Submitted:
29 August 2024
Posted:
30 August 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Phytochemical Analyses
2.2. Yield of the Extraction, Total Polyphenols and Flavonoids Content and the Amount of Parietin
2.3. Antibacterial Activity
2.4. Antibiofilm Activity
2.5. Antioxidant Activity
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. The Collection and Identification of Lichen Sample
4.2. Extract Preparation
4.3. Isolation of Parietin
4.4. High-Performance Liquid Chromatography (HPLC) Analysis
4.5. Determination of Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
4.6. Determination of Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
4.7. Antibacterial Activity
4.8. Determination of Antibiofilm Activity
4.8.1. Inhibition of Biofilm Formation
4.8.2. Inhibition of Formed Biofilm
4.9. Antioxidant Activity
4.9.1. Determination of DPPH Free Radical Scavenging Activity
4.9.2. Reduction Capacity
4.10. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ranković, B.; Kosanić, M.; Stanojković, T.; Vasiljević, P.; Manojlović, N. Biological activities of Toninia candida and Usnea barbata together with their norstictic acid and usnic acid constituents. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2012, 13, 14707–14722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojlović, N.; Ranković, B.; Kosanić, M.; Vasiljević, P.; Stanojković, T. Chemical composition of three Parmelia lichens and antioxidant, antimicrobial and cytotoxic activities of some their major metabolites. Phytomedicine. 2012, 19, 1166–1172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kosanic, M.; Rankovic, B.; Stanojkovic, T.; Vasiljevic, P.; Manojlovic, N. Biological activities and chemical composition of lichens from Serbia. Excli J. 2014, 13, 1226–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kocovic, A.; Jeremic, J.; Bradic, J.; Sovrlic, M.; Tomovic, J.; Vasiljevic, P.; Andjic, M.; Draginic, N.; Grujovic, M.; Mladenovic, K.; Baskic, D.; Popovic, S.; Matic, S.; Zivkovic, V.; Jeremic, N.; Jakovljevic, V.; Manojlovic, N. Phytochemical Analysis, Antioxidant, Antimicrobial, and Cytotoxic Activity of Different Extracts of Xanthoparmelia stenophylla Lichen from Stara Planina, Serbia. Plants. 2022, 11, 1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solárová, Z.; Liskova, A.; Samec, M.; Kubatka, P.; Büsselberg, D.; Solár, P. Anticancer Potential of Lichens' Secondary Metabolites. Biomol. 2020, 10, 87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Breuss, O. An updated world-wide key to the catapyrenioid lichens (Verrucariaceae). Herzogia. 2010, 23, 205–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prieto, M.; Martınez, I.; Aragon, G.; Gueidan, C.; Lutzoni, F. Molecular phylogeny of Heteroplacidium, Placidium, and related catapyrenioid genera (Verrucariaceae, lichen-forming Ascomycota). Am. J. Bot. 2012, 99, 23–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Usman, M.; Dyer, P.S.; Khalid, A.N. A novel arctic-alpine lichen from Deosai National Park, Gilgit Baltistan, Pakistan. Bryologist. 2021, 124, 484–493. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, Z. Vegetation analysis, grassland productivity and carrying capacity of Deosai National Park, Gilgit-Baltistan. Doctoral dissertation, Arid Agriculture University Rawalpindi Pakistan, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, K.S.; Jan, S.A. Deosai National Park: conservation, control and conflicts. PUTAJ-HSS. 2018, 25, 59–66. [Google Scholar]
- WAPDA. Meteorological Data on Deosai Plains (Watersheds of Sadpara Dam Skardu). Unpublished Data recorded from Water & Power Development Authority, Government of Pakistan, Lahore. 2012.
