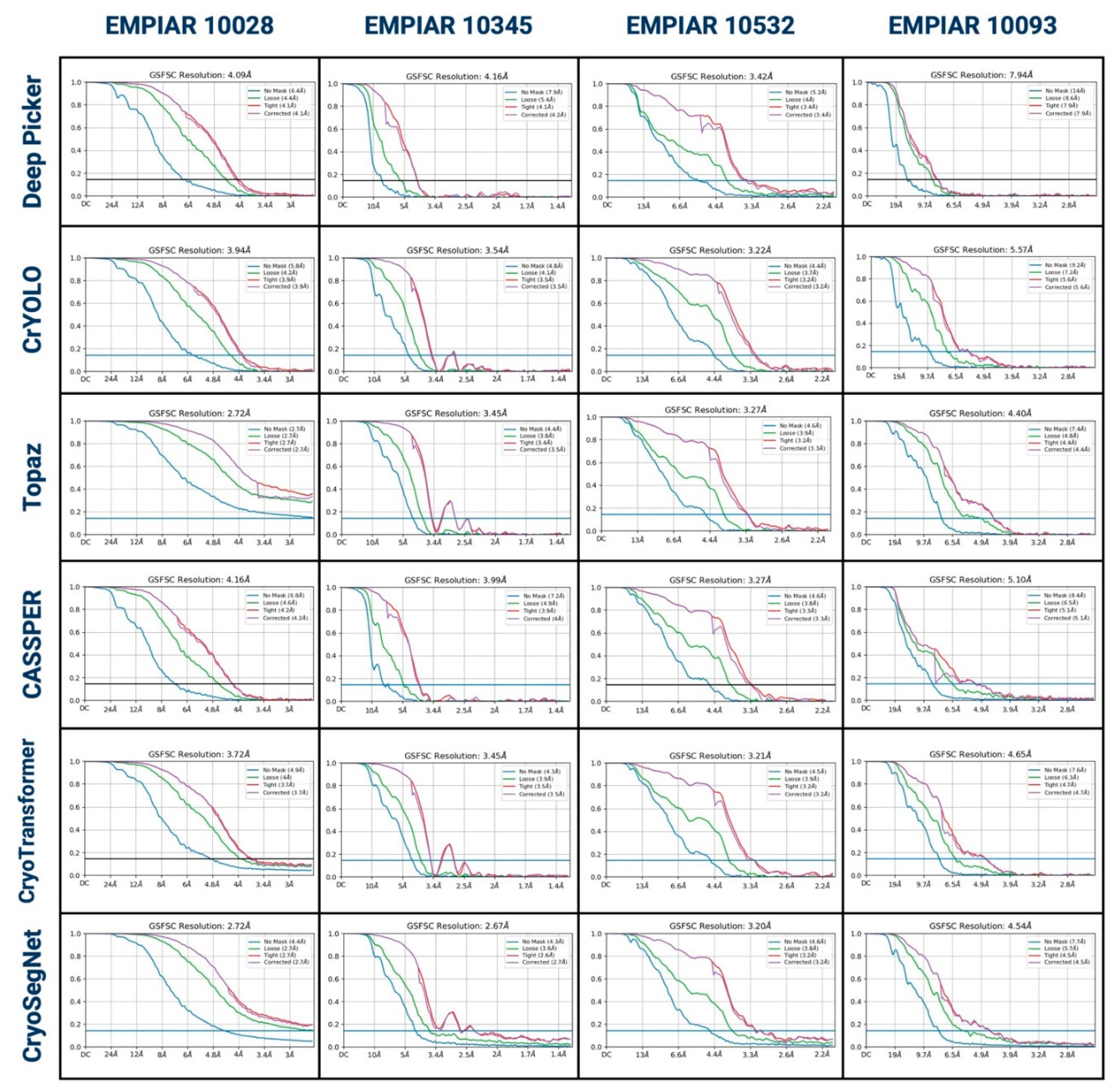
1. Evaluation in Terms of the Resolution of 3D Density Maps Reconstructed from Picked Particles
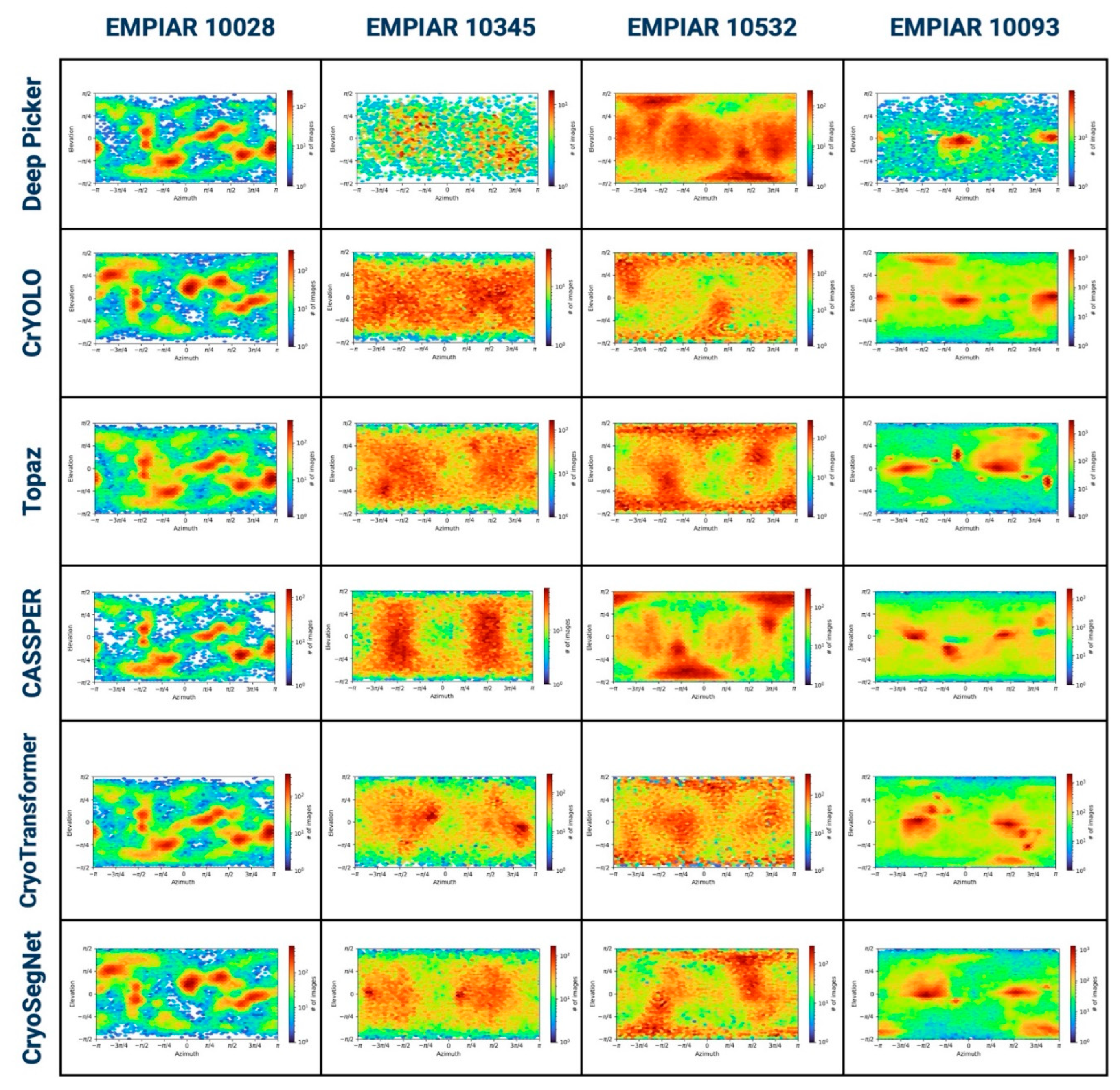
2. Evaluation in Terms of the Viewing Directions of Picked Particles
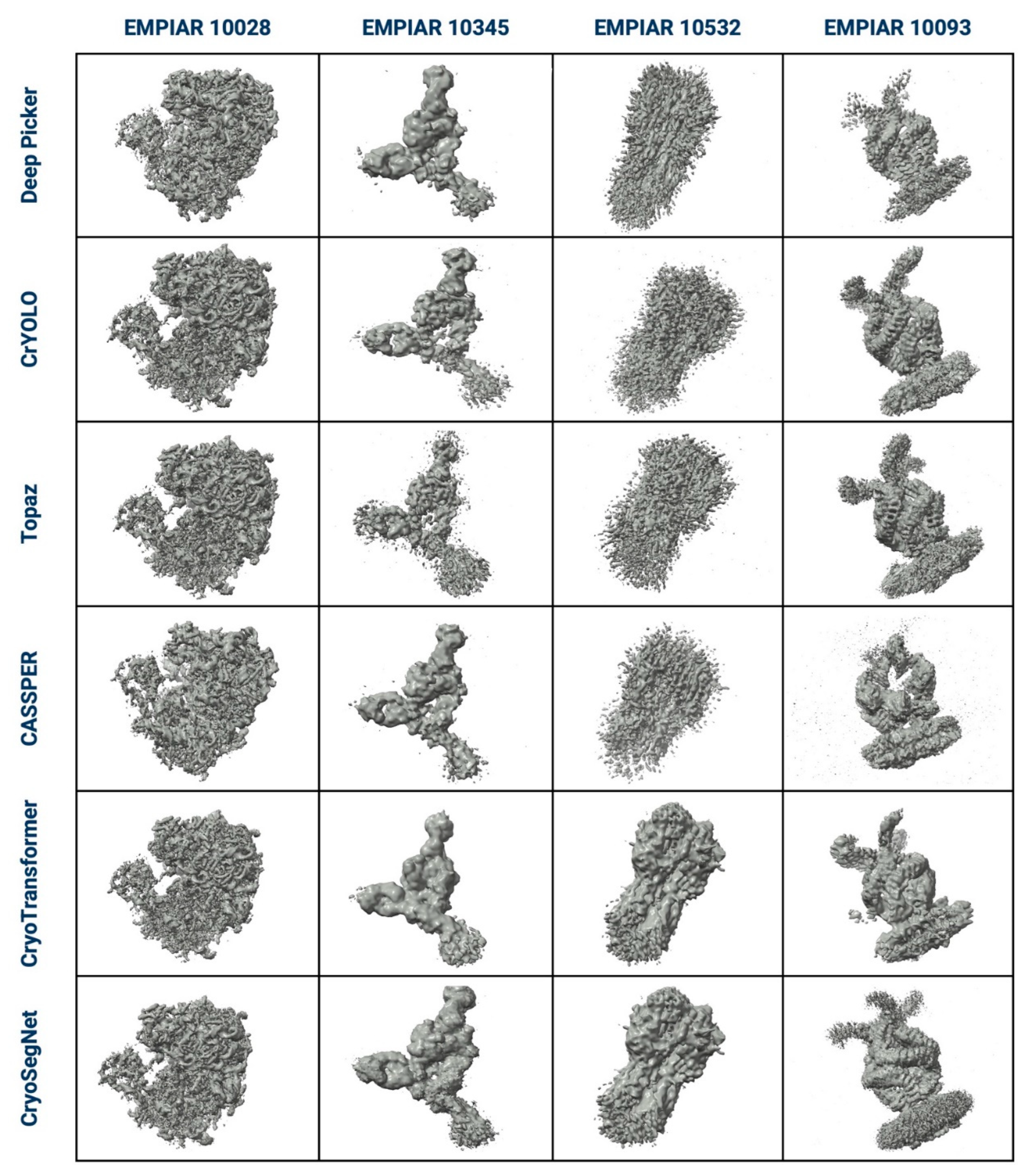
3. Evaluation in Terms of the Visualized Reconstructed 3D Maps and Their GSFSC Curves
4. Evaluation in Terms of the Local Resolution of 3D Maps Reconstructed from Picked Particles
IV. Remaining Challenges in Particle Picking
1. Complexity within Cryo-EM Micrographs
2. Lack of Benchmarking Data
3. Lack of Standard Evaluation Metrics for Particle Picking
V. Potential Future Development
1. Addressing Data Scarcity
2. Preprocessing and Efficient Representation of Cryo-EM Micrographs
3. Adoption of Comprehensive Performance Evaluation Metrics
a) 2D Class Resolution of Picked Particles
b) Elevation vs Azimuthal Plot
c) 3D Resolution of Density Maps with Multiple Trails
d) Local Resolution of Density Maps
4. Exploration of Advanced AI Architectures and Ensemble Methods
Conclusions
Key Points
References
- Frank, J. Single-particle imaging of macromolecules by cryo-electron microscopy. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct 2002, 31, 303–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhakal A, Gyawali R, Wang L, et al. A large expert-curated cryo-EM image dataset for machine learning protein particle picking. Sci Data 2023, 10.
