Submitted:
03 September 2024
Posted:
03 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
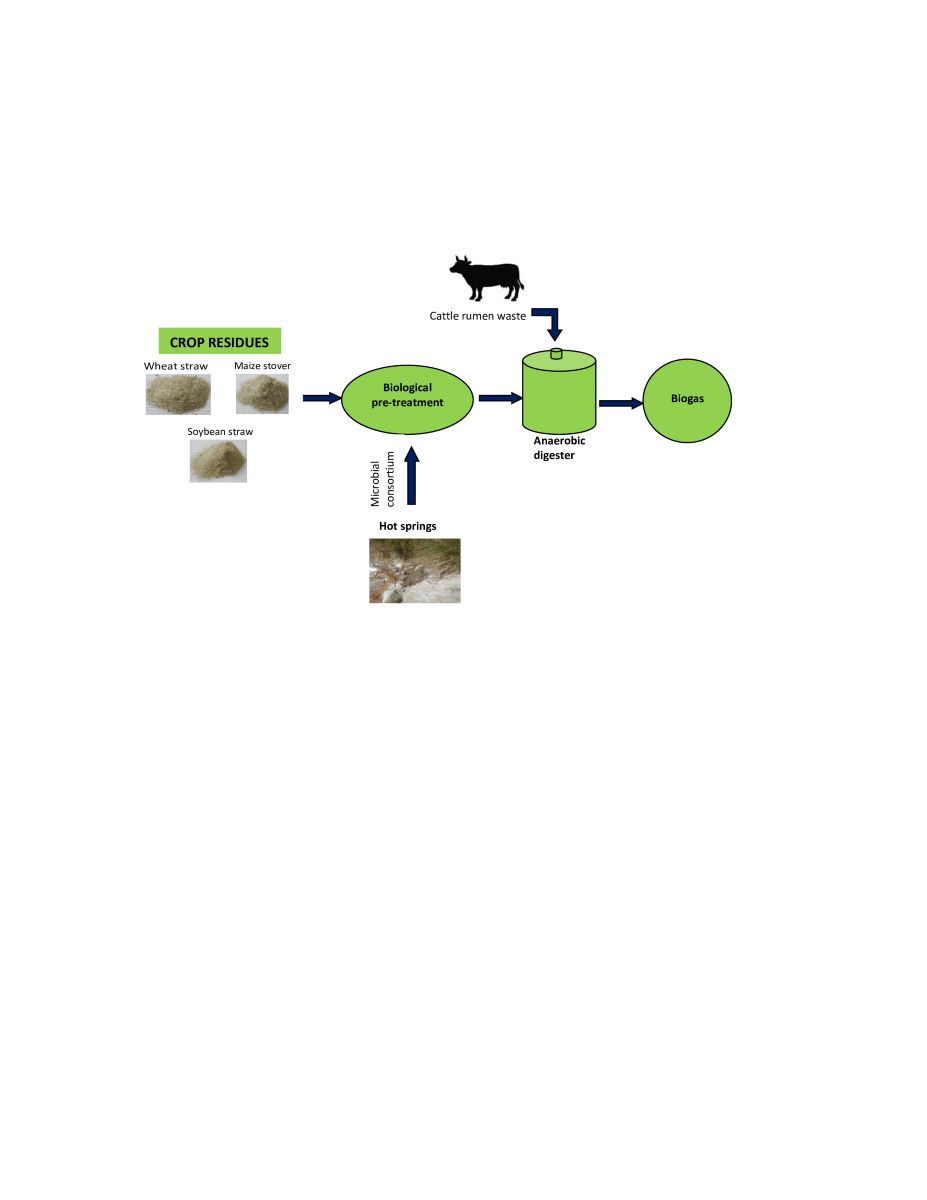
2.1. Experimental Design
2.2. Raw Materials
2.3. Construction of Microbial Consortium
2.4. Biological Pre-Treatment of Crop Residues by Microbial Consortium
2.5. Characterization of Pre-treated Crop Residues
2.6. Anaerobic Digestion of Crop Residues
2.7. Data Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Effect of Biological Pre-Treatment on Chemical Characteristics of Crop Residues
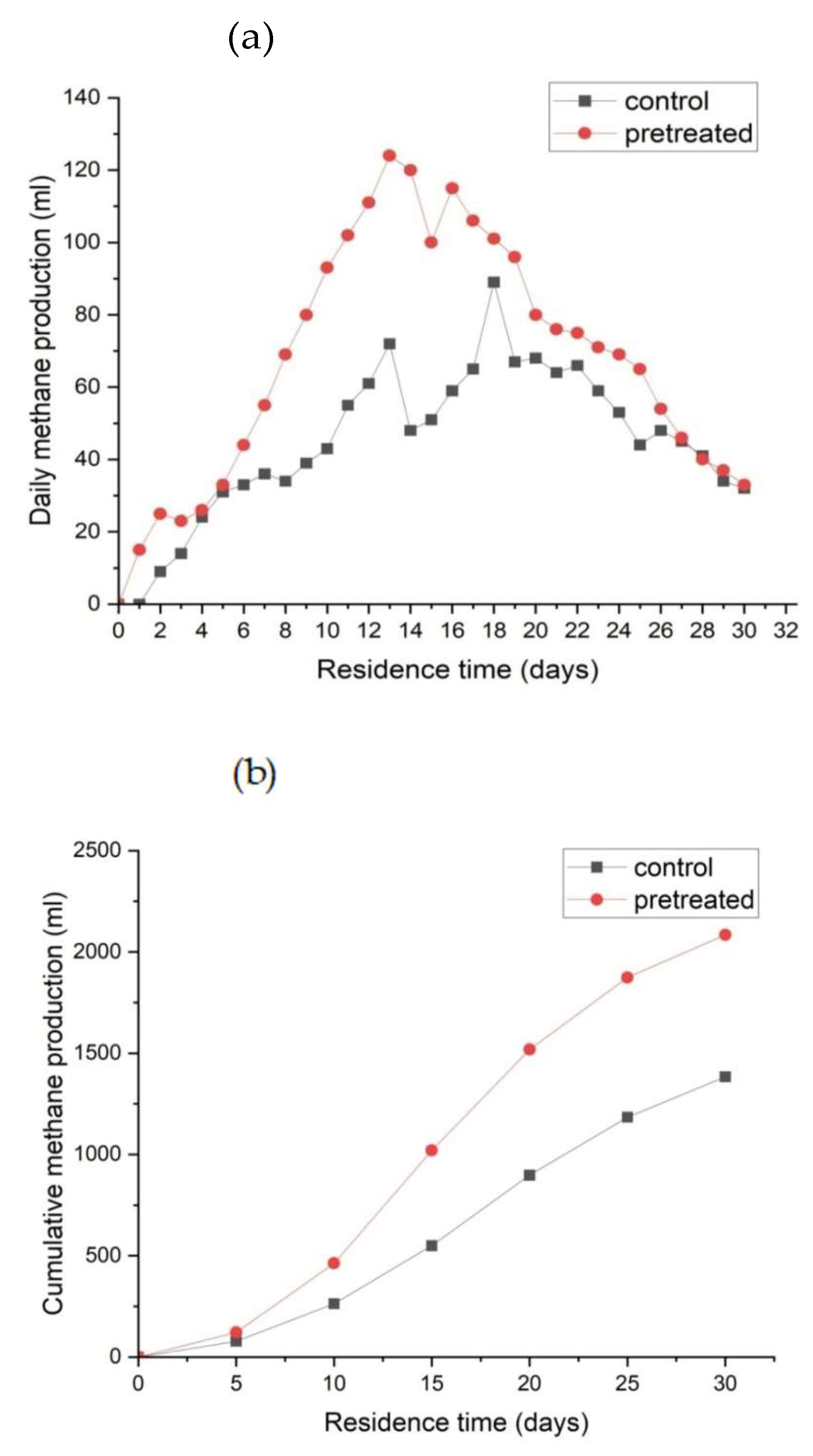
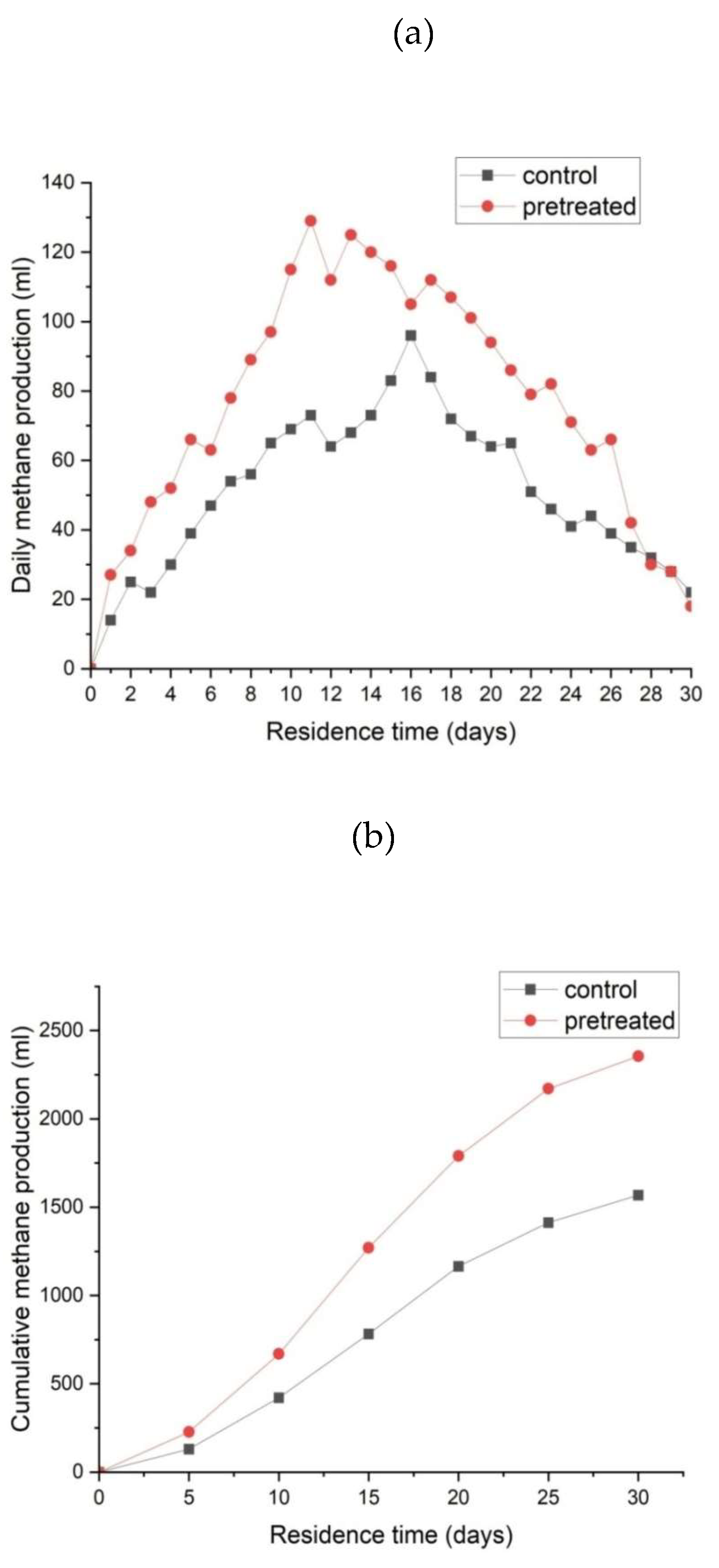
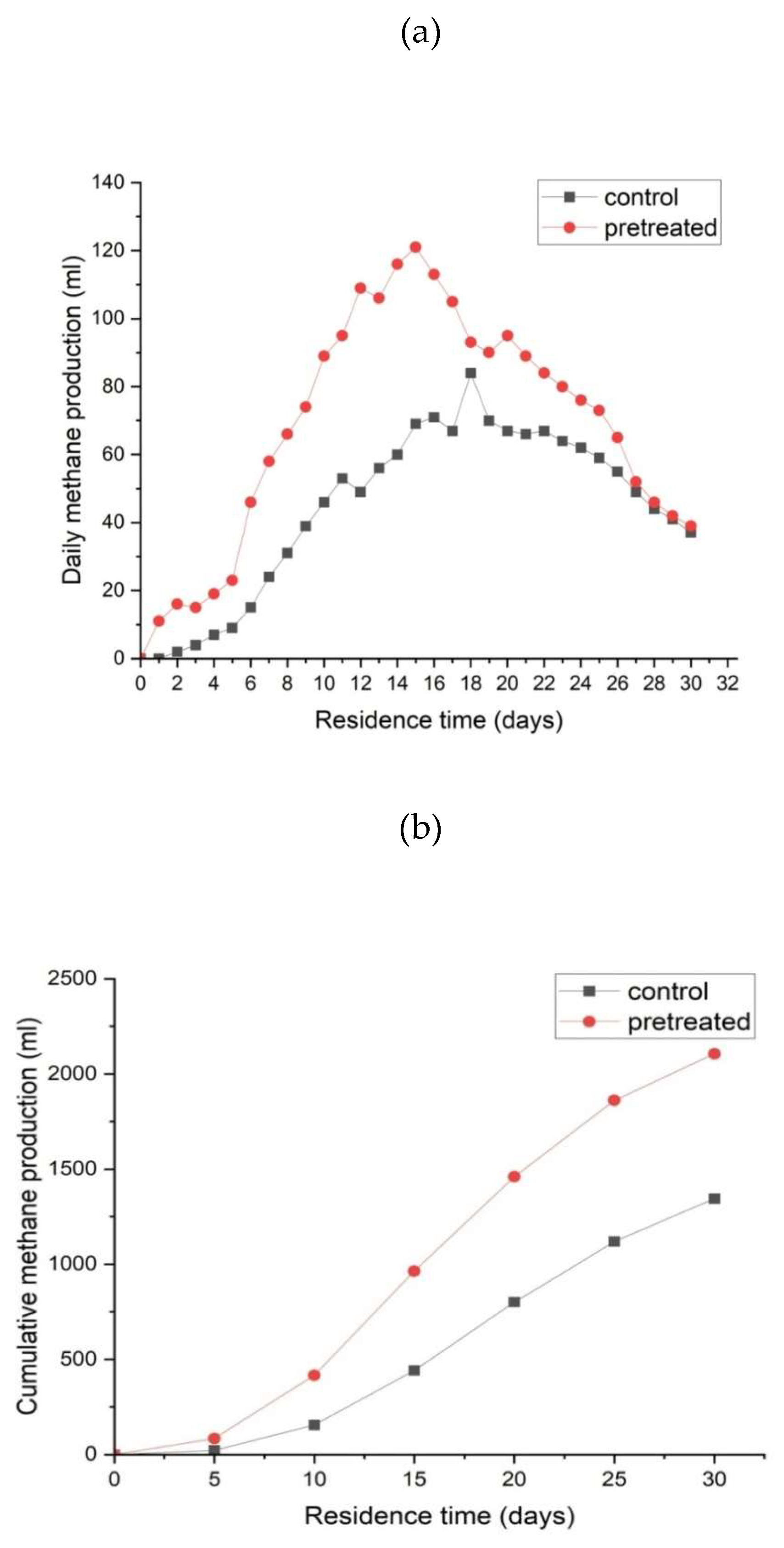
3.2. Effect of Microbial Pre-Treatment on Biomethane Production
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ali, S.S.; Abomohra, A.E.; Sun, J. Effective bio-pretreatment of sawdust waste with a novel microbial consortium for enhanced biomethanation. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 238, 425–432. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kong, X.P.; Du, J.; Ye, X.; Xi, Y.; Jin, H.; Zhang, M.; Guo, D. Enhanced methane production from wheat straw with the assistance from lignocellulolytic microbial consortium TC-5. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 263, 33–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamusoko, R.; Jingura, R.M.; Parawira, W.; Chikwambi, Z. Characterization of lignocellulosic crop residues for potential biogas production in Zimbabwe. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2022, 16, 1165–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jingura, R.M.; Matengaifa, R. The potential for energy production from crop residues in Zimbabwe. Biomass Bioenergy. 2008, 32, 1287–1292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, W.; Zhang, Z.; Luo, Y.; Sun, S.; Qiao, W.; Xiao, M. Effect of biological pre-treatments in enhancing corn straw biogas production. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 11177–11182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinde, R.; Shahi, D.K.; Mahapatra, P.; Singh, C.S.; Naik, S.K.; Thombare, N.; Singh, A.K. Management of crop residues with special reference to the on-farm utilization methods: A review. Ind. Crops Prod. 2022, 181, 114772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamusoko, R.; Jingura, R.M.; Chikwambi, Z.; Parawira, W. Strategies for valorization of crop residues into biofuels and other value-added products. Biofuels Bioprod. Bioref. 2021, 15, 1950–1964. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Achinas, S.; Achinas, V.; Euverink, G.J.W. A technological overview of biogas production from biowaste. Engineering. 2017, 3, 299–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sukhesh, M.J.; Rao, P.V. Anaerobic digestion of crop residues: Technological developments and environmental impact in the Indian context. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2018, 16, 513–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sindhu, R.; Gnansounou, E.; Rebello, S.; Binod, P.; Varjani, S.; Thakur, I.S.; Thakur, I.S.; Nair, R.; Pandey, A. Conversion of food and kitchen waste to value-added products. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 241, 619–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dar, R.A.; Parmar, M.; Dar, E.A.; Sani, R.K.; Phutela, U.G. Biomethanation of agricultural residues: Potential, limitations and possible solutions. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2021, 135, 110217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paudel, S.R.; Banjara, S.P.; Choi, O.K.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, Y.M.; Lee, J.W. Pre-treatment of agricultural biomass for anaerobic digestion: Current state and challenges. Bioresour. Technol. 2017, 245, 1194–1205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, A.; Mathew, A.K.; Park, H.; Choi, O.; Sindhu, R.; Parameswaran, B.; Pandey, A.; Park, J.H.; Sang, B. Pre-treatment strategies for enhanced biogas production from lignocellulosic biomass. Bioresour. Technol. 