Introduction
In the complex process of kinetic recovery, an essential aspect that is often underestimated is the recovery of the vestibular system. Integrating and understanding the importance of this system is crucial for a complete insight into how the human body works and how the interactions between its various systems influence the healing and rehabilitation process [
1,
2].
The vestibular system plays an essential role in maintaining balance, perception of body movement and position in space, contributing to proprioception by integrating sensory information about head and body movements [
2,
3]. Benign Proximal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) can affect the vestibular system, causing vertigo and light-headedness that affects general balance and induces vicious body positions [
3,
4]. These disturbances generate sensory confusion, affecting the precision of movements, including of the shoulder, even if the joint is clinically healthy [
4].
BPPV can also cause anxiety and stress, diminishing the brain's ability to correctly integrate sensory information and negatively influencing body movements and coordination [
5].
Different types of proprioceptors are active during distinct body movements and pick up different types of information: limb speed and movement, limb loading and their limits. The central nervous system integrates proprioception and other sensory systems (vision and the vestibular system) to create a global representation of body position, motion, and acceleration [
5,
6].
Proprioception, mediated by proprioceptors, mechanosensory neurons located in muscles, tendons, and joints, involves constant feedback between the nervous system and body components. The central nervous system integrates proprioception with other sensory systems, including vision and the vestibular system, to create a global representation of body position and movement [
6].
In addition to maintaining balance, the vestibular system collects information to control movement and reflexes that mobilize various body segments to compensate for changes in body position. This interplay between proprioception, kinesthesia, and vestibular information is vital for optimal body function [
1,
3,
7].
There are many orthopedic conditions at the shoulder level, which can be divided into degenerative conditions (such as omarthrosis) and traumatic conditions (dislocations, fractures, muscle or ligament tears, etc.). Physiotherapy procedures for the recovery of conditions at the level of the scapulohumeral joint must be adapted according to age, sex, the treated condition, sports branch, respectively the specifics of daily life [
8,
9].
Recovery considers, as the first objective, the relief of pain, together with the reduction of inflammation, re-education, toning of the affected muscles and the restoration of joint function, followed by the reintegration of the patient into daily life, respectively the return of the athlete to training and competitions. A broad and open approach to the treated pathology is needed to achieve these objectives [
8].
The general objective of the study includes the initiation and carrying out of a fundamental multidisciplinary research with clinical applicability on the mechanisms involved in the functioning of the shoulder joint, following various conditions located at the level of the scapulohumeral joint (traumatic or degenerative), with an emphasis on the involvement of the vestibular system in the recovery process . By integrating expertise from diverse fields such as ENT, orthopedics, neuroscience and physical therapy, this research aims to provide a deeper understanding of how impairment of vestibular function can influence the recovery process even at the level of the shoulder joint, which is a non-bearing joint.
Materials and Methods
We conducted a prospective observational study that included 48 subjects diagnosed with Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) and a degenerative or traumatic condition located at the shoulder joint. The subjects of the study came from the trauma and orthopedics department or from the specialized outpatient clinic of the Municipal Hospital in Sighișoara, Romania. All patients who presented symptoms specific to BPPV (intense and short-lasting dizziness, in repeated episodes; nystagmus; nausea, vomiting; balance loss) benefited from an ENT consultation and a complete evaluation to establish the diagnosis of BPPV.
The study was conducted over a period of 4 years and 6 months (September 2019 – April 2024).
Study participants were informed about their rights and obligations, had the opportunity to withdraw from the study without repercussions, and signed an informed consent form.
Inclusion criteria: a degenerative or traumatic condition at the scapulohumeral level, the diagnosis of BPPV, the consent of the subjects regarding enrollment in the study, the compliance of the subjects with the recovery program.
Exclusion criteria: cervical spondylosis, bone or other cancer, conditions that contraindicate physical exertion or electrotherapy procedures, disagreement about enrollment in the study or non-compliance with the recovery program.
Study Design
In order to improve proprioception at the level of the scapulohumeral joint, in designing the recovery program we used the following tools: elastic band (three different degrees of difficulty), balance pillow (with three different inflation pressures), Bosu balance ball (with three different inflation pressures), Bobath ball (three different inflation pressures) and other means used in medical recovery such as 1kg weights, low diameter sponge ball, pedal board, consultation couch, etc.
Electrotherapy procedures for pain relief - TECAR.
Procedures used to relieve symptoms caused by BPPV: Epley maneuver, Brandt-Daroff, Cawthrone-Cooksey exercises, gaze stabilization exercises, and walking exercises.
The length of time the recovery program was applied varied based on the individual and the extent of damage to the shoulder joint's anatomical structures.
The interdisciplinary character of the study results from precise evaluations carried out by orthopedic doctors, otorhinolaryngologists and the follow-up of kinetic programs by the physiotherapist and the adaptation of recovery according to the needs of the individual.
Physiotherapy Assessments Applied to Study Subjects
The DGI (Dynamic Gait Index) for dynamic balance assessment and joint posture matching for proprioception assessment at the beginning of the recovery program and at the end of it in both the affected upper limb and the unaffected upper limb.
For joint position matching shoulder external rotation was not assessed because the subjects undergoing surgery did not have permission from the orthopedic surgeon to perform this movement at the start of the recovery program.
Flexion and abduction - the subject is positioned at 60° flexion, respectively abduction from the shoulder joint - with visual control, 3 times. The upper limb is brought to a neutral anatomical; the subject with closed eyes reproduces the positioning of the upper limb at 60°. The difference in degrees between 60° and the angle at which the subject positioned the upper limb without visual control is noted.
Notes: If the subject performs less than 60°, then the difference is scored as a minus, and if the subject positions the upper limb, without visual control, at more than 60°, then the difference is scored as a plus.
Example: 50° (made by subject) – difference to 60° is 10° = -10°
70° (made by subject) – difference from 60° is 10° = +10°
60° (performed by subject) – no differences = 0°
The evaluation was carried out with the help of a digital goniometer.
In the study we evaluated stages 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 of the DGI index.
Score and interpretation for DGI:
0–complete inability to perform the task;
1-uncertain performance, with frequent loss of balance;
2-performance with minor balance problems;
3-performance without balance problems.
Maximum possible score: 15 points.
The recovery program included the following stages:
commencement of procedures to alleviate BPPV symptoms, along with the introduction of exercises to restore joint mobility, conducted from a decubitus position.
verticalization of the subject in the recovery process - recovery of muscle strength and continuation of exercises to improve the symptoms of benign paroxysmal positional vertigo;
continuation of the procedures to improve BPPV, simultaneously with the recovery of coordination and proprioception;
increasing resistance to effort, especially in subjects with cardiovascular system issues;
socio-professional reintegration
This study is not experimental – the physiotherapy procedures used conform to standardized protocols. The present study analyzes the interdependence and interconnectivity of different systems of the human body in the recovery process of the scapulohumeral joint.
Statistical Analysis
The collected data were processed in MS Excel. The statistical analysis was performed using the SPSS program (Statistical Package for the Special Sciences).
Descriptive statistics for the entire sample of 48 subjects, respectively for subjects with an orthopedic diagnosis at the level of the scapulohumeral joint and vestibular system impairment (VPPB) are presented in the form of central numerical values (mean and median), variation (standard deviation ) and extremes (minimum and maximum), as well as by dividing the data into four equal segments (quartiles). These statistics include test results taken at two assessment points: initial and final. Results are compared between the affected upper limb and the unaffected upper limb.
Results
The study included 48 subjects between the ages of 22 and 74, of which: 21 (43.75%) were male and 27 (56.25%) were female. Among the subjects of the study: 15 (31.25%) subjects carried out professional activity in a dynamic environment, 30 (62.5%) performed recreational physical activities systematically, and three (6.25%) athletes of performance – handball. 19 (39.58%) subjects underwent surgery at the scapulohumeral level following the orthopedic diagnosis. Among the 48 participants in the study, 12 (25%) have comorbidities such as: HTN, tachycardia, osteoporosis, DM type II, rheumatological conditions.
The average age of the study participants was 52 years, with the youngest study participant being 22 years old and the oldest 74 years old.
1.1. Joint Position Matching
It is observed that, at the time of the initial evaluation, the affected upper limb shows negative position average values, unlike the unaffected upper limb, where the position indicator shows/display/presents positive values. Although the joint position matching test was adapted so that all study participants (operated and non-operated) had equal chances in performing the test, we can see that for the affected upper limb, at the initial assessment, the 60
0 flexion and abduction, respectively, were not achieved by most subjects (table 1). This fact was not due to the lack of joint mobility in the direction of abduction or flexion (with visual control the subjects performed the 60
0 necessary for the evaluation), but to the proprioceptive sense. Although for the initial assessment at the level of the unaffected upper limb the values of the position averages are positive, this still indicates an impairment of proprioception, but it shows that the subjects performed the movement over 60
0 (
Table 1).
