Submitted:
27 August 2024
Posted:
29 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Target Selection and Epitope Screening
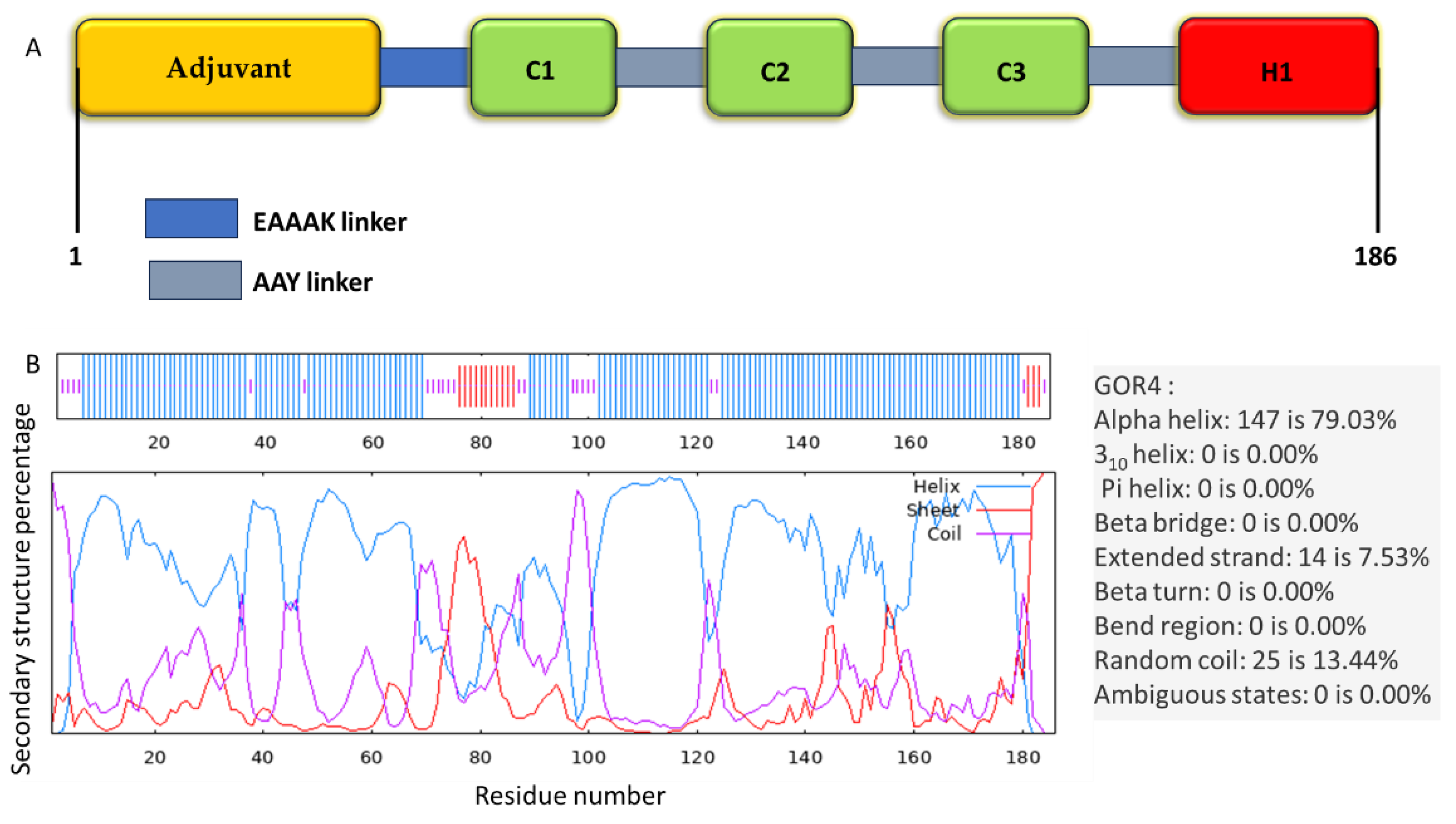
2.2. Assembly of the Multi-Epitope Vaccine
2.3. Assessment of the Vaccine's Antigenicity, Allergenicity, and Physicochemical Characteristics
2.4. Secondary Structure Prediction
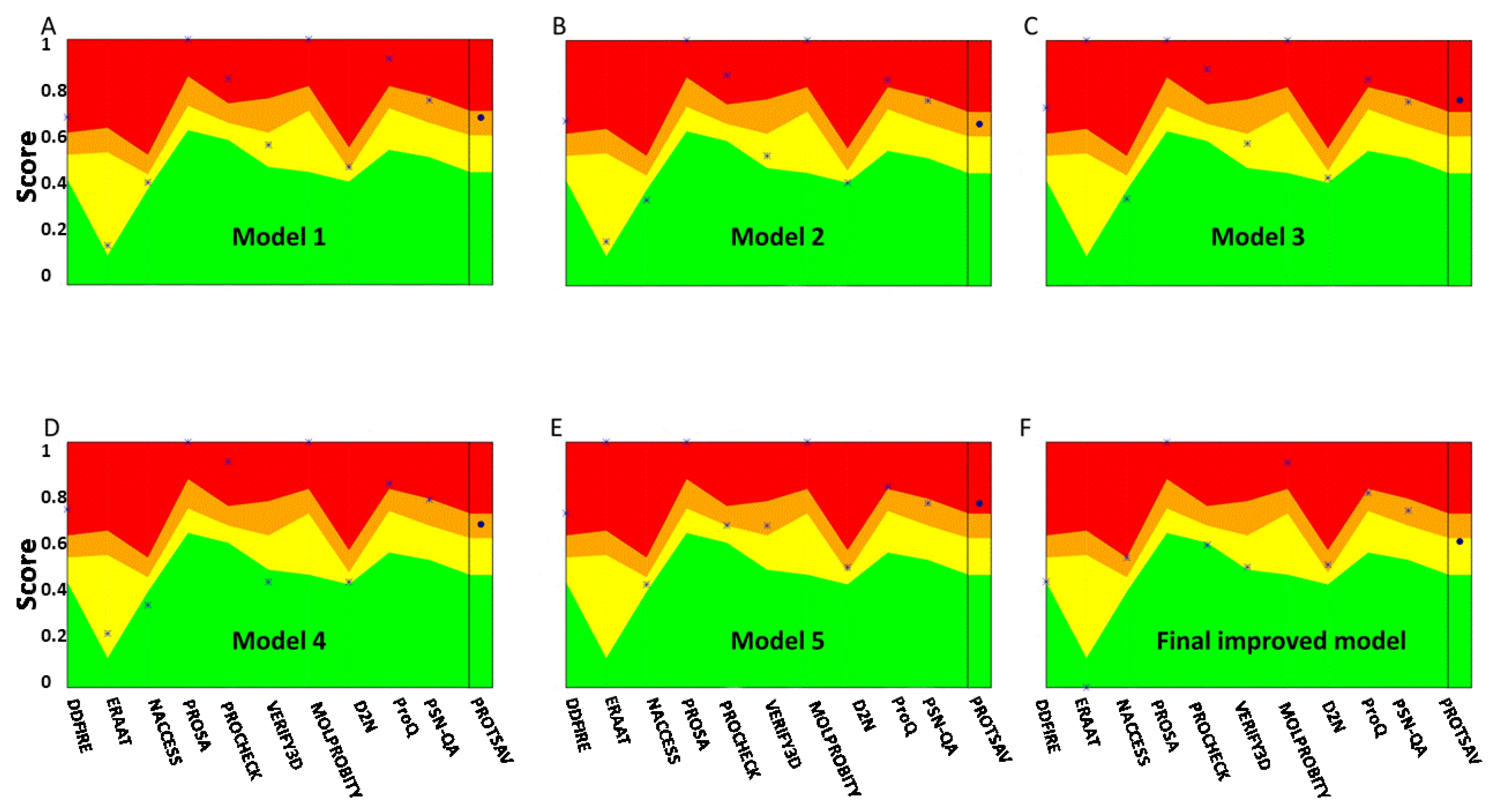
2.5.3. D Structure Modeling, Refinement, and Verification of the Multi-Epitope Vaccine
2.6. B-cell Epitopes Prediction
2.7. Molecular Docking and MD Simulations
2.8. Analysis of the Immune Profile for the Multi-Epitope Vaccine Construct
3. Results
3.1. Target Selection and Preliminary Analysis
3.2. Constructing the Vaccine
3.3. Antigenicity, Allergenicity, and Physico-Chemical Properties Assessment
3.4. Secondary Structure Prediction, Tertiary Structure Modeling, Refinement, and Validation
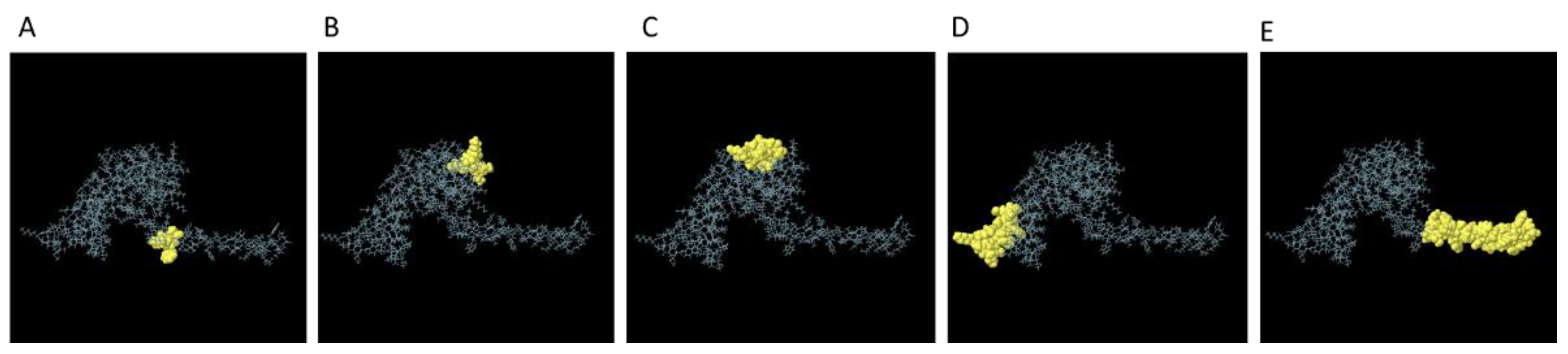
3.5. Prediction of the B-Cell Epitope
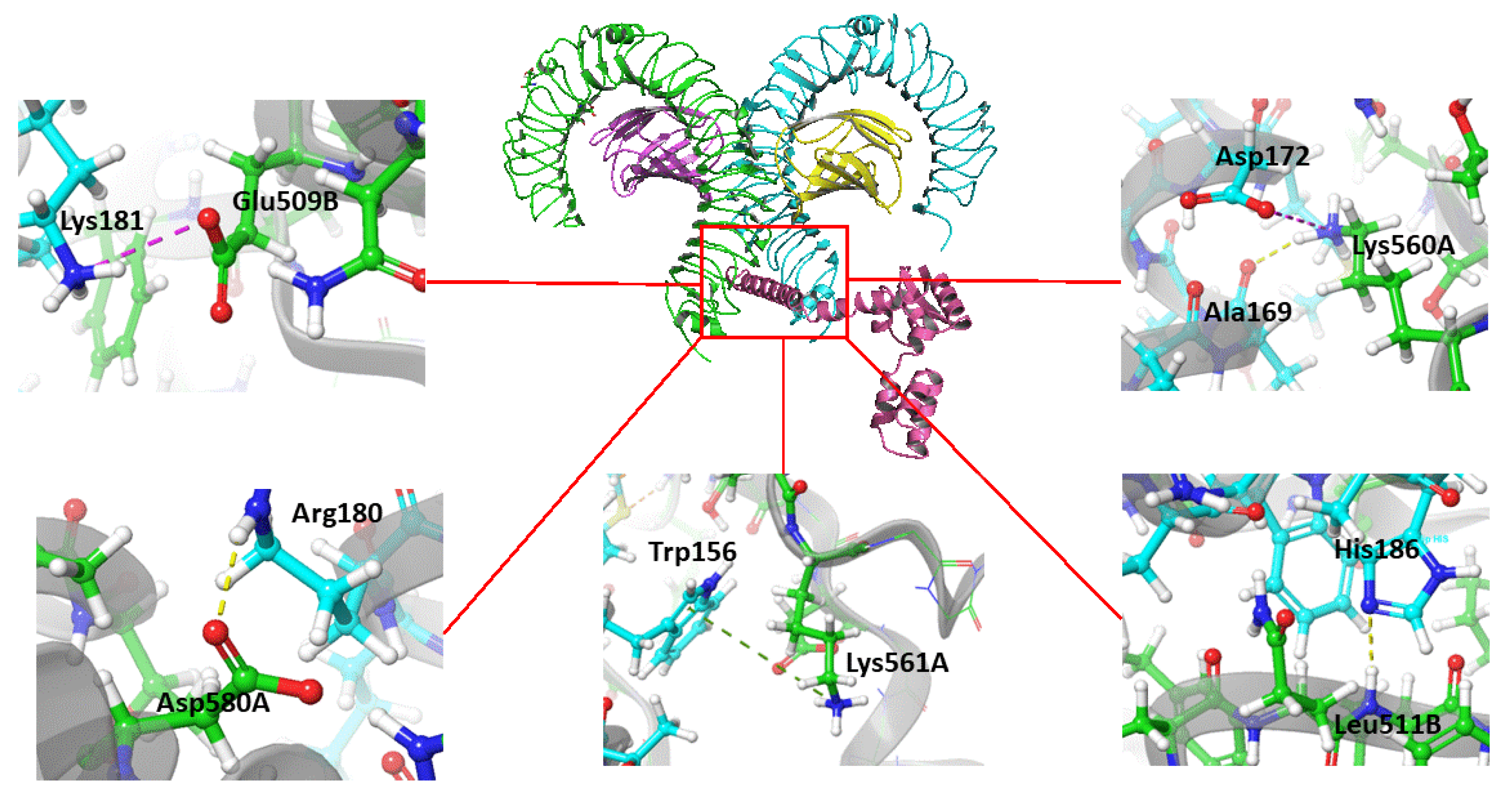
3.6. Predicted Interaction of the Vaccine Construct with TLR4
