1. Introduction
Hydrogen energy has garnered significant interest as a potential future energy source due to its clean nature, widespread availability, and high energy density [
1,
2,
3,
4]. Chemical hydrides, including NH
3BH
3, NaBH
4, and LiBH
4, have risen in popularity as effective hydrogen storage materials due to their ability to securely store hydrogen and release it efficiently through catalytic hydrolysis [
5,
6,
7,
8]. Ammonia borane (NH
3BH
3) is especially notable for its impressive theoretical hydrogen storage potential, containing up to 19.6 wt.% H
2, and its capacity to release hydrogen through both pyrolysis and hydrolysis in neutral water [
9,
10,
11,
12,
13,
14,
15,
16]. When catalyzed, the hydrolysis of NH
3BH
3, as shown in equation 1, produces hydrogen with an output of 8.96 wt.% [
17].
The efficiency of NH
3BH
3 hydrolysis is largely dependent on the effectiveness of the catalysts used, making it essential to develop high-performance catalysts for rapid hydrogen production [
18,
19,
20]. Precious metals like Ru and Pt have been employed to accelerate the hydrolysis of NH
3BH
3 [
21,
22]. However, the high cost of these metals limits their commercial viability. To address this issue, research has shifted towards exploring more affordable yet efficient alternatives, particularly those based on Co and Ni [
23,
24,
25,
26,
27,
28]. Co-P catalysts have been widely used in various catalytic applications due to their high electrochemical activity, including in chemical hydride catalysis. This superior activity is believed to stem from the electronic state separation caused by the difference in electronegativity between cobalt and phosphorus [
23,
25]. Researchers have pursued two primary strategies to enhance the activity of Co-P catalysts. The first strategy focuses on increasing the catalyst's surface area by employing porous structures, with foam-like frameworks being the most commonly explored [
24,
25]. The second approach involves altering the electronic structure by incorporating transition metals. Studies have shown that adding transition metals such as Fe, Ni, and Cr results in the development of ternary catalysts with improved performance [
29,
30,
31]. Notably, Fe has received significant attention due to its excellent catalytic activity, prompting further advancements in the design of Fe-doped Co-based catalysts [
29,
30,
31,
32]. This has led to extensive research efforts aimed at the fabrication of Co-Fe-P catalysts using various synthesis methods including electrodeposition technique [
32,
33,
34]. However, research on the synthesis of Co-Fe-P catalysts via electroless deposition, specifically for use as catalysts in chemical hydride of NH
3BH
3, has not yet been reported.
In this work, we synthesized Co-Fe-P catalysts through electroless deposition method. And we examined the effects of electroless deposition conditions such as deposition time, bath composition, temperature on the hydrogen generation kinetics were examined in NH3BH3 solution.
2. Experimental
The Co-Fe-P catalysts were synthesized through electroless deposition on Cu sheet, Ni foam, and Cu foam. Before electroless deposition, a catalyzing process was conducted. This process involved immersion in a SnCl2 (1 g L−1) + HCl (1 ml L−1) solution for 3 minutes at 25°C, followed by acceleration in a PdCl2 (0.1 g L−1) + HCl (1 ml L−1) solution for 1 minute at 25°C. The substrates were then washed with distilled water before the electroless deposition process. The electroless deposition bath for the Co-Fe-P catalysts contained 0.1 M CoCl2 ·6H2O, 0.6 M NH2CH2COOH, 0.5 M NaH2PO2 ·H2O, and 0.1 M FeCl2, with continuous stirring by a magnetic agitator. The pH of the Co-Fe-P bath was adjusted to a range between 10 and 13 by adding NaOH, and the temperature was controlled within a range of 30 to 60°C. The electroless deposition process was carried out for durations between 1 to 10 minutes. The surface morphology and composition of the Co-Fe-P catalysts were characterized by scanning electron microscopy (SEM) and energy dispersive spectroscopy (EDS). Hydrogen generation tests were performed in a 60 ml reactor using a 1 wt.% NH3BH3 solution at temperatures ranging from 30 to 60°C in ambient air. The reactor was submerged in a water bath to ensure temperature stability. The amount of hydrogen gas produced was quantified using a mass flow meter (MFM). The effects of various parameters, including applied current density, electro-deposition time, NH3BH3 concentration, and temperature, on the hydrogen generation kinetics of the Co-Fe-P catalysts were investigated.
3. Results and Discussion
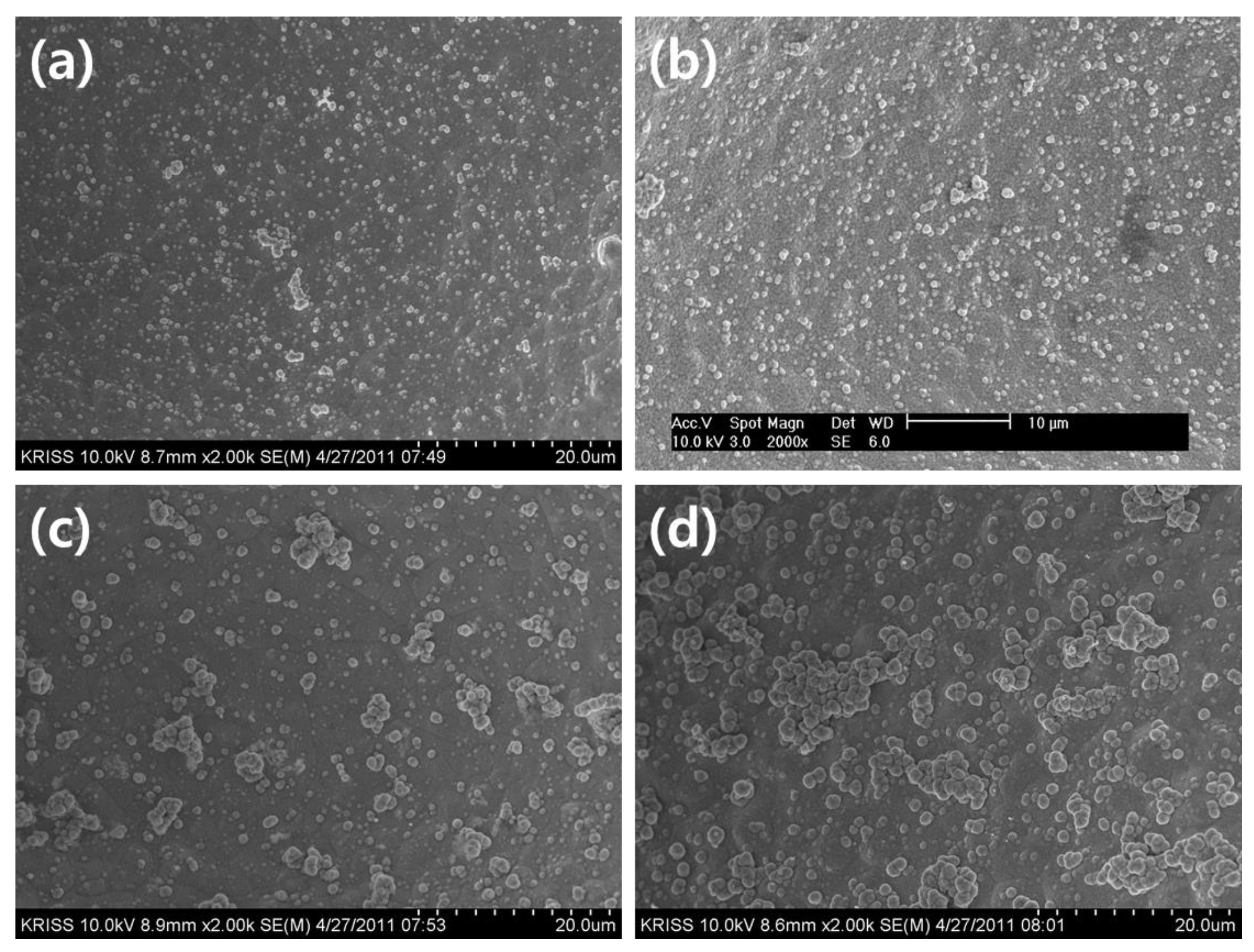
Figure 1 shows the surface morphologies of Co-Fe-P catalysts fabricated by electroless deposition with the change of deposition time from 1 min to 10 min. All the Cu foams were pretreated in Sn based solution containing of SnCl
2 and HCl for 3min at 25˚C. After that, they were immersed in Pd solution containing of PdCl
2 and HCl for 1min at 25 ˚C.
