1. Introduction
The Mycotoxins are naturally occurring, low molecular weight toxic chemicals produced as secondary metabolites by certain filamentous fungi [
1]. Among over 300 mycotoxins detected and reported, aflatoxins are among the most commonly found, highly toxic and presents a significant global food safety concern [
2]. Aflatoxins are primarily produced by
Aspergillus flavus,
Aspergillus parasiticus and infrequently
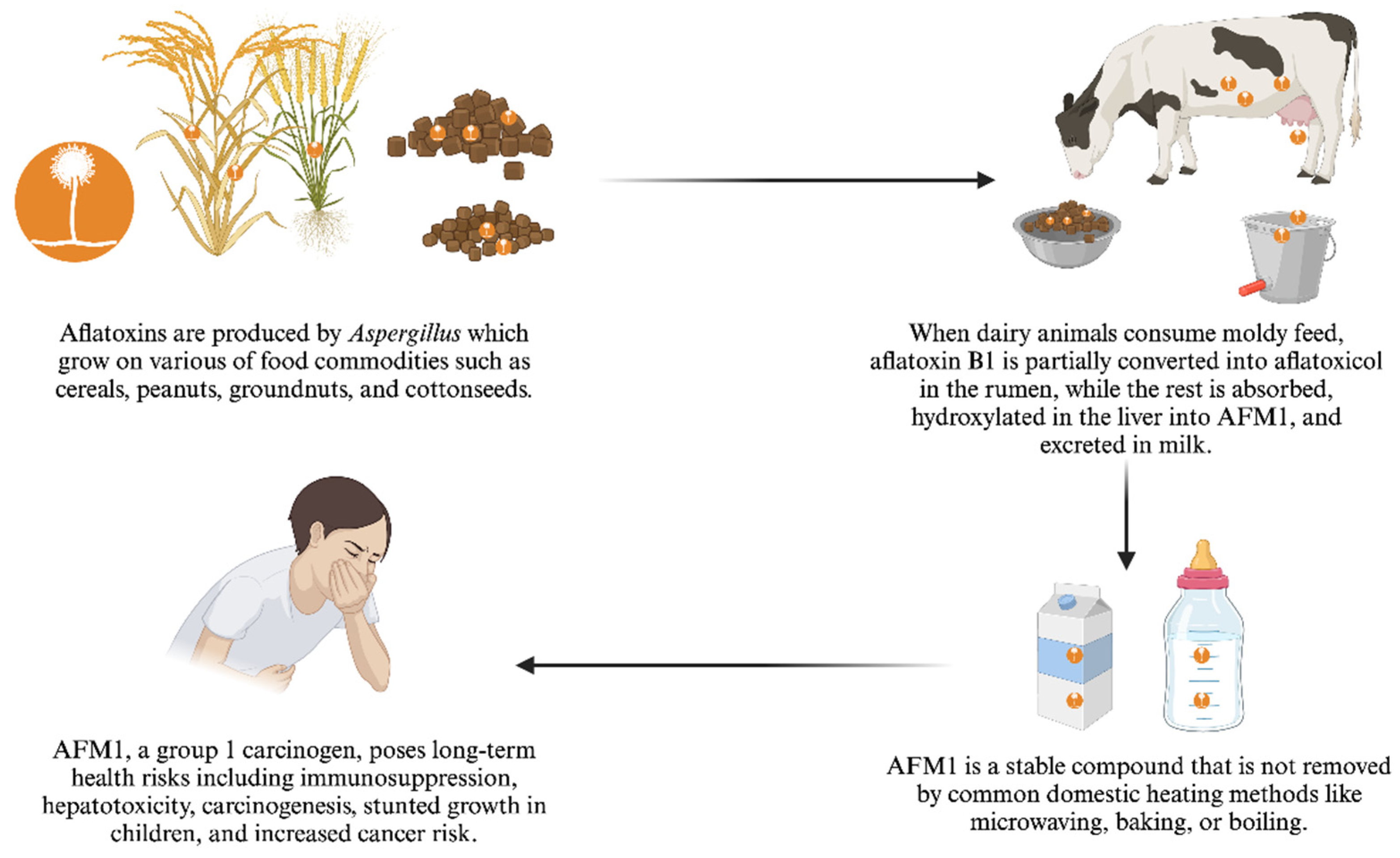
Aspergillus nomius, which grow on various of food commodities such as cereals, peanuts, groundnuts, cottonseeds [
3]. Among the dozens of identified aflatoxins, aflatoxin B1, B2, G1, G2, M1 are considered important due to their toxicity and associated health risks to both the domesticated animals and the humans [
2]. Aflatoxin B and G are usually found in dairy animal feeds of dairy animal, which is a major source of exposure [
4].
Aflatoxin M1(AFM1) is metabolite form of aflatoxin B1, excreted through the milk, thereby posing a public health risk to milk consumers [
5,
6]. AFM1 is a stable compound that is not removed by common domestic heating methods like microwaving, baking, or boiling. However, its stability during pasteurization is debated. Some studies suggest that pasteurization does not affect AFM1 levels [
7,
8,
9], while others report a 16% reduction, possibly due to the breakdown of casein during heat treatment [
10]. Agricultural residues such as rice straw, wheat straw, maize stovers, and crop hulls, along with feed components like maize grain, rice bran, and wheat bran, are important animal feeds but are susceptible to aflatoxin contamination, particularly under poor storage conditions [
11,
12]. When dairy animals consume moldy feeds contaminated with aflatoxin, they ingest AFB1, which is partially converted in the rumen into aflatoxicol (
Figure 1). The remaining AFB1 is absorbed through the digestive tract, hydroxylated in the liver by cytochrome P450 enzymes into AFM1, and then excreted in milk [
13].
