1. Introduction
Stroke remains one of the leading causes of disability and mortality worldwide, underscoring the urgent need for advanced technologies to enhance its diagnosis, treatment, and patient prognosis. Recent advancements in machine learning (ML) have emerged as a promising tool in stroke medicine, offering the capability to analyze large datasets efficiently and drive personalized and precision medicine approaches. This review explores the application, challenges, and future directions of ML in stroke medicine.
Over recent years, various ML algorithms have been introduced and widely applied across different domains of stroke medicine. These models have demonstrated significant accuracy in imaging analysis, stroke subtype classification, risk assessment, treatment guidance, and prognosis prediction. Despite the substantial potential of ML in stroke medicine, several challenges remain. Key issues include the need for standardized and interoperable data collection, robust model validation and generalization, and ethical considerations concerning privacy and bias. Furthermore, integrating ML models into clinical workflows and establishing regulatory frameworks are crucial for ensuring widespread adoption and impact in routine stroke care.
Machine learning has the potential to revolutionize stroke medicine through precise diagnosis, tailored treatment options, and improved prognostication. Ongoing research and collaboration among clinicians, researchers, and technologists are essential to overcoming these challenges and fully realizing the potential of ML in stroke care, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life. This review aims to summarize the current impacts of ML on stroke diagnosis, treatment, and prognosis assessment while also exploring the prospects of these technologies in combating this debilitating disease.
2. Related Work
2.1. Prediction Analysis of Stroke Incidence
Stroke is a medical condition in which cells die due to insufficient blood flow to the brain. There are two main types of stroke: ischemic stroke (caused by lack of blood flow) and hemorrhagic stroke (caused by bleeding). Both cause parts of the brain to stop functioning properly.
Signs and symptoms of a stroke may include an inability to move or feel on one side of the body, problems understanding or speaking, dizziness, or loss of vision on one side. Signs and symptoms usually appear shortly after a stroke has occurred. If symptoms last less than an hour or two, a stroke is a transient ischemic attack (TIA), also known as a mini-stroke. Hemorrhagic strokes can also be accompanied by severe headaches. The symptoms of a stroke can be permanent. Long-term complications may include pneumonia and loss of bladder control.
The main risk factor for stroke is high blood pressure. Other risk factors include high blood cholesterol, smoking, obesity, diabetes, previous TIA, end-stage kidney disease, and atrial fibrillation.
Ischemic stroke is usually caused by a blocked blood vessel, although there are some less common causes. Hemorrhagic strokes are caused by bleeding directly into the brain or the space between the large meninges.
A ruptured brain aneurysm could have caused the bleeding. Diagnosis is usually based on a physical examination, supplemented by medical imaging such as CT or MRI scans. A CT scan can rule out bleeding but not necessarily ischemia, and early CT scans usually do not show ischemia. Other tests, such as an electrocardiogram (ECG) and blood tests, are done to identify risk factors and rule out other possible causes. Hypoglycemia may also cause similar symptoms.
Early identification of learning difficulties is a key challenge and need in education. The learning difficulties that many students face can be caused by a variety of factors, including individual differences, learning styles, socioeconomic background, and mental health [
6,
7]. Traditional educational assessment methods often rely on standardized tests and periodic exams, which, while providing certain data, often fail to capture students' overall learning status and potential learning difficulties. In addition, educators and school administrators are often faced with the challenge of effectively identifying and supporting students who may face learning challenges, given limited resources. Traditional methods of educational assessment rely mainly on standardized tests and periodic examinations [
8,
9]. For example, the annual standardized tests used by many schools, despite providing a comprehensive assessment framework, often fail to identify students' specific learning difficulties on time. For example, one study showed that standardized tests. At the same time, they can assess students' subject basics but are not effective at capturing the specific challenges students face at each stage of the learning process due to their long testing cycles, which limits the effectiveness of schools in academic support and personalized instruction.
2.2. China National Stoke Registry, CNSR
Stroke is the second leading cause of death globally and the leading cause of death and disability in our country. Acute ischemic stroke (AIS), which accounts for 80% of all strokes, has a high rate of disability, mortality and recurrence. The use of predictive models to accurately predict the prognosis of AIS patients, improve the accurate risk stratification of patients and the management of diagnosis and treatment strategies, optimize the allocation of medical resources, and thus improve the prognosis of patients are indispensable links in the secondary prevention of stroke. With the advent of the era of big data, the improvement of computer computing power, and the update of algorithms, machine learning has made great progress in disease prediction. Among them, various integrated models (such as various tree models) have gradually shown some advantages in disease prediction. In this study, the China National Stroke Registry (CNSR) database was used to investigate the factors related to 1-year functional prognosis of newly diagnosed AIS patients, and the predictive performance of the machine learning model and logistic model was compared, providing references for related research and clinical work.
