Submitted:
02 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET) Depolymerization
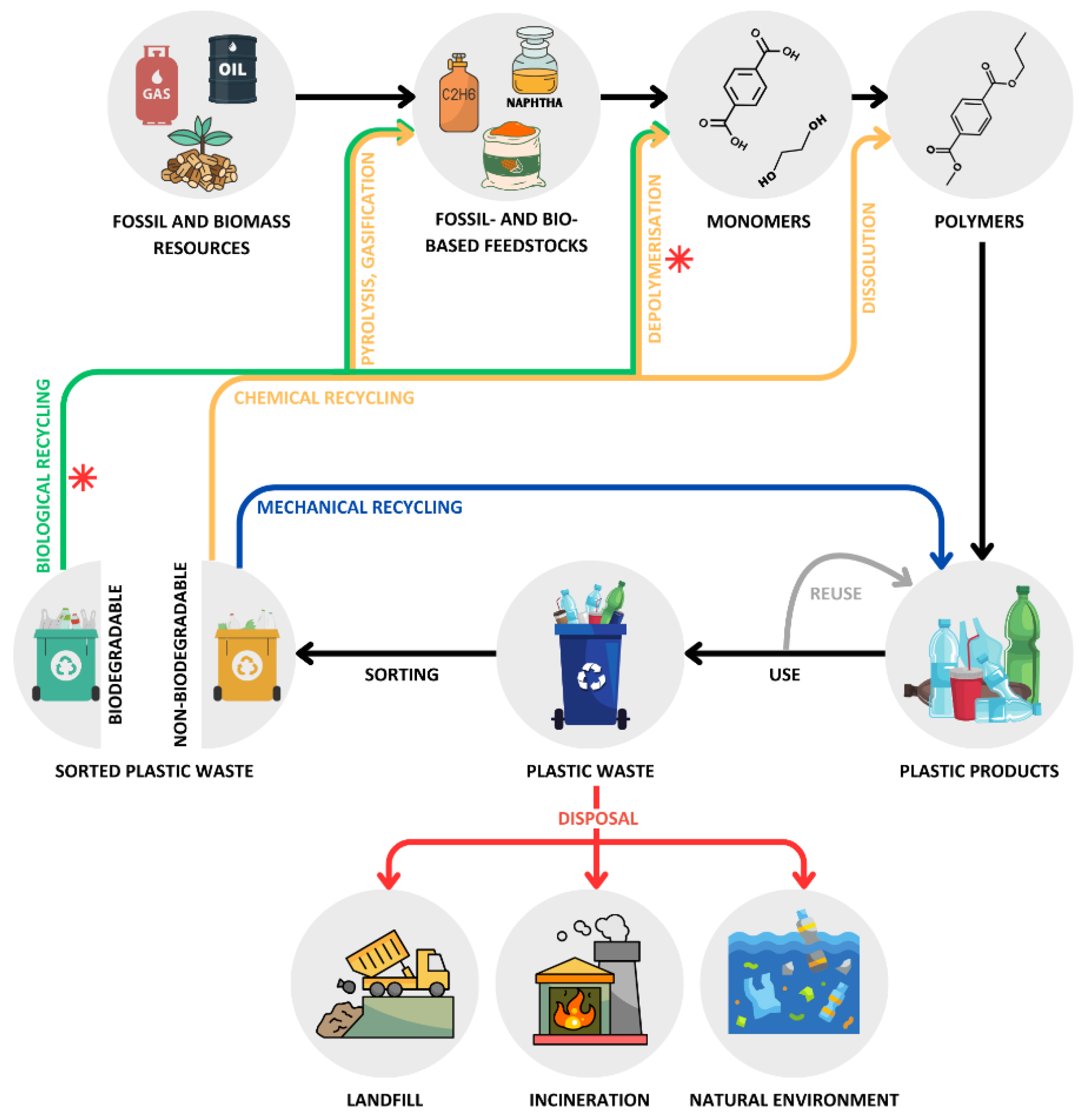
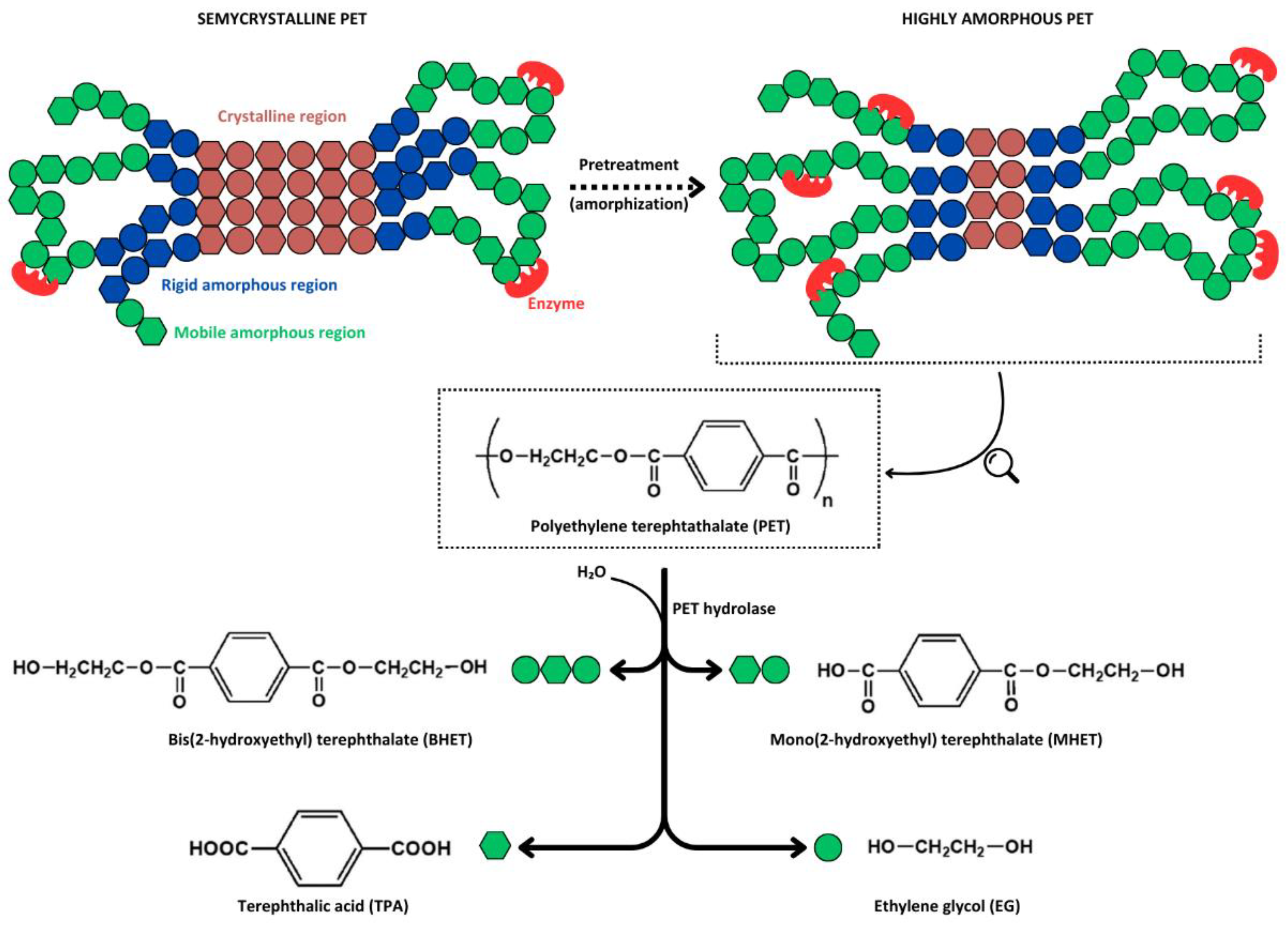
2.1. About PET and Its Recycling Strategies
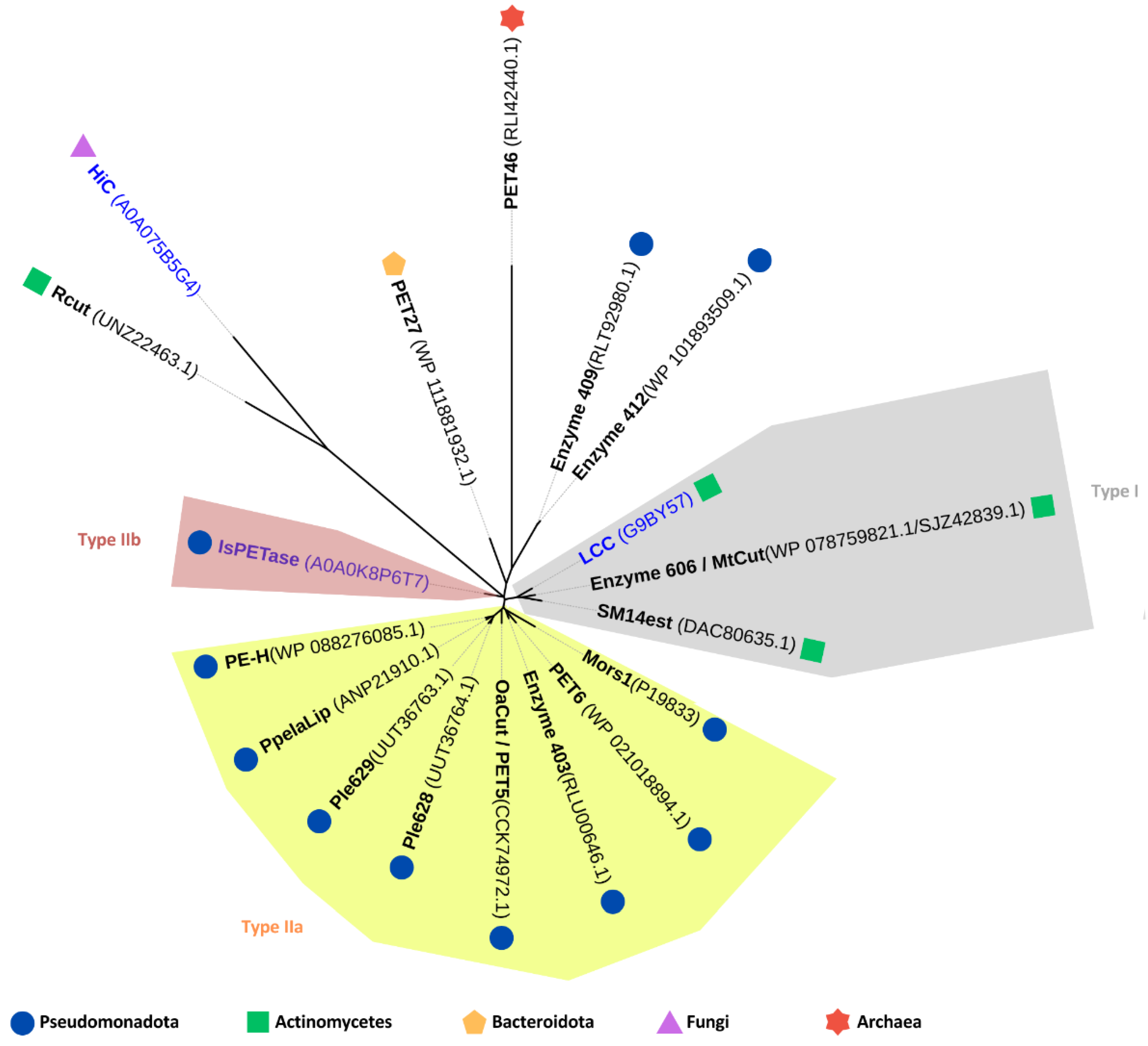
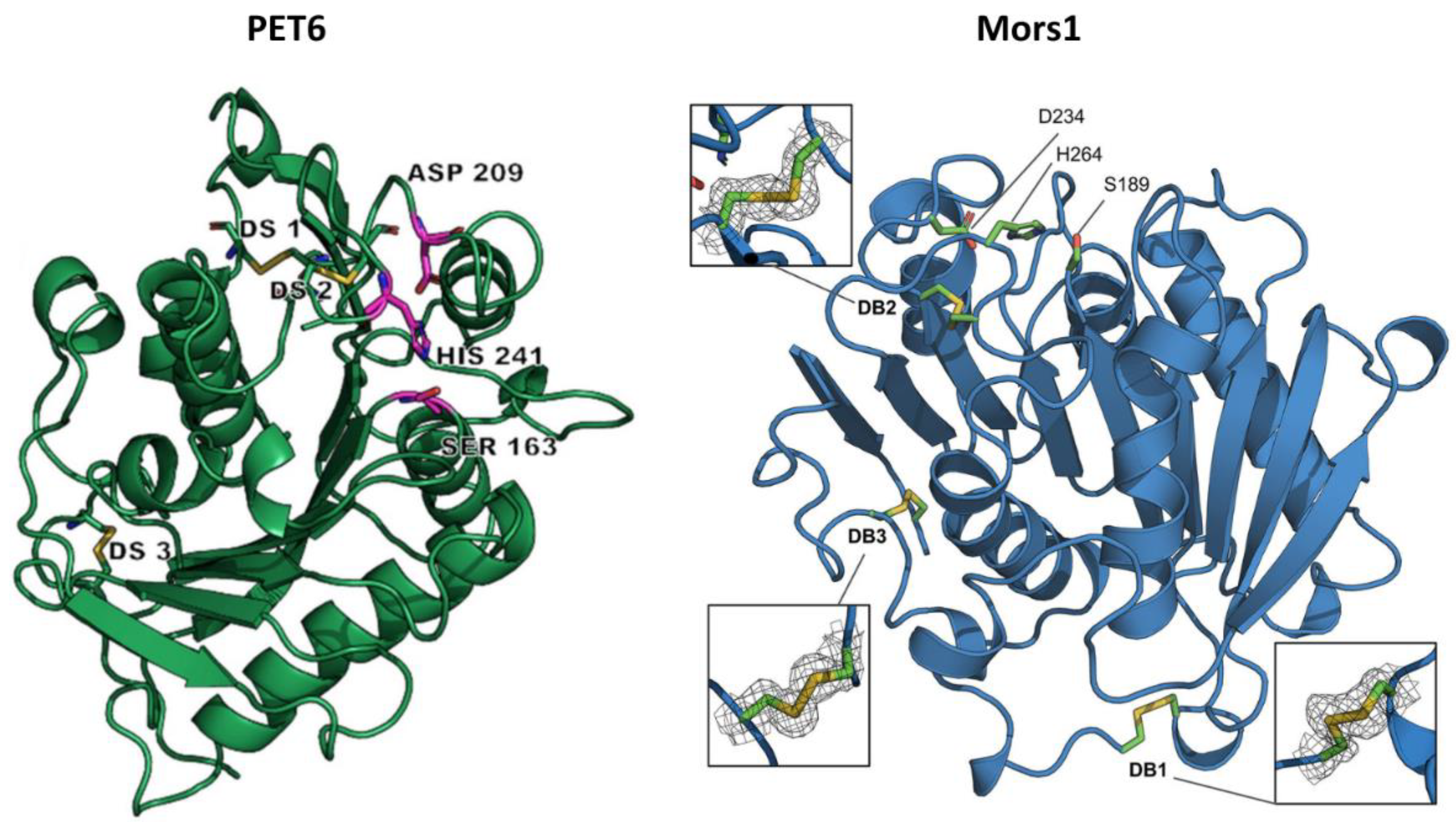
2.2. PET-Depolymerizing Marine Enzymes
3. Polylactic Acid (PLA) Depolymerization
3.1. About PLA and Its Biodegradation
3.2. PLA-Depolymerizing Marine Enzymes
4. Depolymerization of Other Plastics by Marine-Derived Enzymes
5. Perspectives in Enzymatic Plastic Depolymerization
5.1. PET
5.2. PLA
5.3. Other Plastics
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Geyer, R. A Brief History of Plastics. In Mare Plasticum - The Plastic Sea: Combatting Plastic Pollution Through Science and Art; Streit-Bianchi, M., Cimadevila, M., Trettnak, W., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2020; pp. 31–47. [Google Scholar]
- Geyer, R.; Jambeck, J.R.; Law, K.L. Production, use, and fate of all plastics ever made. Sci Adv 2017, 3, e1700782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plastics - the fast Facts 2023. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/plastics-the-fast-facts-2023/ (accessed on 5th June 2024).
