Submitted:
27 August 2024
Posted:
28 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
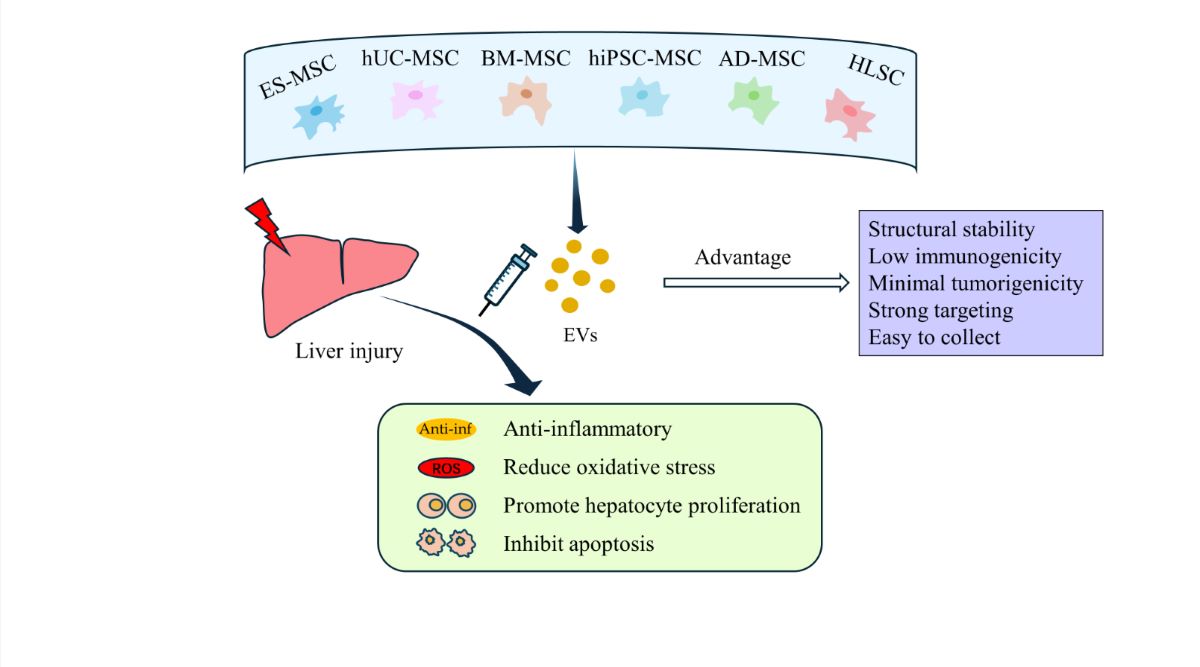
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Extracellular Vesicles
3. Therapeutic Studies of SC-EVs In Vitro and in Animal Models of Liver Injury
3.1. EVs Derived from Embryonic Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (ES-MSCs)
3.2. EVs Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells (hUC-MSCs)
3.3. EVs Derived from Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells (BM-MSCs)
3.4. EVs Derived from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (AD-MSCs)
3.5. EVs Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (hiPSC-MSCs)
3.6. EVs Derived from Human Liver Stem Cells (HLSCs)
4. Clinical Research Progress on SC-EVs in Liver Diseases
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Zhang, Q.; Piao, C.; Ma, H.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Liu, G.; Wang, H. Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Liver Ischaemia Reperfusion Injury Subsequent to Hepatectomy in Rats by Regulating Mitochondrial Dynamics and Biogenesis. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2021, 25, 10152–10163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, C. Y.; Lai, R. C.; Wong, W.; Dan, Y. Y.; Lim, S.-K.; Ho, H. K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes Promote Hepatic Regeneration in Drug-Induced Liver Injury Models. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2014, 5, 76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Feng, B.; Xu, Y.; Zhu, J.; Feng, X.; Chen, W.; Sheng, X.; Shi, X.; Pan, Q.; Yu, J.; Zeng, X.; Cao, H.; Li, L. Immunomodulatory Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells in Chemical-Induced Liver Injury: A High-Dimensional Analysis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, M.; Meng, H.; Dai, C.; Yao, Z.; Lin, N. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells Inhibit Hepatic Fibrosis via the AABR07028795.2/Rno-miR-667-5p Axis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, P.; Mao, Y.; Xie, Y.; Wei, J.; Yao, J. Stem Cells for Treatment of Liver Fibrosis/Cirrhosis: Clinical Progress and Therapeutic Potential. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elkhenany, H.; Shekshek, A.; Abdel-Daim, M.; El-Badri, N. Stem Cell Therapy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Future Perspectives. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2020, 1237, 97–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, T.-T.; Wang, Z.-R.; Yao, W.-Q.; Linghu, E.-Q.; Wang, F.-S.; Shi, L. Stem Cell Therapies for Chronic Liver Diseases: Progress and Challenges. Stem Cells Transl. Med. 2022, 11, 900–911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hass, R.; Kasper, C.; Böhm, S.; Jacobs, R. Different Populations and Sources of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSC): A Comparison of Adult and Neonatal Tissue-Derived MSC. Cell Commun. Signal. CCS 2011, 9, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saat, T. C.; van den Engel, S.; Bijman-Lachger, W.; Korevaar, S. S.; Hoogduijn, M. J.; IJzermans, J. N. M.; de Bruin, R. W. F. Fate and Effect of Intravenously Infused Mesenchymal Stem Cells in a Mouse Model of Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury and Resection. Stem Cells Int. 2016, 2016, 5761487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, M.; Hu, X.; Yao, L.; Jiang, Y.; Li, L. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Homing to Improve Therapeutic Efficacy in Liver Disease. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lou, G. H.; Chen, Z.; Zheng, M.; Liu, Y. N. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes as a New Therapeutic Strategy for Liver Diseases. Exp. Mol. Med. 2017, 49, e346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Furlani, D.; Ugurlucan, M.; Ong, L.; Bieback, K.; Pittermann, E.; Westien, I.; Wang, W.; Yerebakan, C.; Li, W.; Gaebel, R.; Li, R.; Vollmar, B.; Steinhoff, G.; Ma, N. Is the Intravascular Administration of Mesenchymal Stem Cells Safe? Mesenchymal Stem Cells and Intravital Microscopy. Microvasc. Res. 2009, 77, 370–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, R. H.; Pulin, A. A.; Seo, M. J.; Kota, D. J.; Ylostalo, J.; Larson, B. L.; Semprun-Prieto, L.; Delafontaine, P.; Prockop, D. J. Intravenous hMSCs Improve Myocardial Infarction in Mice Because Cells Embolized in Lung Are Activated to Secrete the Anti-Inflammatory Protein TSG-6. Cell Stem Cell 2009, 5, 54–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Lou, R.; Huang, F.; Peng, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Huang, K.; Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Fan, Z.; Zhou, H.; Liu, C.; Xiao, Y.; Sun, J.; Li, Y.; Xiang, P.; Liu, Q. Immunomodulation Effects of Mesenchymal Stromal Cells on Acute Graft-versus-Host Disease after Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation. Biol. Blood Marrow Transplant. J. Am. Soc. Blood Marrow Transplant. 