1. Introduction
Fine needle aspiration (FNA) is the most common and widely utilized method worldwide to determine the malignancy of thyroid cancer. Its simplicity, safety, cost-effectiveness, and diagnostic accuracy make it the preferred choice. However, FNA has its limitations, with inconclusive results such as non-diagnostic nodules or interpretation as indeterminate nodules like Atypia of undetermined significance (AUS), Follicular neoplasm, or suspicious for malignancy.
Among these, AUS is reported to have a 13-30% probability of ultimately being diagnosed as cancer, although there is considerable variability across institutions [
1]. This ongoing issue has prompted concerns, with some studies reporting a higher frequency of reclassification of indeterminate nodules than the reported range. To address these challenges and guide treatment decisions accurately, various guidelines, including the ATA guidelines, generally recommend repetitive FNA and molecular testing. However, repeated FNA in AUS patients can lead to a significant problem, with literature indicating more than 60% inconclusive results (either reclassified as Category Ⅰ or again as Category Ⅲ. Additionally, despite ongoing research on molecular testing, there is currently no widely used screening tool globally, except for the BRAFV600E mutation for distinguishing papillary thyroid cancer (PTC). Overcoming these challenges, products like Thyroseq, pioneering NGS-based multi-gene analysis, are under continuous investigation, but widespread use faces remaining issues such as economic constraints.
The most definitive diagnostic approach ultimately involves performing a diagnostic lobectomy. However, the feasibility of surgery itself may be limited based on the patient's general condition, underlying conditions, and socio-economic background, among other factors.
On a different note, research consistently reports that hematologic indices, such as the Delta neutrophil index, Neutrophil lymphocyte ratio (NLR), and Platelet lymphocyte ratio (PLR), which rise in the presence of systemic inflammatory diseases, can aid in predicting the malignancy and character of tumors in the oncologic field [
2,
3,
4]. In particular, NLR has been suggested in previous studies as a potential marker for predicting differential thyroid cancer [
5]. Leveraging this insight, the authors hypothesized that these hematologic indices could contribute to discriminating malignancy in AUS cases. If these indices indeed prove helpful in diagnosing malignancy, their affordability and accessibility make them a promising tool to explore, prompting the initiation of this study.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design and Patient Selection
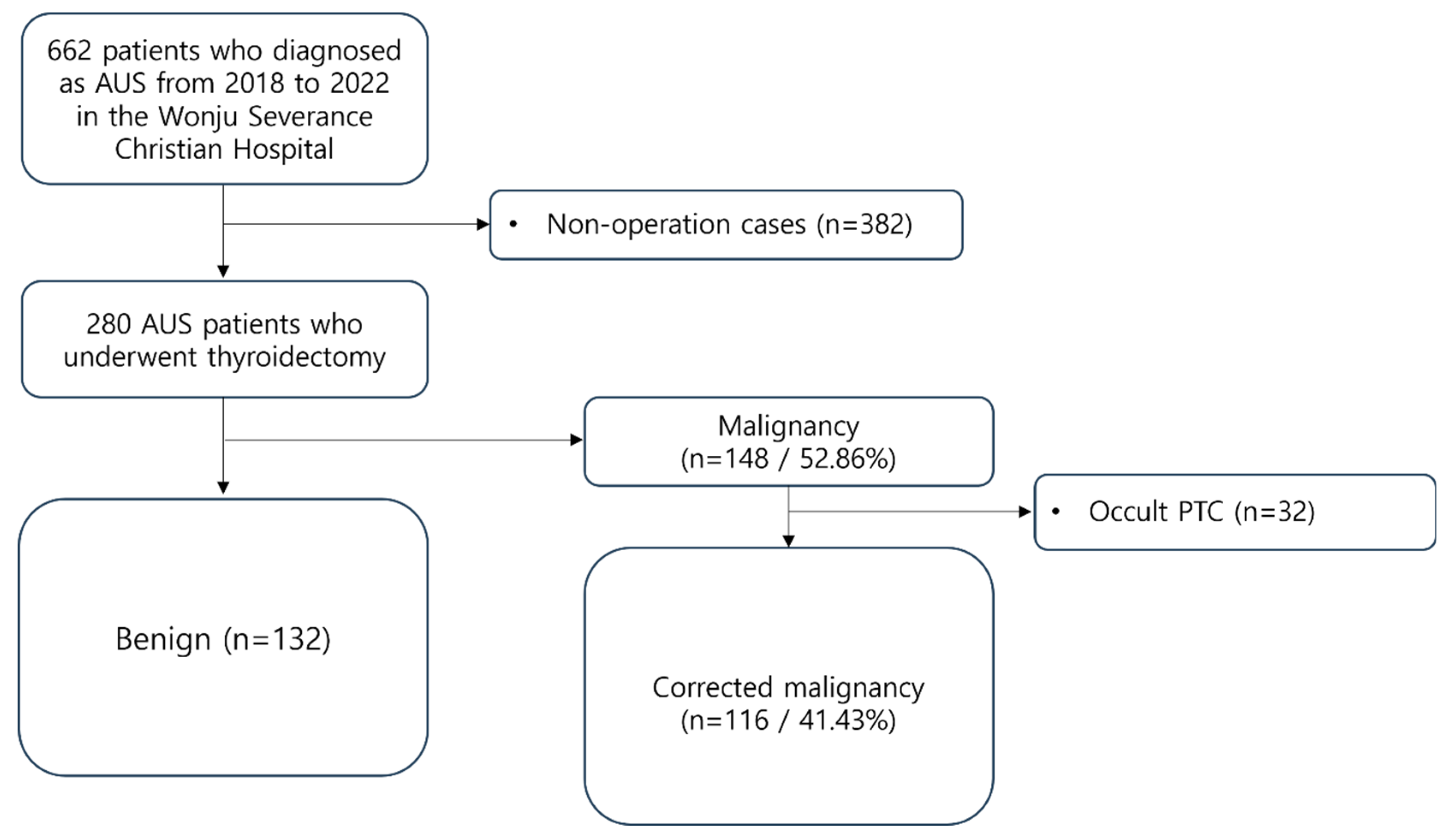
From 2018 to 2022, patients who underwent thyroid surgery at Wonju Severance Christian Hospital (Wonju, Korea) after being diagnosed with AUS through FNA were selected and reviewed retrospectively. A total of 662 patients fell under this category. FNA results were classified according to the Bethesda System 2nd version during the selection process. Among them, 280 patients underwent surgery, and their final histopathological examination results were confirmed. These 280 patients were enrolled as study subjects.
2.2. Hematologic Indices and Laboratory Data
DNI, Neutrophil count, Lymphocyte count, Platelet count, NLR, and PLR were determined using the closest preoperative laboratory data based on the surgery date.