- Frank J, Radermacher M, Penczek P, et al. SPIDER and WEB: Processing and visualization of images in 3D electron microscopy and related fields. J Struct Biol 1996, 116, 190–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhakal A, Gyawali R, Wang L, et al. CryoPPP: A Large Expert-Labelled Cryo-EM Image Dataset for Machine Learning Protein Particle Picking. bioRxiv 2023. 2023.02.21.529443.
- Dhakal A, McKay C, Tanner JJ, et al. Artificial intelligence in the prediction of protein-ligand interactions: recent advances and future directions. Brief Bioinform 2022, 23.
- Corso G, Stärk H, Jing B, et al. Diffdock: Diffusion steps, twists, and turns for molecular docking. arXiv preprint 2022, arXiv:2210.01776.
- Stärk H, Ganea O, Pattanaik L, et al. Equibind: Geometric deep learning for drug binding structure prediction. International conference on machine learning 2022, 20503–20521.
- Dhakal A, Gyawali R, Cheng J. Predicting Protein-Ligand Binding Structure Using E(n) Equivariant Graph Neural Networks. bioRxiv 2023. 2023.08.06.552202.
- Scheres SHW. RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J Struct Biol 2012, 180, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang G, Peng L, Baldwin PR, et al. EMAN2: An extensible image processing suite for electron microscopy. J Struct Biol 2007, 157, 38–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali R, Dhakal A, Wang L, et al. CryoVirusDB: A Labeled Cryo-EM Image Dataset for AI-Driven Virus Particle Picking. bioRxiv 2023.
- Iudin A, Korir PK, Somasundharam S, et al. EMPIAR: the Electron Microscopy Public Image Archive. Nucleic Acids Res 2023, 51, D1503–D1511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bradski, G. The opencv library. Dr. Dobb’s Journal: Software Tools for the Professional Programmer 2000, 25, 120–123. [Google Scholar]
- Mallick SP, Zhu Y, Kriegman D. Detecting particles in cryo-EM micrographs using learned features. J Struct Biol 2004, 145, 52–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoang T V, Cavin X, Schultz P, et al. gEMpicker: a highly parallel GPU-accelerated particle picking tool for cryo-electron microscopy. BMC Struct Biol 2013, 13, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Langlois R, Pallesen J, Ash JT, et al. Automated particle picking for low-contrast macromolecules in cryo-electron microscopy. J Struct Biol 2014, 186, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimowitz A, Andén J, Singer A. APPLE picker: Automatic particle picking, a low-effort cryo-EM framework. J Struct Biol 2018, 204, 215–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu Y, Carragher B, Glaeser RM, et al. Automatic particle selection: Results of a comparative study. J Struct Biol 2004, 145, 3–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azzawi A Al, Ouadou A, Tanner JJ, et al. A super-clustering approach for fully automated single particle picking in cryo-em. Genes (Basel) 2019, 10.
- Al-Azzawi A, Ouadou A, Tanner JJ, et al. Autocryopicker: An unsupervised learning approach for fully automated single particle picking in cryo-em images. BMC Bioinformatics 2019, 20.
- Rona G, Wynder EL, Helman P, et al. Plasma Hormone Profiles in Populations at Different Risk for Breast Cancer. Elife 2018, 36, 1883–1885. [Google Scholar]
- Li S, Li H, Zhang C, et al. A Segmentation-aware Synergy Network for Single Particle Recognition in Cryo-EM. Proceedings - 2022 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, BIBM 2022, 1066–1071.