- Bellemain, E.; Nawaz, M.A.; Valentini, A.; Swenson, J.E.; Taberlet, P. Genetic tracking of the brown bear in northern Pakistan and implications for conservation. Biol. Conserv. 2007, 134, 537–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halıcı, M.; Güllü, M.; Kahraman, Y.M.; Barták, M. Three new records of lichenised fungi for Antarctica. Polar Rec. 2022, 58, E22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Zhang, X.; Yang, Q.; Wei, X. Hidden Species Diversity was Explored in Two Genera of Catapyrenioid Lichens (Verrucariaceae, Ascomycota) from the Deserts of China. J. Fungi. 2022, 8, 729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oettl, S.K.; Gerstmeier, J.; Khan, S.Y.; Wiechmann, K.; Bauer, J.; Atanasov, A.G.; Rollinger, J.M. Imbricaric acid and perlatolic acid: Multi-targeting anti-inflammatory depsides from Cetrelia monachorum. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e76929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, T.K.; Siva, B.; Anand, A.; Anusha, K.; Mohabe, S.; Reddy, A.M.; Le Devehat, F.; Tiwari, A.K.; Boustie, J.; Babu, K.S. Comprehensive Lichenometabolomic Exploration of Ramalina conduplicans Vain Using UPLC-Q-ToF-MS/MS: An Identification of Free Radical Scavenging and Anti-Hyperglycemic Constituents. Molecules. 2022, 27, 6720. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, Y. E.; Kodama, T.; Morita, H. Novel insights into the antibacterial activities of cannabinoid biosynthetic intermediate, olivetolic acid, and its alkyl-chain derivatives. J. Nat. Med. 2023, 77, 298–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biskup, I.; Zaczynska, E.; Krauze-Baranowska, M.; Fecka, I. Evaluation of cytotoxicity of 5-n-alkylresorcinol homologs and fraction on mouse fibroblast cell line L929. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2017, 243, 1137–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnson, C.J. Imbricaric Acid and Perlatolic Acid: Multi-Targeting Anti-Inflammatory Depsides from Cetreliamonachorum. PLoS One. 2013, 8, e76929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kearsey, L.J.; Prandi, N.; Karuppiah, V.; Yan, C.; Leys, D.; Toogood, H.; Takano, E.; Scrutton, N.S. Structure of the Cannabis sativa olivetol-producing enzyme reveals cyclization plasticity in type III polyketide synthases. FEBS J. 2020, 287, 1511–1524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Đukić, V.; Usman, M.; Khalid, A.N.; Manojlović, A.; Zarić, M.; Čanović, P.; Živković-Zarić, R.; Manojlović, N. Phytochemical composition and antitumor activity of a new arctic lichen Anamylopsora pakistanica. Nat. Prod. Res. 2024, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojlović, T.N.; Solujić, S.; Sukdolak, S.; Krstić, L.J. Anthraquinones from the lichen Xanthoria parietina. J. Serb. Chem. Soc. 1998, 63, 7–11. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A.H.; Negi, N.; Gahtori, R.; Kumari, A.; Joshi, P.; Tewari, L.M.; Joshi, Y.; Rajesh, B.; Upreti, D.K.; Upadhyay, S. K. A review of anti-cancer and related properties of lichen-extracts and metabolites. Anti-Cancer Agent. ME. 2022, 22, 115–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stanly, C.; Hag Ali, D.M.; Keng, C.L.; Boey, P.L.; Bhatt, A. Comparative evaluation of antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of selected lichen species from Malaysia. J Pharm Res 2011, 4, 2824–2827. [Google Scholar]
