Submitted:
27 August 2024
Posted:
28 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
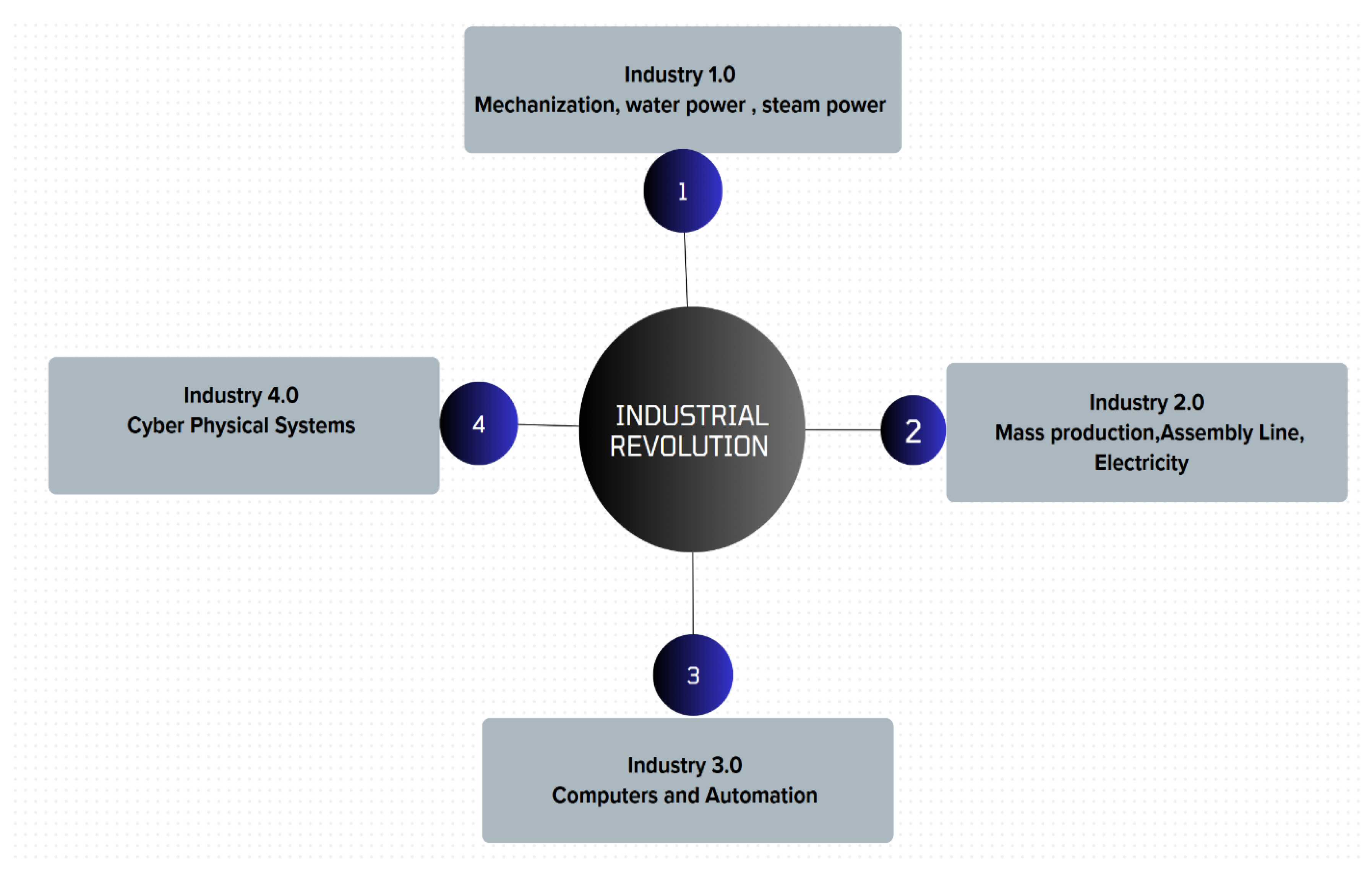
1. Introduction
2. Overview of Challenges in Automation of Education 4.0
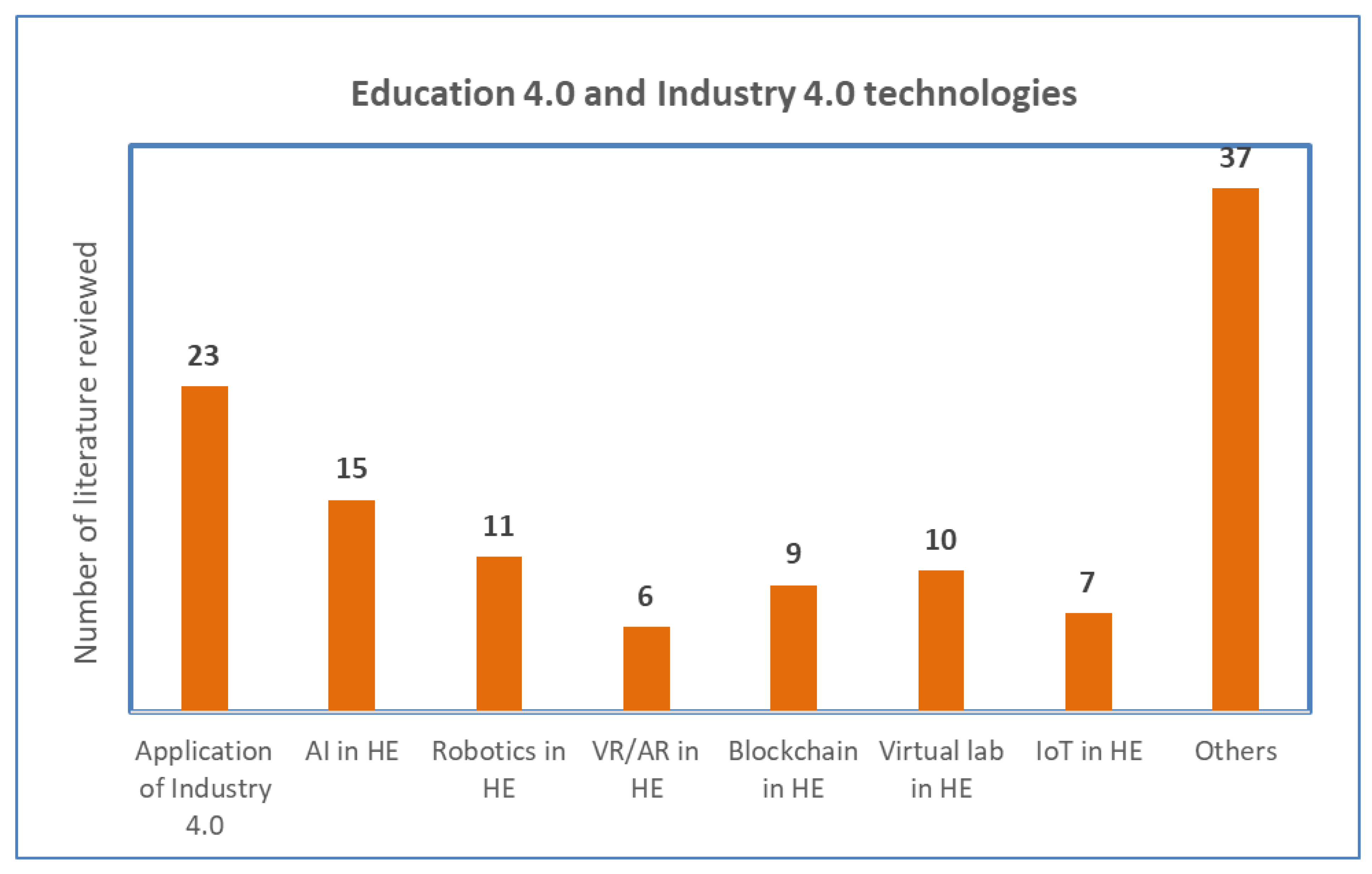
3. Literature Review
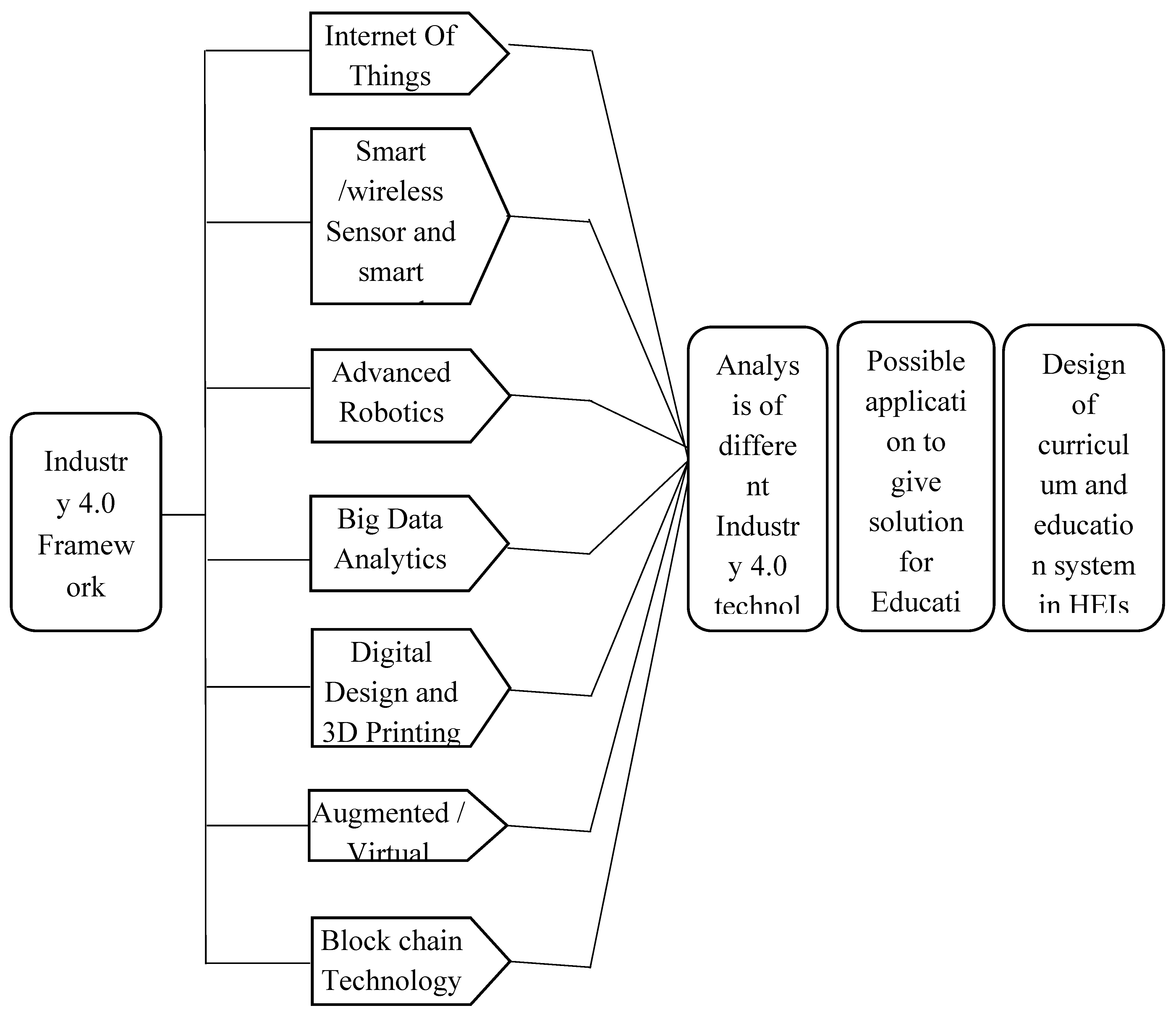
4. Review of Technologies in Industry 4.0
- Cyber-physical systems
- Big data
- Internet of things
- Artificial intelligence
- Additive manufacturing
- Cloud computing
- Virtual reality
- Robotics
- Block chain technology
4.1. Review of Artificial Intelligence in Online Learning and Teaching
4.1.1. Smart Learning Content
4.1.2. Real Time Questioning
4.1.3. Natural Language Processing
4.1.4. Fresh Learning Content Generation
4.1.5. Gamification
4.1.6. Intelligent Tutoring System
4.1.7. Challenges in Implementation of AI in HEIs
5. Review of Robotics in Online Learning and Teaching
5.1. Major Reasons for Using Robots in Online Learning and Teaching
- The present Jobs are completely technology oriented and now require higher-level creative thinking, broader knowledge, and communicative collaboration for complex problem-solving. Robot based delivery will build new confidence and the introduction of new technology to the learners
- Robot with artificial intelligence will serve more information than a traditional delivery in teaching
- Robot structured tasks for learners enable them to work with minimal contact with faculty input
- Robot based learning and teaching will increase student control over learning and gives more time for teachers to prepare his/her content
5.2. Advantages of Using Robots in Online Learning and Teaching
- Robots can be used to bring students into the classroom and can be increased the attendance and direct learning
- Robots can be used as smart personnel in learning and teaching with the help of artificial intelligence
- Robotics is very good for school level students which will attract the students to learn technologies in parallel to their regular curriculum
- Robotics based online learning and teaching is one of the best solution for physically challenged students
- Robotics are good for healthcare sector students to get more information and latest medicine, development in health care etc
5.3. Various Robots Used in Learning and Teaching
5.3.1. Emotional Robots
5.3.2. Casual Robots
5.3.3. Walk, Dance and Singing Robots
5.3.4. Programmable Robots
5.3.5. Humanoid Robots
5.3.6. Training Robotics
5.4. Challenges in Implementation of Robots in HEIs
- ➢
- Scarcity of resources
- ➢
- Funding for equipment, software and trained educators
- ➢
- Accessibility to all
- ➢
- Financial gap between institutes
- ➢
- Integrating robotics into the curriculum
- ➢
- Teacher readiness
- ➢
- Staying updated
6. Virtual Reality (VR) and Augmented Reality (AR) in online learning and teaching:
6.1. Five Key Aspects of VR Learning Experiences
- Immersive. It makes to have real time feeling in learning environment.