Analyzing the data contained in
Table 1, we can conclude the following:
proprioception is affected both in the affected upper limb and in the unaffected one, at the level of the scapulohumeral joint;
although movement up to an angle of 600 is possible, in the subjects evaluated in this study, this may not be achieved without visual control. This fact is due to the impairment of proprioception, which compromises the ability to perceive and precisely control the movement of the joint;
at the level of the unaffected joint, although the values of the position averages are positive, they still indicate a deviation from the 600 angle, proving an impairment of proprioception.
Following the initial assessment, the physiotherapy recovery program was outlined and applied to improve the symptoms caused by BPPV and to recover the scapulohumeral joint. While the recovery program of the shoulder joint went through several stages (recovery of joint mobility, regaining muscle strength identical to the contralateral upper limb, recovery of coordination and proprioception), the procedures applied for the recovery of the vestibular system continued throughout the recovery period until to the socio-professional reintegration of the individual.
It is observed that, at the time of the final assessment, both the affected upper limb and the unaffected upper limb show positive position average values - except for the minimum value (
Table 2).
Comparing the minimum value of the postural averages between the initial assessment and the final assessment, for both the affected and the unaffected limb, a significant improvement in proprioceptive sense can be seen.
For the maximum value, comparing the results of the initial testing with those of the final testing, we observe that for the affected upper limb, the abduction movement, there is still a significant deviation (of 40) between performing the movement with visual control and without visual control; however we consider that the maximum mean value for the affected upper limb at initial testing suggested a deviation of -70 from the target value. Thus, we can say that there has been an improvement in proprioceptive perception, but expressed as a value of 30 benefit, considering that there is still a deviation of 40 from the target angle.
Differences between the Time of Testing and the Affected Upper Limb Compared to the Unaffected Upper Limb - Joint Position Matching
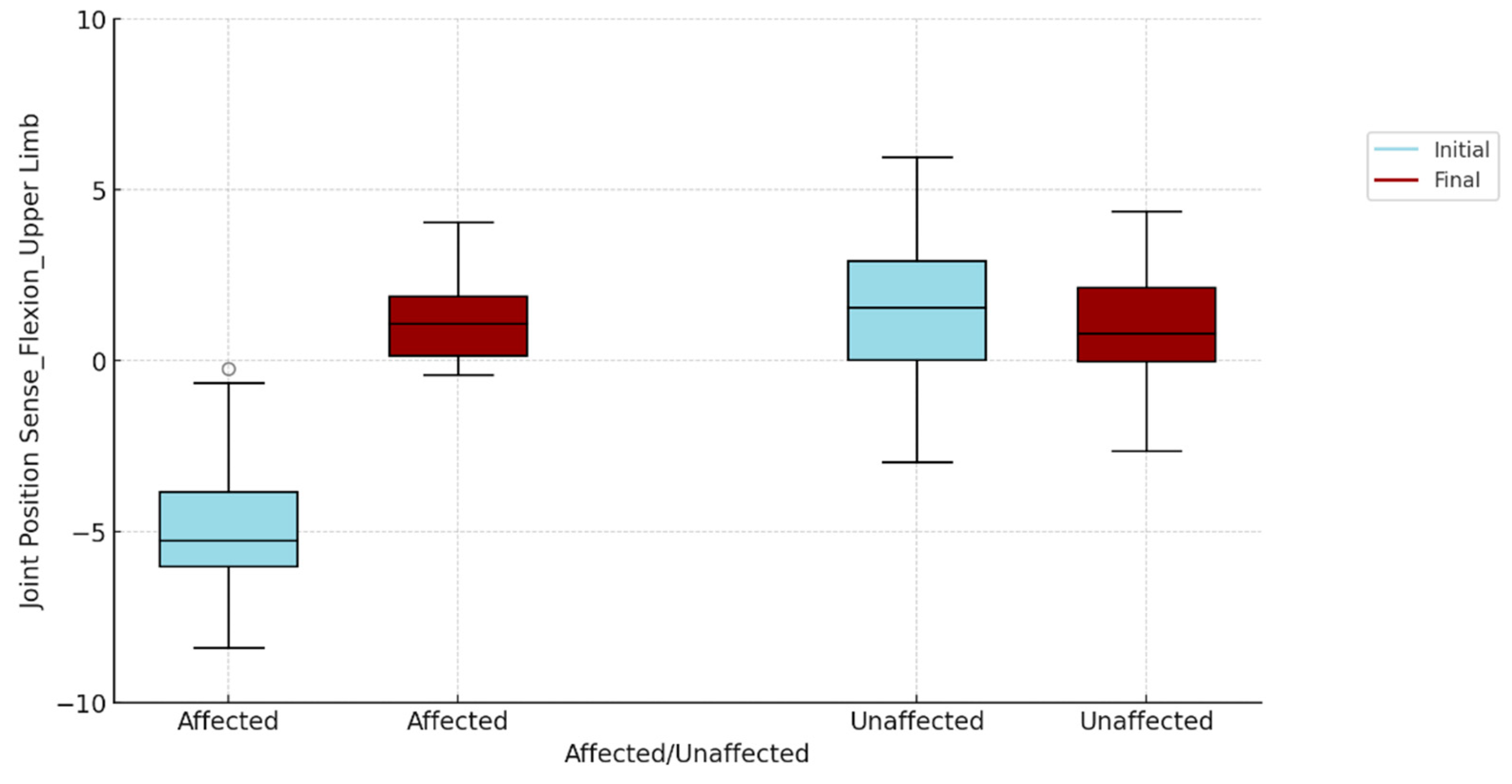
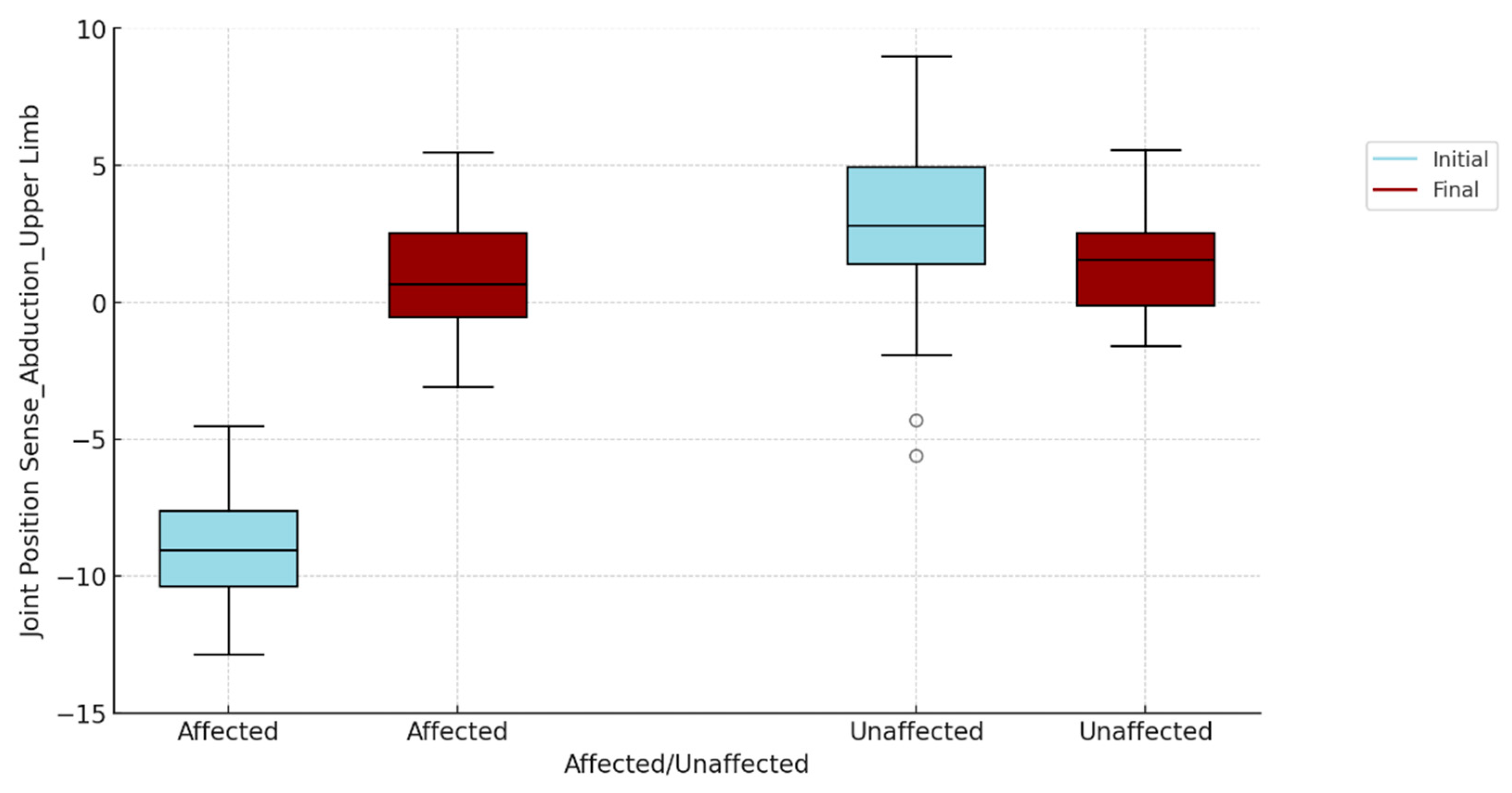
To visualize if there are differences, for each of the two tests (flexion and abduction), between the two evaluation moments (initial and final), between the affected and unaffected upper limb, we opted for the box-plots graphic representation , presented in
Figure 1 and
Figure 2. The "gap" between the initial and the final assessment for the affected and the unaffected is thus evident, also visually.