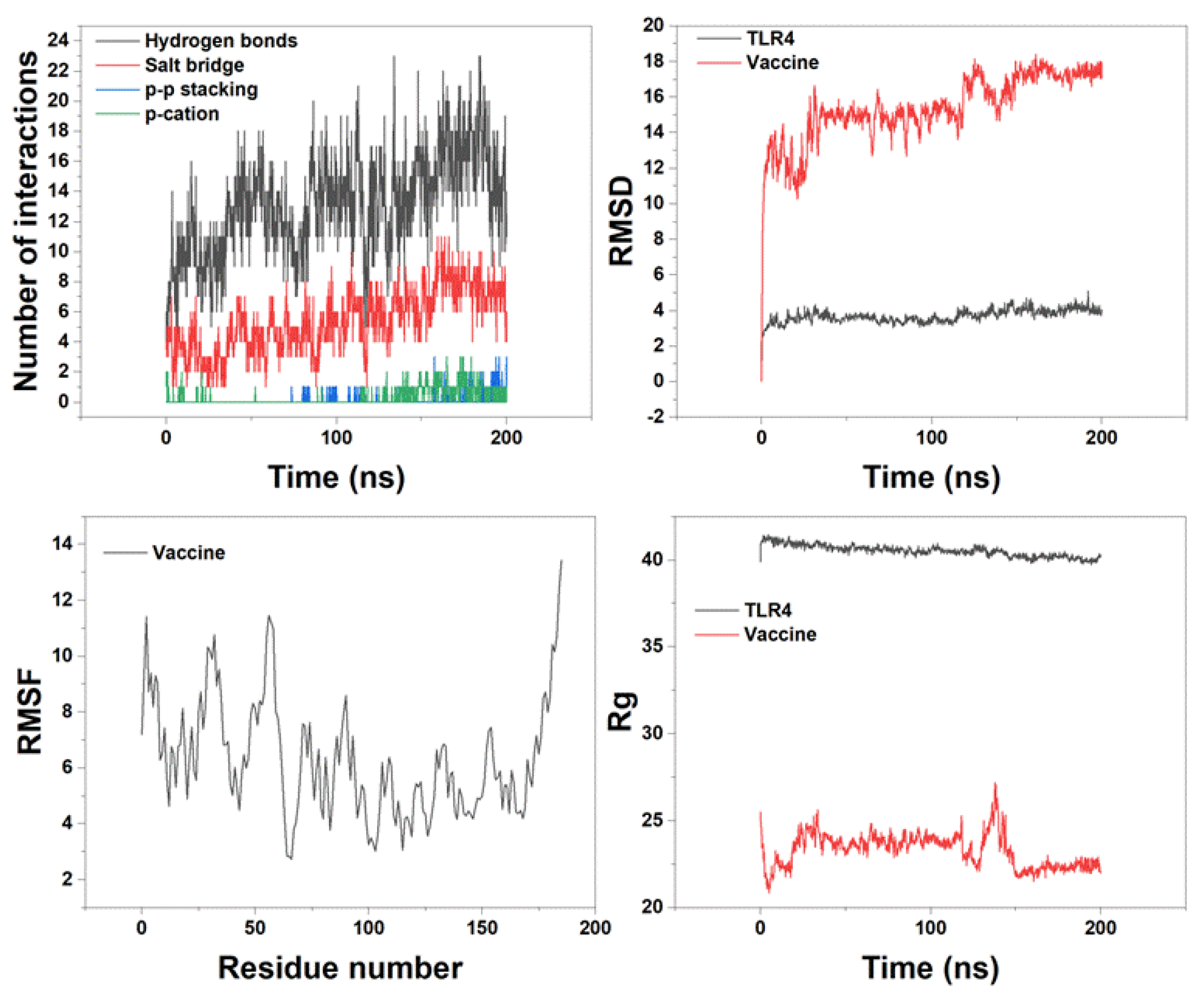
3.7. MD Simulation of Vaccine Construct with TLR4
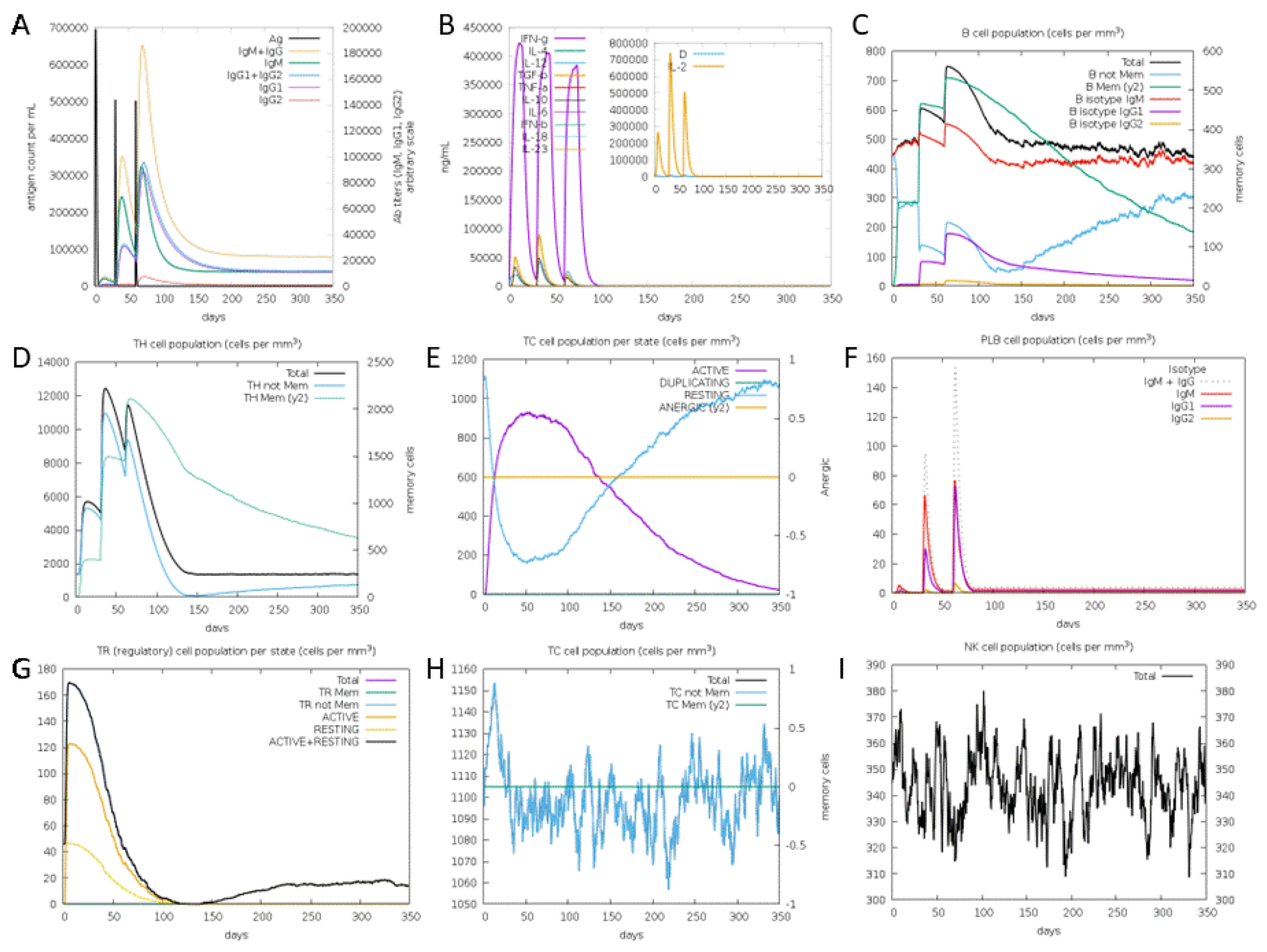
3.8. Immune Simulation
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Reifenberger, G.; Von Deimling, A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Kleihues, P.; Ellison, D.W. The 2016 World Health Organization classification of tumors of the central nervous system: a summary. Acta neuropathologica 2016, 131, 803-820. [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Gittleman, H.; Patil, N.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and other central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2012–2016. Neuro-oncology 2019, 21, v1-v100. [CrossRef]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Gittleman, H.; Fulop, J.; Liu, M.; Blanda, R.; Kromer, C.; Wolinsky, Y.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS statistical report: primary brain and central nervous system tumors diagnosed in the United States in 2008-2012. Neuro-oncology 2015, 17, iv1-iv62. [CrossRef]
