1. Introduction
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO), is a form of extracorporeal life support, providing prolonged cardiac and respiratory support to persons whose heart and lungs are unable to provide an adequate amount of oxygen, gas exchange or blood supply to sustain life [
1]. ECMO is also used to support patients with the acute viral pneumonia associated with COVID-19 in cases where artificial ventilation alone is not sufficient to sustain blood oxygenation levels [
2].
Dexmedetomidine (DEX) is an alpha-2 adrenergic receptor agonist which presents sympatholytic action in parts of the brain with anxiolytic, sedative, and pain relieving effect, that is used for its sedative and analgesic properties in patients undergoing ECMO treatment [
3]. DEX is considerable to induce a sedative state similar to natural sleep, so that patients under DEX are easily woken [
4]. The sedative effect of DEX is dependent on the plasma concentration [
5]. Variations in patient characteristics and in pharmacokinetics (PK) during ECMO might contribute to the large interpatient variability in clinical responses to DEX [
6]. Pathophysiological changes appear to be most prevalent in critically ill patients, including those affected by septic shock, multiple organ dysfunction, and ARDS. Adsorption by ECMO circuits has been considered for various drugs to date. Adsorption is strongly affected by lipophilic and protein-binding characteristics [
7,
8,
9]. The adsorption of drugs by ECMO circuits changes PK in patients, and may also impact the pharmacological efficacy or side effects of drugs. DEX and albumin associated with protein-binding are extracted by the oxygenator in the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit [
9,
10,
11,
12]. At present, few data are available concerning the effect of ECMO on the PK of DEX.
This study is the first to examine the effect of ECMO on the PK of DEX. In this paper, we describe how we conducted in vivo studies to provide a more general exploration of the effect of ECMO on the PK of DEX.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Animals
This study was approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of the Niigata University of Health and Welfare (ethical code: 22003). This study was performed in accordance with guidelines for laboratory animal welfare issued by national institutes of health. Sprague–Dawley rats (males, 14–16 w, 400–450 g, n=12) were housed in cages (3 animals per cage) under a 12 h light–dark cycle with food and water available ad libitum. All animals were provided by CLEA Japan, Inc. (Tokyo, Japan).
2.2. Anesthesia, Surgical Preparation, and ECMO
Animal and experimental procedure specifications were published by Fujii et al. [
13]. After the rats were anesthetized by 4.5–5.0% isoflurane-mixed oxygen-enriched air inhalation using a vaporizer, they were placed in the supine position and a rectal temperature probe was then inserted. The rats were orotracheally intubated using a 14 G cannula (Terumo Corp., Tokyo, Japan) and ventilated with a respirator for small animals (Model 683, Harvard Apparatus Ltd., Holliston, MA, USA). Ventilation was volume-controlled at a frequency of 70 breaths/min, a tidal volume of 10 mL/kg, and a fraction of inspired oxygen of 40%. Anesthesia was maintained with 1.5–2.0% isoflurane (without neuromuscular blocking agents), and rectal temperature was maintained at 35.5–36.5 °C throughout the experiment. The right femoral artery was cannulated using polyethylene tubing with an inner diameter of 0.5 mm and an outer diameter of 0.8 mm (Natsume Seisakusho Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) so that arterial blood pressure could be monitored using a Power-Lab (ML880, AD Instruments, Bella Vista, NSW, Australia). Polyethylene tubing with an inner diameter of 0.8 mm and an outer diameter of 1.2 mm (Natsume Seisakusho Co. Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) was used to cannulate the left common carotid artery as the outflow cannula for the ECMO system. Heparin sodium (500 IU/kg) was then administered through the outflow cannula. The right internal jugular vein was cannulated using a 16 G cannula with 4 side holes, each with a depth of 38 mm (Togomedkit Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan) for venous uptake. The ECMO system consisted of a PVC tubing circuit (Senko Medical Co., Ltd., Tokyo, Japan), a membranous oxygenator specially designed for small animals which was made of polypropylene and had a membrane area of 0.03 m
2 (Senko Medical Co., Ltd., Osaka, Japan), and a mini roller pump (REGLO Digital ISM831, ISMATEC, Wertheim, Germany) primed by 7 mL of saline and 1 mL (1,000 IU) of heparin.