- Tournier, V.; Duquesne, S.; Guillamot, F.; Cramail, H.; Taton, D.; Marty, A.; André, I. Enzymes’ Power for Plastics Degradation. Chem Rev 2023, 123, 5612–5701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ford, H.V.; Jones, N.H.; Davies, A.J.; Godley, B.J.; Jambeck, J.R.; Napper, I.E.; Suckling, C.C.; Williams, G.J.; Woodall, L.C.; Koldewey, H.J. The fundamental links between climate change and marine plastic pollution. Sci Total Environ 2022, 806, 150392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barnes, D.K.; Galgani, F.; Thompson, R.C.; Barlaz, M. Accumulation and fragmentation of plastic debris in global environments. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci 2009, 364, 1985–1998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, H.; Liu, K.; Fu, H.; Ji, R.; Qu, X. Sunlight mediated cadmium release from colored microplastics containing cadmium pigment in aqueous phase. Environ Pollut 2020, 263, 114484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paluselli, A.; Fauvelle, V.; Galgani, F.; Sempéré, R. Phthalate Release from Plastic Fragments and Degradation in Seawater. Environ Sci Technol 2019, 53, 166–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crippa, M.; De Wilde, B.; Koopmans, R.; Leyssens, J.; Linder, M.; Muncke, J.; Ritschkoff, A.-C.; Van Doorsselaer, K.; Velis, C.; Wagner, M. A circular economy for plastics – Insights from research and innovation to inform policy and funding decisions; De Smet, M., Linder, M., Eds.; European Commission: Brussels, Belgium, 2019; pp. 112–162. [Google Scholar]
- The Circular Economy for Plastics – A European Analysis 2024. Available online: https://plasticseurope.org/knowledge-hub/the-circular-economy-for-plastics-a-european-analysis-2024/ (accessed on 7th June 2024).
- Ragaert, K.; Delva, L.; Van Geem, K. Mechanical and chemical recycling of solid plastic waste. Waste Manag 2017, 69, 24–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babaremu, K.; Adediji, A.; Olumba, N.; Okoya, S.; Akinlabi, E.; Oyinlola, M. Technological Advances in Mechanical Recycling Innovations and Corresponding Impacts on the Circular Economy of Plastics. Environments 2024, 11, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, J.M.; Robertson, M.L. The future of plastics recycling. Science 2017, 358, 870–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahimi, A.; García, J.M. Chemical recycling of waste plastics for new materials production. Nature Reviews Chemistry 2017, 1, 0046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, L.D.; Rorrer, N.A.; Sullivan, K.P.; Otto, M.; McGeehan, J.E.; Román-Leshkov, Y.; Wierckx, N.; Beckham, G.T. Chemical and biological catalysis for plastics recycling and upcycling. Nature Catalysis 2021, 4, 539–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Q.; Zhen, M.; Qian, H.; Nie, Y.; Bai, X.; Xia, T.; Laiq Ur Rehman, M.; Li, Q.; Ju, M. Upcycling and catalytic degradation of plastic wastes. Cell Reports Physical Science 2021, 2, 100514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, F.; Wei, X.; Yang, Y.; Xu, S.; Deng, D.; Wang, Y.-Z. From trash to treasure: Chemical recycling and upcycling of commodity plastic waste to fuels, high-valued chemicals and advanced materials. Journal of Energy Chemistry 2022, 69, 369–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Boruah, B.; Chin, K.F.; Đokić, M.; Modak, J.M.; Soo, H.S. Upcycling to Sustainably Reuse Plastics. Adv Mater 2022, 34, e2100843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehanno, C.; Alty, J.W.; Roosen, M.; De Meester, S.; Dove, A.P.; Chen, E.Y.; Leibfarth, F.A.; Sardon, H. Critical advances and future opportunities in upcycling commodity polymers. Nature 2022, 603, 803–814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, M.; Zuo, Z.; Niu, Z. Recent advances in plastic recycling and upgrading under mild conditions. Green Chemistry 2023, 25, 6949–6970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, K.; Wlodawer, A. Development of Enzyme-Based Approaches for Recycling PET on an Industrial Scale. Biochemistry 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, R.; Sadeghi, K.; Jang, J.; Seo, J. Mechanical, chemical, and bio-recycling of biodegradable plastics: A review. Sci Total Environ 2023, 882, 163446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, J.E.; Clendinning, R.A.; Ackart, W.B.; Niegisch, W.D. The Biodegradability of Synthetic Polymers. In Polymers and Ecological Problems, Guillet, J., Ed.; Springer US: Boston, MA, 1973; pp. 61–79. [Google Scholar]
- Tokiwa, Y.; Suzuki, T. Hydrolysis of polyesters by lipases. Nature 1977, 270, 76–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Müller, R.-J.; Schrader, H.; Profe, J.; Dresler, K.; Deckwer, W.-D. Enzymatic Degradation of Poly(ethylene terephthalate): Rapid Hydrolyse using a Hydrolase from T. fusca. Macromolecular Rapid Communications 2005, 26, 1400–1405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.-S.; Wu, W.-M.; Pang, J.-W.; He, L.; Ding, M.-Q.; Li, M.-X.; Zhao, Y.-L.; Sun, H.-J.; Xing, D.-F.; Ren, N.-Q.; et al. Bibliometric analysis of publications on biodegradation of plastics: Explosively emerging research over 70 years. Journal of Cleaner Production 2023, 428, 139423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gambarini, V.; Pantos, O.; Kingsbury, J.M.; Weaver, L.; Handley, K.M.; Lear, G. PlasticDB: A database of microorganisms and proteins linked to plastic biodegradation. Database (Oxford) 2022, 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchholz, P.C.F.; Feuerriegel, G.; Zhang, H.; Perez-Garcia, P.; Nover, L.L.; Chow, J.; Streit, W.R.; Pleiss, J. Plastics degradation by hydrolytic enzymes: The plastics-active enzymes database-PAZy. Proteins 2022, 90, 1443–1456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PlasticDB. Available online: https://plasticdb.org/about (accessed on 14th June 2024).
- Tournier, V.; Topham, C.M.; Gilles, A.; David, B.; Folgoas, C.; Moya-Leclair, E.; Kamionka, E.; Desrousseaux, M.L.; Texier, H.; Gavalda, S.; et al. An engineered PET depolymerase to break down and recycle plastic bottles. Nature 2020, 580, 216–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F. The Current State of Research on PET Hydrolyzing Enzymes Available for Biorecycling. Catalysts 2021, 11, 206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Oeser, T.; Then, J.; Kühn, N.; Barth, M.; Schmidt, J.; Zimmermann, W. Functional characterization and structural modeling of synthetic polyester-degrading hydrolases from Thermomonospora curvata. AMB Express 2014, 4, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oda, M.; Yamagami, Y.; Inaba, S.; Oida, T.; Yamamoto, M.; Kitajima, S.; Kawai, F. Enzymatic hydrolysis of PET: Functional roles of three Ca(2+) ions bound to a cutinase-like enzyme, Cut190*, and its engineering for improved activity. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2018, 102, 10067–10077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sulaiman, S.; Yamato, S.; Kanaya, E.; Kim, J.J.; Koga, Y.; Takano, K.; Kanaya, S. Isolation of a novel cutinase homolog with polyethylene terephthalate-degrading activity from leaf-branch compost by using a metagenomic approach. Appl Environ Microbiol 2012, 78, 1556–1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sonnendecker, C.; Oeser, J.; Richter, P.K.; Hille, P.; Zhao, Z.; Fischer, C.; Lippold, H.; Blázquez-Sánchez, P.; Engelberger, F.; Ramírez-Sarmiento, C.A.; et al. Low Carbon Footprint Recycling of Post-Consumer PET Plastic with a Metagenomic Polyester Hydrolase. ChemSusChem 2022, 15, e202101062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, S.; Hiraga, K.; Takehana, T.; Taniguchi, I.; Yamaji, H.; Maeda, Y.; Toyohara, K.; Miyamoto, K.; Kimura, Y.; Oda, K. A bacterium that degrades and assimilates poly(ethylene terephthalate). Science 2016, 351, 1196–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blázquez-Sánchez, P.; Engelberger, F.; Cifuentes-Anticevic, J.; Sonnendecker, C.; Griñén, A.; Reyes, J.; Díez, B.; Guixé, V.; Richter, P.K.; Zimmermann, W.; et al. Antarctic Polyester Hydrolases Degrade Aliphatic and Aromatic Polyesters at Moderate Temperatures. Appl Environ Microbiol 2022, 88, e0184221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, H.; Diaz, D.J.; Czarnecki, N.J.; Zhu, C.; Kim, W.; Shroff, R.; Acosta, D.J.; Alexander, B.R.; Cole, H.O.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Machine learning-aided engineering of hydrolases for PET depolymerization. Nature 2022, 604, 662–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, D.; Schmeisser, C.; Chow, J.; Zimmermann, W.; Wei, R.; Leggewie, C.; Li, X.; Hazen, T.; Streit, W.R. New Insights into the Function and Global Distribution of Polyethylene Terephthalate (PET)-Degrading Bacteria and Enzymes in Marine and Terrestrial Metagenomes. Appl Environ Microbiol 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tchigvintsev, A.; Tran, H.; Popovic, A.; Kovacic, F.; Brown, G.; Flick, R.; Hajighasemi, M.; Egorova, O.; Somody, J.C.; Tchigvintsev, D.; et al. The environment shapes microbial enzymes: Five cold-active and salt-resistant carboxylesterases from marine metagenomes. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2015, 99, 2165–2178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Erickson, E.; Gado, J.E.; Avilán, L.; Bratti, F.; Brizendine, R.K.; Cox, P.A.; Gill, R.; Graham, R.; Kim, D.