- Alexander, B.M.; Cloughesy, T.F. Adult glioblastoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017, 35, 2402-2409. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D.; Weinberg, R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. cell 2011, 144, 646-674.
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; Van Den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. The lancet oncology 2009, 10, 459-466. [CrossRef]
- Frosina, G. Limited advances in therapy of glioblastoma trigger re-consideration of research policy. Critical reviews in oncology/hematology 2015, 96, 257-261. [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-X.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Liu, J.-L.; Li, D.; Li, J.-L.; Liu, Y.-S.; Wang, M.; Xu, B.-L.; Wang, H.-B.; Wang, Z.-X. Clinical efficacy of tumor antigen-pulsed DC treatment for high-grade glioma patients: evidence from a meta-analysis. PloS one 2014, 9, e107173. [CrossRef]
- Maxwell, R.; Jackson, C.M.; Lim, M. Clinical trials investigating immune checkpoint blockade in glioblastoma. Current treatment options in oncology 2017, 18, 1-22. [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M.K.; Kunita, A.; Abe, S.; Tsujimoto, Y.; Fukayama, M.; Goto, K.; Sawa, Y.; Nishioka, Y.; Kato, Y. Chimeric anti-podoplanin antibody suppresses tumor metastasis through neutralization and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity. Cancer science 2012, 103, 1913-1919. [CrossRef]
- Kumai, T.; Fan, A.; Harabuchi, Y.; Celis, E. Cancer immunotherapy: moving forward with peptide T cell vaccines. Current opinion in immunology 2017, 47, 57-63. [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Kalinski, P.; Ueda, R.; Hoji, A.; Kohanbash, G.; Donegan, T.E.; Mintz, A.H.; Engh, J.A.; Bartlett, D.L.; Brown, C.K. Induction of CD8+ T-cell responses against novel glioma–associated antigen peptides and clinical activity by vaccinations with α-type 1 polarized dendritic cells and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid stabilized by lysine and carboxymethylcellulose in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Journal of clinical oncology 2011, 29, 330.