2.3. Pathological and Ultrasonographic Information
For patients where cancer was pathologically confirmed post-surgery, tumor size was measured based on pathological data. For patients without confirmed cancer, tumor size was measured using preoperative ultrasonography. The Ultrasonographic risk classification of nodules was assessed according to K-TIRADS 2016.
For precise analysis, patients who were pathologically confirmed with cancer post-surgery were compared with preoperative imaging examinations (ultrasound, CT) to verify whether nodules initially reported AUS before surgery were indeed identified as cancer. If nodules initially reported as AUS were not confirmed as cancer, but other nodules in the same patient were reported as cancer, we classified them as occult cancer. These cases were included in the benign group eventually.
2.4. Data Collection
All data were retrospectively collected based on Electronic Medical Record (EMR) records. Radiation exposure history and family history of thyroid cancer were investigated in all patients.
2.5. Statistical Analysis
Statistical evaluation and machine learning tasks were carried out using the R language. All demographic and clinical variables were compared between the benign and malignancy groups using Student’s t-test or Fisher’s exact test. To assess the predictive utility of preoperative patient information—including age, sex, K-TIRADS classification, tumor size, history of radiation exposure, familial history of thyroid cancer, DNI, NLR, and PLR—we conducted both univariate and multivariate logistic regression analyses. Due to the limited representation of patients with a history of radiation exposure and familial history of thyroid cancer in the overall study cohort, these variables were excluded from the multivariate analysis.
For model development and validation, the dataset was divided into training and testing sets using 4-fold cross-validation, repeated 250 times to generate 1000 random training datasets and their corresponding testing datasets. Logistic regression was employed to train the models on each of these training datasets, resulting in 1000 sets of model coefficients. The performance of each model was then evaluated on the testing datasets using the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUROC) as the primary performance metric. AUROC values were calculated for each iteration, and boxplots were used to depict the distribution of these AUROC values across the 1000 iterations.
The final malignancy prediction model was constructed using multivariate logistic regression. Model parameters (beta coefficients) were estimated as the mean values of the coefficients obtained from the 1000 training iterations. The AUROC was used to evaluate the model's classification performance on the testing datasets, with AUROC values averaged across the 1000 iterations to provide a robust measure of model performance. The optimal threshold for the thyroid cancer prediction index was determined by maximizing the F1 score across the 1000 iterations, with the average of these optimal thresholds used as the cut-off for predicting thyroid cancer from AUS.
3. Results
The clinicopathological characteristics of the study cohort are in
Table 1. The mean age of all patients was 56.2 years, with 82.9% being female. The primary tumor size averaged 1.86 cm. K-TIRADS classification revealed 135 cases (48.2%) as class 4, 94 cases (33.6%) as class 3, 44 cases (15.7%) as class 5, and 7 cases (2.5%) as class 2. The mean values for DNI, NLR, and PLR were 0.17, 2.08, and 148.3, respectively.
Among the entire patient group, 148 individuals (52.86%) were reported as having thyroid cancer. Excluding 32 occult cancer patients based on the aforementioned criteria, a total of 116 patients (41.43%) were classified into the Malignancy group (
Figure 1). Of the diagnosed cancer cases, 56 (48.3%) were Follicular variant PTC, followed by 47 (40.5%) Classic PTC, 9 (7.8%) Follicular thyroid carcinoma, 3 (2.6%) Hurthle cell carcinoma, and 1 (0.9%) Medullary thyroid carcinoma (
Table 2).
In univariate analysis, K-TIRADS classification and Tumor size showed statistically significant associations with cancer diagnosis. In the multivariate analysis for the entire patient group, K-TIRADS classification, Tumor size, and Age remained significant. When DNI, NLR, and PLR were individually added as variables in the multivariate analysis, none exhibited statistical significance (
Table 3).
Considering the widely adopted 8th AJCC/TNM cancer staging system, which divides patients into age groups of <55 years (young patients) and ≥55 years (old patients), multivariate analysis was separately conducted. In the old patient group, none of the variables demonstrated statistically significant predictive ability. In the young patient group, Age, K-TIRADS classification, and Tumor size were significant variables, while DNI, NLR, and PLR showed no statistical significance.
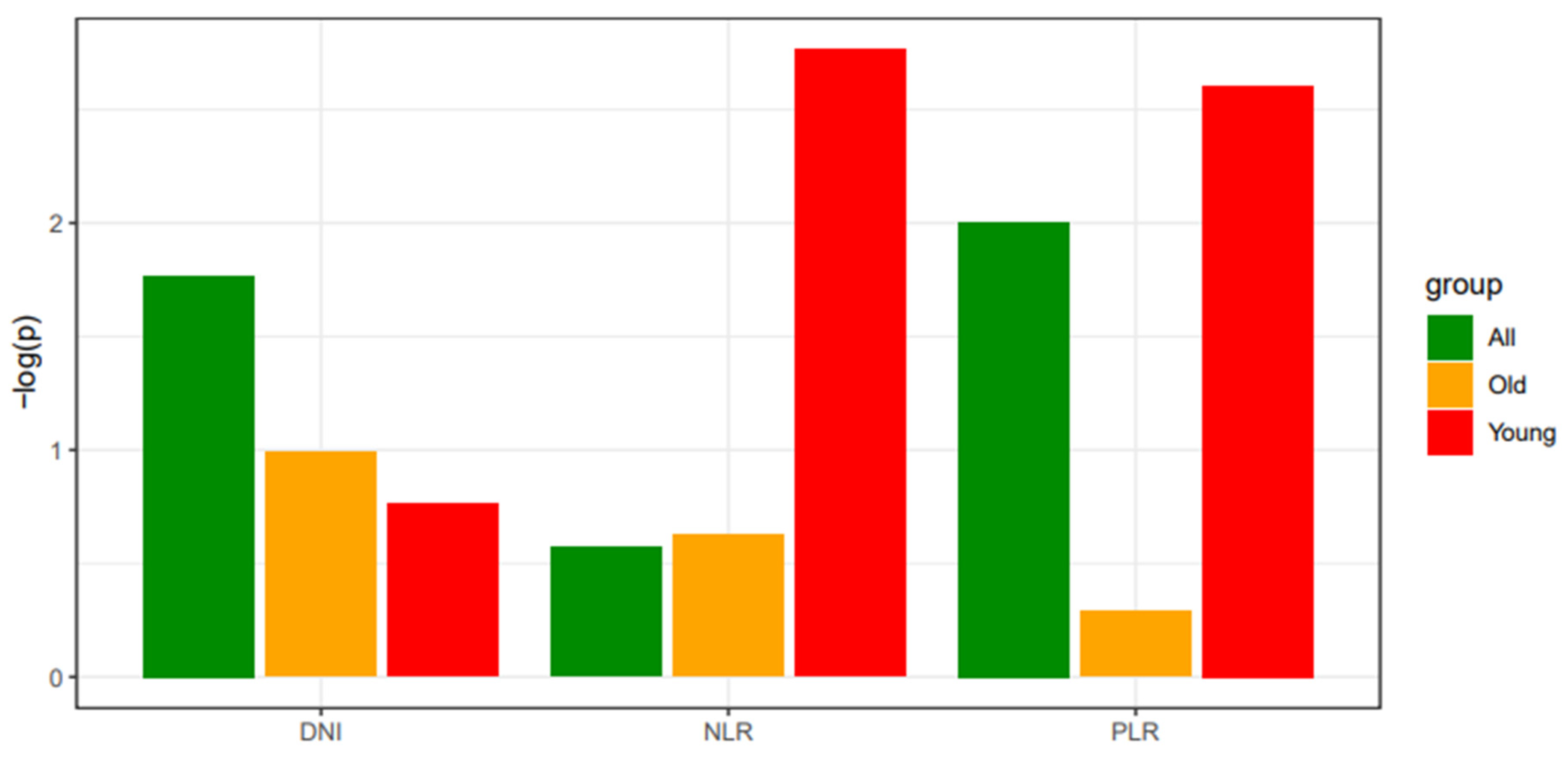
Hematologic indices DNI, NLR, and PLR were not independently significant predictors in multivariate analysis for the entire patient group, old patient group, or young patient group. However, for NLR and PLR, a trend toward proximity to a P-value of 0.05 was observed in the young patient group compared to the entire patient group. To visualize this trend, P-values were negated and log-transformed for comparison (
Figure 2).