2020, 301, 122725. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awogbemi, O.; Kallon, D.V.V. Pre-treatment techniques for agricultural waste. Case Stud. Chem. Environ. Eng. 2022, 6, 100229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, X.; Cao, Y.; Li, J.; Wen, B.; Zhu, W.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z. Effect of pre-treatment by a microbial consortium on methane production of waste paper and cardboard. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 281–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Catherine, C.; Twizerimana, M. Biogas production from thermo-chemically pre-treated sweet potato root waste. Heliyon 2022, 8, e10376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Q.; He, J.; Tian, M.; Mao, Z.; Tang, L.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, H. Enhancement of methane production from cassava residues by biological pre-treatment using a constructed microbial consortium. Bioresour. Technol. 2011, 102, 8899–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Li, W.; Chen, C.; Liao, P. Biological pre-treatment of cotton stalks and domestication of inocula in biogas fermentation. Microbiol. China 2010, 37, 513–519. [Google Scholar]
- Zhong, C.; Wang, C.; Wang, F.; Jia, H.; Wei, P.; Zhao, Y. Enhanced biogas production from wheat straw with the application of synergistic microbium consortium pre-treatment. RSC Adv. 2016, 6, 60187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamusoko, R.; Jingura, R.M.; Parawira, W.; Chikwambi, Z. Isolation and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria from Lubimbi hot springs in Binga, Zimbabwe. J. Biosci. Biotechnol. 2023, 12, 33–39. [Google Scholar]
- American Public Health Association (APHA). Standard Methods for the Examination of Water and Wastewater, 19th edn.; APHA Inc.: New York, United States of America, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Liu. Effect of sample size, dry ashing, temperature and duration on determination of ash content in algae and other biomass. Algal Res. 2019, 40, 101486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, B.; Yuan, X.; Cao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wang, X.; Cui, Z. Optimization of liquid fermentation of microbial consortium WSD-5 followed by saccharification and acidification of wheat straw. Bioresour. Technol. 2012, 118, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, H.; Zhang, P.; Ye, J.; Wu, Y.; Fang, W.; Gou, X.; Zeng, G. Improvement of methane production from rice straw with rumen fluid pre-treatment: A feasibility study. Inter. Biodeter. Biodegradation. 