-J.; König, G.; et al. Sourcing thermotolerant poly(ethylene terephthalate) hydrolase scaffolds from natural diversity. Nature Communications 2022, 13, 7850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Distaso, M.A.; Chernikova, T.N.; Bargiela, R.; Coscolín, C.; Stogios, P.; Gonzalez-Alfonso, J.L.; Lemak, S.; Khusnutdinova, A.N.; Plou, F.J.; Evdokimova, E.; et al. Thermophilic Carboxylesterases from Hydrothermal Vents of the Volcanic Island of Ischia Active on Synthetic and Biobased Polymers and Mycotoxins. Appl Environ Microbiol 2023, 89, e0170422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omura, T.; Isobe, N.; Miura, T.; Ishii, S.; Mori, M.; Ishitani, Y.; Kimura, S.; Hidaka, K.; Komiyama, K.; Suzuki, M.; et al. Microbial decomposition of biodegradable plastics on the deep-sea floor. Nat Commun 2024, 15, 568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.-T.; Li, X.; Yang, Y.; Huang, J.-W.; Shen, P.; Liew, R.K.; Chen, C.-C. Natural and engineered enzymes for polyester degradation: A review. Environmental Chemistry Letters 2024, 22, 1275–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F.; Iizuka, R.; Kawabata, T. Engineered polyethylene terephthalate hydrolases: Perspectives and limits. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2024, 108, 404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, S.; Li, Y.; Zhao, S.; Shao, Z. Biodegradation of Typical Plastics: From Microbial Diversity to Metabolic Mechanisms. Int J Mol Sci 2024, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atanasova, N.; Stoitsova, S.; Paunova-Krasteva, T.; Kambourova, M. Plastic Degradation by Extremophilic Bacteria. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schyns, Z.O.G.; Shaver, M.P. Mechanical Recycling of Packaging Plastics: A Review. Macromolecular Rapid Communications 2021, 42, 2000415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barnard, E.; Rubio Arias, J.J.; Thielemans, W. Chemolytic depolymerisation of PET: A review. Green Chemistry 2021, 23, 3765–3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddiqui, M.N.; Redhwi, H.H.; Al-Arfaj, A.A.; Achilias, D.S. Chemical Recycling of PET in the Presence of the Bio-Based Polymers, PLA, PHB and PEF: A Review. Sustainability 2021, 13, 10528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tricker, A.W.; Osibo, A.A.; Chang, Y.; Kang, J.X.; Ganesan, A.; Anglou, E.; Boukouvala, F.; Nair, S.; Jones, C.W.; Sievers, C. Stages and Kinetics of Mechanochemical Depolymerization of Poly(ethylene terephthalate) with Sodium Hydroxide. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2022, 10, 11338–11347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, C.M.; Clarke, D.J.; Dobson, A.D.W. Microbial Polyethylene Terephthalate Hydrolases: Current and Future Perspectives. Frontiers in Microbiology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carniel, A.; Waldow, V.A.; Castro, A.M. A comprehensive and critical review on key elements to implement enzymatic PET depolymerization for recycling purposes. Biotechnol Adv 2021, 52, 107811. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawai, F.; Kawabata, T.; Oda, M. Current knowledge on enzymatic PET degradation and its possible application to waste stream management and other fields. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2019, 103, 4253–4268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Cebe, P. Vitrification and Devitrification of Rigid Amorphous Fraction of PET during Quasi-Isothermal Cooling and Heating. Macromolecules 2009, 42, 288–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Liu, X.; Dong, S.; Tian, Y.e.; Qiao, Y.; Mitra, R.; Han, J.; Li, C.; Han, X.; et al. Computational Redesign of a PETase for Plastic Biodegradation under Ambient Condition by the GRAPE Strategy. ACS Catalysis 2021, 11, 1340–1350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, R.; Breite, D.; Song, C.; Gräsing, D.; Ploss, T.; Hille, P.; Schwerdtfeger, R.; Matysik, J.; Schulze, A.; Zimmermann, W. Biocatalytic Degradation Efficiency of Postconsumer Polyethylene Terephthalate Packaging Determined by Their Polymer Microstructures. Advanced Science 2019, 6, 1900491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gambarini, V.; Pantos, O.; Kingsbury, J.M.; Weaver, L.; Handley, K.M.; Lear, G. Phylogenetic Distribution of Plastic-Degrading Microorganisms. mSystems 2021, 6, 10–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- PAZy. Available online: https://www.pazy.eu/doku.php?id=start (accessed on 14th June 2024).
- Blázquez-Sánchez, P.; Vargas, J.A.; Furtado, A.A.; Griñen, A.; Leonardo, D.A.; Sculaccio, S.A.; Pereira, H.D.M.; Sonnendecker, C.; Zimmermann, W.; Díez, B.; et al. Engineering the catalytic activity of an Antarctic PET-degrading enzyme by loop exchange. Protein Science 2023, 32, e4757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weigert, S.; Perez-Garcia, P.; Gisdon, F.J.; Gagsteiger, A.; Schweinshaut, K.; Ullmann, G.M.; Chow, J.; Streit, W.R.; Höcker, B. Investigation of the halophilic PET hydrolase PET6 from Vibrio gazogenes. Protein Science 2022, 31, e4500. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer Cifuentes, I.E.; Wu, P.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, W.; Neumann-Schaal, M.; Pfaff, L.; Barys, J.; Li, Z.; Gao, J.; Han, X.; et al. Molecular and Biochemical Differences of the Tandem and Cold-Adapted PET Hydrolases Ple628 and Ple629, Isolated From a Marine Microbial Consortium. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meyer-Cifuentes, I.E.; Werner, J.; Jehmlich, N.; Will, S.E.; Neumann-Schaal, M.; Öztürk, B. Synergistic biodegradation of aromatic-aliphatic copolyester plastic by a marine microbial consortium. Nature Communications 2020, 11, 5790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haernvall, K.; Zitzenbacher, S.; Wallig, K.; Yamamoto, M.; Schick, M.B.; Ribitsch, D.; Guebitz, G.M. Hydrolysis of Ionic Phthalic Acid Based Polyesters by Wastewater Microorganisms and Their Enzymes. Environ Sci Technol 2017, 51, 4596–4605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bollinger, A.; Thies, S.; Knieps-Grünhagen, E.; Gertzen, C.; Kobus, S.; Höppner, A.; Ferrer, M.; Gohlke, H.; Smits, S.H.J.; Jaeger, K.-E. A Novel Polyester Hydrolase From the Marine Bacterium Pseudomonas aestusnigri – Structural and Functional Insights. Frontiers in Microbiology 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Liu, H.; Zeng, Q.; Tian, X.; Long, L.; Yang, J. Catalytic Features and Thermal Adaptation Mechanisms of a Deep Sea Bacterial Cutinase-Type Poly(Ethylene Terephthalate) Hydrolase. Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology 2022, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Won, S.J.; Yim, J.H.; Kim, H.K. Functional production, characterization, and immobilization of a cold-adapted cutinase from Antarctic Rhodococcus sp. Protein Expr Purif 2022, 195-196, 106077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carr, C.M.; Keller, M.B.; Paul, B.; Schubert, S.W.; Clausen, K.S.R.; Jensen, K.; Clarke, D.J.; Westh, P.; Dobson, A.D.W. Purification and biochemical characterization of SM14est, a PET-hydrolyzing enzyme from the marine sponge-derived Streptomyces sp. SM14. Frontiers in Microbiology 2023, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Perez-Garcia, P.; Dierkes, R.F.; Applegate, V.; Schumacher, J.; Chibani, C.M.; Sternagel, S.; Preuss, L.; Weigert, S.; Schmeisser, C.; et al. The Bacteroidetes Aequorivita sp. and Kaistella jeonii Produce Promiscuous Esterases With PET-Hydrolyzing Activity. Frontiers in Microbiology 2022, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-Garcia, P.; Chow, J.; Costanzi, E.; Gurschke, M.; Dittrich, J.; Dierkes, R.F.; Molitor, R.; Applegate, V.; Feuerriegel, G.; Tete, P.; et al. An archaeal lid-containing feruloyl esterase degrades polyethylene terephthalate. Communications Chemistry 2023, 6, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Joo, S.; Cho, I.J.; Seo, H.; Son, H.F.; Sagong, H.Y.; Shin, T.J.; Choi, S.Y.; Lee, S.Y.; Kim, K.J. Structural insight into molecular mechanism of poly(ethylene terephthalate) degradation. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamura, K.; Stecher, G.; Kumar, S. MEGA11: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis Version 11. Mol Biol Evol 2021, 38, 3022–3027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Giuliano, L.; Gentile, G.; Crisafi, E.; Chernikova, T.N.; Abraham, W.R.; Lünsdorf, H.; Timmis, K.N.; Golyshin, P.N. Oleispira antarctica gen. nov., sp. nov., a novel hydrocarbonoclastic marine bacterium isolated from Antarctic coastal sea water. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2003, 53, 779–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harwood, C.S. Beneckea gazogenes sp. nov., a red, facultatively anaerobic, marine bacterium. Current Microbiology 1978, 1, 233–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feller, G.; Thiry, M.; Arpigny, J.-L.; Mergeay, M.; Gerday, C. Lipases from psychrotropic antarctic bacteria. FEMS Microbiology Letters 1990, 66, 239–243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shi, C.; Zhu, S.; Wei, R.; Yin, C.C. Structural and functional characterization of polyethylene terephthalate hydrolase from Ideonella sakaiensis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 2019, 508, 289–294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, C.Y.; Zhang, G.I.; Kang, S.H.; Kim, H.J.; Cho, B.C. Pseudomonas pelagia sp. nov., isolated from a culture of the Antarctic green alga Pyramimonas gelidicola. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009, 59, 3019–3024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haernvall, K.; Zitzenbacher, S.; Biundo, A.; Yamamoto, M.; Schick, M.B.; Ribitsch, D.; Guebitz, G.M. Enzymes as Enhancers for the Biodegradation of Synthetic Polymers in Wastewater. Chembiochem 2018, 19, 317–325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bollinger, A.; Thies, S.; Katzke, N.; Jaeger, K.E. The biotechnological potential of marine bacteria in the novel lineage of Pseudomonas pertucinogena. Microb Biotechnol 2020, 13, 19–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez, D.; Mulet, M.; Rodríguez, A.C.; David, Z.; Lalucat, J.; García-Valdés, E. Pseudomonas aestusnigri sp. nov., isolated from crude oil-contaminated intertidal sand samples after the Prestige oil spill. Syst Appl Microbiol 2014, 37, 89–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molitor, R.; Bollinger, A.; Kubicki, S.; Loeschcke, A.; Jaeger, K.E.; Thies, S. Agar plate-based screening methods for the identification of polyester hydrolysis by Pseudomonas species. Microb Biotechnol 2020, 13, 274–284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Kim, J.G.; Jung, M.Y.; Kim, S.J.; Gwak, J.H.; Yu, W.J.; Roh, S.W.; Kim, Y.H.; Rhee, S.K. Ketobacter alkanivorans gen. nov., sp. nov., an n-alkane-degrading bacterium isolated from seawater. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2018, 68, 2258–2264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.P.; Tang, S.K.; Dong, J.D.; Zhang, Y.Q.; Xu, L.H.; Zhang, S.; Li, W.J. Marinactinospora thermotolerans gen. nov., sp. nov., a marine actinomycete isolated from a sediment in the northern South China Sea. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 2009, 59, 948–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawai, F.; Oda, M.; Tamashiro, T.; Waku, T.; Tanaka, N.; Yamamoto, M.; Mizushima, H.; Miyakawa, T.; Tanokura, M. A novel Ca2+-activated, thermostabilized polyesterase capable of hydrolyzing polyethylene terephthalate from Saccharomonospora viridis AHK190. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2014, 98, 10053–10064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Almeida, E.L.; Carrillo Rincón, A.F.; Jackson, S.A.; Dobson, A.D.W. In silico Screening and Heterologous Expression of a Polyethylene Terephthalate Hydrolase (PETase)-Like Enzyme (SM14est) With Polycaprolactone (PCL)-Degrading Activity, From the Marine Sponge-Derived Strain Streptomyces sp. SM14. Frontiers in Microbiology 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palma Esposito, F.; Ingham, C.J.; Hurtado-Ortiz, R.; Bizet, C.; Tasdemir, D.; de Pascale, D. Isolation by Miniaturized Culture Chip of an Antarctic bacterium Aequorivita sp. with antimicrobial and anthelmintic activity. Biotechnol Rep (Amst) 2018, 20, e00281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dombrowski, N.; Teske, A.P.; Baker, B.J. Expansive microbial metabolic versatility and biodiversity in dynamic Guaymas Basin hydrothermal sediments. Nat Commun 2018, 9, 4999. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bell, E.L.; Smithson, R.; Kilbride, S.; Foster, J.; Hardy, F.J.; Ramachandran, S.; Tedstone, A.A.; Haigh, S.J.; Garforth, A.A.; Day, P.J.R.; et al. Directed evolution of an efficient and thermostable PET depolymerase. Nature Catalysis 2022, 5, 673–681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arnal, G.; Anglade, J.; Gavalda, S.; Tournier, V.; Chabot, N.; Bornscheuer, U.T.; Weber, G.; Marty, A. Assessment of Four Engineered PET Degrading Enzymes Considering Large-Scale Industrial Applications. ACS Catal 2023, 13, 13156–13166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zheng, Y.; Li, Q.; Liu, P.; Yuan, Y.; Dian, L.; Wang, Q.; Liang, Q.; Su, T.; Qi, Q. Dynamic Docking-Assisted Engineering of Hydrolases for Efficient PET Depolymerization. ACS Catalysis 2024, 14, 3627–3639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Chen, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhu, T.; Pang, H.; Li, C.; Geng, W.-C.; Wu, B. Computational redesign of a hydrolase for nearly complete PET depolymerization at industrially relevant high-solids loading. Nature Communications 2024, 15, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Madhavan Nampoothiri, K.; Nair, N.R.; John, R.P. An overview of the recent developments in polylactide (PLA) research. Bioresour Technol 2010, 101, 8493–8501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samantaray, P.K.; Little, A.; Wemyss, A.M.; Iacovidou, E.; Wan, C. Design and Control of Compostability in Synthetic Biopolyesters. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering 2021, 9, 9151–9164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Hiyama, M.; Kabe, T.; Kimura, S.; Iwata, T. Enzymatic Self-Biodegradation of Poly(l-lactic acid) Films by Embedded Heat-Treated and Immobilized Proteinase K. Biomacromolecules 2020, 21, 3301–3307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DelRe, C.; Jiang, Y.; Kang, P.; Kwon, J.; Hall, A.; Jayapurna, I.; Ruan, Z.; Ma, L.; Zolkin, K.; Li, T.; et al. Near-complete depolymerization of polyesters with nano-dispersed enzymes. Nature 2021, 592, 558–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guicherd, M.; Ben Khaled, M.; Guéroult, M.; Nomme, J.; Dalibey, M.; Grimaud, F.; Alvarez, P.; Kamionka, E.; Gavalda, S.; Noël, M.; et al. An engineered enzyme embedded into PLA to make self-biodegradable plastic. Nature 2024, 631, 884–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williams, D.F. Enzymic Hydrolysis of Polylactic Acid. Engineering in Medicine 1981, 10, 5–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pranamuda, H.; Tsuchii, A.; Tokiwa, Y. Poly (L-lactide)-Degrading Enzyme Produced by Amycolatopsis sp. Macromolecular Bioscience 2001, 1, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalem, A.; Yehezkeli, O.; Fishman, A. Enzymatic degradation of polylactic acid (PLA). Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology 2024, 108, 413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hajighasemi, M.; Nocek, B.P.; Tchigvintsev, A.; Brown, G.; Flick, R.; Xu, X.; Cui, H.; Hai, T.; Joachimiak, A.; Golyshin, P.N.; et al. Biochemical and Structural Insights into Enzymatic Depolymerization of Polylactic Acid and Other Polyesters by Microbial Carboxylesterases. Biomacromolecules 2016, 17, 2027–2039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, B.; Zhang, J.; Sun, H.; Bai, R.; Lu, D.; Zhu, Y.; Dong, W.; Zhou, J.; Jiang, M. Computational design of an efficient and thermostable esterase for polylactic acid depolymerization. Green Chemistry 2024, 26, 7268–7279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popovic, A.; Hai, T.; Tchigvintsev, A.; Hajighasemi, M.; Nocek, B.; Khusnutdinova, A.N.; Brown, G.; Glinos, J.; Flick, R.; Skarina, T.; et al. Activity screening of environmental metagenomic libraries reveals novel carboxylesterase families. Scientific Reports 2017, 7, 44103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajighasemi, M.; Tchigvintsev, A.; Nocek, B.; Flick, R.; Popovic, A.; Hai, T.; Khusnutdinova, A.N.; Brown, G.; Xu, X.; Cui, H.; et al. Screening and Characterization of Novel Polyesterases from Environmental Metagenomes with High Hydrolytic Activity against Synthetic Polyesters. Environmental Science & Technology 2018, 52, 12388–12401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yakimov, M.M.; Golyshin, P.N.; Lang, S.; Moore, E.R.; Abraham, W.R.; Lünsdorf, H.; Timmis, K.N. Alcanivorax borkumensis gen. nov., sp. nov., a new, hydrocarbon-degrading and surfactant-producing marine bacterium. Int J Syst Bacteriol 1998, 48 Pt 2, 339–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Larimer, F.W.; Chain, P.; Hauser, L.; Lamerdin, J.; Malfatti, S.; Do, L.; Land, M.L.; Pelletier, D.A.; Beatty, J.T.; Lang, A.S.; et al. Complete genome sequence of the metabolically versatile photosynthetic bacterium Rhodopseudomonas palustris. Nat Biotechnol 2004, 22, 55–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uefuji, M.; Kasuya, K.-i.; Doi, Y. Enzymatic degradation of poly[(R)-3-hydroxybutyrate]: Secretion and properties of PHB depolymerase from Pseudomonas stutzeri. Polymer Degradation and Stability 1997, 58, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saito, Y.; Honda, M.; Yamashita, T.; Furuno, Y.; Kato, D.-i.; Abe, H.; Yamada, M. Marine bacterial enzyme degrades polyamide 4 into gamma-aminobutyric acid oligomers. Polymer Degradation and Stability 2023, 215, 110446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Huang, J.; Liu, S. The production, recovery, and valorization of polyhydroxybutyrate (PHB) based on circular bioeconomy. Biotechnology Advances 2024, 72, 108340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ohura, T.; Kasuya, K.I.; Doi, Y. Cloning and characterization of the polyhydroxybutyrate depolymerase gene of Pseudomonas stutzeri and analysis of the function of substrate-binding domains. Appl Environ Microbiol 1999, 65, 189–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Min, J.; Xue, T.; Jiang, P.; Liu, X.; Peng, R.; Huang, J.-W.; Qu, Y.; Li, X.; Ma, N.; et al. Complete bio-degradation of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) via engineered cutinases. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 1645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y.; Wang, Z.; Zheng, Y.; Cheng, S.; Chen, C.-C.; Guo, R.-T. Structural insights of poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) depolymerases. Advanced Agrochem 2024, 3, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbios. Available online: https://www.carbios.com/en/enzymatic-recycling/ (accessed on 29th July 2024).