Figure 1(a-b) illustrates the spherical morphology of Co-Fe-P particles deposited on Cu foam. The particle size appears to be less than approximately 1 µm. These particles exhibit nucleation on the substrate surface, and in some areas, they aggregate to form powdery structures on the sub-micron scale. After 1 minute of deposition, the amount of deposited catalyst was confirmed to be approximately 3.92 mg, increasing to 4.23 mg after 3 minutes. As the deposition time increased from 3 to 5 minutes, the nucleated particles partially aggregated to form powdery structures of approximately 3-5 µm in size. After 10 minutes of deposition, the nucleated particles grew visibly to approximately 1-2 µm in size, and in some areas, powdery structures around 10 µm in size were observed. The amount of deposited catalyst also increased from 5.78 mg at 5 minutes to 7.59 mg at 10 minutes.
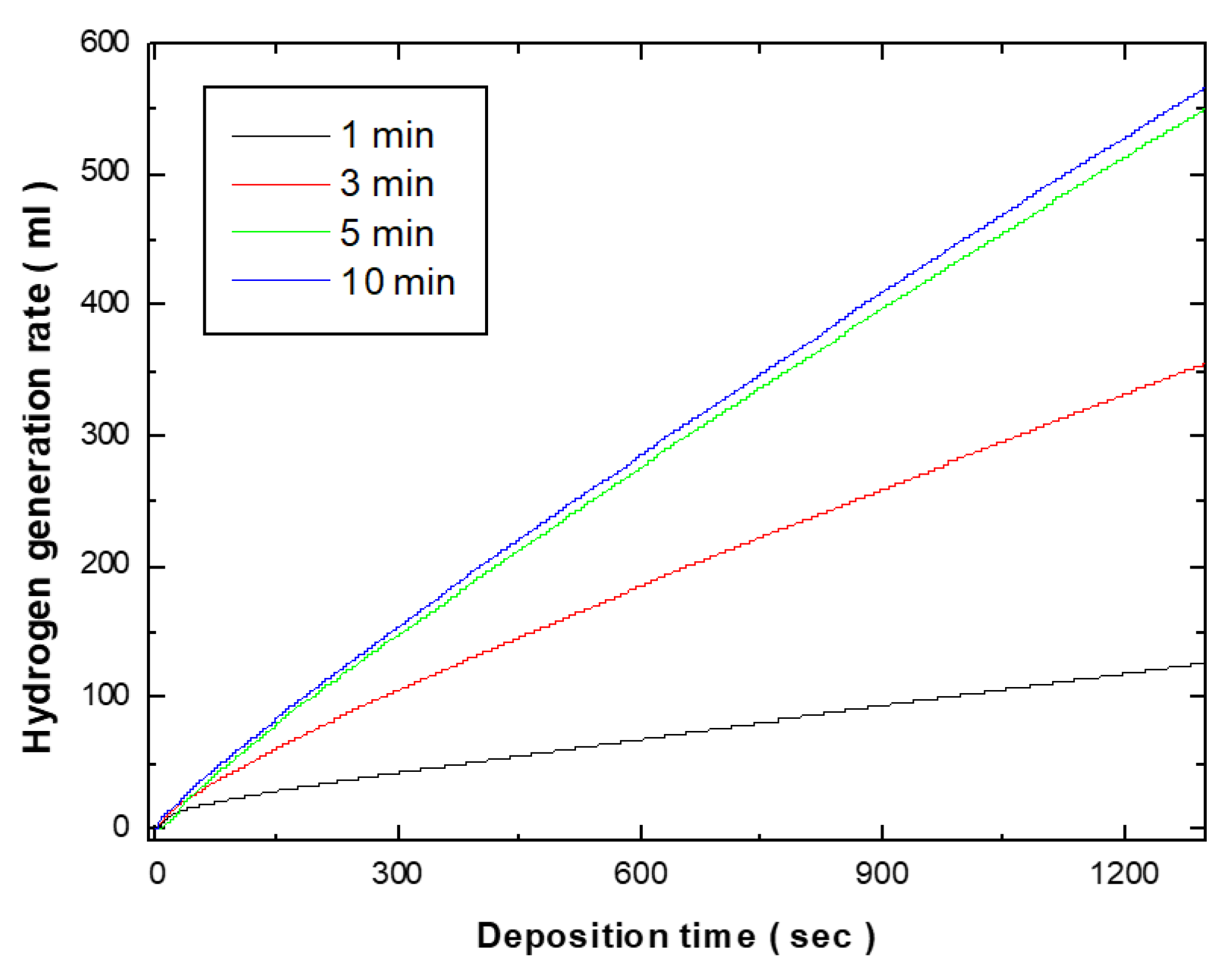
Figure 2 shows the hydrogen generation kinetics of the electroless deposited Co-Fe-P catalysts in the 1 wt.% NH
3BH
3 solution at 25 ˚C. The catalytic activity was evaluated by measuring the rate of hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane (NH₃BH₃). With a 1-minute electroless deposition, the hydrogen generation rate was 6.89 ml/min, and this increased to 18.56 ml/min as the deposition time was extended to 3 minutes. Further increasing the deposition time to 5 minutes, the hydrogen generation kinetics were increased to 27.66 ml/min. When considering the weight of the deposited catalyst, the catalytic activity per unit weight was calculated to be 4785 ml/min.g-catalyst. However, when the deposition time was extended to 10 minutes, the hydrogen generation rate showed a similar trend to that observed at 5 minutes. Given the weight of the catalyst deposited after 10 minutes was 28.56 ml/min, the catalytic activity per unit weight was calculated to be 3762 ml/min.g-catalyst. This demonstrates that the hydrogen generation rate of the catalyst deposited for 5 minutes is higher than that of the catalyst deposited for 10 minutes. The increase in particle size and the formation of powdery structures as the deposition time increased led to a more aggregated catalyst layer, which likely caused the decrease in catalytic activity per unit weight.