- Wang F, Gong H, Liu G, et al. DeepPicker: A deep learning approach for fully automated particle picking in cryo-EM. J Struct Biol 2016, 195, 325–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu Y, Ouyang Q, Mao Y. A deep convolutional neural network approach to single-particle recognition in cryo-electron microscopy. BMC Bioinformatics 2017, 18.
- Girshick, R. Fast R-CNN. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2015, Inter, 1440–1448. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao Y, Yang G. A fast method for particle picking in cryo-electron micrographs based on fast R-CNN. AIP Conf Proc 2017, 1836.
- Zhang J, Wang Z, Chen Y, et al. PIXER: An automated particle-selection method based on segmentation using a deep neural network. BMC Bioinformatics 2019, 20.
- Chen LC, Papandreou G, Kokkinos I, et al. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans Pattern Anal Mach Intell 2018, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoumzadeh A, Brubaker M. HydraPicker: Fully automated particle picking in cryo-em by utilizing dataset bias in single shot detection. 30th British Machine Vision Conference 2019, BMVC 2019 2020.
- Wagner T, Merino F, Stabrin M, et al. SPHIRE-crYOLO is a fast and accurate fully automated particle picker for cryo-EM. Commun Biol 2019, 2.
- Tegunov D, Cramer P. Real-time cryo-electron microscopy data preprocessing with Warp. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 1146–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheres SHW. RELION: Implementation of a Bayesian approach to cryo-EM structure determination. J Struct Biol 2012, 180, 519–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bepler T, Morin A, Rapp M, et al. Positive-unlabeled convolutional neural networks for particle picking in cryo-electron micrographs. Nat Methods 2019, 16, 1153–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Azzawi A, Ouadou A, Max H, et al. DeepCryoPicker: fully automated deep neural network for single protein particle picking in cryo-EM. BMC Bioinformatics 2020, 21.
- McSweeney DM, McSweeney SM, Liu Q. A self-supervised workflow for particle picking in cryo-EM. IUCrJ 2020, 7, 719–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen NP, Ersoy I, Gotberg J, et al. DRPnet: automated particle picking in cryo-electron micrographs using deep regression. BMC Bioinformatics 2021, 22.
- Zhang C, Li H, Wan X, et al. TransPicker: A Transformer-based Framework for Particle Picking in cryoEM Micrographs. Proceedings - 2021 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine, BIBM 2021, 1179–1184.
- George B, Assaiya A, Roy RJ, et al. CASSPER is a semantic segmentation-based particle picking algorithm for single-particle cryo-electron microscopy. Commun Biol 2021, 4.
- Ouyang J, Zhang Y, Fang K, et al. Urdnet: A Cryo-EM Particle Automatic Picking Method. Computers, Materials and Continua 2022, 72, 1593–1610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gyawali R, Dhakal A, Wang L, et al. CryoSegNet: accurate cryo-EM protein particle picking by integrating the foundational AI image segmentation model and attention-gated U-Net. Brief Bioinform 2024, 25, bbae282. [Google Scholar]
- Dhakal A, Gyawali R, Wang L, et al. CryoTransformer: a transformer model for picking protein particles from cryo-EM micrographs. Bioinformatics 2024, 40. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu X, Su W, Lu L, et al. Deformable detr: Deformable transformers for end-to-end object detection. arXiv preprint 2020, arXiv:2010.04159.
- Pratyush P, Bahmani S, Pokharel S, et al. LMCrot: an enhanced protein crotonylation site predictor by leveraging an interpretable window-level embedding from a transformer-based protein language model. Bioinformatics 2024, 40, btae290. [Google Scholar]
- Kirillov A, Mintun E, Ravi N, et al. Segment Anything. Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision 2023, 3992–4003. [Google Scholar]
- Gyawali R, Dhakal A, Wang L, et al. Accurate cryo-EM protein particle picking by integrating the foundational AI image segmentation model and specialized U-Net. bioRxiv 2024. 2023.10.02.560572.