2.3. Experimental Design
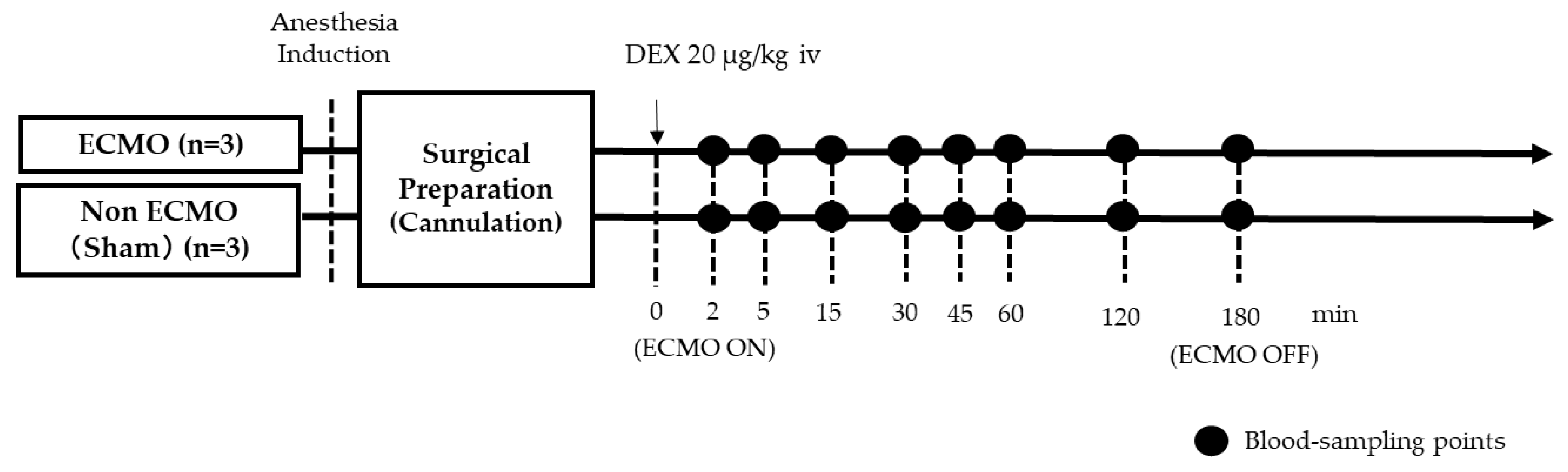
Six rats were divided into two groups: a normal DEX-treated ECMO group (ECMO rats: n= 3); and a DEX-treated non-ECMO group (sham rats: n = 3) which only underwent surgical preparation without ECMO. ECMO perfusion flow was initiated and maintained at 60–70 mL/kg/min. Arterial pressures of carbon dioxide (PaCO
2) and oxygen (PaO
2) were maintained at 35–45 mmHg and 250–350 mmHg, respectively, and managed with α-stat. Blood samples were collected at 8 defined timepoints: first, 2 min after treatment of DEX (20 g/kg body weight) before ECMO; then, at specified intervals from 5–180 min after the initiation of ECMO.
Figure 1 is a schematic diagram of the experimental design. Saline was used for fluid replacement management. Saline was injected with 1.0 mL increments at blood sampling, so that the total injection volume during the experiment was 5.0 mL. After collection, the plasma samples were immediately stored at −80 °C.
2.4. Analysis of Samples
Plasma samples of DEX was prepared via protein precipitation and were quantified by a high-performance liquid chromatography with mass spectrometry (HPLC-MS/MS) [
14]. Carteorol was used as an internal standard (IS). The method was accurate and precise at linearity range of 1–100 ng/mL. Intra-day and inter-day assay variability were below 10% for all quality control samples. The analytical validation was treated with full validation of the total densitometry system according to the guidance of the U.S. Food and Drug Administration on bioanalytical method validation [
15].
2.5. Pharmacokinetics Analysis
Exploration of PK was carried out using two conventional approaches: noncompartmental analysis using moment analysis; and compartmental modeling using NONMEM software, version 7.5.1 (ICON Development Solutions, Gaithersburg, Maryland). NONMEM runs were executed using Perl-speaks-NONMEM, version 5.4.0 (University of Uppsala, Uppsala, Sweden). Different approaches were tested, including one- or two-compartment modeling, to describe the DEX kinetic profile, while proportional and combined (additive) modeling were tested to determine the residual variability. Once the null model was selected, one documented covariate (ECMO) was tested.
The model was parameterized with the following key PK parameters: volume of distribution of the central compartment (V1); CL; Vd in the peripheral compartment (V2); and intercompartmental clearance (Q). Inter-individual variability was modeled using an exponential model, as follows:
where
θi is the estimated individual pharmacokinetics parameter for the
ith individual;
θ is the median value of the pharmacokinetics parameter of the population; and
ηi is the inter-individual random effect for the
ith individual assumed to be normally distributed with a mean of 0 and a variance ω
2.