2015, 21, 97–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, K.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. M.; Liu, F. B. Exosomes Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury via Delivering miR-1246. Cell Cycle Georget. Tex 2019, 18, 3491–3501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camussi, G.; Deregibus, M. C.; Cantaluppi, V. Role of Stem-Cell-Derived Microvesicles in the Paracrine Action of Stem Cells. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 2013, 41, 283–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.-H.; Chen, K.-H.; Sung, Y.-T.; Yang, C.-C.; Chien, C.-T. Intrarenal Arterial Transplantation of Dexmedetomidine Preconditioning Adipose Stem-Cell-Derived Microvesicles Confers Further Therapeutic Potential to Attenuate Renal Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury through miR-122-5p/Erythropoietin/Apoptosis Axis. Antioxidants 2022, 11, 1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F.; Wu, J.; Li, D.; Hao, L.; Li, Y.; Yi, D.; Yeung, K. W. K.; Chen, D.; Lu, W. W.; Pan, H.; Wong, T. M.; Zhao, X. Engineering Stem Cells to Produce Exosomes with Enhanced Bone Regeneration Effects: An Alternative Strategy for Gene Therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardpour, S.; Hassani, S.-N.; Mardpour, S.; Sayahpour, F.; Vosough, M.; Ai, J.; Aghdami, N.; Hamidieh, A. A.; Baharvand, H. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Embryonic Stem Cell-MSCs Ameliorate Cirrhosis in Thioacetamide-Induced Chronic Liver Injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2018, 233, 9330–9344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, H.; Lee, M. J.; Bae, E.-H.; Ryu, J. S.; Kaur, G.; Kim, H. J.; Kim, J. Y.; Barreda, H.; Jung, S. Y.; Choi, J. M.; Shigemoto-Kuroda, T.; Oh, J. Y.; Lee, R. H. Comprehensive Molecular Profiles of Functionally Effective MSC-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Immunomodulation. Mol. Ther. J. Am. Soc. Gene Ther. 2020, 28, 1628–1644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Penders, J.; Nagelkerke, A.; Cunnane, E. M.; Pedersen, S. V.; Pence, I. J.; Coombes, R. C.; Stevens, M. M. Single Particle Automated Raman Trapping Analysis of Breast Cancer Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles as Cancer Biomarkers. ACS Nano 2021, 15, 18192–18205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rong, X.; Liu, J.; Yao, X.; Jiang, T.; Wang, Y.; Xie, F. Human Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes Alleviate Liver Fibrosis through the Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, R.; Uemoto, S.; Tabata, Y. Immunosuppressive Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes on a Concanavalin A-Induced Liver Injury Model. Inflamm. Regen. 2016, 36, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, M.; Liu, H.; Zhang, T.; Zhang, M.; Tang, X.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, W.; Yang, S.; Jiang, Z.; Cui, Q.; Li, Z. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Peritoneal Healing by Activating MAPK-ERK1/2 and PI3K-Akt to Alleviate Postoperative Abdominal Adhesion. Stem Cells Int. 2022, 2022, 1940761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, Z.; Yin, Z.; Song, P.; Wu, Y.; He, Y.; Zhu, M.; Wu, Z.; Zhao, S.; Huang, H.; Wang, H.; Tong, C.; Qi, Z. Safety and Biodistribution of Exosomes Derived from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells. Front. Bioeng. Biotechnol. 2022, 10, 949724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.; Yan, M.; Bai, Z.; Xie, Y.; Ren, L.; Wei, J.; Zhu, D.; Wang, H.; Liu, Y.; Luo, J.; Li, X. Huc-MSC-Derived Exosomes Modified with the Targeting Peptide of aHSCs for Liver Fibrosis Therapy. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeo, R. W. Y.; Lai, R. C.; Zhang, B.; Tan, S. S.; Yin, Y. J.; Teh, B. J.; Lim, S. K. Mesenchymal Stem Cell: An Efficient Mass Producer of Exosomes for Drug Delivery. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2013, 65, 336–341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tkach, M.; Théry, C. Communication by Extracellular Vesicles: Where We Are and Where We Need to Go. Cell 2016, 164, 1226–1232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Jin, S.; Huang, W.; Li, Y.; Wang, J.; Ling, X.; Huang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Li, C.; Meng, Y.; Li, X. LPS-Induced Macrophage HMGB1-Loaded Extracellular Vesicles Trigger Hepatocyte Pyroptosis by Activating the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Cell Death Discov. 