Since the box-plots presented above show quantitative differences between the affected and unaffected upper limb, and between the initial and final assessment, and to analyze whether these differences are statistically significant according to operated/non-operated subjects, we applied the Mann – Whitney U test for independent samples, the results are shown in
Table 3.
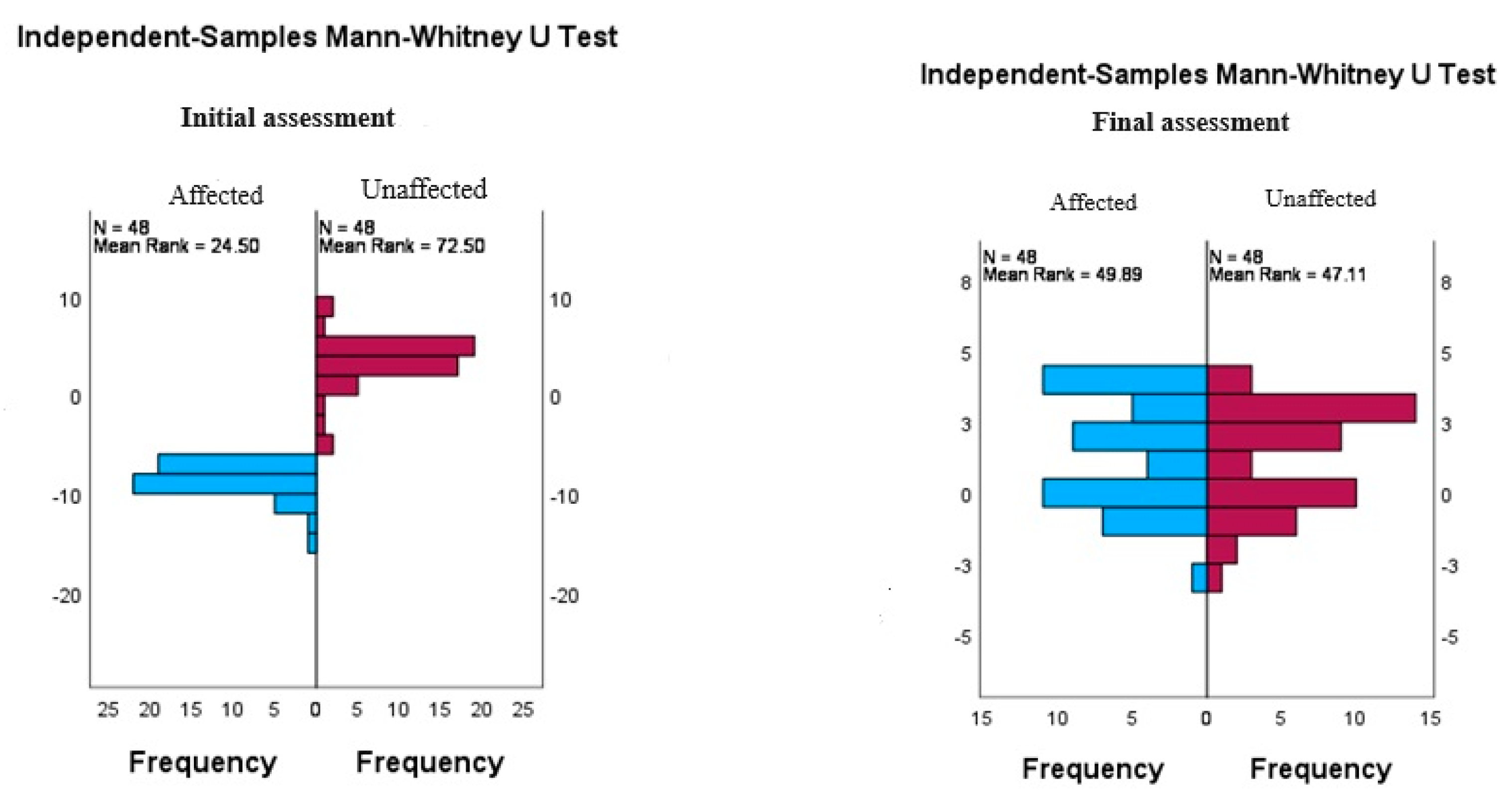
Table 3 compares the subjects' initial and final ratings analyzing the differences between the affected and unaffected upper limb in terms of joint position fit (flexion and abduction). At the initial evaluation, the results indicate statistically significant differences (p<0.001) between the affected upper limb and the contralateral (unaffected) upper limb for both flexion and abduction, suggesting a pronounced impairment of proprioception of the affected shoulder.
However, at the final assessment, no statistically significant differences were observed (p=0.091 for flexion and p=0.621 for abduction), which may indicate an improvement in proprioception or compensatory adaptation of the subjects. This suggests the effectiveness of therapeutic procedures implemented to reduce proprioception differences between the affected and unaffected upper limb.
For a detailed presentation of the results of the Mann-Whitney U test, we compared the differences between two independent groups, in the case of the present study, between the affected upper limb and the unaffected upper limb, at the initial and final assessment for flexion (
Table 4) and for abduction (
Table 5).
Table 4 provides a detailed analysis of the Mann-Whitney U test for the initial and final assessments of the affected and unaffected upper limb for joint position–flexion matching. At the initial assessment, the results indicate a statistically significant difference between the two groups, with a U-value of 2244.500 and a Z-score (Standardized Test Statistic) of 8.077, reflecting a p value < .001. This suggests a notable and significant difference between the affected and unaffected upper limb in baseline proprioception, highlighting the severe impact of the condition on the ability to perceive and control flexion movements.
In contrast, at the final assessment, the differences between the groups are no longer statistically significant, with a U-value of 926,000, a Z-score of -1,690, and a p-value=.091. This result indicates that after applying the physiotherapy procedures, the initial differences improved significantly, suggesting an improvement in proprioception (
Table 4).
Table 5 provides a detailed analysis of the Mann-Whitney U test for the initial and final ratings of the affected and unaffected upper limb for joint position–abduction matching. At the initial assessment the statistical values indicates a significant difference between the two groups, with a U of 2304.000, a Z-score (Standardized Test Statistic) of 8.499 and a p< .001. These results suggest a statistically significant difference in abduction proprioception between the affected and unaffected upper limb, reflecting a significant impact of the condition on the ability to perceive and control abduction movements at baseline. At the final assessment, the results do not indicate a statistically significant difference, with a U of 1085.500, a Z-score of -0.495 and a p-value of .621.
These data indicate that after the application of the physicaltherapy program the initial differences were significantly reduced. This reduction in differences indicates an improvement in proprioception regarding shoulder abduction. The results highlight the effectiveness of interventions and recovery processes in reversing the initial impact of the condition on proprioception (
Table 5).
In order to have a clearer view of the results obtained at the final evaluation, we graphically represented shoulder abduction and flexion, affected upper limb vs. unaffected upper limb at initial and final testing.
Figure 4 provides a suggestive image of the progress achieved, for the abduction movement, following the application of the recovery program of the affected upper limb, and in
Figure 5, the flexion movement is represented. The differences between the two upper limb, in both directions of mobilization, are similar.
