Submitted:
29 August 2024
Posted:
02 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Background
Purpose
History of Ransomware
How does ransomware work (Architecture of ransomware)
- ➢
- Stage 1: Infection- The infection is usually spread through a few notable methods such as email(malware) where this email contains trap attachments or links redirecting to malicious websites (Choi, Lee and Merizalde, 2023), spear phishing where the attacker impersonates as someone else which required you to click on some link via email where the email is a malware, social engineering where it uses the Trojan Horse Virus and lastly software vulnerability. These are the few common methods that will lead to infection.
- ➢
- Stage 2: Execution- The execution method used is via command and control(C&C) server. Once this server is set up, the attackers will send encryption keys to the target system, download additional malware if needed facilitate the following progress, and give instructions.
- ➢
- Stage 3: Discovery and lateral movement- This 2-step action involves where attackers familiarize themselves with the victim network structure, allowing them to seek out important data before launching the attack. In this stage, they will also spread the infection to other devices.
- ➢
- Stage 4: Deployment- After identifying the targeted data, attackers will encrypt these data using an encryption algorithm and prevent the victim from accessing them lock the device screen and flood them with pop-ups, or disable the victim form using the computer.
- ➢
- Stage 5: Ransom demand- A note will be then displayed to the victim demanding payment to regain access to its data or computer system in exchange for the decryption key.
Technologies Involved in Ransomware
- Infect and Execution- Attackers need a few tools to aid them in infecting and executing their attack. The tools are phishing tools, exploited kits, and commands to control servers. Phishing tools are used to create fake emails and websites that look legitimate to hook victims to click on them, while exploited kits are used to exploit vulnerabilities in the victim's system. (Öztürk. 2024), (Trendmicro. n.d.) Lastly, the command and control servers are used to obtain confidential information from a target network and issue commands to malware-infected systems. (Trendmicro. n.d.)