Based on the statistical analysis, the thyroid cancer prediction model was developed by dividing patients into two groups: young patients (<55 years old) and old patients (≥55 years old). The group comprising Age, Sex, Tumor size, and K-TIRADS classification variables was designated as the "Base" model, while groups including DNI, NLR, and PLR in addition to the Base model were named the "DNI" model, "NLR" model, and "PLR" model, respectively.
In the young patient group (<55 years old), we computed 1000 AUC values for the four models of preoperative biomarkers after conducting 250 x 4 CV (cross-validation) on the electronic medical records dataset. Our results indicated that the "NLR" model exhibited superior cancer-predictive performance compared to the other models (
Figure 3A). We validated the significantly higher predictive accuracy of the NLR model compared to other models using the Bonferroni-adjusted method (
Figure 3B).
Similarly, in the old patient group (≥55 years old), following the same procedure, the AUC values of the Base model were consistently below 0.6, and the models with additional DNI, NLR, and PLR exhibited even lower AUC values than the Base model (
Figure 4). Consequently, due to statistical challenges in establishing prediction models based on these four models, we decided to only create prediction models for the young patients group.
The beta-coefficients for each biomarker were derived using Logistic Regression (LR) analysis. To ensure generalizability, a 250 × 4 CV approach was used to generate 1000 training sets, with LR applied to these sets resulting in 1000 lists of coefficients following a Gaussian distribution, in line with the central limit theorem (
Figure 5A). The average value from these distributions was adopted as the final parameters for the thyroid cancer prediction equation (
Figure 5B). To determine the cutoff value for the thyroid cancer prediction index from the LR-based network, a 4-fold cross-validation was iterated 250 times. This process produced 1000 distributions of F-scores, from which the maximum F-score values were extracted. Ultimately, the optimal cutoff value of 0.28 for the thyroid cancer prediction index was established (
Figure 5D).
K-TIRADS, Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System; NLR, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; AUC, area under the curve; WSCH, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital; AUROC, area under ROC curve; LR, logistic regression; CV, cross-validation; AUS, atypia of undetermined significance
4. Discussion
The current study was designed to identify factors aiding in the prediction of cancer in patients diagnosed with AUS. This research stems from the incomplete nature of the treatment guidelines for AUS, which, unlike Bethesda categories IV (Follicular neoplasm) and V (Suspicious for malignancy), suggests repeat FNA and molecular testing as the basic principles for AUS diagnosis [
1,
6,
7].
However, continual reports indicate that repeating FNA in AUS often results in same diagnosis again. In Korean guideline publication, it was noted that repeat FNA may exhibit over 60% inconclusive results, as reported in studies. The guideline expressed some skepticism regarding repeat FNA and suggested that to overcome this issue, performing a core needle biopsy during reassessment for AUS could be considered as an alternative option to reduce inconclusive results [
6].
In the realm of molecular biology testing, the availability is currently limited to BRAF mutations in PTC in real-world scenarios, necessitating additional research for other gene mutations. The BRAF V600E mutation is practically the sole molecular marker used for predicting thyroid cancer in clinical settings. In a study that meta-analyzed 18 studies, out of 2766 thyroid FNA samples, 581 samples were positive for BRAF mutation, among which 580 were ultimately diagnosed with PTC. Even considering one sample that was not diagnosed with PTC but showed a benign nature as a false negative, the rate of malignancy in BRAF-positive nodules was 99.8% [
8]. Furthermore, in other studies, when retrospectively examining BRAF-positive FNA samples, 15-39% of the samples were reported to have indeterminate or non-diagnostic results in cytology. This strongly suggests that BRAF testing could be a valuable tool in diagnosing cancer in cases of indeterminate cytology [
9].
Another gene mutation test that can be considered for use in PTC is the TERT mutation test. This test is particularly relevant for patients who are older and have a higher likelihood of lymph node metastasis and distant metastasis, as well as a higher probability of showing resistance to radioactive iodine therapy. When accompanied by BRAF mutation or RAS mutation, it may indicate a worse prognosis and can be used as a prognostic factor [
10]. However, this mutation exhibits high specificity but low sensitivity. A recent prospective meta-analysis study involving 3,366 PTC patients in South Korea revealed that only 2.6% showed this mutation. This suggests that its practical utility as a predictive factor in clinical settings may be somewhat limited [
11]. Therefore, this genetic mutation is used more as a prognostic marker rather than a diagnostic marker.
RAS mutation is most commonly observed in follicular thyroid carcinoma (FTC), appearing in 40-50% of cases of this cancer subtype. However, this mutation can also be detected in benign nodules and non-invasive follicular thyroid neoplasms with papillary-like nuclear features (NIFTP), contributing to an increased false positive rate for RAS mutation detection. As an example, in a meta-analysis study focusing on cases categorized as category Ⅲ and Ⅳ, RAS mutation was reported to have a positive predictive value (PPV) of 66% for thyroid malignancy [
12]. In another study focusing on Bethesda categories III, IV, and V, RAS mutation was reported to have a risk of malignancy (ROM) of 76% for thyroid malignancy [
13].