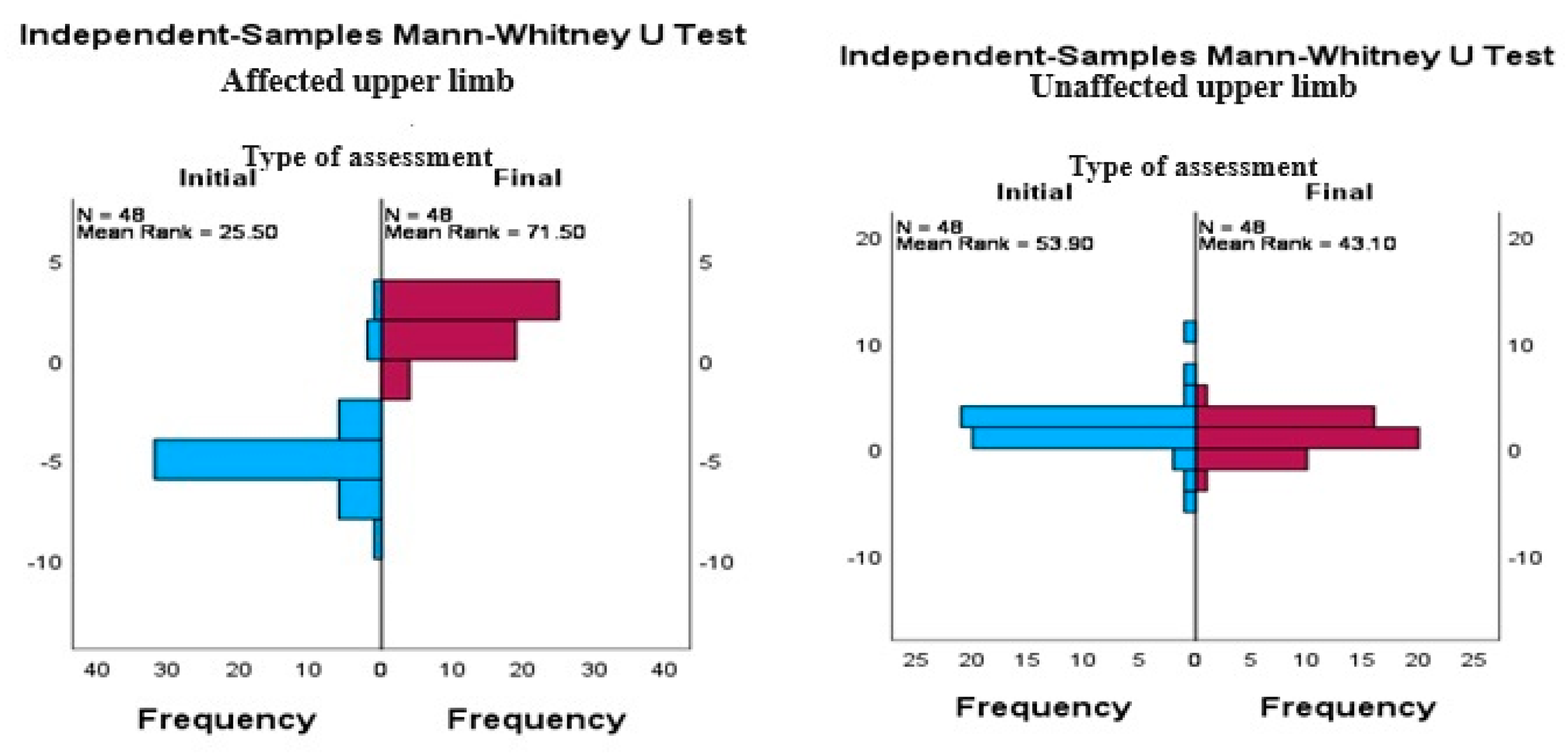
We repeated the testing of differences with the Mann-Whitney U test for independent samples, analyzing data from each subgroup (affected and unaffected member) to determine if there was a statistically significant differences between initial and final assessments.
The obtained results indicate that for the affected upper limb there are statistically significant differences between the initial and the final assessment in both joint position fit assessment tests (p< 0.001). This suggests that the therapeutic interventions had a significant positive impact on the ability to perceive and control joint position in flexion and abduction. The observed differences demonstrate a considerable improvement in proprioception and joint function following the treatment, highlighting the effectiveness of the applied physiotherapeutic procedures (
Table 6).
Also, for the unaffected upper limb, the tests revealed statistically significant differences between the initial and final assessment (p< 0.001). This aspect is particularly interesting because it suggests the therapeutic interventions not only had a beneficial impact on the affected limb, but also contributed to the improvement of motor and proprioceptive control in the unaffected limb (table 6). This phenomenon can be explained by the generalized effects of the physiotherapy on the vestibular system, especially the BPPV rehabilitation program applied in our study. These interventions not only improve balance and vestibular function, but also contributes to the recalibration of the whole body's neuromuscular and proprioceptive system, leading to more accurate perception.
1.1. DGI Index. Descriptive Statistics
Assessment of motor function and balance in patients with orthopedic and vestibular conditions is essential to understand the impact of these health dysfunctiones on quality of life and to develop effective rehabilitation programs. The Dynamic Gait Index is a commonly used assessment tool to measure an individual's ability to adapt their gait and balance in various dynamic situations. This is particularly relevant for people with BPPV and impairments of the scapulohumeral joint, as these conditions can significantly influence stability and motor function.
The data in
Table 7 suggest a significant improvement in the subjects' balance and walking ability after the physiotherapy intervention. The increase in means (from 9.81 initial to 14.77 final), the median (from 10.00 to 15.00) and the decrease in variability (standard deviation from 1.797 initial to 0.774 final) indicate an even and efficient recovery. In addition, the increase in minimum (from initial 6 to final 10) and maximum (from 12 to 15) values underlines the success of the interventions in achieving optimal performance by the subjects. The fact that the values corresponding to the 25th, 50th, and 75th quartiles are all at 15.00 at the final assessment shows that most subjects achieved maximum or near maximum scores, reflecting the high uniformity and effectiveness of the treatment.
We used the Mann-Whitney U-test to determing whether there were statistically significant differences between baseline and final assessment for DGI scores in our study subjects. The results indicate significant improvements in the subjects' DGI scores, which underlines the success of the physiotherapy interventions. The p value < 0.001 indicates that these improvements are not due to chance and are statistically significant (
Table 8).
To obtain a more detailed picture of the distribution of DGI scores and their variation before and after the application of the recovery program, we applied the Mann-Whitney U test for independent samples (
Table 9). The statistics provide satisfactory results, showing that the therapeutic interventions had a significant impact on the walking ability and balance of the subjects, reflected by significant improvements in the DGI scores. The p value < 0.001 indicates that these improvements are highly unlikely to be subject to chance, underscoring the effectiveness of the rehabilitation program.
Total N=192 represents the total number of assessments analyzed in the Mann-Whitney U test for independent samples, including DGI assessments for 48 subjects, each assessed for joint position matching in the affected and unaffected upper limb at two assessment times (initial and final).
We plotted the distribution of DGI scores for subjects assessed at baseline and final, using the Mann-Whitney U test for independent samples (
Figure 6). One can see the mean rank of 49.54 at the initial assessment, suggesting a low level of gait and balance function. At the final assessment the scores increase significantly, the average rank being 143.46, reflecting a significant improvement.