Although AFM1 is less toxic than AFB1it still poses serious long-term health risks, especially to children and the elderly, as it is a potent immunosuppressive agent, hepatotoxin, and carcinogen [
14]. AFM1, along with AFB1, AFB2, AFG1 and AFG2, is categorized as group 1 carcinogen by the International Agency for the Research on Cancer (IARC) [
15]. Exposure to AFM1 in early life and childhood is associated with reduced Height-for-Age Z (HAZ) scores in children [
16], reduced birth weight [
17], reduced height at birth [
5] and stunted growth [
18]. The cumulative effects of the toxin are also correlated to the higher risk of cancer, immune suppression, hepatocellular carcinoma, Reye’s syndrome, cirrhosis and Kwashikor [
1,
19]. A study in Egypt showed a correlation between increased AFM1 levels in blood and high hepatitis C virus titer in patients with chronic liver disease [
20].
Aflatoxin contamination in human food and dairy products is a global issue, affecting approximately 25% of food products annually, with particularly severe impacts in developing and underdeveloped countries due to poor husbandry practices and socioeconomic conditions [
21]. The European Commission has set the maximum permissible level (MPL) for AFM1 as 0.025 μg/kg for infant formulae and 0.05 μg/kg for raw milk [
22]. This MPL is found violated by a marketed milk in many African, Middle East and South Asian countries. In some studies from these regions, the prevalence of AFM1 in milk exceeding the EU limit has been found to be 100%, highlighting a concerning food safety situation [
23].
Nearly all Nepalese, from children to the elderly, consume milk; however, there is a significant lack of information about AFM1 contamination in milk, and the public remains largely unaware of the potential health risks associated with consuming AFM1-contaminated milk [
24,
25]. This issue is particularly severe in the Kathmandu district, where milk consumption is high, yet milk is rarely screened for adulteration and contamination, leaving its safety for human consumption uncertain [
26]. Similarly, livestock management on peri-urban farms near large cities like Kathmandu faces challenges, particularly in feeding, housing, and storage space, due to land and feed scarcity, which has been found to be significantly associated with higher levels of aflatoxicosis in milk [
26]. A study by Pokharel et al. (2021) found AFM1 in 94% (i.e. 1355/1439) of breast milk samples, highlighting the significant risk of toxin exposure to humans in Nepal [
25]. Similarly, research in neighboring countries like India, Pakistan, China has reported AFM1 levels in milk exceeding permissible limits (≥50 ppt.) [
27,
28,
29,
30], reflecting a broader regional concern.
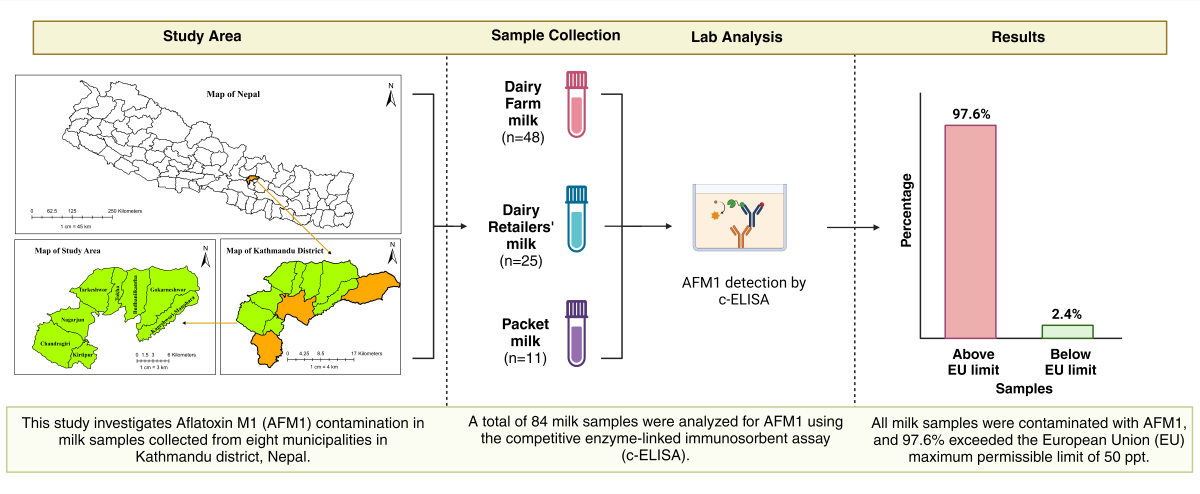
This study aimed to determine the prevalence of AFM1 in various types of milk (farm raw, dairy retailers’, and packet) in the Kathmandu district and to compare the contamination level to international standard to assess whether milk was hazardous for human consumption. Additionally, the study sought to evaluate the different farm management factors that might increase the risk for aflatoxin contamination in milk and to guide the relevant authorities in developing strategic measures to mitigate this contamination.
