Submitted:
10 September 2024
Posted:
10 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
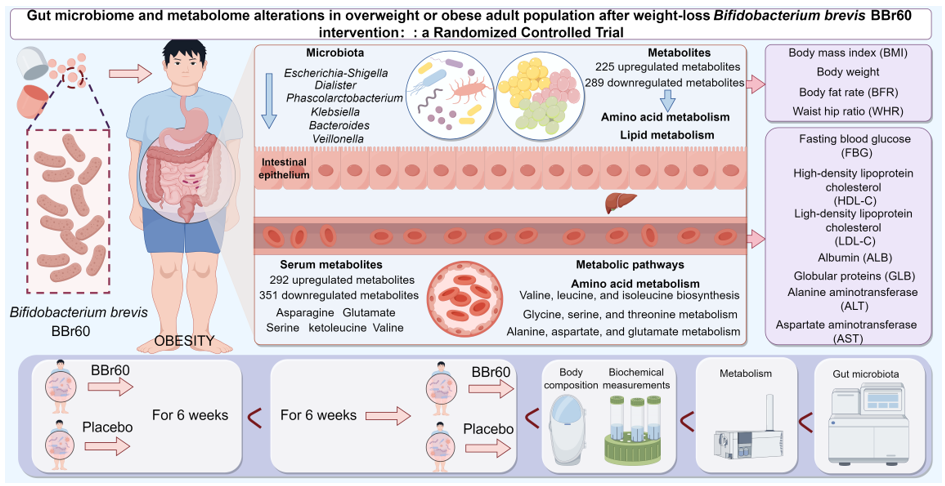
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Ethics and Informed Consent
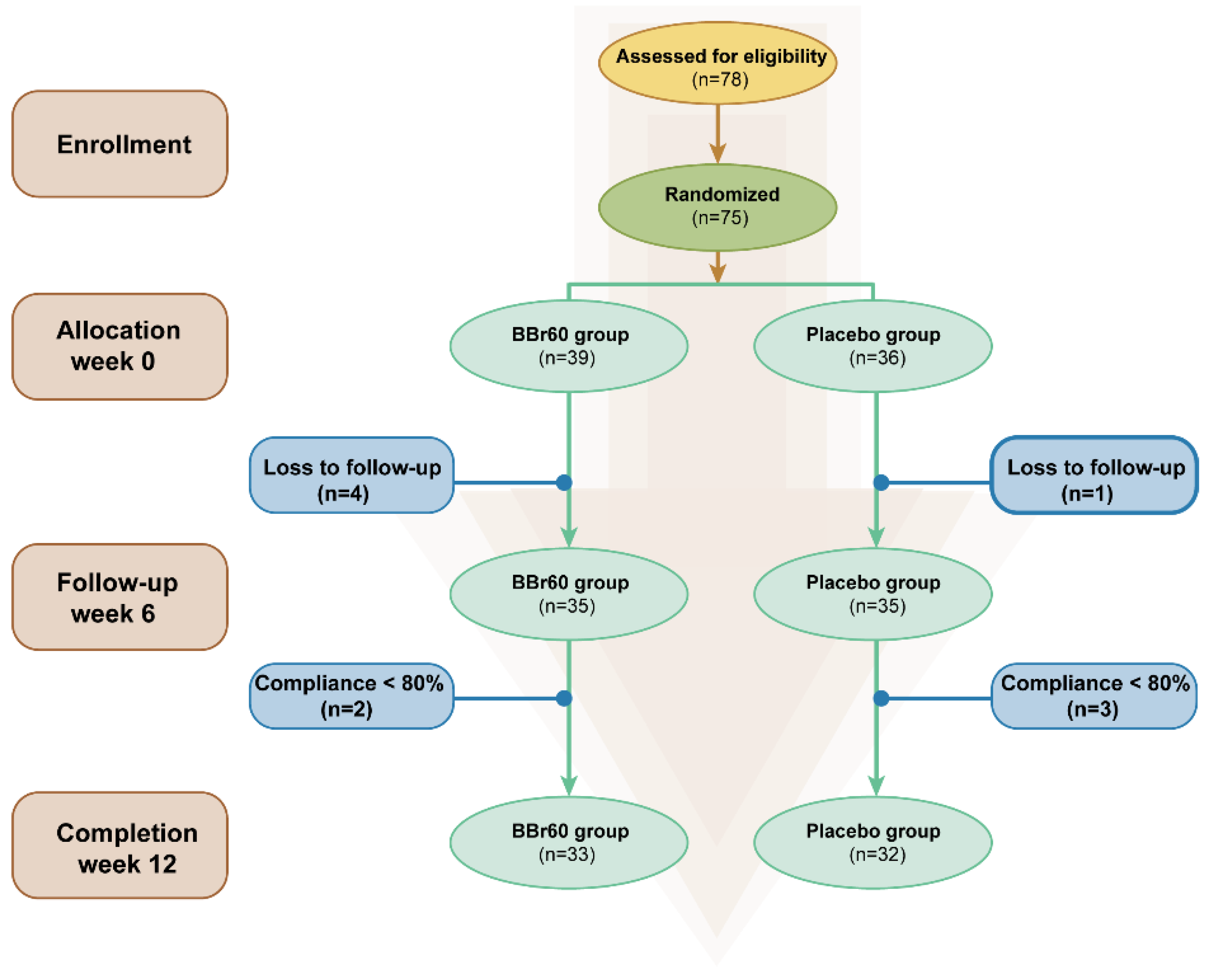
2.2. Study Design and Population
2.3. Sample Size and Randomization
2.4. Primary Outcome and Secondary Outcomes
2.5. Assessment of Body Composition