- Yao, J.; Liu, Y.; Gu, Z.; Zhang, L.; Guo, Z. Deconstructing PET: Advances in enzyme engineering for sustainable plastic degradation. Chemical Engineering Journal 2024, 154183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Zhang, Q.; Yang, H.; Cui, L.; Qian, H. Mining strategies for isolating plastic-degrading microorganisms. Environmental Pollution 2024, 346, 123572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carbiolice. Available online: https://www.carbiolice.com/en/carbiosactive/ (accessed on 8th August 2024).
- Gao, R.; Liu, R.; Sun, C. A marine fungus Alternaria alternata FB1 efficiently degrades polyethylene. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2022, 431, 128617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Z.; Ding, Z.-H.; Wu, Y.-H.; Xu, X.-W. Degradation of low-density polyethylene by the bacterium Rhodococcus sp. C-2 isolated from seawater. Science of The Total Environment 2024, 907, 167993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Hao, X.; Zhang, X.; Ma, Y.; Niu, Z. A novel marine bacterium Exiguobacterium marinum a-1 isolated from in situ plastisphere for degradation of additive-free polypropylene. Environmental Pollution 2023, 336, 122390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui, Z.; Liu, G.; Liu, X.; Cai, R.; Liu, R.; Sun, C. A Deep-Sea Bacterium Is Capable of Degrading Polyurethane. Microbiology Spectrum 2023, 11, e00073–00023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh Kumar, A.; Hinduja, M.; Sujitha, K.; Nivedha Rajan, N.; Dharani, G. Biodegradation of polystyrene by deep-sea Bacillus paralicheniformis G1 and genome analysis. Science of The Total Environment 2021, 774, 145002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, R.; Zhao, S.; Zhang, B.; Li, G.; Fu, X.; Yan, P.; Shao, Z. Biodegradation of polystyrene (PS) by marine bacteria in mangrove ecosystem. Journal of Hazardous Materials 2023, 442, 130056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandare, S.D.; Chaudhary, D.R.; Jha, B. Bioremediation of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) films by marine bacteria. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2021, 169, 112566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, H.; Yu, T.; Zheng, Y.; Ma, H.; Shan, J.; Yi, X.; Liu, Y.; Zhan, J.; Wang, W.; Zhou, H. Isolation, characteristics, and poly(butylene adipate-co-terephthalate) (PBAT) degradation mechanism of a marine bacteria Roseibium aggregatum ZY-1. Marine Pollution Bulletin 2024, 201, 116261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.H.; Cho, J.Y.; Cho, D.H.; Jung, H.J.; Kim, B.C.; Bhatia, S.K.; Park, S.-H.; Park, K.; Yang, Y.-H. Acceleration of Polybutylene Succinate Biodegradation by Terribacillus sp. JY49 Isolated from a Marine Environment. Polymers 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de Vogel, F.A.; Schlundt, C.; Stote, R.E.; Ratto, J.A.; Amaral-Zettler, L.A. Comparative Genomics of Marine Bacteria from a Historically Defined Plastic Biodegradation Consortium with the Capacity to Biodegrade Polyhydroxyalkanoates. Microorganisms 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
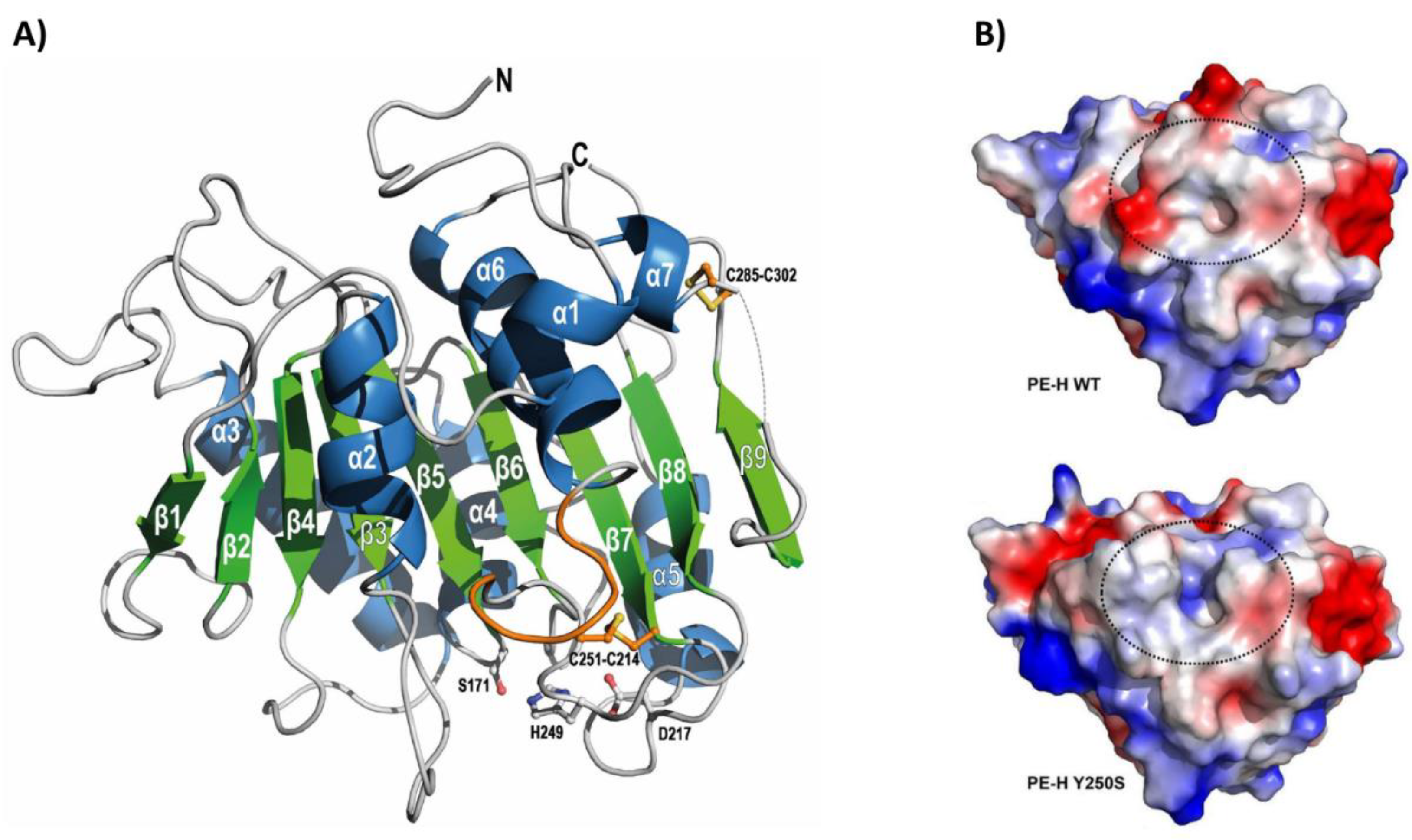
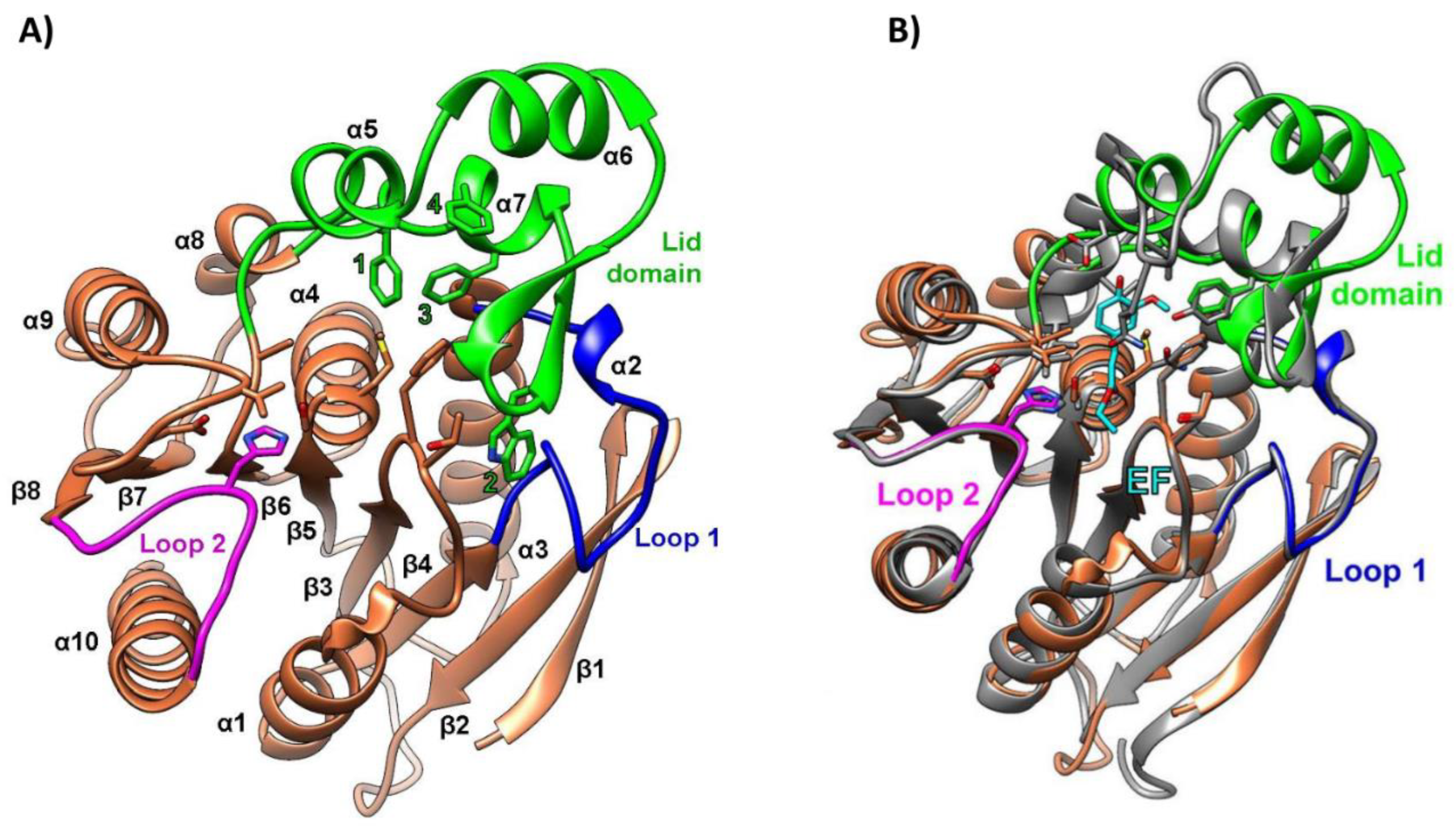
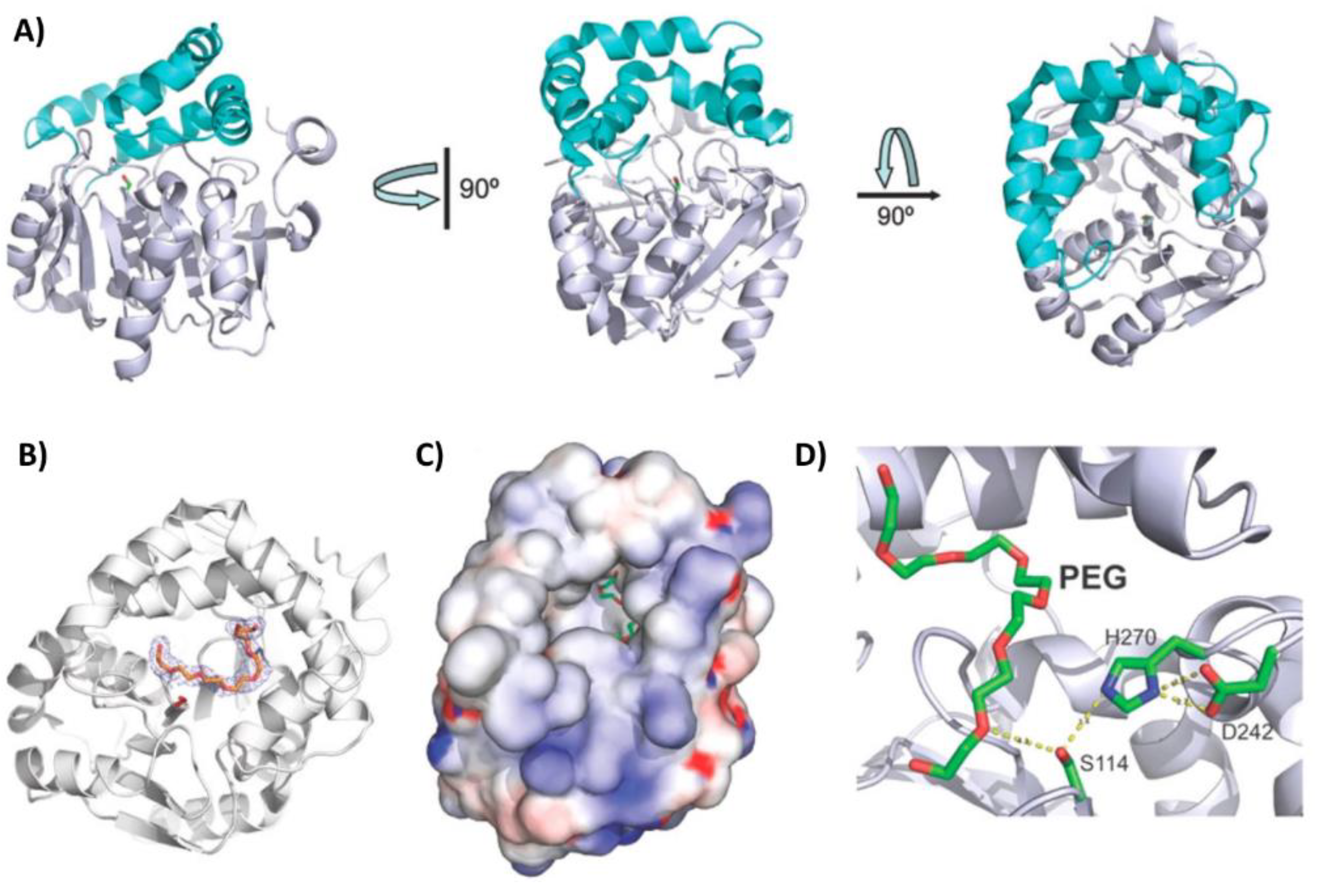