- Encryption- Advanced Encryption Standard (AES) and Rivest, Shamir, Adleman (RSA) are the 2 most common algorithms used for encrypting data. AES is a type of symmetric encryption algorithm that could quickly encrypt many files. (Murphy. 2023) RSA is client asymmetric encryption where there will be 2 keys- a public and a private key. RSA is used for a more secure key exchange however; it needs a much longer time to encrypt data. (Murphy. 2023)
- Ransom Payment- Payments are likely to be carried out via cryptocurrency due to its anonymity. The most common forms of cryptocurrency used for payment are Bitcoin and Monero. Bitcoin allows ease of transfer whereas Monero has been favored lately due to its enhanced security protocol which makes it harder to trace. (Gren. 2024; James, 2024)
Discussion on Security Issues
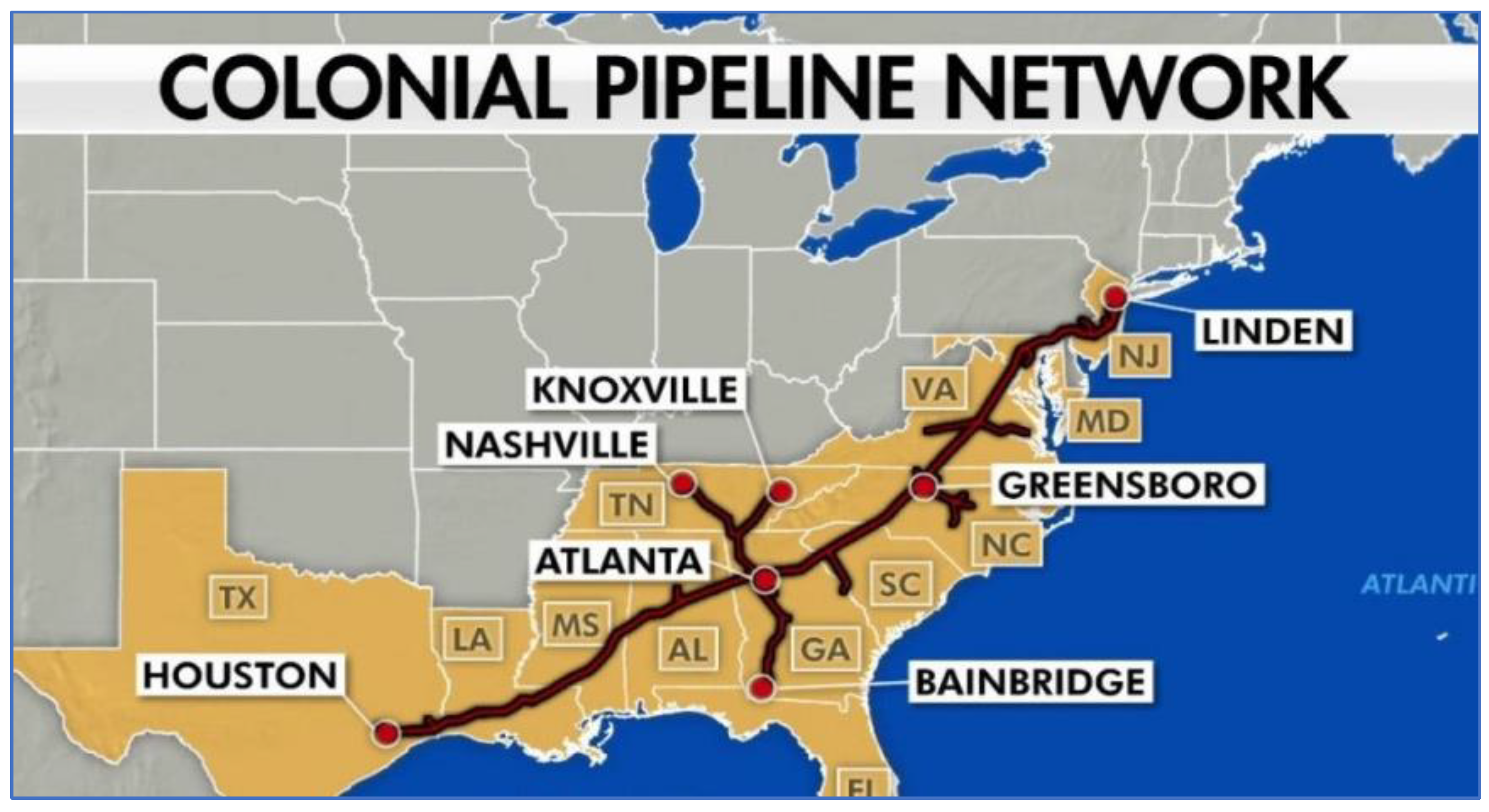
Case 1 (Colonial Pipeline. 2021)Figure 1
Introduction
Security Issues
Potential Security Threats
Lessons
Recommendations For Improving
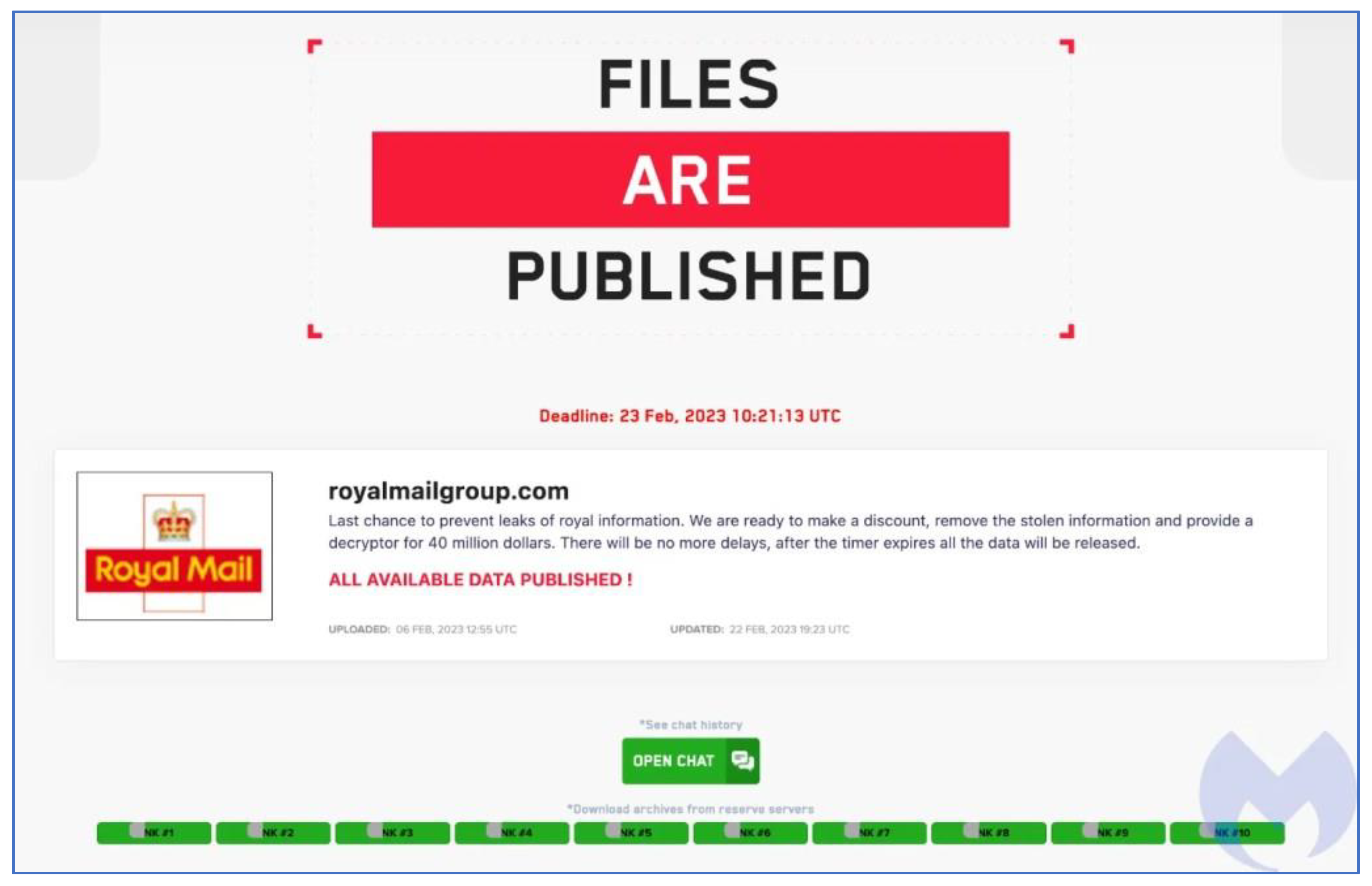
Case 2 (Royal Mail, LockBit Ransomware. 2023) Figure 2
Impact
Security Issue
Potential Security Threats
Recommendations For Improvement
Discussion on Security Countermeasures
Security Countermeasures
Case 1 (Colonial Pipeline. 2021)
- (a)
- Antivirus and Antimalware
- (b)
- Regular Backups
- (c)
- Patch Management
- (d)
- Security Awareness Training
- (e)
- Network Segmentation
Case 2 (Royal Mail, LockBit Ransomware. 2023)
- (a)
- Antivirus and Antimalware
- (b) Regular Backups
- (c) Patch Management
- (d) Security Awareness Training
- (e) Network Segmentation
Proposed Counterm easures
Case 1 (Colonial Pipeline. 2021)
- (a)
- Implementation of Advanced VPN Security:
- (b)
- Enhanced Password Management:
- (c)
- Network Segmentation and Zero Trust Architecture:
- (d)
- Regular Security Audits and Penetration Testing:
- (e)
- Incident Response and Backup Strategy:
- (f)
- Threat Intelligence and Monitoring:
Case 2 (Royal Mail, LockBit Ransomware. 2023)
- (a)
- AI-Driven Threat Detection
- (b)
- Dynamic Analysis of Malware
- (c)
- Automated Patching and Updates
Conclusion
References
