1. Introduction
Fibrillinopathies are different phenotipic expressions of FBN
1 encoding gene mutation.They are ranging from mild conditions, to the most severe, MS. MLSF expresses skeletal findings, without cardiovascular, and ocular manifestations[
1]. This is the mildest type of fibrillinopathy, and the patients prognosis is good. The consequences in MLSF are related especially with psychological distress, due to skeletal modifications, and joints pain.
MVPS is another fibrillinopathy, with skeletal, and cardiovascular abnormalities. MVP, is the central finding of this syndrome. Myxomatous degeneration of the mitral valve is a consequence of abnormal fibrillin, and this degeneration leads to the prolapse of mitral leaflets[
2,
3].
The third type of fibrillinopathy is MASS phenotype. MASS has the involvement of aortic root, with a borderline dilation[
1]. The enlargement of aortic root diameter is not so severe like in MS, and MVP ussually has a mild/moderate expression in MASS.
MS is the most severe fibrillinopathy, due to cardiovascular findings. Mitral regurgitation , MR, can be severe in MS, with hemodynamic implications , and surgical correction requirements. Aortic root dilation in MS can complicate with aortic aneurysm, aortic dissection, or rupture[
4,
5]. International guidelines includes systemic features, and echocardiographic findings, for a correct diagnosis in fibrillinopathies. Loeys et al established in 2010 the revised Ghent criteria. These guidelines have the aortic root dilation, and ectopia lentis, as cardinal features in MS. The systemic score, according to these criteria, encomprises skeletal, facial, lung, dura, mitral valve, and skin modifications[
6].
There aren’t estimates regarding the incidence of MLSF, MASS, and MVPS. Only the incidence rate of MS is estimated: 1 in 5, 000 persons, according to several studies [
7,
8,
9,
10]. However, the real incidence of MS is underestimated. The phenotype is expressed after the first decade of life, and children below 10 years can be underdiagnosed[
11,
12]. Systemic features prevalence, like pectus carinatum or excavatum; wrist sign; cutaneous striae, significantly increases at 15-17 years. Aortic root diameter, and ectopia lentis remains stable during the first two decades of life[
13,
14]. Four decades ago, mean life expectancy in MS was 32 years[
15]. Improvement in cardiovascular treatment(medical, and surgical) has doubled life expectancy of patients with MS [
16].
Apart from classical features previously mentioned, MS has other modifications which are worsening the outcome. Pulmonary artery dilation have been noticed in half of MS patients, and the rupture of a pulmonary artery aneurysm can cause the death[
17]. Intrinsic cardiomyopathy[
18,
19], and severe ventricular arrythmias in MS can represent an important cause of death[
20].
Increased tortuosity of aortic branch arteries( vertebral, carotid, subclavian, iliac arteries) suggests an aggressive form of MS[
21]. Tricuspide valve prolapse(TVP) is another marker for a severe disease; significant aortic root dilation, severe mitral valve prolapse are frequently noticed when the patient has TVP[
22].
The first class of medication in MS is represented by BB, which improved aortic stifness, and elasticity[
23]. Angiotensine converting enzyme inhibitors, ACEI, are an alternative treatment to BB, and this medication is proven to diminish aortic stifness[
24]. ARB have comparable effects with BB, towards aortic root
, and clinical events in MS. Although ARB are not superior to BB in monotherapy in MS patients, they might be an alternative to BB, especially when BB are not tolerated, or are contraindicated[
25].
Surgical treatment is recommended when aortic root diameter exceeds 50 mm in adults, or when aortic Z score is above 4 in children. Usually, the David procedure, and the Bentall procedure are preffered in aortic root surgery in MS[
26]. The surgical repairement of aortic root is similar with the techniques utilized in other aortitis – Takayasu’s arteritis[
27], syphilis, systemic erythematous lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, sarcoidosis. Severe MR, with hemodynamic consequences(pulmonary hypertension) requires surgical repairement. The majority of severe MR can be restored by the cardiac surgery; only a small number of MS patients requires mitral valve replacement[
28].
TMD is an extracardiac modification in MS, usually underestimated; its symptoms, and signs are noticed in almost half of MS[
29]. MRI increases the prevalence of TMD to 81% in MS[
30]. The prominent symptom in TMD is pain in the jaw, temple, or ear, modified with jaw movements. The signs in TMD are clicking during jaw movements, and pain after palpation of masseter/temporalis muscles[
31]. The MRI diagnosis of TMD has DDwR, and DDwoR, as major findings. De Stefano et al noticed the association between generalized joint hypermobility, and MRI diagnosis of TMD[
32,
33]. Their studies gave us the idea to investigate the correlation betweenTMD, and major cardiac findings in fibrillinopathies, as generalized joint hypermobility is a common feature in these diseases.