2. Results
2.1. Aflatoxin Contamination
Milk samples collected from eight municipalities in the Kathmandu district were analyzed for aflatoxin M1 using competitive enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (c-ELISA). All 84 tested milk samples had aflatoxin levels above the lower limit of detection (5 ppt), indicating that 100% of the milk samples were contaminated
(Table 1). Of these, 82 samples (97.6%) exceeded the EU’s maximum permissible limit of 50 ppt. The two samples that did not exceed the EU limit were from pooled milk collected from farms.
2.2. Farm Characteristics
Forty-eight cattle farms from the Kathmandu district were enrolled in the study. Among the farmers who responded to the questionnaire, the average age was 39 years, and 70.8% were male. Only two respondents had ever heard of aflatoxin contamination in milk. Most of the respondents were small-scale herders, with an average herd size of 15.8 animals per farm (SD=17.3), ranging from 4 to 86 animals (Q1=6, Q2=8, Q3=20). Daily milk yield varied from 9 liters to 400 liters, with an average of 88.8 liters. Of these farms, 87.5% were managed intensively, while the remaining 12.5% were managed semi-intensively with mixed grazing practices. The two farms with AFM1 levels below 50 ppt both had smaller herd sizes and were located Pre-Urban areas
(Table 2).
2.3. Feeding Practice
All farms (n=48), except for two, included cut-and-carry forage in their livestock feeding practices. The exceptions relied on other feed sources, such as concentrates and straw. Only three farms incorporated silage into their feeding regimen. On 98.5% of the farms, the feedstuffs consisted of paddy straw, with all but one sourced from the Terai, the southern region of the country. All farms used concentrates, either as “homemade ready-made feed” or “commercial compound pellet feed”. Eleven farms exclusively used commercial feed, two relied solely on homemade feed, and the remaining 35 farms used a combination of both in varying ratios. Twenty-three farms also included unconventional feedstuffs, such as leftovers and brewers’ dry yeast. Crushed maize and paddy husk were the primary ingredients in the “homemade ready-made” feed. The inclusion percentages of the various ingredients in “homemade ready-made feed” and the different unusual feedstuffs are provided in supplementary file
(Table S1) and
(Table S2). None of the farms used antitoxins in their regimen. Data on the inclusion of these ingredients in animal feed and the percentage of samples exceeding the EU limit are presented in (
Table 3).
2.4. Storage Practice
Although farmers were aware of mold infestation in stored feedstuffs, they had few options other than to store them for future use, particularly dry fodder (straw) sourced from outside the valley, especially the Terai region of the country. The duration of straw storage (Mean = 35.76 days, SD = 34 days, IQR = 19-30 days) was longer than that of concentrates (Mean = 22.40 days, SD = 10.7 days, IQR =15-30 days). Farmers stored straw for up to 6 months and concentrates for up to 2 months. Only 52% of farms had dedicated storage facilities, most of which were simply open spaces allocated for storage next to the farms. Farmers used different storage methods for storing straw and concentrates, including sacks, sheds (open or with compartments), and rooms (with open or closed doors), illustrated in
Figure 2, and adopted various storage practices
(Table 4).
3. Discussion
The study was conducted to assess AFM1 contamination in milk samples from Kathmandu district. Given the limited data and scarce research on AFM1 in milk in Nepal, this study aimed to provide insights into the current situation and guide future surveillance in the region and other part of the country. The results were alarmingly concerning. Of the 84 milk samples analyzed by competitive ELISA for AFM1, all samples exhibited some level of contamination, indicating a 100% prevalence of AFM1 in the milk. Even more troubling, 97.6% of the samples had AFM1 levels exceeding the EU’s permissible limit of 50 ppt, which is considered for human consumption. This presents a serious food safety issue for consumers in Kathmandu district. Since the same milk is used to produce dairy products such as yogurt, cheese, and sweets, these products may also exhibit similar contamination trends, as observed in India and Pakistan [
29,
31].
Several studies from South Asian countries have reported a very high prevalence of AFM1 in milk and milk products, and our study is no exception. The prevalence rate in Nepal is comparable to findings from the Middle East, Africa, and South America also. For instance, Iran has documented a significant number of research articles on AFM1, highlighting it as a serious issue, with multiple reports indicating a 100% prevalence rate [
32]. Similar findings have been reported in Ethiopia, where Tadesse et al. (2017) and Gizachew et al. (2016) found AFM1 contamination in 100% of milk samples [
33,
34]. In Kenya and South Africa also, studies reported occurrence levels above 85% [
35,
36]. In Brazil, AFM1 was found in 100% of pasteurized and Ultra Heat Treated (UHT) milk samples [
37]. Prevalence levels above 90% have also been reported in Thailand [
38], Taiwan [
39] and Indonesia [
40]. This widespread aflatoxin contamination in milk and dairy products in tropical countries is largely attributed to the common contamination of crops, crop residues, and animal feedstuffs [
41]. The environmental conditions in tropical areas are conducive to fungal growth and mycotoxin production [
42]. The problem is particularly severe in low- and middle-income countries, where poor harvesting, storage, and transportation practices are prevalent, and where policies or the implementation of regulations and mitigation strategies are often lacking [
43].