- Saleh, M.; Davis, I.D.; Wilks, A.F. The paracrine role of tumour-derived mIL-4 on tumour-associated endothelium. International journal of cancer 1997, 72, 664-672. [CrossRef]
- Gadani, S.P.; Cronk, J.C.; Norris, G.T.; Kipnis, J. IL-4 in the brain: a cytokine to remember. The journal of immunology 2012, 189, 4213-4219. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carlsson, A.; Persson, O.; Ingvarsson, J.; Widegren, B.; Salford, L.; Borrebaeck, C.A.; Wingren, C. Plasma proteome profiling reveals biomarker patterns associated with prognosis and therapy selection in glioblastoma multiforme patients. PROTEOMICS–Clinical Applications 2010, 4, 591-602. [CrossRef]
- Ferrandez, E.; Gutierrez, O.; Segundo, D.S.; Fernandez-Luna, J.L. NFκB activation in differentiating glioblastoma stem-like cells is promoted by hyaluronic acid signaling through TLR4. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 6341. [CrossRef]
- Brennan, C.W.; Verhaak, R.G.; McKenna, A.; Campos, B.; Noushmehr, H.; Salama, S.R.; Zheng, S.; Chakravarty, D.; Sanborn, J.Z.; Berman, S.H. The somatic genomic landscape of glioblastoma. Cell 2013, 155, 462-477. [CrossRef]
- Schumacher, T.; Bunse, L.; Pusch, S.; Sahm, F.; Wiestler, B.; Quandt, J.; Menn, O.; Osswald, M.; Oezen, I.; Ott, M. A vaccine targeting mutant IDH1 induces antitumour immunity. Nature 2014, 512, 324-327. [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Butowski, N.; Tran, D.; Recht, L.; Lim, M.; Hirte, H.; Ashby, L.; Mechtler, L.; Goldlust, S.; Iwamoto, F. ATIM-03. ACT IV: an international, double-blind, phase 3 trial of rindopepimut in newly diagnosed, EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma. 2016.
- Rose, M.; Cardon, T.; Aboulouard, S.; Hajjaji, N.; Kobeissy, F.; Duhamel, M.; Fournier, I.; Salzet, M. Surfaceome proteomic of glioblastoma revealed potential targets for immunotherapy. Frontiers in Immunology 2021, 12, 746168. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, B.-T.; Tian, H.; Sun, J.; Zou, J.-B.; Zhang, X.-F.; Cheng, J.-X.; Shi, Y.-J.; Fan, Y.; Guo, D.-Y. Urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor (uPAR) as a therapeutic target in cancer. Journal of Translational Medicine 2022, 20, 135. [CrossRef]
- Echavidre, W.; Picco, V.; Faraggi, M.; Montemagno, C. Integrin-αvβ3 as a Therapeutic Target in Glioblastoma: Back to the Future? Pharmaceutics 2022, 14, 1053. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shraibman, B.; Barnea, E.; Kadosh, D.M.; Haimovich, Y.; Slobodin, G.; Rosner, I.; López-Larrea, C.; Hilf, N.; Kuttruff, S.; Song, C. Identification of tumor antigens among the HLA peptidomes of glioblastoma tumors and plasma. Molecular & Cellular Proteomics 2018, 17, 2132-2145.
- Consortium, U. Reorganizing the protein space at the Universal Protein Resource (UniProt). Nucleic acids research 2012, 40, D71-D75. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandrashekar, D.S.; Karthikeyan, S.K.; Korla, P.K.; Patel, H.; Shovon, A.R.; Athar, M.; Netto, G.J.; Qin, Z.S.; Kumar, S.; Manne, U. UALCAN: An update to the integrated cancer data analysis platform. Neoplasia 2022, 25, 18-27. [CrossRef]
- Doytchinova, I.A.; Flower, D.R. VaxiJen: a server for prediction of protective antigens, tumour antigens and subunit vaccines. BMC bioinformatics 2007, 8, 1-7. [CrossRef]
- Dimitrov, I.; Bangov, I.; Flower, D.R.; Doytchinova, I. AllerTOP v. 2—a server for in silico prediction of allergens. Journal of molecular modeling 2014, 20, 1-6. [CrossRef]
- Wold, S.; Jonsson, J.; Sjörström, M.; Sandberg, M.; Rännar, S. DNA and peptide sequences and chemical processes multivariately modelled by principal component analysis and partial least-squares projections to latent structures. Analytica Chimica Acta 1993, 277, 239-253. [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Gupta, S.; Vir, P.; Raghava, G. Prediction of IL4 inducing peptides. Clinical and Developmental Immunology 2013, 2013. [CrossRef]
- Dhanda, S.K.; Vir, P.; Raghava, G.P. Designing of interferon-gamma inducing MHC class-II binders. Biology direct 2013, 8, 1-15. [CrossRef]
- Magnan, C.N.; Zeller, M.; Kayala, M.A.; Vigil, A.; Randall, A.; Felgner, P.L.; Baldi, P. High-throughput prediction of protein antigenicity using protein microarray data. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 2936-2943. [CrossRef]
- Gasteiger, E.; Hoogland, C.; Gattiker, A.; Duvaud, S.e.; Wilkins, M.R.; Appel, R.D.; Bairoch, A. Protein identification and analysis tools on the ExPASy server; Springer: 2005.
- Garnier, J. GOR secondary structure prediction method version IV. Meth. Enzym., RF Doolittle Ed. 1998, 266, 540-553.
- Roy, A.; Kucukural, A.; Zhang, Y. I-TASSER: a unified platform for automated protein structure and function prediction. Nature protocols 2010, 5, 725-738. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Kaushik, R.; Mishra, A.; Shanker, A.; Jayaram, B. ProTSAV: A protein tertiary structure analysis and validation server. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Proteins and Proteomics 2016, 1864, 11-19. [CrossRef]
- Lee, G.R.; Won, J.; Heo, L.; Seok, C. GalaxyRefine2: simultaneous refinement of inaccurate local regions and overall protein structure. Nucleic acids research 2019, 47, W451-W455. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Khan, S.; Ali, A.; Akbar, H.; Sayaf, A.M.; Khan, A.; Wei, D.-Q. Immunoinformatics approaches to explore Helicobacter Pylori proteome (Virulence Factors) to design B and T cell multi-epitope subunit vaccine. Scientific reports 2019, 9, 13321. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, S.; Raghava, G.P.S. BcePred: prediction of continuous B-cell epitopes in antigenic sequences using physico-chemical properties. In Proceedings of the International conference on artificial immune systems, 2004; pp. 197-204.
