Submitted:
05 September 2024
Posted:
09 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
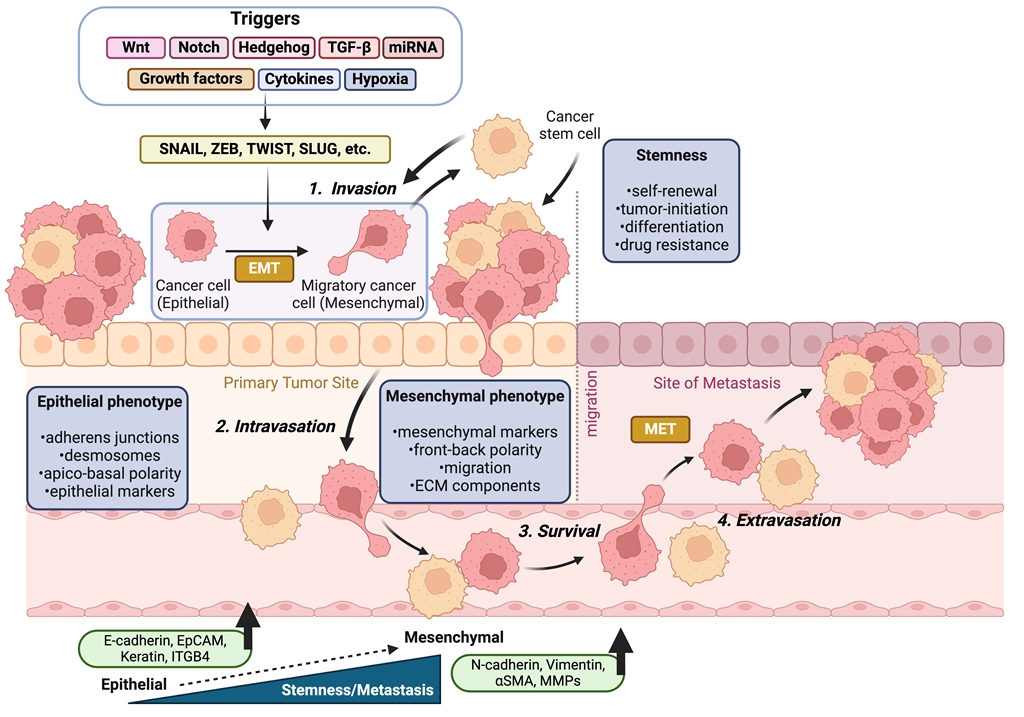
1. Introduction
2. CSCs and Cancer
3. EMT and Cancer
4. EMT-CSCs Nexus
4.1. Mechanisms Governing EMT-CSC Pathways
4.2. Involvement of EMT and CSCs in Hypoxia
4.3. Plasticity in EMT and CSCs
4.4. EMT and CSCs and Their Involvement in Chemoresistance
5. Signaling Pathways in CSCs and EMT
5.1. Wnt Signaling
5.2. Notch Signaling
5.3. Hedgehog Signaling
5.4. TGF-β Signaling
5.5. MicroRNAs
6. EMT as Therapeutic Target against CSCs
7. Conclusions
References
- Acloque, H., et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: the importance of changing cell state in development and disease. J Clin Invest, 2009. 119(6): p. 1438-49. [CrossRef]
- Thiery, J.P., et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell, 2009. 139(5): p. 871-90. [CrossRef]
- Huang, T., et al., Stem cell programs in cancer initiation, progression, and therapy resistance. Theranostics, 2020. 10(19): p. 8721-8743. [CrossRef]
- Ribatti, D., R. Tamma, and T. Annese, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer: A Historical Overview. Transl Oncol, 2020. 13(6): p. 100773. [CrossRef]
- Saitoh, M., Involvement of partial EMT in cancer progression. J Biochem, 2018. 164(4): p. 257-264. [CrossRef]
- Clevers, H., The cancer stem cell: premises, promises and challenges. Nat Med, 2011. 17(3): p. 313-9. [CrossRef]
- Greaves, M. and C.C. Maley, Clonal evolution in cancer. Nature, 2012. 481(7381): p. 306-13. [CrossRef]
- .
- Paget, S., The distribution of secondary growths in cancer of the breast. 1889. Cancer Metastasis Rev, 1989. 8(2): p. 98-101.
- Yauch, R.L., et al., Epithelial versus mesenchymal phenotype determines in vitro sensitivity and predicts clinical activity of erlotinib in lung cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res, 2005. 11(24 Pt 1): p. 8686-98. [CrossRef]
- Visvader, J.E. and G.J. Lindeman, Cancer stem cells in solid tumours: accumulating evidence and unresolved questions. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008. 8(10): p. 755-68. [CrossRef]
- Alison, M.R., S.M. Lim, and L.J. Nicholson, Cancer stem cells: problems for therapy? J Pathol, 2011. 223(2): p. 147-61.
- Chatterjee, S., C.R. Patil, and C.N. Kundu, An Overview of Antioxidative Anticancer Therapies with Reference to the Cancer Stem Cells, in Handbook of Oxidative Stress in Cancer: Therapeutic Aspects, S. Chakraborti, Editor. 2021, Springer Singapore: Singapore. p. 1-23.