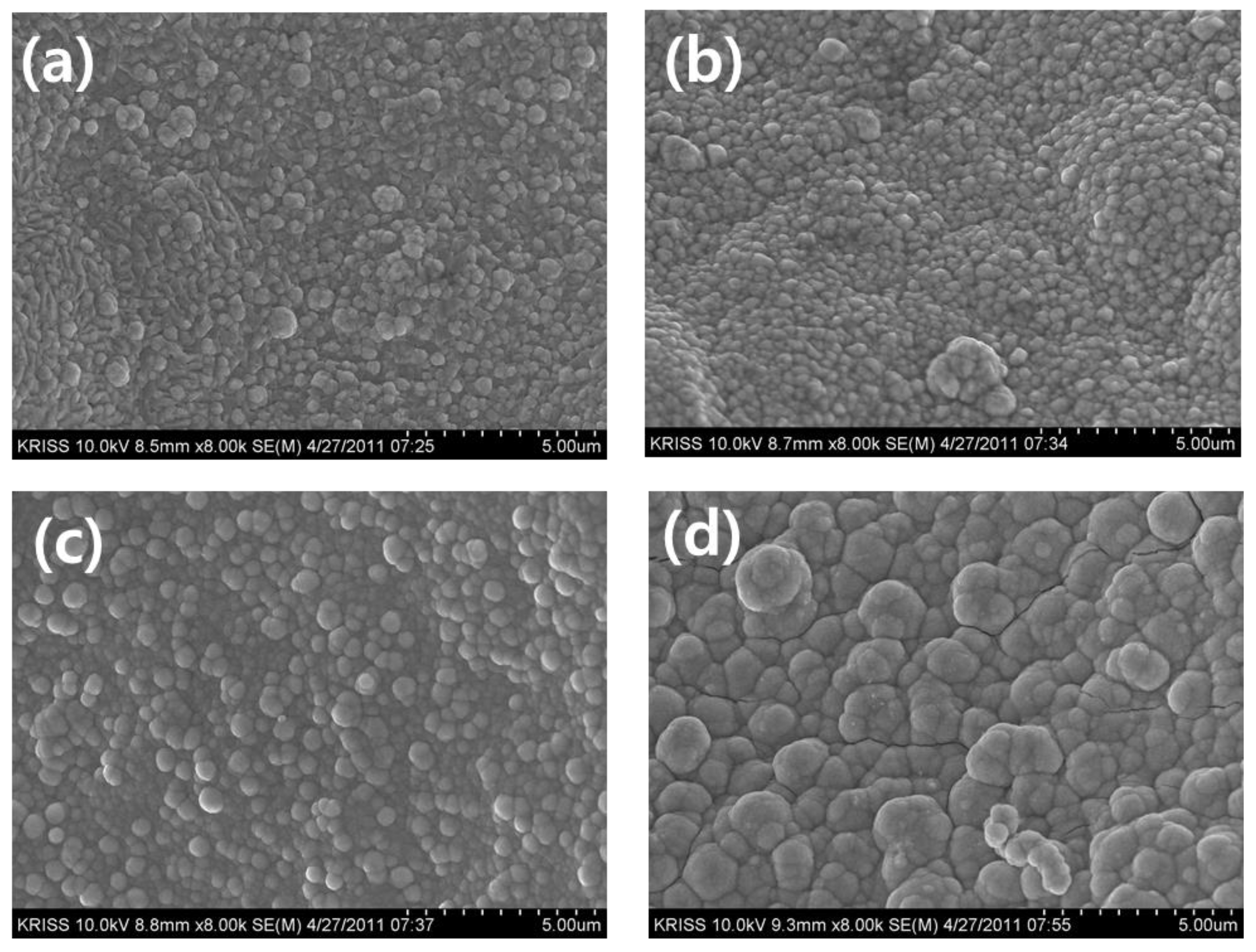
Figure 3 illustrates the effects of bath temperature on the morphology of Co-Fe-P catalysts. When the bath temperature was increased from 30°C to 50°C, small particles, less than approximately 0.5 µm in size, were well deposited on the substrate surface, partially forming a powdery structure. At a deposition temperature of 60°C, the particle size of Co-Fe-P increased, and particles with diameters of approximately 1-2 µm were observed. The compositional variation of the catalyst with changing bath temperature showed that the Fe content varied from 2.3 wt.% to 9.32 wt.%, while the P content changed from 2.7 wt.% to 6.03 wt.%.