- Easy to use. It is not required and special skills to interact with a VR app.
- Meaningful. The text, video and audio with visual effects will make a meaningful learning. This is much useful for designers and storytellers.
- Adaptable. Based on feedback from the learners, it is possible to establish complete control over the level of difficulty. It is possible to design the course based on how students learn and then use this knowledge to design VR products to allow effective learning.
- ∙ Measurable. Teachers can measure the metrics of education so they can realize the resulting knowledge of a subject. Using this, it is possible to understand the success and failure of the teaching methodology.
6.2. Advantages and Disadvantages of using VR in Education
- Enhanced engagement
- improved retention and experiential learning
- Real time experience – making experience more memorable
- Visual learning will improve the quality of learners.
- Real world technical skills
- VR creates an entire digital environment, a 360-degree
- Develop creativity
- Learning by doing
- To make user to adapt new technology
- Design learning students can check out 3D geometric forms from multiple perspectives
- VR gadgets are so costly
- Need to give more care to the VR gadgets since it is made up of glass
- Wearing VR headset for more time may result health issues to the learners
- Not useful for long time learning
6.3. Challenges in VR Based Teaching
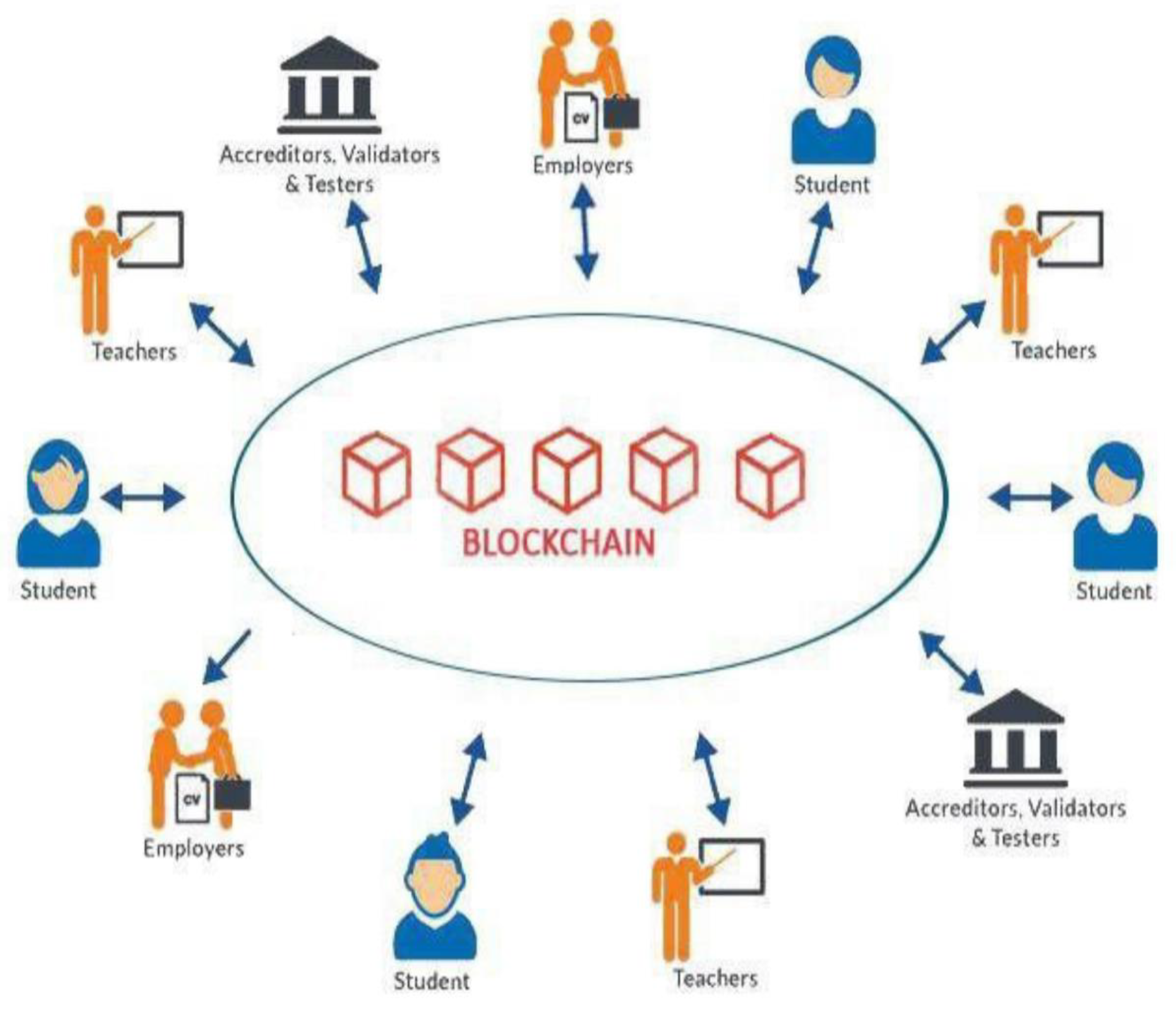
7. Block Chain Technology in Education
7.1. Challenges in Implementation of Block Chain in HEIs:
8. Online or Digital Laboratories
8.1. Challenges in Implementation of Virtual Laboratories in HEIs
9. IoT in Education
9.1. Challenges in Implementation of IoT in HEIs
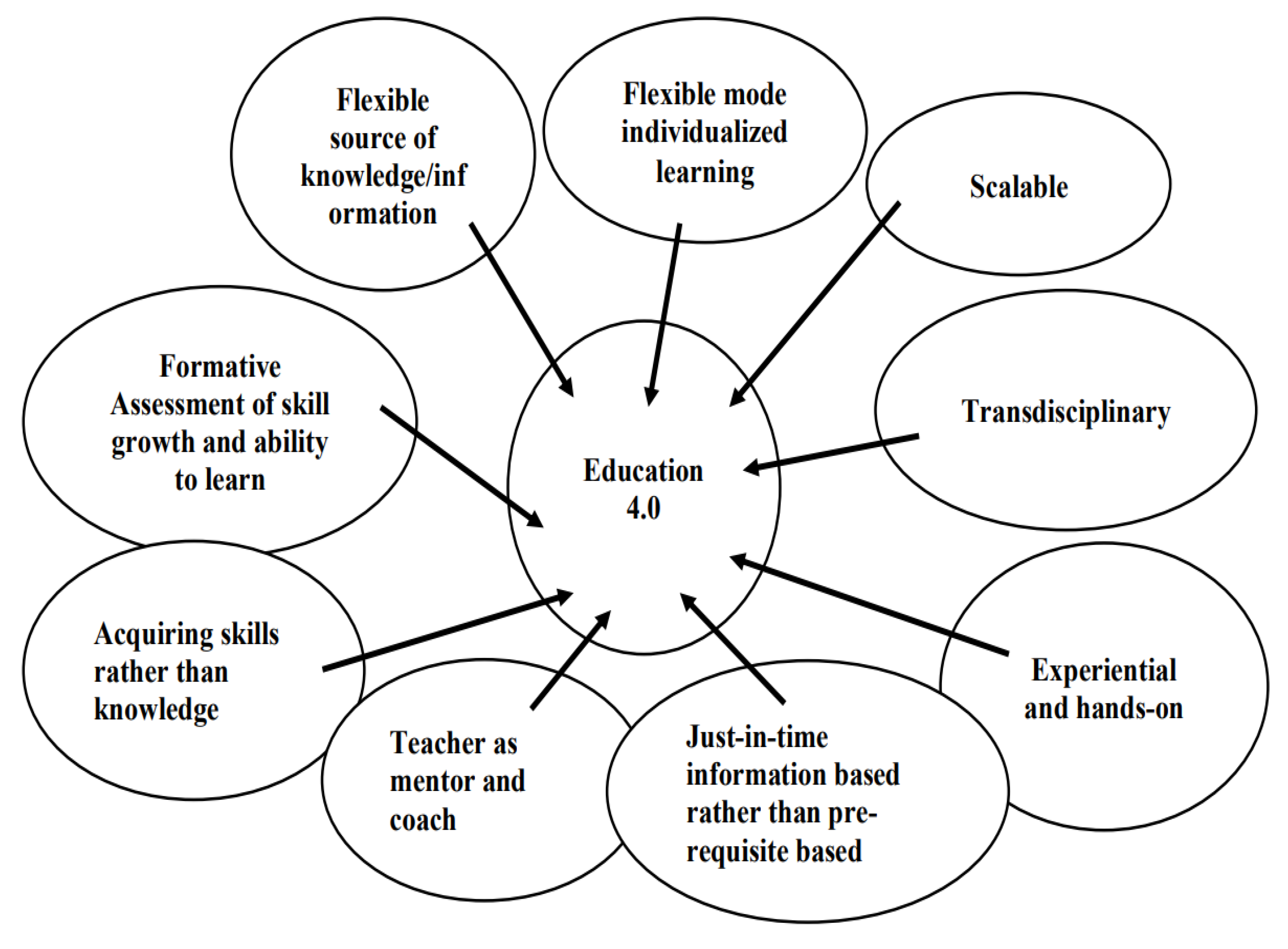
10. Conclusion and Future of Education 4.0
- Best prepare the university learners for the new careers that are driven by 4IR
- Redefining Class room culture: Online delivery (flipped Classes) and blended learning,
- Using AI to assist learning
- Develop institutional agility for 4IR target area
- Capacity building: Provide opportunity for staff to develop in the focus area of 4IR
- Train and provide opportunity for students to improve their learning experience and qualifications through online courses, credentialed certificate programs, self-teaching and entrepreneurship.
- Need to encourage students to take charge of their self-learning ability
- Moving out with traditional degree with in the academic four walls, which is widely considered the standard requirement for career success.
- Forging stronger linkages between industry and academia.
- Encourage to develop real-world skills through project-based/ case studies learning
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Latinovic, T. and Sikman, L., 2022, June. Impact of COVID 19 on the information technology for online education, education 4.0, challenges and solutions. In International Symposium on Innovative and Interdisciplinary Applications of Advanced Technologies (pp. 707-716). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Benešová, A. and Tupa, J., 2017. Requirements for education and qualification of people in Industry 4.0. Procedia manufacturing, 11, pp.2195-2202.