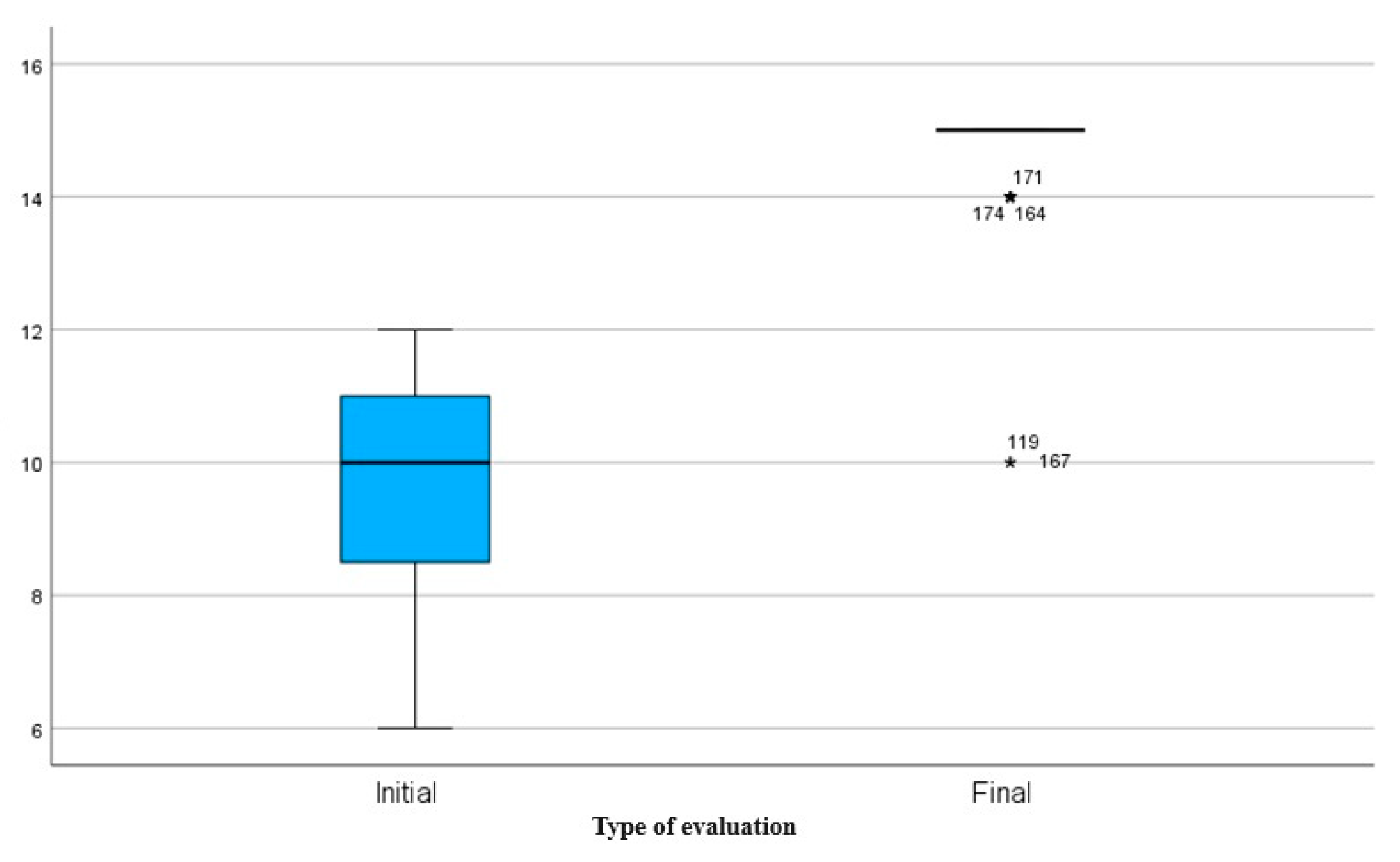
Box plot
Figure 7 compares DGI scores at baseline to final assessment. At initial assessment, a median of approximately 10 is highlighted, with a greater variation in scores indicated by a wider interquartile range (IQR) and the presence of extreme values (outliers). This suggests considerable variability in subjects' gait and balance prior to recovery procedures. At the final assessment, the median score is 15, with a very small IQR, reflecting a highly concentrated distribution around the maximum value. This indicates an even and significant improvement in DGI scores after the intervention, demonstrating the effectiveness of the rehabilitation program in improving walking ability and balance.
1.1. Correlations
Table 10 shows the Pearson correlations between the DGI index and joint position matching (PPC) for flexion and abduction of the affected upper limb at both baseline and final assessments. At baseline assessment there are no statistically significant correlations between DGI and PPC for flexion (r = .022, p = .884) or abduction (r = .186, p = .205), suggesting that before physiotherapy intervention, DGI scores are not significantly associated with upper limb joint position matching. At final assessment, there are also no statistically significant correlations between DGI and PPC for flexion (r = -.094, p = .524) or abduction (r = .047, p = .752), indicating that after the intervention, the scores DGIs remain insignificantly associated with upper limb joint position matching.
Table 11 shows Pearson correlations between DGI and PPC for flexion and abduction in the unaffected upper limb at both baseline and final assessments. At the initial assessment there are no statistically significant correlations between DGI and PPC for flexion (r = .073, p = .622) or abduction (r = .247, p = .090). At final assessment, there are also no statistically significant correlations between DGI and PPC for flexion (r = -.142, p = .335) or abduction (r = .048, p = .745). These results suggest that, regardless of time of assessment, DGI scores are not significantly associated with joint position matching of the unaffected upper limb.
The results of
Table 10 and
Table 11 show the Pearson correlations between the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) and joint position matching (PPC) for flexion and abduction, in both the affected and the unaffected upper limb, before and after the application of the physiotherapy procedures. This suggests that improvements in walking ability and balance, reflected by DGI scores, are not directly associated with changes in upper limb joint position matching, hence highlighting the complexity of the interactions between the vestibular and proprioceptive systems in the rehabilitation process.
4. Discussion
The recovery of shoulder function following an orthopedic condition is inherently complex and demands a multifaceted approach. A critical, yet often underestimated, component of this process is the vestibular system. This system plays a pivotal role in maintaining balance, coordination, and proprioception—key factors in achieving a full and effective recovery [
1]. The integration of vestibular assessments and targeted interventions into rehabilitation programs could potentially lead to the development of more holistic and effective physiotherapy strategies that address both the primary symptoms and the underlying contributing factors of dysfunction [
2]. Such an integrated approach can ensure sustainable recovery and significantly enhance the quality of life for affected individuals [
3].
The findings of this study suggest that, as symptoms related to Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo (BPPV) improve—assessed using the Dynamic Gait Index (DGI)—there is also an improvement in scapulohumeral proprioception, as indicated by joint position matching in flexion and abduction. Although the study did not find statistically significant correlations between DGI scores and joint position matching in either the affected or unaffected limbs, the overall trend underscores the importance of incorporating vestibular assessments and interventions into shoulder rehabilitation programs. The vestibular system's role in coordination, a fundamental aspect of scapulohumeral joint function, is particularly noteworthy in this context.
This study's results demonstrate that bilateral therapeutic interventions were effective in restoring functional symmetry and proprioceptive accuracy among the study's participants. By the final assessment, the initial significant differences between the affected and contralateral, unaffected upper limbs had become non-significant, indicating a balanced and effective recovery process. These outcomes highlight the critical importance of applying integrated therapeutic interventions to maximize rehabilitation outcomes.
The effectiveness of vestibular rehabilitation in enhancing postural stability and reducing fall risk has been well-documented in the literature. Whitney et al. (2000) demonstrated that vestibular rehabilitation can lead to significant improvements in balance and gait in patients with vestibular disorders [
10]. Similarly, Marchetti and Whitney (2006) emphasized the necessity of specific vestibular rehabilitation interventions to reduce fall risk and enhance balance confidence in patients with vestibular imbalances [
11]. Furthermore, Herman et al. (2013) validated the use of the Dynamic Gait Index as a reliable tool for evaluating and monitoring patient progress in rehabilitation, thereby contributing to reduced fall risk and improved motor function [
12].
The improvements observed in DGI scores post-intervention underscore the positive impact of integrated rehabilitation programs that simultaneously address vestibular and proprioceptive components. Such comprehensive interventions contribute to a more uniform and effective recovery, as evidenced by the reduced variability in scores and increased consistency in improvements, as reflected in the analysis of standard deviations and percentiles.
These results underline the necessity for a holistic approach in shoulder rehabilitation, one that includes vestibular evaluations and interventions to optimize recovery and enhance the patient's quality of life. Integrating vestibular rehabilitation into orthopedic treatments offers significant benefits, leading to improved recovery outcomes and better long-term functionality.
The primary objective of this research was to initiate and conduct a fundamental multidisciplinary study with direct clinical applicability, focusing on the mechanisms involved in shoulder joint function following various conditions, whether traumatic or degenerative. A particular emphasis was placed on understanding the vestibular system's role in the recovery process. By integrating expertise from fields such as ENT, orthopedics, neuroscience, and physical therapy, the study aimed to provide a deeper understanding of how vestibular dysfunction can impact recovery, even in a non-weight-bearing joint like the shoulder.
The study's findings confirm this objective by demonstrating that vestibular rehabilitation, when integrated into shoulder rehabilitation protocols, significantly enhances scapulohumeral joint function. Despite the lack of statistically significant correlations between DGI scores and joint position matching, the overall improvements in proprioception and joint function support the hypothesis that the vestibular system is crucial to the recovery process. These results advocate for a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates vestibular elements to optimize shoulder joint recovery and improve patient outcomes.
However, the study's limitations include a relatively small sample size, which may affect the validity and generalizability of the results. To strengthen these aspects, future studies should expand the sample size and include a control group to allow for more rigorous assessments of the effects of physiotherapy interventions. Additionally, controlling for potentially confounding variables, such as baseline severity of conditions and adherence to treatment protocols, is essential to ensuring more accurate interpretations of the results. Implementing a larger experimental design would facilitate direct comparisons of outcomes and provide a stronger foundation for drawing conclusions.