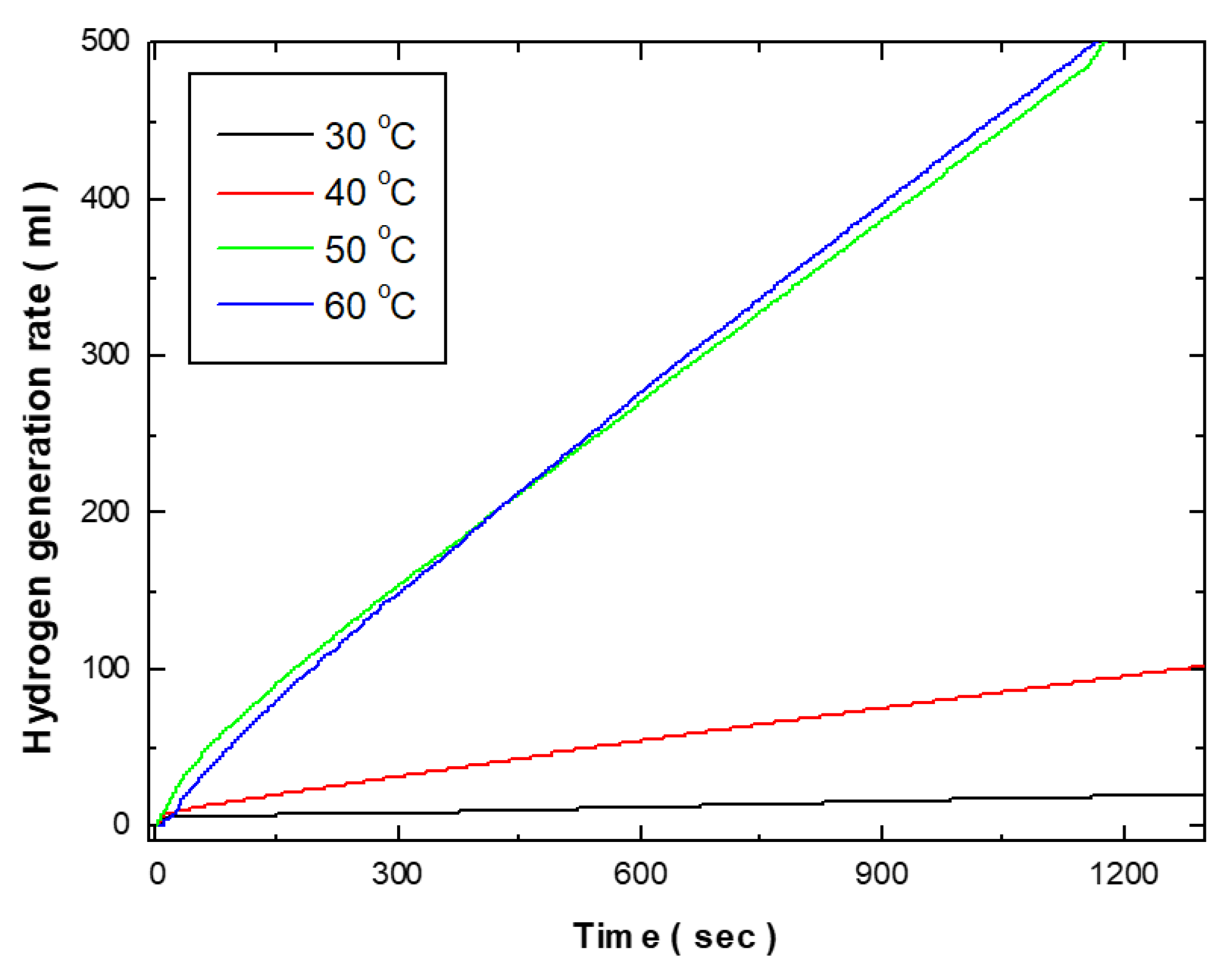
Figure 4 shows the effects of electroless deposition bath temperature on the hydrogen generation kinetics of Co-Fe-P catalysts. As the bath temperature increased from 30°C to 40°C, the hydrogen generation rate rose from 1.218 ml/min to 5.42 ml/min. Further increases in temperature to 50°C and 60°C resulted in dramatic increases in the hydrogen generation rate, reaching 27.06 ml/min and 27.66 ml/min, respectively. Morphologically, as shown in
Figure 3, the surface at 30°C and 40°C exhibits small grains, primarily in a 2D structure deposited on the substrate. However, at bath temperatures above 50°C, a 3D structure extending outward from the substrate was observed. Catalytic activity is fundamentally related to surface area, and the increase in surface area due to this 3D growth is considered to be a significant factor in enhancing catalytic activity. Additionally, the activity of the deposited catalyst is closely related to its composition. According to the literature, Co-Fe-P catalysts exhibit higher activity when the Fe and P contents are each around 10 wt.%. Below a deposition temperature of 40°C, the Fe content was approximately 4 wt.% and the P content was around 5 wt.%. However, at temperatures above 50°C, the Fe content increased to approximately 9.3 wt.% and the P content to 10 wt.%, similar to compositions reported in previous studies. Therefore, the higher hydrogen generation rates observed at deposition temperatures above 50°C can be attributed not only to the 3D structure of the deposited morphology but also to the higher Fe and P content in the deposited composition.
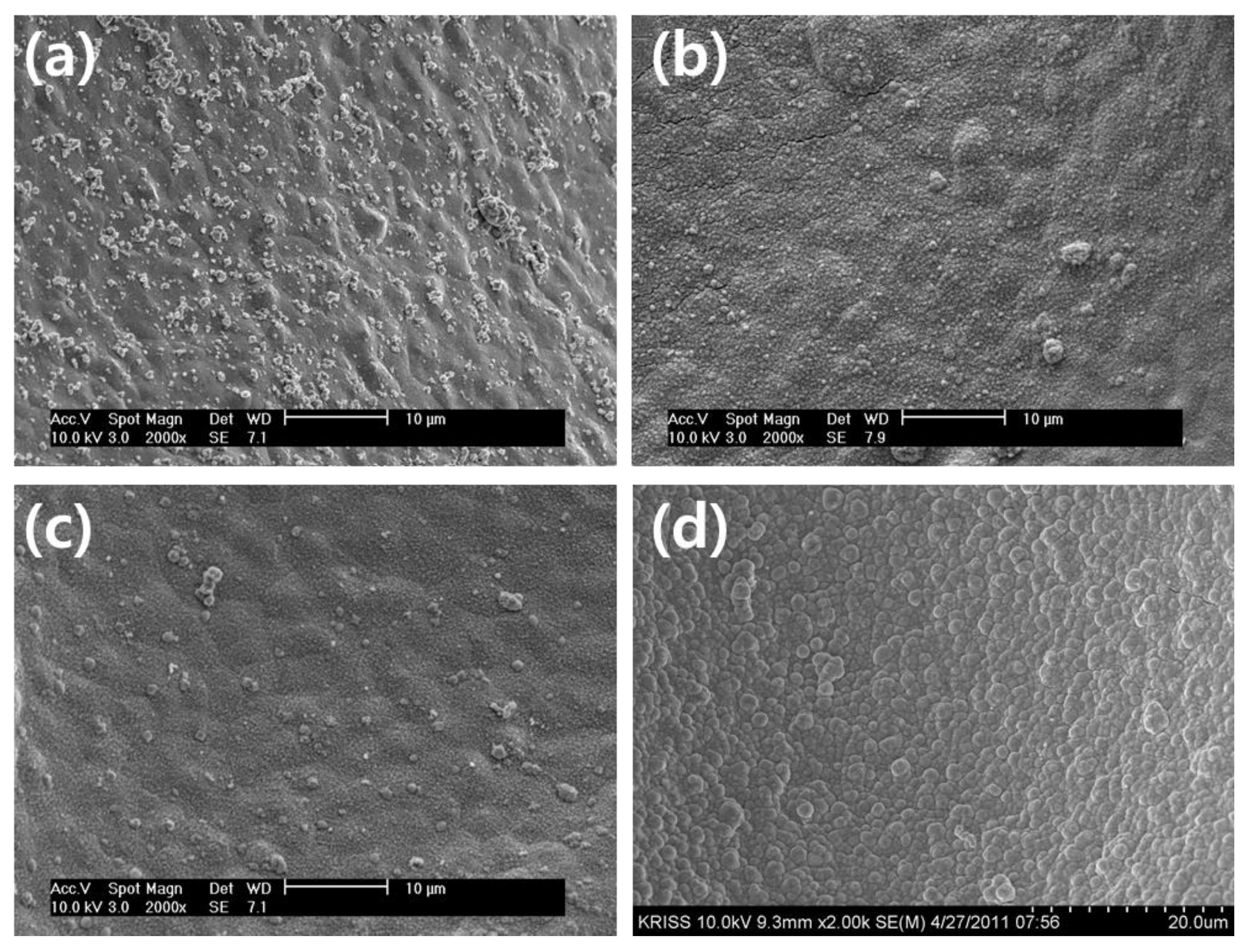
Figure 5 illustrates the surface morphology of Co-Fe-P catalysts deposited using an electroless deposition bath with varying NaOH concentrations of 0.6 M ~ 0.9 M. The figures indicate that all catalyst samples exhibited a relatively uniform distribution of catalyst particles across the surface of the substrate. It is evident that when the NaOH concentration increased from 0.5 