- Bonnet, D. and J.E. Dick, Human acute myeloid leukemia is organized as a hierarchy that originates from a primitive hematopoietic cell. Nat Med, 1997. 3(7): p. 730-7. [CrossRef]
- Lapidot, T., et al., A cell initiating human acute myeloid leukaemia after transplantation into SCID mice. Nature, 1994. 367(6464): p. 645-8. [CrossRef]
- Huang, F., et al., Oncolytic viruses against cancer stem cells: A promising approach for gastrointestinal cancer. World J Gastroenterol, 2016. 22(35): p. 7999-8009. [CrossRef]
- Dontu, G., et al., In vitro propagation and transcriptional profiling of human mammary stem/progenitor cells. Genes Dev, 2003. 17(10): p. 1253-70. [CrossRef]
- Liu, R., et al., The prognostic role of a gene signature from tumorigenic breast-cancer cells. N Engl J Med, 2007. 356(3): p. 217-26.
- Zheng, X., et al., Communication Between Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity and Cancer Stem Cells: New Insights Into Cancer Progression. Front Oncol, 2021. 11: p. 617597. [CrossRef]
- Ginestier, C., et al., ALDH1 is a marker of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells and a predictor of poor clinical outcome. Cell Stem Cell, 2007. 1(5): p. 555-67.
- Chou, M.Y., et al., Sox2 expression involvement in the oncogenicity and radiochemoresistance of oral cancer stem cells. Oral Oncol, 2015. 51(1): p. 31-9. [CrossRef]
- Yeh, D.W., et al., Interplay between Inflammation and Stemness in Cancer Cells: The Role of Toll-Like Receptor Signaling. J Immunol Res, 2016. 2016: p. 4368101.
- Baumann, M., M. Krause, and R. Hill, Exploring the role of cancer stem cells in radioresistance. Nat Rev Cancer, 2008. 8(7): p. 545-54. [CrossRef]
- Dhawan, A., et al., Mathematical modelling of phenotypic plasticity and conversion to a stem-cell state under hypoxia. Sci Rep, 2016. 6: p. 18074. [CrossRef]
- Chen, X., et al., Epithelial mesenchymal transition and hedgehog signaling activation are associated with chemoresistance and invasion of hepatoma subpopulations. J Hepatol, 2011. 55(4): p. 838-45.
- Najafi, M., K. Mortezaee, and J. Majidpoor, Cancer stem cell (CSC) resistance drivers. Life Sci, 2019. 234: p. 116781.
- Wang, L., et al., Enrichment of prostate cancer stem-like cells from human prostate cancer cell lines by culture in serum-free medium and chemoradiotherapy. Int J Biol Sci, 2013. 9(5): p. 472-9.
- Wu, M.J., et al., Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition Directs Stem Cell Polarity via Regulation of Mitofusin. Cell Metab, 2019. 29(4): p. 993-1002 e6.
- Caramel, J., M. Ligier, and A. Puisieux, Pleiotropic Roles for ZEB1 in Cancer. Cancer Res, 2018. 78(1): p. 30-35. [CrossRef]
- Lee, I.C., Y.C. Wu, and W.S. Hung, Hyaluronic Acid-Based Multilayer Films Regulate Hypoxic Multicellular Aggregation of Pancreatic Cancer Cells with Distinct Cancer Stem-Cell-like Properties. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2018. 10(45): p. 38769-38779.
- Zhang, Z., et al., Hypoxia potentiates gemcitabine-induced stemness in pancreatic cancer cells through AKT/Notch1 signaling. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2018. 37(1): p. 291. [CrossRef]
- Todaro, M., et al., Colon cancer stem cells dictate tumor growth and resist cell death by production of interleukin-4. Cell Stem Cell, 2007. 1(4): p. 389-402.
- D'Andrea, F.P., et al., Cancer stem cell overexpression of nicotinamide N-methyltransferase enhances cellular radiation resistance. Radiother Oncol, 2011. 99(3): p. 373-8. [CrossRef]
- Prochazkova, J., M. Lanova, and J. Pachernik, Multidrug resistance-associated ABC transporters - too much of one thing, good for nothing. Biomol Concepts, 2012. 3(4): p. 319-31.
- Balkwill, F.R., M. Capasso, and T. Hagemann, The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci, 2012. 125(Pt 23): p. 5591-6.
- Jaggupilli, A. and E. Elkord, Significance of CD44 and CD24 as cancer stem cell markers: an enduring ambiguity. Clin Dev Immunol, 2012. 2012: p. 708036.
- Greenburg, G. and E.D. Hay, Epithelia suspended in collagen gels can lose polarity and express characteristics of migrating mesenchymal cells. J Cell Biol, 1982. 95(1): p. 333-9.
- Kalluri, R. and R.A. Weinberg, The basics of epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest, 2009. 119(6): p. 1420-8. [CrossRef]
- Abdullah, A., et al., Epigenetic targeting of neuropilin-1 prevents bypass signaling in drug-resistant breast cancer. Oncogene, 2021. 40(2): p. 322-333.
- Babaei, G., S.G. Aziz, and N.Z.Z. Jaghi, EMT, cancer stem cells and autophagy; The three main axes of metastasis. Biomed Pharmacother, 2021. 133: p. 110909. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, D., et al., Emerging Concepts of Hybrid Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancer Progression. Biomolecules, 2020. 10(11). [CrossRef]
- Moustakas, A. and C.H. Heldin, Signaling networks guiding epithelial-mesenchymal transitions during embryogenesis and cancer progression. Cancer Sci, 2007. 98(10): p. 1512-20.
- Hollier, B.G., K. Evans, and S.A. Mani, The epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: a coalition against cancer therapies. J Mammary Gland Biol Neoplasia, 2009. 14(1): p. 29-43.
- Turley, E.A., et al., Mechanisms of disease: epithelial-mesenchymal transition--does cellular plasticity fuel neoplastic progression? Nat Clin Pract Oncol, 2008. 5(5): p. 280-90.