- Ab Rahman, R., Ahmad, S. and Hashim, U.R., 2019. A study on gamification for higher education students’ engagement towards education 4.0. In Intelligent and Interactive Computing: Proceedings of IIC 2018 (pp. 491-502). Springer Singapore.
- Oztemel, E. and Gursev, S., 2020. Literature review of Industry 4.0 and related technologies. Journal of intelligent manufacturing, 31(1), pp.127-182.
- Mukul,E Büyüközkan,G, (2023), Digital transformation in education: A systematic review of education 4.0, Technological Forecasting and Social Change, Volume 194,2023, ISSN 0040-1625. [CrossRef]
- Alex Sander Clemente de Souza, Luciana Debs,Concepts, innovative technologies, learning approaches and trend topics in education 4.0: A scoping literaturereview,Social Sciences & Humanities Open,Volume 9,2024,100902,ISSN 2590-2911. [CrossRef]
- Caratozzolo, P., Lara-Prieto, V., Martinez-Leon, C., Rodríguez-Ruiz, J., Ponce, R., Vázquez-Villegas, P. and Membrillo-Hernández, J., 2022, October. Developing skills for industry 4.0: Challenges and opportunities in engineering education. In 2022 IEEE Frontiers in Education Conference (FIE) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Times News Service,(2018) , Oman ready for fourth industrial revolution: TRC, Times of Oman Article published on 15 May 2018, Available at : https://timesofoman.com/article/59068-oman-ready-for-fourth-industrial-revolution-trc.
- Miranda, J., and A. Molina, A. Designing 2020 Hybrid learning programs in higher education by applying education 4.0: The innovation challenge bootcamp as case study 2020 IEEE learning with MOOCS (LWMOOCS), antigua Guatemala, Guatemala, 2020 (2020), pp. 31-36. [CrossRef]
- Caratozzolo,P., Alvarez-Delgado, A., Sirkis, G. Fostering digital literacy through active learning in engineering education, 2021 IEEE frontiers in education conference (FIE), IEEE (2021), pp. 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Reza Ghanei Gheshlagh1 , Mehrdad Ahsan2 , Mojtaba Jafari3 and Hassan Mahmoodi2, Identifying the challenges of online education from the perspective of University of Medical Sciences Students in the COVID-19 pandemic: a Q-methodology-based study, . BMC Medical Education (2022) 22:895. [CrossRef]
- Caratozzolo, P. and Membrillo-Hernández, J., 2021, September. Challenge based learning approaches for education 4.0 in engineering. In Proceedings of the 2021 SEFI Conference (pp. 110-118).
- Al-Ghamdi, A.S.A.M. and Ragab, M., 2022. Artificial intelligence Techniques based learner authentication in cyber security higher education institutions. Computers, Materials & Continua, 72(2), pp.3131-3144.
- Das, Shuvra & Kleinke, Darrell & Pistrui, David, “Reimagining Engineering Education: Does Industry 4.0 Need Education 4.0?