5. Conclusions
The results of our research demonstrate that integrating vestibular rehabilitation into shoulder recovery protocols significantly improves joint function. Bilateral physiotherapy interventions proved effective in restoring functional symmetry and proprioceptive perception. At the conclusion of the study, the initial significant differences between the affected and unaffected upper limbs became non-significant, suggesting a balanced and efficient recovery.
The study findings highlight the importance of a multidisciplinary approach that includes vestibular assessments and therapeutic interventions in scapulohumeral rehabilitation. The integration of vestibular and proprioceptive elements into orthopedic treatments contributes to improved motor function and reduced fall risk, positively impacting the quality of life of the subjects. This study provides new insights into the role of the vestibular system in scapulohumeral joint rehabilitation, offering a more comprehensive understanding of the interactions between different body systems.
These results are particularly relevant in the context of orthopedic rehabilitation, demonstrating the specific benefits of integrating vestibular rehabilitation into shoulder recovery treatments. The findings contribute to the existing literature, emphasizing the need for more comprehensive and personalized therapeutic strategies that address both the primary symptoms and underlying factors of orthopedic conditions.
Our research has several important limitations that should be considered. The relatively small sample size may influence the validity and applicability of the results. Additionally, baseline variability in the degree of orthopedic impairment and adherence to the treatment protocol are factors that could affect the interpretation of the results. Tighter control of these variables could provide a more accurate assessment of the effects of therapeutic interventions.
Validation and generalization of the results obtained in this study could be achieved by including an extended sample of subjects, distributed into control and experimental groups. It is necessary to explore the specific mechanisms through which the vestibular system influences scapulohumeral recovery and to develop personalized physiotherapy strategies accordingly. Additionally, investigating the long-term effects of integrating vestibular rehabilitation could provide valuable insights into the durability of the benefits obtained.
Benign Paroxysmal Positional Vertigo affects the vestibular system, which can lead to imbalances, sensory confusion, and compensatory strategies that compromise proprioception and movement control, even in a shoulder unaffected by an orthopedic condition. This phenomenon underscores the importance of including vestibular rehabilitation in treatment plans to ensure complete and effective shoulder function recovery, highlighting the systemic impact of BPPV on general motor control.
In conclusion, the results of the present research confirm the importance of integrating vestibular rehabilitation into shoulder rehabilitation treatments. The proposed multidisciplinary approach not only improves scapulohumeral joint function but also contributes to a more balanced and efficient recovery, reducing variability in results and increasing uniformity in rehabilitation improvements. These findings underscore the need for comprehensive physiotherapy strategies that include vestibular assessments and interventions.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization: Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Methodology, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Software, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Validation, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Formal analysis Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Investigation: Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean and Pál Fodor; Resources, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean.; Data curation, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean and Pál Fodor; Writing—original draft preparation: Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Writing—review and editing, Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Visualization: Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Supervision: Gheorghe Mühlfay and Klara Brînzaniuc; Project administration, Patricia-Maria Crișan-Mălăncrăvean; Funding acquisition, This project was carried out without financial assistance from any organization or institution. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Appendix A
Initial Assessment
| Nr.Crt. |
Initials of name and surname |
Gender |
Age |
Orthopedic diagnosis |
Operated/Unoperated |
Joit position sense – flexion of affected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Joit position sense – flexion of unaffected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Joit position sense – abduction of affected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Joit position sense – abduction of unaffected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3,4,5,6 si 7 (expressed in points) |
| 1. |
A.C |
M |
38 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-7 |
+1 |
-8 |
+2 |
12 |
| 2. |
D.M |
F |
43 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+3 |
-10 |
+4 |
9 |
| 3. |
R.H |
M |
50 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
0 |
-9 |
+5 |
8 |
| 4. |
D.I |
F |
53 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
-2 |
-11 |
+3 |
6 |
| 5. |
M.R |
F |
22 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
0 |
11 |
| 6. |
H.D |
F |
51 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-7 |
+2 |
-10 |
+4 |
7 |
| 7. |
K.R |
F |
32 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-4 |
+1 |
-7 |
+2 |
10 |
| 8. |
P.M |
M |
56 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+3 |
-9 |
+4 |
6 |
| 9. |
S.C |
M |
68 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+3 |
-15 |
+8 |
8 |
| 10. |
K.J |
F |
37 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-3 |
+2 |
-8 |
+5 |
12 |
| 11. |
U.T |
F |
54 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+1 |
-9 |
+3 |
7 |
| 12. |
H.M |
M |
39 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
0 |
-7 |
+4 |
8 |
| 13. |
P.R |
M |
40 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-6 |
+3 |
-8 |
+5 |
11 |
| 14. |
S.R |
M |
23 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-9 |
0 |
-7 |
+6 |
12 |
| 15. |
P.P |
F |
30 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
12 |
| 16. |
M.C |
M |
47 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-6 |
+3 |
-10 |
+4 |
12 |
| 17. |
B.S |
F |
30 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-7 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
11 |
| 18. |
A.D |
F |
56 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
6 |
| 19. |
L.T |
F |
53 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-8 |
-2 |
-10 |
+5 |
11 |
| 20. |
O.R |
F |
37 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-10 |
+3 |
10 |
| 21. |
N.M |
M |
74 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
0 |
-9 |
-2 |
7 |
| 22. |
M.M |
F |
52 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-8 |
+3 |
9 |
| 23. |
T.F |
F |
64 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
0 |
-12 |
-5 |
8 |
| 24. |
G.A |
F |
66 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-9 |
0 |
10 |
| 25. |
O.M |
F |
51 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-10 |
+3 |
10 |
| 26. |
S.V |
F |
48 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-9 |
+4 |
12 |
| 27. |
D.O |
M |
55 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-7 |
-3 |
-9 |
+2 |
12 |
| 28. |
B.S |
F |
24 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-3 |
0 |
-7 |
0 |
11 |
| 29. |
A.D |
M |
29 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-4 |
+2 |
-7 |
+5 |
11 |
| 30. |
D.I |
M |
63 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-6 |
+3 |
-9 |
0 |
11 |
| 31. |
P.M |
F |
56 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+10 |
-8 |
+3 |
9 |
| 32. |
S.B |
M |
35 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
-4 |
12 |
| 33. |
C.R |
M |
30 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
+3 |
-11 |
+4 |
11 |
| 34. |
P.D |
F |
38 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-7 |
+2 |
12 |
| 35. |
B.A |
M |
34 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-6 |
+3 |
-9 |
+4 |
12 |
| 36. |
H.M |
F |
50 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
11 |
| 37. |
C.M |
F |
58 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-4 |
-5 |
-12 |
-6 |
9 |
| 38. |
P.E |
F |
60 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
+6 |
-8 |
+3 |
8 |
| 39. |
G.B |
M |
48 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-4 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
10 |
| 40. |
B.D |
M |
42 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-7 |
+2 |
-13 |
0 |
10 |
| 41. |
P.T |
M |
31 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
10 |
| 42. |
D.P |
F |
56 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
11 |
| 43. |
N.C |
F |
52 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
9 |
| 44. |
U.M |
F |
53 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
8 |
| 45. |
Z.V |
M |
31 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
11 |
| 46. |
D.S |
M |
33 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
9 |
| 47. |
M.A |
M |
30 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