- Baum, B., J. Settleman, and M.P. Quinlan, Transitions between epithelial and mesenchymal states in development and disease. Semin Cell Dev Biol, 2008. 19(3): p. 294-308.
- Garg, M., Epithelial Plasticity, Autophagy and Metastasis: Potential Modifiers of the Crosstalk to Overcome Therapeutic Resistance. Stem Cell Rev Rep, 2020. 16(3): p. 503-510.
- Thomson, S., et al., Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is a determinant of sensitivity of non-small-cell lung carcinoma cell lines and xenografts to epidermal growth factor receptor inhibition. Cancer Res, 2005. 65(20): p. 9455-62. [CrossRef]
- Ye, X. and R.A. Weinberg, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Plasticity: A Central Regulator of Cancer Progression. Trends Cell Biol, 2015. 25(11): p. 675-686.
- Mani, S.A., et al., The epithelial-mesenchymal transition generates cells with properties of stem cells. Cell, 2008. 133(4): p. 704-15. [CrossRef]
- May, C.D., et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cells: a dangerously dynamic duo in breast cancer progression. Breast Cancer Res, 2011. 13(1): p. 202.
- Guo, W., et al., Slug and Sox9 cooperatively determine the mammary stem cell state. Cell, 2012. 148(5): p. 1015-28.
- Scheel, C. and R.A. Weinberg, Phenotypic plasticity and epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer and normal stem cells? Int J Cancer, 2011. 129(10): p. 2310-4.
- Korpal, M., et al., Direct targeting of Sec23a by miR-200s influences cancer cell secretome and promotes metastatic colonization. Nat Med, 2011. 17(9): p. 1101-8. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z., et al., Acquisition of epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype of gemcitabine-resistant pancreatic cancer cells is linked with activation of the notch signaling pathway. Cancer Res, 2009. 69(6): p. 2400-7.
- Morel, A.P., et al., Generation of breast cancer stem cells through epithelial-mesenchymal transition. PLoS One, 2008. 3(8): p. e2888. [CrossRef]
- Fan, F., et al., Overexpression of snail induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and a cancer stem cell-like phenotype in human colorectal cancer cells. Cancer Med, 2012. 1(1): p. 5-16.
- Kong, D., et al., Epithelial to mesenchymal transition is mechanistically linked with stem cell signatures in prostate cancer cells. PLoS One, 2010. 5(8): p. e12445. [CrossRef]
- Long, H., et al., CD133+ ovarian cancer stem-like cells promote non-stem cancer cell metastasis via CCL5 induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Oncotarget, 2015. 6(8): p. 5846-59. [CrossRef]
- Rasheed, Z.A., et al., Prognostic significance of tumorigenic cells with mesenchymal features in pancreatic adenocarcinoma. J Natl Cancer Inst, 2010. 102(5): p. 340-51. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y., et al., CCL21/CCR7 interaction promotes EMT and enhances the stemness of OSCC via a JAK2/STAT3 signaling pathway. J Cell Physiol, 2020. 235(9): p. 5995-6009.
- Akbar, M.W., et al., A Stemness and EMT Based Gene Expression Signature Identifies Phenotypic Plasticity and is A Predictive but Not Prognostic Biomarker for Breast Cancer. J Cancer, 2020. 11(4): p. 949-961.
- Rhim, A.D., et al., EMT and dissemination precede pancreatic tumor formation. Cell, 2012. 148(1-2): p. 349-61.
- Ding, Q., et al., CD133 facilitates epithelial-mesenchymal transition through interaction with the ERK pathway in pancreatic cancer metastasis. Mol Cancer, 2014. 13: p. 15.
- Oskarsson, T., E. Batlle, and J. Massague, Metastatic stem cells: sources, niches, and vital pathways. Cell Stem Cell, 2014. 14(3): p. 306-21. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez-Garcia, I., The crossroads of oncogenesis and metastasis. N Engl J Med, 2009. 360(3): p. 297-9. [CrossRef]
- Rojas-Puentes, L., et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition, proliferation, and angiogenesis in locally advanced cervical cancer treated with chemoradiotherapy. Cancer Med, 2016. 5(8): p. 1989-99. [CrossRef]
- Holderfield, M.T. and C.C. Hughes, Crosstalk between vascular endothelial growth factor, notch, and transforming growth factor-beta in vascular morphogenesis. Circ Res, 2008. 102(6): p. 637-52.
- Desai, S., S. Laskar, and B.N. Pandey, Autocrine IL-8 and VEGF mediate epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasiveness via p38/JNK-ATF-2 signalling in A549 lung cancer cells. Cell Signal, 2013. 25(9): p. 1780-91.
- Gonzalez-Moreno, O., et al., VEGF elicits epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) in prostate intraepithelial neoplasia (PIN)-like cells via an autocrine loop. Exp Cell Res, 2010. 316(4): p. 554-67. [CrossRef]
- Yang, A.D., et al., Vascular endothelial growth factor receptor-1 activation mediates epithelial to mesenchymal transition in human pancreatic carcinoma cells. Cancer Res, 2006. 66(1): p. 46-51.
- Chatterjee, S., S. Sinha, and C.N. Kundu, Nectin cell adhesion molecule-4 (NECTIN-4): A potential target for cancer therapy. Eur J Pharmacol, 2021. 911: p. 174516. [CrossRef]
- Kang, Y. and J. Massague, Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions: twist in development and metastasis. Cell, 2004. 118(3): p. 277-9.
- Wick, W., M. Platten, and M. Weller, Glioma cell invasion: regulation of metalloproteinase activity by TGF-beta. J Neurooncol, 2001. 53(2): p. 177-85.