An initial combined proportional and additive residual error model was tested, as expressed in Equation (2), as follows:
where
Yo,ii and
Yp,ij are the observed and predicted
jth drug concentrations for the
ith individual, respectively;
εpro,ij is the proportional error; and
εadd,ij is the additional error, with a mean of 0 and a variance of σ
2.
The influence of ECMO was tested using dichotomic covariates of
θi, as follows:
where
θi is the estimated individual pharmacokinetic parameter for the
ith individual,
θpop is the median value of the PK parameter of the population, and
dic (ECMO) is the dichotomic covariate (0 or 1) for the
ith individual.
2.6. Model Evaluation
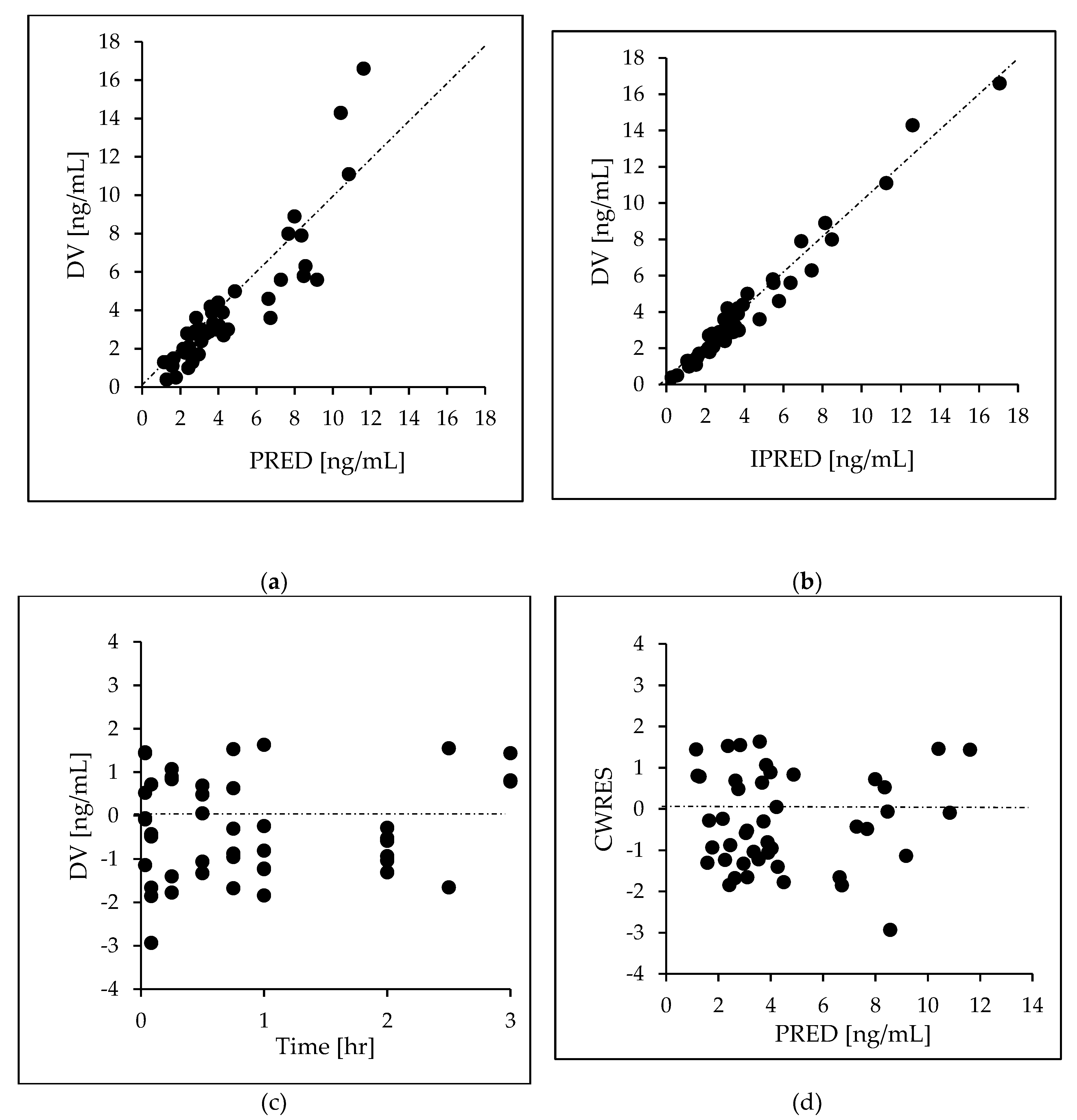
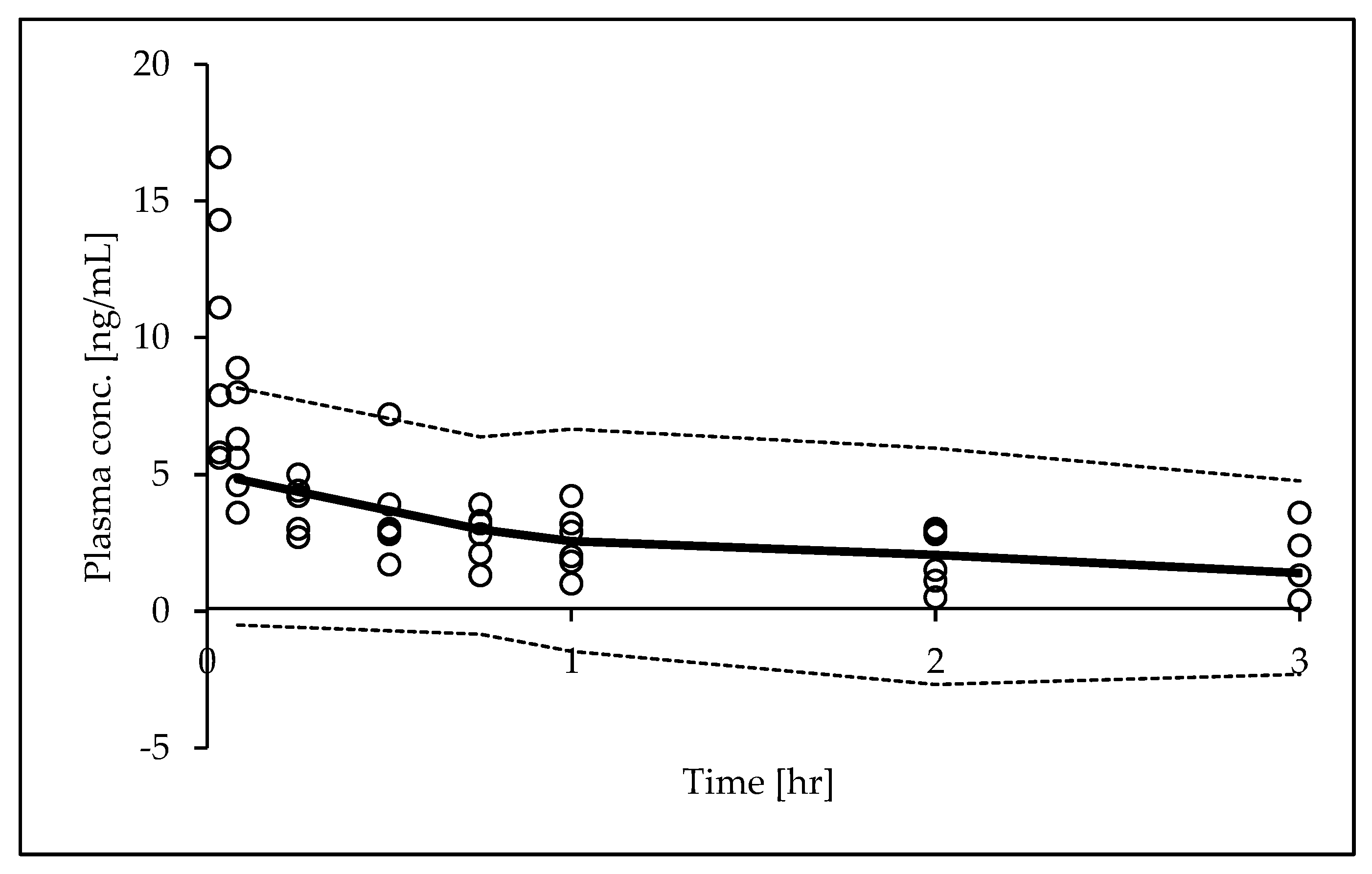
Goodness-of-fit (GOF) plots and a prediction-corrected visual predictive check (pcVPC) were used to illustrate the model performance. The following plots were generated in GOF plots: observed (DV) vs. individual predicted concentrations (IPRED); scatter plots; and residual plots [individual weighted residuals (IWRES) vs. time and predicted concentrations (PRED)]. Any significant influence of a covariate upon inter-individual variability was determined applying the likelihood-ratio test. A decrease of more than 3.84 in the criteria (p-value =0.01, χ2 distribution, 1 degree of freedom) was considered to be significant. The 95% confidence intervals (Ci) for the 10th, median, and 90th percentiles of DEX plasma concentration versus time profiles were plotted so that observations and model predictions could be compared visually.