2021, 7, 337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phan, J.; Kumar, P.; Hao, D.; Gao, K.; Farmer, D.; Wang, A. Engineering Mesenchymal Stem Cells to Improve Their Exosome Efficacy and Yield for Cell-Free Therapy. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2018, 7, 1522236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auger, C.; Brunel, A.; Darbas, T.; Akil, H.; Perraud, A.; Bégaud, G.; Bessette, B.; Christou, N.; Verdier, M. Extracellular Vesicle Measurements with Nanoparticle Tracking Analysis: A Different Appreciation of Up and Down Secretion. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 2310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tang, B.; Zeng, W.; Song, L. L.; Wang, H. M.; Qu, L. Q.; Lo, H. H.; Yu, L.; Wu, A. G.; Wong, V. K. W.; Law, B. Y. K. Extracellular Vesicle Delivery of Neferine for the Attenuation of Neurodegenerative Disease Proteins and Motor Deficit in an Alzheimer’s Disease Mouse Model. Pharmaceuticals 2022, 15, 83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pugholm, L. H.; Revenfeld, A. L. S.; Søndergaard, E. K. L.; Jørgensen, M. M. Antibody-Based Assays for Phenotyping of Extracellular Vesicles. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 524817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y. D.; Li, D. W.; Han, C. H.; Wu, H. Y.; Xu, L.; Zhang, M.; Zhang, J. J.; Chen, X. S. Exosomes from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells (hiPSC-MSCs) Protect Liver against Hepatic Ischemia/ Reperfusion Injury via Activating Sphingosine Kinase and Sphingosine-1-Phosphate Signaling Pathway. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Int. J. Exp. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. Pharmacol. 2017, 43, 611–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nong, K.; Wang, W. W.; Niu, X.; Hu, B.; Ma, C.; Bai, Y. Q.; Wu, B.; Wang, Y.; Ai, K. X. Hepatoprotective Effect of Exosomes from Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stromal Cells against Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Rats. Cytotherapy 2016, 18, 1548–1559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Duan, W.; Wei, L.; Zhao, Y.; Han, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, M.; Dai, C.; Zhang, B.; Chen, D.; Chen, Z. Bone Marrow Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Hepatocyte-Like Cell Exosomes Reduce Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Enhancing Autophagy. Stem Cells Dev. 2020, 29, 372–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajidah, E. S.; Lim, K.; Yamano, T.; Nishide, G.; Qiu, Y.; Yoshida, T.; Wang, H.; Kobayashi, A.; Hazawa, M.; Dewi, F. R. P.; Hanayama, R.; Ando, T.; Wong, R. W. Spatiotemporal Tracking of Small Extracellular Vesicle Nanotopology in Response to Physicochemical Stresses Revealed by HS-AFM. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2022, 11, 12275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abels, E. R.; Breakefield, X. O. Introduction to Extracellular Vesicles: Biogenesis, RNA Cargo Selection, Content, Release, and Uptake. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2016, 36, 301–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bi, J.; Zhang, J.; Ren, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, Q.; Wang, Y.; Wei, S.; Yang, L.; Zhang, J.; Liu, C.; Lv, Y.; Wu, R. Irisin Alleviates Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Inhibiting Excessive Mitochondrial Fission, Promoting Mitochondrial Biogenesis and Decreasing Oxidative Stress. Redox Biol. 2019, 20, 296–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, R.-J.; Lv, G.-Y.; Liu, H.-Q. The Mechanisms and Strategies to Protect from Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2015, 19, 2036–2047. [Google Scholar]