| Name | Source | Isolation habitat | Tm (°C) | PET hydrolysis and reaction conditions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| OaCut (PET5) | Oleispira antarctica | Antarctic seawater | 40.41 | 0.4 µM enzyme produced 0.4% weight loss of amorphous PET films after 6 days at 25 °C, pH 8.0 | [37,39] |
| Mors1 (wild type) |
Moraxella sp. | Antarctic seawater | 52.01 | 0.4 µM enzyme produced 1.98% weight loss of amorphous PET films after 6 days at 25 °C, pH 8.0; ~0.26 mM hydrolysis products were released after 24 h under the same reaction conditions | [37] |
| CMA266C (chimeric Mors1 variant) |
Moraxella sp. | Antarctic seawater | 55.71 | 0.7 µM enzyme produced 2.5% weight loss of amorphous PET films (~1.5 mM hydrolysis products) after 24 h at 45 °C, pH 8.0 | [60] |
| PET6 (wild type) |
Vibrio gazogenes | Marine mud | 49.8- 57.72,3 |
2 µM enzyme produced 1.1 mM hydrolysis products from post-consumer PET (~10% crystallinity) after 18 h at 50 °C, pH 8.5 and 1 M NaCl | [39,61] |
| PET6-VSTA (PET6 variant) |
Vibrio gazogenes | Marine mud | 48.8- 56.72,3 |
2 µM enzyme produced ~1.75 mM hydrolysis products from post-consumer PET (~10% crystallinity) after 18 h at 50 °C, pH 8.5 and 1 M NaCl | [61] |
| PET6-ExLoop (PET6 variant) |
Vibrio gazogenes | Marine mud | n.d. | 2 µM enzyme produced ~2 mM hydrolysis products from post-consumer PET (~10% crystallinity) after 18 h at 50 °C, pH 8.5 and 1 M NaCl | [61] |
| Ple628 | Marinobacter sp. | Marine sediment | 41.41 47.12 |
0.6 µM enzyme produced 0.062 mM hydrolysis products from PET nanoparticles after 72 h at 30 °C, pH 7.4 | [62,63] |
| Ple629 | Marinobacter sp. | Marine sediment | 38.11 43.22 |
0.6 µM enzyme produced 1.5 mM hydrolysis products from PET nanoparticles after 72 h at 30 °C, pH 7.4 | [62,63] |
| PpelaLip |
Halopseudomonas pelagia |
Antarctic algae | n.d. | 1 µM enzyme produced ~10 mmol TPA/mol polyester (equivalent to ~17 µM TPA) from amorphous (<1% crystallinity) in-house synthesized PET analog after 7 days at 28 °C, pH 7.0 | [64] |
| PE-H |
Halopseudomonas aestusnigri |
Intertidal sand | 50.81 | 0.5 µM enzyme produced 4.2 mg/L MHET (equivalent to 20 µM MHET) from amorphous PET film after 48 h at 30 °C, pH 7.4 | [65] |
| PE-HY250S (PE-H variant) |
Halopseudomonas aestusnigri |
Intertidal sand | 49.81 | 0.5 µM enzyme produced 5.4 mg/L MHET (equivalent to 26 µM MHET) from amorphous PET film, and 0.12 mg/L MHET (equivalent to 0.57 µM) from semicrystalline PET after 48 h at 30 °C, pH 7.4 | [65] |
| Enzyme 403 | Ketobacter sp. | Deep-sea metagenome | n.d. | 0.7 mg enzyme/g PET (equivalent to ~0.65 µM enzyme) produced 1.4-1.7 mg/L aromatic products (equivalent to ~9 µM) from amorphous PET film after 96 h at 70 °C, pH 6.0-9.0 | [41] |
| Enzyme 409 | Ketobacter sp. | Deep-sea metagenome | n.d. | 0.7 mg enzyme/g PET (~0.69 µM enzyme) produced 9.8 mg/L aromatic products (equivalent to ~50 µM) from amorphous PET film after 96 h at 60 °C, pH 9.0 | [41] |
| Enzyme 412 | Ketobacter sp. | Surface seawater | n.d. | 0.7 mg enzyme/g PET (~0.65 µM enzyme) produced 2.2 mg/L aromatic products (equivalent to ~11 µM) from amorphous PET film after 96 h at 60 °C, pH 6.0 | [41] |
| Enzyme 606 (MtCut) |
Marinactinospora thermotolerans |
Deep-sea sediment | 53.92 | 0.7 mg enzyme/g PET (~0.69 µM enzyme) produced 67 mg/L aromatic products (equivalent to ~345 µM) from amorphous PET film after 96 h at 60 °C, pH 9.0 | [41] |
| 33.0- 41.51,4 |