2.7. Statistical Analysis
Data were presented in the form of mean ± standard deviation. Continuous variables were compared using repeated-measures one-way analysis of variance, and also using Tukey’s test. Two-sided P < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Change of Hemodynamic Variables During ECMO on the In Vivo Model
Table 1 shows the changes in each group in terms of the hemodynamic variables PaO
2, and PaCO
2, blood pressure (BP), heart rate (HR), pH, and Hb concentration. BP and Hb decreased during ECMO in both the ECMO and sham groups. PaO
2 levels were higher in the ECMO group than in the sham group, although the differences were not statistically significant. Finally, no statistical differences between the groups were recorded with respect to pH or PaCO
2 levels.
3.2. Pharmacokinetic Analysis
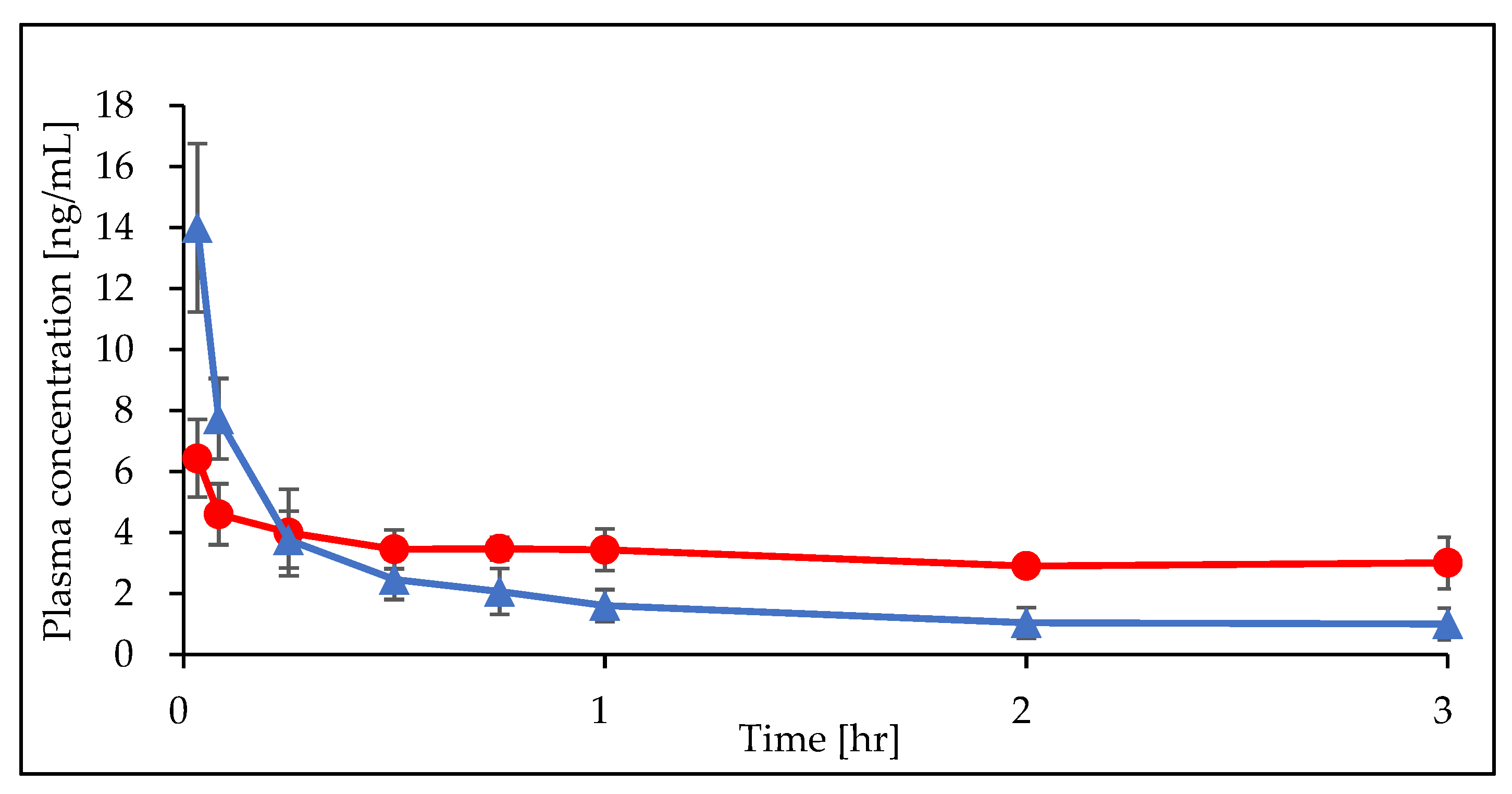
A total of 48 plasma samples from six rats were collected and analyzed. All DEX concentrations were measured. DEX concentration profiles obtained from the ECMO and sham groups are presented in
Figure 2.