- Alkinani, M.H.; et al. (2021) '5G and IoT Based Reporting and Accident Detection (RAD) System to Deliver First Aid Box Using Unmanned Aerial Vehicle,' Sensors, 21(20), p. 6905. [CrossRef]
- Almusaylim, Z.A. , Zaman, N. and Jung, L.T. (2018) 'Proposing A Data Privacy-Aware Protocol for Roadside Accident Video Reporting Service Using 5G In Vehicular Cloud Networks Environment,' 2018 4th International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCOINS) [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. , Hafeez, Y., Humayun, M., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Le, D. N. (2022). Towards aspect based requirements mining for trace retrieval of component-based software management process in globally distributed environment. Information Technology and Management, 23(3), 151-165.
- Almoysheer, Najd, Mamoona Humayun, and N. Z. Jhanjhi. "Enhancing Cloud Data Security using Multilevel Encryption Techniques." Turkish Online Journal of Qualitative Inquiry 12, no. 3 (2021).
- Alsharif, Mohammed H., Abu Jahid, Anabi Hilary Kelechi, and Raju Kannadasan. "Green IoT: A review and future research directions." Symmetry 15, no. 3 (2023): 757.
- Alqahtani, A. and Sheldon, F.T. (2024) 'EMIFS: a normalized hyperbolic ransomware deterrence model yielding greater accuracy and overall performance,' Sensors, 24(6), p. 1728. [CrossRef]
- Amaan, R. (2024). LockBit Ransomware Creator’s Face Revealed and Sanctioned [online]. Available from: https://www.techworm.net/2024/05/lockbit-ransomware-creator-face-revealed.html [accessed 16 May 2024].
- Amanda, S. (2023). What Is a Countermeasure in Computer Security. Available from: https://www.comptia.org/blog/what-is-a-countermeasure-in-computer-security [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Anastasia (2024) Ransomware goes political and other extortion activity of 2023, Analyst1. Available from: https://analyst1.com/ransomware-goes-political-and-other-extortion-activity-of-2023/ [Accessed: 17 May 2024].
- Anon (n.d.) A guide to ransomware [internet]. Available from: https://www.ncsc.gov.uk/ransomware/home. [Accessed: 17 May 2024].
- Anon (n.d.) Exploit Kit [Internet]. Available from: https://www.trendmicro.com/vinfo/us/security/definition/exploit-kit [Accessed: 17 May 2024].