Continued research is underway on NGS-based multi-gene analysis technology, which includes a multi-gene assay based on NGS to predict malignancy, encompassing representative gene mutations such as RET, PAX8, and PPAR, among others, as previously discussed. Among these, ThyroSeq v3, a well-known assay kit, was evaluated in a study targeting 175 patients with Bethesda categories III, IV, and V. The kit demonstrated a sensitivity of 98%, specificity of 82%, and accuracy of 91% in distinguishing thyroid malignancy [
14]. This study encompassed all types of thyroid malignancies, including DTC, PDTC, ATC, and MTC. However, the high cost, exceeding
$3000, associated with this technology is currently a significant drawback, and its practical implementation and commercialization still require further time and development.
In addition to gene mutation, immunohistochemistry is being explored as a supplementary method for determining the malignancy of indeterminate nodules. Key studies include those on Galectin-3, HBME-1, CK19, and the loss of CD 56 expression. In a multicenter study using 465 FNA samples diagnosed as follicular neoplasm pre-surgery, Galectin-3 positivity was observed in 134 of the 465 samples, of which 101 (75%) were cancerous. It was also found that 29 Galectin-3 negative samples were reported as cancerous. The study concluded that the Galectin-3 test had a sensitivity of 78%, a specificity of 93%, and a positive predictive value of 82% [
15].
However, this value is deemed to be too low for use as a standalone predictor of malignancy in actual clinical practice, and it is evident that several studies on the mentioned immunohistochemistry markers, aside from Galectin, also demonstrate relatively low sensitivity and positive predictive value. To address this shortfall, recent efforts have focused on employing a combination of various immunohistochemical markers. Notably, the amalgamation of galectin-3, CK19, and HBME1 has been documented in multiple studies. In research involving 66 patients with Follicular Adenoma (FA) and 66 patients with PTC, this trio of staining techniques yielded a PPV of 97% and a Negative Predictive Value (NPV) of 96% in diagnosing PTC. Nonetheless, this study has its limitations, including the absence of an analysis on PTC variants and the lack of confirmation regarding the inclusion of Follicular Variant of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma (FVPTC) [
16]. Similarly, another study that utilized the combination of these three staining methods analyzed 231 patients and reported a PPV of over 97% for thyroid cancer. However, this study had limitations because it was conducted using only the binary classification of benign and malignant, regardless of the specific type of cancer [
17]. In another study involving 27 patients with Follicular Adenoma (FA) and 45 patients with the FVPTC, it was reported that the combination of these three staining methods showed a sensitivity of 87% and a specificity of 89% in diagnosing FVPTC [
18].
As such, despite the guidelines recommending repeat FNA and molecular biological testing, there are still vulnerabilities and areas that require further research. An additional consideration for the treatment of AUS is that, compared to the reported ROM, a higher actual ROM is being reported in various literatures [
19,
20,
21]. The proportion of patients reported as cancerous in this study, excluding occult cancer patients, also surpassed the reported 13-30% risk of malignancy from existing literature, suggesting potential limitations in the current somewhat conservative approach compared to surgical treatment. Therefore, the development of a new tool to determine whether AUS ultimately leads to a cancer diagnosis is crucial for deciding an appropriate surgical treatment policy.
The authors aimed to address this perspective by creating a Malignancy prediction model that combines hematologic indices like DNI, NLR, and PLR with well-known preoperative risk factors for thyroid cancer. The statistical potential to create such a model was more evident in the young patient group than in the entire patient group through multivariate analysis. Upon confirming the statistical trends in P-values, the authors decided that combining NLR with Age, Sex, tumor size, and K-TIRADS classification in a feature set could enhance predictive power. Through the integration of various variables, a prediction model was developed to forecast thyroid cancer in cases of AUS, utilizing logistic regression via machine learning techniques. The optimal cutoff value was determined through the F1 score.
Contrary to initial assumptions, the prediction model exhibited a negative coefficient for the NLR, indicating that an increase in NLR values correlates with a decreased likelihood of thyroid cancer. During the reclassification of enrolled patients by age, a notably smaller group was categorized as young patients, highlighting the necessity for further research with a larger patient cohort from multiple hospitals. Additionally, this study's inclusion of patients previously or subsequently diagnosed with thyroid conditions such as Graves' disease or Hashimoto thyroiditis suggests the potential impact of these groups on the NLR distribution.
Furthermore, preoperative factors that statistically proved useful in predicting cancer among young patients were found to be insignificantly predictive in older patients, a trend also observed in hematological indices like the DNI, NLR, and PLR. Internationally recognized thyroid cancer classification systems, including the 8th edition of the American Joint Committee on Cancer (AJCC), set the age threshold at 55 years, indicating that cancers tend to be more aggressive and prognoses worse in individuals older than 55. This adjustment was incorporated in the 7th edition based on empirical studies [
22]. Therefore, it can be inferred that thyroid cancer in individuals over 55 years of age will have a pathophysiology distinct from that in younger patients. This difference may explain why factors significant in the young patient group become much less meaningful in the older patient group. Furthermore, elderly patients are more likely to have concomitant underlying diseases compared to younger patients. Indices such as DNI, NLR, and PLR are associated not only with thyroid cancer but also with many other types of carcinomas, infectious diseases, and respiratory-circulatory diseases, which could have affected the statistical analysis. Additionally, in elderly patients, as aging progresses, chronic inflammatory status becomes widespread, and both cell regeneration capacity and phagocytosis decrease. Hence, it is plausible to hypothesize that the sensitivity and predictive accuracy of indicators like DNI, NLR, and PLR would be lower in the older patient group compared to the younger ones [
23,
24,
25].
Figure 1.
Patients’ inclusion and exclusion criteria. AUS, atypia of undetermined significance; PTC, papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Figure 1.
Patients’ inclusion and exclusion criteria. AUS, atypia of undetermined significance; PTC, papillary thyroid carcinoma.
Figure 2.
Comparison of statistical significance across study subgroups for laboratory data. The degree of significance (P-values) of DNI, NLR, and PLR are evaluated by logistic regression analysis, including the binomial distribution of thyroid cancer and laboratory indices as dependent and independent variables, respectively. The logistic model is applied to the entire patient cohort, the old patient (≥ 55 years) group, and the young (< 55 years) patient group, separately. The x-axis denotes the subgroup analysis according to different age groups. The y-axis indicates a negative log-transformed p-value evaluated by logistic regression. DNI, delta neutrophil index; NLR, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; PLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio.
Figure 2.
Comparison of statistical significance across study subgroups for laboratory data. The degree of significance (P-values) of DNI, NLR, and PLR are evaluated by logistic regression analysis, including the binomial distribution of thyroid cancer and laboratory indices as dependent and independent variables, respectively. The logistic model is applied to the entire patient cohort, the old patient (≥ 55 years) group, and the young (< 55 years) patient group, separately. The x-axis denotes the subgroup analysis according to different age groups. The y-axis indicates a negative log-transformed p-value evaluated by logistic regression. DNI, delta neutrophil index; NLR, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; PLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio.