Aflatoxin M1 contamination in milk is associated with various risk factors, with the primary source being the feedstuffs consumed by the animals [
44]. Therefore, the feed regimen and storage practices are critical factors associated with AFM1 contamination in milk. All farms in the study relied on concentrates, with most using a mixture of homemade ready-made feed and commercial pellet feed, both of which have been frequently recognized as potential risk factors for AFM1 contamination in milk [
45,
46]. Although evaluating aflatoxin levels in cattle feed in Nepal is crucial —given the sparse literature on the subject—this aspect was not addressed in our study. However, a study on poultry feed by Aryal and Karki, (2009) revealed a high prevalence (75.4%) of aflatoxin B1 and B2, with levels as high as 366 µg/kg [
47].
The primary ingredients in both commercially produced and homemade concentrates in our study—crushed maize, paddy husk, mustard oil cake, and wheat bran—are particularly susceptible to mold infestation and mycotoxin contamination, especially during storage [
28]. Joshi et al. (2022) found that 78% of maize samples were contaminated with aflatoxin, with a mean concentration of 23.04 ppb, exceeding the permissible limit (20 µg/kg) established by the government of Nepal [
48]. Other studies have also reported the contamination of maize with aflatoxin in Nepal [
48,
49,
50]. In our study, all farms relying on commercial pellet feed had AFM1 levels above EU limits and exhibited higher contamination levels. Studies by Kang’ethe and Lang’a, (2009) and Akbar et al. (2020) found a positive correlation between higher aflatoxin contamination in commercial concentrate feed and increased AFM1 concentrations in milk [
11,
51]. The possible reasons for this include the poor quality of raw materials, suboptimal harvesting practices, and inadequate storage and shipping procedures for both raw materials and the final product.
Additionally, 53% of farms supplemented animal diets with unconventional feedstuffs, mainly leftover grains, vegetables, and fruits, likely due to the scarcity of fodder and roughages and the high cost of concentrates. Patyal et al. (2021) found that the inclusion of leftover grains was significantly associated with higher AFM1 levels in milk [
45].
Storage facilities and the duration of feed storage, particularly for concentrates, have been found to be significantly associated with aflatoxin contamination in animal feed and milk [
45,
46]. Half of the farms in the study lacked proper storage facilities; roughages and concentrates were stored in open areas, either in sheds or outdoors. Observations during farm visits revealed that farms in urban areas had limited space to extend sheds for additional storage, leading to the shared use of sheds for storing straw and concentrates in sacks. In contrast, farms on the outskirts, being more spacious, often had designated storage areas, although these were not always equipped with proper facilities. Among all the samples tested, only two did not exceed the EU MPL, both of which were from peri-urban farms. The lower level of AFM1 in peri-urban farms, compared to urban farms, could be due to the presence of spacious and designated storage areas that help prevent mold growth. Paddy straw, a byproduct of seasonal rice cultivation, constituted a major component of the animal diet and was usually procured in bulk mainly from the southern part of the country. Straw was stored for an average of 35 days, with some farms storing it for up to 6 months. Inadequate transportation and improper storage practices promote fungal growth and mycotoxin production in these roughages [
52].
This study focused exclusively on milk produced within the Kathmandu district, selecting only farms and dairy retailers sourcing their milk from this area. However, the milk produced by these farms significantly falls short of meeting the demand in Kathmandu, the country’s most populous city and capital. To address this shortfall, milk is imported from neighboring districts, particularly Kavre district, which also needs to be assessed to determine the AFM1 contamination level in Kathmandu. The AFM1 concentration could vary in milk from this region due to different feeding and storage practices on farms situated in areas with abundant forages and ample storage space, unlike in Kathmandu.
4. Conclusions
This study has revealed an alarming 100% prevalence of AFM1 contamination in milk samples from the Kathmandu district, with 97.6% of the samples exceeding the EU’s maximum permissible level. The findings underscore the urgent need for comprehensive national investigations to establish contamination trends, identify risk factors, and assess the health and economic impacts of aflatoxicosis. Such efforts will be crucial in supporting the implementation of effective measures and regulations to mitigate the risk of aflatoxin contamination in food, animals, and humans. Furthermore, it is essential to educate the public—especially dairy farmers, retailers, processing companies, and consumers—about the risks and economic impact of aflatoxin in milk.