5 mg enzyme/g PET (~0.3 µM enzyme) produced 400 µM aromatic products from PET microparticles (42% crystallinity) after 120 h at 40 °C, pH 8.5 | [66] | |||
| Rcut | Rhodococcus sp. | Antarctic Ross Sea | n.d. | 0.026 µM of enzyme produced traces of hydrolysis products from PET film after 24 h at 30 °C, pH 9.0 | [67] |
| SM14est | Streptomyces sp. | Marine sponge | 55.01 | 0.5 µM of enzyme produced 0.27 mM hydrolysis products from semicrystalline PET powder (>40% crystallinity) after 7 h at 45 °C, pH 8.0 and 0.5 M NaCl | [68] |
| PET27 | Aequorivita sp. | Antarctic sediments | n.d. | 28.6 mg enzyme/g PET (~26.5 µM enzyme) produced 0.872 mM TPA from amorphous PET film after 120 h at 30 °C, pH 8.0 | [69] |
| PET46 |
Candidatus Bathyarchaeota |
Deep-sea hydrothermal vent sediments (metagenome) | 84.51 | 3 µM enzyme produced 1.6 mM TPA from semicrystalline PET powder (>40% crystallinity) after 72 h at 60 °C, pH 8.0 | [70] |
| Name | Source | Isolation habitat | Tm/Tagg (°C) |
PLA hydrolysis and reaction conditions | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ABO2449 |
Alcanivorax borkumensis |
Seawater/sediments | Tagg = 32.3 | 4 mg enzyme⋅g PLA-1 produced 120 mM lactate (~90% substrate conversion) from PDLLA powder (Mw: 10-18 kDa) after 36 h at 35 °C, pH 8.0, and 0.1% (w/v) Plysurf A210G | [100] |
| RPA1511 | Rhodopseudomonas palustris | Various sources, including marine sediments | Tagg = 70.8 | 4 mg enzyme⋅g PLA-1 produced 50 mM lactate (~40% substrate conversion) from PDLLA powder (Mw: 10-18 kDa) after 36 h at 35 °C, pH 8.0 | [100] |
| Tm = 70.11 | 4 mg enzyme⋅g PLA-1 produced ~70 mM lactate (~60% substrate conversion) from PDLLA powder (Mw: 10-18 kDa) after 72 h at 55 °C, pH 8.0 | [101] | |||
| R5 (RPA1511 variant) | Rhodopseudomonas palustris | Various sources, including marine sediments | Tm = 78.71 | 4 mg enzyme⋅g PLA-1 produced 94.5 mM lactate (~85% substrate conversion) from PDLLA powder (Mw: 10-18 kDa) after 72 h at 65 °C, pH 9.0 | [101] |
| MGS0109 | Uncultured bacterium |
Seawater metagenome | Tagg = 48.1 | The PLA-degrading activity was confirmed through a qualitative assay on agar plates containing emulsified PDLLA (Mw: 2 kDa) after 24 h at 30 °C, pH 8.0 | [40] |
| MGS0010 | Uncultured bacterium |
Seawater metagenome | Tagg = 46.2 | The PLA-degrading activity was confirmed through a qualitative assay on agar plates containing emulsified PDLLA (Mw: 2 kDa) after 24 h at 30 °C, pH 8.0 | [40] |
| MGS0105 | Uncultured bacterium |
Seawater metagenome | Tagg = 46.1 | The PLA-degrading activity was confirmed through a qualitative assay on agar plates containing emulsified PDLLA (Mw: 2 kDa) after 24 h at 30 °C, pH 8.0 | [40] |
| ABO_1197 |
Alcanivorax borkumensis |
Seawater metagenome | Tagg = 47.0 | The PLA-degrading activity was confirmed through a qualitative assay on agar plates containing emulsified PDLLA (Mw: 2 kDa) after 24 h at 30 °C, pH 8.0 | [40] |
| ABO_1251 |
Alcanivorax borkumensis |
Seawater metagenome | Tagg = 45.7 | The PLA-degrading activity was confirmed through a qualitative assay on agar plates containing emulsified PDLLA (Mw: 2 kDa) after 24 h at 30 °C, pH 8.0 | [40] |
| MGS0084 | Uncultured organism |
Tar samples from a sunken shipwreck | n.d. | The PLA-degrading activity was confirmed through a qualitative assay on agar plates containing emulsified PDLLA (Mw: 2 kDa), at 30 °C, pH 8.0 | [102,103] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





