Submitted:
06 September 2024
Posted:
06 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
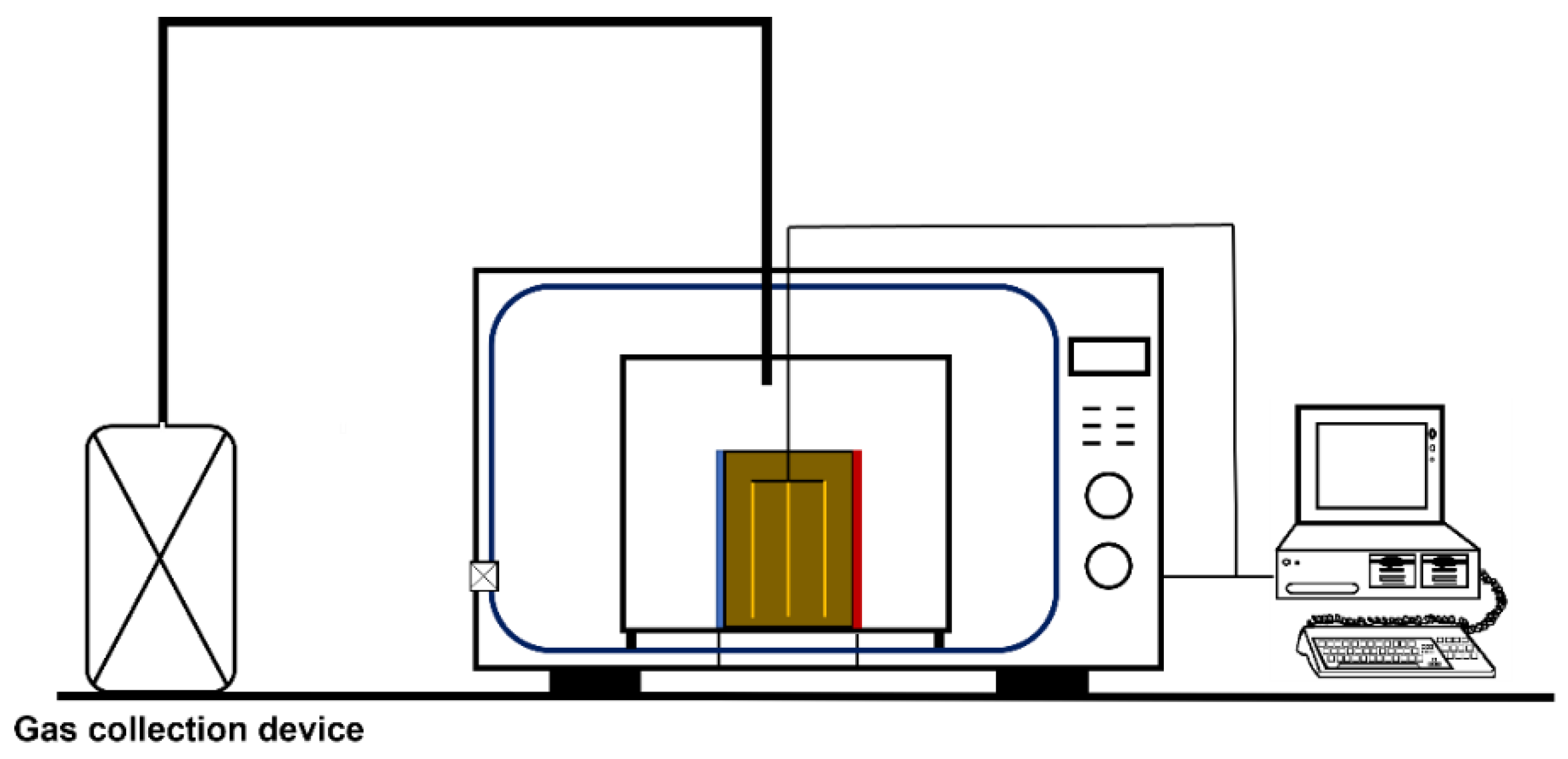
2.1. Experimental Materials and Device
2.2. Experimental Methods
2.2.1. Determination of Organic Matter Content
2.2.2. Determination of Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) in Soil
3. Results and Discussion
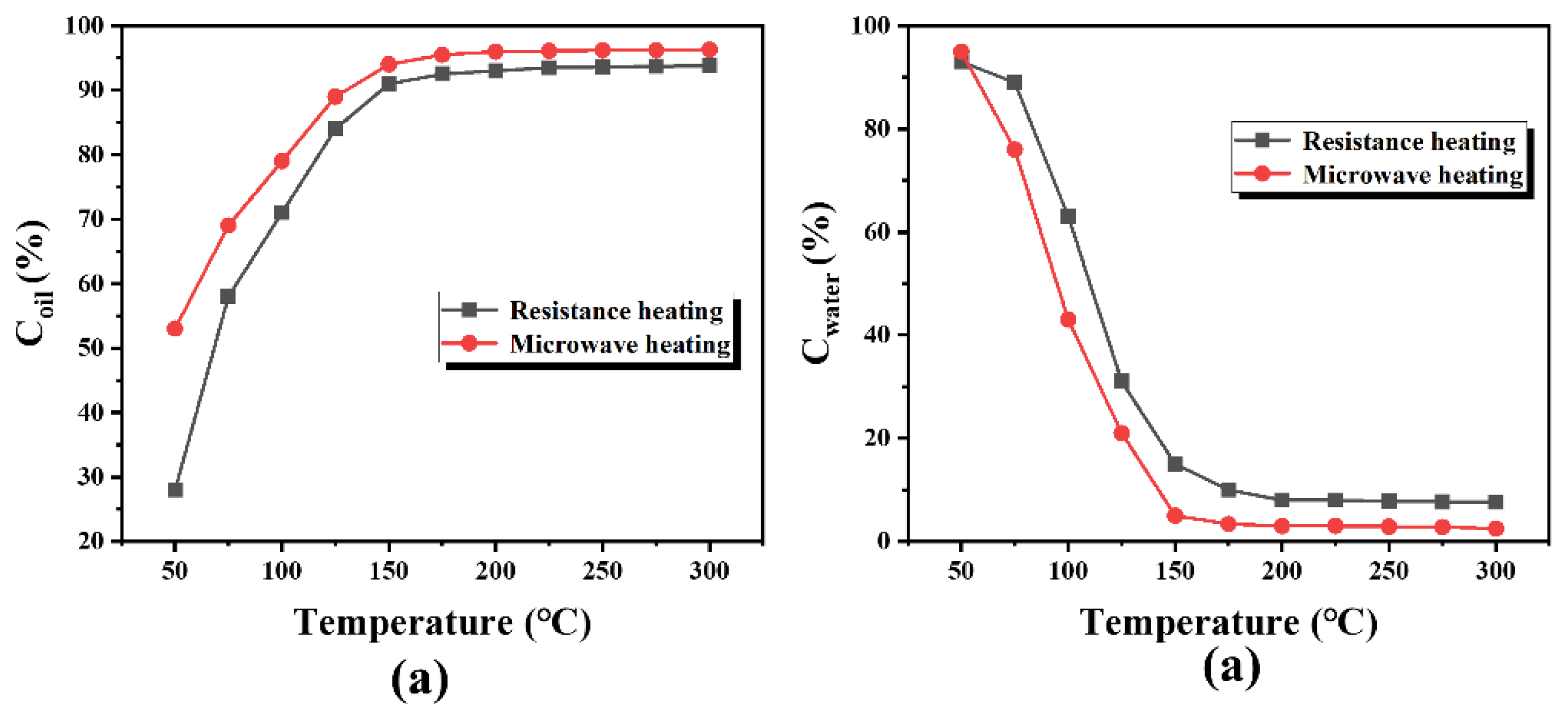
3.1. The Effect of Temperature on Mineral Oil Removal Efficiency
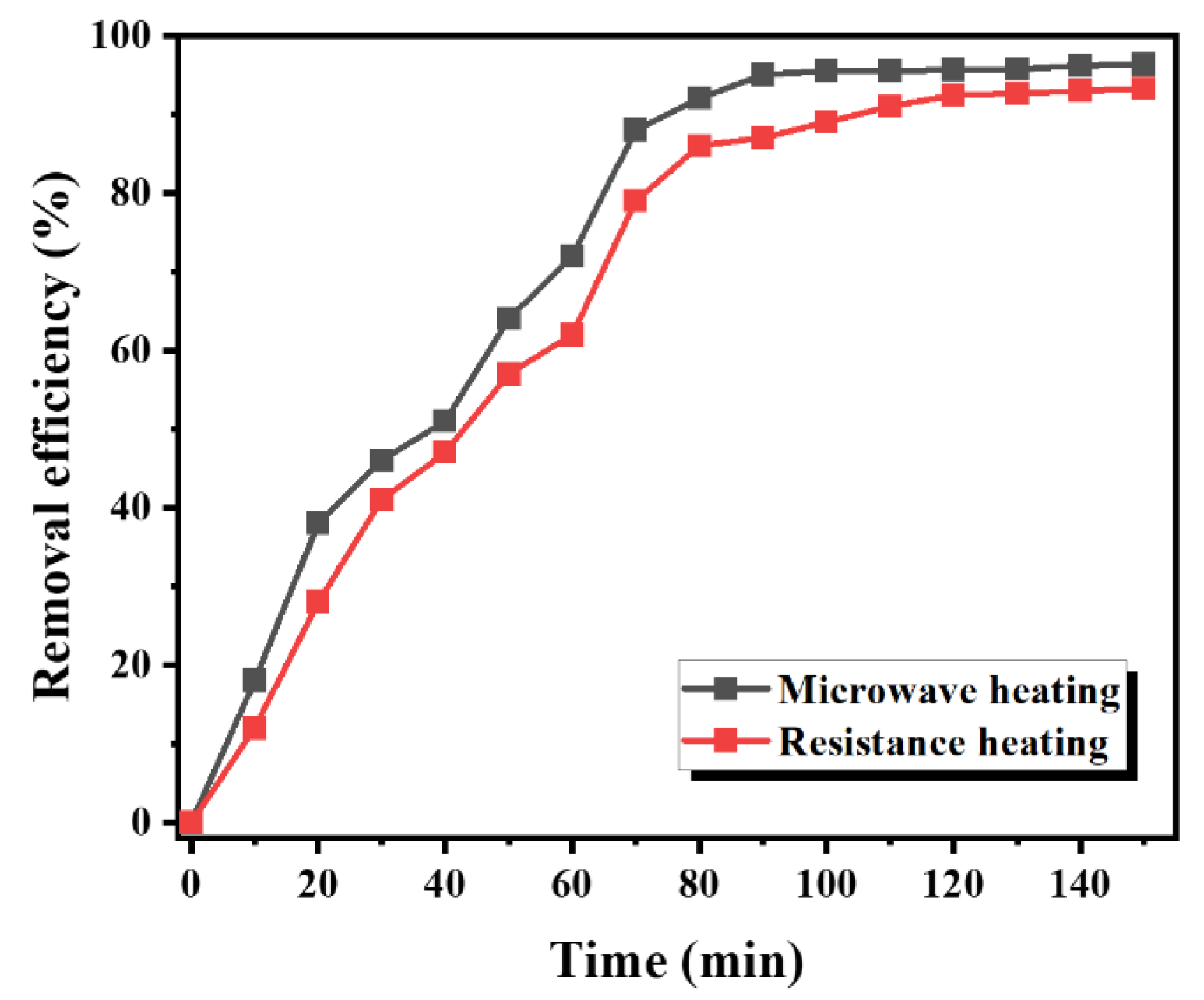
3.2. The Effect of Heating Time on the Removal Rate of Mineral Oil Pollutants
3.3. Comparative Study on Soil Physical and Chemical Properties
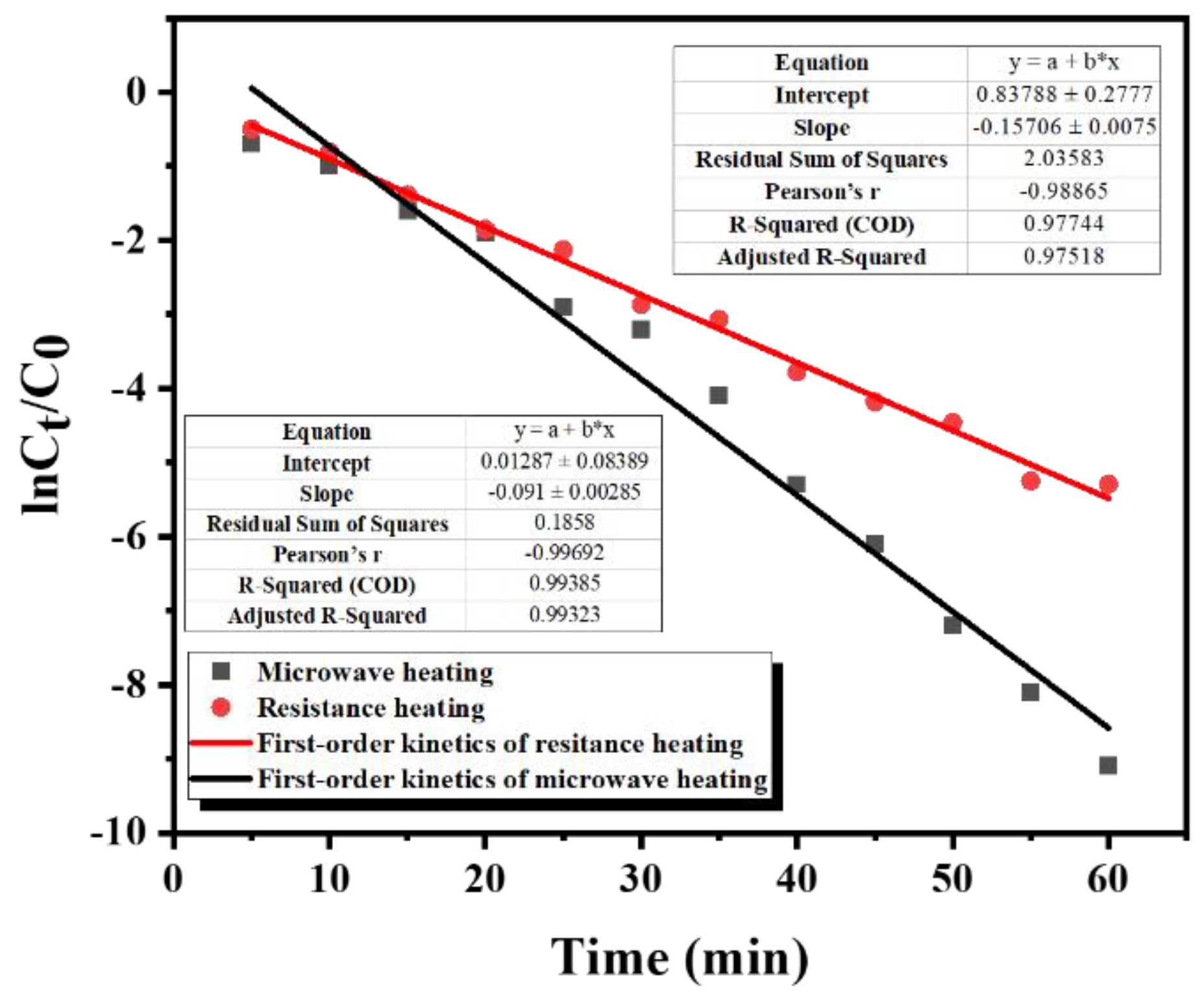
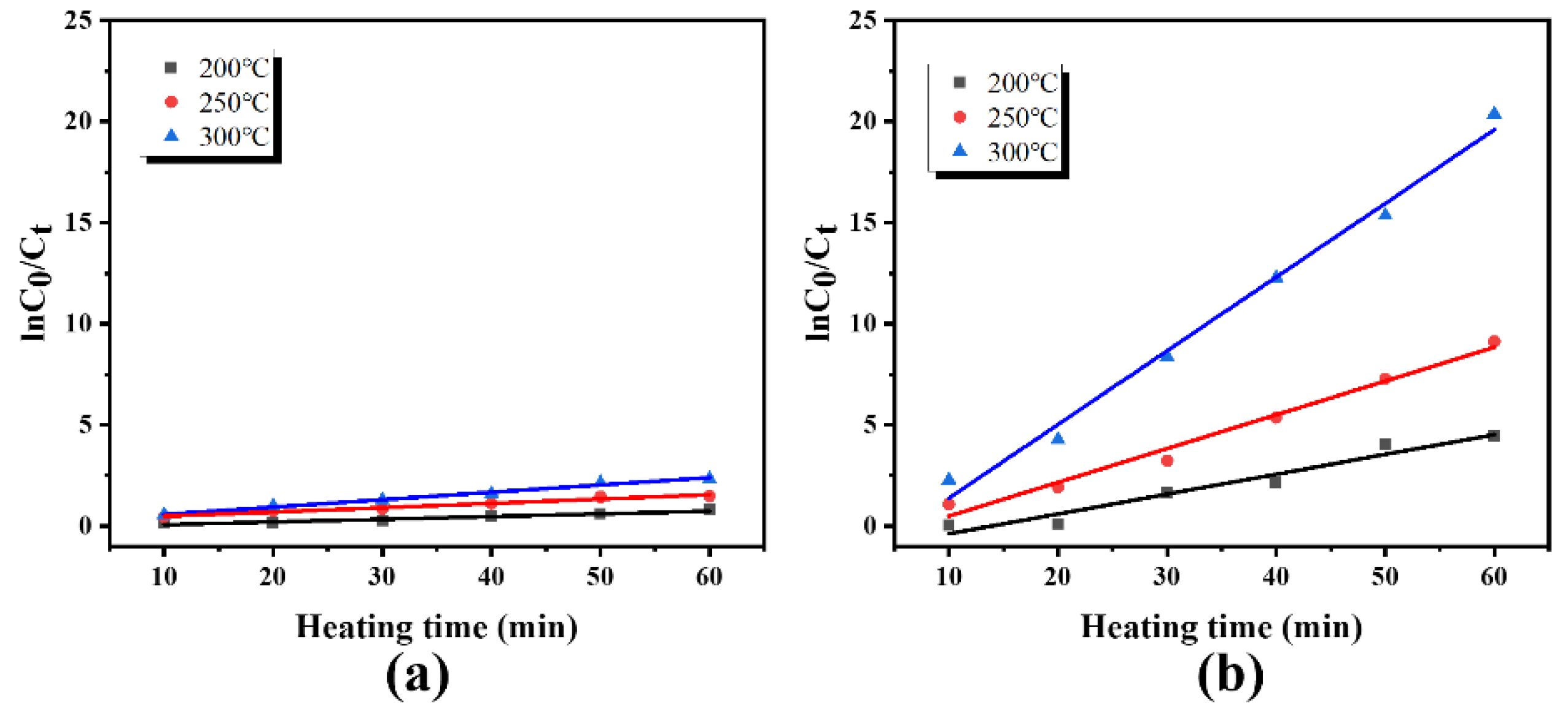
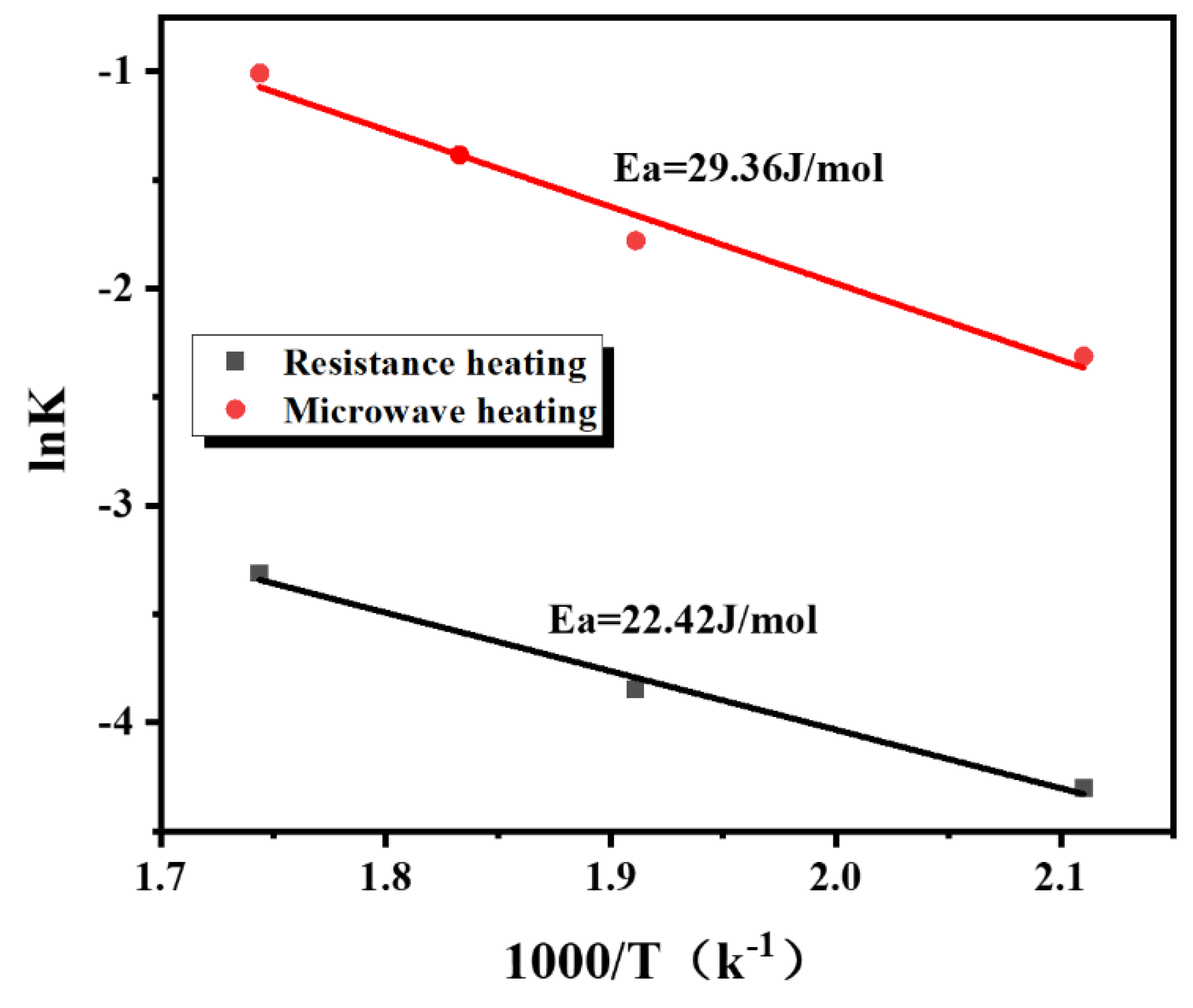
3.4. Study on Desorption Kinetics
4. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Li, J.; He, C.; Cao, X.; et al. Low temperature thermal desorption-chemical oxidation hybrid process for the remediation of organic contaminated model soil: A case study. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 243, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Falciglia, P.P.; Roccaro, P.; Bonanno, L.; et al. A review on the microwave heating as a sustainable technique for environmental remediation/detoxification applications. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2018, 95, 147–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegazy, A.K.; et al. Assessment of Vinca rosea (Apocynaceae) potentiality for remediation of crude petroleum oil pollution of soil. Sustainability, 2023, 15, 11046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Li, L.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Microwave heating remediation of light and heavy crude oil-contaminated soil. Energy Fuels 2023, 37, 5323–5330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, S.-H.; et al. Application of soil washing and thermal desorption for sustainable remediation and reuse of remediated soil. Sustainability 2021, 13, 12523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; et al. Formation of Secondary Pollutants during Thermal Desorption of Organic Contaminants in Soil. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 428, 128214. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, B.; Wu, A.; Li, X.; et al. Progress in fundamental research on thermal desorption remediation of organic compound-contaminated soil. Waste Dispos. Sustain. Energy 2021, 3, 83–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bykova, M.V.; Alekseenko, A.V.; Pashkevich, M.A.; et al. Thermal desorption treatment of petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soils of tundra, taiga, and forest steppe landscapes. Environ. Geochem. Health 2021, 43, 2331–2346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Y.; Tao, Y.; Meng, Q.; et al. Microwave-combined advanced oxidation for organic pollutants in the environmental remediation: An overview of influence, mechanism, and prospective. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 441, 135924. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, H.; Wang, H.; Kong, L.; et al. Insights into oil recovery, soil rehabilitation and low temperature behaviors of microwave-assisted petroleum-contaminated soil remediation. J. Hazard. Mater. 2019, 377, 341–348. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, K.S.; Lo, W.H.; Lin, W.M.; et al. Microwave-assisted thermal remediation of diesel contaminated soil. Eng. J. 2016, 20, 93–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, J.; Dong, M.; Bi, F.; et al. Microwave-assisted one-pot synthesis of β-cyclodextrin modified biochar for stabilization of Cd and Pb in soil. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 346, 131165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, H.; et al. Microwave-assisted thermal desorption for remediation of heavy oil-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 2018, 200, 375–383. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, J.; et al. Enhanced microwave remediation of hydrocarbon-contaminated soil by adding carbon-based materials. Chemosphere 2018, 193, 629–635. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Z.; et al. A review of microwave soil remediation: Progress, challenges, and prospects. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 426, 128086. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, D.; Kan, H.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Pyrene contaminated soil remediation using microwave/magnetite activated persulfate oxidation. Chemosphere 2022, 286, 131787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, M.; Xu, P.; Tian, K.; et al. Recent advances in microwave-enhanced advanced oxidation processes (MAOPs) for environmental remediation: A review. Chem. Eng. J. 2023, 144208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Evaluation of microwave-assisted soil remediation technology for petroleum hydrocarbon-contaminated soil. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 269, 110732. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, Q.; et, a. l. Bioavailability of 2, 4, 6-trinitrotoluene (TNT) to earthworms in three different types of soils in China. Soil and Sediment Contamination: An International Journal. 2016, 25, 38–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Y.; et al. Monitoring in situ microbial growth and decay in soil column experiments by induced polarization. Geophysical Research Letters. 2022, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; et al. Redistribution and isotope fractionation of endogenous Cd in soil profiles with geogenic Cd enrichment. Science of the Total Environment. 2022, 852, 158447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mavrogianopoulos, G.N.; Frangoudakis, A.; Pandelakis, J. Energy efficient soil disinfestation by microwaves. J. Agric. Eng. Res. 2000, 75, 149–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jon, C.J.G.; Tai, H.S. Application of granulated activated carbon packed-bed reactor in microwave radiation field to treat BTX. Chemosphere 1998, 37, 685–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ogunniran, O.; Binner, E.R.; Sklavounos, A.H.; et al. Enhancing evaporative mass transfer and steam strip using microwave heating. Chem. Eng. Sci. 2017, 165, 147–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, D.; et al. Adsorption Characteristics of Polycyclic Aromatic Hydrocarbons (PAHs) on Soil Organic Matter: Effect of Soil Aging and Temperature. Environ. Pollut. 