The main objective of our study was to establish the relationship between TMD, an extracardiac finding, and aortic root score in MS, MASS, MVPS. Abnormal fibrillin is a protein located all over the connective tissue in fibrillinopathies. We investigated the hypothesis that temporomandibular joint modification, in fibrillinopathies, has similarities with aortic root alteration. TMD was confirmed by MRI, and disc displacement, DD, was the major imagistic finding. Aortic root alteration was quantified by echocardiography, through aortic Z score. The predictive power of DD towards the aortic Z score was also included in the main objective of our research.
The secondary objectives of the research were the following: the correlations between echocardiographic parameters, the discreet association with relevance for the prognosis of these diseases, and the association between job satisfaction, and SS.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
The study was conducted in accordance with the rules, and principles of evidence-based medicine, in compliance with the requirements of the Declaration of Helsinki of the World Medical Association 2013, and was approved by the Committee of Ethics of “Gr.T.Popa” University of Medicine and Pharmacy, protocol no 206, dated 30 June 2015.
The recruitment of patients, the investigations, and their treatment was completed from August 2015 to August 2016. The research type was a retrospective cross-sectional study. The study comprised 83 patients, diagnosed with fibrillinopathy. The entire sample was divided in four groups, according to phenotype expression. The first group included 24 patients with MLSF, the second group comprised 22 patients with MVPS, the third group had 16 patients with MASS , and the fourth group had 21 patients with MS.
2.2. Inclusion Criteria
The diagnosis, and the treatment protocol were explained with each patient, and with each parent, in case of pediatric patients. All patients, and their parents( for pediatric patients) were informed about the benefits, and risks of participating in this research. An informed consent approved by the ethics comitee was signed by adult patients, or by their parents, for pediatric patients. This consent also included the permission for publication the data in present, and in future researches. The inclusion criteria were the revised Ghent criteria for the diagnosis of MS, and related conditions, which are detailed in 2.3 Methods section[
6].
2.3. Methods
The following signs were investigated, and the sum of the points given to each sign was the systemic score, SS[
6]:
Wrist and thumb sign –3 (Wrist or thumb sign –1)
Pectus carinatum deformity –2 (pectus excavatum or chest asymmetry –1)
Hindfoot deformity –2 (plain pes planus –1)
Pneumothorax –2
Dural ectasia –2
Protrusio acetabuli –2
Reduced upper skeleton/lower skeleton, and increased arm span /height >1.05 –1
Scoliosis or thoracolumbar kyphosis –1
Reduced elbow extension –1
Facial features (3/5) –1 (dolichocephaly, enophtalmos, downslanting palpebral fissures, malar hyoplasia, retrognathia)
Skin striae –1
Myopia > 3 diopters –1
Mitral valve prolapse –1
- b.
Transthoracic echocardiography
Echocardiography was made with Fukuda Denshi 850XTD, using B-mode, color, color Doppler.The aortic Z score was the parameter for severity of aortic root involvement. The aortic root diameter was measured at the level of sinuses of Valsalva, during the end of diastole. We calculated Z score with the following ecuation: Z score= (aortic root diameter – estimed aortic root diameter)/ 0.24. Estimated aortic root diameter= 1.12x body surface. Aortic root diameter was expressed in cm, and body surface in m
2[
34].
Mitral valve prolapse, MVP, was diagnosed according to European Association of Echocardiography. We utilized long axis parasternal view. MVP meaned more than 2 mm displacement of the leaflets, into the left atrium. This situation had to be during systole. The mitral leaflet thickness had to be more than 5 mm in MVP. Mitral regurgitation, MR, associated to MVP, was assessed by color Doppler. We utilized parasternal long, and short axis views, and apical long axis 2 and 4 chambers views, for MR assessment. Severe MR was defined by quantitative methods: color Doppler jet area, and vena contracta( the smallest region of the color jet at the regurgitant orifice)[
35]). Severe MR had a color Doppler jet area> 60% of left atrium area, and a vena contracta width≥ 7 mm[
36,
37].
- c.
Fibrillinopathy diagnosis
Ectopia lentis was the displacement of the crystalline lens, and was diagnosed by the ophthalmologist. Only MS patients had this medical condition. The Z score, and SS were diagnosed by the cardiologist.
Table 1 summarized the diagnosis criteria utilised in our study, for different phenotypes.
- d.
TMD diagnosis
Clinical TMD diagnosis was established by a dentist, according to the symptoms, and signs, discussed in Introduction. The patients with clinical TMD were reffered to MRI, made with Philips 1.5 Tesla MRI machine. Sagital, and coronal projection were used, with sections made every 3 mm. The images were obtained in complete occlusion of opposing teeth, and in opened-mouth. The evaluation of the articular disc with MRI confirmed two types of disc displacement, DD, in TMD: DDwR, and DDwoR. In DDwR, the articular disc was displaced in closed mouth position. In opened-mouth position, the disc reestablished the normal position relative to the condyle, in DDwR. The other type of DD, so-called DDwoR, had the following features: the patient had DD, in both opened and closed-mouth positions, and opened-mouth position couldn’t restore the correct relationship disc-condyle(as in DDwR).