- Yuefan Xia1 Yawen Hu2 Chenyi Wu1 Ling Yang2 Man Lei3* Challenges of online learning amid the COVID-19: College students’ perspective, Frontiers in Psychology, Volume 13 - 2022. [CrossRef]
- Wheatley B, Greer E. Interactive television: a new delivery system for atraditional reading course. J Technol Teacher Educ 1995;3(4):343–50.
- Emad Mushtaha a,1,⇑, Saleh Abu Dabous a,2, Imad Alsyouf a,3, Amr Ahmed a,4, Naglaa Raafat Abdraboh bThe challenges and opportunities of online learning and teaching at engineering and theoretical colleges during the pandemic , Ain Shams Engineering Journal, Vol.13 (2022)\.
- Akturk, C., Talan, T. and Cerasi, C.C., 2022, September. Education 4.0 and University 4.0 from Society 5.0 Perspective. In 2022 12th International conference on advanced computer information technologies (ACIT) (pp. 577-582). IEEE.
- Anshari, M., Almunawar, M.N. and Razzaq, A., 2021. Developing talents vis-à-vis fourth industrial revolution. International Journal of Asian Business and Information Management (IJABIM), 12(4), pp.20-32.
- Bakkar, M.N. and Axmann, M., 2021. Industry 4.0: Learning analytics using artificial intelligence and advanced industry applications. In Manage Your Own Learning Analytics: Implement a Rasch Modelling Approach (pp. 193-204). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Caratozzolo,P., and Alvarez-Delgado, A. Education 4.0 framework: Enriching active learning with virtual and technological tools, October,Proceedings of the international conference on education, Vol. 7 (2021), pp. 614-628. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z., Zhang, J., Jiang, X., Hu, Z., Han, X., Xu, M., Savitha, V. and Vivekananda, G.N., 2020. Education 4.0 using artificial intelligence for students performance analysis. Inteligencia Artificial, 23(66), pp.124-137.
- Ivanciu, L.N. and ŞIPOŞ, E., 2020. TRANSITION TOWARDS EDUCATION 4.0 IN THE ELECTRONIC DEVICES AND CIRCUITS LAB. eLearning & Software for Education, 1.
- Laurent, A. and Fabiano, B., 2022. A Critical perspective on the impact of industry 4.0's new professional safety management skills on process safety education. Chemical Engineering Transactions, 91, pp.67-72.
- Mourtzis, D. (2018), “Development of skills and competences in manufacturing towards education 4.0: a teaching factory approach”, In International Conference on the Industry 4.0 Model for Advanced Manufacturing, Springer, Cham, pp. 194-210.
- Mourtzis, D., Vlachou, E., Dimitrakopoulos, G. and Zogopoulos, V. (2018), “Cyber- physical systems and education 4.0 –the teaching factory 4.0 concept”, Procedia Manufacturing, Vol. 23, pp. 129-134. [CrossRef]
- Jedaman, P., Buaraphan, K., Pimvichai, J., Yuenyong, C. and Jeerasombat, S., 2019, March. Educational management in transition of science: Policies and strategic leaders for sustainable education 4.0 in the 21st century science classroom. In AIP Conference Proceedings (Vol. 2081, No. 1). AIP Publishing.
- Moraes,E.B.,Kipper,L.M.,Hackenhaar Kellermann.A.C.,Austria,L.,Leivas,P.,Maraes,J.A.R.,Witczak,M(2023). Integration of Industry 4.0 technologies with 4.0 Advantages for improvements in learning. Interactive Technology and smart Education, 20 (2), 271-287.
- Saragih, M.J., Cristanto, R.M.R.Y., Effendi, Y. and Zamzami, E.M., 2020, June. Application of blended learning supporting digital education 4.0. In Journal of Physics: Conference Series (Vol. 1566, No. 1, p. 012044). IOP Publishing.
- Toma, M.V. and Turcu, C.E., 2022, May. Towards Education 4.0: Enhancing Traditional Textbooks with Augmented Reality and Quick Response codes. In 2022 International Conference on Development and Application Systems (DAS) (pp. 144-149). IEEE.
- Verma, A. and Singh, A., 2021, September. New era of technology empowered education: education 4.0 a systematic review. In 2021 9th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions)(ICRITO) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
- Ramírez-Montoya, M.S., Castillo-Martínez, I.M., Sanabria-Z, J. and Miranda, J., 2022. Complex thinking in the framework of Education 4.0 and Open Innovation—A systematic literature review. Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, 8(1), p.4.
- Silva, D.E., Lopes, T., Sobrinho, M.C. and Valentim, N.M.C., 2021. Investigating initiatives to promote the advancement of education 4.0: A systematic mapping study. CSEDU (1), pp.458-466.
- Butt, R., Siddiqui, H., Soomro, R.A. and Asad, M.M. (2020), “Integration of industrial revolution 4.0 and IOTs in academia: a state-of-the-art review on the concept of education 4.0 in Pakistan [review]”, Interactive Technology and Smart Education, Vol. 17 No. 4, pp. 337-354. [CrossRef]
- González-Pérez, L.I. and Ramírez-Montoya, M.S., 2022. Components of Education 4.0 in 21st century skills frameworks: systematic review. Sustainability, 14(3), p.1493.
- Hariharasudan, A. and Kot, S., 2018. A scoping review on Digital English and Education 4.0 for Industry 4.0. Social sciences, 7(11), p.227.
- Huk, T. (2021), “From education 1.0 to education 4.0 – challenges for the contemporary school”, The New Educational Review, Vol. 66 No. 4, pp. 36-46. [CrossRef]
- Krstikj, A., Sosa Godina, J., García Bañuelos, L., González Peña, O.I., Quintero Milián, H.N., Urbina Coronado, P.D. and Vanoye García, A.Y., 2022. Analysis of competency assessment of educational innovation in upper secondary school and higher education: a mapping review. Sustainability, 14(13), p.8089.
- Lai, J.W.M. and Bower, M. (2020), “Evaluation of technology use in education: findings from a critical analysis of systematic literature reviews”, Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, Vol. 36 No. 3, pp. 241-259. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C., Zowghi, D., Kearney, M. and Bano, M. (2021), “Inquiry-based mobile learning in secondary school science education: a systematic review”, Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, Vol. 37 No. 1, pp. 1-23. [CrossRef]
- Müller F, Denk A, Lubaway E, Sälzer C, Kozina A, Perše TV, et al. Assessingsocial, emotional, and intercultural competences of students and school staff:A systematic literature review. Educ Res Rev 2020;29:100304. [CrossRef]
- Parmaxi, A. and Demetriou, A.A. (2020), “Augmented reality in language learning: a state-of-the-art review of 2014–2019”, Journal of Computer Assisted Learning, Vol. 36 No. 6, pp. 861-875. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, M.I., Khan, N., Raza, H., Imran, A. and Ismail, F. (2021), “Digital technologies in education 4.0. Does it enhance the effectiveness of learning? A systematic literature review”, International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies, Vol. 15 No. 4, pp. 31-47.
- Costan, E.; Gonzales, G.; Gonzales, R.; Enriquez, L.; Costan, F.; Suladay, D.; Atibing, N.M.; Aro, J.L.; Evangelista, S.S.; Maturan, F.; et al. Education 4.0 in Developing Economies: A Systematic Literature Review of Implementation Barriers and Future Research Agenda. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnold, M.G.; Vogel, A.; Ulber, M. [40] 2021 Digitalizing Higher Education in Light of Sustainability and Rebound Effects—Surveys in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic. Sustainability ,13,12912. [CrossRef]
- Chiu, W.-K. Pedagogy of Emerging Technologies in Chemical Education during the Era of Digitalization and Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tselegkaridis, S.; Sapounidis, T. Simulators in Educational Robotics: A Review. Educ. Sci. 2021, 11, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Chila, R.; Llerena-Izquierdo, J.; Sumba-Nacipucha, N.; Cueva-Estrada, J. Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: An Analysis of Existing Bibliometrics. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurzo, A.; Strunga, M.; Urban, R.; Surovková, J.; Afrashtehfar, K.I. Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Dental Education: A Review and Guide for Curriculum Update. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laura Icela, G. P., María Soledad, R. M., & Juan Antonio, E. G. (2023). Education 4.0 Maturity Models for Society 5.0: Systematic literature review. Cogent Business & Management, 10(3). [CrossRef]
- Ghobakhloo, M., Iranmanesh, M., Tseng, M. L., Grybauskas, A., Stefanini, A., & Amran, A. (2023). Behind the definition of Industry 5.0: a systematic review of technologies, principles, components, and values. Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering, 40(6), 432–447. [CrossRef]
- Miranda,J.,Navarrete, C.,Noguez,J.,Molina-Espinosa, J.M.,Ramírez-Montoya,M.S., Navarro-Tuch,S.A., and Molina,A. 2021,The core components of education 4.0 in higher education: Three case studies in engineering education, Computers & Electrical Engineering, 93 (2021), Article 107278. [CrossRef]
- Lasi, H., Fettke, P., Kemper, H.G., Feld, T. and Hoffmann, M. (2014), “Industry 4.0”, Business and Information Systems Engineering, Vol. 6 No. 4, pp. 239-242. [CrossRef]
- Miranda,J., M.S. Ramírez-Montoya,M.S., E.O. López-Caudana,E.O., Y. Escalera-Matamoros,Y., Molina, A. 2022, Collaborative networks and sustainability in Education 4.0: An approach to achieve complex thinking competencies in higher education, September, Working conference on virtual enterprises, Springer International Publishing, Cham (2022), pp. 663-674. [CrossRef]
- Caratozzolo, P., Rosas-Melendez, S. and Ortiz-Alvarado, C., 2021, April. Active learning approaches for sustainable energy engineering education. In 2021 IEEE Green Technologies Conference (GreenTech) (pp. 251-258). IEEE.