- Punjani A, Rubinstein JL, Fleet DJ, et al. CryoSPARC: Algorithms for rapid unsupervised cryo-EM structure determination. Nat Methods 2017, 14, 290–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pettersen EF, Goddard TD, Huang CC, et al. UCSF ChimeraX: Structure visualization for researchers, educators, and developers. Protein Science 2021, 30, 70–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He F, Yang Z, Gao M, et al. Adapting Segment Anything Model (SAM) through Prompt-based Learning for Enhanced Protein Identification in Cryo-EM Micrographs. ArXiv 2023.
- Xu C, Zhan X, Xu M. CryoMAE: Few-Shot Cryo-EM Particle Picking with Masked Autoencoders. ArXiv 2024.
- Zamanos A, Koromilas P, Bouritsas G, et al. Towards generalizable particle picking in Cryo-EM images by leveraging Masked AutoEncoders. ICML 2024 Workshop on Efficient and Accessible Foundation Models for Biological Discovery 2024.
- Liu Z, Lin Y, Cao Y, et al. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF international conference on computer vision 2021, 10012–10022.
- Carion N, Massa F, Synnaeve G, et al. End-to-end object detection with transformers. European conference on computer vision 2020, 213–229.
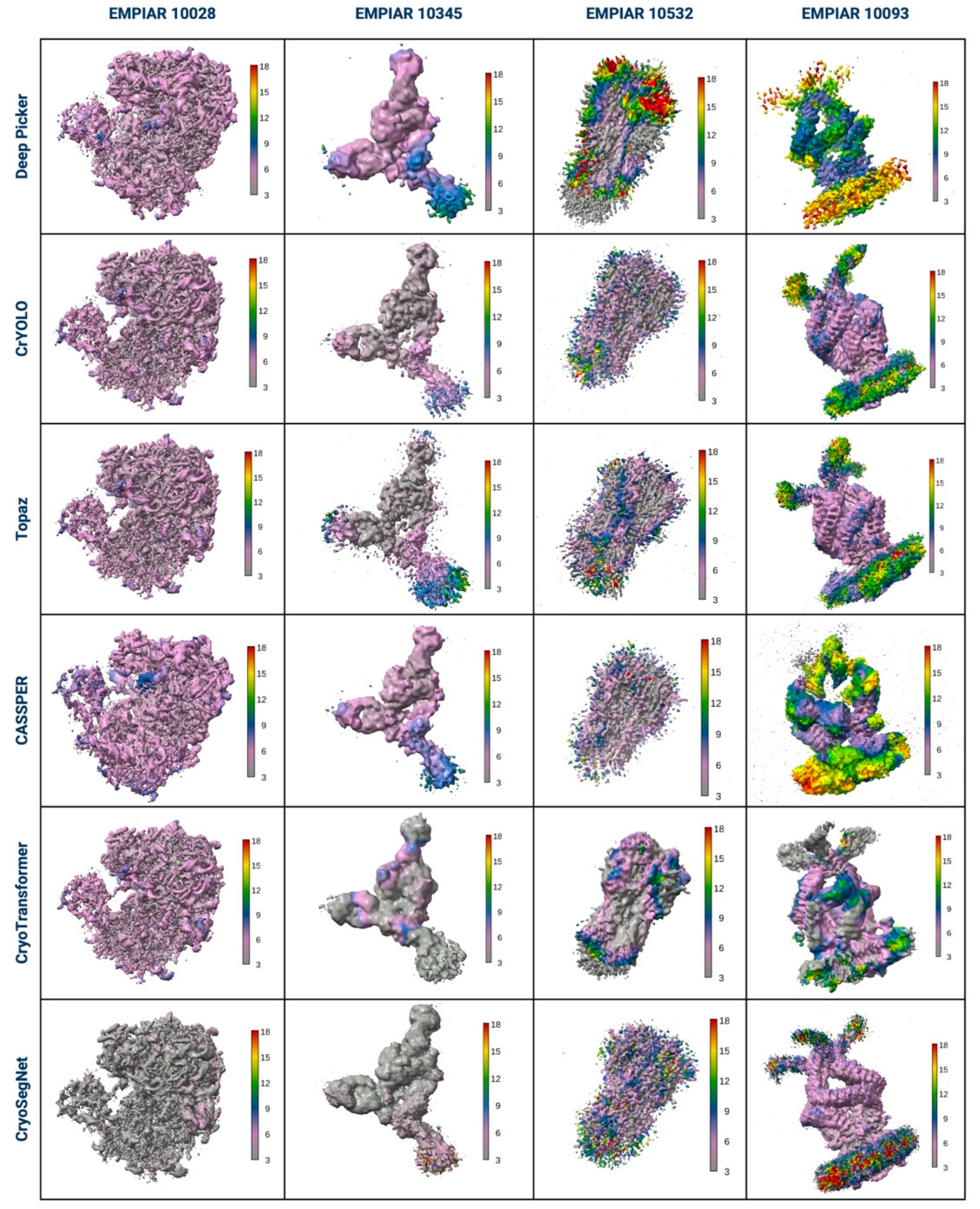
| EMPIAR ID | Method | CryoPPP (~300 micrographs per protein) | EMPIAR (all micrographs for each protein) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of Micrographs | Best Resolution of 3 Trials (Å) | Number of Picked Particles | Number of Micrographs | Best Resolution of 3 Trials (Å) | Number of Picked Particles | ||