12 |
| 48. |
T.L |
F |
69 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+2 |
+5 |
-12 |
+9 |
11 |
FINAL Assessment
| Nr.Crt. |
Initials of name and surname |
Gender |
Age |
Orthopedic diagnosis |
Operated/Unoperated |
Joit position sense – flexion of affected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Joit position sense – flexion of unaffected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Joit position sense – abduction of affected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Joit position sense – abduction of unaffected upper limb (expressed in degrees) |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3,4,5,6 si 7 (expressed in points) |
| 1) |
A.C |
M |
38 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+1 |
+1 |
+2 |
+2 |
15 |
| 2) |
D.M |
F |
43 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+2 |
+3 |
+3 |
15 |
| 3) |
R.H |
M |
50 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+3 |
+1 |
+4 |
+4 |
15 |
| 4) |
D.I |
F |
53 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+3 |
+3 |
+2 |
14 |
| 5) |
M.R |
F |
22 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+1 |
0 |
-1 |
0 |
15 |
| 6) |
H.D |
F |
51 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+1 |
+2 |
+2 |
+3 |
15 |
| 7) |
K.R |
F |
32 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+3 |
-1 |
+4 |
+3 |
15 |
| 8) |
P.M |
M |
56 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-1 |
+3 |
-1 |
+4 |
14 |
| 9) |
S.C |
M |
68 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
+3 |
-1 |
0 |
15 |
| 10) |
K.J |
F |
37 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+3 |
-2 |
+4 |
-1 |
15 |
| 11) |
U.T |
F |
54 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+1 |
-3 |
+2 |
15 |
| 12) |
H.M |
M |
39 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+3 |
+2 |
+4 |
+3 |
15 |
| 13) |
P.R |
M |
40 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+1 |
+3 |
+2 |
-1 |
15 |
| 14) |
S.R |
M |
23 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
0 |
-1 |
+2 |
0 |
15 |
| 15) |
P.P |
F |
30 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+3 |
-2 |
+1 |
+3 |
15 |
| 16) |
M.C |
M |
47 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+3 |
+3 |
+4 |
0 |
15 |
| 17) |
B.S |
F |
30 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
0 |
+1 |
+2 |
+1 |
15 |
| 18) |
A.D |
F |
56 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+3 |
0 |
+2 |
15 |
| 19) |
L.T |
F |
53 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-2 |
0 |
-1 |
+3 |
15 |
| 20) |
O.R |
F |
37 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+3 |
+1 |
0 |
0 |
15 |
| 21) |
N.M |
M |
74 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+2 |
0 |
+3 |
14 |
| 22) |
M.M |
F |
52 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+2 |
+1 |
0 |
15 |
| 23) |
T.F |
F |
64 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+2 |
-1 |
+3 |
15 |
| 24) |
G.A |
F |
66 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
+1 |
0 |
+2 |
15 |
| 25) |
O.M |
F |
51 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
+2 |
+2 |
+1 |
+3 |
15 |
| 26) |
S.V |
F |
48 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+1 |
+1 |
0 |
+2 |
15 |
| 27) |
D.O |
M |
55 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+3 |
-2 |
+4 |
0 |
15 |
| 28) |
B.S |
F |
24 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
+2 |
0 |
0 |
14 |
| 29) |
A.D |
M |
29 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+3 |
-2 |
+4 |
0 |
15 |
| 30) |
D.I |
M |
63 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+2 |
-3 |
0 |
-1 |
15 |
| 31) |
P.M |
F |
56 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
0 |
+2 |
0 |
+3 |
14 |
| 32) |
S.B |
M |
35 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
-1 |
+2 |
-2 |
15 |
| 33) |
C.R |
M |
30 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
+3 |
-11 |
+4 |
11 |
| 34) |
P.D |
F |
38 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-7 |
+2 |
12 |
| 35) |
B.A |
M |
34 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-6 |
+3 |
-9 |
+4 |
12 |
| 36) |
H.M |
F |
50 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
11 |
| 37) |
C.M |
F |
58 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-4 |
-5 |
-12 |
-6 |
9 |
| 38) |
P.E |
F |
60 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
0 |
+6 |
-8 |
+3 |
8 |
| 39) |
G.B |
M |
48 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-4 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
10 |
| 40) |
B.D |
M |
42 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-7 |
+2 |
-13 |
0 |
10 |
| 41) |
P.T |
M |
31 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
10 |
| 42) |
D.P |
F |
56 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
11 |
| 43) |
N.C |
F |
52 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
9 |
| 44) |
U.M |
F |
53 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
8 |
| 45) |
Z.V |
M |
31 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
11 |
| 46) |
D.S |
M |
33 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-6 |
+2 |
-9 |
+4 |
9 |
| 47) |
M.A |
M |
30 |
Sholder |
UNOPERATED |
-5 |
+1 |
-8 |
+3 |
12 |
| 48) |
T.L |
F |
69 |
Sholder |
OPERATED |
+2 |
+5 |
-12 |
+9 |
11 |
References
- Grüsser, O.J. , et al. “Integration of Vestibular, Visual and Proprioceptive Inputs in the Cerebral Cortex during Movement Control”. Human Physiology vol.86 no.4, 2001, pg.1991-2005. Springer. [CrossRef]
- Blanke, O. , et al. “The vestibular system: a spatial reference for bodily self-consciousness”. Frontiers in Psychology vol. 4, 2013. Pg.309-326. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y. , et al. “Proprioceptive Cervicogenic Dizziness: A Narrative Review of Pathogenesis, Diagnosis and Treatment”, Journal of Clinical Medicine, vol.11 no.21, 2022, MDPI. [CrossRef]
- Brandt, T. “Vertigo: It’s Multisensory Syndromes” 2nd edition, 2003, pg. 45-67, Springer-Verlag, London. [CrossRef]
- Herdman, SJ. , et al. „Effectiveness of vestibular rehabilitation on postural balance in patients with Parkinson’s disease“, BMC Neurology, vol.20, 2020, BMC. [CrossRef]
- Jarett Casale; Tivon Browne; Ian V. Murray; Gunjan Gupta. “Physiology, Vestibular System”, NIH, 2023. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532978/.
- Lopez, C. , et al. “Spacial orientation, postural control and the vestibular system in humans”, PeerJ vol.11, 2023. [CrossRef]
- Ellenbecker, T.S. , Cools A., “Rehabilitation of Shoulder Impingement Syndrome and Rotator Cuff Injuries: an evidence-based review”, British Journal of Sports Medicine, vol.44, issue 5, 2010, pp. 319-327. [CrossRef]
- Mariya K Chepisheva „Spatial orientation, postural control and the vestibular system in healthy elderly and Alzheimer's dementia”, PeerJ Aticle, vol.11, 2023 May 2:11:e15040. [CrossRef]
- Meldrum, D. , et al, “Effectiveness of conventional versus virtual reality-based balance exercises in vestibular rehabilitation for unilateral peripheral vestibular loss: results of a randomized controlled trial”, vol.96, no.7, 2015, pp.1319-1328. [CrossRef]
- McGibbon, C.A. , et al “Tai Chi and vestibular rehabilitation improve vestibulopathic gait via different neuromuscular mechanisms: preliminary report”, BMC Neurology, vol.5, 2005. [CrossRef]
- Deanna, C. Deanna C. Dye, A.M.Eakman, K.M. Bolton, “Assessing the Validity of the Dynamic Gait Index in a Balance Disorders Clinic: An Application of Rasch Analysis”, Physical Therapy, Volume 93, Issue 6, 1 June 2013, Pages 809–818. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Joint position matching – flexion - initial and final limb assessment.
Figure 1.
Joint position matching – flexion - initial and final limb assessment.
Figure 2.
Joint position matching – abduction - initial and final limb assessment.
Figure 2.
Joint position matching – abduction - initial and final limb assessment.
Figure 4.
Initial assessment vs. final – abduction - affected and unaffected upper limb.
Figure 4.
Initial assessment vs. final – abduction - affected and unaffected upper limb.
Figure 5.
Joint position matching – affected and unaffected upper limb flexion – initial and final assessment.
Figure 5.
Joint position matching – affected and unaffected upper limb flexion – initial and final assessment.
Figure 6.
Distribution of DGI Scores before and after physiotherapy intervention.
Figure 6.
Distribution of DGI Scores before and after physiotherapy intervention.
Figure 7.
Comparative box plot of DGI scores at initial and final assessment.
Figure 7.
Comparative box plot of DGI scores at initial and final assessment.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics – initial assessment of joint position matching.
Table 1.
Descriptive statistics – initial assessment of joint position matching.
| Affected/unaffected |
Joint Position Sense Assessment_Flexion_upper limb |
Joint Position Sense Assessment_Abduction_upper limb |
| affected |
N |
Valid |
48 |
48 |
| Missing |
0 |
0 |
| Mean |
-5.17 |
-9.08 |
| Median |
-5.00 |
-9.00 |
| Std. Deviation |
1.906 |
1.661 |
| Minimum |
-9 |
-15 |
| Maximum |
2 |
-7 |
| Percentiles |
25 |
-6.00 |
-10.00 |
| 50 |
-5.00 |
-9.00 |
| 75 |
-5.00 |
-8.00 |
| unaffected |
N |
Valid |
48 |
48 |
| Missing |
0 |
0 |
| Mean |
1.52 |
2.79 |
| Median |
1.50 |
3.00 |
| Std. Deviation |
2.212 |
2.805 |
| Minimum |
-5 |
-6 |
| Maximum |
10 |
9 |
| Percentiles |
25 |
1.00 |
2.00 |
| 50 |
1.50 |
3.00 |
| 75 |
2.00 |
4.00 |
Table 2.
Descriptive statistics – final assessment of joint position matching.
Table 2.