- Avey, C. (2024). Essential steps to prevent a ransomware attack. Available from: https://www.bcs.org/articles-opinion-and-research/essential-steps-to-prevent-a-ransomware-attack/ [accessed 26 May 2024].
- Bachchas, K S. (2024). The rise of ransomware: Strategies for prevention. Available from: https://cybersecurity.att.com/blogs/security-essentials/the-rise-of-ransomware-strategies-for-prevention [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Begovic, K. , Al-Ali, A. and Malluhi, Q. (2023) 'Cryptographic ransomware encryption detection: Survey,' Computers & Security, 132, p. 103349. [CrossRef]
- Buikema, N. (2023). International Deliveries in Limbo – How Royal Mail Could Have Avoided Ransomware Attack. Available from: https://www.pcmatic.com/blog/international-deliveries-in-limbo-how-royal-mail-could-have-avoided-ransomware-attack/ [accessed 26 May 2024].
- Cen, M.; et al. (2024) 'Ransomware early detection: A survey,' Computer Networks, 239, p. 110138. [CrossRef]
- Chin, K. , 2024. How to Prevent Ransomware Attack: Top 10 Best Practices. [Online] Available at: https://www.upguard.com/blog/best-practices-to-prevent-ransomware-attacks [Accessed 18 5 2024].
- Choi, K.-S. , Lee, C.S. and Merizalde, J. (2023) 'Spreading viruses and malicious codes,' in Edward Elgar Publishing eBooks, pp. 232–250. [CrossRef]
- CIS. (2023). 7 Steps to Help Prevent & Limit the Impact of Ransomware. Available from: https://www.cisecurity.org/insights/blog/7-steps-to-help-prevent-limit-the-impact-of-ransomware [accessed 15 May 2024].
- CM-Alliance. (2024). Ransomware Resilience: Prevention and Recovery in 2024. Available from: https://www.cm-alliance.com/cybersecurity-blog/ransomware-resilience-prevention-and-recovery-in-2024 [accessed 26 May 2024].
- Connor, J. (2023). LockBit leaks 44GB of Royal Mail's data and sets fresh £33 million ransom [online]. Available from: https://www.itpro.com/security/ransomware/370124/lockbit-leaks-44gb-royal-mails-data-sets-fresh-ps33-million-ransom [accessed 16 May 2024].
- Cybersecurity & Infrastructure Security Agency (CISA). (2024). The Attack on Colonial Pipeline: What We’ve Learned & What We’ve Done Over the Past Two Years. [online] Available from: https://www.cisa.gov/news-events/news/attack-colonial-pipeline-what-weve-learned-what-weve-done-over-past-two-years [accessed 14 May 2024].
- Dogra, V. , Singh, A., Verma, S., Kavita, Jhanjhi, N.Z., Talib, M.N. (2021). Analyzing DistilBERT for Sentiment Classification of Banking Financial News. In: Peng, SL., Hsieh, SY., Gopalakrishnan, S., Duraisamy, B. (eds) Intelligent Computing and Innovation on Data Science. Lecture Notes in Networks and Systems, vol 248. Springer, Singapore. [CrossRef]
- Edwards, L. , Iqbal, M.Z. and Hassan, M. (2024) 'A multi-layered security model to counter social engineering attacks: a learning-based approach,' International Cybersecurity Law Review, 5(2), pp. 313–336. [CrossRef]
- Fatima-Tuz-Zahra, N.; et al. (2020) 'Proposing a Hybrid RPL Protocol for Rank and Wormhole Attack Mitigation using Machine Learning,' 2020 2nd International Conference on Computer and Information Sciences (ICCIS) [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Fazzino. (2023). Cybersecurity Defense-in-Depth Using AI and ML. Available from: https://www.jackhenry.com/fintalk/cybersecurity-defense-in-depth-using-ai-and-ml [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Ferdowsi, O. (2021). Lessons from Colonial Pipeline- How Your Company Can Avoid Ransomware Attacks. Available from: https://www.comtechlocation.com/blog/lessons-from-colonial-pipeline-how-your-company-can-avoid-ransomware-attacks [accessed 26 May 2024].
- Fox, J. (2023). 11 Biggest Ransomware Attacks in History. [online] Available from: https://www.cobalt.io/blog/11-biggest-ransomware-attacks-in-history [accessed 13 May 2024].
- Gatlan, S. (2023). LockBit ransomware gang claims Royal Mail cyberattack. Available from: https://www.bleepingcomputer.com/news/security/lockbit-ransomware-gang-claims-royal-mail-cyberattack/ [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Gaur, L. & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (Eds.). (2023). Digital Twins and Healthcare: Trends, Techniques, and Challenges, IGI Global. [CrossRef]
- Ghani, Norjihan Binti Abdul, Suraya Hamid, Muneer Ahmad, Younes Saadi, N. Z. Jhanjhi, Mohammed A. Alzain, and Mehedi Masud. "Tracking Dengue on Twitter Using Hybrid Filtration-Polarity and Apache Flume." Comput. Syst. Sci. Eng. 40, no. 3 (2022): 913-926.
