Submitted:
06 September 2024
Posted:
06 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods, Cases
2.1. Case Patient
- 89-year-old male.
- Height 172 cm, weight 68 kg, body surface area 1,800 m2.
- Smoking history: None.
- Diagnosis: Interstitial pneumonia.
- Age at onset of interstitial pneumonia: 85 years old (as of 2020)
- Underlying diseases: None.
- Platinum-palladium intake: 18 ml/day (6 ml/1 vial x 3 vials).
- Duration: 32 months.
- Drug treatment: None.
- Oxygen inhalation: None.
2.2. History
3. Measurements at In Vitro and In Vivo Levels
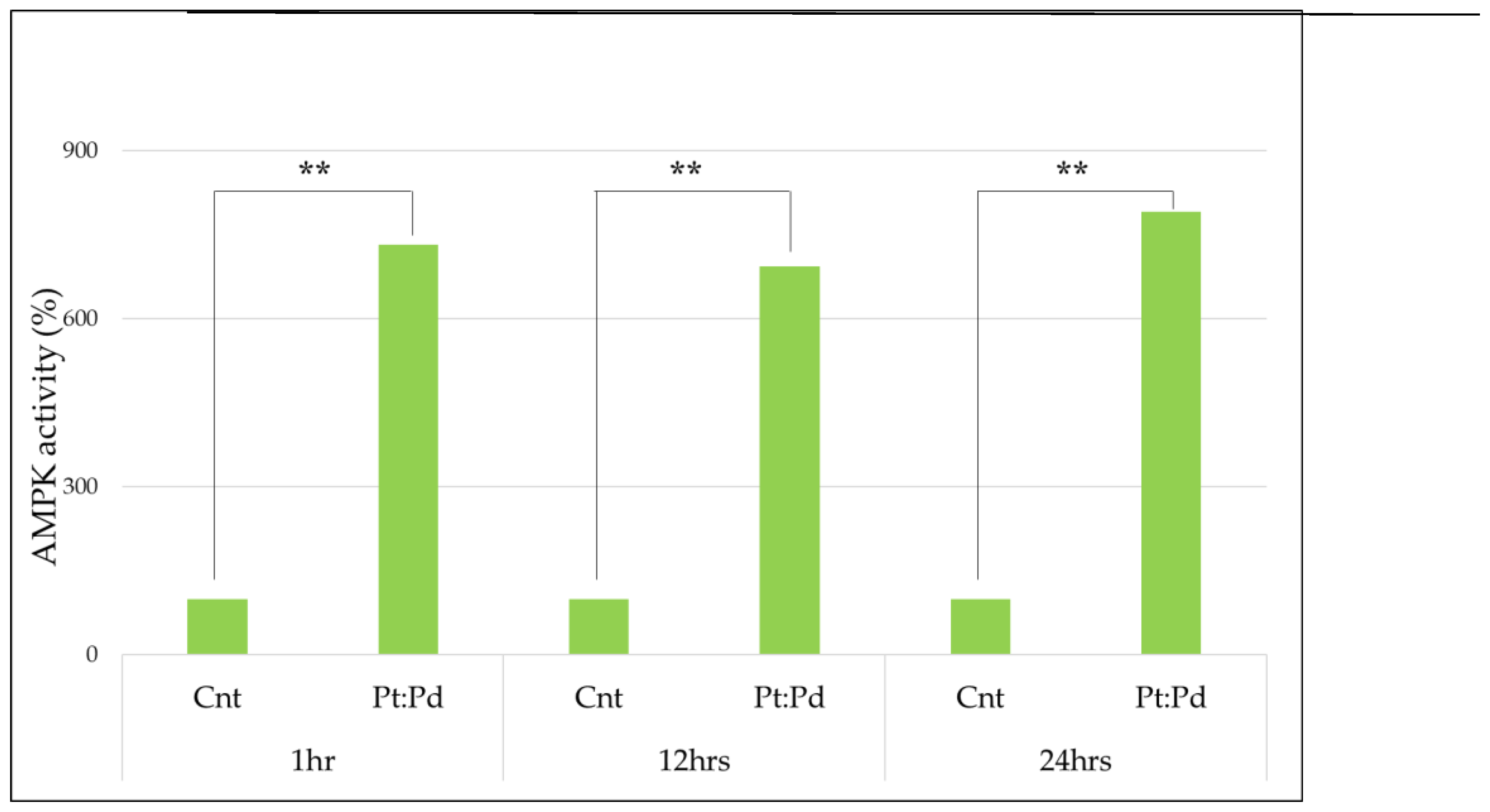
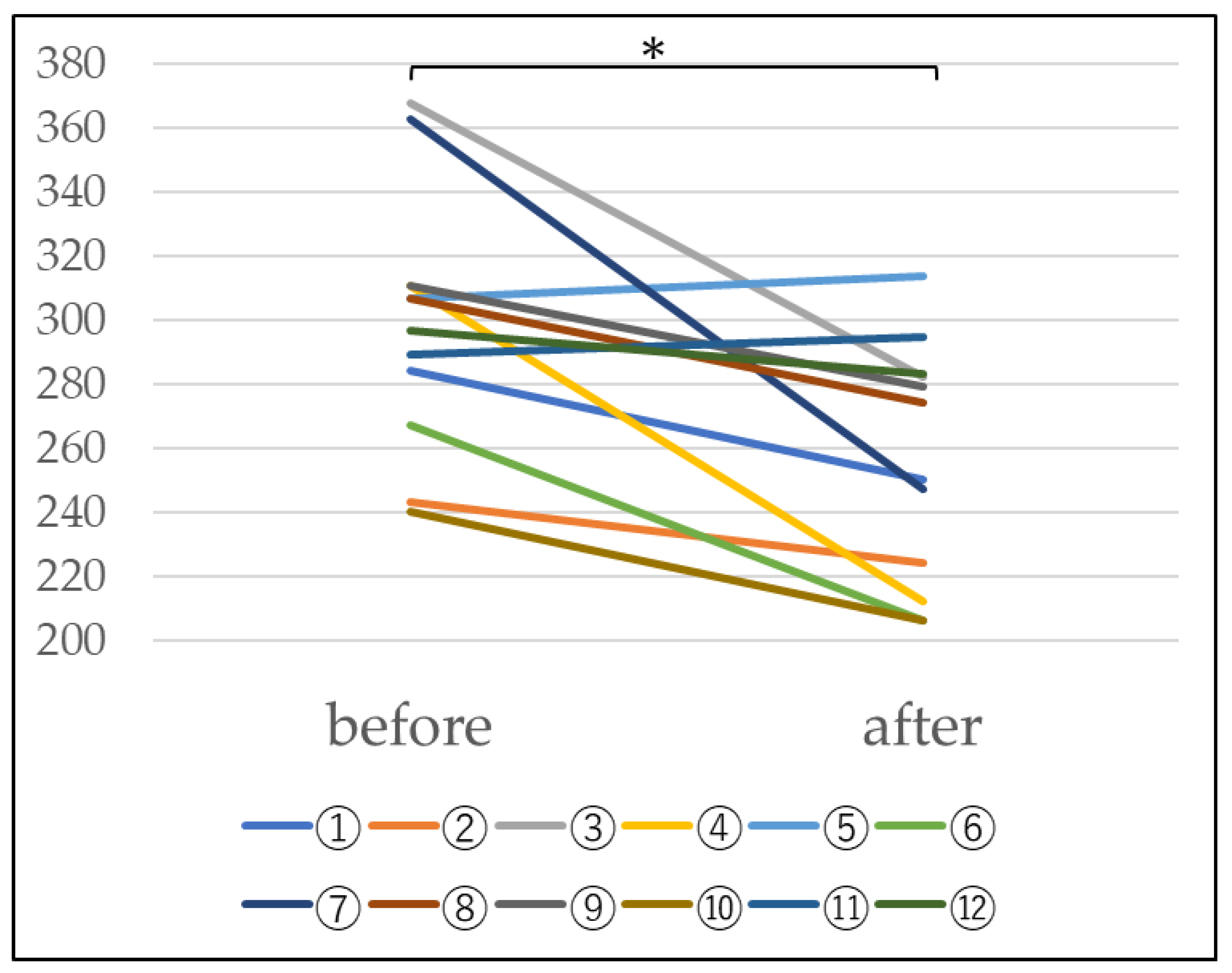