Using the noncompartmental approach, it was found that, among the mean individual parameters determined for the ECMO and the sham groups. Area Under the Curve (AUC
0→180 min), Mean Residence Time (MRT), t
1/2, and steady-state volume of distribution (Vd
ss) all increased in the ECMO group, compared with the sham group, while total clearance (CL
tot) decreased (
Table 2).
The best-fitting model to describe the PK profile of DEX was a two-compartment proportional-error model. The estimate of the PK parameters, the inter-individual variability, and the residue error for the final model are summarized in
Table 3. The typical value of CL was 1.15 (L/hr) in the sham group and 0.34 (L/hr) in ECMO group. The typical values of V1 and V2 were 0.93 (L) and 2.33 (L), respectively. The typical value of Q was 5.32 (L/hr). The estimated inter-individual variability (expressed as CV%) was 19 for CL and 2.6 for V1. The ECMO significantly influenced the CL of DEX, so that CL was 75% lower in the presence of ECMO, compared with the absence of ECMO.
After a visual check for prespecified covariates was carried out, the effect of the covariates on PK parameters was then assessed using ECMO. As shown in
Figure 3, the basic GOF plots revealed that the final model was acceptable, as the predicted population and individual concentrations were generally in agreement with observed concentrations. Additionally, most conditional weighted residual values were evenly distributed in a random manner around the line of unity (±2 standard deviations of the mean), indicating the suitability of the error model. The results of the pcVPC showed that the 10th to 90th percentiles of the simulated data overlaid most of the observed data, supporting the predictive performance of the model (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
This is the first study to assess the PK of DEX using an in vivo ECMO rat model. The use of sedatives in critically ill patients is usually complicated due to the degree to which PK parameters are subject to inter-individual variability. One of the factors of variability is extracorporeal membrane oxygenation, which induces considerable fluctuation in the concentrations of sedatives at the same levels of dosage [
16]. This point is especially important because the effectiveness of sedatives such as DEX depends on the blood level of the drug. For ICU patients, the effective blood concentration of DEX is 0.2–0.6 ng/mL; this ensures treatment efficacy regardless of intra-individual PK variability [
3]. However, fluctuations in the PK profile of DEX might significantly reduce the likelihood of obtaining a therapeutic effect.
The aim of the present study was to clarify the effect of ECMO on the PK of DEX. In vivo studies were performed using rat models with PK analysis (noncompartmental analysis and nonlinear mixed-effects modeling). For in vivo experiments, the human adult ECMO device was reduced to 1/50~1/100 and a rat model was selected [
13]. In this study, a two-compartment model was selected, as used previously in the Population PK analysis of DEX in humans [
6]. Based on the evidence, the sedative protocol was chosen for the purpose of minimum sedation. Clinical practitioners must therefore consider any changes in pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics (PK/PD) parameters arising from treatment involving ECMO therapy [
20]. According to Shaker et al. (2012), an increase in unbound drugs and Vd causes a reduction in plasma levels in the circuit of neonates [
21]. Cardiac output hemodilution and drug adsorption are considered to be factors that increase Vd. There are some reports that the Vd of lipophilic drugs increases in patients, although no reports have been conclusive in this regard [
17]. In plasma, 94% of DEX is bound to albumin and α1-glycoprotein [
12]. For DEX, both prolonged [
22] and shortened [
23] elimination half-times have been reported in patients with hypoalbuminemia. Total clearance of DEX is only marginally affected by hypoalbuminemia. In previous study, we investigated an in vitro extracorporeal circuit [
11]. As a result, the DEX concentrations tended to decrease after injection. DEX adsorption in the circuit was transient, but only slightly so, in line with our previous results. DEX is a hydrophobic drug which is highly protein-bound. During a critical illness, albumin concentrations decrease in response to increased vascular permeability, decreased production, and increased catabolism. The adsorption of albumin on PVC tubing might potentially increase the adsorption of drugs that have a high rate of protein binding [
17]. It is a well-known principle that proteins in general are adsorbed by artificial surfaces, depending on the surface charge and the proteins involved [
18,
19]. The results obtained from in vitro models do not suggest an effect of circuits on DEX concentrations.