2.6. Blood Sample Collection and Biochemical Measurements
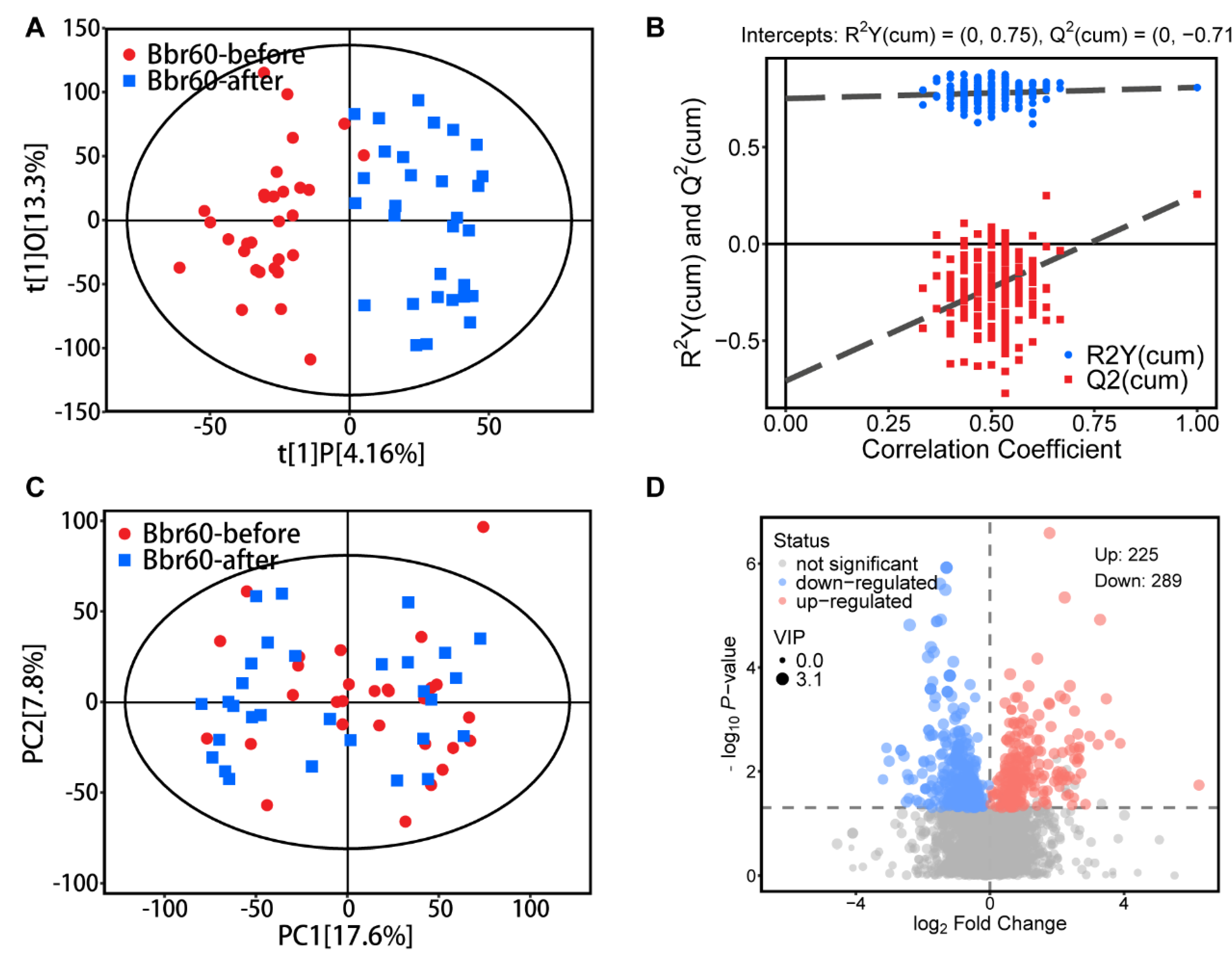
2.7. Serum and Fecal Metabolomic Analysis
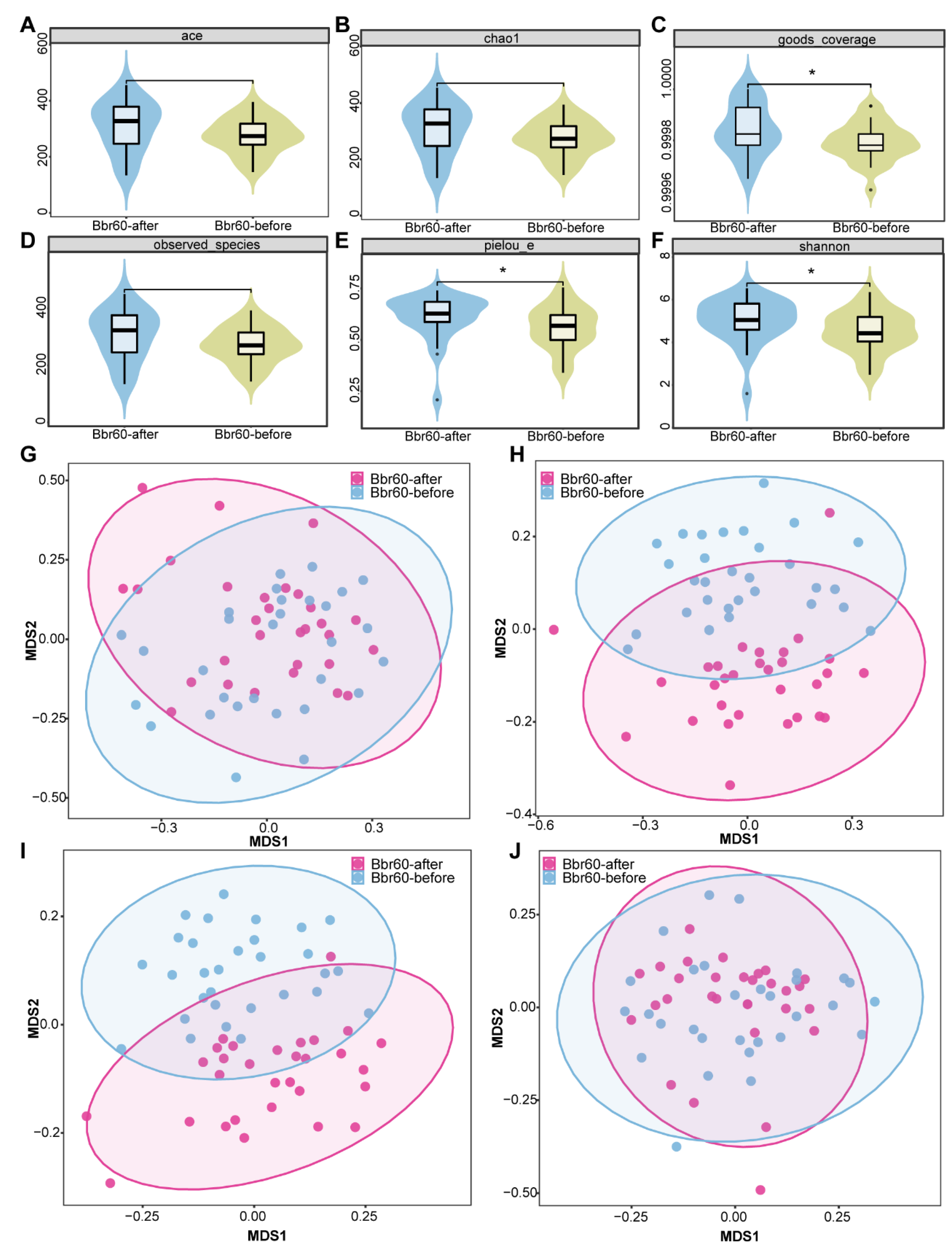
2.8. Gut Microbiota Analysis
2.9. Safety Monitoring
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Baseline Characteristics
3.2. Primary Outcome
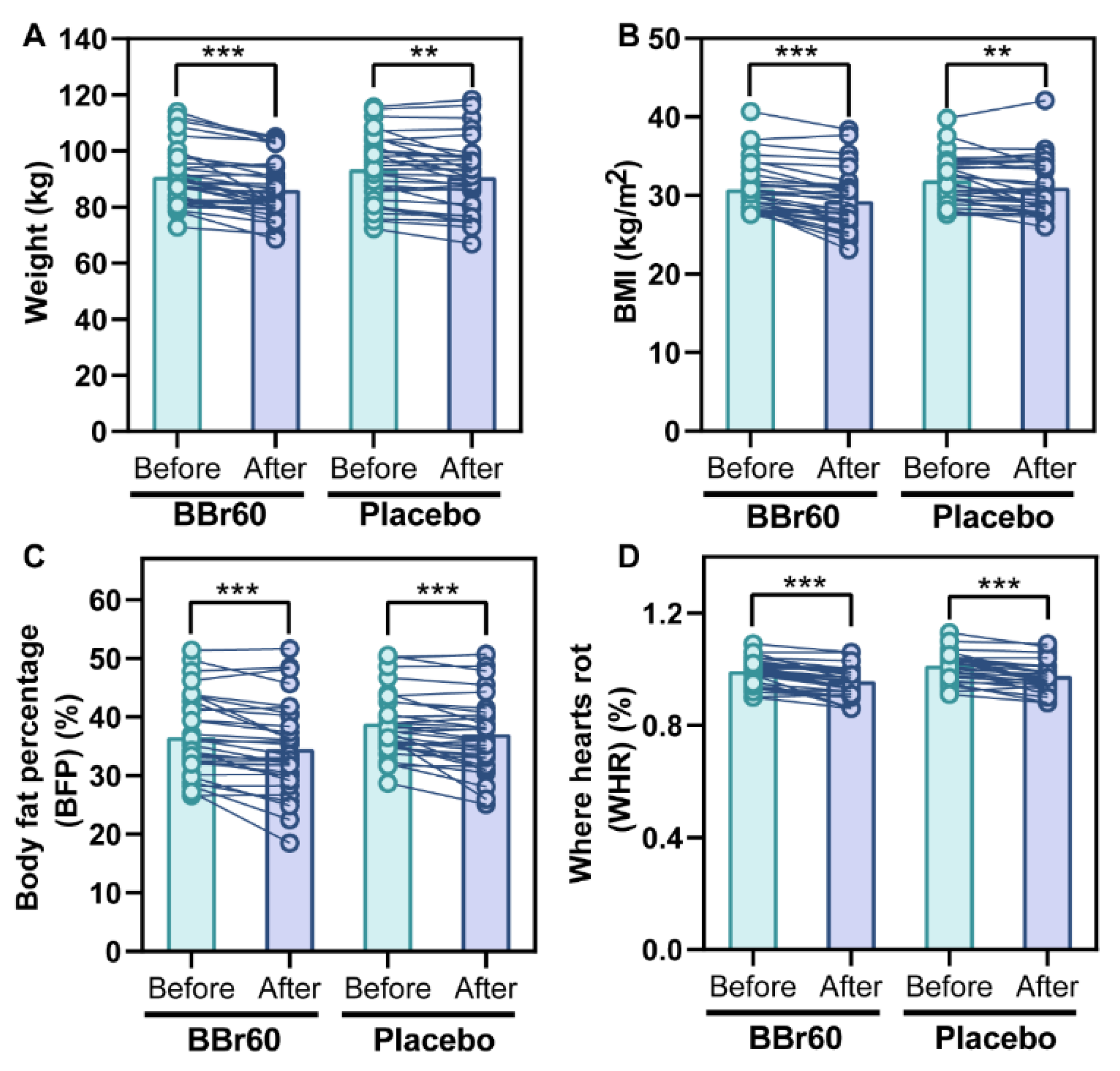
Efficacy of BBr60 on Weight and BMI
3.3. Secondary Outcomes