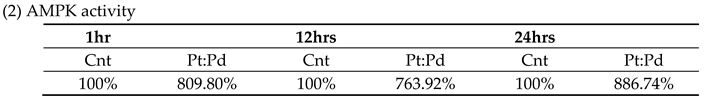
3.1. AMPK Measurement
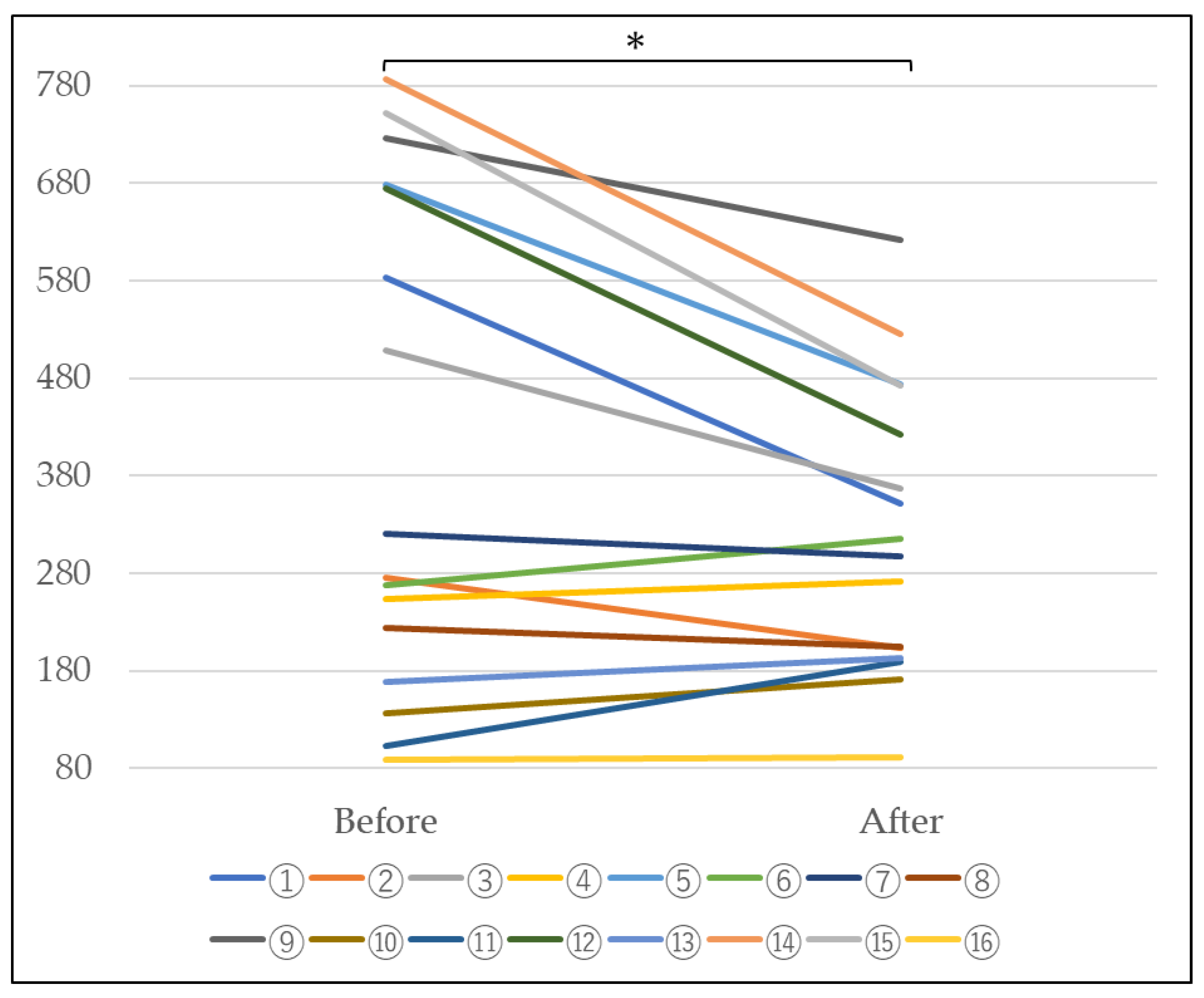
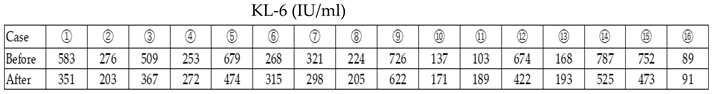
3.2. Measurement of Blood KL-6
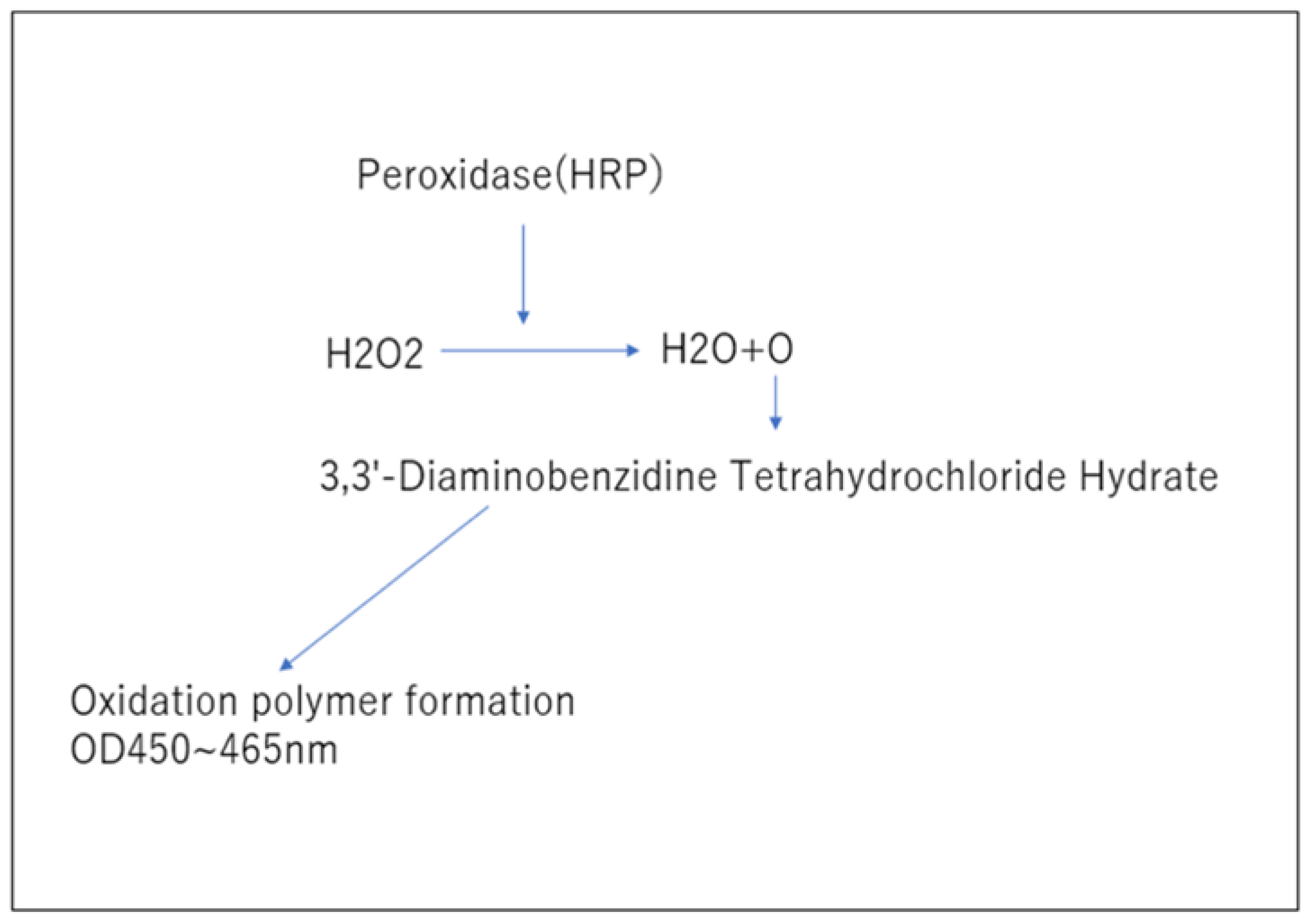
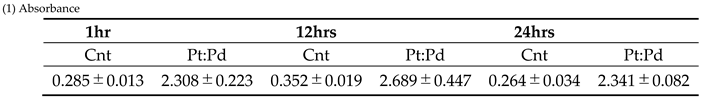
3.3. Measurement of Blood hydrogen Peroxide (Figure 3.)
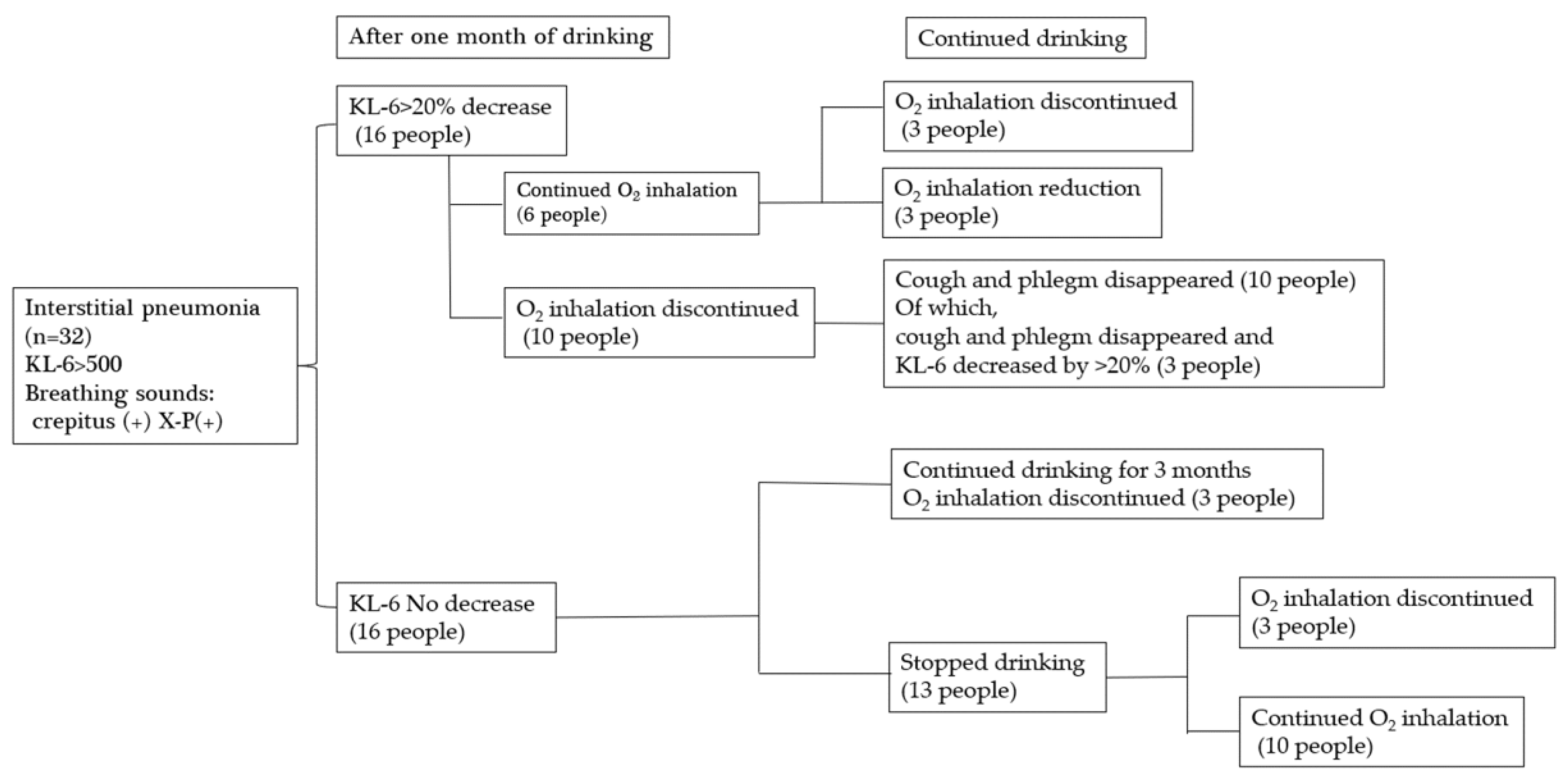
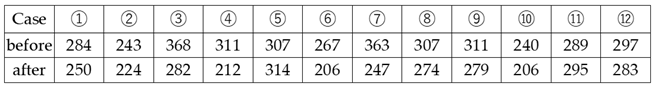
3.4. Study on the Effect Of Platinum-Palladium on Symptom Improvement in Patients With Interstitial Pneumonia
4. Results
4.1. AMPK Measurement
4.2. Measurement of Blood KL-6
4.3. Measurement of Blood Hydrogen Peroxide