- Díaz-Reinoso, B.; Rodríguez-González, I.; Domínguez, H. Towards greener approaches in the extraction of bioactives from lichens. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2021, 20, 917–942. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, P.; Logesh, A.; Upreti, D.; Dhole, T.; Srivastava, A. In-vitro evaluation of some Indian lichens against human pathogenic bacteria. Mycosphere 2013, 4, 734–743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valadbeigi, T.; Shaddel, M. Antibacterial and Antifungal Activities of Gelatinose and non-Gelatinose Lichen Species. J. Arch. Mil. Med. 2015, 3, e31610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, B.; Nath, A.; Saikia, H.; Sengupta, M. Bactericidal activity of selected medicinal plants against multidrug resistant bacterial strains from clinical isolates. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2014, 7, S435–S441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, M.Z.; Rao, T.; Khan, N.A.; Aslam, M.; Pane, Y.S. Antimicrobial Activities of Lichens. In Chemistry, Biology and Pharmacology of Lichen, 1st ed.; John Wiley & Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; Volume 13, pp. 169–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, P.; Nayaka, S.; Verma, T.; Niranjan, A.; Upreti, D.K. Comparative analysis of antimicrobial, antioxidant activities and phytochemicals of Himalayan lichens. Biomass Conv. Bioref. 2024, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sargsyan, R.; Gasparyan, A.; Tadevosyan, G.; Panosyan, H. Antimicrobial and antioxidant potentials of non-cytotoxic extracts of corticolous lichens sampled in Armenia. AMB Expr. 2021, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basile, A.; Rigano, D.; Loppi, S.; Di Santi, A.; Nebbioso, A.; Sorbo, S.; Conte, B.; Paoli, L.; De Ruberto, F.; Molinari, A.M.; Altucci, L.; Bontempo, P. Antiproliferative, Antibacterial and Antifungal Activity of the Lichen Xanthoria parietina and Its Secondary Metabolite Parietin. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 7861–7875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- May Zin, W.W.; Buttachon, S.; Dethoup, T.; Pereira, J.A.; Gales, L.; Inácio, A.; Costa, P.M.; Lee, M.; Sekeroglu, N.; Silva, A.M.S.; Pinto, M.M.M.; Kijjoa, A. Antibacterial and antibiofilm activities of the metabolites isolated from the culture of the mangrove-derived endophytic fungus Eurotium chevalieri KUFA 0006. Phytochem. 2017, 141, 86–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmir, M.; Serrano, R.; Silva, O. Anthraquinones as potential antimicrobial Agents–a Review. In Antimicrobial Research: Novel Bioknowledge and educational Programs, 1st ed.; Méndez Vilas, A., Ed.; Formatex Research Center S.L.: Badajoz, Spain, 2017; Volume 20, pp. 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitrovic, T.; Stamenkovic, S.; Cvetkovic, V.; Radulovic, N.; Mladenovic, M.; Stankovic, M.; Topuzovic, M.; Radojevic, I.; Stefanovic, O.; Vasic, S.; Comic, L. Platismatia glaucia and Pseudevernia furfuracea lichens as sources of antioxidant, antimicrobial and antibiofilm agents. EXCLI J. 2014, 13, 938–953. [Google Scholar]
- Nomura, H.; Isshiki, Y.; Sakuda, K.; Sakuma, K.; Kondo, S. Effects of oakmoss and its components on biofilm formation of Legionella pneumophila. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2013, 36, 833–837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pompilio, A.; Pomponio, S.; Di Vincenzo, V.; Crocetta, V.; Nicoletti, M.; Piovano, M.; Garbarino, J.A.; Di Bonaventura, G. Antimicrobial and antibiofilm activity of secondary metabolites of lichens against methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus strains from cystic fibrosis patients. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 281–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gökalsın, B.; Sesal, N.C. Lichen Secondary Metabolite Evernic Acid as Potential Quorum Sensing Inhibitor Against Pseudomonas Aeruginosa. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2016, 32, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sweidan, A. Antibiofilm activity of lichen secondary metabolites. Doctoral dissertation, Human health and pathology. Institut des Sciences Chimiques de Rennes. Université de Rennes, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Tomović, J.; Kosanić, M.; Ranković, B.; Vasiljević, P.; Najman, S.; Manojlović, N. Phytochemical analysis and biological ac-tivity of extracts of lichen Physcia Semipinnata: As a new source of pharmacologically active compounds. Farmacia. 2019, 67, 346–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Güllüce, M.; Sökmen, M.; Adιgüzel, A.; Sahin, F.; Özkan, H. Antioxidant and Antimicrobial Properties of the Lichens Cladonia foliacea., Dermatocarpon miniatum., Everinia divaricata., Evernia prunastri., and Neofuscella pulla. Pharm. Biol. 2006, 44, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Taslimi, P.; Gulçin, İ. Antioxidant and anticholinergic properties of olivetol. J. Food Biochem 2018, 42, e12516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yenigun, S.; Ipek, Y.; Marah, S.; Demirtas, I.; Ozen, T. DNA protection, molecular docking, antioxidant, antibacterial, enzyme inhibition, and enzyme kinetic studies for parietin, isolated from Xanthoria parietina (L.) Th. Fr. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2024, 42, 848–862. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boulebd, H.; Spiegel, M. Computational assessment of the primary and secondary antioxidant potential of alkylresorcinols in physiological media. RSC Adv. 2023, 13, 29463–29476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ranković, B.; Ranković, D.; Kosanić, M.; Marić, D. Antioxidant and antimicrobial properties of the lichen Anaptychia ciliaris, Nephroma parile, Ochrolechia tartarea and Parmelia centrifuga. Cent. Eur. J. Biol. 2010, 5, 649–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P. A.; Oliveira, R.C.; Oliveira, A.P.; Serafini, M.R.; Araújo, A.A.; Gelain, D.P.; Moreira, J.C.F.; Almeida, J.R.G.S.; Quintans, J.S.S.; Quintans-Junior, L.J.; Santos, M.R. Antioxidant activity and mechanisms of action of natural compounds isolated from lichens: A systematic review. Molecules 2014, 19, 14496–14527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dobson, F.S. Lichens. In An illustrated guide to the British and Irish species, 6th ed.; Richmond Publishing Co.: London, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Huneck, S.; Yoshimura, I. Identification of Lichen Substances, 1st ed.; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1996; pp. 125–446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manojlović, N.T.; Rančić, A.B.; Décor, R.; Vasiljević, P.; Tomović, J. Determination of chemical composition and antimicrobial, antioxidant and cytotoxic activities of lichens Parmelia conspersa and Parmelia perlata. J. Food Meas. Charact. 2020, 15, 686–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aoussar, N.; Achmit, M.; Es-Sadeqy, Y.; Vasiljević, P.; Rhallabi, N.; Ait Mhand, R.; Zerouali, K.; Manojlović, N.; Mellouki, F. Phytochemical constituents, antioxidant and antistaphylococcal activities of Evernia prunastri (L.) Ach., Pseudevernia furfuracea (L.) Zopf. and Ramalina farinacea (L.) Ach. from Morocco. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 2887–2894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singleton, V.L.; Orthofer, R.; Lamuela-Raventós, R.M. Analysis of total phenols and other oxidation substrates and antioxidants by means of folin-ciocalteu reagent. Methods. Enzymol. 1999, 299, 152–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brighente, I.M.C.; Dias, M.; Verdi, L.G.; Pizzolatti, M.G. 2007. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of some brazilian species. Pharm. Biol. 2007, 45, 156–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute (CLSI). Methods for Dilution Antimicrobial Susceptibility Tests for Bacteria That Grow Aerobically; Approved Standard – Ninth Edition. CLSI document M07-A9, Wayne, Pennsylvania, USA, 2012.