5. Materials and Methods
5.1. Study Design and Study Area
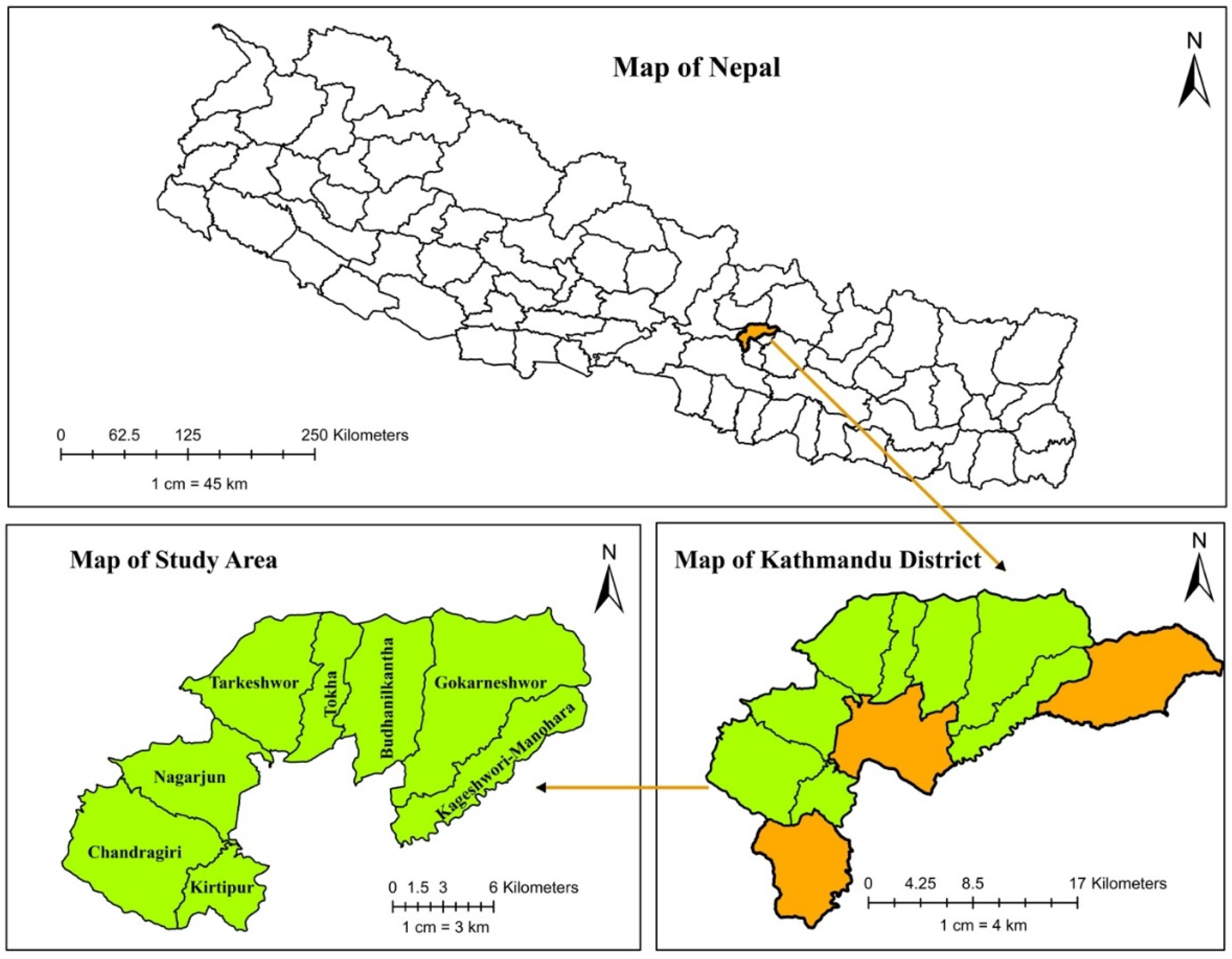
The cross-sectional study was conducted from October to November 2022 in the Kathmandu district, located in the Bagmati province of central Nepal. The study focused on major milk-producing and distributing areas within the district. Out of the 11 municipalities, eight were selected: Kageswori-Manohara, Kirtipur, Gokarneshwor, Chandragiri, Tokha, Tarkeshwor, Nagarjun, and Budanilakantha (
Figure 3). Kathmandu (latitude 27°41′38.76″ North, longitude 85°22′39.00″ East), the nation’s capital, is densely populated and has one of the highest rates of milk and dairy product consumption. The areas within the district were classified as urban and peri-urban; ‘peri-urban’ refers to areas transitioning towards urbanization, while “urban” describes areas that have fully transitioned and exhibit the characteristics of a developed city or town.
5.2. Sample Collection
A total of 84 samples were collected for the study, categorized into three groups: farm raw milk (48 samples), dairy retail shop milk (25 samples), and packet milk (11 samples). Forty-eight commercially registered farms with varying herd sizes were randomly selected from eight municipalities within the Kathmandu district. Fresh raw milk samples were collected in sterile, screw-capped 100 ml centrifuge tubes from the bulk milk tanks after proper mixing during early morning visits. Similarly, milk samples were obtained from the bulk tanks of 25 dairy retail shops in these municipalities. These retail shops, which pool milk from various nearby farms, are major distributors of milk in Kathmandu, alongside packet milk. Eleven milk packets from different brands were purchased from supermarkets for the study. After collection, all milk samples were placed in an insulated cold box and transported to the Central Veterinary Laboratory, Kathmandu where they were stored in a refrigerator at −20°C. All samples were analyzed for AFM1 within two days of collection. During the farm visits for sample collection, a pretested questionnaire was administered via Kobo Toolbox [
53] to farmers, owners, or managers to collect data on farm characteristics, as well as feeding and storage practices.