- e.
Treatment
MS, MASS, and MVPS patients were adviced to avoid isometric exercises such as weight training, and high-resistance activities that activate the Valsalva maneuver.
Medical treatment was recommended for patients with MS, in order to control aortic root involvement. They received BB, Bisoprolol 2.5-5 mg twice dailly(11 patients with tachycardia), or ARB, Telmisartan 40-80 mg daily(10 patients).
Open surgical reconstruction of aortic root was recommended for aortic root dilation >
50 mm in adults, or in Z score > 4 in children. All these MS patients with surgical indication for aortic root dilation, had also symptomatic severe MR, and they undergone mitral valve surgery.
DDwR benefited by dental conservatory treatment, and DDwoR underwent surgical treatment for DD.
- f.
Job strain score in employees with fibrillinopathies
We utilized a specific questionnaire : satisfaction with work scale (SWWS) [
38]. The questions were addressed to the level of satisfaction on workplace, and the answers were scored from 1 to 5. Likert score 1 meant the patient was “totally disagree”with the affirmations, so he/she had severe dissatisfaction on workplace. Likert score 2 meant “partially disagree”, 3 was “almost agree”, 4 meant“agree”, and 5 meant “totally agree” with the affirmations.
- g.
Statistical analysis
Statistical analysis was made with IBM SPSS Statistics, version 22. Kolmogorov- Smirnov test revealed that statistical variables as age, SS, and Z score had not normal distribution; non-parametric statistical tests were suitable in our study. Correlations between Z score, and DDwR/DDwoR/TVP/MR/AR were established with Spearman test. Spearman’s correlation coefficient, Rho, was calculated with non-parametric bivariate correlation, from SPSS v22. Rho< 0.3 signified weak correlation; 0.3≤ Rho< 0.7 was a moderate correlation, and 0.7≤ Rho≤ 1 was a powerful correlation. P value< 0.05 signified statistical significance, and p value< 0.05 meant high statistical significance. For the association between DD (both DDwR, and DDwoR), and Z score, for the entire sample, Smart PLS v 4.1.0.4. programming was necessary. Liniary regression analysis was applied for investigate the predictive power of DDwR , and DDwoR, towards Z score. Clustering analysis used K-Means Clustering Algorithm; it clarified subtle associations, important for the disease prognosis.
3. Results
3.1. The Clinical Characteristics of the Entire Sample
The entire sample had almost similar numbers of females, and males, as well as MLSF, MASS, and MS groups. Only MVPS group had a predominance of females. Gender disparities were noticed in the aortic aneurysm prevalence. Men had a higher prevalence of aortic events(aortic aneurysm for our research) than women in our research( 8 of 11 patients with surgical aortic root indication were men: 72% of surgical patients).
Mean age for the entire sample was 20.9 years, with 8.8 SD. The youngest patient was 8 years old, and the eldest was 45 years old. Age was implicated in the prevalence of aortic root dilation. Adults with MS had a higher prevalence of this finding (13 of 21 patients: 61%), comparative with children patients with MS (8 of 21 patients: 39%). Age was not implicated in the prevalence of aortic events for MS patients: 6 adults, and respectively 5 children required surgical intervention( the number of adults with aortic aneurysm were equal with the number of children with this condition).
The most frequent findings were cranio-facial modifications( 83.1%). Other common signs were the following: chest deformity(81.9%), MVP(71%), cutaneous striae(69.8%), foot deformity(67.3%), wrist± thumb sign(43.3%). TMD was diagnosed in 24 patients(28.9%), and only these 24 patients underwent MRI for imaging diagnosis of TMD. The mean aortic Z score was 1.88 ± 1.18 ( minimum= 0.7, and maximum= 4.78). The mean SS was 6.36± 3.61(minimum=3, and maximum= 16). More than half of our patients had family agregation of the fibrillinopathies.These observations are summarized in Table 2.
Table 2.
Characteristics of the entire sample.
Table 2.
Characteristics of the entire sample.
| Characteristics |
n |
% |
Mean ± SD |
| Sex -females |
43 |
51.8 |
- |
| -males |
40 |
48.2 |
- |
| Age |
- |
- |
20.9± 8.8 |
| Wrist± thumb sign |
36 |
43.3 |
- |
| Chest deformity |
68 |
81.9 |
- |
| Foot deformity |
56 |
67.4 |
- |
| Cutaneous striae |
58 |
69.8 |
- |
| Cranio-facial aspects |
69 |
83.1 |
- |
| Aortic Z- score |
- |
- |
1.88 ± 1.18 |
| Systemic score |
- |
- |
6.36± 3.61 |
| MVP TMD |
5926 |
7131.2 |
- |
| Family medical history |
45 |
54.1 |
- |
3.2. The Relationship between TMD, and Z Score
The severity of TMD was established by MRI, meanwhile aortic Z score was quantified by echocardiography. Disc displacement was the major MRI finding for TMD.