- Chen, J.; Liu, H.; Yang, J.; Chou, K.-C. Prediction of linear B-cell epitopes using amino acid pair antigenicity scale. Amino acids 2007, 33, 423-428. [CrossRef]
- Ponomarenko, J.; Bui, H.-H.; Li, W.; Fusseder, N.; Bourne, P.E.; Sette, A.; Peters, B. ElliPro: a new structure-based tool for the prediction of antibody epitopes. BMC bioinformatics 2008, 9, 1-8. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laxmi, D.; Priyadarshy, S. HyperChem 6.03. Biotech Software & Internet Report: The Computer Software Journal for Scientists 2002, 3, 5-9.
- Trott, O.; Olson, A.J. AutoDock Vina: improving the speed and accuracy of docking with a new scoring function, efficient optimization, and multithreading. Journal of computational chemistry 2010, 31, 455-461. [CrossRef]
- Ohto, U.; Yamakawa, N.; Akashi-Takamura, S.; Miyake, K.; Shimizu, T. Structural analyses of human Toll-like receptor 4 polymorphisms D299G and T399I. Journal of Biological Chemistry 2012, 287, 40611-40617. [CrossRef]
- Desta, I.T.; Porter, K.A.; Xia, B.; Kozakov, D.; Vajda, S. Performance and its limits in rigid body protein-protein docking. Structure 2020, 28, 1071-1081. e1073. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Release, S. 3: Desmond molecular dynamics system, DE Shaw research, New York, NY, 2017. Maestro-Desmond Interoperability Tools, Schrödinger, New York, NY 2017.
- Banks, J.L.; Beard, H.S.; Cao, Y.; Cho, A.E.; Damm, W.; Farid, R.; Felts, A.K.; Halgren, T.A.; Mainz, D.T.; Maple, J.R. Integrated modeling program, applied chemical theory (IMPACT). Journal of computational chemistry 2005, 26, 1752-1780. [CrossRef]
- Toukmaji, A.Y.; Board Jr, J.A. Ewald summation techniques in perspective: a survey. Computer physics communications 1996, 95, 73-92. [CrossRef]
- Mark, P.; Nilsson, L. Structure and dynamics of the TIP3P, SPC, and SPC/E water models at 298 K. The Journal of Physical Chemistry A 2001, 105, 9954-9960. [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Tuckerman, M.E.; Tobias, D.J.; Klein, M.L. Explicit reversible integrators for extended systems dynamics. Molecular Physics 1996, 87, 1117-1157. [CrossRef]
- Martyna, G.J.; Klein, M.L.; Tuckerman, M. Nosé–Hoover chains: The canonical ensemble via continuous dynamics. The Journal of chemical physics 1992, 97, 2635-2643. [CrossRef]
- Humphrey, W.; Dalke, A.; Schulten, K. VMD: visual molecular dynamics. Journal of molecular graphics 1996, 14, 33-38. [CrossRef]
- Rapin, N.; Lund, O.; Bernaschi, M.; Castiglione, F. Computational immunology meets bioinformatics: the use of prediction tools for molecular binding in the simulation of the immune system. PloS one 2010, 5, e9862. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikai, A. Thermostability and aliphatic index of globular proteins. The Journal of Biochemistry 1980, 88, 1895-1898.
- Dey, M.; Chang, A.L.; Miska, J.; Wainwright, D.A.; Ahmed, A.U.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Pytel, P.; Han, Y.; Tobias, A.; Zhang, L. Dendritic cell–based vaccines that utilize myeloid rather than plasmacytoid cells offer a superior survival advantage in malignant glioma. The Journal of Immunology 2015, 195, 367-376. [CrossRef]
- Iglesia, R.P.; Fernandes, C.F.d.L.; Coelho, B.P.; Prado, M.B.; Melo Escobar, M.I.; Almeida, G.H.D.R.; Lopes, M.H. Heat shock proteins in glioblastoma biology: where do we stand? International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2019, 20, 5794. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, I.; Han, S.; Parsa, A.T. Heat-shock protein vaccines as active immunotherapy against human gliomas. Expert review of anticancer therapy 2009, 9, 1577-1582. [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Miao, L.; Sui, J.; Hao, Y.; Huang, G. Nanoparticle cancer vaccines: Design considerations and recent advances. Asian Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2020, 15, 576-590. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kiyotani, K.; Chan, H.T.; Nakamura, Y. Immunopharmacogenomics towards personalized cancer immunotherapy targeting neoantigens. Cancer Science 2018, 109, 542-549. [CrossRef]
- Yougbare, I.; Lang, S.; Yang, H.; Chen, P.; Zhao, X.; Tai, W.-S.; Zdravic, D.; Vadasz, B.; Li, C.; Piran, S. Maternal anti-platelet β3 integrins impair angiogenesis and cause intracranial hemorrhage. The Journal of clinical investigation 2015, 125, 1545-1556. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Sullivan, J.A.; Ni, H. Pathophysiology of immune thrombocytopenia. Current opinion in hematology 2018, 25, 373-381. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ni, H.; Freedman, J. Platelets in hemostasis and thrombosis: role of integrins and their ligands. Transfusion and Apheresis Science 2003, 28, 257-264. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nezafat, N.; Karimi, Z.; Eslami, M.; Mohkam, M.; Zandian, S.; Ghasemi, Y. Designing an efficient multi-epitope peptide vaccine against Vibrio cholerae via combined immunoinformatics and protein interaction based approaches. Computational biology and chemistry 2016, 62, 82-95. [CrossRef]