- Ghosh, G.; et al. (2020) 'Secure surveillance system using chaotic image encryption technique,' IOP Conference Series Materials Science and Engineering, 993(1), p. 012062. [CrossRef]
- Gopi, R.; et al. (2021) 'Enhanced method of ANN based model for detection of DDoS attacks on multimedia internet of things,' Multimedia Tools and Applications, 81(19), pp. 2 6739–26757. [CrossRef]
- Gouda, W.; et al. (2022) 'Detection of COVID-19 based on chest x-rays using deep learning,' Healthcare, 10(2), p. 343. [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M. , Ashfaq, F., et al. (2022) 'Traffic management: Multi-Scale vehicle detection in varying weather conditions using YOLOV4 and spatial pyramid pooling network,' Electronics, 11(17), p. 2748. [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M. , Sujatha, R., et al. (2022) 'A Transfer Learning Approach with a Convolutional Neural Network for the Classification of Lung Carcinoma,' Healthcare, 10(6), p. 1058. [CrossRef]
- Humayun, M. , Khalil, M. I., Alwakid, G., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2022). Superlative feature selection based image classification using deep learning in medical imaging. Journal of Healthcare Engineering 2022, 2022, 7028717. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Humayun, M. Z. Jhanjhi, B. Hamid, and G. Ahmed. "Emerging smart logistics and transportation using IoT and blockchain. IEEE Internet of Things Magazine, 3 (2), 58-62." (2020).
- H. Ashraf, F. H. Ashraf, F. Khan, U. Ihsan, F. Al-Quayed, N. Z. Jhanjhi and M. Humayun, "MABPD: Mobile Agent-Based Prevention and Black Hole Attack Detection in Wireless Sensor Networks," 2023 International Conference on Business Analytics for Technology and Security (ICBATS), Dubai, United Arab Emirates, 2023, pp. 1-11. [CrossRef]
- Hurley, A. , 2023. How AI is changing ransomware and how you can adapt to stay protected. [Online] Available at: https://blog.barracuda.com/2023/11/13/ai-ransomware-adapt-stay-protected [Accessed 26 5 2024].
- Intel. (2023). What Is Patch Management. Available from: https://www.intel.com/content/www/us/en/business/enterprise-computers/resources/patch-management.html [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Intelligence, T. , 2024. Network Segmentation and How it Can Prevent Ransomware. [Online] Available at: https://www.threatintelligence.com/blog/network-segmentation [Accessed 26 5 2024].
- Jayakumar, P. , Brohi, S. N., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2021). Artificial intelligence and military applications: Innovations, cybersecurity challenges & open research areas.
- Javaid, Mohd, Abid Haleem, Ravi Pratap Singh, Shahbaz Khan, and Rajiv Suman. "An extensive study on Internet of Behavior (IoB) enabled Healthcare-Systems: Features, facilitators, and challenges." BenchCouncil Transactions on Benchmarks, Standards and Evaluations 2, no. 4 (2022): 100085.
- Jhanjhi, N. Z. , Sahil Verma, M. N. Talib, and Gagandeep Kaur. "A canvass of 5G network slicing: Architecture and security concern." In IOP Conference Series: Materials Science and Engineering, vol. 993, no. 1, p. 012060. IOP Publishing, 2020.
- J.P. Morgan. (2024). The Potential Impacts of Ransomware. [online] Available from:https://www.jpmorgan.com/technology/news/the-potential-impacts-of-ransomware [accessed 13 May 2024].
- James, A T. (2024). From Origins to Double-Extortion: The Evolution of Ransomware Tactics. Available from: https://www.spiceworks.com/it-security/vulnerability-management/guest-article/evolution-of-ransomware-tactics/ [accessed 28 May 2024].
- James, M. (2020). How to Deal with Ransomware Attacks. Available from: https://www.metacompliance.com/blog/cyber-security-awareness/how-to-deal-with-ransomware-attacks [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Jasper, J. (2023). Royal Mail ransomware attackers threaten to publish stolen data [online]. Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2023/jan/12/royal-mail-ransomware-attackers-threaten-to-publish-stolen-data [accessed 13 May 2024].
- Jones, C. (2023). Royal Mail’s recovery from ransomware attack will cost business at least $12M. Available from: https://www.theregister.com/2023/11/16/royal_mail_recovery_from_ransomware/ [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Kelly, S. & Resnick-ault, J. (2021). One password allowed hackers to disrupt Colonial Pipeline, CEO tells senators. [online] Available from: https://www.reuters.com/business/colonial-pipeline-ceo-tells-senate-cyber-defenses-were-compromised-ahead-hack-2021-06-08/ [accessed 13 May 2024].