- Ocana, O.H., et al., Metastatic colonization requires the repression of the epithelial-mesenchymal transition inducer Prrx1. Cancer Cell, 2012. 22(6): p. 709-24.
- Tsai, J.H., et al., Spatiotemporal regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transition is essential for squamous cell carcinoma metastasis. Cancer Cell, 2012. 22(6): p. 725-36. [CrossRef]
- Shibue, T., M.W. Brooks, and R.A. Weinberg, An integrin-linked machinery of cytoskeletal regulation that enables experimental tumor initiation and metastatic colonization. Cancer Cell, 2013. 24(4): p. 481-98.
- Adams, D.L., et al., Mitosis in circulating tumor cells stratifies highly aggressive breast carcinomas. Breast Cancer Res, 2016. 18(1): p. 44.
- Yu, M., et al., Circulating breast tumor cells exhibit dynamic changes in epithelial and mesenchymal composition. Science, 2013. 339(6119): p. 580-4. [CrossRef]
- Grunert, S., M. Jechlinger, and H. Beug, Diverse cellular and molecular mechanisms contribute to epithelial plasticity and metastasis. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol, 2003. 4(8): p. 657-65.
- Hay, E.D., An overview of epithelio-mesenchymal transformation. Acta Anat (Basel), 1995. 154(1): p. 8-20.
- Huber, M.A., N. Kraut, and H. Beug, Molecular requirements for epithelial-mesenchymal transition during tumor progression. Curr Opin Cell Biol, 2005. 17(5): p. 548-58. [CrossRef]
- Yaguchi, T., et al., The mechanisms of cancer immunoescape and development of overcoming strategies. Int J Hematol, 2011. 93(3): p. 294-300.
- Fernando, R.I., et al., IL-8 signaling plays a critical role in the epithelial-mesenchymal transition of human carcinoma cells. Cancer Res, 2011. 71(15): p. 5296-306. [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, N.J., et al., Interleukin-6 induces an epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype in human breast cancer cells. Oncogene, 2009. 28(33): p. 2940-7.
- Wu, Y., et al., Stabilization of snail by NF-kappaB is required for inflammation-induced cell migration and invasion. Cancer Cell, 2009. 15(5): p. 416-28.
- Kachroo, P., et al., IL-27 inhibits epithelial-mesenchymal transition and angiogenic factor production in a STAT1-dominant pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2013. 32(1): p. 97. [CrossRef]
- Tlsty, T.D. and L.M. Coussens, Tumor stroma and regulation of cancer development. Annu Rev Pathol, 2006. 1: p. 119-50.
- Kong, D., et al., Platelet-derived growth factor-D overexpression contributes to epithelial-mesenchymal transition of PC3 prostate cancer cells. Stem Cells, 2008. 26(6): p. 1425-35. [CrossRef]
- Thompson, E.W., D.F. Newgreen, and D. Tarin, Carcinoma invasion and metastasis: a role for epithelial-mesenchymal transition? Cancer Res, 2005. 65(14): p. 5991-5; discussion 5995.
- Thiery, J.P., Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer, 2002. 2(6): p. 442-54.
- Hass, R., J. von der Ohe, and H. Ungefroren, Potential Role of MSC/Cancer Cell Fusion and EMT for Breast Cancer Stem Cell Formation. Cancers (Basel), 2019. 11(10).
- Giannoni, E., et al., Reciprocal activation of prostate cancer cells and cancer-associated fibroblasts stimulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stemness. Cancer Res, 2010. 70(17): p. 6945-56.
- Yu, Y., et al., Cancer-associated fibroblasts induce epithelial-mesenchymal transition of breast cancer cells through paracrine TGF-beta signalling. Br J Cancer, 2014. 110(3): p. 724-32.
- Bonde, A.K., et al., Intratumoral macrophages contribute to epithelial-mesenchymal transition in solid tumors. BMC Cancer, 2012. 12: p. 35.
- Akalay, I., et al., Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and autophagy induction in breast carcinoma promote escape from T-cell-mediated lysis. Cancer Res, 2013. 73(8): p. 2418-27.
- Hamilton, D.H., et al., Immunological targeting of tumor cells undergoing an epithelial-mesenchymal transition via a recombinant brachyury-yeast vaccine. Oncotarget, 2013. 4(10): p. 1777-90. [CrossRef]
- Ricciardi, M., et al., Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by inflammatory priming elicits mesenchymal stromal cell-like immune-modulatory properties in cancer cells. Br J Cancer, 2015. 112(6): p. 1067-75. [CrossRef]
- Mak, M.P., et al., A Patient-Derived, Pan-Cancer EMT Signature Identifies Global Molecular Alterations and Immune Target Enrichment Following Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition. Clin Cancer Res, 2016. 22(3): p. 609-20.
- Lu, Y., et al., CXCL1-LCN2 paracrine axis promotes progression of prostate cancer via the Src activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cell Commun Signal, 2019. 17(1): p. 118.
- Pelizzo, G., et al., Microenvironment in neuroblastoma: isolation and characterization of tumor-derived mesenchymal stromal cells. BMC Cancer, 2018. 18(1): p. 1176.
- Gao, D., et al., Microenvironmental regulation of epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in cancer. Cancer Res, 2012. 72(19): p. 4883-9.
- Labelle, M., S. Begum, and R.O. Hynes, Direct signaling between platelets and cancer cells induces an epithelial-mesenchymal-like transition and promotes metastasis. Cancer Cell, 2011. 20(5): p. 576-90.