- Ciolacu, M., Tehrani, A.F., Binder, L. and Svasta, P.M., 2018, October. Education 4.0-Artificial Intelligence assisted higher education: early recognition system with machine learning to support students' success. In 2018 IEEE 24th International Symposium for Design and Technology in Electronic Packaging(SIITME) (pp. 23-30). IEEE.
- Adel, A.; Ahsan, A.; Davison, C. ChatGPT Promises and Challenges in Education: Computational and Ethical Perspectives. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.F.; Rahmat, M.K.; Mubarik, M.S.; Alam, M.M.; Hyder, S.I. Artificial Intelligence and Its Role in Education. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichinger, P., Hofig, B. and Richter, C., 2017, September. Education 4.0 for mechatronics–agile and smart. In 2017 International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
- Ellahi, R.M., Ali Khan, M.U. and Shah, A. (2019), “Redesigning curriculum in line with industry 4.0”, Procedia Computer Science, Vol. 151, pp. 699-708. [CrossRef]
- Hussin, A.A., 2018. Education 4.0 made simple: Ideas for teaching. International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies, 6(3), pp.92-98.
- Hımmetoglu, B., Aydug, D. and Bayrak, C., 2020. Education 4.0: Defining the teacher, the student, and the school manager aspects of the revolution. Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education, 21(Special Issue-IODL), pp.12-28.
- Haderer, B. and Ciolacu, M., 2022. Education 4.0: Artificial intelligence assisted task-and time planning system. Procedia computer science, 200, pp.1328-1337.
- Sonntag, D., Albuquerque, G., Magnor, M. and Bodensiek, O. (2019), “Hybrid learning environments by data-driven augmented reality”, Procedia Manufacturing, Vol. 31, pp. 32-37. [CrossRef]
- Lye, C.Y.; Lim, L. Generative Artificial Intelligence in Tertiary Education: Assessment Redesign Principles and Considerations. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.D., Sobrino, Á.F., Soto, L.R., Romero, D., Biosca, P.F. and Martínez, L.R., 2019, September. Active learning based laboratory towards engineering education 4.0. In 2019 24th IEEE international conference on emerging technologies and factory automation (ETFA) (pp. 776-783). IEEE.
- Pandey, V.K. and Singh, V.K., 2022, April. Framework for Disruptive Technologies Based E-Learning System Architecture for Education 4.0. In Computer Science On-line Conference (pp. 1-12). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Chen, Yanhan & Wang, Hanxuan & Yu, Kaiwen & Zhou, Ruoshui. (2024). Artificial Intelligence Methods in Natural Language Processing: A Comprehensive Review. Highlights in Science, Engineering and Technology. 85. 545-550. [CrossRef]
- Zairon, I.Y., Wook, T.S.M.T., Salleh, S.M., Dahlan, H.A. and Rahmat, M., 2021, October. Analysis of Behaviour and Learning Style on Education 4.0 in Virtual Mentoring using Gamification. In 2021 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI) (pp. 1-6). IEEE.
- Bradáč, Vladimír & Kostolányová, Kateřina. (2016). Intelligent Tutoring Systems. Journal of Intelligent Systems. 26. [CrossRef]
- Akinwalere, Susan & Ivanov, Ventsislav. (2022). Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: Challenges and Opportunities. Border Crossing. 12. 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Sîrghi, Nicoleta; Voicu, Mirela-Catrinel; Noja, Gratiela Georgiana; Socoliuc, OanaRamona (2024) : Challenges of artificial intelligence on the learning process in higher education, Amfiteatru Economic, ISSN 2247-9104, The Bucharest University of Economic Studies, Bucharest, Vol. 26, Iss. 65, pp. 53-70. [CrossRef]
- E. Luiz, L., Pilarski, L., Baidi, K., Braun, J., Oliveira, A., Lima, J. and Costa, P., 2022, November. Robot at factory lite-a step-by-step educational approach to the robot assembly. In Iberian Robotics Conference (pp. 550-561). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Verner, I.M., Cuperman, D. and Reitman, M. (2021), “Exploring robot connectivity and collaborative sensing in a high-school enrichment program”, Robotics, Vol. 10 No. 1, pp. 1-19. [CrossRef]
- Karalekas, G.; Vologiannidis, S.; Kalomiros, J. Teaching Machine Learning in K–12 Using Robotics. Educ. Sci. 2023, 13, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braun, J., Júnior, A.O., Berger, G., Pinto, V.H., Soares, I.N., Pereira, A.I., Lima, J. and Costa, P., 2022. A robot localization proposal for the RobotAtFactory 4.0: A novel robotics competition within the Industry 4.0 concept. Frontiers in Robotics and AI, 9, p.1023590.
- Ferreira, T., Braun, J., Lima, J., Pinto, V.H., Santos, M. and Costa, P., 2022, November. Robot at factory 4.0: an auto-referee proposal based on artificial vision. In Iberian Robotics conference (pp. 475-487). Cham: Springer International Publishing.
- Schiavo, F.; Campitiello, L.; Todino, M.D.; Di Tore, P.A. Educational Robots, Emotion Recognition and ASD: New Horizon in Special Education. Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purdue University Article, 2024, The use of robotics and simulators in the education environment Available at :https://online.purdue.edu/blog/education/robotics-simulators-education-environment).
- Lima, J., Kalbermatter, R.B., Braun, J., Brito, T., Berger, G. and Costa, P., 2022, October. A realistic simulation environment as a teaching aid in educational robotics. In 2022 Latin American Robotics Symposium (LARS), 2022 Brazilian Symposium on Robotics (SBR), and 2022 Workshop on Robotics in Education (WRE) (pp. 430-435). IEEE.
- Makers' muse(2023), Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Robotics Education in Schools, Available at: https://medium.com/@makermuse3/overcoming-challenges-in-implementing-robotics-education-in-schools-de147ff7b685.
- Marcial, C.H et al, (2023), Challenges of Educational Robotics: A Perspective from the Teacher's Home, Social science Journal, RES MILITARIS, vol.13, No. 2, January Issue 2023, pp 3393-3399.
- Khanlari, Ahmad. (2015). Teachers’ perceptions of the benefits and the challenges of integrating educational robots into primary/elementary curricula. European Journal of Engineering Education. 41. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Vivas Fernandez, L., & Sáez López, J. M. (2019). Integration of educational robotics in Primary Education. Latin American Journal of Educational Technology, 18(1), 107– 128.
- Vergara, D.; Antón-Sancho, Á.; Extremera, J.; Fernández-Arias, P. Assessment of Virtual Reality as a Didactic Resource in Higher Education. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernández-Chávez, M., Cortés-Caballero, J.M., Pérez-Martínez, Á.A., Hernández-Quintanar, L.F., Roa-Tort, K., Rivera-Fernández, J.D. and Fabila-Bustos, D.A., 2021. Development of virtual reality automotive lab for training in engineering students. Sustainability, 13(17), p.9776.
- Adnan, A.H.M., Shak, M.S.Y., Karim, R.A., Tahir, M.H.M. and Shah, D.S.M. (2020), “360 Degree videos, VR experiences and the application of education 4.0 technologies in Malaysia for exposure and immersion”, Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal, Vol. 5 No. 1, pp. 373-381. [CrossRef]
- Hoole, R. and Jahankhani, H., 2021. Security Framework for Delivery of Training, Using VR Technology. Information Security Technologies for Controlling Pandemics, pp.357-386.
- Martin, J., Bohuslava, J. and Igor, H., 2018, September. Augmented reality in education 4.0. In 2018 ieee 13th international scientific and technical conference on computer sciences and information technologies (CSIT) (Vol. 1, pp. 231-236). IEEE.
- Caroline Graeske & Sofia Aspling Sjöberg , 2021, VR-Technology in Teaching: Opportunities and Challenges , International Education Studies; Vol. 14, No. 8; 2021 ISSN 1913-9020 E-ISSN 1913-9039 Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education.
- Nazari, Z.; Vahidi, A.R.; Musilek, P. Blockchain and Artificial Intelligence Non-Formal Education System (BANFES). Educ. Sci. 2024, 14, 881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atienza-Mendez,C. and Bayyou D.G. Blockchain technology applications in educationInternational Journal of Computing and Technology, 6 (11) (2019), pp. 68-74, ISSN (Online) : 2348-6090.
- Al-Zoubi, A., Dmour, M. and Aldmour, R., 2022. Blockchain as a learning management system for laboratories 4.0. iJOE, 18(12), p.17.
- Rahardja, U., Ngadi, M.A., Sutarman, A., Apriani, D. and Nabila, E.A., 2022, November. A mapping study research on block chain technology in education 4.0. In 2022 IEEE Creative Communication and Innovative Technology (ICCIT) (pp. 1-5). IEEE.