Efficacy of BBr60 on BFP and WHR
Efficacy of BBr60 on Blood Glucose and Lipid
Efficacy of BBr60 on Liver Function and Renal Function
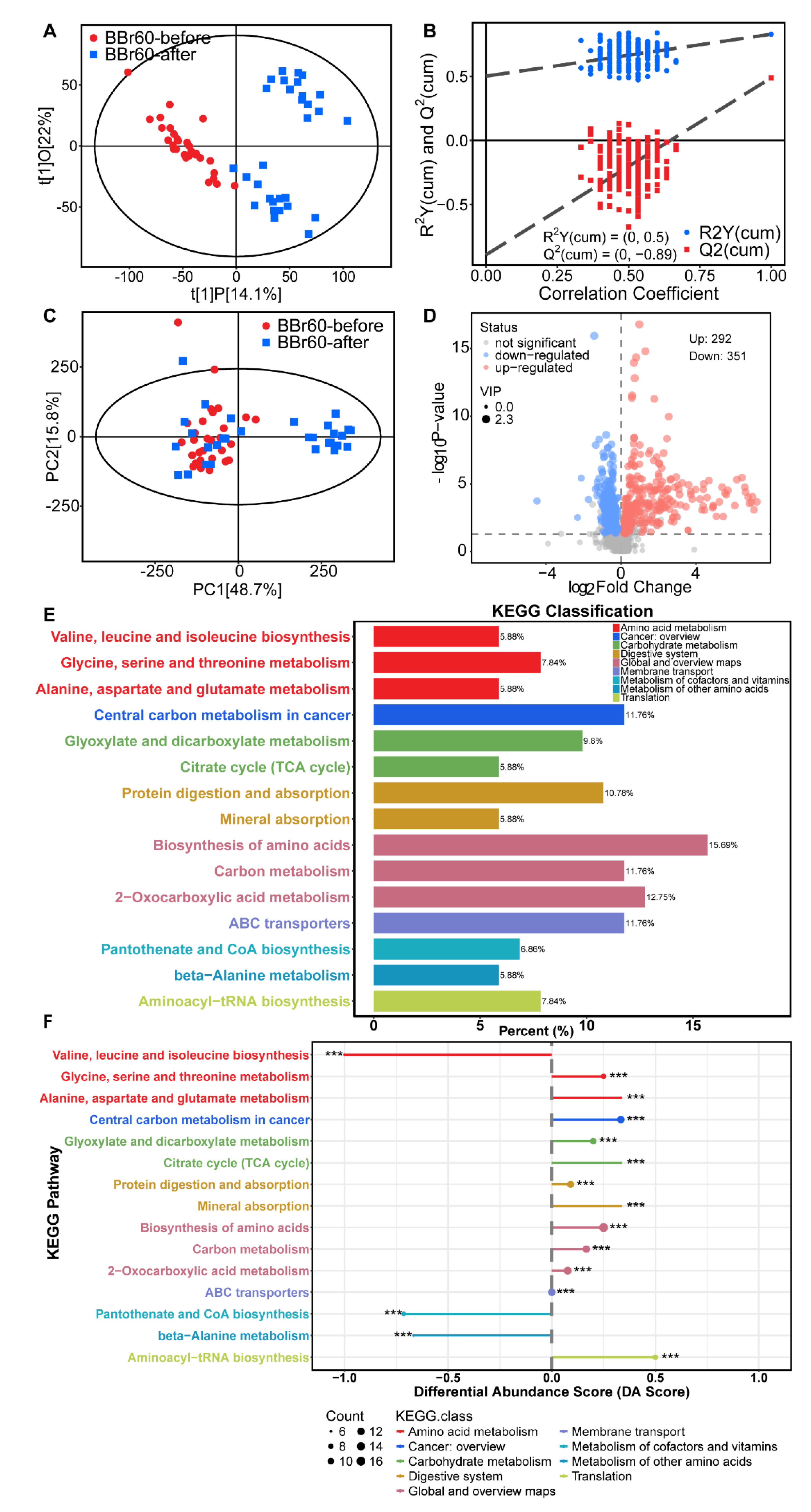
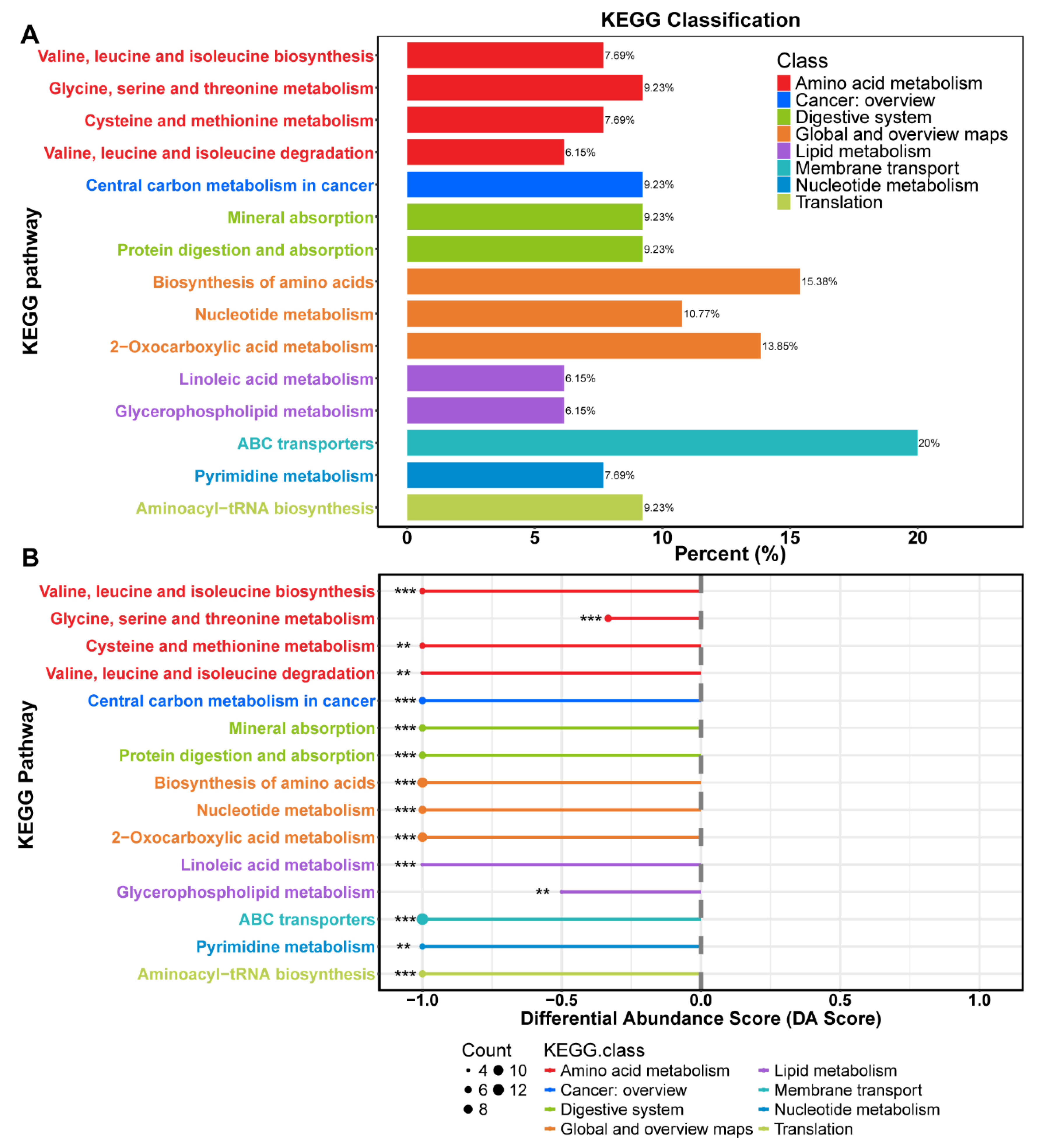
Efficacy of BBr60 on Metabolic Pathway
Alteration of Serum Metabolism after 12 Weeks of BBr60 Intervention
Alteration of Fecal Metabolism after 12 Weeks of BBr60 Intervention