- Techasen, A., et al., Cytokines released from activated human macrophages induce epithelial mesenchymal transition markers of cholangiocarcinoma cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev, 2012. 13 Suppl: p. 115-8.
- Lopez-Novoa, J.M. and M.A. Nieto, Inflammation and EMT: an alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression. EMBO Mol Med, 2009. 1(6-7): p. 303-14. [CrossRef]
- Yan, Y., et al., High tumor-associated macrophages infiltration is associated with poor prognosis and may contribute to the phenomenon of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in gastric cancer. Onco Targets Ther, 2016. 9: p. 3975-83.
- Hu, Y., et al., Tumor-associated macrophages correlate with the clinicopathological features and poor outcomes via inducing epithelial to mesenchymal transition in oral squamous cell carcinoma. J Exp Clin Cancer Res, 2016. 35: p. 12.
- Fu, X.T., et al., Macrophage-secreted IL-8 induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma cells by activating the JAK2/STAT3/Snail pathway. Int J Oncol, 2015. 46(2): p. 587-96.
- Deng, Y.R., et al., Sorafenib inhibits macrophage-mediated epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(25): p. 38292-38305. [CrossRef]
- Fan, Q.M., et al., Tumor-associated macrophages promote cancer stem cell-like properties via transforming growth factor-beta1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett, 2014. 352(2): p. 160-8. [CrossRef]
- Long, X., et al., IL-8, a novel messenger to cross-link inflammation and tumor EMT via autocrine and paracrine pathways (Review). Int J Oncol, 2016. 48(1): p. 5-12.
- Cohen, E.N., et al., Inflammation Mediated Metastasis: Immune Induced Epithelial-To-Mesenchymal Transition in Inflammatory Breast Cancer Cells. PLoS One, 2015. 10(7): p. e0132710. [CrossRef]
- Vega, S., et al., Snail blocks the cell cycle and confers resistance to cell death. Genes Dev, 2004. 18(10): p. 1131-43.
- Emanuele, M.J., et al., Proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-associated KIAA0101/PAF15 protein is a cell cycle-regulated anaphase-promoting complex/cyclosome substrate. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. 108(24): p. 9845-50. [CrossRef]
- Blick, T., et al., Epithelial mesenchymal transition traits in human breast cancer cell lines. Clin Exp Metastasis, 2008. 25(6): p. 629-42.
- Weidenfeld, K., et al., Dormant tumor cells expressing LOXL2 acquire a stem-like phenotype mediating their transition to proliferative growth. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(44): p. 71362-71377.
- Fischer, K.R., et al., Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is not required for lung metastasis but contributes to chemoresistance. Nature, 2015. 527(7579): p. 472-6.
- Zheng, X., et al., Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition is dispensable for metastasis but induces chemoresistance in pancreatic cancer. Nature, 2015. 527(7579): p. 525-530.
- Bao, Y., et al., Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 5A2 (eIF5A2) regulates chemoresistance in colorectal cancer through epithelial mesenchymal transition. Cancer Cell Int, 2015. 15: p. 109.
- Hu, T., et al., Mechanisms of drug resistance in colon cancer and its therapeutic strategies. World J Gastroenterol, 2016. 22(30): p. 6876-89.
- Tato-Costa, J., et al., Therapy-Induced Cellular Senescence Induces Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition and Increases Invasiveness in Rectal Cancer. Clin Colorectal Cancer, 2016. 15(2): p. 170-178 e3.
- Tsoumas, D., et al., ILK Expression in Colorectal Cancer Is Associated with EMT, Cancer Stem Cell Markers and Chemoresistance. Cancer Genomics Proteomics, 2018. 15(2): p. 127-141.
- Yang, Y., et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell-like phenotype induced by Twist1 contribute to acquired resistance to irinotecan in colon cancer. Int J Oncol, 2017. 51(2): p. 515-524.
- Sangaletti, S., et al., Mesenchymal Transition of High-Grade Breast Carcinomas Depends on Extracellular Matrix Control of Myeloid Suppressor Cell Activity. Cell Rep, 2016. 17(1): p. 233-248. [CrossRef]
- Farmer, P., et al., A stroma-related gene signature predicts resistance to neoadjuvant chemotherapy in breast cancer. Nat Med, 2009. 15(1): p. 68-74.
- Byers, L.A., et al., An epithelial-mesenchymal transition gene signature predicts resistance to EGFR and PI3K inhibitors and identifies Axl as a therapeutic target for overcoming EGFR inhibitor resistance. Clin Cancer Res, 2013. 19(1): p. 279-90.
- Gjerdrum, C., et al., Axl is an essential epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition-induced regulator of breast cancer metastasis and patient survival. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2010. 107(3): p. 1124-9. [CrossRef]
- Terry, S., et al., New insights into the role of EMT in tumor immune escape. Mol Oncol, 2017. 11(7): p. 824-846.
- Dongre, A., et al., Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition Contributes to Immunosuppression in Breast Carcinomas. Cancer Res, 2017. 77(15): p. 3982-3989.
- Ansieau, S., et al., Induction of EMT by twist proteins as a collateral effect of tumor-promoting inactivation of premature senescence. Cancer Cell, 2008. 14(1): p. 79-89.
- Liu, Y., et al., Zeb1 links epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cellular senescence. Development, 2008. 135(3): p. 579-88.
- Ohashi, S., et al., Epidermal growth factor receptor and mutant p53 expand an esophageal cellular subpopulation capable of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition through ZEB transcription factors. Cancer Res, 2010. 70(10): p. 4174-84.
- Coppe, J.P., et al., Senescence-associated secretory phenotypes reveal cell-nonautonomous functions of oncogenic RAS and the p53 tumor suppressor. PLoS Biol, 2008. 6(12): p. 2853-68.