Figure 3.
Comparison of performance of four thyroid cancer prediction models (< 55 years old). Four classification models were established according to four different combinations of clinical biomarkers. The “Base” model includes Age, Sex, Primary tumor size and K-TIRADS classification as input variables. Adding to this, the "DNI" model integrates DNI alongside the variables in the Base model. In the "NLR" model, NLR is included along with the Base model variables. Similarly, the "PLR" model incorporates PLR together with the Base model variables. Iteration of 4-fold cross-validation at 250 times was applied to an original dataset obtained from the WSCH, yielding 1000 sampling training datasets. Logistic regression was implemented to establish the classification model for the binomial distribution of thyroid malignancy status (thyroid cancer vs. benign nodule). Logistic model was iteratively run for the 1000 random training datasets, yielding 1000 performance values. The 1000 performance levels were obtained from the 1000 matched sampling testing datasets. A boxplot depicts the distribution of the 1000 performance measures. K-TIRADS, Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System; DNI, delta neutrophil index; NLR, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; PLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio; WSCH, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital.
Figure 3.
Comparison of performance of four thyroid cancer prediction models (< 55 years old). Four classification models were established according to four different combinations of clinical biomarkers. The “Base” model includes Age, Sex, Primary tumor size and K-TIRADS classification as input variables. Adding to this, the "DNI" model integrates DNI alongside the variables in the Base model. In the "NLR" model, NLR is included along with the Base model variables. Similarly, the "PLR" model incorporates PLR together with the Base model variables. Iteration of 4-fold cross-validation at 250 times was applied to an original dataset obtained from the WSCH, yielding 1000 sampling training datasets. Logistic regression was implemented to establish the classification model for the binomial distribution of thyroid malignancy status (thyroid cancer vs. benign nodule). Logistic model was iteratively run for the 1000 random training datasets, yielding 1000 performance values. The 1000 performance levels were obtained from the 1000 matched sampling testing datasets. A boxplot depicts the distribution of the 1000 performance measures. K-TIRADS, Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System; DNI, delta neutrophil index; NLR, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; PLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio; WSCH, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital.
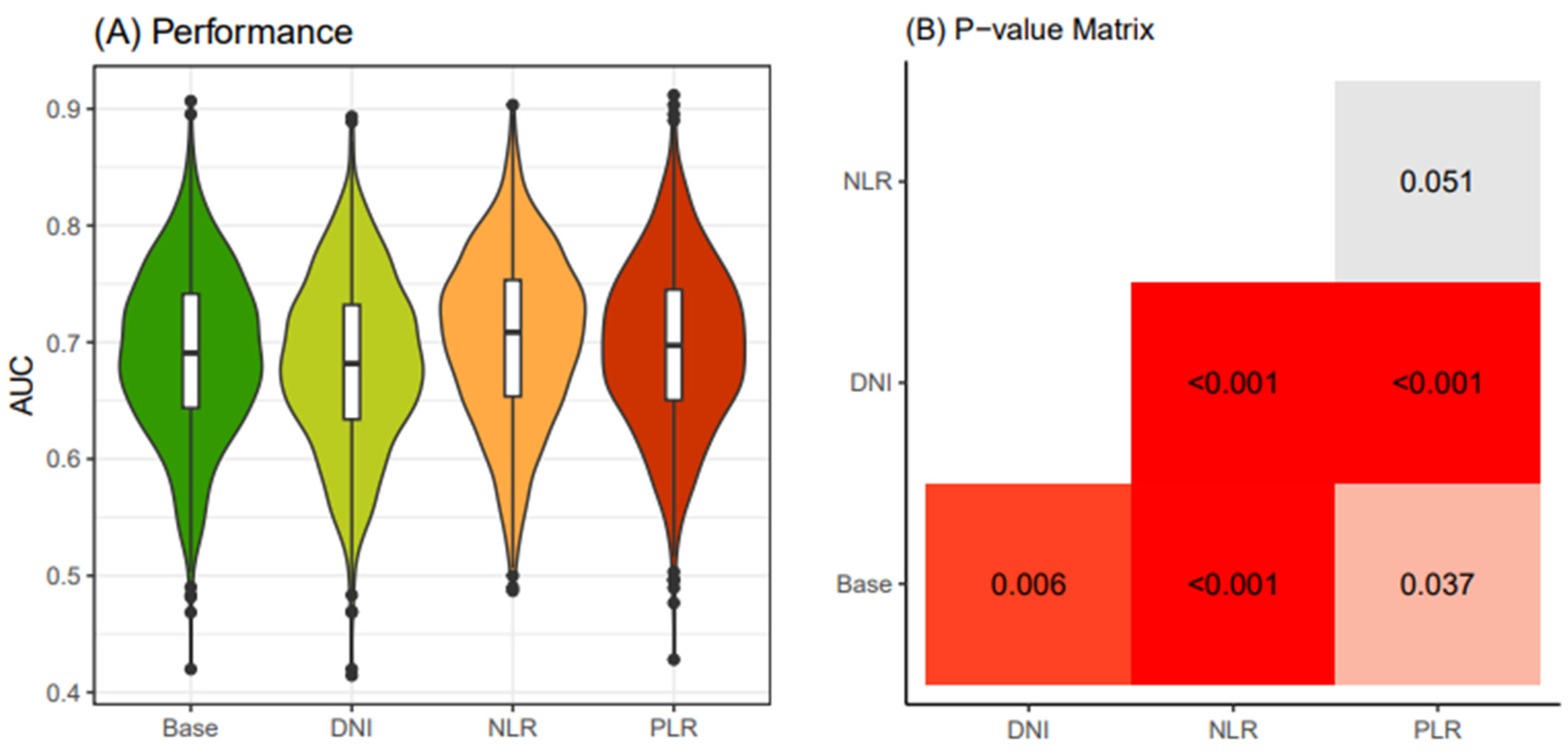
Figure 4.
Comparison of performance of four thyroid cancer prediction models (≥ 55 years old). Four classification models were devised utilizing different combinations of clinical biomarkers. The "Base" model was constructed with Age, Sex, Primary tumor size, and K-TIRADS classification as input variables. In addition, the "DNI" model featured DNI in conjunction with the Base model variables. The "NLR" model included NLR along with the Base model variables, while the "PLR" model incorporated PLR together with the Base model variables. An iterative process of 4-fold cross-validation was conducted 250 times on an initial dataset sourced from the WSCH, resulting in the generation of 1000 training datasets through sampling. Logistic regression was employed to construct a classification model for the binomial distribution of thyroid malignancy status (thyroid cancer vs. benign nodule). The logistic model underwent iterative execution across the 1000 random training datasets, producing 1000 performance values. These performance levels were derived from corresponding 1000 testing datasets obtained through matched sampling. The distribution of the 1000 performance measures is visually represented in a boxplot. K-TIRADS, Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System; DNI, delta neutrophil index; NLR, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; PLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio; WSCH, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital.