- Arai, R.; Ueda, H.; Kitayama, A.; Kamiya, N.; Nagamune, T. Design of the linkers which effectively separate domains of a bifunctional fusion protein. Protein engineering 2001, 14, 529-532. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.K.; Narula, A.; Naskar, M.; Srivastava, S.; Verma, P.; Malik, R.; Shah, P.; Prajapati, V.K. Exploring dual inhibitory role of febrifugine analogues against Plasmodium utilizing structure-based virtual screening and molecular dynamic simulation. Journal of Biomolecular Structure and Dynamics 2017, 35, 791-804. [CrossRef]
- Deng, H.; Yu, S.; Guo, Y.; Gu, L.; Wang, G.; Ren, Z.; Li, Y.; Li, K.; Li, R. Development of a multivalent enterovirus subunit vaccine based on immunoinformatic design principles for the prevention of HFMD. Vaccine 2020, 38, 3671-3681. [CrossRef]
- Pandey, R.K.; Prajapati, V.K. Exploring sand fly salivary proteins to design multiepitope subunit vaccine to fight against visceral leishmaniasis. Journal of cellular biochemistry 2019, 120, 1141-1155. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, N.; Ojha, R.; Khatoon, N.; Prajapati, V.K. Scrutinizing Mycobacterium tuberculosis membrane and secretory proteins to formulate multiepitope subunit vaccine against pulmonary tuberculosis by utilizing immunoinformatic approaches. International journal of biological macromolecules 2018, 118, 180-188. [CrossRef]
- Barh, D.; Barve, N.; Gupta, K.; Chandra, S.; Jain, N.; Tiwari, S.; Leon-Sicairos, N.; Canizalez-Roman, A.; Rodrigues dos Santos, A.; Hassan, S.S. Exoproteome and secretome derived broad spectrum novel drug and vaccine candidates in Vibrio cholerae targeted by Piper betel derived compounds. PloS one 2013, 8, e52773. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gharbavi, M.; Danafar, H.; Amani, J.; Sharafi, A. Immuno-informatics analysis and expression of a novel multi-domain antigen as a vaccine candidate against glioblastoma. International immunopharmacology 2021, 91, 107265. [CrossRef]
- Sanami, S.; Azadegan-Dehkordi, F.; Rafieian-Kopaei, M.; Salehi, M.; Ghasemi-Dehnoo, M.; Mahooti, M.; Alizadeh, M.; Bagheri, N. Design of a multi-epitope vaccine against cervical cancer using immunoinformatics approaches. Scientific Reports 2021, 11, 12397. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Shuaib, M.; Prajapati, K.S.; Singh, A.K.; Choudhary, P.; Singh, S.; Gupta, S. A candidate triple-negative breast cancer vaccine design by targeting clinically relevant cell surface markers: an integrated immuno and bio-informatics approach. 3 Biotech 2022, 12, 72. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finocchiaro, G. TLRgeting evasion of immune pathways in glioblastoma. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 20, 422-424. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Candolfi, M.; Curtin, J.F.; Yagiz, K.; Assi, H.; Wibowo, M.K.; Alzadeh, G.E.; Foulad, D.; Muhammad, A.G.; Salehi, S.; Keech, N. B cells are critical to T-cell—mediated antitumor immunity induced by a combined immune-stimulatory/conditionally cytotoxic therapy for glioblastoma. Neoplasia 2011, 13, 947-IN923. [CrossRef]
- Pucci, F. Location-dependent B-cell function in glioblastoma. Cancer Immunology Research 2019, 7, 1902-1902. [CrossRef]
- Wiencke, J.K.; Accomando, W.P.; Zheng, S.; Patoka, J.; Dou, X.; Phillips, J.J.; Hsuang, G.; Christensen, B.C.; Houseman, E.A.; Koestler, D.C. Epigenetic biomarkers of T-cells in human glioma. Epigenetics 2012, 7, 1391-1402. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woroniecka, K.; Fecci, P.E. T-cell exhaustion in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 35287. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crawford, A.; MacLeod, M.; Schumacher, T.; Corlett, L.; Gray, D. Primary T cell expansion and differentiation in vivo requires antigen presentation by B cells. The Journal of Immunology 2006, 176, 3498-3506. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oji, Y.; Hashimoto, N.; Tsuboi, A.; Murakami, Y.; Iwai, M.; Kagawa, N.; Chiba, Y.; Izumoto, S.; Elisseeva, O.; Ichinohasama, R. Association of WT1 IgG antibody against WT1 peptide with prolonged survival in glioblastoma multiforme patients vaccinated with WT1 peptide. International journal of cancer 2016, 139, 1391-1401. [CrossRef]
- Busch, S.; Talamini, M.; Brenner, S.; Abdulazim, A.; Hänggi, D.; Neumaier, M.; Seiz-Rosenhagen, M.; Fuchs, T. Circulating monocytes and tumor-associated macrophages express recombined immunoglobulins in glioblastoma patients. Clinical and translational medicine 2019, 8, 1-14. [CrossRef]
- Turki, S.G. Immunoglobulins Levels and Complements in Patients with Brain Tumour (Meningioma and Glioma). Iraqi National Journal of Nursing Specialties 2017, 30. [CrossRef]
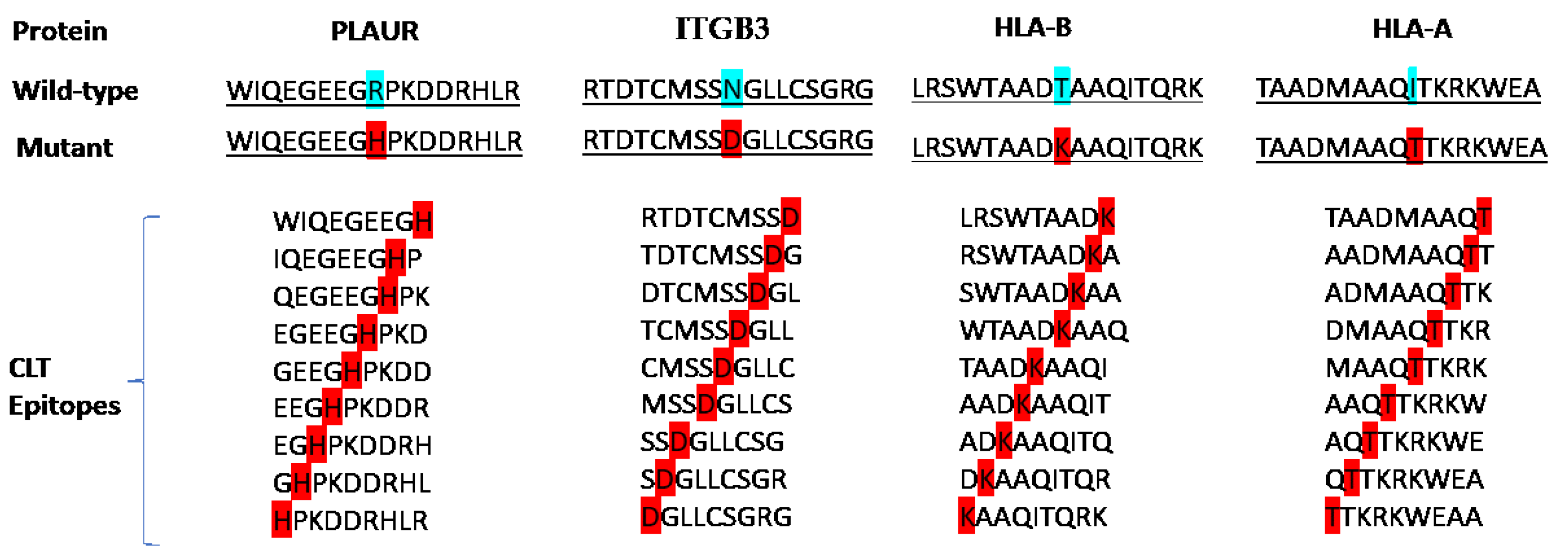
| Protein | Epitopes | VaxiJen | Allergenicity | Toxicity | IFN-γ –inducing | IL-4- inducing | Final decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLAUR | WIQEGEEGH | 1.1681 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - |
| IQEGEEGHP | 1.4977 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| QEGEEGHPK | 1.3359 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | - | |
| EGEEGHPKD | 1.1271 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | - | |
| GEEGHPKDD | 0.8220 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| EEGHPKDDR | 0.2950 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| EGHPKDDRH | -0.1423 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| GHPKDDRHL | -0.1795 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| HPKDDRHLR | -0.4382 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| RTDTCMSSD | 0.0279 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| TDTCMSSDG | 0.1181 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| DTCMSSDGL | -0.1421 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| ITGB3 | TCMSSDGLL | -0.0823 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | - |
| CMSSDGLLC | -0.3962 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| MSSDGLLCS | -0.0032 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | - | |
| SSDGLLCSG | 0.0546 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| SDGLLCSGR | -0.0087 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| DGLLCSGRG | 0.4925 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| LRSWTAADK | 0.0708 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| RSWTAADKA | 0.1046 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| SWTAADKAA | 0.1046 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| WTAADKAAQ | 0.5204 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| HLA-B | TAADKAAQI | 1.5233 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - |
| AADKAAQIT | 1.5395 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| ADKAAQITQ | 1.6355 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| DKAAQITQR | 1.6396 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| KAAQITQRK | 1.2152 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| TAADMAAQT | 0.6747 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| AADMAAQTT | 0.6145 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| ADMAAQTTK | 0.8434 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| DMAAQTTKR | 1.0065 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| HLA-A | MAAQTTKRK | 1.0223 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - |
| AAQTTKRKW | 0.5899 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| AQTTKRKWE (C1) |
0.7411 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | * | |
| QTTKRKWEA (C2) |
0.6981 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | * | |
| TTKRKWEAA (C3) |
0.5519 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | * |
| Protein | Epitopes | VaxiJen | Allergenicity | Toxicity | IFN-γ –inducing | IL-4- inducing | Final decision |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HLA-A | ADMAAQTTKRKWEAA | 0.6847 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - |
| AADMAAQTTKRKWEA | 0.6458 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| DMAAQTTKRKWEAAH | 0.6882 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | - | |
| TAADMAAQTTKRKWE | 0.6752 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| MAAQTTKRKWEAAHE | 0.6191 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| ADMAAQTTKRKWEAA | 0.6847 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| AADMAAQTTKRKWEA | 0.6458 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| DMAAQTTKRKWEAAH (H1) | 0.6882 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | IL4-inducer | * | |
| TAADMAAQTTKRKWE | 0.6752 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | IL4-inducer | - | |
| WTAADMAAQTTKRKW | 0.4225 (Probable Non-Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| MAAQTTKRKWEAAHE | 0.6191 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Non-Toxin | Positive | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| DGLLCSGRGKCECGS | 0.8628 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - | |
| ITGB3 | SDGLLCSGRGKCECG | 0.5730 (Probable Antigen)) | Probable Non-Allergen | Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - |
| SSDGLLCSGRGKCEC | 0.7534 (Probable Antigen) | Probable Non-Allergen | Toxin | Negative | Non-IL4-inducer | - |
| Start | End | Peptide | Number of residues | Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 158 | 186 | AYTTKRKWEAAAAYDMAAQTTKRKWEAAH | 29 | 0.826 |
| 1 | 16 | MAKLSTDELLDAFKEM | 16 | 0.716 |
| 114 | 127 | DEAKAKLEAAGATV | 14 | 0.656 |
| 69 | 76 | AAGDKKIG | 8 | 0.602 |
| 153 | 156 | KWEA | 4 | 0.539 |
| Vaccine residue | TLR4 residue and chain | Distance(Å) | Type of interaction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Glu 183 | Gln 616A | 2.5 | Hydrogen bond |
| Glu 183 | Ser 613A | 1.9 | Hydrogen bond |
| Lys 181 | Gln 510B | 1.9 | Hydrogen bond |
| Arg 180 | Asp 580A | 2.1 | Hydrogen bond |
| Gln 176 | Asp 580A | 1.8 | Hydrogen bond |
| Gln 176 | His 555A | 1.9 | Hydrogen bond |
| Glu 166 | Gln 616B | 2.1 | Hydrogen bond |
| Arg 163 | Gln 616B | 1.9 | Hydrogen bond |
| Lys 151 | Gly 617B | 2.5 | Hydrogen bond |
| Tyr 147 | Ser 622B | 1.9 | Hydrogen bond |
| Lys 94 | Glu 24B | 2.2 | Hydrogen bond |
| Lys 94 | Glu 27B | 2 | Salt-bridge |
| Lys 91 | Glu 24B | 2.3 | Salt-bridge |
| Lys 91 | Glu 31B | 2 | Salt-bridge |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