- Yuan, A., et al., The role of interleukin-8 in cancer cells and microenvironment interaction. Front Biosci, 2005. 10: p. 853-65.
- Laberge, R.M., et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition induced by senescent fibroblasts. Cancer Microenviron, 2012. 5(1): p. 39-44.
- Hanahan, D. and R.A. Weinberg, Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 2011. 144(5): p. 646-74. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan, D., Hallmarks of Cancer: New Dimensions. Cancer Discov, 2022. 12(1): p. 31-46.
- Lu, H., et al., A breast cancer stem cell niche supported by juxtacrine signalling from monocytes and macrophages. Nat Cell Biol, 2014. 16(11): p. 1105-17.
- Brown, R.L., et al., CD44 splice isoform switching in human and mouse epithelium is essential for epithelial-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer progression. J Clin Invest, 2011. 121(3): p. 1064-74.
- Brabletz, T., et al., Opinion: migrating cancer stem cells - an integrated concept of malignant tumour progression. Nat Rev Cancer, 2005. 5(9): p. 744-9.
- Roy, S., et al., EMT imparts cancer stemness and plasticity: new perspectives and therapeutic potential. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed), 2021. 26(2): p. 238-265.
- Scheel, C. and R.A. Weinberg, Cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition: concepts and molecular links. Semin Cancer Biol, 2012. 22(5-6): p. 396-403. [CrossRef]
- Brabletz, T., et al., EMT in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer, 2018. 18(2): p. 128-134.
- Loret, N., et al., The Role of Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Plasticity in Ovarian Cancer Progression and Therapy Resistance. Cancers (Basel), 2019. 11(6).
- Sorlie, T., et al., Gene expression patterns of breast carcinomas distinguish tumor subclasses with clinical implications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2001. 98(19): p. 10869-74. [CrossRef]
- Deng, Z., et al., Adoptive T-cell therapy of prostate cancer targeting the cancer stem cell antigen EpCAM. BMC Immunol, 2015. 16(1): p. 1.
- da Silveira, W.A., et al., Transcription Factor Networks derived from Breast Cancer Stem Cells control the immune response in the Basal subtype. Sci Rep, 2017. 7(1): p. 2851.
- Saygin, C., et al., Targeting Cancer Stemness in the Clinic: From Hype to Hope. Cell Stem Cell, 2019. 24(1): p. 25-40. [CrossRef]
- Terry, S. and S. Chouaib, EMT in immuno-resistance. Oncoscience, 2015. 2(10): p. 841-2.
- Li, S., et al., Tumor-associated macrophages remodeling EMT and predicting survival in colorectal carcinoma. Oncoimmunology, 2018. 7(2): p. e1380765. [CrossRef]
- Del Barco, S., et al., Metformin: multi-faceted protection against cancer. Oncotarget, 2011. 2(12): p. 896-917.
- Olivos, D.J. and L.D. Mayo, Emerging Non-Canonical Functions and Regulation by p53: p53 and Stemness. Int J Mol Sci, 2016. 17(12).
- Steinbichler, T.B., et al., Therapy resistance mediated by cancer stem cells. Semin Cancer Biol, 2018. 53: p. 156-167. [CrossRef]
- Tsubakihara, Y. and A. Moustakas, Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Metastasis under the Control of Transforming Growth Factor beta. Int J Mol Sci, 2018. 19(11).
- Iqbal, W., et al., Targeting signal transduction pathways of cancer stem cells for therapeutic opportunities of metastasis. Oncotarget, 2016. 7(46): p. 76337-76353. [CrossRef]
- Imai, T., et al., Hypoxia attenuates the expression of E-cadherin via up-regulation of SNAIL in ovarian carcinoma cells. Am J Pathol, 2003. 163(4): p. 1437-47. [CrossRef]
- Lester, R.D., et al., uPAR induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition in hypoxic breast cancer cells. J Cell Biol, 2007. 178(3): p. 425-36. [CrossRef]
- Yang, M.H., et al., Direct regulation of TWIST by HIF-1alpha promotes metastasis. Nat Cell Biol, 2008. 10(3): p. 295-305.
- Esteban, M.A., et al., Regulation of E-cadherin expression by VHL and hypoxia-inducible factor. Cancer Res, 2006. 66(7): p. 3567-75. [CrossRef]
- Krishnamachary, B., et al., Hypoxia-inducible factor-1-dependent repression of E-cadherin in von Hippel-Lindau tumor suppressor-null renal cell carcinoma mediated by TCF3, ZFHX1A, and ZFHX1B. Cancer Res, 2006. 66(5): p. 2725-31.
- Magee, J.A., E. Piskounova, and S.J. Morrison, Cancer stem cells: impact, heterogeneity, and uncertainty. Cancer Cell, 2012. 21(3): p. 283-96.
- Meacham, C.E. and S.J. Morrison, Tumour heterogeneity and cancer cell plasticity. Nature, 2013. 501(7467): p. 328-37.
- Plaks, V., N. Kong, and Z. Werb, The cancer stem cell niche: how essential is the niche in regulating stemness of tumor cells? Cell Stem Cell, 2015. 16(3): p. 225-38. [CrossRef]
- Brozovic, A., The relationship between platinum drug resistance and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Arch Toxicol, 2017. 91(2): p. 605-619.
- Borovski, T., et al., Cancer stem cell niche: the place to be. Cancer Res, 2011. 71(3): p. 634-9.