Figure 4.
Comparison of performance of four thyroid cancer prediction models (≥ 55 years old). Four classification models were devised utilizing different combinations of clinical biomarkers. The "Base" model was constructed with Age, Sex, Primary tumor size, and K-TIRADS classification as input variables. In addition, the "DNI" model featured DNI in conjunction with the Base model variables. The "NLR" model included NLR along with the Base model variables, while the "PLR" model incorporated PLR together with the Base model variables. An iterative process of 4-fold cross-validation was conducted 250 times on an initial dataset sourced from the WSCH, resulting in the generation of 1000 training datasets through sampling. Logistic regression was employed to construct a classification model for the binomial distribution of thyroid malignancy status (thyroid cancer vs. benign nodule). The logistic model underwent iterative execution across the 1000 random training datasets, producing 1000 performance values. These performance levels were derived from corresponding 1000 testing datasets obtained through matched sampling. The distribution of the 1000 performance measures is visually represented in a boxplot. K-TIRADS, Korean Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System; DNI, delta neutrophil index; NLR, neutrophil-lymphocyte ratio; PLR, platelet-lymphocyte ratio; WSCH, Wonju Severance Christian Hospital.
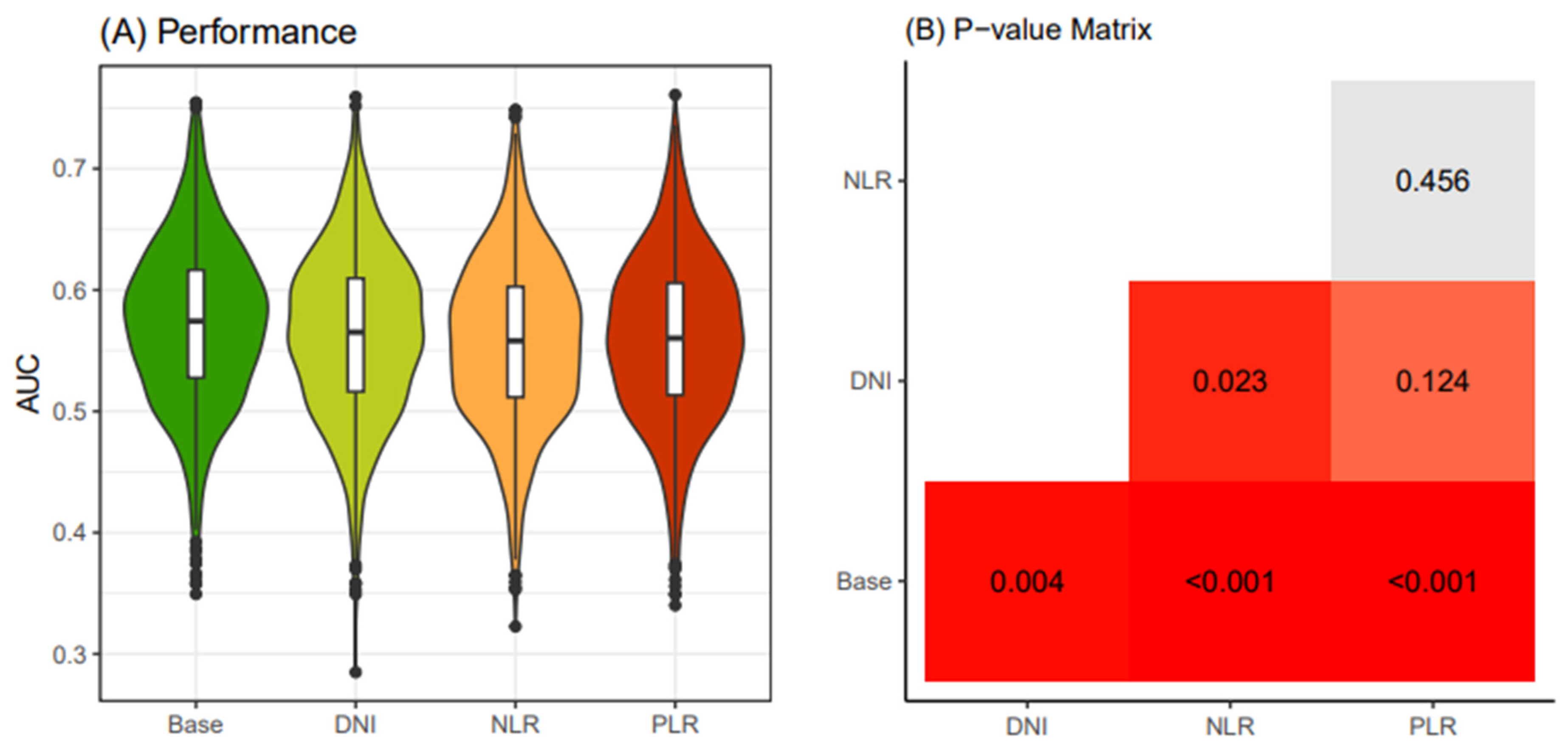
Figure 5.
Final malignancy prediction model. (A) Iteration of 4-fold cross-validation at 250 times was applied to an original dataset obtained from the WSCH, yielding 1000 sampling training datasets. Multivariate logistic regression was iteratively trained for the 1000 random training sets for the binomial distribution of thyroid malignancy status (thyroid cancer vs. benign nodule), yielding 1000 beta-coefficients per variable. (B) The equation for the thyroid cancer prediction model was established by computing the mean value of the 1000 parameters for each predictor. (C) AUROC evaluated the classification performance for the dichotomous status of thyroid cancer condition. AUROC was measured using the 1000 testing datasets matched with the 1000 training sets obtained from the 250×4 CV. (D) The LR-based thyroid cancer index provides predictive value ranging from 0 to 1. Then, we selected the cut-off of the thyroid cancer index showing the maximum value of the F1 score. We employed 250×4 CV for the selection of the optimal predictive value of thyroid cancer, yielding 1000 cut-off values of the thyroid cancer index. The average of the 1000 cut-offs of LR indices was identified as the optimal threshold for predicting thyroid cancer from AUS.
Figure 5.