2016, 113, 9e16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Fu, S.; Yang, Z.; Lu, J.; Guo, R. Improved methane production from corn straw by micro-aerobic pre-treatment with pure bacteria system. Bioresour. Technol. 2018, 259, 18–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, T.A.; Lee, C.C.; Orts, W.J.; Tabassum, R. Biological pre-treatment of rice straw by ligninolytic Bacillus sp. strains for enhancing biogas production. Environ. Prog. Sustain. Energy. 2019, 38, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, Z.; Yan, W.; Ding, M.; Yuan, Y. Construction of microbial consortia for microbial degradation of complex compounds. Front. Bioengin. Biotechnol. 2012, 10, 1051233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Z.; Guan, X.; Xu, Y.; Huang, N.; Liu, K. Improving pulping performance as well as reducing consumption and increasing efficiency via microbial consortium pre-treating bamboo. Fermentation 2023, 9, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamusoko, R. Isolation and characterization of cellulolytic bacteria for improving biogas production from crop residues through biological pre-treatment and co-digestion. PhD Thesis. Unpublished.
- Zhu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Tan, F.; Wu, B.; Dai, L.; He, M.; Hu, G. Promotion of biogasification efficiency by pre-treatment and bioaugmentation of corn straw with microbial consortium. E3S Web of