4.4. Investigation Into The Effectiveness Of Platinum-Palladium In Improving Symptoms In Patients With Interstitial Pneumonia (Figure 7.)
4. Discussion
5. Ethical Considerations
Acknowledgements
References
- Lamb YN. Nintedanib: A Review in Fibrotic Interstitial Lung Diseases [published correction appears in Drugs. 2021 Apr 13;:] [published correction appears in Drugs. 2021 Jun;81(9):1133]. Drugs. 2021;81(5):575-586. [CrossRef]
- Renzoni EA, Poletti V, Mackintosh JA. Disease pathology in fibrotic interstitial lung disease: is it all about usual interstitial pneumonia? Lancet. 2021 Oct 16;398(10309):1437-1449.
- Graney BA, Fischer A. Interstitial Pneumonia with Autoimmune Features. Ann Am Thorac Soc. 2019 May;16(5):525-533.
- Reynolds C, Feary J, Cullinan P. Occupational Contributions to Interstitial Lung Disease. Clin Chest Med. 2020 Dec;41(4):697-707.
- Renzoni EA, Poletti V, Mackintosh JA. Disease pathology in fibrotic interstitial lung disease: is it all about usual interstitial pneumonia? Lancet. 2021 Oct 16;398(10309):1437-1449.
- Belloli EA, Beckford R, Hadley R, Flaherty KR. Idiopathic non-specific interstitial pneumonia. Respirology. 2016 Feb;21(2):259-68.
- ATS Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2002;165:277.
- Maher TM, Wuyts W. Management of Fibrosing Interstitial Lung Diseases. Adv Ther. 2019;36(7):1518-1531.
- akahashi H, Fujishima T, Koba H, Murakami S, Kurokawa K, Shibuya Y, Shiratori M, Kuroki Y, Abe S. Serum surfactant proteins A and D as prognostic factors in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis and their relationship to disease extent. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2000 Sep;162(3 Pt 1):1109-14. [CrossRef]
- Chiba H, Otsuka M, Takahashi H. Significance of molecular biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: A mini review. Respir Investig. 2018 Sep;56(5):384-391.
- Brasch, F. Interstitielle Lungenerkrankungen [Interstitial pulmonary diseases]. Pathologe. 2006;27(2):116-132.