In our in vivo studies, ECMO induced a decrease in total clearance (0.34 vs. 1.15 L/h) using the nonlinear mixed-effects modeling approach and a decrease in total clearance (0.20 vs. 1.59 L/h) using noncompartmental analysis. DEX is mainly metabolized by the liver, and a hepatic extraction ratio of 0.7 was obtained in the previous study [
5]. DEX has been reported to be dependent on rates of hepatic blood flow. A decrease in total clearance suggests a decrease in hepatic clearance. In our study, BP and HR were lower in the ECMO group than in the sham group. The DEX clearance as a result of changes in liver blood flow via changes in cardiac output was studied by Dutta et al. [
25]. They described a reduction in cardiac output of 19% associated with a reduction in clearance of 12% at plasma DEX levels of 1.2 ng/mL. DEX produces a typical biphasic hemodynamic response, resulting in hypotension at low plasma concentrations and hypertension at higher plasma concentrations. IV bolus administration of DEX results in a high (peak) plasma concentration and an increase in blood pressure combined with a marked decrease in heart rate [
24]. Fluctuations in vitals might also be affected by DEX administration. Similar fluctuations in vitals were found to occur in a previous study which used the same ECMO rat model as in the present work, suggesting that these fluctuations are due to the ECMO [
12]. Therefore, if a patient is suspected of having reduced ECMO-related clearance, a slight overexposure of DEX can be expected, but no serious side effects.
The experiments conducted in the present study had several limitations. First, this was a pilot study involving a small number of animals (n=6). We did not use rat models of pneumonia or ARDS, for which ECMO is indicated. Future studies will allow us to elucidate the sequential mechanisms of the pathological condition by evaluating the histopathological severity of disorders. Finally, we evaluated pharmacokinetics during short-term ECMO. Further studies are needed to assess systemic inflammatory response and organ damage during long-term ECMO and after weaning from ECMO.
5. Conclusions
In the present study, we obtained preliminary data on DEX PK obtained using an ECMO model. Population PK models were also developed for study purposes. The ECMO model represented decreased CL. Larger studies are needed to characterize the disposition of DEX during ECMO.
Author Contributions
Y.S. and Y.F. conceived and designed the study; Y.S., E.M., R.K., T.A., and Y.F. performed the experiment and analyzed the data; Y.S. wrote the manuscript; Y.N. and Y.F. revised the manuscript. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all members of the Department of Pharmaceutical Sciences, Faculty of Pharmacy and Pharmaceutical Sciences at Fukuyama University
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
| AUC |
Area under the curve |
| BP |
Blood pressure |
| CWRES |
conditional weighted residuals |
| CL |
clearance |
| DEX |
Dexmedetomidine |
| ECMO |
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation |
| Hb |
Hemoglobin |
| HR |
Heart rate |
| IPRED |
Individual predictions |
| MRT |
Mean residence time |
| PaO2
|
Arterial pressure of oxygen |
| PaCO2
|
Arterial pressure of carbon dioxide |
| PK |
Pharmacokinetics |
| PRED |
Population predictions |
| Vd |
volume of distribution |
References
- Millar, J.E.; Fanning, J.P.; McDonald, C.I.; McAuley, D.F.; Fraser, J.F. The inflammatory response to extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO): a review of the pathophysiology. Crit. Care 2016, 20, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Savarimuthu, S.; BinSaeid, J.; Harky, A. ; The role of ECMO in COVID-19: Can it provide rescue therapy in those who are critically ill? J Card Surg 2020, 35, 1298–1301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belleville, J.P.; Ward, D.S.; Bloor, B.C.; Maze, M. ; Effects of intravenous dexmedetomidine in humans Sedation, ventilation, and metabolic rate. Anesthesiology 1992, 77, 1125–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabbe, M.B.; Penning, J.P.; Ozaki, T.; Yaksh, L. ; Spinal and systemic action of the alpha 2 receptor agonist dexmedetomidine in dogs. Antinociception and carbon dioxide response. Anesthesiology 1994, 80, 1057–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weerink, M.A.S.; Struys, M.M.R.F.; Hannivoort, L.N.; Barends, C.R.M.; Absalom, A.R.; Colin, P. Clinical Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Dexmedetomidine. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2017, 56, 893–913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Tse, A.H.W. Lee, A.; Zhang, L.; Yang, M.; Zuo, Z.; Joynt, G.M.; Protein Binding and Population Pharmacokinetics of Dexmedetomidine after Prolonged Infusions in Adult Critically Ill Patients. Clin Ther 2021, 43(8), 1356-1369. [CrossRef]