- Supriati, R., Lutfiani, N., Apriani, D. and Rizky, A., 2022, February. Utilizing the potential of blockchain technology for leading education 4.0. In 2022 International Conference on Science and Technology (ICOSTECH) (pp. 01-08). IEEE.
- Mohammad, A.; Vargas, S. Barriers Affecting Higher Education Institutions’ Adoption of Blockchain Technology: A Qualitative Study. Informatics 2022, 9, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raimundo R, Rosário A. Blockchain System in the Higher Education. Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2021 Mar 16;11(1):276-293. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dwivedi, S., & Vig, S. (2023). Blockchain adoption in higher-education institutions in India: Identifying the main challenges. Cogent Education, 11(1). [CrossRef]
- Ninda Lutfiani , Qurotul Aini , Untung Rahardja , Lidya Wijayanti , Efa Ayu Nabila , Mohammed Iftequar Ali 2021Transformation of blockchain and opportunities for education 4.0, International Journal of Education and Learning, Vol. 3, No. 3, December 2020, pp. 222-231. [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Loro, F., Plaza, P., Quintana, B., San Cristobal, E., Gil, R., Perez, C., Fernandez, M. and Castro, M., 2021, April. Laboratories 4.0: Laboratories for emerging demands under industry 4.0 paradigm. In 2021 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) (pp. 903-909). IEEE.
- Soni, K.M., Hasteer, N. and Bhardwaj, A., 2020, December. Aspects to foster competences for engineering graduates: Education 4.0 paradigm. In 2020 9th International Conference System Modeling and Advancement in Research Trends (SMART) (pp. 480-484). IEEE.
- Grodotzki, J., Ortelt, T.R. and Tekkaya, A.E. (2018), “Remote and virtual labs for engineering education 4.0: achievements of the ELLI project at the TU Dortmund university”, Procedia Manufacturing, Vol. 26, pp. 1349-1360. [CrossRef]
- Ciolacu, M.I., Haderer, B., Berl, A. and Svasta, P., 2021, October. Education 4.0: Innovation Learning Lab for AI-Analysis and Concept Proposal. In 2021 IEEE 27th International Symposium for Design and Technology in Electronic Packaging (SIITME) (pp. 45-50). IEEE.
- Cordero-Guridi, J.D.J., Cuautle-Gutiérrez, L., Alvarez-Tamayo, R.I. and Caballero-Morales, S.O., 2022. Design and development of a i4. 0 engineering education laboratory with virtual and digital technologies based on iso/iec tr 23842-1 standard guidelines. Applied Sciences, 12(12), p.5993.
- Miranda, J., López, C.S., Navarro, S., Bustamante, M.R., Molina, J.M. and Molina, A., 2019, June. Open innovation laboratories as enabling resources to reach the vision of education 4.0. In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation (ICE/ITMC) (pp. 1-7). IEEE.
- Deriba FG, Saqr M and Tukiainen M (2024) Assessment of accessibility in virtual laboratories: a systematic review. Front. Educ. 9:1351711. [CrossRef]
- Alnagrat, A. J. A., Ismail, R. C., and Idrus, S. Z. S. (2021). Extended reality (XR) in virtual laboratories: a review of challenges and future training directions. J. Phys. Conf. Ser. 1874:12031. [CrossRef]
- Misiejuk, K., Khalil, M., and Wasson, B. (2023) Tackling the challenges with data access in learning analytics research: a case study of virtual labs, Proceedings of the Technology-Enhanced Learning in Laboratories workshop (TELL 2023), April 27, 2023, Online.
- Aldowah, H., Rehman, S.U., Ghazal,S and Umar, I.N., 2017 Internet of Things in Higher Education: A Study on Future LearningJournal of Physics: Conference Series, Volume 892, The 6th International Conference on Computer Science and Computational Mathematics (ICCSCM 2017) 4–5 May 2017, Langkawi, MalaysiaCitation Hanan Aldowah et al 2017 J. Phys.: Conf. Ser. 892 012017.
- Ciolacu, M.I., Binder, L. and Popp, H., 2019, October. Enabling IoT in Education 4.0 with biosensors from wearables and artificial intelligence. In 2019 IEEE 25th international symposium for design and technology in electronic packaging (SIITME) (pp. 17-24). IEEE.
- Som, S. and Rana, A., 2020, June. IoT Based Educational Model for Better Teaching-Learning Environment. In 2020 8th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions)(ICRITO) (pp. 824-828). IEEE.
- Ramlowat, Dosheela & Pattanayak, Binod. (2019). Exploring the Internet of Things (IoT) in Education: A Review: Proceedings of Fifth International Conference INDIA 2018 Volume 2. [CrossRef]
- Souza, A. S. C. de, & Debs, L. (2024). Concepts, innovative technologies, learning approaches and trend topics in education 4.0: A scoping literature review. Social Sciences & Humanities Open, 9, 100902. [CrossRef]
- Nur Fitria, Tira & Simbolon, Nurmala & Afdaleni,. (2023). Internet of Things (IoT) in Education: Opportunities and Challenges. Conference: Teknologi Informasi Sebagai Sebuah Peluang atau Ancaman Bagi Dunia Usaha di Indonesia at Institut Teknologi Bisnis AAS Indonesia, December 2023.
- Saudamini Mowade, 2024, Internet of Things (IOT) in Education Sector: Challenges and Opportunity, International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Research (IJSER) ISSN (Online): 2347-3878.
- Rojas, Carolina & Alomía, Gustavo & Loaiza, Diego & Romero, Carlos. (2021). Society 5.0: A Japanese Concept for a Superintelligent Society. Sustainability. 13. 6567. [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, K.K.D.S. and De Souza, R.A., 2022. Digital transformation towards education 4.0. Informatics in Education, 21(2), pp.283-309.
- Swartz, B., 2021. Ethics in engineering education 4.0: The educator’s perspective. SAIEE Africa Research Journal, 112(4), pp.181-188.

| No | Author | Year | Title | Journal/Conference | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Alex Sander Clemente de Souza, Luciana Debs, , [6] | 2024 | Concepts, innovative technologies, learning approaches and trend topics in education 4.0: A scoping literature review | Social Sciences & Humanities Open |
Education 4.0 - Review paper |
| 2. | Butt, R., Siddiqui, H., Soomro, R.A. and Asad, M.M. [34] | 2020 | Integration of industrial revolution 4.0 and IOTs in academia: a state-of-the-art review on the concept of education 4.0 in Pakistan [review]”, | Interactive Technology and Smart Education | Education 4.0 - Review paper |
| 3. | González-Pérez, L.I. and Ramírez-Montoya, M.S.[35] | 2022 | Components of Education 4.0 in 21st century skills frameworks: systematic review. | Sustainability , MDPI | Education 4.0 - Review paper |
| 4. | Hariharasudan, A. and Kot, S., 2018[36] | 2018 | A scoping review on Digital English and Education 4.0 for Industry 4.0 | Social sciences , MDPI | Digital English and Education 4.0 - Review paper |
| 5. | Huk, T. [37] | 2021 | From education 1.0 to education 4.0 – challenges for the contemporary school | The New Educational Review | Education 1.0 to Education 4.0 – review and analysis |
| 6. | Krstikj, A., Sosa Godina, J., García Bañuelos, L., González Peña, O.I., Quintero Milián, H.N., Urbina Coronado, P.D. and Vanoye García, A.Y. [38] | 2022 | Analysis of competency assessment of educational innovation in upper secondary school and higher education: a mapping review |
Sustainability
, MDPI |
Competency assessment – mapping review |
| 7. | Lai, J.W.M. and Bower, M. [39] | 2020 | Evaluation of technology use in education: findings from a critical analysis of systematic literature reviews | Journal of Computer Assisted Learning |
Use of technology in education- Review and analysis - Review paper |
| 8. | Liu, C., Zowghi, D., Kearney, M. and Bano, M. [40] | 2021 | Inquiry-based mobile learning in secondary school science education: a systematic review | Journal of Computer Assisted Learning |
Mobile learning –Review paper |
| 9. | Müller F, Denk A, Lubaway E, Sälzer C, Kozina A, Perše TV, et al. [41] |
2020 | Assessing social, emotional, and intercultural competences of students and school staff:A systematic literature review. | Educational Research Review, Elsevier | Competency analysis of students - Review paper |
| 10. | Parmaxi, A. and Demetriou, A.A. [42] | 2020 | Augmented reality in language learning: a state-of-the-art review of 2014–2019” | Journal of Computer Assisted Learning |
Augmented reality in learning - Review paper |
| 11. | Qureshi, M.I., Khan, N., Raza, H., Imran, A. and Ismail, F.[43] | 2021 | Digital technologies in education 4.0. Does it enhance the effectiveness of learning? A systematic literature review | International Journal of Interactive Mobile Technologies |
Digital technologies in Education 4.0 - Review paper |
| 12. | Ramírez-Montoya, M.S., Castillo-Martínez, I.M., Sanabria-Z, J. and Miranda, J. [32] | 2022 | Complex thinking in the framework of Education 4.0 and Open Innovation—A systematic literature review | Journal of Open Innovation: Technology |