Conf. 2019, 118, 01032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, C.; Ai, S.; Wang, H.; Gao, Y.; Yan, L.; Mei, Z.; Wang, W. Biological pretreatment enhances the activity of functional microorganisms and the ability of methanogenesis during anaerobic digestion. Bioresour. Technol. 2019, 290, 121660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan-zhuan, C.; Hai-bo, Z.; Wan, S.; Hong-yan, C.; Shuang-dui, Y.; Yu-shan, B.; Zong-jan, C.; Jia-jia, L. Effects of MC1 pre-treatment on hydrolysis characteristics and methane production efficiency of soybean straw. J. Agro-Environ. Sci. 2010, 39, 2074–2080. [Google Scholar]
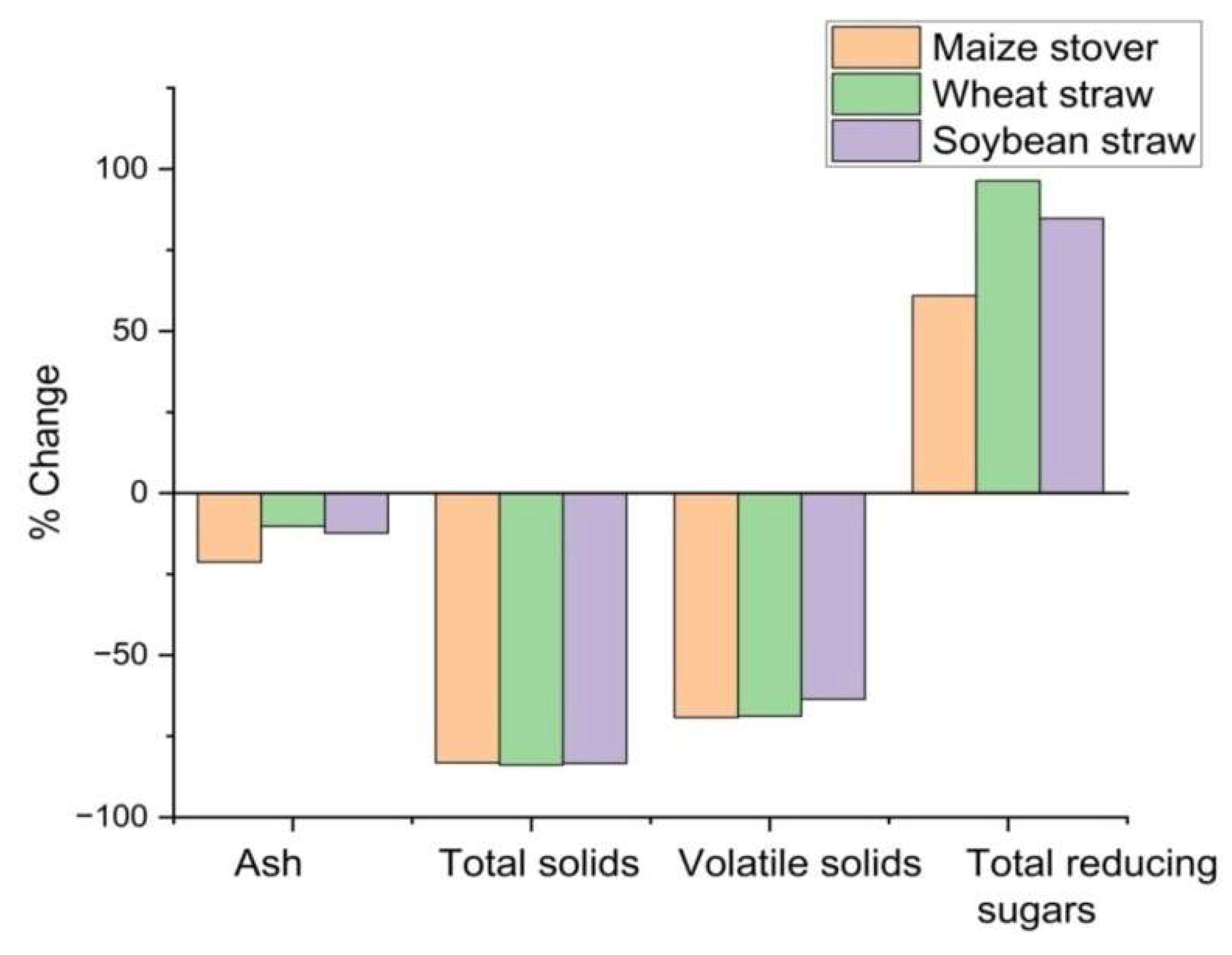
| Parameter | Maize stover | Wheat straw | Soybean straw | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | Treated | Control | Treated | Control | Treated | |
| Ash | 5.34 ± 0.49 | 4.20 ± 0.25* | 6.67 ± 0.58 | 5.99 ± 0.28** | 4.55 ± 0.70 | 3.99 ± 0.21** |
| Volatile solids | 85.53 ± 3.31 | 26.33 ± 0.51* | 89.60 ± 0.40 | 28.00 ± 0.87* | 87.26 ± 2.09 | 31.73 ± 0.98* |
| Total solids | 94.63 ± 0.78 | 15.90 ± 0.76* | 92.70 ± 0.80 | 14.93 ± 0.24* | 91.23 ± 2.04 | 15.17 ± 0.44* |
| Total reducing sugars (mg L-1) | 65.13 ± 0.71 | 126.03 ± 2.47* | 52.60 ± 1.31 | 103.27 ± 2.58* | 48.80 ± 1.71 | 90.17 ± 2.74* |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