- Sameri, M. J.; Savari, F.; Hoseinynejad, K.; Danyaei, A.; Mard, S. A. The Hepato-Protective Effect of H2S-Modified and Non-Modified Mesenchymal Stem Cell Exosomes on Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury in Mice: The Role of MALAT1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2022, 635, 194–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Su, L.; Chen, Z.; Wu, M.; Wei, J.; Lin, Y. Exosomes Derived from Baicalin-Pretreated Bone Mesenchymal Stem Cells Improve Th17/Treg Imbalance after Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion via FGF21 and the JAK2/STAT3 Pathway. IUBMB Life 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, S.; Huang, M.; Yan, L.; Zhang, H.; Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, H.; Wang, B. Exosomes Derived from Baicalin-Pretreated Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Hepatocyte Ferroptosis after Acute Liver Injury via the Keap1-NRF2 Pathway. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 8287227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, N.; Li, X. J.; Zhong, Z. Y.; Qiu, Y. Q.; Liu, S.; Wu, H.; Tang, X.; Chen, C.; Fu, Y.; Chen, Q.; Guo, T.; Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Zern, M. A.; Ma, K.; Wang, B.; Ou, Y.; Gu, W.; Cao, J.; Chen, H.; Duan, Y. 3D hESC Exosomes Enriched with miR-6766-3p Ameliorates Liver Fibrosis by Attenuating Activated Stellate Cells through Targeting the TGFβRII-SMADS Pathway. J. Nanobiotechnology 2021, 19, 437. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, J.; Lu, T. Y.; Zhou, C. R.; Cai, J.; Zhang, X. M.; Liang, J. L.; Sui, X.; Chen, X. Y.; Chen, L.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J. B.; Chen, W. J.; Zhang, Y. C.; Yao, J.; Chen, G. H.; Yang, Y. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury by Reducing CD154 Expression on CD4+ T Cells via CCT2. Adv. Sci. Weinh. Baden-Wurtt. Ger. 2020, 7, 1903746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, K.; Liu, L.; Chen, J. M.; Liu, F. B. Exosomal miR-1246 Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Blood Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia Reperfusion Injury by Modulating T Helper 17/Regulatory T Balance. IUBMB Life 2019, 71, 2020–2030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Song, Y. L.; Chen, L.; Li, D.; Feng, H.; Lu, Z.; Fan, T.; Chen, Z.; Livingston, M. J.; Geng, Q. MiR-20a-Containing Exosomes from Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviates Liver Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. J. Cell. Physiol. 2020, 235, 3698–3710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.-J.; Zhang, L.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Ding, F.-H.; Li, X. hUCB-MSC Derived Exosomal miR-124 Promotes Rat Liver Regeneration after Partial Hepatectomy via Downregulating Foxg1. Life Sci. 2021, 265, 118821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, J.; Zheng, J.; Cai, J. Y.; Zeng, K. N.; Zhou, C.; Zhang, J. B.; Li, S. H. ui; Li, H.; Chen, L.; He, L. Y.; Chen, H. X.; Fu, H. Y.; Zhang, Q.; Chen, G. H.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, Y. C. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells Alleviate Rat Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Suppressing Oxidative Stress and Neutrophil Inflammatory Response. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2019, 33, 1695–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T. Y.; Zhang, J. B.; Cai, J. Y.; Xiao, J. Q.; Sui, X.; Yuan, X. F.; Li, R.; Li, Y.; Yao, J.; Lv, G.; Chen, X. Y.; Chen, H. T.; Zeng, K. N.; Liu, Y. S.; Chen, W. J.; Chen, G. H.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, J.; Zhang, Y. C. Extracellular Vesicles Derived from Mesenchymal Stromal Cells as Nanotherapeutics for Liver Ischaemia-Reperfusion Injury by Transferring Mitochondria to Modulate the Formation of Neutrophil Extracellular Traps. Biomaterials 2022, 284, 121486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y.; Jiang, W.; Tan, Y.; Zou, S.; Zhang, H.; Mao, F.; Gong, A.; Qian, H.; Xu, W. hucMSC Exosome-Derived GPX1 Is Required for the Recovery of Hepatic Oxidant Injury. Mol. Ther. 2017, 25, 465–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haga, H.; Yan, I. K.; Borrelli, D. A.; Matsuda, A.; Parasramka, M.; Shukla, N.; Lee, D. D.; Patel, T. Extracellular Vesicles from Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Protect against Murine Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Liver Transplant. Off. Publ. Am. Assoc. Study Liver Dis. Int. Liver Transplant. Soc. 2017, 23, 791–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anger, F.; Camara, M.; Ellinger, E.; Germer, C.-T.; Schlegel, N.; Otto, C.; Klein, I. Human Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Improve Liver Regeneration After Ischemia Reperfusion Injury in Mice. Stem Cells Dev. 2019, 28, 1451–1462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, H.; Lin, W.; Zhang, G.; Liu, R.; Qu, M.; Zhang, J.; Xing, X. BMSC-Exosomes miR-25-3p Regulates the P53 Signaling Pathway Through PTEN to Inhibit Cell Apoptosis and Ameliorate Liver Ischemia‒reperfusion Injury. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2023, 19, 2820–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, H.; Song, P.; Pan, W.; Xu, P.; Wang, G.; Hu, P.; Wang, Z.; Huang, K.; Zhang, X.; Wang, H.; Zhang, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Extracellular Vesicles Alleviate Traumatic Hemorrhagic Shock Induced Hepatic Injury via IL-10/PTPN22-Mediated M2 Kupffer Cell Polarization. Front. Immunol. 2022, 12, 811164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zheng, W.; Tian, P.; Liu, H.; He, Y.; Peng, M.; Liu, X.; Li, X. Administration of Glycyrrhetinic Acid Reinforces Therapeutic Effects of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosome against Acute Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2020, 24, 11211–11220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Damania, A.; Jaiman, D.; Teotia, A. K.; Kumar, A. Mesenchymal Stromal Cell-Derived Exosome-Rich Fractionated Secretome Confers a Hepatoprotective Effect in Liver Injury. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.-K.; Chen, C.-H.; Chang, C.-L.; Chiang, H.-J.; Sung, P.-H.; Chen, K.-H.; Chen, Y.-L.; Chen, S.-Y.; Kao, G.-S.; Chang, H.-W.; Lee, M. S.; Yip, H.-K. Melatonin Treatment Enhances Therapeutic Effects of Exosomes against Acute Liver Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2017, 9, 1543–1560. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Y.; Li, Y.; Wang, Q.; Zheng, D.; Feng, X.; Zhao, W.; Cai, L.; Zhang, Q.; Xu, H.; Fu, H. Attenuation of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury by Adipose Stem Cell-Derived Exosome Treatment via ERK1/2 and GSK-3β Signaling Pathways. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2022, 49, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Pinky, null; Vishal, null; Sharma, H.; Soni, N.; Rao, E. P.; Dalela, M.; Yadav, A.; Nautiyal, N.; Kumar, A.; Nayak, B.; Banerjee, A.; Dinda, A. K.; Mohanty, S. Comparative Evaluation of Anti-Fibrotic Effect of Tissue Specific Mesenchymal Stem Cells Derived Extracellular Vesicles for the Amelioration of CCl4 Induced Chronic Liver Injury. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2022, 18, 1097–1112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fang, J.; Liang, W. L. ASCs -Derived Exosomes Loaded with Vitamin A and Quercetin Inhibit Rapid Senescence-like Response after Acute Liver Injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2021, 572, 125–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gong, Y.; Dai, H.; Liu, W.; Liao, R.; Chen, H.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X.; Chen, Z. Exosomes Derived from Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Alleviate Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion (I/R) Injury through the miR-183/ALOX5 Axis. FASEB J. Off. Publ. Fed. Am. Soc. Exp. Biol. 2023, 37, e22782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piao, C.; Sang, J.; Kou, Z.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Lu, X.; Jiao, Z.; Wang, H. Effects of Exosomes Derived from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Pyroptosis and Regeneration of Injured Liver. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 12065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Piao, C.; Liu, T.; Lu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Liu, G.; Wang, H. Effects of the Exosomes of Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells on Apoptosis and Pyroptosis of Injured Liver in Miniature Pigs. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2023, 169, 115873. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Piao, C.; Xu, J.; Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Ma, H.; Wang, H. ADSCs-Exo Attenuates Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury after Hepatectomy by Inhibiting Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress and Inflammation. J. Cell. Physiol. 2023, 238, 659–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Piao, C.; Liu, T.; Lu, X.; Ma, Y.; Zhang, J.; Ma, H.; Wang, H. Exosomes Derived from Adipose Mesenchymal Stem Cells Promote Regeneration of Injured Liver in Minipigs. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 6604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Liu, T.; Jiao, G.; Lv, Y.; Piao, C.; Lu, X.; Ma, H.; Wang, H. Exosomes from Adipose-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Can Attenuate Liver Injury Caused by Minimally Invasive Hemihepatectomy Combined with Ischemia-Reperfusion in Minipigs by Modulating the Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress Response. Life Sci. 2023, 321, 121618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Stefano, N.; Navarro-Tableros, V.; Roggio, D.; Calleri, A.; Rigo, F.; David, E.; Gambella, A.; Bassino, D.; Amoroso, A.; Patrono, D.; Camussi, G.; Romagnoli, R. Human Liver Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles Reduce Injury in a Model of Normothermic Machine Perfusion of Rat Livers Previously Exposed to a Prolonged Warm Ischemia. Transpl. Int. Off. J. Eur. Soc. Organ Transplant. 