Framework of Education 4.0- Review paper |
| 13. | Silva, D.E., Lopes, T., Sobrinho, M.C. and Valentim, N.M.C., 2021. [33] | Investigating initiatives to promote the advancement of education 4.0: A systematic mapping study. | 13th International Conference on Computer Supported Education (CSEDU 2021) | Advancement of education 4.0 – Review and mapping study | |
| 14. | Verma, A. and Singh, A. [31] | 2021 | New era of technology empowered education: education 4.0 a systematic review. |
9th International Conference on Reliability, Infocom Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO) |
Education 4.0 - Review paper |
| 15. | Costan,E.;Gonzales, G.; Gonzales, R.;Enriquez,L.;Costan, F.; Suladay, D.; Atibing,N.M.;Aro,J.L.;Evangelista,S.S.; Maturan, F.; et al [44] |
2021 | Education 4.0 in Developing Economies: A Systematic Literature Review of Implementation Barriers and Future Research Agenda. | Sustainability , MDPI | Education 4.0 in economy development - Review paper |
| 16. | Arnold, M.G.; Vogel, A.; Ulber, M. [45] | 2021 | Digitalizing Higher Educatio n in Light of Sustainability and Rebound Effects—Surveys in Times of the COVID-19 Pandemic. | Sustainability ,MDPI | Digitizing Higher Education |
| 17. | Chiu, W.-K. [46] | 2021 | Pedagogy of Emerging Technologies in Chemical Education during the Era of Digitalization and Artificial Intelligence: A Systematic Review. | Education sciences, MDPI | AI in education - Review paper |
| 18. | Tselegkaridis , S.; Sapounidis, T. [47] |
2021 | Simulators in Educational Robotics: A Review. Educ. Sci. | Education science,MDPI | Education robots – Review paper |
| 19. | López-Chila, R.; Llerena-Izquierdo, J.; Sumba-Nacipucha, N.; Cueva-Estrada, J. [48] | 2024 | Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: An Analysis of Existing Bibliometrics. | Education Science, MDPI | AI in higher education – Review paper |
| 20. | Thurzo, A.; Strunga, M.; Urban, R.; Surovková, J.; Afrashtehfar, K.I. [48] | 2023 | Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Dental Education: A Review and Guide for Curriculum Update. | Education Science , MDPI | AI in dental education – Review paper |
| 21. | Mukul,E Büyüközkan,G, [5] |
2023 |
Digital transformation in education: A systematic review of education 4.0, |
Technological Forecasting and Social Change, Elsevier |
Education 4.0 – Review Paper |
| 22. | Laura Icela, G. P., María Soledad, R. M., & Juan Antonio, E. G. [50] |
2023 | Education 4.0 Maturity Models for Society 5.0: Systematic literature review. | Cogent Business & Management | Education 4.0 and Society 5.0 – Review Paper |
| 23. | Ghobakhloo, M., Iranmanesh, M., Tseng, M. L., Grybauskas, A., Stefanini, A., & Amran, A. [51] | 2023 | Behind the definition of Industry 5.0: a systematic review of technologies, principles, components, and values. |
Journal of Industrial and Production Engineering |
Industry 5.0 – Review paper |
| No | Author | Year | Title | Journal/Conference | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
1 |
Caratozzolo, P. and Membrillo-Hernández, J., [12] | 2021 | Challenge based learning approaches for education 4.0 in engineering |
In Proceedings of the 2021 SEFI Conference |
Education 4.0 in engineering |
| 2 | Ciolacu, M., Tehrani, A.F., Binder, L. and Svasta, P.M., [58] | 2018 | Education 4.0-Artificial Intelligence assisted higher education: early recognition system with machine learning to support students' success. | In 2018 IEEE 24th International Symposium for Design and Technology in Electronic Packaging(SIITME) | AI in higher education |
| 3 | Eichinger, P., Hofig, B. and Richter, C [59] | 2017 |
Education 4.0 for mechatronics–agile and smart. |
In 2017 International Conference on Research and Education in Mechatronics (REM) | Education 4.0 for Mechatronics |
| 4. | Adel, A.; Ahsan, A.; Davison, C. [57] | 2024 | ChatGPT Promises and Challenges in Education: Computational and Ethical Perspectives. | Education Sciences,MDPI | Challenges of Chatgpt in Education |
| 5. | Ahmad, S.F. et al.,[58] | 2021 | Artificial Intelligence and Its Role in Education |
Sustainability,MDPI |
AI in education |
| 6. | Parmaxi and Demetriou [42] | 2020 | Augmented reality in language learning: a state-of-the-art review of 2014–2019 | Journal of Computer Assisted Learning | AR in education – Review |
| 7. | Ellahi, R.M., Ali Khan, M.U. and Shah, A. [60] |
201`9 | “Redesigning curriculum in line with industry 4.0”, | Procedia Computer Science, | Change of curriculum using Industry 4.0 techniques |
| 8. | Hussin, A.A., [61] | 2018 | Education 4.0 made simple: Ideas for teaching. |
International Journal of Education and Literacy Studies |
Education 4.0 implementation |
| 9. | Hımmetoglu, B., Aydug, D. and Bayrak, C., [62] |
2020 | Education 4.0: Defining the teacher, the student, and the school manager aspects of the revolution. | Turkish Online Journal of Distance Education. | Education 4.0 for schools |
| 10. | Haderer, B. and Ciolacu, M., [63] | 2022 | Education 4.0: Artificial intelligence assisted task-and time planning system. | Procedia computer science. | AI based Education 4.0 |
| 11. | Sonntag, D et al.,[64] | 2019 | Hybrid learning environments by data-driven augmented reality | Procedia Manufacturing | AR in education |
| 12. | Lye, C.Y. and Lim, L. [65] | 2024 | Generative Artificial Intelligence in Tertiary Education: Assessment Redesign Principles and Considerations | Education Sciences | AI in education |
| 13. | Zairon, I.Y., Wook, T.S.M.T., Salleh, S.M., Dahlan, H.A. and Rahmat, M., [69] |
2021 | Analysis of Behaviour and Learning Style on Education 4.0 in Virtual Mentoring using Gamification. | In 2021 International Conference on Electrical Engineering and Informatics (ICEEI) | Analysis of Education 4.0 |
| 14. | Akinwalere, Susan & Ivanov, Ventsislav. [71] |
2022 | Artificial Intelligence in Higher Education: Challenges and Opportunities. | Border Crossing. | Challenges of AI in education |
| 15 | Sîrghi, Nicoleta; Voicu, Mirela-Catrinel; Noja, Gratiela Georgiana; Socoliuc, OanaRamona [72] | 2024 |
Challenges of artificial intelligence on the learning process in higher education, |
Amfiteatru Economic, The Bucharest University of Economic Studies, Bucharest. | Challenges of AI in education |
| No | Author | Year | Title | Journal/Conference | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | E.Luiz,L., et al [73] | 2022 | Robot at factory lite-a step-by-step educational approach to the robot assembly | In Iberian Robotics Conference | Robotics in education |
| 2 | Karalekas, G. et al [75] | 2023 | Teaching Machine Learning in K–12 Using Robotics | Education Sciences,MDPI | Robotics in education |
| 3 | Braun,J et al. [76] | 2022 | A robot localization proposal for the RobotAtFactory 4.0: A novel robotics competition within the Industry 4.0 concept | Frontiers in Robotics and AI | Robotics and Industry 4.0 |
| 4 | Ferreira ,T et al [77] | 2022 | Robot at factory 4.0: an auto-referee proposal based on artificial vision | In Iberian Robotics conference | Robotics and Industry 4.0 |
| 5 | Schiavo, F et al [78] | 2024 | Educational Robots, Emotion Recognition and ASD: New Horizon in Special Education | Education Sciences | Robotics in education |
| 6 | Purdue University Article [79] | 2024 |
The Use of Robotics and Simulators in the Education Environment |
https://online.purdue.edu/blog/education/robotics-simulators-education-environment)[79] |
Robotics in the education environment |
| 7 | Lima, J., Kalbermatter, R.B., Braun, J., Brito, T., Berger, G. and Costa, P., [80] |
2022, | A realistic simulation environment as a teaching aid in educational robotics. | In 2022 Latin American Robotics Symposium (LARS), 2022 Brazilian Symposium on Robotics (SBR), and 2022 Workshop on Robotics in Education (WRE) | Teaching using Education robot |
|
8 |
Makers' muse [81] | 2023 | Overcoming Challenges in Implementing Robotics Education in Schools |
https://medium.com/@makermuse3/overcoming-challenges-in-implementing-robotics-education-in-schools-de147ff7b685 |
Challenges in implementing robots in education |
| 9 | Marcial, C.H et al, (2023), [82] | 2023 |
Challenges of Educational Robotics: A Perspective from the Teacher's Home, |
Social science Journal, RES MILITARIS. | Challenges in implementing robots in education |
| 10 | Khanlari, Ahmad. [83] | 2015 |
Teachers’ perceptions of the benefits and the challenges of integrating educational robots into primary/elementary curricula. |
European Journal of Engineering Education. | Challenges in implementing robots in education |
| 11 | Vivas Fernandez, L., & Sáez López, J. M. [84] |
2019 | Integration of educational robotics in Primary Education. Latin American Journal of | Educational Technology | Challenges in implementing robots in education |