- Shekar, K.; A Roberts, J.; I Mcdonald, C.; Fisquet, S.; Barnett, A.G.; Mullany, D.V.; Ghassabian, S.; Wallis, S.C.; Fung, Y.L.; Smith, M.T.; et al. Sequestration of drugs in the circuit may lead to therapeutic failure during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Crit. Care 2012, 16, R194–R194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, K.; A Roberts, J.; I Mcdonald, C.; Ghassabian, S.; Anstey, C.; Wallis, S.C.; Mullany, D.V.; Fung, Y.L.; Fraser, J.F. Protein-bound drugs are prone to sequestration in the extracorporeal membrane oxygenation circuit: results from an ex vivo study. Crit. Care 2015, 19, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nasr, V.G.; Meserve, J.; Pereira, L.M.; Faraoni, D.; Brediger, S.; Goobie, S.; Thiagarajan, R.; DiNardo, J.A. Sedative and Analgesic Drug Sequestration After a Single Bolus Injection in an Ex Vivo Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation Infant Circuit. Asaio J. 2019, 65, 187–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wagner, D.; Pasko, D.; Phillips, K.; Waldvogel, J.; Annich, G. In vitro clearance of dexmedetomidine in extracorporeal membrane oxygenation. Perfusion 2012, 28, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michihara, A.; Hanada, M.; (Handa), Y.N.; Mizoguchi, T.; Ohchi, Y.; Sato, Y. Change of dexmedetomidine and midazolam concentrations by simultaneous injection in an in vitro extracorporeal circuit. Perfusion 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamasaki, K.; Tokuno, M.; Tsukigawa, K.; Nagatsuka, Y.; Nishi, K.; Otagiri, M.; Sato, Y. Possible Involvement of Protein Binding Inhibition in Changes in Dexmedetomidine Concentration in Extracorporeal Circuits during Midazolam Use. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2024, 47, 389–393. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujii, Y.; Abe, T.; Ikegami, K. Diabetic Pathophysiology Enhances Inflammation during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation in a Rat Model. Membranes 2021, 11, 283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, W.; Liu, Q.; Xiong, S.; Qiao, L. LC-MS/MS Method for Simultaneous Quantification of Dexmedetomidine, Dezocine, and Midazolam in Rat Plasma and Its Application to Their Pharmacokinetic Study. J. Anal. Methods Chem. 2018, 2018, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- 15. US Department of Health and Human Services, Food and Drug Administration, Guidance for Industry, Bioanalytical Method Validation Available online: https://www.regulations.gov/document/FDA-2013-D-1020-0002 (accessed on July 18th, 2024).
- Dzierba, A.L.; Abrams, D.; Brodie, D. Medicating patients during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: the evidence is building. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unger, J.K.; Kuehlein, G.; Schroers, A.; Gerlach, J.C.; Rossaint, R. Adsorption of xenobiotics to plastic tubing incorporated into dynamic in vitro systems used in pharmacological research — limits and progress. Biomaterials 2001, 22, 2031–2037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, H.; King, W.; Mason, R. INTERACTION OF PLASMA-PROTEINS WITH ARTIFICIAL SURFACES - PROTEIN ADSORPTION-ISOTHERMS. 1978, 92, 483–496.
- Uniyal, S.; Brash, J.L. Patterns of Adsorption of Proteins From Human Plasma Onto Foreign Surfaces. Thromb. Haemost. 1982, 47, 285–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzierba, A.L.; Abrams, D.; Brodie, D. Medicating patients during extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: the evidence is building. Crit. Care 2017, 21, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shekar, K.; A Roberts, J.; Welch, S.; Buscher, H.; Rudham, S.; Burrows, F.; Ghassabian, S.; Wallis, S.C.; Levkovich, B.; Pellegrino, V.; et al. ASAP ECMO: Antibiotic, Sedative and Analgesic Pharmacokinetics during Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation: a multi-centre study to optimise drug therapy during ECMO. BMC Anesthesiol. 2012, 12, 29–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iirola, T.; Aantaa, R.; Laitio, R.; Kentala, E.; Lahtinen, M.; Wighton, A.; Garratt, C.; Ahtola-Sätilä, T.; Olkkola, K.T. Pharmacokinetics of prolonged infusion of high-dose dexmedetomidine in critically ill patients. Crit. Care 2011, 15, R257–R257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, T.; Deng, Y.; He, P.; He, Z.; Wang, X. Effects of mild hypoalbuminemia on the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of dexmedetomidine in patients after major abdominal or thoracic surgery. J. Clin. Anesthesia 2015, 27, 632–637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ebert, T.J.; Hall, J.E.; Barney, J.A.; Uhrich, T.D.; Colinco, M.D. The Effects of Increasing Plasma Concentrations of Dexmedetomidine in Humans. Anesthesiology 2000, 93, 382–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dutta, S.; Lal, R.; Karol, M.D.; Cohen, T.; Ebert, T. Influence of Cardiac Output on Dexmedetomidine Pharmacokinetics. J. Pharm. Sci. 2000, 89, 519–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).