5.3. Laboratory Analysis
The milk samples were thawed and then centrifuged at 1000 rpm for 5 minutes. The upper layer of fat was removed, and AFM1 was screened in the defatted milk samples using a competitive ELISA (CUSABIO Technology LLC), following the manufacturer’s instructions provided with the ELISA kit. The kit included a precoated ELISA plate, standards (0, 5, 15, 45, and 135 ppt), HRP-conjugate, substrates, wash buffer, and stop solution. Briefly, 100 microliters of standards and milk samples were added to the precoated ELISA plate and incubated for 30 minutes at 25°C. The plate was then washed five times, and 100 microliters of HRP conjugate were added to each well, followed by a 15-minute incubation at 25°C. After another five washes, 50 microliters of substrate A and substrate B were added, mixed, and incubated for 15 minutes at 25°C in the dark. Finally, 50 microliters of stop solution were added, and absorbance was measured at 450 nm using an ELISA reader (Multiskan™ FC Microplate Photometer). The calibration curve was constructed from the standard solutions and their absorbance, and the regression equation (R² = 0.98) was used to quantify aflatoxin levels.
5.4. Statistical Analysis
All data from the questionnaire and laboratory analysis were compiled into an Excel file (Microsoft Excel 2019) and subsequently imported into SPSS version 25 for a descriptive assessment of the farms and husbandry practices. Contamination levels of AFM1 in milk were categorized based on the EU’s maximum permissible limit (MPL) of 50 ppt, above which milk is considered unsafe for human consumption. Consequently, contamination levels were reported as either below or above 50 ppt, indicating whether the milk compiled with or exceeding the EU limit.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org, Table S1: Inclusion percentage of various ingredients in ‘homemade ready-made feed’ in dairy farms in Kathmandu district, Nepal; Table S2: Inclusion percentage of different unusual feedstuffs in dairy farms in Kathmandu district, Nepal.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.K.; methodology, S.K., M.P., K.B.K.; software, SK, M.P, DS.; validation, C.S., R.C.S.,D.S and A.T.; formal analysis, S.K. and M.P.,; investigation, S.K. and M.P.; resources, C.S., K.B.K and R.C.S; data curation, S.K. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, S.K.; writing—review and editing, S.K., M.P., A.T., and D.S; visualization, S.K., M.P. and D.S.; supervision, C.S., R.C.S., A.T., and D.S.; project administration, C.S and R.C.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Internship Advisory Committee of Veterinary Teaching Hospital, Faculty of Animal Science, Veterinary Science and Fisheries, Agriculture and Forestry University (AFU).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data are included in the article and supplementary files. Further inquiries or data requests can be directed to the authors.
Acknowledgments
We extend our heartfelt gratitude to the dedicated staff members of the Central Veterinary Laboratory, Kathmandu, Nepal, whose invaluable assistance made the laboratory analyses possible. We are also profoundly grateful to all the respondents, including farmers, farm managers, staff, and other supportive individuals from the Kathmandu District. The cooperation during the sample and data collection process was instrumental to the success of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Bennett, J.W.; Klich, M. Mycotoxins. Clin Microbiol Rev 2003, 16, 497–516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zain, M.E. Impact of Mycotoxins on Humans and Animals. Journal of Saudi Chemical Society 2011, 15, 129–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alshannaq, A.; Yu, J.-H. Occurrence, Toxicity, and Analysis of Major Mycotoxins in Food. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 2017, 14, 632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, A.; Pathak, H.; Bhadauria, S.; Sudan, J. Aflatoxin Contamination in Food Crops: Causes, Detection, and Management: A Review. Food Prod Process and Nutr 2021, 3, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giovati, L.; Magliani, W.; Ciociola, T.; Santinoli, C.; Conti, S.; Polonelli, L. AFM₁ in Milk: Physical, Biological, and Prophylactic Methods to Mitigate Contamination. Toxins (Basel) 2015, 7, 4330–4349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esam, R.M.; Hafez, R.S.; Khafaga, N.I.M.; Fahim, K.M.; Ibrahim Ahmed, L. Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 and B1 in Some Dairy Products with Referring to the Analytical Performances of Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay in Comparison to High-Performance Liquid Chromatography. Vet World 2022, 15, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Delaimy, K.; Mahmoud, I. Aflatoxin M1 in Milk and Milk Products in Jordan and Methods for Its Reduction: A Preliminary Study. BJAST 2015, 6, 597–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iha, M.H.; Barbosa, C.B.; Okada, I.A.; Trucksess, M.W. Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in Dairy Products in Brazil. Food Control 2011, 22, 1971–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omeiza, G.K.; Mwanza, M.; Enem, S.I.; Godwin, E.; Adeiza, M.A.; Okoli, C. Reducing Efficiencies of the Commonly Used Heat Treatment Methods and Fermentation Processes on Aflatoxin M1 in Naturally Contaminated Fresh Cow Milk. OJVM 2018, 08, 134–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deveci, O.; Sezgin, E. Changes in Concentration of Aflatoxin M1 during Manufacture and Storage of Skim Milk Powder. Journal of Food Protection 2006, 69, 682–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kang’ethe, E.K.; Lang’a, K.A. Aflatoxin B1 and M1 Contamination of Animal Feeds and Milk from Urban Centers in Kenya. Afr Health Sci 2009, 9, 218–226. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sharma, H.; Jadhav, V.J.; Garg, S.R. Aflatoxin M1 in Milk in Hisar City, Haryana, India and Risk Assessment. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part B 2020, 13, 59–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ismail, A.; Akhtar, S.; Levin, R.E.; Ismail, T.; Riaz, M.; Amir, M. Aflatoxin M1: Prevalence and Decontamination Strategies in Milk and Milk Products. Critical Reviews in Microbiology 2016, 42, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrari, L.; Rizzi, N.; Grandi, E.; Clerici, E.; Tirloni, E.; Stella, S.; Bernardi, C.E.M.; Pinotti, L. Compliance between Food and Feed Safety: Eight-Year Survey (2013–2021) of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw Milk and Aflatoxin B1 in Feed in Northern Italy. Toxins (Basel) 2023, 15, 168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paniel, N.; Radoi, A.; Marty, J.-L. Development of an Electrochemical Biosensor for the Detection of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk. Sensors (Basel) 2010, 10, 9439–9448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ILRI; Kiarie, G.; School of Health Sciences, Mount Kenya University, P.O. Box 342 - 01000, Thika, Kenya Aflatoxin Exposure among Young Children in Urban Low-Income Areas of Nairobi and Association with Child Growth. AJFAND 2016, 16, 10967–10990. [CrossRef]