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Bonaventura, G.D.; Djukić, S.; Ćirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. APMIS. 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ali, I.A.; Matinlinna, J.P.; Lévesque, C.M.; Neelakantan, P. Trans-cinnamaldehyde attenuates Enterococcus faecalis virulence and inhibits biofilm formation. Antibiotics 2021, 10, 702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takao, T.; Kitatani, F.; Watanabe, N.; Yagi, A.; Sakata, K. A simple screening method for antioxidants and isolation of several antioxidants produced by marine bacteria from fish and shellfish. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 1994, 58, 1780–1783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oyaizu, M. Studies on products of browning reaction prepared from glu-coseamine. Jpn. J. Nutr. 1986, 44, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Solhaug, K.A.; Gauslaa, Y. Parietin, a photoprotective secondary product of the lichen Xanthoria parietina. Oecologia. 1996, 108, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahselt, D. Secondary biochemistry of lichens. Symbiosis. 1994, 16, 117–165. [Google Scholar]
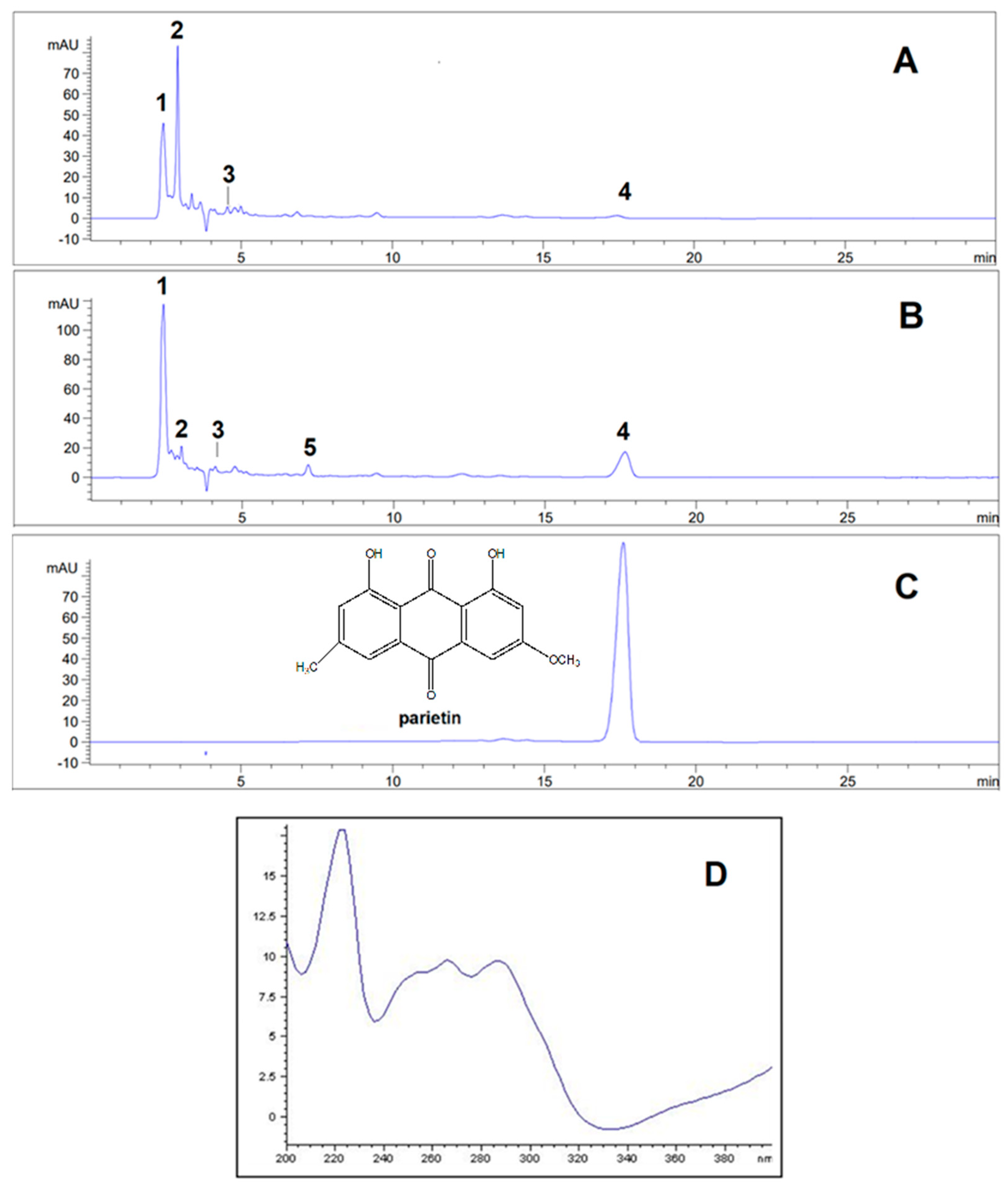
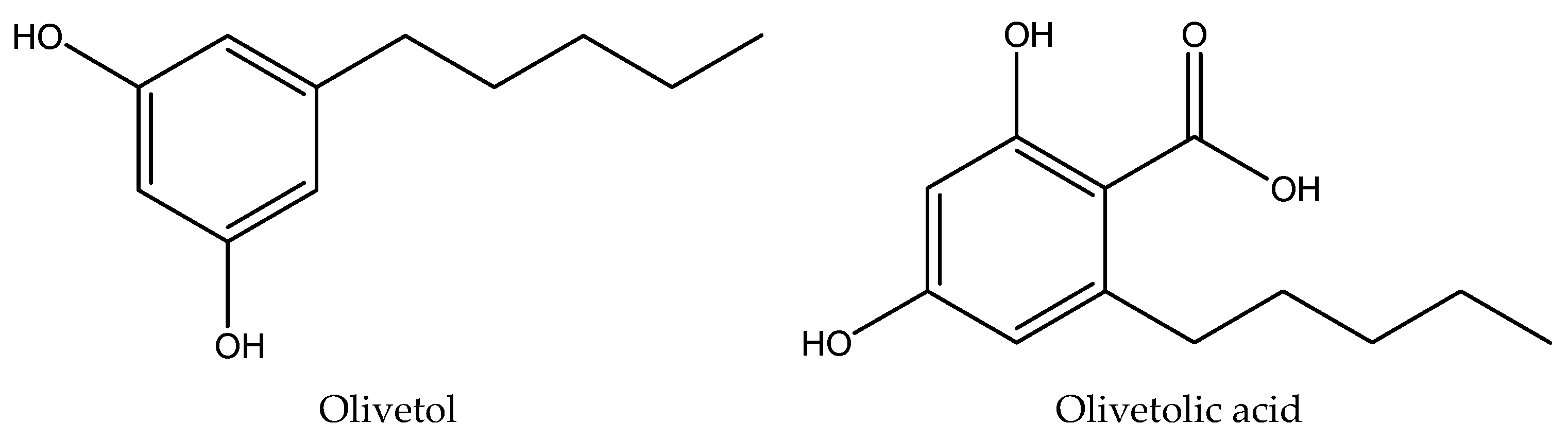
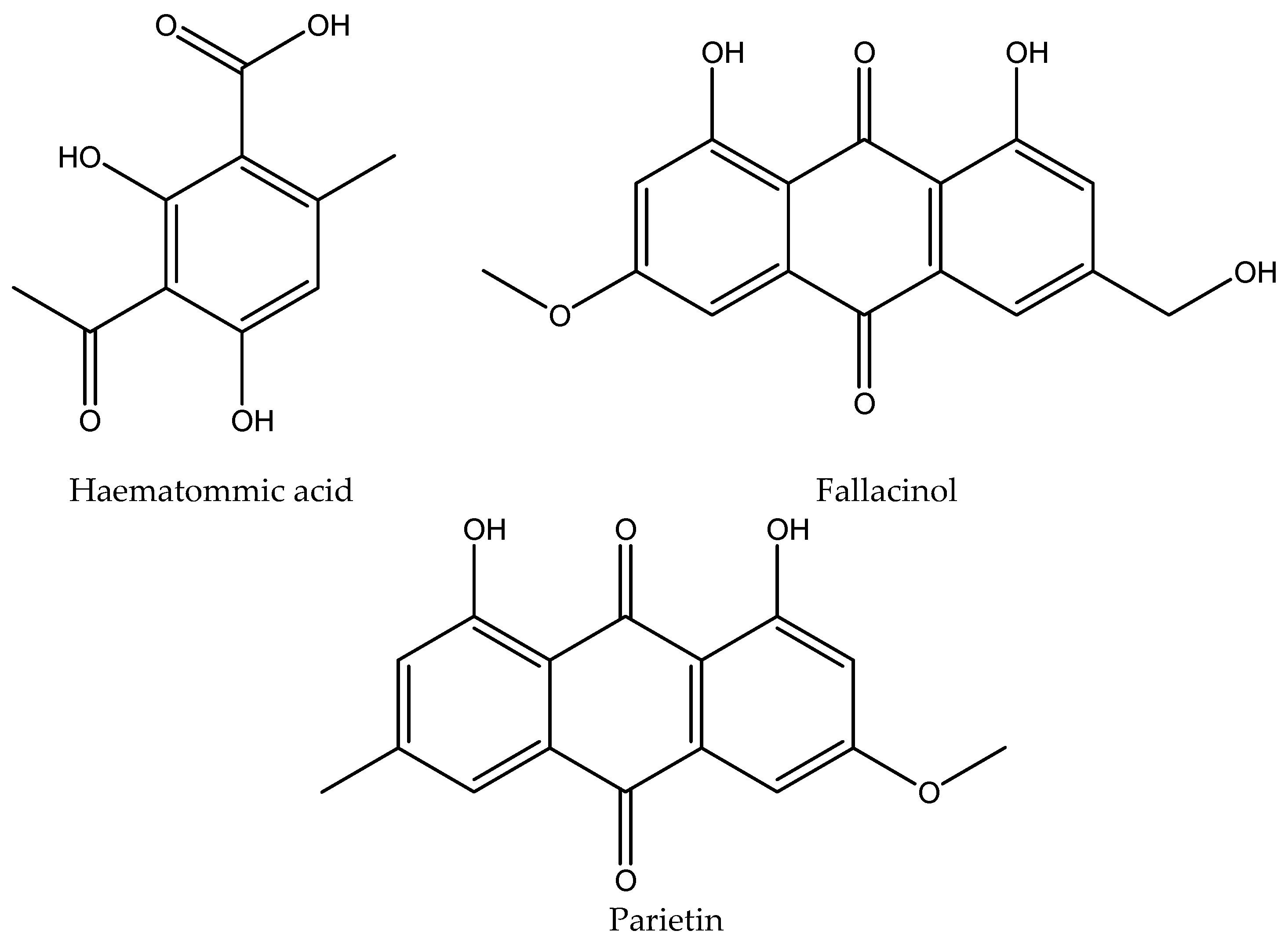
| Sr. no | Compound |
Retention time (tR±SD)* (min) |