2021, 34, 1607–1617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigo, F.; De Stefano, N.; Navarro-Tableros, V.; David, E.; Rizza, G.; Catalano, G.; Gilbo, N.; Maione, F.; Gonella, F.; Roggio, D.; Martini, S.; Patrono, D.; Salizzoni, M.; Camussi, G.; Romagnoli, R. Extracellular Vesicles from Human Liver Stem Cells Reduce Injury in an Ex Vivo Normothermic Hypoxic Rat Liver Perfusion Model. Transplantation 2018, 102, e205–e210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calleri, A.; Roggio, D.; Navarro-Tableros, V.; De Stefano, N.; Pasquino, C.; David, E.; Frigatti, G.; Rigo, F.; Antico, F.; Caropreso, P.; Patrono, D.; Bruno, S.; Romagnoli, R. Protective Effects of Human Liver Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles in a Mouse Model of Hepatic Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury. Stem Cell Rev. Rep. 2021, 17, 459–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-Y.; Liu, Z.-S.; Wang, J.; Wang, H.-X.; Li, A.; Yang, Y.; Wang, X.-Z.; Zhao, Y.-Q.; Han, Q.-Y.; Cai, H.; Liang, B.; Song, N.; Li, W.-H.; Li, T. Glutathione Peroxidase-1 Is Required for Self-Renewal of Murine Embryonic Stem Cells. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 448, 454–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Y.; Wang, X. F.; Mao, L. W.; Yang, D.; Gao, W.; Tian, Z.; Zhang, M.; Yang, X.; Ma, K.; Wu, Y.; Ni, B. Dual Roles of IL-22 at Ischemia-Reperfusion Injury and Acute Rejection Stages of Rat Allograft Liver Transplantation. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 115384–115397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Feldstein, A. E.; Canbay, A.; Angulo, P.; Taniai, M.; Burgart, L. J.; Lindor, K. D.; Gores, G. J. Hepatocyte Apoptosis and Fas Expression Are Prominent Features of Human Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterology 2003, 125, 437–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valentim, L.; Laurence, K. M.; Townsend, P. A.; Carroll, C. J.; Soond, S.; Scarabelli, T. M.; Knight, R. A.; Latchman, D. S.; Stephanou, A. Urocortin Inhibits Beclin1-Mediated Autophagic Cell Death in Cardiac Myocytes Exposed to Ischaemia/Reperfusion Injury. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2006, 40, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, W.; Tan, Y.; Cai, M.; Zhao, T.; Mao, F.; Zhang, X.; Xu, W.; Yan, Z.; Qian, H.; Yan, Y. Human Umbilical Cord MSC-Derived Exosomes Suppress the Development of CCl 4 -Induced Liver Injury through Antioxidant Effect. Stem Cells Int. 2018, 2018, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, H.; Tohme, S.; Al-Khafaji, A. B.; Tai, S.; Loughran, P.; Chen, L.; Wang, S.; Kim, J.; Billiar, T.; Wang, Y.; Tsung, A. Damage-Associated Molecular Pattern-Activated Neutrophil Extracellular Trap Exacerbates Sterile Inflammatory Liver Injury. Hepatol. Baltim. Md 2015, 62, 600–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.-L.; Zhuang, X.-Y.; Sriwastva, M. K.; Mu, J.; Teng, Y.; Deng, Z.; Zhang, L.; Sundaram, K.; Kumar, A.; Miller, D.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H.-G. Blood Exosomes Regulate the Tissue Distribution of Grapefruit-Derived Nanovector via CD36 and IGFR1 Pathways. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4912–4924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamada, N.; Karasawa, T.; Kimura, H.; Watanabe, S.; Komada, T.; Kamata, R.; Sampilvanjil, A.; Ito, J.; Nakagawa, K.; Kuwata, H.; Hara, S.; Mizuta, K.; Sakuma, Y.; Sata, N.; Takahashi, M. Ferroptosis Driven by Radical Oxidation of N-6 Polyunsaturated Fatty Acids Mediates Acetaminophen-Induced Acute Liver Failure. Cell Death Dis. 2020, 11, 144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Go, K. L.; Lee, S.; Zendejas, I.; Behrns, K. E.; Kim, J.-S. Mitochondrial Dysfunction and Autophagy in Hepatic Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. BioMed Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 183469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasralla, D.; Coussios, C. C.; Mergental, H.; Akhtar, M. Z.; Butler, A. J.; Ceresa, C. D. L.; Chiocchia, V.; Dutton, S. J.; García-Valdecasas, J. C.; Heaton, N.; Imber, C.; Jassem, W.; Jochmans, I.; Karani, J.; Knight, S. R.; Kocabayoglu, P.; Malagò, M.; Mirza, D.; Morris, P. J.; Pallan, A.; Paul, A.; Pavel, M.; Perera, M. T. P. R.; Pirenne, J.; Ravikumar, R.; Russell, L.; Upponi, S.; Watson, C. J. E.; Weissenbacher, A.; Ploeg, R. J.; Friend, P. J.; Consortium for Organ Preservation in Europe. A Randomized Trial of Normothermic Preservation in Liver Transplantation. Nature 2018, 557, 50–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ravikumar, R.; Jassem, W.; Mergental, H.; Heaton, N.; Mirza, D.; Perera, M. T. P. R.; Quaglia, A.; Holroyd, D.; Vogel, T.; Coussios, C. C.; Friend, P. J. Liver Transplantation After Ex Vivo Normothermic Machine Preservation: A Phase 1 (First-in-Man) Clinical Trial. Am. J. Transplant. Off. J. Am. Soc. Transplant. Am. Soc. Transpl. Surg. 2016, 16, 1779–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