2019, 248, 944–952. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.; et al. Influence of Polar Molecules on Microwave Heating Efficacy in Contaminated Soils: A Mechanistic Study. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 292, 112777. [Google Scholar]
- Han, W.; Ye, Y.; Liu, S.; et al. Characterization and thermal removal of organophosphorus pesticides in soils from a former agrochemical factory. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2022, 19, 10845–10854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domingues, R.R.; Sánchez-Monedero, M.A.; Spokas, K.A.; et al. Enhancing cation exchange capacity of weathered soils using biochar: Feedstock, pyrolysis conditions and addition rate. Agronomy 2020, 10, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruba, P.; Mulder, J. Tree species affect cation exchange capacity (C12EC) and cation binding properties of organic matter in acid forest soils. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 511, 655–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, D.C.; Xu, W.F.; Mu, Y.; et al. Remediation of petroleum-contaminated soil and simultaneous recovery of oil by fast pyrolysis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 5330–5338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, É.C.; Adebayo, M.A.; Machado, F.M. Kinetic and equilibrium models of adsorption. Carbon Nanomater. Adsorb. Environ. Biol. Appl. 2015, 33–69. [Google Scholar]
- Simonin, J.P. On the comparison of pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws in the modeling of adsorption kinetics. Chem. Eng. J. 2016, 300, 254–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Adsorption kinetic models: Physical meanings, applications, and solving methods. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 390, 122156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; He, C.; Cao, X.; et al. Low temperature thermal desorption-chemical oxidation hybrid process for the remediation of organic contaminated model soil: A case study. J. Contam. Hydrol. 2021, 243, 103908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piskulich, Z.A.; Mesele, O.O.; Thompson, W.H. Activation energies and beyond. J. Phys. Chem. A 2019, 123, 7185–7194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grant, E.H.; Halstead, B.S. Halstead. Dielectric parameters relevant to microwave dielectric heating. Chemical society reviews. 1998, 27, 213–224. [Google Scholar]