- Iliopoulos, D., et al., Inducible formation of breast cancer stem cells and their dynamic equilibrium with non-stem cancer cells via IL6 secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A, 2011. 108(4): p. 1397-402. [CrossRef]
- de Wit, S., et al., EpCAM(high) and EpCAM(low) circulating tumor cells in metastatic prostate and breast cancer patients. Oncotarget, 2018. 9(86): p. 35705-35716.
- Onidani, K., et al., Monitoring of cancer patients via next-generation sequencing of patient-derived circulating tumor cells and tumor DNA. Cancer Sci, 2019. 110(8): p. 2590-2599.
- Begicevic, R.R. and M. Falasca, ABC Transporters in Cancer Stem Cells: Beyond Chemoresistance. Int J Mol Sci, 2017. 18(11).
- Jiang, Z.S., et al., Epithelial-mesenchymal transition: potential regulator of ABC transporters in tumor progression. J Cancer, 2017. 8(12): p. 2319-2327. [CrossRef]
- Sinha, S., K.C. Hembram, and S. Chatterjee, Targeting signaling pathways in cancer stem cells: A potential approach for developing novel anti-cancer therapeutics. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol, 2024. 385: p. 157-209.
- Wang, S.S., et al., Links between cancer stem cells and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Onco Targets Ther, 2015. 8: p. 2973-80.
- McCoy, E.L., et al., Six1 expands the mouse mammary epithelial stem/progenitor cell pool and induces mammary tumors that undergo epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest, 2009. 119(9): p. 2663-77.
- DiMeo, T.A., et al., A novel lung metastasis signature links Wnt signaling with cancer cell self-renewal and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in basal-like breast cancer. Cancer Res, 2009. 69(13): p. 5364-73.
- Wu, Y., et al., Expression of Wnt3 activates Wnt/beta-catenin pathway and promotes EMT-like phenotype in trastuzumab-resistant HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells. Mol Cancer Res, 2012. 10(12): p. 1597-606.
- Liu, T., et al., MicroRNA-1 down-regulates proliferation and migration of breast cancer stem cells by inhibiting the Wnt/beta-catenin pathway. Oncotarget, 2015. 6(39): p. 41638-49.
- Hwang, W.L., et al., MicroRNA-146a directs the symmetric division of Snail-dominant colorectal cancer stem cells. Nat Cell Biol, 2014. 16(3): p. 268-80.
- Wei, X., et al., Activation of the JAK-STAT3 pathway is associated with the growth of colorectal carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep, 2014. 31(1): p. 335-41. [CrossRef]
- Wang, F., et al., Hedgehog Signaling Regulates Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Pancreatic Cancer Stem-Like Cells. J Cancer, 2016. 7(4): p. 408-17. [CrossRef]
- Feldmann, G., et al., Blockade of hedgehog signaling inhibits pancreatic cancer invasion and metastases: a new paradigm for combination therapy in solid cancers. Cancer Res, 2007. 67(5): p. 2187-96.
- Liu, S., et al., Hedgehog signaling and Bmi-1 regulate self-renewal of normal and malignant human mammary stem cells. Cancer Res, 2006. 66(12): p. 6063-71.
- Rangwala, F., A. Omenetti, and A.M. Diehl, Cancer stem cells: repair gone awry? J Oncol, 2011. 2011: p. 465343.
- Mulholland, D.J., et al., Pten loss and RAS/MAPK activation cooperate to promote EMT and metastasis initiated from prostate cancer stem/progenitor cells. Cancer Res, 2012. 72(7): p. 1878-89.
- Shao, S., et al., Notch1 signaling regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer in a Slug-dependent manner. Mol Cancer, 2015. 14(1): p. 28.
- Dian, L., et al., Berberine alkaloids inhibit the proliferation and metastasis of breast carcinoma cells involving Wnt/beta-catenin signaling and EMT. Phytochemistry, 2022. 200: p. 113217.
- van der Horst, G., et al., Targeting of alpha(v)-integrins in stem/progenitor cells and supportive microenvironment impairs bone metastasis in human prostate cancer. Neoplasia, 2011. 13(6): p. 516-25.
- Dang, H., et al., Snail1 induces epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and tumor initiating stem cell characteristics. BMC Cancer, 2011. 11: p. 396. [CrossRef]
- Bocci, F., et al., A mechanism-based computational model to capture the interconnections among epithelial-mesenchymal transition, cancer stem cells and Notch-Jagged signaling. Oncotarget, 2018. 9(52): p. 29906-29920. [CrossRef]
- Cao, W., et al., Dynamics of Proliferative and Quiescent Stem Cells in Liver Homeostasis and Injury. Gastroenterology, 2017. 153(4): p. 1133-1147. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y., et al., Combinatorial TGF-beta attenuation with paclitaxel inhibits the epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and breast cancer stem-like cells. Oncotarget, 2015. 6(35): p. 37526-43.
- Sun, Y., et al., Jatrorrhizine inhibits mammary carcinoma cells by targeting TNIK mediated Wnt/beta-catenin signalling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT). Phytomedicine, 2019. 63: p. 153015.
- Gupta, P.B., et al., Stochastic state transitions give rise to phenotypic equilibrium in populations of cancer cells. Cell, 2011. 146(4): p. 633-44.
- You, X., et al., MicroRNA-495 confers inhibitory effects on cancer stem cells in oral squamous cell carcinoma through the HOXC6-mediated TGF-beta signaling pathway. Stem Cell Res Ther, 2020. 11(1): p. 117.
- Hao, J., et al., MicroRNA control of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in cancer stem cells. Int J Cancer, 2014. 135(5): p. 1019-27.