M to 0.7 M, no significant alteration in surface morphology was observed. The catalyst particles maintained a consistent structure, without any noticeable changes in particle size or arrangement. However, a more pronounced change in the surface morphology became apparent when the NaOH concentration reached 0.8 M. Under this condition, the nanometer-scale particles, which initially covered the surface, experienced significant growth, resulting in the formation of a powdery surface structure with particles measuring approximately 1 µm in size. This transformation in surface morphology is attributed to the increased pH of the solution, which facilitated the growth of the deposited particles.
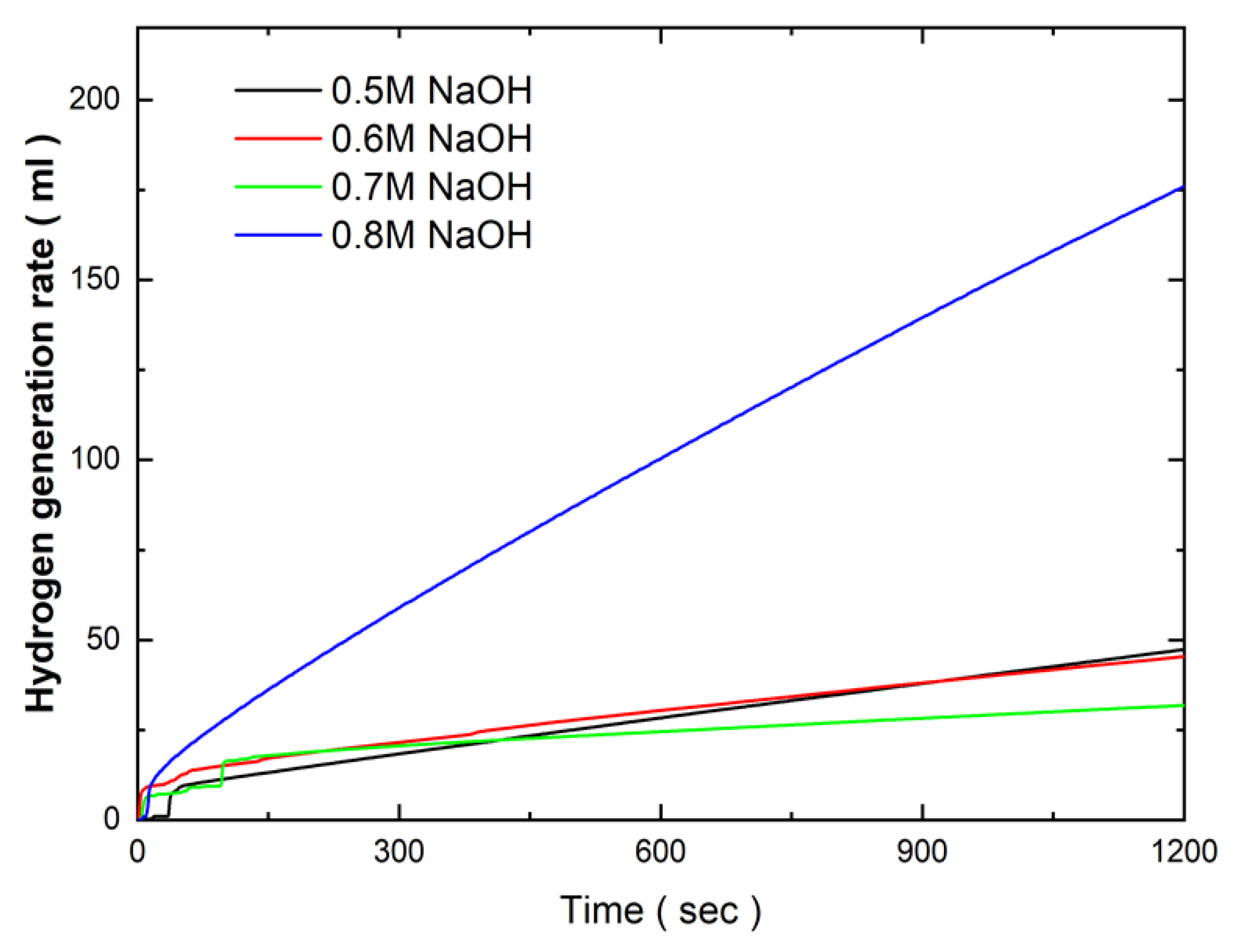
Figure 6 presents the effects of NaOH concentration in the electroless deposition bath on the hydrogen generation kinetics of Co-Fe-P catalysts in a 1 wt.% NH₃BH₃ solution at 25°C. The results indicate that the hydrogen generation rate remained relatively consistent, ranging from 2.8 ml/min to 3 ml/min, as the NaOH concentration increased from 0.5 M to 0.7 M. This consistency in catalytic activity corresponds with the limited changes observed in the surface morphology over the same concentration range. The stability of the hydrogen generation rate suggests that the surface area and active sites of the catalysts were not significantly affected by the increase in NaOH concentration within this range. However, a substantial enhancement in hydrogen generation kinetics was observed when the NaOH concentration reached 0.8 M. At this concentration, the hydrogen generation rate increased sharply to 10.03 ml/min. This marked improvement in catalytic performance is likely due to the significant surface morphological changes, where the initially flat catalyst surface developed powdery, protruding structures. These new surface features increased the overall surface area of the catalyst, thereby enhancing the number of active sites available for the hydrolysis reaction, leading to improved hydrogen generation efficiency.