None of the MLSF patients revealed DD on MRI, so this group was not included in DD, and Z-score correlation.
Both in MVPS, and in MASS patients, TMD was expressed only by DDwR( none of the patients from these groups had DDwoR ). Statistical analysis revealed that in MVPS patients, the correlation DDwR- Z score was weak: Rho= 0.276, and without statistical significance: p value= 0.213. For MASS, the association DDwR- Z score was powerful: Rho= 0.787, and with high statistical significance, p value< 0.01.
Among MS group, 9 of 21 patients(42.8%) had DDwoR( severe DD), and 6 of 21 patients (28, 5%) had DDwR( mild DD). The prevalence of TMD( both types of DD) among MS patients was 71.3%. For MS patients with DDwoR, the relationship DDwoR- Z score was powerful: Rho= 0.819, and with high statistical significance, p value< 0.01. For MS patients, with DDwR, the correlation DDwR- Z-score was weak : Rho=0.143, without statistical significance: p-value> 0.05.
These observations suggested us that TMD can be correlated with aortic root dilation, in our study, only in MASS, and MS patients. In MASS patients, this correlation, DD- Z score, was available for all of the patients; in MS patients, this association was available only for the patients with severe DD( DDwoR). These results are illustrated in Table 2.
Table 2.
Correlation between TMD, and Z score.
Table 2.
Correlation between TMD, and Z score.
| Disease type |
DDwR: n(%) |
DDwoR(n, %) |
Rho† (Zscore-DD) |
p† (Zscore-DD) |
| MVPS |
1(4.5%) |
- |
0.276 |
0.213 |
| MASS |
10(19.2%) |
- |
0.787** |
< 0.01** |
| MS |
6(7.2%) |
- |
0.143 |
0.536 |
| MS |
- |
9(10.8%) |
0.819** |
< 0.01** |
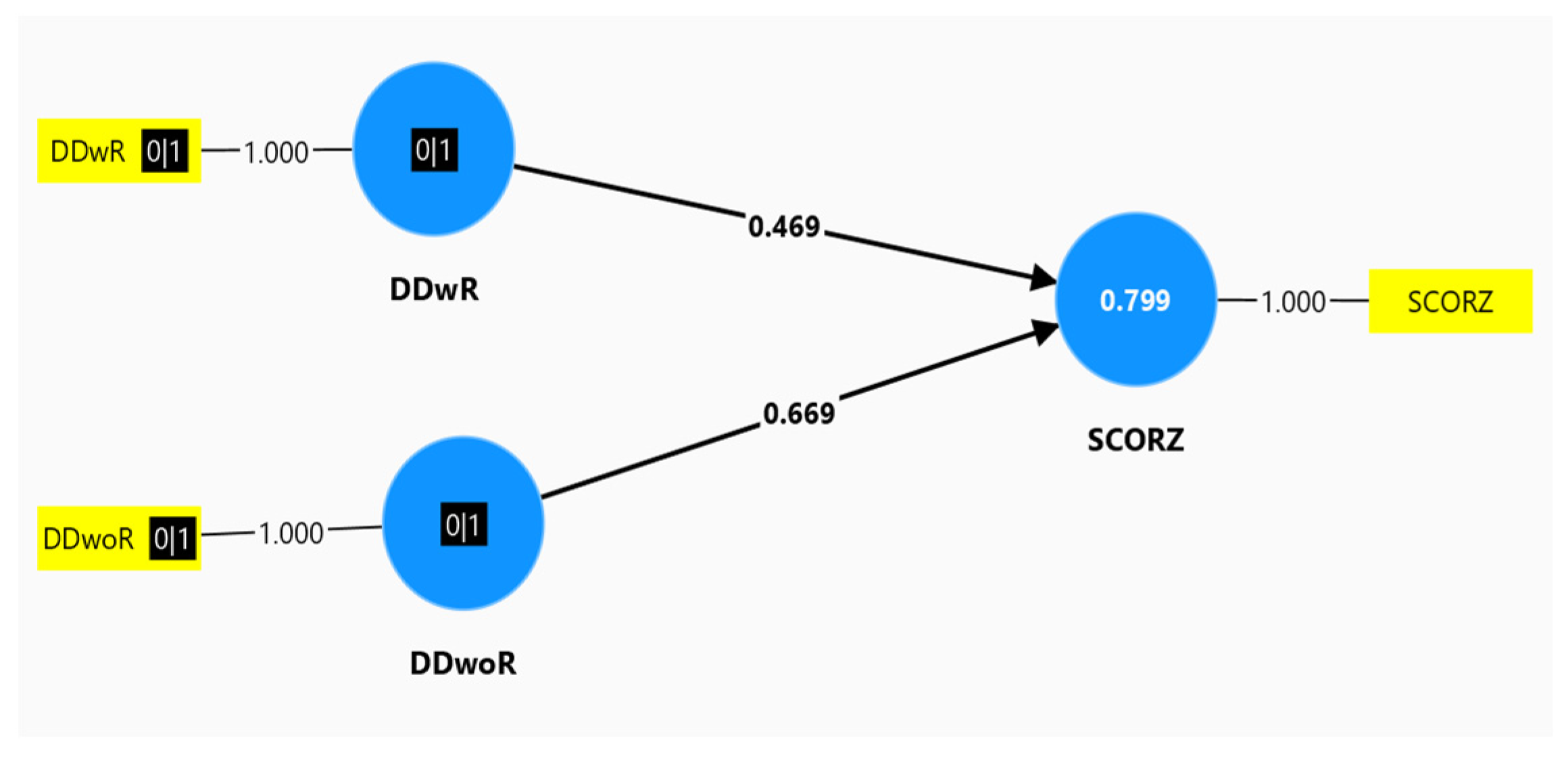
We investigated the correlation between DD, and Z score, for the entire sample, and the results were the following: DDwR , and Z score had a moderate correlation( Rho= 0.469, the superior arm, in
Figure 1), comparative with DDwoR, and Z score, which had a moderate to powerful correlation(Rho= 0.669, the lower arm, in
Figure 1). The number 0.799 above Z score, signified the following: 79.9%, so almost 80% of the sample, had this moderate correlation between DD, and Z score. The statistical model was available for 80% of the entire sample, and this result was represented below.
3.3. The Predictive Value of TMD for Z Score
We proved the following supposition: TMD, expressed by DD on MRI examination, was an accurate predictor for aortic root dilation, expressed by Z score on echocardiography.
The liniary regression analysis investigated the predictive value of DDwR, and DDwoR, towards the dependent variable, Z score. The analysis was validated by the following parameters:
a. R= 0.894, a powerful correlation(0.7≤ R≤ 1) between DD, and Z score
b. R-square= 0.799, and Adjusted R-square= 0.794. All these 3 parameters: R, R-square, and Adjusted R-square, confirmed that statistical model explained very well the clinical supposition.
We confirmed that the regression model had statistical significance: p-value< 0.05. This was illustrated in
Table 3.
Unstandardized coefficients, B, derived from this regression analysis, allowed us to determine which DD type had the most influence towards Z score. Both B coefficients were positive, and had statistical significance(p-value< 0.05).These results validated the fact that both DDwR, and DDwoR had a predictive value for Z score. Much more, B for DDwoR= 3.281, and this was an almost double value, comparative with B for DDwR= 1.661. These results suggested us that DDwoR had an almost double predictive value for Z score, than the predictive power of DDwR, for Z score. These results were illustrated in
Table 4.
3.3 Correlation between Echocardiographic Parameters
We investigated the association between aortic root score, and mitral regurgitation, MR. We noticed a powerful correlation (Rho=0.817), with high statistical significance(p< 0.01), for the entire sample. For MASS , and MVPS patients, this correlation, Z score-MR, had no statistical significance. For MS patients, the association had moderate significance( Rho= 0.442), with statistical significance for p-value(p=0.045).These results were summarized in
Table 5.
The association between aortic root score, and aortic regurgitation, AR, revealed a moderate correlation, Rho=0, 536, with statistical significance, p= 0, 012, only for MS patients group.The correlation between Z-score, and AR had no statistical significance for the entire sample, and both in MASS, and MVPS patients.
These results suggested us that both MR, and RA had a moderate, and statistically significant correlation with Z score, only in MS patients. The severity of these valvulopathies are related with the aortic root dilation severity, in MS patients.
We correlated Z score with another echocardiographic findings in MS patients: tricuspide valve prolapse, TVP. We noticed that the patients with TVP had higher values for aortic root dilation. A moderate correlation (Rho= 0.481) with statistical significance (p= 0.027) was noticed for the association PVT- Z score. The PVT investigation in MS patients, suggested us the usefulness of this valvulopathy, as a marker of severity for MS.