- Shimono, Y., et al., Downregulation of miRNA-200c links breast cancer stem cells with normal stem cells. Cell, 2009. 138(3): p. 592-603.
- Wang, Q., et al., Enhanced and Prolonged Antitumor Effect of Salinomycin-Loaded Gelatinase-Responsive Nanoparticles via Targeted Drug Delivery and Inhibition of Cervical Cancer Stem Cells. Int J Nanomedicine, 2020. 15: p. 1283-1295.
- Wang, Q., et al., Combined delivery of salinomycin and docetaxel by dual-targeting gelatinase nanoparticles effectively inhibits cervical cancer cells and cancer stem cells. Drug Deliv, 2021. 28(1): p. 510-519.
- Chatterjee, S. and C.N. Kundu, Nanoformulated quinacrine regulates NECTIN-4 domain specific functions in cervical cancer stem cells. Eur J Pharmacol, 2020. 883: p. 173308.
- Cheng, K. and M. Hao, Metformin Inhibits TGF-beta1-Induced Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition via PKM2 Relative-mTOR/p70s6k Signaling Pathway in Cervical Carcinoma Cells. Int J Mol Sci, 2016. 17(12).
- Tang, J., et al., MiR-612 suppresses the stemness of liver cancer via Wnt/beta-catenin signaling. Biochem Biophys Res Commun, 2014. 447(1): p. 210-5.
- Liang, Z., et al., Curcumin reversed chronic tobacco smoke exposure induced urocystic EMT and acquisition of cancer stem cells properties via Wnt/beta-catenin. Cell Death Dis, 2017. 8(10): p. e3066.
- Dou, J., et al., Decreasing lncRNA HOTAIR expression inhibits human colorectal cancer stem cells. Am J Transl Res, 2016. 8(1): p. 98-108.
- Wu, L., et al., TROY Modulates Cancer Stem-Like Cell Properties and Gefitinib Resistance Through EMT Signaling in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Front Genet, 2022. 13: p. 881875.
- Han, M., et al., Antagonism of miR-21 reverses epithelial-mesenchymal transition and cancer stem cell phenotype through AKT/ERK1/2 inactivation by targeting PTEN. PLoS One, 2012. 7(6): p. e39520.
- Liu, Q., et al., Targeted delivery of miR-200c/DOC to inhibit cancer stem cells and cancer cells by the gelatinases-stimuli nanoparticles. Biomaterials, 2013. 34(29): p. 7191-203.
- Deng, Y., et al., MiR-429 suppresses the progression and metastasis of osteosarcoma by targeting ZEB1. EXCLI J, 2017. 16: p. 618-627.
- Liu, X., et al., Tumor-suppressing effects of miR-429 on human osteosarcoma. Cell Biochem Biophys, 2014. 70(1): p. 215-24.
- Tanabe, S., et al., Interplay of EMT and CSC in Cancer and the Potential Therapeutic Strategies. Front Pharmacol, 2020. 11: p. 904. [CrossRef]

| EMT association | Findings | References |
|---|---|---|
| Stemness | EMT activation is closely linked to the generation of CSCs, contributing to tumorigenesis, metastasis, drug resistance, and relapse. EMT transcription factors, such as Zeb1, suppress epithelial differentiation and facilitate stemness, while signaling pathways like TGF-β, Snail1/Twist1, and Notch promote the acquisition of stem-like traits. | [48,49,50,51,52,53,54,55,56,57,58,59,60,61,62,63,64] |
| Tumor Angiogenesis | Angiogenesis and EMT are unified; VEGF, EGF, NECTIN-4 pathways promote EMT and are associated with increased tumor cell motility and invasion. | [65,66,67,68,69,70,71] |
| Metastasis | EMT is also linked with early metastatic processes, which includes cell invasion, cytoskeletal reorganization, and MMPs-mediated basement membrane degradation. | [38,72,73,74,75,76] |
| Circulating Tumor Cells (CTCs) | CTCs show incomplete EMT, express both epithelial and mesenchymal markers, and are involved in metastasis and poor patient prognosis. | [77,78] |
| Cytokine involvement | Cytokines like HGF, FGF, EGF, IL-6, IL-8, TGF-β, TNF-α, and IL-27 play important roles in stimulating or regulating EMT in different cancer types. | [79,80,81,82,83,84,85,86] |
| Stromal Tumor Cells | Cytokines and growth factors from tumor stroma (EGF, HGF, TGF-β, PDGF etc.) activate transcription factors (Snail, Slug, ZEB1, Twist) that induce EMT. | [87,88,89,90,91,92,93,94] |
| Immune interactions | EMT also contributes to immune evasion; a strong association exists between high EMT activity in tumors and the presence of inflammatory cytokines and immune checkpoints (e.g., PD-1, PD-L1). | [95,96,97,98,99,100,101,102,103] |
| Inflammation | Inflammatory mediators (e.g., TNF-α and IL-8) promote EMT in cancer cells, upregulating tumor progression and metastasis, particularly in inflammatory breast cancer. | [104,105,106,107,108,109,110,111] |
| Tumor dormancy | EMT aids in tumor dormancy, with Snail and LOXL2 involved in persevering the mesenchymal phenotype and CSC-like traits. | [112,113,114,115] |
| Chemoresistance | EMT contributes to cancer drug resistance by influencing cell survival, cell fate transition, elevating the drug-resistance-involved genes, promoting stemness, dysregulating transcription factors, and immune suppression. | [116,117,118,119,120,121,122,123,124,125,126,127,128] |
| Senescence | Senescence and EMT are interconnected; EMT can prohibit senescence, promoting tumor progression and invasion. | [129,130,131,132,133,134] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