- Wong AW, Ryerson CJ, Guler SA. Progression of fibrosing interstitial lung disease. Respir Res. 2020;21(1):32. Published 2020 Jan 29.
- GERARD, M. TURIN: Natural History and Clinical Management of Emphysema in Patients with and without Alpha1-Antitrypsin Inhibitor Deficiency. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1991; 624(1), 18-29.
- D P Tashkin, R Detels, M Simmons, H Liu, A H Coulson, J Sayre, S Rokaw: The UCLA population studies of chronic obstructive respiratory disease. XI. Impact of air pollution and smoking an annual change in forced expiratory volume in one second. Amer J Respir Crit Care Med. 1994; 149(5), 1209-1217.
- Stoller JK, Panos RJ, Krachman S, Doherty DE, Make B; Long-term Oxygen Treatment Trial Research Group. Oxygen therapy for patients with COPD: current evidence and the long-term oxygen treatment trial. Ches. 2010; 138(1), 179-187. [CrossRef]
- Organization WH. World health statistics 2010. World Health Organization, Geneva, 2010. https://scholar.google.com/scholar?hl=en&q=Organization+WH.+World+health+statistics+2010.+World+Health+Organization%2C+Geneva%2C+2010. Retrieved June 8, 2022.
- R. P. Young, R. J. Hopkins, T. Christmas, P. N. Black, P. Metcalf, G. D. Gamble: COPD prevalence is increased in lung cancer, independent of age, sex and smoking history. European Respiratory Journal. 2009; 34, 380-386.
- Fischer BM, Voynow JA, Ghio AJ. COPD: balancing oxidants and antioxidants. Int J Chron Obstruct Pulmon Dis. 2015;10:261-276. Published 2015 Feb 2.
- Alexandra, Moreira-Pais, Rita Ferreira, Rui Gil da Costa: Platinum-induced muscle wasting in cancer chemotherapy: Mechanisms and potential targets for therapeutic intervention. Life Sciences. 2018; 208, 1-9.
- Malinowska Katarzyna, Szczepanska Anna, Hanna Zielinska-Blizniewska, Majsterek Ireneusz: An Evaluation of the Antioxidant and Anticancer Properties of Complex Compounds of Copper (II), Platinum (II), Palladium (II) and Ruthenium (III) for Use in Cancer Therapy. Mini-Reviews in Medicinal Chemistry. 2018; 18(16), 1373 – 1381.
- Seung JunLeea, YiseulYua, Hyeon Jin Jung, Shreyanka Shankar Naik, Sanghun Yeon, Myong Yong Choi: Efficient recovery of palladium nanoparticles from industrial wastewater and their catalytic activity toward reduction of 4-nitrophenol. Chemosphere. 2021; 262, 128358.
- Yurdanur Ucar, William A Brantley, Sreenivas N Bhattiprolu, William M Johnston, Edwin A McGlumphy: Characterization of cast-to implant components from five manufacturers. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry. 2009; 102(4), 216-223.
- Hiroya Okamoto, Kentaro Horii, Akio Fujisawa, Yorihiro Yamamoto: Oxidative deterioration of platinum nanoparticle and its prevention by palladium. Experimental Dermatology. 2012; 21(S1), 5-7.
- Shuichi Shibuya, Yusuke Ozawa, Kenji Watanabe, Naotaka Izuo, Toshihiko Toda, Koutaro Yokote, Takahiko Shimizu: Palladium and platinum nanoparticles attenuate aging-like skin atrophy via antioxidant activity in mice. PLoS One, 2014; 9(10), e109288.
- Satoshi Kawakami, Hiroyuki Ichikawa, Tsutomu Sato, Hiroki Kataoka, Takaharu Ide, Hayato Terayama, Kou Sakabe: Antioxidant ability of platinum-palladium -Study using soft drinks containing platinum-palladium-. Journal of the Japan Society for Oral Functional Water. 2021; 22(1), 3-9.
- Bowen Yang, Yu Chen, Jianlin Shi: Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS)-Based Nanomedicine. Chemical Reviews. 2019; 119(8):4881-4985.
- Binks SP, Dobrota M. Kinetics and mechanism of uptake of platinum-based pharmaceuticals by the rat small intestine. Biochem Pharmacol. 1990; Sep 15;40(6):1329-36.
- Sable, V. , Maindan, K., Kapdi, A. R., Shejwalkar, P. S., & Hara, K: Active Palladium Colloids via Palladacycle Degradation as Efficient Catalysts for Oxidative Homocoupling and Cross-Coupling of Aryl Boronic Acids. ACS omega. 2017; 2(1), 204–217.
- Lee JS, Lee EY, Ha YJ, Kang EH, Lee YJ, Song YW. Serum KL-6 levels reflect the severity of interstitial lung disease associated with connective tissue disease. Arthritis Res Ther. 2019 ; 21(1):58.