Final malignancy prediction model. (A) Iteration of 4-fold cross-validation at 250 times was applied to an original dataset obtained from the WSCH, yielding 1000 sampling training datasets. Multivariate logistic regression was iteratively trained for the 1000 random training sets for the binomial distribution of thyroid malignancy status (thyroid cancer vs. benign nodule), yielding 1000 beta-coefficients per variable. (B) The equation for the thyroid cancer prediction model was established by computing the mean value of the 1000 parameters for each predictor. (C) AUROC evaluated the classification performance for the dichotomous status of thyroid cancer condition. AUROC was measured using the 1000 testing datasets matched with the 1000 training sets obtained from the 250×4 CV. (D) The LR-based thyroid cancer index provides predictive value ranging from 0 to 1. Then, we selected the cut-off of the thyroid cancer index showing the maximum value of the F1 score. We employed 250×4 CV for the selection of the optimal predictive value of thyroid cancer, yielding 1000 cut-off values of the thyroid cancer index. The average of the 1000 cut-offs of LR indices was identified as the optimal threshold for predicting thyroid cancer from AUS.
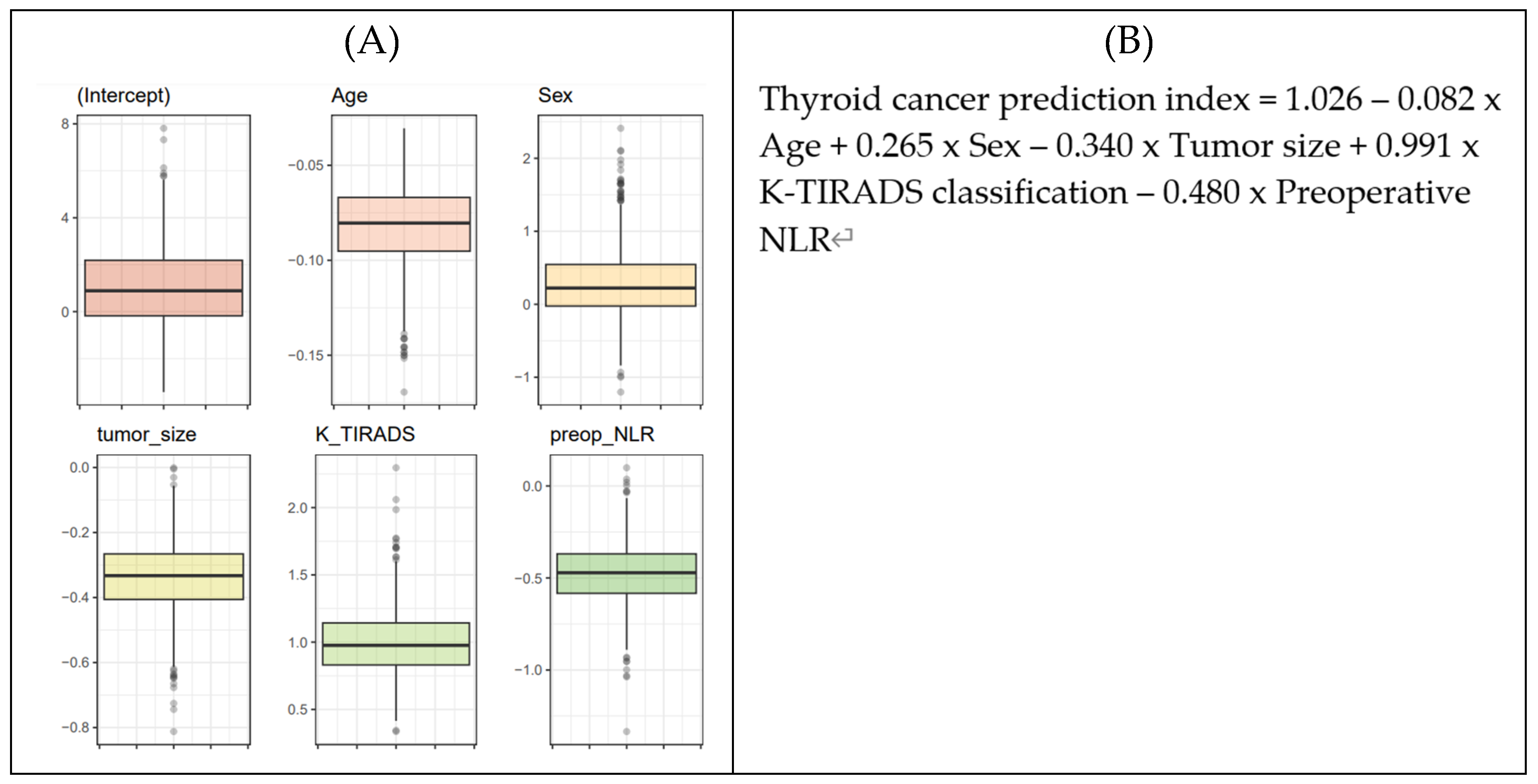
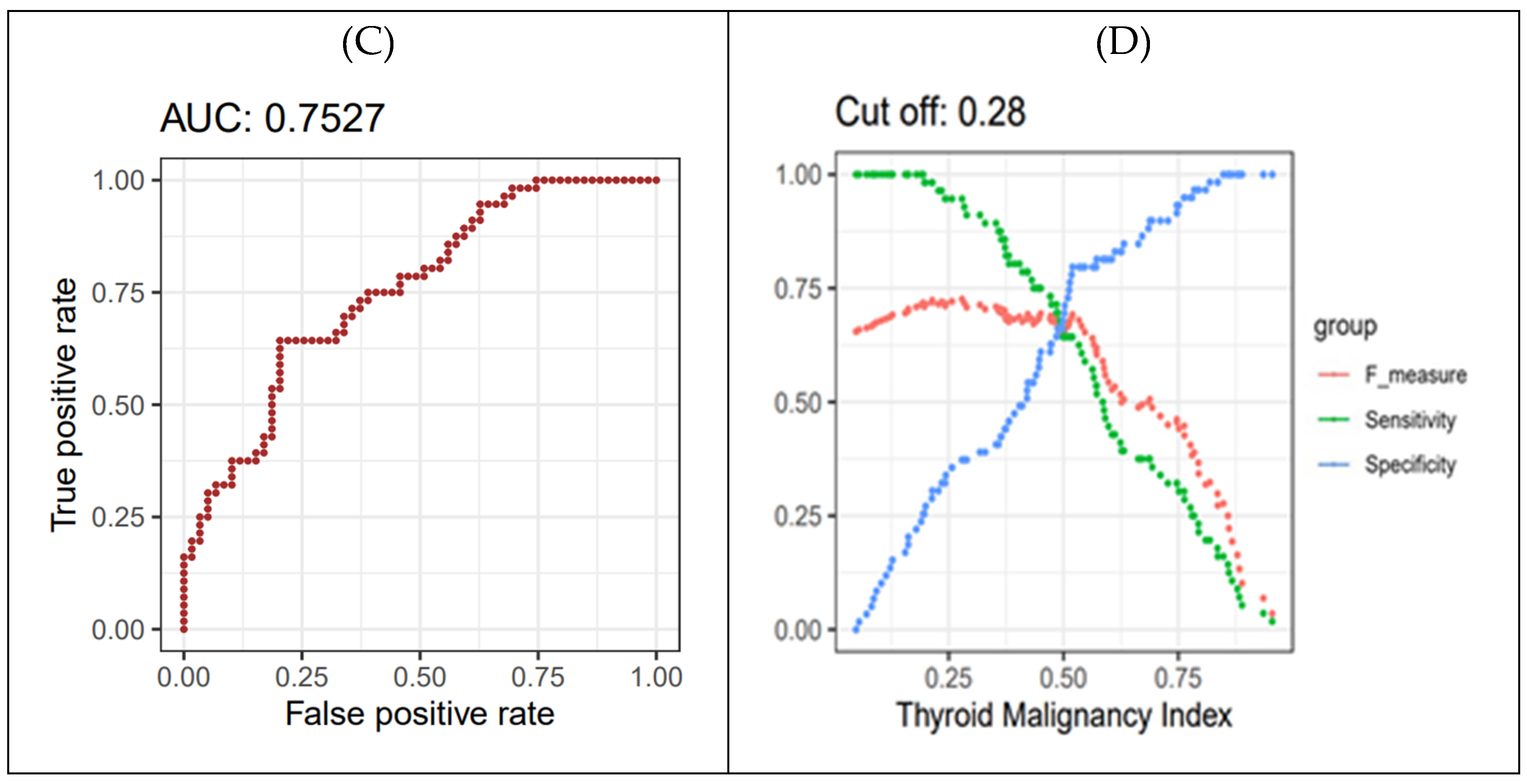
Table 1.