- Abdulrazzaq, Y.M.; Osman, N.; Yousif, Z.M.; Al-Falahi, S. Aflatoxin M 1 in Breast-Milk of UAE Women. Annals of Tropical Paediatrics 2003, 23, 173–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdavi, R.; Nikniaz, L.; Arefhosseini, S.R.; Vahed Jabbari, M. Determination of Aflatoxin M1 in Breast Milk Samples in Tabriz–Iran. Matern Child Health J 2010, 14, 141–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlberg, S.; Grace, D.; Kiarie, G.; Kirino, Y.; Lindahl, J. A Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 Exposure in Low and Mid-Income Dairy Consumers in Kenya. Toxins 2018, 10, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahat, A.; MA, S.; Mohamed, A.F.; Abdel-Wahhab, P.M. Correlation Study Between Aflatoxin M 1 and Hepatitis C Virus in Egyptian Patients with Chronic Liver Disease. World Journal of Medical Sciences 2012, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jallow, A.; Xie, H.; Tang, X.; Qi, Z.; Li, P. Worldwide Aflatoxin Contamination of Agricultural Products and Foods: From Occurrence to Control. Comp Rev Food Sci Food Safe 2021, 20, 2332–2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Torović, L. Aflatoxin M 1 in Processed Milk and Infant Formulae and Corresponding Exposure of Adult Population in Serbia in 2013–2014. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part B. [CrossRef]
- Mollayusefian, I.; Ranaei, V.; Pilevar, Z.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Rostami, A.; Nematolahi, A.; Khedher, K.M.; Thai, V.N.; Fakhri, Y.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. The Concentration of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw and Pasteurized Milk: A Worldwide Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 115, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chamlagain, S.; Dahal, T. Status of Production and Distribution of Fresh Milk by Villagers in Bariyarpatti, Sohpur. J. Mgt. 2020, 3, 110–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pokharel, A.; Webb, P.; Andrews-Trevino, J.; Lamichhane, A.; Shrestha, R.; Acharya, S.; Davis, D.; Baral, K.; Wang, J.-S.; Xue, K.; et al. Prevalence and Associated Factors of Breastmilk Aflatoxin M1 Levels in Mothers from Banke, Nepal. Food Control 2021, 126, 108069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kafle, P.; Sedai, D.; Rai, K.P.; Pokharel, B.B. Study on the Level of Aflatoxin M1 Contamination in Raw and Processed Milk Marketed in Kathmandu Valley. Journal of Food Science and Technology Nepal 2012, 7, 52–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asghar, M.A.; Ahmed, A.; Asghar, M.A. Aflatoxin M 1 in Fresh Milk Collected from Local Markets of Karachi, Pakistan. Food Additives & Contaminants: Part B 2018, 11, 167–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dhavan, A.S.; Choudary, M.R. Incidence of Aflatoxins in Animal Feedstuffs: A Decade’s Scenario in India. Journal of AOAC INTERNATIONAL 1995, 78, 693–697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hattimare, D.; Shakya, S.; Patyal, A.; Chandrakar, C.; Kumar, A. Occurrence and Exposure Assessment of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk and Milk Products in India. J Food Sci Technol 2022, 59, 2460–2468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollayusefian, I.; Ranaei, V.; Pilevar, Z.; Cabral-Pinto, M.M.S.; Rostami, A.; Nematolahi, A.; Khedher, K.M.; Thai, V.N.; Fakhri, Y.; Mousavi Khaneghah, A. The Concentration of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw and Pasteurized Milk: A Worldwide Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 115, 22–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S.Z.; Asi, M.R.; Jinap, S. Variation of Aflatoxin M1 Contamination in Milk and Milk Products Collected during Winter and Summer Seasons. Food Control 2013, 34, 714–718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahmani, J.; Alipour, S.; Miri, A.; Fakhri, Y.; Riahi, S.-M.; Keramati, H.; Moradi, M.; Amanidaz, N.; Pouya, R.H.; Bahmani, Z.; et al. The Prevalence of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk of Middle East Region: A Systematic Review, Meta-Analysis and Probabilistic Health Risk Assessment. Food Chem Toxicol 2018, 118, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadesse, B.T.; Ashley, E.A.; Ongarello, S.; Havumaki, J.; Wijegoonewardena, M.; González, I.J.; Dittrich, S. Antimicrobial Resistance in Africa: A Systematic Review. BMC Infect Dis 2017, 17, 616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gizachew, D.; Szonyi, B.; Tegegne, A.; Hanson, J.; Grace, D. Aflatoxin Contamination of Milk and Dairy Feeds in the Greater Addis Ababa Milk Shed, Ethiopia. Food Control 2016, 59, 773–779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuboka, M.M.; Imungi, J.K.; Njue, L.; Mutua, F.; Grace, D.; Lindahl, J.F. Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw Milk Traded in Peri-Urban Nairobi, and the Effect of Boiling and Fermentation. Infection Ecology & Epidemiology 2019, 9, 1625703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulunda, M.; Mike, D. Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 from Rural Subsistence and Commercial Farms from Selected Areas of South Africa. Food Control 2014, 39, 92–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sifuentes dos Santos, J.; França, V.; Katto, S.; Santana, E.H. Aflatoxin M1 in Pasteurized, UHT Milk and Milk Powder Commercialized in Londrina, Brazil and Estimation of Exposure. Archivos latinoamericanos de nutricion 2015, 65, 181–185. [Google Scholar]
- Ruangwises, S.; Saipan, P.; Ruangwises, N. Occurrence of Aflatoxin M1 in Raw and Pasteurized Goat Milk in Thailand. In Aflatoxins - Recent Advances and Future Prospects; Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M., Ed.; InTech, 2013 ISBN 978-953-51-0904-4.