3.4. The Clustering Analysis
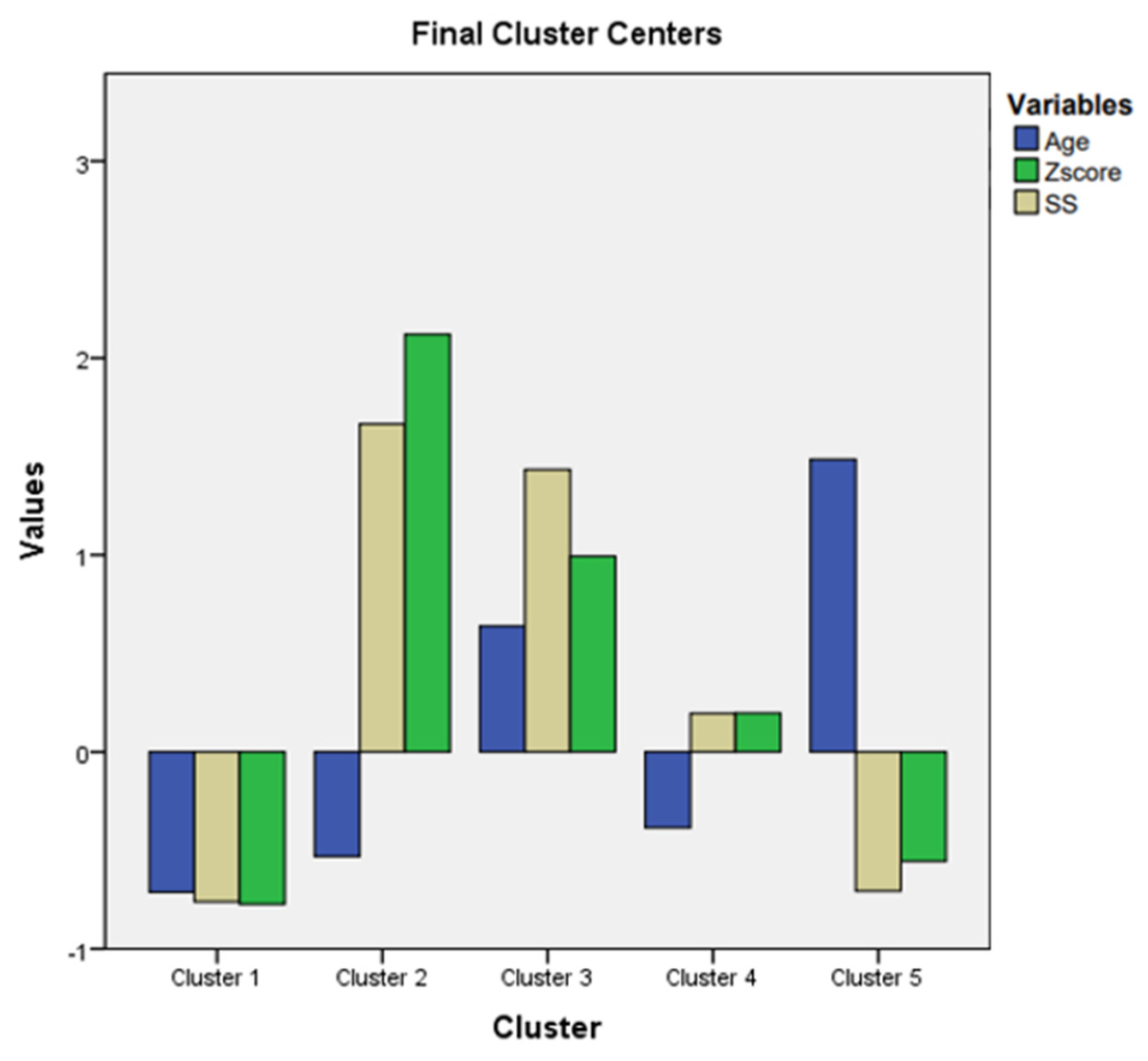
This specific method from statistic analysis permitted us to discover obscure associations that can be useful to identify disease evolution, and severity. The variables utilized for this technique were the following: age, Z score, and SS. The adequate clustering model for these parameters comprised five clusters. Age was represented in blue column, Z score in green, and SS in beige. Mean value for variables was represented by 0, and standard deviation values were represented by 1, 2, 3.
Patients distribution on the five clusters was represented in
Table 6.
For the five clusters model we noticed the following:
cluster 1 had 17 patients with MLSF, and 14 patients with MVPS. Low values for age, Z score, and SS were noticed in this cluster.
cluster 2 had 8 patients with MS. Low values for age, but the maximum values for Z score, and for SS, were registered in this cluster.
cluster 3 had 13 patients with MS. High values for age( above 21 years), and high values for Z score , and for SS ( but not so high like in cluster 2) were noticed in this cluster.
cluster 4 had 15 patients with MASS. Low values for age( below 21 years), and middle levels for Z score , and for SS were revealed in this cluster.
cluster 5 had 1 patient with MASS, 7 patients with MLSF, and 9 patients with MVPS. They were the “eldest” patients( the highest values for age); low values for Z score, and SS were registered in this cluster.