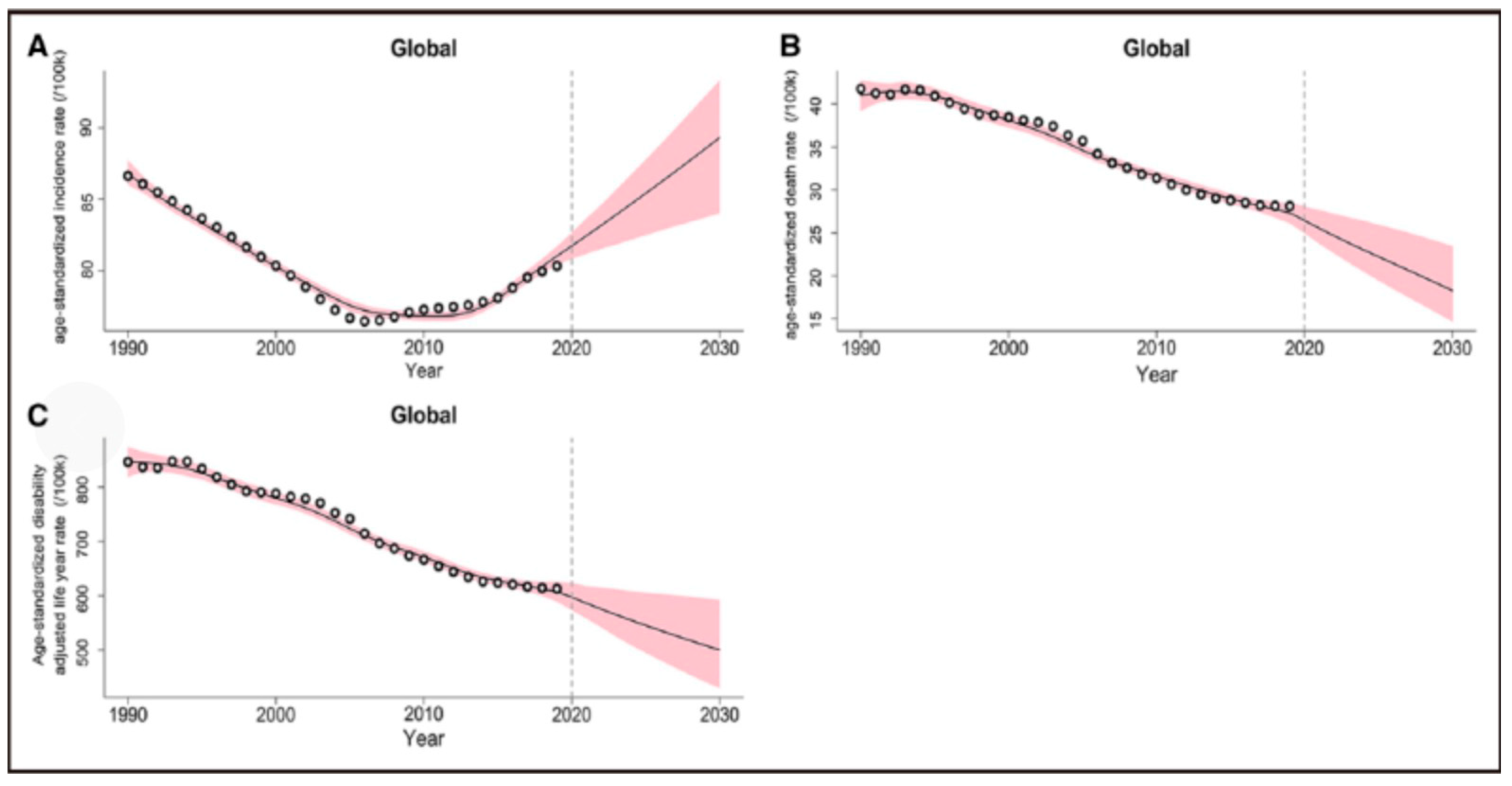
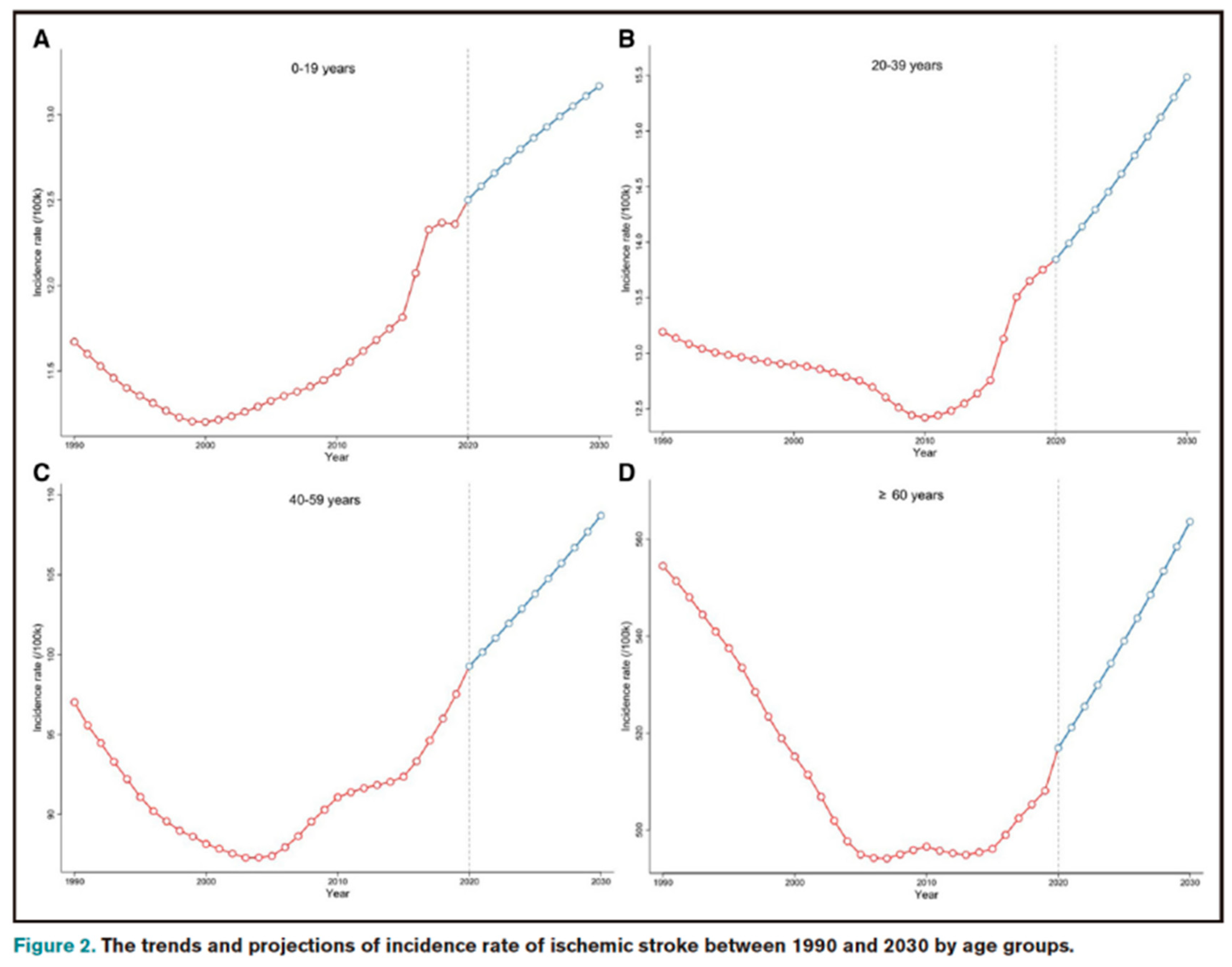
Globally, stroke is the second leading cause of death, accounting for 11.6% of all deaths in 2019, of which ischemic stroke, accounting for 62.4% of all stroke cases, is the most common type and is the leading cause of neurological death and adult disability, creating a significant health and economic burden. Recently, Chinese scholar Pu et al. published a study based on GBD data from 1990 to 2019 in the journal Stroke, predicting a significant increase in the incidence of ischemic stroke from 2020 to 2030. Mortality and Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) may decline significantly. Using data from the 1990-2019 Global Burden of Disease Study, A generalized additive model was used to estimate the Estimated annual percentage change (EAPCs) and predict trends in ischemic stroke mortality and DALYs from 2020 to 2030.