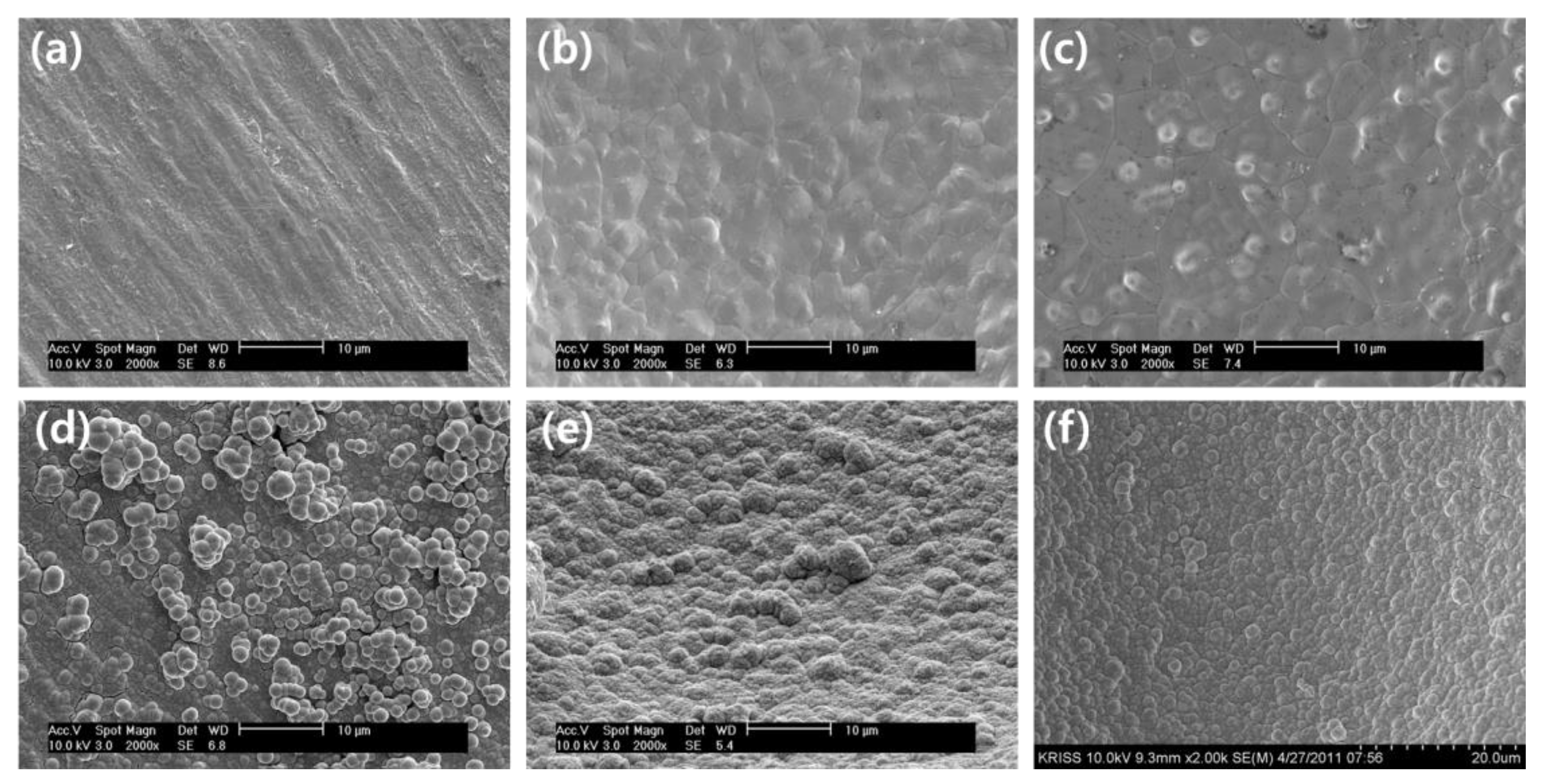
Figure 7 compares the surface morphology of various substrates, including a Cu sheet, Ni foam, and Cu foam, both before and after the deposition of Co-Fe-P catalysts via electroless deposition. The surface of the Cu sheet displayed a relatively rough and uneven texture, characterized by irregularities and imperfections on the surface. In contrast, the Ni foam and Cu foam exhibited more organized and compact structures with dense, interconnected networks. After the Co-Fe-P catalysts were deposited, it was observed that the Cu sheet did not achieve uniform catalyst deposition. In several regions, the catalyst particles appeared to cluster together, forming powdery agglomerates, while other areas remained largely uncovered, revealing the original Cu sheet surface. This uneven deposition may have resulted from the surface roughness of the Cu sheet, which hindered uniform nucleation and growth of the catalyst particles. In contrast, both the Ni foam and Cu foam exhibited a much more uniform distribution of Co-Fe-P catalysts across their entire surface areas. The foam structures appeared to promote more even nucleation and growth, leading to a homogeneous coating of catalyst particles. The catalytic performance of Co-Fe-P catalysts on different substrates was evaluated through hydrogen generation experiments, as illustrated in
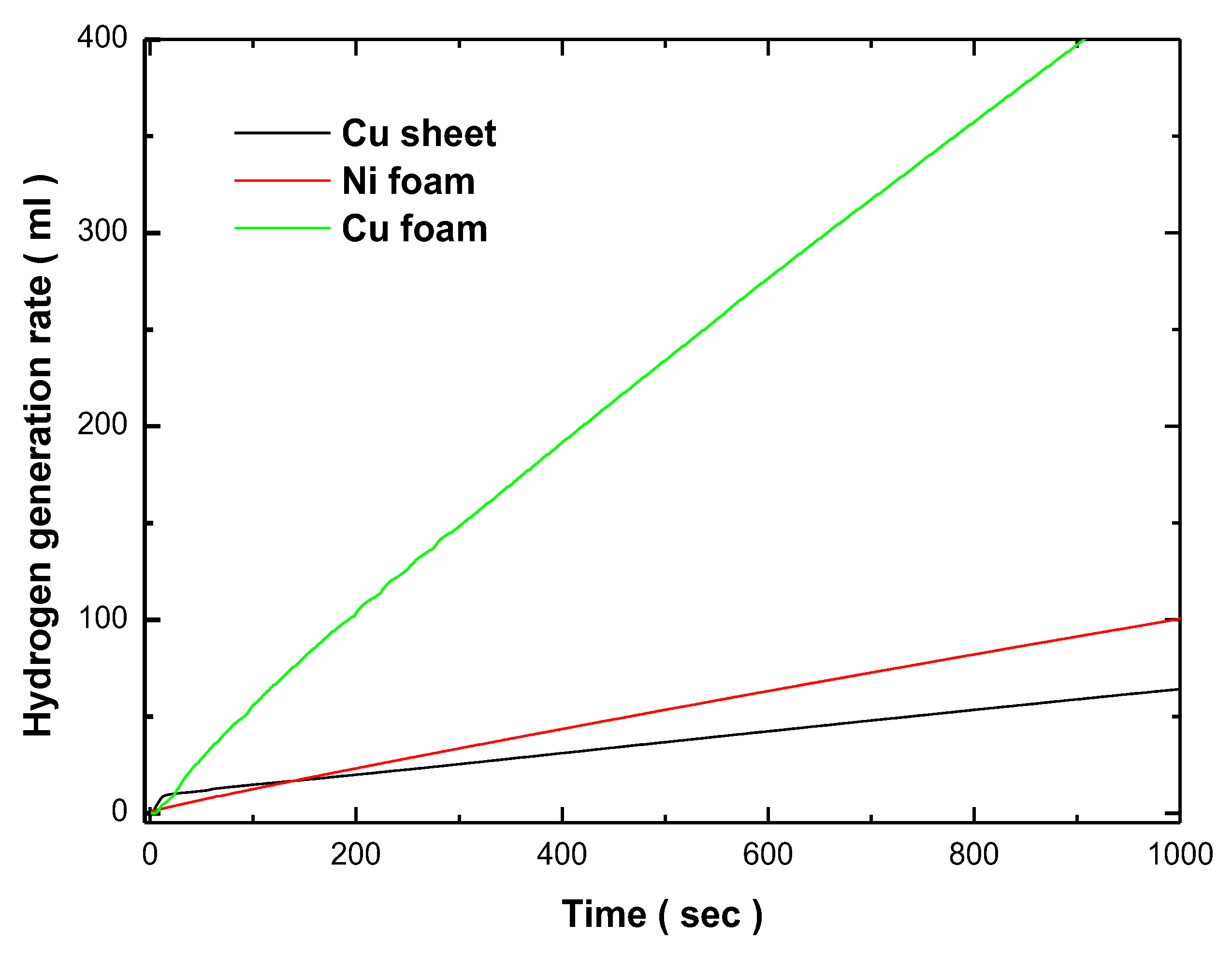
Figure 8. The hydrogen generation rates were measured during the hydrolysis of a 1 wt.% NH₃BH₃ solution at room temperature. The Cu sheet exhibited the lowest catalytic activity, with a hydrogen generation rate of 4.236 ml/min, which could be attributed to the non-uniform deposition and reduced surface area of the catalyst on this substrate. On the other hand, the Co-Fe-P/Ni foam catalyst demonstrated a moderate improvement in activity, with a hydrogen generation rate of 6.317 ml/min. However, the most significant catalytic performance was observed with the Co-Fe-P/Cu foam catalyst, which achieved a hydrogen generation rate of 27.66 ml/min. According to previous studies, copper catalysts has been recognized as a highly efficient catalyst for NH₃BH₃ hydrolysis, and there have been reports on the development of binary high-performance catalysts composed of cobalt and copper. The enhanced hydrogen generation rate of Co-Fe-P/Cu foam, compared to Co-Fe-P/Cu foam, is attributed to its larger active surface area. Furthermore, the superior catalytic performance of copper foam over Co-Fe-P/Ni foam is likely due to the stronger synergistic interaction between copper and cobalt, which has a more pronounced effect on catalytic activity than the interaction between nickel and cobalt [
35].
4. Conclusions
This study effectively synthesized Co-Fe-P catalysts using electroless deposition, highlighting the importance of deposition parameters like time, temperature, NaOH concentration, and substrate type on catalyst morphology and performance. Increasing deposition time from 1 to 5 minutes improved catalyst particle growth and aggregation, with the 5-minute deposit achieving the highest hydrogen generation rate of 27.66 ml/min in a 1 wt.% NH₃BH₃ solution. Extending the time to 10 minutes resulted in larger, more aggregated particles, which reduced catalytic efficiency, as the hydrogen rate did not improve beyond the 5-minute mark. The deposition temperature also significantly influenced catalyst morphology and activity. Temperatures above 50°C led to better 3D structures and higher Fe and P contents, with optimal performance observed at 60°C. Increasing NaOH concentration to 0.8 M improved surface morphology, enhancing catalytic efficiency and boosting the hydrogen generation rate to 10.03 ml/min. Among various substrates, the Co-Fe-P/Cu foam catalyst performed best, with a hydrogen rate of 27.66 ml/min, outperforming Co-Fe-P catalysts on Ni foam and Cu sheet substrates. This superior performance is attributed to the foam's uniform catalyst distribution and high surface area, which promoted effective particle nucleation and growth. The study underscores the need for precise control of deposition conditions and substrate selection to maximize Co-Fe-P catalyst performance for hydrogen generation.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Ministry of Trade, Industry and Energy (MOTIE) of Korea (No. 20019192).