Descriptive statistics – final assessment of joint position matching.
| Affected/unaffected |
Joint Position Sense Assessment_Flexion_upper limb |
Joint Position Sense Assessment_Abduction_upper limb |
| affected |
N |
Valid |
48 |
48 |
| Missing |
0 |
0 |
| Mean |
1.31 |
1.48 |
| Median |
2.00 |
2.00 |
| Std. Deviation |
1.323 |
1.913 |
| Minimum |
-2 |
-3 |
| Maximum |
3 |
4 |
| Percentiles |
25 |
.00 |
.00 |
| 50 |
2.00 |
2.00 |
| 75 |
2.00 |
3.00 |
| unaffected |
N |
Valid |
48 |
48 |
| Missing |
0 |
0 |
| Mean |
.75 |
1.29 |
| Median |
1.00 |
2.00 |
| Std. Deviation |
1.682 |
1.821 |
| Minimum |
-3 |
-3 |
| Maximum |
4 |
4 |
| Percentiles |
25 |
.00 |
.00 |
| 50 |
1.00 |
2.00 |
| 75 |
2.00 |
3.00 |
Table 3.
Initial assessment vs. final affected and unaffected upper limb – joint position matching - flexion and abduction.
Table 3.
Initial assessment vs. final affected and unaffected upper limb – joint position matching - flexion and abduction.
| Hypothesis Test Summary |
Type of
assessment
|
Null Hypothesis |
Test |
Sig.a,b |
Decision |
| Initial |
1 |
The distribution of joint position sense_Flexion_upper limb is the same across categories of Afeected/unaffected. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
<.001 |
Reject the null hypothesis. |
| 2 |
The distribution of joint position sense_Abduction_upper limb is the same across categories of Afeected/unaffected. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
<.001 |
Reject the null hypothesis. |
| Final |
1 |
The distribution of joint position sense_Flexion_upper limb is the same across categories of Afeected/unaffected. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
.091 |
Retain the null hypothesis. |
| 2 |
The distribution of joint position sense_Abduction_upper limb is the same across categories of Afeected/unaffected. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
.621 |
Retain the null hypothesis. |
Table 4.
Matching the joint position - flexion - affected/unaffected across upper limb.
Table 4.
Matching the joint position - flexion - affected/unaffected across upper limb.
| Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test Summary |
| Initial |
Total N |
96 |
| Mann-Whitney U |
2244.500 |
| Wilcoxon W |
3420.500 |
| Test Statistic |
2244.500 |
| Standard Error |
135.257 |
| Standardized Test Statistic |
8.077 |
| Asymptotic Sig.(2-sided test) |
<.001 |
| Final |
Total N |
96 |
| Mann-Whitney U |
926.000 |
| Wilcoxon W |
2102.000 |
| Test Statistic |
926.000 |
| Standard Error |
133.711 |
| Standardized Test Statistic |
-1.690 |
| Asymptotic Sig.(2-sided test) |
.091 |
Table 5.
Matching joint position - abduction - affected/unaffected across upper limb.
Table 5.
Matching joint position - abduction - affected/unaffected across upper limb.
| Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test Summary |
| Initial |
Total N |
96 |
| Mann-Whitney U |
2304.000 |
| Wilcoxon W |
3480.000 |
| Test Statistic |
2304.000 |
| Standard Error |
135.547 |
| Standardized Test Statistic |
8.499 |
| Asymptotic Sig.(2-sided test) |
<.001 |
| Final |
Total N |
96 |
| Mann-Whitney U |
1085.500 |
| Wilcoxon W |
2261.500 |
| Test Statistic |
1085.500 |
| Standard Error |
134.359 |
| Standardized Test Statistic |
-.495 |
| Asymptotic Sig.(2-sided test) |
.621 |
Table 6.
Initial and final evaluation upper limb affected vs. unaffected – matching joint position - flexion and abduction.
Table 6.
Initial and final evaluation upper limb affected vs. unaffected – matching joint position - flexion and abduction.
| Hypothesis Test Summary |
| Affected/unaffected |
Null Hypothesis |
Test |
Sig.a,b |
Decision |
| Affected |
1 |
The distribution of Joint position sense_flexion _upper limb is the same across categories of assessment type. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
<.001 |
Reject the null hypothesis. |
| |
2 |
The distribution of Joint position sense_abduction _upper limb is the same across categories of assessment type. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
<.001 |
Reject the null hypothesis. |
| Unaffected |
1 |
The distribution of Joint position sense_flexion _upper limb is the same across categories of assessment type. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
.053 |
Retain the null hypothesis. |
| |
2 |
The distribution of Joint position sense_abduction _upper limb is the same across categories of assessment type. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
<.001 |
Reject the null hypothesis. |
Table 7.
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 initial and final assessment.
Table 7.
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 initial and final assessment.
| Initial |
N |
Valid |
96 |
| |
Missing |
0 |
| Mean |
|
9.81 |
| Median |
|
10.00 |
| Std. Deviation |
|
1.797 |
| Minimum |
|
6 |
| Maximum |
|
12 |
| Percentiles |
25 |
8.25 |
| 50 |
10.00 |
| 75 |
11.00 |
| Final |
N |
Valid |
96 |
| |
Missing |
0 |
| Mean |
|
14.77 |
| Median |
|
15.00 |
| Std. Deviation |
|
.774 |
| Minimum |
|
10 |
| Maximum |
|
15 |
| Percentiles |
25 |
15.00 |
| 50 |
15.00 |
| 75 |
15.00 |
Table 8.
Initial assessment and final assessment – Mann-Whitney U test Hypothesis Test Summary.
Table 8.
Initial assessment and final assessment – Mann-Whitney U test Hypothesis Test Summary.
| |
Null Hypothesis |
Test |
Sig.a,b
|
Decision |
| 1 |
The distribution of Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 is the same across categories of assessment type. |
Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test |
<.001 |
Reject the null hypothesis. |
Table 9.
Results of the Mann-Whitney U Test for comparing DGI scores stages 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 across Type of assessment.
Table 9.
Results of the Mann-Whitney U Test for comparing DGI scores stages 3, 4, 5, 6 and 7 across Type of assessment.
| Independent-Samples Mann-Whitney U Test Summary |
| Total N |
192 |
| Mann-Whitney U |
9116.000 |
| Wilcoxon W |
13772.000 |
| Test Statistic |
9116.000 |
| Standard Error |
368.789 |
| Standardized Test Statistic |
12.224 |
| Asymptotic Sig.(2-sided test) |
<.001 |
Table 10.
Pearson correlations separately for initial assessment and final assessment – affected upper limb.
Table 10.
Pearson correlations separately for initial assessment and final assessment – affected upper limb.
| Assessment type |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 (points) |
Joint position sense_flexion_
upper limb |
Joint position sense_abduction_upper limb |
| Initial |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 (points) |
Pearson Correlation |
1 |
.022 |
.186 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
.884 |
.205 |
| N |
48 |
48 |
48 |
| Joint position sense_flexion_upper limb |
Pearson Correlation |
|
1 |
-.065 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
.661 |
| N |
|
48 |
48 |
| |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 (points) |
Pearson Correlation |
|
|
1 |
| |
Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
|
| |
N |
|
|
48 |
| Final |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stadiile 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 (puncte) |
Pearson Correlation |
1 |
-.094 |
.047 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
.524 |
.752 |
| N |
48 |
48 |
48 |
| Joint position sense_flexion_upper limb |
Pearson Correlation |
|
1 |
.318*
|
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
.028 |
| N |
|
48 |
48 |
| Joint position sense_abduction_upper limb |
Pearson Correlation |
|
|
1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
|
| N |
|
|
48 |
Table 11.
Pearson correlations separately for initial assessment and final assessment – unaffected upper limb.
Table 11.
Pearson correlations separately for initial assessment and final assessment – unaffected upper limb.
| Assessment Type |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 (points) |
Joint position sense_flexion_
upper limb |
Joint position sense_abduction_upper limb |
| Initial |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 (points) |
Pearson Correlation |
1 |
.073 |
-.247 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
.622 |
.090 |
| N |
48 |
48 |
48 |
Joint position sense_flexion_
upper limb |
Pearson Correlation |
|
1 |
.378**
|
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
.008 |
| N |
|
48 |
48 |
| Joint position sense_abduction_upper limb |
Pearson Correlation |
|
|
1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
|
| N |
|
|
48 |
| Final |
Dynamic Gait Index (DGI) stages 3, 4, 5, 6 și 7 (points) |
Pearson Correlation |
1 |
-.142 |
.048 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
.335 |
.745 |
| N |
48 |
48 |
48 |
Joint position sense_flexion_
upper limb |
Pearson Correlation |
|
1 |
.392**
|
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
.006 |
| N |
|
48 |
48 |
| Joint position sense_abduction_upper limb |
Pearson Correlation |
|
|
1 |
| Sig. (2-tailed) |
|
|
|
| N |
|
|
48 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).