All these observations are illustrated in
Figure 2.
This clustering analysis revealed the following observations:
MLSF, and MVPS(cluster 1 and cluster 5) had the lowest Z scores, and SS, independent of age values. We noticed on
Figure 2 that Z score, and SS, in cluster 1 and cluster 5, were represented below 0 ( mean=0); the meaning of these results was that Z- score, and SS had the lowest values for MLSF, and MVPS patients. The age, was below 0, (below mean age= 21 years) in cluster 1, with the youngest patients from the study. In cluster 5, age exceeded 1(standard deviation=1), and the patients were “the eldest” from the study (above mean age= 21 years). MLSF, and MVPS patients were the youngest(cluster1), and ‘’the eldest”(cluster 5) patients of our study. They all had the lowest scores for both aortic, and systemic involvement, independent of their age. These 2 groups, MLSF, and MVPS, had the mildest expression in our study.
the majority of MASS patients(15 of 16 MASS patients, 93%) had average levels of Z score , and SS. MASS had a moderate expression in our study, and the phenotypic findings were defined early, during childhood, or teenage; the majority of MASS, 93%, were aged below 21 years)- cluster 4.
MS patients with the maximum values for Z score, and maximum values for SS were children, or teenager(cluster 2). These young MS patients(age is below 0, so patients age was below 21 years) had the most severe phenotypic expression of the fibrillinopathy. The other MS patients, from cluster 3 had high values( but not as high as in cluster 2) for Z score, and for SS; the 3rd cluster had ”elderly “MS patients, aged above 21 years. This last category of MS patients (cluster 3) had a severe form of the disease, but not as severe as the first MS category( cluster 2). The youngest MS patients( cluster 2) had the worst prognosis in our study( the highest values for Z score, above 2, and the highest values for SS, above 1.5). The “eldest”MS patients had a severe prognosis, but not as severe as the youngest MS patients( high values for Z score, and for SS in cluster 3, but not as high as in cluster 2).
3.5. SWWS Results
We investigated the satisfaction on workplace in 25 of 83 patients( the employees).They were teachers, engineers, and clerks. The MS patients( 9 of 25 employees) had the worst Likert score: 1, and 2. These MS patients had severe dissatisfaction on workplace. The other patients (16 of 25 employees) had Likert score 3; they had the following distribution: MLSF employees group had 6 patients; MVPS- 9 patients, and MASS- 1 patient. These 3 groups had moderate satisfaction on workplace. We noticed that Likert score had a reverse correlation with SS. Correlation coefficient(r ) value was - 0.7, for all the employees group (r=- 0.6 to - 0.8 means negative strong association). A high value for SS was associated with a severe dissatisfaction on work place.
4. Discussion
The study comprised 83 patients, diagnosed with fibrillinopathy, with four different phenotypic expression: MLSF, MVPS, MASS, and MS. The main aim of the research was the association between an extracardiac finding: DD on MRI for TMD, and a cardiac finding: Z score, for the entire sample, and for different phenotypes.This is a peculiar aspect of the research, to investigate, and compare the results obtained for each phenotype. Usually the studies with fibrillinopathies investigate separately these phenotypes; especially MS, or MVPS patients are included in other researches. Only a few studies comprise MASS, or MLSF patients.
The incidence of these diseases was almost equal among men and women in the study, and these results were similar with other researches[
39]. Although there were no gender differences for MS incidence, men had a higher prevalence for aortic dissection/aortic aneurysm in several studies[
40,
41]. We noticed the same gender disparities of aortic aneurysm prevalence in our research, like in previously mentioned studies : higher prevalence of aortic aneurysm in men, compared with women. None of our MS patients evolved to aortic dissection.
The prevalence of aortic root replacement, and mitral valve surgery in MS was similar in adults( 6 patients), and in chidren (5 patients) in our research. Other studies noticed disparities between childhood, and adulthood surgical requirements: adults developed aortic events with a higher prevalence than children[
41].
Aortic Z score was the central parameter in our study, and it was associated with all the other findings: DD on MRI; MR/AR/TVP on echocardiography. Mean value of Z score was 1.88, for the entire sample. The highest values for Z score were in MS patients, the lowest values for aortic score had MLSF patients, an medium values were noticed in MASS, and MVPS patients. Other studies, with MS patients, noticed comparable values of their mean aortic Z score, with our mean Z score: mean Z score in Lopez et al was 1.72[
42], in Pettersen et al was 1.23[
43], and in Gautier et al was 1.49[
44].