Absorbance maxima (nm) | Relative abundance % (254 nm) |
|
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Extracts** | |||||
| Acetone | Methanol | ||||
| 1 | Olivetol | 2.42±0.01 | 278 | 20.3995 | 34.0514 |
| 2 | Olivetolic acid | 2.91±0.02 | 218, 263, 301 | 25.8901 | 4.0678 |
| 3 | Haematommic acid | 4.56±0.01 | 202, 237, 259 | 5.3064 | 2.2663 |
| 4 | Parietin | 17.54±0.02 | 222, 266, 286, 438 | 1.0588 | 10.7476 |
| 5 | Fallacinol | 7.20±0.01 | 223, 325, 435 | / | 1.6712 |
| Lichen extracts | Yield (%) |
Phenolics content (mg GA/g) |
Flavonoids content (mg RE/g) |
Amount of parietin (mg/mL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acetone Methanol |
0.676 | 19.46 ± 0.75 | 44.29 ± 2.79 | 0.028 |
| 1.063 | 21.67 ± 0.41 | 377.40 ± 10.38 | 0.310 |
| Bacterial species | Acetone | Methanol | Parietin | Tetracycline | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | MIC | MBC | |
| mg/mL | µg/mL | |||||||
| Escherichia coli ATCC 25922 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | 4 | 6 |
| Proteus mirabilis ATCC 12453 | 2.5 | >10 | 1.25 | >10 | >10 | >10 | 64 | >128 |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | 32 | >128 |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | 2 | 3 |
| Staphylococcus aureus MRSA ATCC 43300 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | <0.25 | 3 |