- Song X, Bai S, He N, Wang R, Xing Y, Lv C, Yu F. Real-Time Evaluation of Hydrogen Peroxide Injuries in Pulmonary Fibrosis Mice Models with a Mitochondria-Targeted Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probe. ACS Sens. 2021; 6(3): 1228-1239. [CrossRef]
- NaoyaSakuraba, YokoTogami: FundamentalandclinicalevaluationofKL-6measurementbychemiluminescentenzymeimmunoassaysystem.
- “LumipulsePrestoKL-6Eisai”. Jpn J Med Pharm Sci. 2009; 61(4): 629-635. (in Japanese).
- Ogihara T, Hirano K, Morinobu T, Ogawa S, Hiroi M, Ban R, Ogihara H, Tamai H. KL-6, a mucinous glycoprotein, as an indicator of chronic lung disease of the newborn. J Pediatr. 2000 Aug;137(2):280-2.
- Wei-Zheng Zhang, Kylie Venardos, Jaye Chin-Dusting, David M Kaye: Adverse effects of cigarette smoke on NO bioavailability: role of arginine metabolism and oxidative stress. Hypertension. 2006; 48(2), 278-285.
- RonMittler: ROS Are Good. Trends in Plant Science. 2017; 22(1),11-19.
- 35. Ilaria Liguori, Gennaro Russo, Francesco Curcio, Giulia Bulli, Luisa Aran, David Della-Morte, Gaetano Gargiulo, Gianluca Testa, Francesco Cacciatore, Domenico Bonaduce, Pasquale Abete: Oxidative stress, aging, and diseases, Clinical Interventions in Aging. 2018; 13: 757–772.
- David Carling: AMPK signalling in health and disease. Current Opinion in Cell Biology. 2017; 45, 31-37.
- P.D. Boyer, B. Chance, L. Ernster, P. Mitchell, E. Racker, E.C. Slater: Oxidative phosphorylation and photophosphorylation. Annual Review of Biochemistry. 1977; 46, 955-1026.
- Barbara Cool, Bradley Zinker, William Chiou, Lemma Kifle, Ning Cao, Matthew Perham, Robert Dickinson, Andrew Adler, Gerard Gagne, Rajesh Iyengar, Gang Zhao, Kennan Marsh, Philip Kym, Paul Jung, Heidi S Camp, Ernst Frevert: Identification and characterization of a small molecule AMPK activator that treats key components of type 2 diabetes and the metabolic syndrome. Cell Metabolism. 2006; 3(6), 403-416.
- Fabrizio Giordanetto, David Karis: Direct AMP-activated protein kinase activators: a review of evidence from the patent literature. Expert Opinion on Therapeutic Patents. 2012; 22(12), 1467-77.
- Bing Xiao, Matthew J. Sanders, David Carmena, Nicola J. Bright, Lesley F. Haire, Elizabeth Underwood, Bhakti R. Patel, Richard B. Heath, Philip A. Walker, Stefan Hallen, Fabrizio Giordanetto, Stephen R. Martin, David Carling & Steven J. Gamblin: Structural basis of AMPK regulation by small molecule activators. Nature Communications. 2013; 4, 3017.
- Herzig S, Shaw RJ. AMPK: guardian of metabolism and mitochondrial homeostasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2018;19(2), 121-135.
- Mihaylova MM, Shaw RJ. The AMPK signalling pathway coordinates cell growth, autophagy and metabolism. Nature cell biology. 2011; 13, 1016–1023.
- Russell FM, Hardie DG. AMP-Activated Protein Kinase: Do We Need Activators or Inhibitors to Treat or Prevent Cancer?. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;22(1), 186. [CrossRef]
- Wu S, Zou MH. AMPK, Mitochondrial Function, and Cardiovascular Disease. Int J Mol Sci. 2020;21(14), 4987.
- Zhang D, Wang W, Sun X, et al. AMPK regulates autophagy by phosphorylating BECN1 at threonine 388. Autophagy. 2016;12(9):1447-1459.
- Bergeron R, et al. Chronic activation of AMP kinase results in NRF-1 activation and mitochondrial biogenesis. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 2001; 281, E1340–E1346.
- Hwang, Jung Hwan et al.: Enhanced Production of Adenosine Triphosphate by Pharmacological Activation of Adenosine Monophosphate-Activated Protein Kinase Ameliorates Acetaminophen-Induced Liver Injury. Molecules and cells. 2015; 38(10), 843-50.
- Hardie, D.G. , Schaffer B.E., Brunet A. AMPK: an energy-sensing pathway with multiple inputs and out-puts. Trends Cell Biol. 2016;26(3), 190–201.