Preoperative baseline characteristics.
Table 1.
Preoperative baseline characteristics.
| Characteristics |
All a
|
Benign a
|
Malignancy a
|
p |
| (n = 280) |
(n=164) |
(n=116) |
| Age, years, mean ± SD |
56.2 ± 12.1 |
57.3 ± 10.4 |
54.5 ± 14.0 |
0.061 |
| Sex |
|
|
|
0.721 |
| Female |
232 (82.9) |
27 (16.5) |
21 (18.1) |
|
| Male |
48 (17.1) |
137 (83.5) |
95 (81.9) |
|
| Primary tumor size, cm |
1.86 ± 1.45 |
2.05 ± 1.65 |
1.59 ± 1.06 |
0.005 |
| K-TIRADS |
|
|
|
0.001 |
| 2 |
7 (2.5) |
5 (3) |
2 (1.7) |
|
| 3 |
94 (33.6) |
65 (39.6) |
29 (25) |
|
| 4 |
135 (48.2) |
77 (47) |
58 (50) |
|
| 5 |
44 (15.7) |
17 (10.4) |
27 (23.3) |
|
| History of radiation exposure, n |
4 (1.4) |
2 (1.2) |
2 (1.7) |
0.727 |
| Familial history of thyroid cancer, n |
12 (4.3) |
7 (4.3%) |
5 (4.3) |
0.986 |
| DNI, % |
0.17 ± 0.60 |
0.23 ± 0.73 |
0.1± 0.32 |
0.047 |
| NLR |
2.08 ± 1.01 |
2.06 ± 1.03 |
2.04 ± 0.97 |
0.868 |
| PLR |
148.3 ± 59.96 |
152.26 ± 69.85 |
142.7 ± 41.88 |
0.155 |
Table 2.
Pathologic information of thyroid cancer patients.
Table 2.
Pathologic information of thyroid cancer patients.
| |
Malignancy (n=116) a
|
| Cancer type |
|
| Classic papillary thyroid carcinoma |
47 (40.5) |
| Follicular variant papillary thyroid carcinoma |
56 (48.3) |
| Follicular thyroid carcinoma |
9 (7.8) |
| Hurthle cell carcinoma |
3 (2.6) |
| Medullary thyroid carcinoma |
1 (0.9) |
| Extrathyroidal extension |
|
| No |
99 (80.2) |
| Minimal |
17 (14.7) |
| Multifocality |
42 (36.2) |
| Bilaterality |
23 (19.8) |
| Lymphatic invasion |
4 (3.4) |
| Vascular invasion |
0 |
| Perineural invasion |
3 (2.6) |
| Central lymph node metastasis |
11 (9.5) |
Table 3.
Association of preoperative variables with the diagnosis of malignancy in patients with atypia of undetermined significance nodules.
Table 3.
Association of preoperative variables with the diagnosis of malignancy in patients with atypia of undetermined significance nodules.
| Characteristics |
Univariate |
Multivariate |
| |
|
All |
|
Old Patients
(≥ 55 Years Old) |
|
Young Patients
(<55 Years Old) |
|
| OR (95% CI) |
p |
OR (95% CI) |
p |
OR (95% CI) |
p |
OR (95% CI) |
p |
| Age, years |
0.98
(0.961 - 1) |
0.051 |
0.979
(0.959 - 1) |
0.048 |
1.05
(0.999 - 1.104) |
0.057 |
0.928
(0.876 - 0.984) |
0.012 |
| Female |
0.892
(0.476 - 1.67) |
0.72 |
0.764
(0.396 - 1.474) |
0.422 |
0.588
(0.255 - 1.357) |
0.213 |
1.013
(0.32 - 3.204) |
0.982 |
| K-TIRADS classification |
1.783
(1.268 - 2.506) |
0.001 |
1.718
(1.208 - 2.443) |
0.003 |
1.353
(0.865 - 2.116) |
0.185 |
2.588
(1.369 - 4.894) |
0.003 |
| Primary tumor size, cm |
0.782
(0.648 - 0.944) |
0.01 |
0.812
(0.671 - 0.983) |
0.033 |
0.792
(0.601 - 1.042) |
0.096 |
0.739
(0.548 - 0.997) |
0.048 |
| History of radiation exposure * |
1.421
(0.197 - 10.237) |
0.727 |
|
- |
- |
|
|
|
| Familial history of thyroid cancer* |
1.01
(0.313 - 3.265) |
0.986 |
|
- |
- |
|
|
|
| DNI** |
0.639
(0.378 - 1.079) |
0.094 |
0.689
(0.404 - 1.175) |
0.171 |
0.727
(0.362 -1.463) |
0.372 |
0.725
(0.304 - 1.727) |
0.467 |
| NLR** |
0.98
(0.772 - 1.243) |
0.867 |
0.928
(0.721 - 1.195) |
0.564 |
1.108
(0.802 - 1.532) |
0.534 |
0.627
(0.383 - 1.026) |
0.063 |
| PLR** |
0.997
(0.993 - 1.001) |
0.194 |
0.996
(0.991 - 1.001) |
0.135 |
0.999
(0.993 - 1.005) |
0.749 |
0.993
(0.984 - 1.001)) |
0.074 |