Figure 1.
The tren'is and projections of age-standardized incidence rate, death rate, and disabilityadjusted life years rate of is chemic stroke between 1990 and 2030 at the global level.
Figure 1.
The tren'is and projections of age-standardized incidence rate, death rate, and disabilityadjusted life years rate of is chemic stroke between 1990 and 2030 at the global level.
Globally, the number of ischemic stroke cases, deaths and DALYs increased from 4.07 million, 2.05 million and 40.5 million respectively in 1990 to 7.86 million, 3.15 million and 62.53 million in 2020. It is estimated that by 2030, the global incidence of ischemic stroke will continue to rise to 9.62 million, and the number of deaths and DALYs will decrease to 2.45 million and 57.89 million, respectively. In the meantime, the global age-standardized incidence, mortality and DALY rates of ischemic stroke decreased from 86.64/100,000, 41.76/100,000 and 846.06/100,000 in 1990 to 81.72/100,000, 2644/100,000 and 597.41/100,000 in 2020, respectively. The age-standardized incidence rate will continue to rise to 89.32/100,000 (EAPC=0.89), while the standardized mortality rate and DALY rate will decrease to 18.28/100,000 (EAPC= 3.58) and 500.37/100,000 (EAPC=1.75), respectively.
The age-standardized incidence of ischemic stroke in 2030 was higher in women (90.70/100,000) than in men (87.64/100,000). In addition, projections indicate increased age-standardized mortality and DALY rates due to ischemic stroke (EAPC 3.68 and 5.30, respectively) in countries with the lower sociodemographic index (SDI) quintile.
At the country level, the largest increase in age-standardised incidence of ischemic stroke is projected for 2020-2030 in Cyprus (EAPC=4.16), followed by Palestine (EAPC=3.50) and South Africa (EAPC=2.64).
Current strategies and measures for primary prevention of ischemic stroke may be inadequate, and universal primary prevention of stroke must be promoted globally. In low SDI countries, measures are needed to prevent further increases in age-standardized mortality and DALY rates due to ischemic stroke. In some developed countries, the rise in DALY due to ischemic stroke should be vigilant.
3. Predictive Characteristics of Ischemic Stroke Patients
3.1. Pathophysiology of Stroke
A stroke or cerebrovascular accident is a sudden onset of neurological dysfunction caused by a focal blockage of a blood vessel. Due to the complex anatomy of the brain and blood vessels, the manifestations of stroke are variable. It is caused by a decrease in blood flow to the brain and lasts for more than a few seconds, leading to a rapid depletion of neuronal energy and, if it continues to stop blood flow, death of brain tissue. If blood flow returns, the symptoms may be temporary and are called transient ischemic attacks. The decrease in blood flow to the brain depends on the location of the blockage, systemic blood pressure, and the anatomy of individual blood vessels. Infarct occurs when blood flow falls below a certain threshold, while non-infarct ischemia occurs if blood flow recovers within a certain time. If blood flow is not restored, the surrounding reversible dysfunctional tissue will become infarcted, defined as an "ischemic penumbra." Infarcts occur in two ways: necrosis and apoptosis. Ischemia causes cell death by losing glucose and oxygen in neurons, leading to adenosine triphosphate failure and blockage of the ion pump, cell depolarization, and cell damage. It also causes the release of free radicals, which can further damage cells.
As shown in the penumbra, cell death occurs when ischemia is mild. Fever and hyperglycemia can aggravate brain damage during ischemia, so preventive measures are recommended. The value of mild hypothermia in improving stroke outcomes is still being investigated (Kuriakose and Xiao, 2020).
3.2. Diagnosis of Stroke: Clinical Approach
Evidence suggests that "time is brain" (Von Kummer, 2019), and accurate diagnosis is critical to enhancing stroke treatment. According to the NINDS study group, patients treated with tissue plasminogen activators showed evidence of early and long-term improvement, were more than 30% more likely to have mild or no disability on the assessment scale after three months, and accurate stroke diagnosis allowed appropriate interventions to be implemented promptly. Significantly improved patient outcomes and recovery (National Neurological Disorders and Stroke rt-PA Study Group, 1995). When the patient arrives at the emergency department, the correct clinical approach is the first and most critical step to an accurate diagnosis. The presentation of a stroke can largely depend on the area of the lesion.