| Enterococcus faecalis ATCC 29212 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | >10 | 8 | 12 |
| Bacillus cereus ATCC 11778 | 5 | 5 | 10 | 10 | >10 | >10 | 0.25 | 0.5 |
| Acetone extract | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial species | 10 mg/mL | 5 mg/mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 1.25 mg/mL | 0.625 mg/mL | 0.3125 mg/mL |
| Proteus mirabilis ATCC 12453 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 | 92.1 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 92.0 | 91.1 | 87.9 | 90.6 | 66.8 | 54.2 |
| Methanol extract | ||||||
| Proteus mirabilis ATCC 12453 | 36.0 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 | 81.7 | 4.7 | / | / | / | / |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 90.3 | 89.7 | 85.2 | 73.4 | 68.9 | 63.7 |
| Parietin | ||||||
| Proteus mirabilis ATCC 12453 | 92.5 | 25.6 | / | / | / | / |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 | 99.8 | 48.1 | / | / | / | / |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 99.6 | 91.1 | 89.8 | 92.3 | 93.5 | 63.6 |
| Acetone extract | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Bacterial species | 10 mg/mL | 5 mg/mL | 2.5 mg/mL | 1.25 mg/mL | 0.625 mg/mL | 0.3125 mg/mL |
| Proteus mirabilis ATCC 12453 | 10.2 | 8.3 | 5.1 | / | / | / |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 | 28.8 | 23.7 | 20.2 | / | / | / |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 69.8 | 63.6 | 59.8 | 62.0 | 52.0 | / |
| Methanol extract | ||||||
| Proteus mirabilis ATCC 12453 | 20.4 | 11.9 | / | / | / | / |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 | / | / | / | / | / | / |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 75.5 | 72.3 | 68.9 | 66.8 | 59.9 | 48.4 |
| Parietin | ||||||
| Proteus mirabilis ATCC 12453 | 3.4 | 3.0 | / | / | / | / |
| Pseudomonas aeruginosa ATCC 10145 | 59.58 | / | / | / | / | / |
| Staphylococcus aureus ATCC 25923 | 85.3 | 73.7 | 56.4 | 51.85 | 47.3 | 39.4 |
| Lichen extract/ compound |
DPPH scavenging IC50 (μg/mL) | Reducing power Absorbance (700 nm) |
|||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1000 μg/mL | 500 μg/mL | 250 μg/mL | 125 μg/mL | 62.5 μg/mL | 31.25 μg/mL | ||
| Acetone | 270.22±4.80 | 0.074±0.001 | 0.059±0.001 | 0.060±0.001 | 0.056±0.001 | 0.055±0.001 | 0.053±0.002 |
| Methanol | 275.124±9.713 | 0.0853±0.001 | 0.066±0.004 | 0.066±0.001 | 0.062±0.002 | 0.062±0.002 | 0.061±0.002 |
| Parietin | 51.616±0.490 | 0.1036±0.001 | 0.1026±0.001 | 0.097±0.001 | 0.095±0.001 | 0.093±0.001 | 0.091±0.001 |
| Ascorbic acid | 4.451±0.202 | 1.541±0.054 | 0.853±0.005 | 0.406±0.017 | 0.215±0.004 | 0.110±0.015 | 0.105±0.003 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