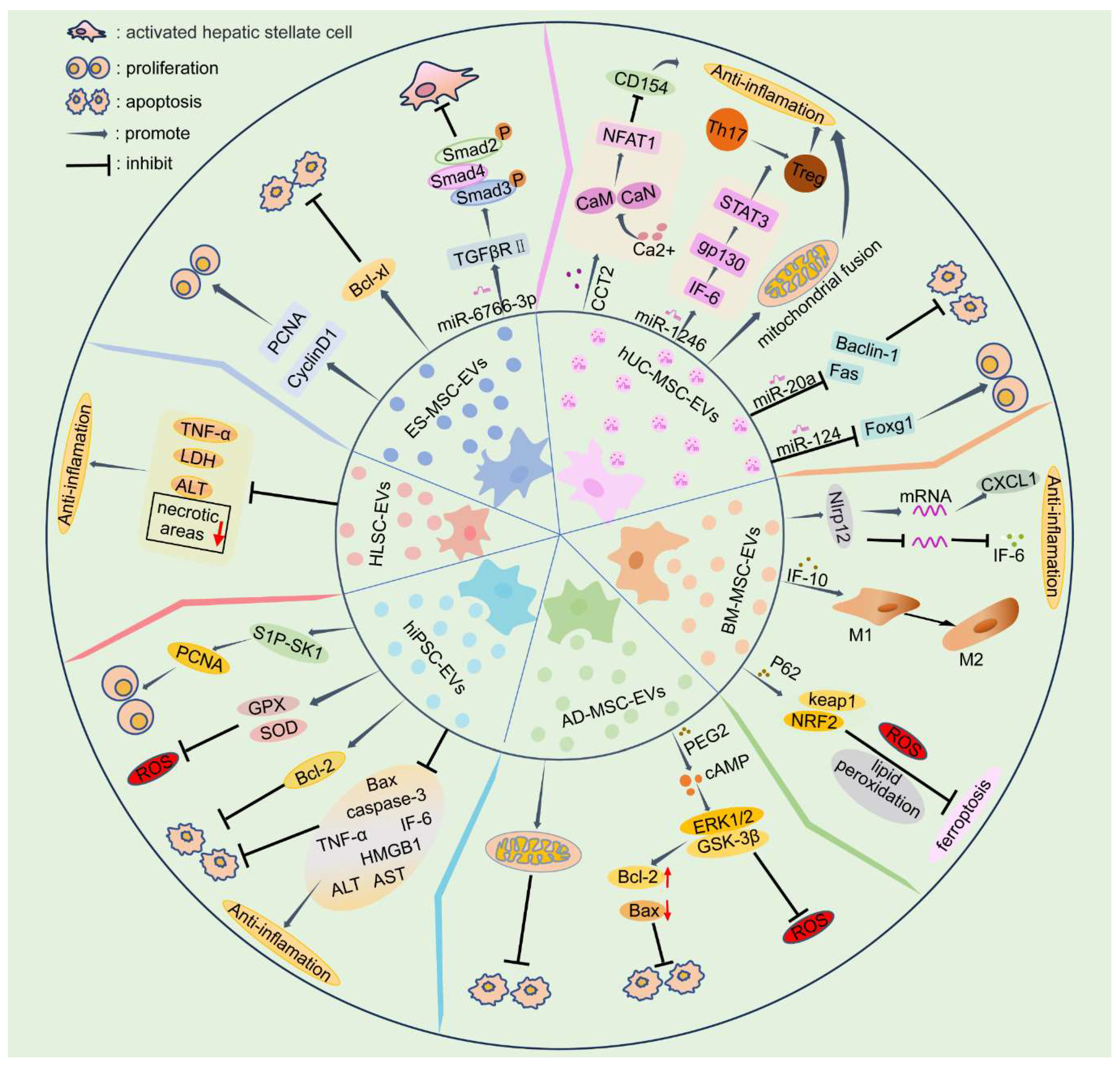
| Reference | Animal model | In vitro | EV source | Dose | Mode of administration | Signaling pathway/mechanism | Therapeutic effect |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tan et al. 2014[2] | mouse | + | ES-MSC | 0.4 μg/dose | Splenic injection | Increase hepatocyte proliferation (PCNA elevation); inhibit hepatocyte apoptosis | |
| Wang et al. 2021[43] | mouse | + | 3D-hESC | Vein | TGFβRII/SMADS pathway | reduce HSC activation | |
| Mardpour et al. 2018[18] | rat | + | ES-MSC | 350 µg/dose | Splenic injection | Reduce inflammation; reduce apoptosis | |
| Sameri et al. 2022[40] | mouse | + | hUC-MSC | 100 μg/dose | Caudal vein | Reduce inflammation; reduce apoptosis; Inhibit oxidative stress | |
| Zheng et al. 2020[44] | mouse | + | hUC-MSC | 4 mg/kg | Caudal vein | The Ca2+-calcineurin-NFAT1 signaling pathway | Inhibit the initiation of inflammatory responses |
| Xie et al. 2019[45] | mouse | + | hUC-MSC | 10 μg/dose | Vein | Transfer miR-1246 targeting the IL-6-gp130-STAT3 pathway | Reduce inflammation (decreased Th17/Treg ratio among CD4+ T cells) |
| Xie et al. 2019[15] | mouse | + | hUC-MSC | 2.5 × 1012 particles/dose | Portal vein | Transfer miR-1246 targeting the GSK3β/Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Inhibit apoptosis and inflammation (the inflammatory factors TNF-α, IL-6a, and IL-1β are significantly reduced) |
| Zhang et al. 2020[46] | rat | + | hUC-MSC | By secreting miR-20a, it targets Fas and Beclin-1 and inhibits their expression | Inhibit autophagy and apoptosis | ||
| Song et al. 2021[47] | rat | hUC-MSC | 0.4 μg/dose | Caudal vein | The expression of Foxg1 is downregulated by the secretion of miR-124 | Promote hepatocyte proliferation (the proliferation marker PCNA was elevated) | |
| Yao et al. 2019[48] | rat | + | hUC-MSC | 10 mg/kg | Caudal vein | Inhibit oxidative stress (increased levels of the mitochondrial antioxidant enzyme MnSOD); inhibit inflammation (prevent neutrophils from entering the inflammatory microenvironment) | |
| Lu et al. 2022[49] | mouse | hUC-MSC | 100 μg/dose | Caudal vein | Transfer of mitochondria to modulate the formation of NETs |
Reduce autophagy and apoptosis | |
| Yan et al. 2017[50] | mouse | + | hUC-MSC | 16 mg/kg | Caudal vein/gavage | Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 is induced by the secretion of GPX1 | Inhibit oxidative stress; reduce apoptosis |
| Haga et al. 2017[51] | mouse | + | mBM-MSC | 2 ×1010 particles/dose | Caudal vein | Targeting Nlrp12 | Inhibit inflammation (decreased expression of inflammatory cytokines IL-6 and IL-1β); reduce apoptosis (reduction of caspase-3 positive cells and apoptotic cells) |
| Anger et al.2019[52] | mouse | hBM-MSC | 1 ×109 particles/dose | Vena cava inferior | Reduce inflammation; reduce liver damage | ||
| Zhang et al. 2024[41] | mouse | + | mBM-MSC | Caudal vein | Targeting FGF21 and the JAK2/STAT3 pathway | Ba-EVs can improve Th17/Treg imbalance | |
| Li et al. 2023[53] | mouse | + | mBM-MSC | 50 μg/dose | Caudal vein | Regulates the p53 signaling pathway through PTEN | Inhibit cell apoptosis |
| Yang et al. 2020[35] | mouse | + | mBM-MSC-Heps | 100 μg/dose | Caudal vein | Enhanced autophagy | Reduce apoptosis; reduce liver damage |
| Zhang et al. 2022[54] | mouse | + | mBM-MSC | 20 μg/dose | Arteria femoralis | By delivering IL-10 and interacting with Kupffer cells, it causes Kupffer cells to change to an anti-inflammatory phenotype (M2) | Inhibit inflammation |
| Zhao et al. 2022[42] | mouse | + | BM-MSC | 150 µg/dose | Caudal vein | Ba-EVs inhibits iron death by activating the Keap1-NRF2 pathway through P62 | Inhibit ROS production and lipid peroxide-induced iron death |
| Wei et al. 2020[55] | rat | + | hBM-MSC | Intraperitoneal injection | Inhibit inflammation and apoptosis | ||
| Tamura et al. 2016[22] | mouse | + | mBM-MSC | 10 μg/dose | Vein | Inhibit inflammation; reduce apoptosis | |