| No | Author | Year | Title | Journal/Conference | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Vergara, D et al [85] | 2021 | Assessment of Virtual Reality as a Didactic Resource in Higher Education. | Sustainability,MDPI | VR in education |
| 2. | Hermandez-chavez et al. [86] | 2021 | Development of Virtual Reality Automotive Lab for , Training in Engineering Students. | Sustainability, MDPI | VR in education |
| 3. | Adnan, A.H.M et al [87] | 2020 | 360 Degree videos, VR experiences and the application of education 4.0 technologies in Malaysia for exposure and immersion | Advances in Science, Technology and Engineering Systems Journal | VR in education |
| 4. | Hoole, R and Jahankhani, H [88] | 2021 | Security Framework for Delivery of Training, Using VR Technology | Information Security Technologies for Controlling Pandemics (Book chapter) | VR for Information Security |
| 5. | Martin,J., Bohuslava,J and Igor,H [89] | 2018 | Augmented reality in education 4.0 | 13th international scientific and technical conference on computer sciences and information technologies | AR in education |
| 6. | Caroline Graeske & Sofia Aspling Sjöberg , [90] | 2021 | VR-Technology in Teaching: Opportunities and Challenges , | International Education Studies;Published by Canadian Center of Science and Education | Challenges in implementation of VR in education |
| No | Author | Year | Title | Journal/Conference | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Nazari, Z.; Vahidi, A.R. and Musilek, P [91] | 2024 | Artificial Intelligence Non-Formal Education System | Education Sciences | Blockchain and AI in education |
| 2. | Atienza-Mendez and Bayyou [92] | 2019 | Blockchain technology applications in education | International Journal of Computing and Technology | Blockchain in education |
| 3. | Al – Zoubi, Dmour and Aldmour Al-Zoubi, A. Y., Dmour, M. ., & Aldmour, R. .[93] | 2022 | Blockchain as a Learning Management System for Laboratories 4.0. | International Journal of Online and Biomedical Engineering | Blockchain in education |
| 4. | Rahardja,U et al [94] | 2022 | A mapping study research on block chain technology in education 4.0. | IEEE Creative Communication and Innovative Technology | Blockchain in education |
| 5. | Supriati et al [95] | 2022 | Utilizing the potential of blockchain technology for leading education 4.0. | International Conference on Science and Technology | Blockchain in education |
| 6. | Mohammad, A.; Vargas, S. [96] |
2022 | Barriers Affecting Higher Education Institutions’ Adoption of Blockchain Technology: A Qualitative Study. | Informatics 2022, 9, 64. https://doi.org/10.3390/informatics9030064 | Challenges in applying block chain in learning and teaching |
| 7. | Raimundo R, Rosário A. [97] |
2021 | Blockchain System in the Higher Education. | Eur J Investig Health Psychol Educ. 2021 Mar 16;11(1):276-293. doi: 10.3390/ejihpe11010021. PMID: 34542464; PMCID: PMC8314340. | Challenges in applying block chain in learning and teaching |
| 8. | Dwivedi, S., & Vig, S.. [98] |
2023 | Blockchain adoption in higher-education institutions in India: Identifying the main challenges. | Cogent Education, 11(1). https://doi.org/10.1080/2331186X.2023.2292887 | Challenges in applying block chain in learning and teaching |
| 9. | Ninda Lutfiani , Qurotul Aini , Untung Rahardja , Lidya Wijayanti , Efa Ayu Nabila , Mohammed Iftequar Ali [99] | 2021 | Transformation of block chain and opportunities for education 4.0, |
International Journal of Education and Learning, Vol. 3, No. 3, December 2020, pp. 222-231, DOI:10.31763/ijele.v3i3.283 | Challenges in applying block chain in learning and teaching |
| No | Author | Year | Title | Journal/Conference | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Garcia-Loro, F., Plaza, P., Quintana, B., San Cristobal, E., Gil, R., Perez, C., Fernandez, M. and Castro, M.,[100] | 2021, | Laboratories 4.0: Laboratories for emerging demands under industry 4.0 paradigm | 2021 IEEE Global Engineering Education Conference (EDUCON) | Digital Laboratories 4.0; |
| 2. | Soni, K.M., Hasteer, N. and Bhardwaj, A., [101] | 2020 | Aspects to foster competences for engineering graduates: Education 4.0 paradigm. | In 2020 9th International Conference System Modeling and Advancement in Research Trends (SMART) | Competencies requirement in the implementation of Digital Laboratories 4.0; |
| 3. | Grodotzki, J., Ortelt, T.R. and Tekkaya, A.E. [102] | 2018 | Remote and virtual labs for engineering education 4.0: achievements of the ELLI project at the TU Dortmund university”, | Procedia Manufacturing, | Remote and virtual labs – a case study |
| 4. | Ciolacu, M.I., Binder, L. and Popp, H., , [103] | 2019 | Enabling IoT in Education 4.0 with biosensors from wearables and artificial intelligence. | In 2019 IEEE 25th international symposium for design and technology in electronic packaging (SIITME) | IoT and AI based laboratories. |
| 5. | Cordero-Guridi, J.D.J., Cuautle-Gutiérrez, L., Alvarez-Tamayo, R.I. and Caballero-Morales, S.O.,. [104] | 2022. | Design and development of a i4. 0 engineering education laboratory with virtual and digital technologies based on iso/iec tr 23842-1 standard guidelines. | Applied Sciences | Engineering Education Laboratory – Design and development |
| 6. | Miranda, J., López, C.S., Navarro, S., Bustamante, M.R., Molina, J.M. and Molina, A., , [105] | 2019 | Open innovation laboratories as enabling resources to reach the vision of education 4.0. | In 2019 IEEE International Conference on Engineering, Technology and Innovation | Digital Laboratories in education 4.0; |
| 7. | Prieto, M.D., Sobrino, Á.F., Soto, L.R., Romero, D., Biosca, P.F. and Martínez, L.R., [66] | 2019, | Active learning based laboratory towards engineering education 4.0. | In 2019 24th IEEE international conference on emerging technologies and factory automation (ETFA) | Digital Laboratories 4.0; |
| 8. | Deriba FG, Saqr M and Tukiainen M (2024) [106] | 2024 | Assessment of accessibility in virtual laboratories: a systematic review. | Front. Educ. 9:1351711. | Virtual laboratories- Review |
| 9. | Alnagrat, A. J. A., Ismail, R. C., and Idrus, S. Z. S.[107] | 2021 | Extended reality (XR) in virtual laboratories: a review of challenges and future training directions. | J. Phys. Conf. Ser. |
Virtual laboratories- Review |
| 10. | Misiejuk, K., Khalil, M., and Wasson, B. [108] | (2023): | Tackling the challenges with data access in learning analytics research: a case study of virtual labs | Proceedings of the Technology-Enhanced Learning in Laboratories workshop (TELL 2023). | Challenges in implementation of Virtual laboratories- case study |
| No | Author | Year | Title | Journal/Conference | Theme |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. | Aldowah, H., Rehman, S.U., Ghazal,S and Umar, I.N., [109] |
2017 | Internet of Things in Higher Education: A Study on Future Learning | Journal of Physics, Conference Series, The 6th International Conference on Computer Science and Computational Mathematics (ICCSCM 2017) |
IoT in higher education |
| 2. | Ciolacu, M.I., Binder, L. and Popp, H.,[110] |
2019 | Enabling IoT in Education 4.0 with biosensors from wearables and artificial intelligence. | In 2019 IEEE 25th international symposium for design and technology in electronic packaging (SIITME) | IoT in higher education |
| 3. | Som, S. and Rana, A., [11] |
2020 | IoT Based Educational Model for Better Teaching-Learning Environment. | In 2020 8th International Conference on Reliability, Info com Technologies and Optimization (Trends and Future Directions) (ICRITO). |
IoT based education model |
| 4. | Ramlowat, Dosheela & Pattanayak, Binod.[112] | 2019 | Exploring the Internet of Things (IoT) in Education: A Review: | Proceedings of Fifth International Conference INDIA 2018 . | IoT in higher education – review paper |
| 5. | Souza, A. S. C. de, & Debs, L.[113] | 2024 | Concepts, innovative technologies, learning approaches and trend topics in education 4.0: A scoping literature review | Social Sciences & Humanities Open |
IoT and AI in higher education – review paper |
| 6. | Nur Fitria, Tira & Simbolon, Nurmala & Afdaleni,.[114] | 2023 | Internet of Things (IoT) in Education: Opportunities and Challenges. | Conference: Teknologi Informasi Sebagai Sebuah Peluang atau Ancaman Bagi Dunia Usaha di Indonesia at Institut Teknologi Bisnis AAS Indonesia, December 2023 | Challenges in implementing IoT in HEIs |
| 7. | Saudamini Mowade, [115] | 2024 | Internet of Things (IOT) in Education Sector: Challenges and Opportunity, | International Journal of Scientific Engineering and Research (IJSER) |
Challenges and opportunities in implementing IoT in HEIs |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