- Xiao-Yu Cheng, Yang-Yang Li, Cheng Huang, Jun Li, Hong-Wei Yao: AMP-activated protein kinase reduces inflammatory responses and cellular senescence in pulmonary emphysema. Oncotarget. 2017; 8(14), 22513-22523.
- Osaka A, Yanagihara K, Yamada Y, Hasegawa H, Inokuchi N, Hayashi T, Komoda M, Nakamura S, Aoyama M, Sawada T, Kamihira S. Elevation of serum KL-6 glycoprotein or surfactant protein-D in adult T-cell leukemia with distinct pulmonary complications. Tohoku J Exp Med. 2009;218(2):99-105.
- Okamoto T, Fujii M, Furusawa H, Tsuchiya K, Miyazaki Y, Inase N. The usefulness of KL-6 and SP-D for the diagnosis and management of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis. Respir Med. 2015;109(12):1576-81.
- Kubota M, Haruta T. The role of serum KL-6 measurement in common pediatric respiratory infections. J Infect Chemother. 2006 ;12(1):22-4.
- Zhang Y, Kaminski N. Biomarkers in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Curr Opin Pulm Med. 2012 ;18(5):441-6.
- d'Alessandro M, Bergantini L, Cameli P, Pieroni M, Refini RM, Sestini P, Bargagli E. Serum Concentrations of KL-6 in Patients with IPF and Lung Cancer and Serial Measurements of KL-6 in IPF Patients Treated with Antifibrotic Therapy. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(4):689.
- Miyazaki K, Kurishima K, Kagohashi K, Kawaguchi M, Ishikawa H, Satoh H, Hizawa N. Serum KL-6 levels in lung cancer patients with or without interstitial lung disease. J Clin Lab Anal. 2010;24(5):295-9.
- Knaus, UG. Oxidants in Physiological Processes. Handb Exp Pharmacol. 2021;264:27-47.
- Sies, H. Hydrogen peroxide as a central redox signaling molecule in physiological oxidative stress: Oxidative eustress. Redox Biol. 20171; 11, 613-619.
- Watt BE, Proudfoot AT, Vale JA. Hydrogen peroxide poisoning. Toxicol Rev. 2004;23(1):51-7.
- van der Vliet A, Janssen-Heininger YM. Hydrogen peroxide as a damage signal in tissue injury and inflammation: murderer, mediator, or messenger? J Cell Biochem. 2014 ;115(3):427-35.
- Tang, BL. Glucose, glycolysis, and neurodegenerative diseases. J Cell Physiol. 2020 Nov;235(11):7653-7662.
- Judge A, Dodd MS. Metabolism. Essays Biochem. 2020 Oct 8;64(4):607-647.
- Ministry of Health , Labour and Welfare, Reactive oxygen species and oxidative stress. https://www.e-healthnet.mhlw.go.jp/information/food/e-04-003.html(Accessed April 28, 2023)(in Japanese).
- Beck-Schimmer B, Bonvini JM. Bronchoaspiration: incidence, consequences and management. Eur J Anaesthesiol. 2011 ;28(2):78-84.
- Singh A, Kukreti R, Saso L, Kukreti S. Oxidative Stress: Role and Response of Short Guanine Tracts at Genomic Locations. Int J Mol Sci. 2019;20(17):4258.
- Madreiter-Sokolowski CT, Thomas C, Ristow M. Interrelation between ROS and Ca in aging and age-related diseases. Redox Biol. 2020 ;36:101678.
- Moore, MN. Autophagy as a second level protective process in conferring resistance to environmentally-induced oxidative stress. Autophagy. 2008;4(2):254-6.
- Calimport SRG, Bentley BL. Aging Classified as a Cause of Disease in ICD-11. Rejuvenation Res. 2019 Aug;22(4):281.
- Satoshi Kawakami, Hiroyuki Ichikawa, Tsutomu Sato, Hiroki Kataoka, Takaharu Ide, Hayato Terayama, Kou Sakabe: Antioxidant ability of platinum-palladium -Study using soft drinks containing platinum-palladium-, J Jpn Soc Oral Funct Water, 2021;22,3-10. (in Japanese).
- Nagaraja C, Shashibhushan BL, Sagar, Asif M, Manjunath PH. Hydrogen peroxide in exhaled breath condensate: A clinical study. Lung India. 2012;29(2):123-7.
- Brand, MD. Mitochondrial generation of superoxide and hydrogen peroxide as the source of mitochondrial redox signaling. Free Radic Biol Med. 2016;100:14-31.
- Ramírez-Prieto MT, García-Río F, Villamor J. Papel del estrés oxidativo en las enfermedades respiratorias y su monitorización [Role of oxidative stress in respiratory diseases and its monitoring]. Med Clin (Barc). 2006;127(10):386-96. [CrossRef]
 |
 |
 |
 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