- De la Hoz, A.; Diaz-Ortiz, A.; Moreno, A. Microwaves in organic synthesis. Thermal and non-thermal microwave effects. Chemical Society Reviews 2005, 34, 164–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kappe, C. Oliver. Controlled microwave heating in modern organic synthesis. Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 2004, 43, 6250–6284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lidström, P.; et al. Microwave assisted organic synthesis-a review. Tetrahedron. 2001, 57, 9225–9283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Water content (%) |
Organic matter content a (%) |
Petroleum hydrocarbon contaminant b (%) |
Cation exchange capacity c (%) |
| 11.22 | 6.74 | 9.76 | 6.27 |
| Soil Type | Mass (g) |
Organic Matter Content (%) |
| Primitive soil | 5.32 | 6.74 |
| Soil after Ohmic Heating | 4.21 | 1.88 |
| Soil after Microwave Heating | 3.54 | 4.04 |
| Soil Type | CEC1 cmol/kg |
CEC2 cmol/kg |
CEC3 cmol/kg |
Average cmol/kg |
| Primitive soil | 6.32 | 6.21 | 6.24 | 6.27 |
| Soil after Microwave Heating | 3.98 | 3.34 | 4.04 | 3.79 |
| Soil after Resistance Heating | 1.36 | 1.43 | 1.33 | 1.37 |
| 200℃ | 250℃ | 300℃ | |
| KRH | 0.0135 | 0.0213 | 0.0364 |
| R2RH | 0.9403 | 0.9501 | 0.9483 |
| KMH | 0.0982 | 0.1670 | 0.3645 |
| R2MH | 0.9618 | 0.9817 | 0.9819 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