- Lin, L.-C.; Liu, F.-M.; Fu, Y.-M.; Shih, D.Y.-C. Survey of Aflatoxin M1 Contamination of Dairy Products in Taiwan. Journal of Food and Drug Analysis 2020, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumantri, I.; Purwanti, F.; Nuryono, N.; Agus, A. Estimation of Aflatoxin M1 Exposure through Consumption of Various Dairy Milk Products in Yogyakarta, Indonesia (ESTIMASI PAPARAN AFLATOKSIN M1 MELALUI KONSUMSI BERBAGAI PRODUK SUSU DI YOGYAKARTA, INDONESIA). JVet 2019, 20, 58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Assaf, J.C.; Nahle, S.; Chokr, A.; Louka, N.; Atoui, A.; El Khoury, A. Assorted Methods for Decontamination of Aflatoxin M1 in Milk Using Microbial Adsorbents. Toxins 2019, 11, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashiq, S. Natural Occurrence of Mycotoxins in Food and Feed: Pakistan Perspective. Comp Rev Food Sci Food Safe 2015, 14, 159–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamo, F.T.; Abate, B.A.; Tesfaye, K.; Nie, C.; Wang, G.; Liu, Y. Mycotoxins in Ethiopia: A Review on Prevalence, Economic and Health Impacts. Toxins 2020, 12, 648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yunus, A.W.; Ullah, A.; Lindahl, J.F.; Anwar, Z.; Ullah, A.; Saif, S.; Ali, M.; Zahur, A.B.; Irshad, H.; Javaid, S.; et al. Aflatoxin Contamination of Milk Produced in Peri-Urban Farms of Pakistan: Prevalence and Contributory Factors. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patyal, A.; Gill, J.P.S.; Bedi, J.S.; Aulakh, R.S. Assessment of Aflatoxin Contamination in Dairy Animal Concentrate Feed from Punjab, India. Environ Sci Pollut Res 2021, 28, 37705–37715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tadele, F.; Demissie, B.; Amsalu, A.; Demelash, H.; Mengist, Z.; Ambelu, A.; Yenew, C. Aflatoxin Contamination of Animal Feeds and Its Predictors among Dairy Farms in Northwest Ethiopia: One Health Approach Implications. Front. Vet. Sci. 2023, 10, 1123573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aryal, S.R.; Karki, D. Prevalence of Aflatoxin B1 and B2 in Poultary Feed. Nepal Agriculture Research Journal 2009, 9, 109–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, P.; Chauysrinule, C.; Mahakarnchanakul, W.; Maneeboon, T. Multi-Mycotoxin Contamination, Mold Incidence and Risk Assessment of Aflatoxin in Maize Kernels Originating from Nepal. Microbiology Research 2022, 13, 258–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gautam, D.N.; Bhatta, R.; Bhandary, M.R. Assessment of Aflatoxin B1 Level in Chilli, Maize and Groundnut Samples from Kathmandu Valley. Journal of Food Science and Technology Nepal 2008, 4, 57–60. [Google Scholar]
- Pokhrel, P. Postharvest Handling and Prevalence of Aflatoxin Contamination in Nepalese Maize Produce. Journal of Food Science and Technology Nepal 2016, 9, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akbar, N.; Nasir, M.; Naeem, N.; Ahmad, M.; Saeed, F.; Anjum, F.M.; Iqbal, S.; Imran, M.; Tufail, T.; Shah, F.; et al. Assessment of Aflatoxin in Milk and Feed Samples and Impact of Seasonal Variations in the Punjab, Pakistan. Food Science & Nutrition 2020, 8, 2699–2709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips, S.I.; Wareing, P.W.; Dutta, A.; Panigrahi, S.; Medlock, V. The Mycoflora and Incidence of Aflatoxin, Zearalenone and Sterigmatocystin in Dairy Feed and Forage Samples from Eastern India and Bangladesh. Mycopathologia 1996, 133, 15–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- KoboToolbox. Available online: https://www.kobotoolbox.org/ (accessed on 22 August 2024).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).