We selected the TMD patients confirmed by MRI findings: anterior disc displacement, with and without reduction. The entire sample had the following distribution of TMD: MLSF group, with none of the patients complaining by TMD; MVPS group, with only 1 patient with TMD; MASS group with 10 patients with TMD, and MS group with 15 patients with TMD. The MLSF, and MVPS groups diminished the prevalence of TMD in the entire sample(31.2%). The prevalence of TMD was very high in MS patients(71.4%), and high in MASS patients(38.6%). These results confirmed us that TMD was an important extracardiac aspect in our study. Other researches investigated TMD only in MS patients, and the prevalence of TMD in MS was 81%, a close value to the percentage of TMD prevalence obtained in our study, in MS patients[
30].
The main objective of our study was to establish the correlation TMD- Z score, and the predictive role of TMD for Z score, in fibrillinopathies. This is another peculiar aspect of the study. Other authors revealed correlation between TMD, and quality of life, chronic pain, anxiety, and depression in MS[
45], but no correlation TMD-Z score was investigated. Other researchers investigated the correlation between TMD, and generalized joint hypermobility, which was a common finding in fibrillinopathies, but no association between TMD- Z score was discussed[
32,
33]. In our study, the correlation TMD-Z score was powerful in all MASS patients affected by TMD(Rho= 0.787), and in MS patients(Rho= 0.819) with DDwoR; this correlation TMD- Zscore was moderate for the entire sample(Rho= 0.469 for DDwR- Z score, and Rho= 0.669 for DDwoR-Z score correlation). These results suggested us that we can utilize an extracardiac finding, TMD, for the assesment of cardiovascular severity, in MASS, and MS patients. DD on MRI was an important, and objective finding, provoked by abnormal fibrillin in the temporomandibular joint. Z score in echocardiography was another objective finding, addressed to aortic root dilation. This cardiac finding, aortic root involvement, was also provoked by abnormal fibrillin in the aortic layers, followed by reduced elasticity, and increased stiffness of the aortic root. The powerful association DD- Z score has been noticed in MASS, and MS patients, separately.When we investigated DD- Z score correlation for the entire sample, we noticed a moderate correlation.
The predictive role of TMD for Z score in fibrillinopathies was included in the main aim of the study. We proved with regression analysis that DD was a poweful predictor for Z score. Much more, DDwoR had an almost double predictive value for Z score, than the predictive power of DDwR, for Z score. This result suggested us that the prognosis of cardiac involvement in fibrillinopathies could be stratified by an extracardiac finding: DD on MRI.
A secondary objective of the study was the association between echocardiographic parameters. MR-Z score had a powerful correlation for the entire sample, in our study. The severity of mitral valvulopathy was strongly correlated with the severity of aortic root dilation, in the entire sample. In MS patients, both MR-Z score, and AR-Z score, had a moderate correlation.The severity of both mitral, and aortic valvulopathies, was moderately correlated with the severity of aortic root dilation, in MS patients. TVP-Z score had a moderate association only in MS. We can conclude that the presence of TVP in MS patients suggested a worse prognosis, and this result was noticed also by other authors[
46].
The clustering analysis revealed important data about disease severity in fibrillinopathies. MLSF, and MVPS patients had a mild expression of the disease, independent of their age. MASS patients had a moderate phenotypic expression. The most severe expression of the disease was noticed among the youngest MS patients.
Satisfaction on workplace had a reverse correlation with SS in our study. The patients had low scores for job satisfaction, if their physical appearance(cranio-facial modifications, long upper arms, chest deformities, kyphosis, and other findings from SS) was different from their peers. Physical appearance was more important in our research, for the patients, than cardiac involvement severity. This result can be explained by the mean age of our patients: 21 years; for young patients, their physical appearance decreased their self confidence, and their perception about workplace. In other studies, the severity of cardiac involvement was an important determinant of job satisfaction[
47,
48].
The study had several limitations. One of the limitation was the absence of a longitudinal study, with different stages for investigation. Also, the genetic analysis was not considered in the study. A cardiac MRI was not performed in the study. This investigation could suggest us an intrinsic cardiomyopathy. This cardiac finding was noticed in half of MS patients, in other studies, and consisted in increased left, and right ventricle end diastolic volumes, impaired systolic, and diastolic function of both ventricles. Another limitation of the study was a discussion about life threatening ventricular arrythmias.These findings were noticed in MS, in other researches, and could represent an important cause of death.
Future directions of our study will include an investigation with a 5 years follow up of the patients with fibrillinopathies. We will emphasize especially MASS, and MS patients, as they have important cardiac involvement. Every 6 months, the assesment of aortic Z score, MR, AR, SS, will be performed, and compared, in order to establish the evolution of cardiac findings. A comparison between echocardiography, and cardiac MRI will be another future direction, for a precise assesment of intrinsic cardiomyopathy. Pain symptoms due to arthritis, chest deformities, bony overgrowth, scoliosis, kyphosis, and their implication in anxiety, and depression occurrence, will be another future direction for our research.