- Kerner, S.M. (2022). Colonial Pipeline hack explained: Everything you need to know. [online] Available from: https://www.techtarget.com/whatis/feature/Colonial-Pipeline-hack-explained-Everything-you-need-to-know [accessed 13 May 2024].
- Kok, S. H. , Abdullah, A., Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Supramaniam, M. (2019). A review of intrusion detection system using machine learning approach. International Journal of Engineering Research and Technology 2019, 12, 8–15. [Google Scholar]
- Kyle, C. (2024). How to Prevent Ransomware Attacks: Top 10 Best Practices. Available from: https://www.upguard.com/blog/best-practices-to-prevent-ransomware-attacks. [accessed 15 May 2024].
- LaPorte, B. (2024). History of Ransomware: The Evolution of Attacks and Defense Mechanisms. Available from: https://blog.morphisec.com/ransomware-history-evolution-of-attacks-and-defenses [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Larry, G. (2020). Ransomware Response Safeguards and Countermeasures. Available from: https://www.isaca.org/resources/isaca-journal/issues/2020/volume-4/ransome-response-safeguards-and-countermeasures [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Liongard, 2023. Using Security Automation to Protect Business from Ransomware. [Online] Available at: https://www.linkedin.com/pulse/using-security-automation-protect-business-from-ransomware-liongard/ [Accessed 31 3 2024].
- Lim, Marcus, Azween Abdullah, N. Z. Jhanjhi, Muhammad Khurram Khan, and Mahadevan Supramaniam. "Link prediction in time-evolving criminal network with deep reinforcement learning technique." IEEE Access 7 (2019): 184797-184807.
- Mark Sweney. (2023). Royal Mail resumes overseas deliveries via post offices after cyber-attack [online]. Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2023/feb/21/royal-mail-international-deliveries-cyber-attack-ransom-strikes [accessed 14 May 2024].
- M. Saleh, N. Jhanjhi, A. Abdullah and R. Saher, "IoTES (A Machine learning model) Design dependent encryption selection for IoT devices," 2022 24th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), PyeongChang Kwangwoon_Do, Korea, Republic of, 2022, pp. 239-246. [CrossRef]
- Mark, S. (2023). Royal Mail resumes overseas deliveries via post offices after cyber-attack [online]. Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2023/feb/21/royal-mail-international-deliveries-cyber-attack-ransom-strikes [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Mimecast. (2023). Ransomware prevention is a critical priority. Available from: https://www.mimecast.com/content/ransomware-prevention/#:~:text=Antispam%2C%20antivirus%20and%20anti-malware,block%20new%20and%20emerging%20threats [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Möller, D.P.F. (2023) 'Ransomware Attacks and Scenarios: cost factors and loss of reputation,' in Advances in information security, pp. 273–303. [CrossRef]
- Nayyar, A. , Gadhavi, L. and Zaman, N. (2021) 'Machine learning in healthcare: review, opportunities and challenges,' in Elsevier eBooks, pp. 23–45. [CrossRef]
- Neko, P and Robert, S. (2021). Countermeasures for Ransomware. Available from: https://www.proofpoint.com/us/blog/security-awareness-training/countermeasures-ransomware [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Niamh, L. (2023). Royal Mail cyber-attack carried out by Russian-linked ransomware gang [online]. Available from: https://news.sky.com/story/royal-mail-cyber-attack-carried-out-by-russian-linked-ransomware-gang-12785685 [accessed 13 May 2024].
- Nick, C. (2019). Protect backups from ransomware and other security risks. Available from: https://www.techtarget.com/searchdatabackup/feature/Protect-backups-from-ransomware-and-other-security-risks [accessed 15 May 2024].
- NLC. (2023). Patching: A Necessity in a World of Ransomware. Available from: https://www.nlc.org/article/2023/11/29/patching-a-necessity-in-a-world-of-ransomware/#:~:text=Once%20inside%20your%20system%2C%20they,that%20attackers%20could%20otherwise%20exploit [accessed 15 May 2024]].
- Noone, G. (2023). Royal Mail spent £10m on cybersecurity after LockBit ransomware attack. Available from: https://techmonitor.ai/technology/cybersecurity/royal-mail-spent-10m-on-cybersecurity-after-lockbit-ransomware-attack [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Parsons, M. & Knudtson, B. and Reid, A. (2023). Is cybersecurity .
- PKTech. (2024). Ransomware in 2024: Trends, Tactics, and Prevention Strategies. Available from: https://www.pktech.net/2024/04/ransomware-in-2024-trends-tactics-and-prevention-strategies/ [accessed 28 May 2024].