References
- Pierozyński, B.; Kuczyński, M.; Mikołajczyk, T. Electro-Reactivity of Resorcinol on Pt(111) Single-Crystal Plane and Its Influence on the Kinetics of Underpotentially Deposited Hydrogen and Hydrogen Evolution Reaction Processes in 0. 1 M NaOH Solution. Crystals 2024, 14, 545–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zabielaite, A.; Eicher-Lorka, O.; Kuodis, Z.; Levinas, R.; Simkunaite, D.; Tamasauskaite-Tamasiunaite, L.; Norkus, E. Synthesis of Silver Nanocubes@Cobalt Ferrite/Graphitic Carbon Nitride for Electrochemical Water Splitting. Crystals 2023, 13, 1342–1358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Yin, W.; Liu, S.; Yu, H.; He, Y.; Cai, Y.; Wang, L. Sulfur Line Vacancies in MoS₂ for Catalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Crystals 2022, 12, 1218–1225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Liao, L.; Zhang, Z.; Yusran, Y.; Wang, R.; Fang, J.; Liu, Y.; Hou, Y.; Wang, Y.; Fang, Q. 2D Microporous Covalent Organic Frameworks as Cobalt Nanoparticle Supports for Electrocatalytic Hydrogen Evolution Reaction. Crystals 2022, 12, 880–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.; Cho, K.; Kwon, H. Effects of electroless deposition conditions on microstructures of cobalt–phosphorous catalysts and their hydrogen generation properties in alkaline sodium borohydride solution. J. Power Sources 2008, 180, 484–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.; Kong, K.; Jung, C.; Cho, E.; Yoon, S.; Han, J.; Lee, T.; Nam, S. A structured Co–B catalyst for hydrogen extraction from NaBH4 solution. Catalysis Today 2007, 120, 305–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, P.; Cheng, H. Amorphous cobalt–boron/nickel foam as an effective catalyst for hydrogen generation from alkaline sodium borohydride solution. J. Power Sources 2008, 177, 17–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Liang, Y.; Wang, P.; Yao, X.; Rufford, T.; Lu, M.; Cheng, H. High-performance cobalt–tungsten–boron catalyst supported on Ni foam for hydrogen generation from alkaline sodium borohydride solution. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2008, 33, 4405–4412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.; Shioyama, H.; Xu, Q. Magnetically recyclable Fe–Ni alloy catalyzed dehydrogenation of ammonia borane in aqueous solution under ambient atmosphere. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 478–481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pachfule, P.; Yang, X.; Zhu, Q.; Tsumori, N.; Uchida, T.; Xu, Q. From Ru nanoparticle-encapsulated metal–organic frameworks to highly catalytically active Cu/Ru nanoparticle-embedded porous carbon. J. Mater. Chem. A 2017, 5, 4835–4841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umegaki, T.; Hui, S.; Kojima, Y. Fabrication of hollow silica–nickel particles for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane using rape pollen templates. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 992–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, D.; Yu, G.; Li, Y.; Chen, M.; Pan, Y.; Zhou, L.; Yang, K.; Xiong, X.; Wu, P.; Xia, Q. RuCo NPs supported on MIL-96(Al) as highly active catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 694, 662–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, L.; Sang, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, X.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C. Boron nitride supported Ni nanoparticles as catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demirci, U.; Miele, P. Hydrolysis of solid ammonia borane. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 4030–4035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockman, A.; Zheng, Y.; Gore, J. A study of catalytic hydrolysis of concentrated ammonia borane solutions. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 7350–7356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H.; Xu, Q. Catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane for chemical hydrogen storage. Catal. Today 2011, 170, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossin, A.; Peruzzini, M. Ammonia−Borane and Amine−Borane Dehydrogenation Mediated by Complex Metal Hydrides. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 8848–8872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umegaki, T.; Yan, J.; Zhang, X. Hollow Ni–SiO₂ nanosphere-catalyzed hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane for chemical hydrogen storage. J. Power Sources 2009, 191, 209–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.; Cho, K.; Kwon, H. Hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of NH₃BH₃ by an electroplated Co–P catalyst. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2010, 35, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, J.; Zhang, X.; Han, S.; Shioyama, H.; Xu, Q. Magnetically recyclable Fe–Ni alloy catalyzed dehydrogenation of ammonia borane in aqueous solution under ambient atmosphere. J. Power Sources 2009, 194, 478–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.; Xu, Q. Room temperature hydrogen generation from aqueous ammonia-borane using noble metal nano-clusters as highly active catalysts. J. Power Sources 2007, 168, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chandra, M.; Xu, Q. A high-performance hydrogen generation system: Transition metal-catalyzed dissociation and hydrolysis of ammonia–borane. J. Power Sources 2006, 156, 190–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, K.; Eom, K.; Kwon, H. Effects of electrodeposited Co and Co–P catalysts on the hydrogen generation properties from hydrolysis of alkaline sodium borohydride solution. Catal. Today 2007, 120, 298–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Li, L.; Sang, W.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Z.; Yu, C.; Zhang, X.; Tang, C. Boron nitride supported Ni nanoparticles as catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. J. Alloys Compd. 2017, 693, 642–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eom, K.; Kim, M.; Kim, R.; Nam, D.; Kwon, H. Characterization of hydrogen generation for fuel cells via borane hydrolysis using an electroless-deposited Co–P/Ni foam catalyst. J. Power Sources 2010, 195, 2830–2834. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amoo, K.; Onyeozili, E.; Kalu, E.; Omoleye, J.; Efeovbokhan, V. Activity of varying compositions of Co-Ni-P catalysts for the methanolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2016, 41, 21221–21235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Kim, H.; Kwon, Y.; Kim, M.; Cho, E.; Kwon, H. Porous Co–P foam as an efficient bifunctional electrocatalyst for hydrogen and oxygen evolution reactions. J. Mater. Chem. A 2016, 4, 18272–18277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chou, C.; Chen, B. Hydrogen generation from deliquescence of ammonia borane using Ni-Co/r-GO catalyst. J. Power Sources 2015, 293, 343–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, F.; Dai, Y.; Li, L.; Xu, C.; Huang, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y.; Jiao, L.; Yuan, H. Synthesis of Cu@FeCo core-shell nanoparticles for the catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Int. J. Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 436–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, J.; Li, H.; Zhang, X.; Feng, K.; Yao, Y. Fabrication of a Ti-supported NiCo₂O₄ nanosheet array and its superior catalytic performance in the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 3893–3899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Hu, J.; Lu, H. A stable and efficient 3D cobalt-graphene composite catalyst for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Catal. Sci. Technol. 2016, 6, 7186–7192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oh, S.; Song, D.; Kim, H.; Sohn, D.; Hong, K.; Lee, M.; Son, S.; Cho, E.; Kwon, H. Cobalt-Iron-Phosphorus Catalysts for Efficient Hydrogen Generation from Hydrolysis of Ammonia Borane Solution. J. Alloys Compd. 2019, 806, 643–649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Garcia, A.; Zhu, H.; Yu, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhou, L.; Su, D.; Kramer, M.; Sun, S. Controlled anisotropic growth of Co-Fe-P from Co-Fe-O nanoparticles. Angew. Chem. 2015, 127, 9778–9781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendoza-Garcia, A.; Su, D.; Sun, S. Sea urchin-like cobalt–iron phosphide as an active catalyst for oxygen evolution reaction. Nanoscale 2016, 8, 3244–3247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Zhou, J.; Gao, W.; Zhao, J.; Liu, J.; Zhao, Y.; Wei, M.; Evans, D. G.; Duan, X. Binary Cu–Co Catalysts Derived from Hydrotalcites with Excellent Activity and Recyclability Towards NH3BH3 Dehydrogenation. J. Mater. Chem. A 2013, 1, 5370–5376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).