| Damania et al.2018[56] | rat | + | rBM-MSC | 50 μg/dose | Portal vein | Reduce oxidative stress and apoptosis | |
| Sun et al. 2017[57] | rat | + | Mini-pig AD-MSC | 100 µg/dose | Vein | Inhibit inflammation (the inflammation markers MIF, MMP-9, L-1β, TNF-α, COX-2 are decreased); inhibit oxidative stress (NOX-1, NOX-2 levels decreased; HO-1, NQO-1 levels increased); inhibit apoptosis (reduced caspase 3 and PARP) | |
| Zhang et al. 2022[58] | rat | + | rAD-MSC | 30 μg/dose | Portal vein | Phosphorylation of ERK1/2 and GSK-3β by prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) | Reduce apoptosis and oxidative stress; reduce inflammation |
| Zhang et al. 2021[1] | rat | rAD-MSC | 100 µg/dose | Caudal vein | Reduce mitochondrial division, promote mitochondrial fusion and improve mitochondrial biosynthesis | Inhibit oxidative stress (MDA, ROS oxidation index decreased, antioxidant enzymes SOD, CAT, GSH-px content increased), reduce cell apoptosis (inhibition of Caspase-3 and Caspase-9 activities, decrease Bax mRNA and protein expression, increase Bcl-2 mRNA and protein expression) | |
| Gupta et al.2022[59] | mouse | + | hAD-MSC | 250 µg/dose | Caudal vein | Promote hepatocyte proliferation | |
| Fang and Liang, 2021[60] | mouse | + | mAD-MSC | 200 μL | Caudal vein | EVs loaded with vitamin A and quercetin were more effective in reducing liver damage | |
| Gong et al.2023[61] | rat | + | hAD-MSC | Caudal vein | Through the miR-183/ALOX5 axis | Reduce liver injury | |
| Piao et al.2022[62] | rat | hAD-MSC | 100 µg/dose | Caudal vein | Inhibit the NF-κB pathway and activate the Wnt/β-catenin pathway | Inhibit cell pyroptosis; Promote hepatocyte proliferation | |
| Wang et al.2023[63] | mini-pig | + | mini-pig AD-MSC | 5 × 106 particles/g of liver | Portal vein | Inhibit apoptosis, pyroptosis and inflammatory responses | |
| Zhang et al.2023[64] | rat | rAD-MSC | 100 µg/dose | Caudal vein | Inhibit ERS and inflammation | ||
| Wang et al.2024[65] | mini-pig | + | mini-pig AD-MSC | 5 × 106 particles/g of liver | Portal vein | Inhibit inflammation; Promote hepatocyte proliferation | |
| Wang et al.2023[66] | mini-pig | mini-pig AD-MSC | 5 × 106 particles/g of liver | Portal vein | Modulat the ERS response | ||
| Nong et al. 2016[34] | rat | hiPSC-MSC | 2 mg/kg | Vena cava inferior | Inhibit inflammation (TNF-α, IL-6 and HMGB1 decreased significantly), reduce oxidative stress (increased GSH, GSH-PX and SOD levels), reduce apoptosis (significantly decreased caspase-3 and bax levels), promote hepatocyte proliferation | ||
| Du et al. 2017[33] | mouse | + | hiPSC-MSC | 2.5 × 1012 particles/dose | Vena cava inferior | The sphingosine kinase and sphingosine-1-phosphate-dependent pathway | Reduce liver damage (significantly decreased AST and ALT levels) and promote hepatocyte proliferation (significantly increased expression of the proliferation markers PCNA and PHH3) |
| De Stefano et al. 2021[67] | rat | + | HLSC | 5 or 25 × 108 particles/g of liver | Promote hepatocyte regeneration, damage mitigation | ||
| Rigo et al. 2018[68] | rat | HLSC | 5x 108 HLSC-EV/g liver tissue | Reduce liver damage | |||
| Calleri et al. 2021[69] | mouse | HLSC | 3×109 particles/dose | Vein | Reduce liver damage, reduce inflammation |
| Registration number | Title | Country | Year | Status | Study type | Phase | EVs source |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05940610 | The Safety and Efficacy of MSC-EVs in Acute/Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure | China | 2023 | Withdrawn | Interventional | 1、2 | hMSC |
| NCT05881668 | MSC-EV in Acute-on-Chronic Liver Failure After Liver Transplantation | China | 2023 | Withdrawn | Interventional | 1 | MSC |
| NCT05871463 | Effect of Mesenchymal Stem Cells-derived Exosomes in Decompensated Liver Cirrhosis | Iran | 2023 | Recruiting | Interventional | 2 | hUC-MSC |
| ChiCTR-INR-17010677 | Study on the effect of MSCs-HNF4α exosomes combined with normal mechanical perfusion on liver transplantation of fatty liver | China | 2017 | Not yet recruiting | Interventional | New Treatment Measure Clinical | hMSCs-HNF4α |
| ChiCTR2300075676 | A small sample clinical study of the safety and initial efficacy of exosomes in the treatment of cirrhosis | China | 2023 | Recruiting | Interventional | New Treatment Measure Clinical Study | MB-MSC |
| ChiCTR1800020076 | A clinical study for cancer stem cells exosome loaded dendritic cells vaccine and its activated CTL injection in the treatment of hepatic cell cancer and other solid tumors | China | 2018 | Not yet recruiting | Interventional | 1、2 | cancer stem cells |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