| 10028 | Deep Picker | 300 | 4.08 | 30,242 | 600 | 4.09 | 43,027 |
| CrYOLO | 4.11 | 31,699 | 3.94 | 63,562 | |||
| Topaz | 3.93 | 35,514 | 2.72 | 96,352 | |||
| CASSPER | 4.42 | 15,637 | 4.16 | 29,906 | |||
| CryoTransformer | 3.82 | 40,488 | 3.72 | 52,134 | |||
| CryoSegNet | 2.72 | 45,218 | 2.72 | 92,532 | |||
| 10345 | Deep Picker | 295 | 8.54 | 2,470 | 1644 | 4.16 | 8,399 |
| CrYOLO | 3.83 | 11,369 | 3.54 | 40,047 | |||
| Topaz | 3.64 | 21,343 | 3.45 | 87,472 | |||
| CASSPER | 5.12 | 9,876 | 3.99 | 56,728 | |||
| CryoTransformer | 4.39 | 15,739 | 3.45 | 81,465 | |||
| CryoSegNet | 2.84 | 15,209 | 2.67 | 73,377 | |||
| 10532 | Deep Picker | 300 | 4.88 | 28,711 | 1556 | 3.42 | 95,469 |
| CrYOLO | 4.08 | 29,434 | 3.22 | 161,497 | |||
| Topaz | 4.23 | 38,372 | 3.27 | 206,460 | |||
| CASSPER | 3.94 | 29,290 | 3.27 | 146,022 | |||
| CryoTransformer | 3.96 | 38,345 | 3.21 | 259,757 | |||
| CryoSegNet | 3.89 | 30,155 | 3.2 | 90,477 | |||
| 10093 | Deep Picker | 295 | 7.25 | 2,360 | 1873 | 7.34 | 15,725 |
| CrYOLO | 8.87 | 33,183 | 5.57 | 192,337 | |||
| Topaz | 6.12 | 61,698 | 4.4 | 437,235 | |||
| CASSPER | 7.23 | 32,383 | 5.1 | 156,945 | |||
| CryoTransformer | 6.81 | 51,545 | 4.65 | 204,355 | |||
| CryoSegNet | 6.99 | 27,745 | 4.54 | 169,330 | |||
| Average | Deep Picker | 6.19 | 15,946 | 4.75 | 40,655 | ||
| CrYOLO | 5.22 | 26,421 | 4.07 | 114,361 | |||
| Topaz | 4.48 | 39,232 | 3.46 | 206,880 | |||
| CASSPER | 5.18 | 21,797 | 4.13 | 97,400 | |||
| CryoTransformer | 4.75 | 36,529 | 3.76 | 149,428 | |||
| CryoSegNet | 4.11 | 29,582 | 3.28 | 106,429 | |||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