The strong correlation between clinical neurological signs and symptoms and acute ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke has led to the development of a practical neurological scale that can help emergency departments identify stroke patients and measure stroke severity (Kothari et al., 1999; Harbison et al., 2003; Kwah and Diong, 2014).
In the Cincinnati Prehospital Stroke Scale study, when any of the three-stroke scale items were observed, the score for each scale item showed a high sensitivity of 66% and specificity of 87% for identifying stroke patients, and the score for each scale item was highly repeatable by prehospital healthcare personnel. And excellent intra-class correlation (Kothari et al., 1999).
The face arm language test also proved to be an excellent stroke diagnostic tool, accurately identifying 144 out of 183 (79%) stroke patients who presented to the emergency department (Harbison et al., 2003).
The National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale has moderate to high reliability in assessing stroke severity by medical and non-medical personnel (rater internal κ = 0.66 to 0.77; κ = 0.69 between raters). It also proved very reliable when clinicians rated videos of patients (rater internal ICC = 0.93; ICC = 0.95 between raters) (Kwah and Diong, 2014).
Progressive treatment of stroke patients through neuroimaging technology is the most effective way to identify stroke. CT and MRI are also critical to the correct timing of diagnosis of ischemic/hemorrhagic lesions.
In a prospective study comparing the sensitivity of MRI and CT in 356 patients, 217 of whom had an eventual clinical diagnosis of acute stroke, the sensitivity of MRI and CT to any acute stroke diagnosis was 83% each (181 out of 217; 78% to 88%) and 26%(56 out of 217; 20-32%)(Chalela et al., 2007). In another study, sensitivity to both techniques appeared to increase 48 hours after stroke onset, 85% (75/89) of positive CT diagnoses, 93.5% (115/123) of positive MRI diagnoses, and 98.8% (79/80) of positive DWI diagnoses (Smajlovidic and Sinanovic). 2004).
3.3. Prognosis of Stroke
Proper treatment is not enough to guarantee long-term survival after a stroke. The risk of death at 28 days after stroke was estimated at 28%, one year at 41%, and five years at 60%, with non-fatal stroke patients having five times the risk of death at four weeks to one year after their first stroke and twice the risk of death at one year (Boysen et al., 2009).
This trend is also consistent with the findings of the cohort study, which followed 2447 patients for ten years after a primary minor ischemic stroke or transient ischemic attack, of which 1489 (60%) died, and 1336 (54%) had at least one vascular event. The 10-year risk of death was 42.7% (95% CI 40.8-44.7). Over 65 years of age, diabetes, claudication, previous peripheral vascular surgery, and baseline electrocardiographic pathological Q-waves were all associated with an increased risk of death. The 10-year risk of vascular events was 44.1%(42.0-46.1), and the predictors of vascular events were similar to those of the risk of death. The annual risk of vascular events increased over time after declining in the first three years (van Wijk et al., 2005). In this context, mortality prediction can help clinicians predict prognosis, develop supportive care plans, select the right treatment options, coordinate rehabilitation services, facilitate patient and family counseling, fairly compare hospital outcomes, and evaluate performance related to stroke mortality.
Several previous studies that attempted to predict stroke outcomes, such as the I-score, took into account multivariate predictors of 30-day and 1-year mortality, including old age, male, severe stroke, non-lacunar stroke subtype, blood glucose ≥7.5 mM (135 mg/dL), history of atrial fibrillation, coronary artery disease, congestive heart failure, cancer, dementia, dialysis kidney disease, and other factors—pre stroke dependence.
The study retrospectively analyzed data from 12,262 patients with acute ischemic stroke at several hospitals in Ontario between 2003 and 2008. Patients were recruited from the Canadian Stroke Network Registry and the Ontario Stroke Audit, with a trace-back cohort of 8223, an internal validation cohort of 4039, and an external validation cohort of 3720. The 30-day mortality in the derived and internally validated cohorts was 12.2% and 12.6%, respectively, and the 1-year mortality was 22.5% and 22.9% (Sapopsnik et al., 2011).
3.4. Machine Learning: A New Perspective on Stroke
The above studies highlight the ongoing efforts to develop reliable predictive models that can be used to guide clinical decision-making. For example, accurately predicting the likelihood of a particular outcome can help clinicians choose the most appropriate treatment and tailor treatment to each patient. However, these approaches are limited by traditional biostatistics, which focuses on reducing bias caused by study design, whereas analyzing data from large populations would provide a real-world perspective.