- PMA360. (2021). The Colonial Pipeline Ransomware attack: Lessons for cybersecurity teams. Available from: https://blogs.manageengine.com/corporate/manageengine/pam360/2021/06/15/the-colonial-pipeline-ransomware-attack-lessons-for-cybersecurity-teams.html [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Raj, A.; et al. (2024) 'Modern ransomware: Evolution, methodology, attack model, prevention and mitigation using multi-tiered approach,' Security and Privacy [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Reuters. (2023). Royal Mail faces threat from ransomware group LockBit. Available from: https://www.reuters.com/technology/lockbit-ransomware-group-threatens-publish-stolen-royal-mail-data-techcrunch-2023-02-07/ [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Rob, D. (2023). ‘All we have had is losses’: Royal Mail dismisses ‘absurd’ $80m ransom demand [online]. Available from: https://www.theguardian.com/business/2023/feb/15/under-no-circumstances-will-we-pay-that-absurd-amount-royal-mail-tells-hackers [accessed 14 May 2024].
- Rothschild, M. (2021). Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack: How to Reduce Risk in OT Environments. Available from: https://www.tenable.com/blog/colonial-pipeline-ransomware-attack-how-to-reduce-risk-in-ot-environments [accessed 26 May 2024].
- Saeed, S. , Haron, H., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Naqvi, M., Alhumyani, H. A., & Masud, M. (2022). Improve correlation matrix of discrete fourier transformation technique for finding the missing values of mri images. Mathematical Biosciences and Engineering 2022, 19, 9039–9059. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sangkaran, Theyvaa, Azween Abdullah, N. Z. JhanJhi, and Mahadevan Supramaniam. "Survey on isomorphic graph algorithms for graph analytics." International Journal of Computer Science and Network Security 19, no. 1 (2019): 85-92.
- Saeed, Soobia, Afnizanfaizal Abdullah, N. Z. Jhanjhi, Mehmood Naqvi, Mehedi Masud, and Mohammed A. AlZain. "Hybrid GrabCut Hidden Markov Model for Segmentation." Computers, Materials & Continua 72, no. 1 (2022).
- Sangkaran, Theyvaa, Azween Abdullah, and N. Z. Jhanjhi. "Criminal community detection based on isomorphic subgraph analytics." Open Computer Science 10, no. 1 (2020): 164-174.
- SecureLink. (2021). Back to Basics: A Deeper Look at the Colonial Pipeline Hack. [online] Available from: https://www.govtech.com/sponsored/back-to-basics-a-deeper-look-at-the-colonial-pipeline-hack [accessed 13 May 2024].
- Secureworks. (2023). Ransomware Evolution. Available from: https://www.secureworks.com/research/ransomware-evolution [accessed 28 May 2024].
- SecurityScorecard. (2024). Proactive Strategies to Prevent Ransomware Attacks. Available from: https://securityscorecard.com/blog/proactive-strategies-to-prevent-ransomware-attacks/ [accessed 28 May 2024].
- Sergey, B. (2022). Can Antivirus Protect Against Ransomware? Available from: https://spin.ai/blog/does-antivirus-protect-against-ransomware/ [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Shahid, H.; et al. (2021) 'Energy Optimised Security against Wormhole Attack in IoT-Based Wireless Sensor Networks,' Computers, Materials & Continua/Computers, Materials & Continua (Print), 68(2), pp. 1967–1981. [CrossRef]
- Shah, I. A. , Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Brohi, S. N. (2024). Use of AI-Based Drones in Smart Cities. In I. Shah & N. Jhanjhi (Eds.), Cybersecurity Issues and Challenges in the Drone Industry (pp. 362-380). IGI Global. [CrossRef]
- Shah, I. A. , Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Ujjan, R. M. (2024). Drone Technology in the Context of the Internet of Things. In I. Shah & N. Jhanjhi (Eds.), Cybersecurity Issues and Challenges in the Drone Industry (pp. 88-107). IGI Global. [CrossRef]
- Shah, I. A. , Jhanjhi, N. Z., & Ray, S. K. (2024). Artificial Intelligence Applications in the Context of the Security Framework for the Logistics Industry. In M. Ghonge, N. Pradeep, N. Jhanjhi, & P. Kulkarni (Eds.), Advances in Explainable AI Applications for Smart Cities (pp. 297-316). IGI Global. [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, M.U.R.; et al. (2024) 'Fortifying Against Ransomware: Navigating Cybersecurity Risk Management with a Focus on Ransomware Insurance Strategies,' International Journal of Academic Research in Business and Social Sciences, 14(1). [CrossRef]