With the rise of big data, the growing popularity of electronic health records, and the simultaneous development of machine learning algorithms, healthcare professionals can now solve population health problems that were once considered impossible. This shift to using clinical data at the population level has fundamentally changed how we make inferences about populations, allowing us to identify and address health issues with greater precision and accuracy.
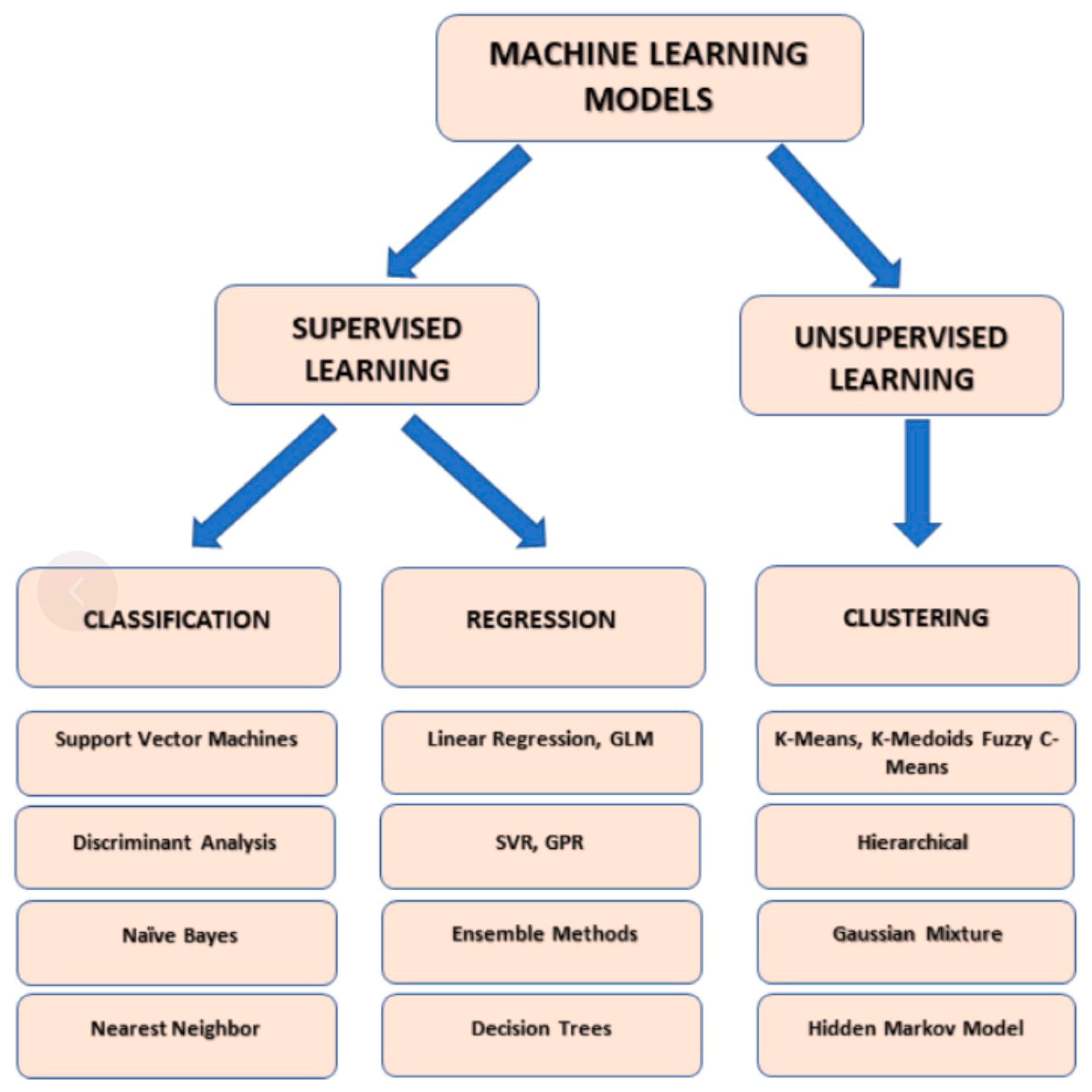
Figure 3.
Main types of machine learning models. Made with Microsoft PowerPoint. GLM: Generalized linear model; GPR: Gaussian process regression; SVR: Support vector regression.
Figure 3.
Main types of machine learning models. Made with Microsoft PowerPoint. GLM: Generalized linear model; GPR: Gaussian process regression; SVR: Support vector regression.
A key benefit of machine learning is its ability to identify patterns and correlations in complex data sets, which can provide valuable insights into disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. In addition, by automating the data analysis process, machine learning reduces human bias and improves the accuracy of predictions.
Machine learning algorithms are well suited for handling "big data." Big data refers to large, complex, and diverse variables that traditional data processing tools or techniques cannot process or analyze. Machine learning can absorb large amounts of data from various sources, both structured and unstructured. Big data has the characteristics of high capacity, high speed, and high diversity and requires specialized technologies and methods to manage, process, and analyze. Big data analytics can provide valuable information for decision-making, research, and innovation, revealing insights and patterns that are difficult to identify from smaller, more structured data sets (Zhou et al., 2017).
3.5. Neural Networks for Predicting Stroke Risk
Neural networks have several advantages that make them useful for solving complex problems. One of these advantages is scalability, as they can be trained on large data sets using distributed computing resources. Scalability makes neural networks suitable for various applications, enabling them to solve complex problems. Another advantage is adaptability, which means neural networks can adapt to new data and situations and generalize well about unknown data. This capability is advantageous in applications where the input data may change over time. Finally, neural networks are easy to parallelize, allowing them to use modern hardware architectures such as graphics and tensor processing units. With scalability, adaptability, and parallel processing capabilities, neural networks are powerful tools for solving complex problems in various fields.
Backpropagation is the best-known example of an algorithm used to train neural networks. Backpropagation computes the gradient vector of the error surface, which represents the steepest descent direction from the current point. Moving along this vector reduces the error, and a series of such moves eventually leads to finding a minimum value. However, determining the appropriate step size can be a challenge. A larger step size can speed up the convergence, but if the error surface is complicated, it will make the solution overshoot or go off course. Small steps, on the other hand, are more reliable but require more iteration. Thus, the step size is proportional to the gradient and the learning rate constant, which is usually determined experimentally and may also vary over time.
As defined by Gonzalez et al. (2005), a support vector machine (SVM) is a classification algorithm that constructs an N-dimensional hyperplane and optimally divides data into two classes. The support vector machine model is similar to the neural network, and the support vector machine model using the sigmoid kernel function is equivalent to a two-layer perceptron neural network. The support vector machine model is closely related to the classical multi-layer perceptron neural network, which is an alternative training method for polynomials, radial basis functions and multi-layer perceptron classifiers. In standard neural network training, the network weight is determined by solving a quadratic programming problem with linear constraints, rather than solving a non-convex, unconstrained minimization problem.
Both random forest and decision tree algorithms are used for classification and regression tasks in machine learning. A decision tree is a tree-like model where each internal node represents a test for an attribute, each branch represents a test result, and each leaf node represents a class label. The tree is constructed by recursively subsetting the data according to the best attributes to be divided to minimize impurities or maximize information gain. Decision trees have the advantage of being easy to interpret, but prone to overfitting and potentially unstable. Random forest is an integrated approach that uses multiple decision trees to improve prediction accuracy and reduce overfitting (Ngiam and Khor, 2019).
4. Conclusions
Machine learning (ML) shows significant potential in the diagnosis, care, and prognosis of ischemic stroke. First, in diagnosis and detection, machine learning algorithms are capable of processing and analyzing large-scale medical data, including brain imaging scans, medical history, and clinical symptoms. By mining patterns from this data, ML can help identify potential stroke risks, providing an earlier and more accurate diagnosis. This ability not only helps in the timely detection of ischemic stroke, but also significantly improves the overall prognosis of patients. In addition, machine learning can reduce the incidence of stroke by predicting the likelihood of stroke occurring, identifying people at high risk, and providing data to support preventive measures.
Second, in treatment and care, the application of machine learning also has far-reaching implications. By analyzing individual patient data, ML algorithms can help doctors develop more personalized treatment plans. This data-driven decision-making process can improve the precision of treatment and optimize treatment outcomes. As technology continues to advance, machine learning is expected to play an increasingly important role in the treatment of ischemic stroke, driving the shift from traditional treatment methods to more personalized and efficient medical models. In conclusion, machine learning shows great potential to improve the diagnosis, care, and prognosis of patients with ischemic stroke, offering new hope for future medical practice.