- Sindiramutty, S.R. (2024) 'Autonomous Threat Hunting: a future paradigm for AI-Driven Threat intelligence,' arXiv (Cornell University) [Preprint]. [CrossRef]
- Sindiramutty, S.R. , Jhanjhi, Noor Zaman, Tan, C.E., Tee, W.J., et al. (2024) 'IoT and AI-Based Smart Solutions for the Agriculture Industry,' in Advances in computational intelligence and robotics book series, pp. 317–351. [CrossRef]
- Sindiramutty, S.R. , Tan, C.E., Lau, S.P., et al. (2024) 'Explainable AI for cybersecurity,' in Advances in computational intelligence and robotics book series, pp. 31–97. [CrossRef]
- Sindiramutty, S.R. , Tan, C.E., Tee, W.J., et al. (2024) 'Modern smart cities and open research challenges and issues of explainable artificial intelligence,' in Advances in computational intelligence and robotics book series, pp. 389–424. [CrossRef]
- Sindiramutty, S.R. , Tee, Wee Jing, Balakrishnan, S., Kaur, S., et al. (2024) 'Explainable AI in healthcare application,' in Advances in computational intelligence and robotics book series, pp. 123–176. [CrossRef]
- Singhal, V.; et al. (2020) 'Artificial Intelligence Enabled Road Vehicle-Train Collision Risk Assessment Framework for Unmanned railway level crossings,' IEEE Access, 8, pp. 11 3790–113806. [CrossRef]
- SOCRadar. (2023). Dark Web Profile: LockBit 3.0 Ransomware [online]. Available from: https://socradar.io/dark-web-profile-lockbit-3-0-ransomware/ [accessed 16 May 2024].
- Sood, M. , Angra, P., Verma, S., & Jhanjhi, N. Z. (2022). Efficient feature grouping for IDS using clustering algorithms in detecting known/unknown attacks. In Information security handbook (pp. 103-116). CRC Press.
- Stockley, M. (2023). Royal Mail schools LockBit in leaked negotiation. Available from: https://www.threatdown.com/blog/royal-mail-schools-lockbit-in-leaked-negotiation/ [accessed 28 May 2024].
- TealTech. (2024). Lessons from the Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Hack. Available from: https://tealtech.com/blog/lessons-from-the-colonial-pipeline-ransomware-hack/ [accessed 26 May 2024].
- Teichmann, F. , Boticiu, S.R. and Sergi, B.S. (2023) 'The evolution of ransomware attacks in light of recent cyber threats. How can geopolitical conflicts influence the cyber climate?,' International Cybersecurity Law Review, 4(3), pp. 259–280. [CrossRef]
- Terranova Security. (2023). 6 Things to Learn from the Garmin Security Breach. [online] Available from: https://www.terranovasecurity.com/blog/garmin-security-breach. [accessed 14 May 2024].
- Terranova Security. (2023). How To Prevent Ransomware. Available from: https://www.terranovasecurity.com/blog/how-to-prevent-ransomware#:~:text=To%20prevent%20ransomware%2C%20companies%20need,can%20have%20on%20the%20company [accessed 15 May 2024].
- Tiwalade Modupe Usman, Yakub Kayode Saheed, Djitog Ignace, Augustine Nsang, Diabetic retinopathy detection using principal component analysis multi-label feature extraction and classification, International Journal of Cognitive Computing in Engineering, Volume 4, 2023.
- Pages 78-88, ISSN 2666-3074, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijcce.2023.02.002. [CrossRef]
- Vijayalakshmi, B. , Ramar, K., Jhanjhi, N. Z., Verma, S., Kaliappan, M., & Vijayalakshmi, K. & Ghosh, U.(2021). An attention-based deep learning model for traffic flow prediction using spatiotemporal features towards sustainable smart city. International Journal of Communication Systems 2021, 34, e4609. [Google Scholar]
- Wood, K. (2023). Cybersecurity Policy Responses to the Colonial Pipeline Ransomware Attack. [online] Available from: https://www.law.georgetown.edu/environmental-law-review/blog/cybersecurity-policy-responses-to-the-colonial-pipeline-ransomware-attack/#_ftn1 [accessed 13 May 2024].
- Worrell, J.L. “Jamey” (2024) 'A SURVEY OF THE CURRENT AND EMERGING RANSOMWARE THREAT LANDSCAPE,' EDPACS, pp. 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Zaman, Noor, and Azween B. Abdullah. "Position responsive routing protocol (prrp)." In 13th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT2011), pp. 644-648. IEEE, 2011.
- Zulfikar, H. (2023). Mengenal Ransomware LockBit 3.0 yang Diduga Serang BSI dan Cara Kerjanya [online]. Available from: https://tekno.kompas.com/read/2023/05/15/12450037/mengenal-ransomware-lockbit-30-yang-diduga-serang-bsi-dan-cara-kerjanya [accessed 16 May 2024].
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