| Variables | BBr60 (n=33) | Placebo (n=32) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before (0 week) |
After (12 week) |
p-Value | Before (0 week) |
After (12 week) |
p-Value | ||
| TP, g/L | 74.45±9.70 | 72.85±3.70 | 0.601 | 72.47±3.46 | 73.19±3.39 | 0.404 | 0.701 |
| ALB, g/L | 47.76±3.93 | 50.09±3.18 | 0.0003 | 47.41±3.07 | 49.31±2.01 | 0.0058 | 0.2037 |
| GLB, g/L | 26.70±7.28 | 22.76±3.85 | 0.0089 | 25.06±3.05 | 23.94±2.96 | 0.0499 | 0.170 |
| ALT, IU/L | 39.27±26.55 | 26.03±17.13 | <0.0001 | 41.53±21.84 | 27.22±15.69 | <0.0001 | 0.631 |
| AST, IU/L | 61.18±58.70 | 38.27±17.75 | 0.0002 | 49.56±17.88 | 39.59±17.49 | 0.0089 | 0.636 |
| BUN, mg/dL | 4.48±1.24 | 4.19±0.83 | 0.219 | 4.65±1.26 | 4.73±1.24 | 0.418 | 0.093 |
Efficacy of BBr60 on Gut Microbiota
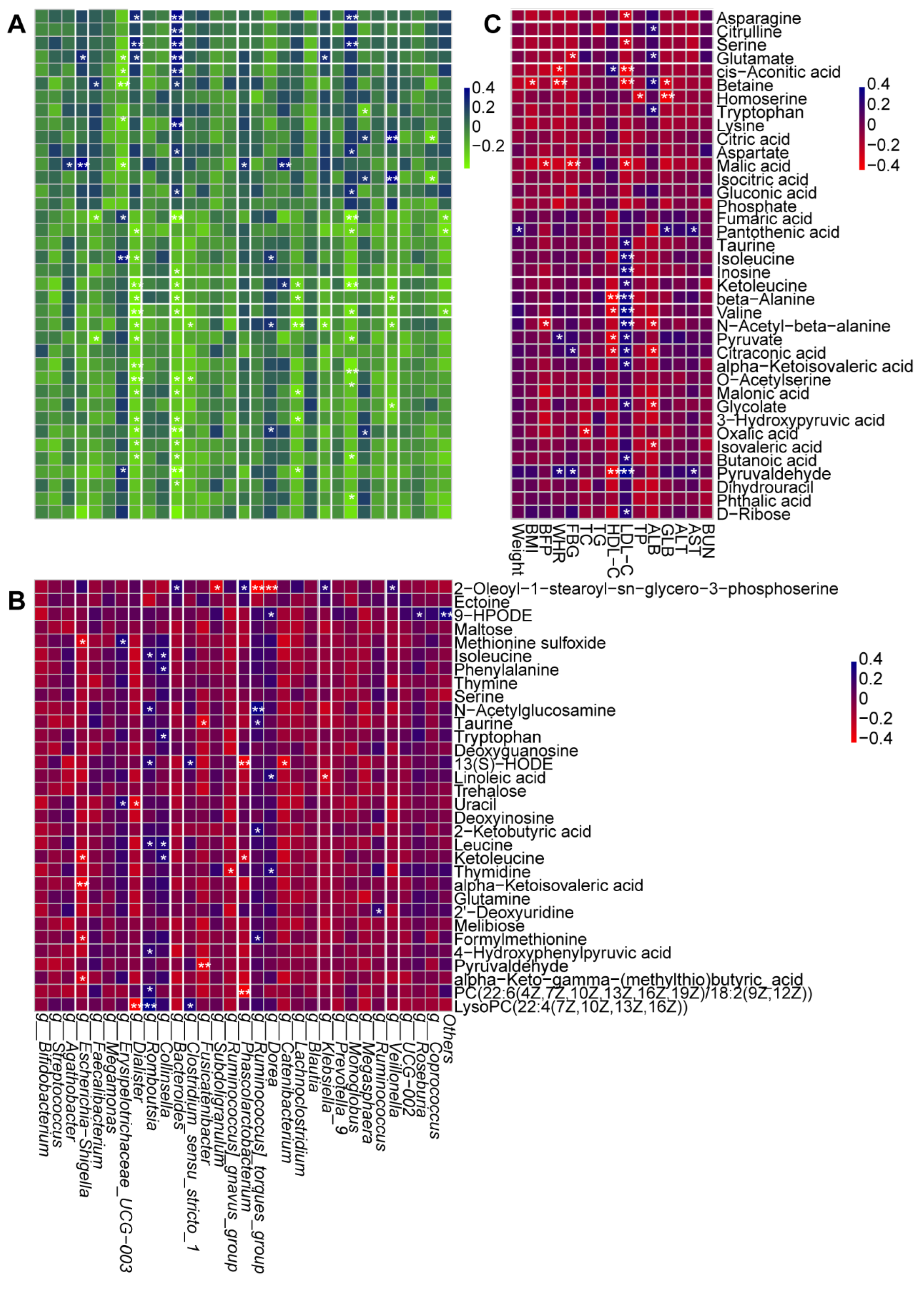
3.4. Correlation Analysis
3.5. Safety and Tolerability
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Funding
Authors’ contributions
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Competing interests
Data Share Statement
Abbreviations
References
- Zhao, Z.; Zhen, S.; Yan, Y.; Liu, N.; Ding, D.; Kong, J. Association of dietary patterns with general and central obesity among Chinese adults: a longitudinal population-based study. BMC Public Heal. 2023, 23, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- World Health Organization. Obesity and Overweight. Available online: http://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. (accessed on 16 July 2021).
- Chen, Y.; Peng, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zheng, S.; Wang, Y.; Lu, W. The prevalence and increasing trends of overweight, general obesity, and abdominal obesity among Chinese adults: a repeated cross-sectional study. BMC Public Heal. 2019, 19, 1–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Château-Degat, M.-L.; Dewailly, E.; Charbonneau, G.; Laouan-Sidi, E.A.; Tremblay, A.; Egeland, G.M. Obesity risks: towards an emerging Inuit pattern. Int. J. Circumpolar Heal. 2011, 70, 166–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rezgui, R.; Walia, R.; Sharma, J.; Sidhu, D.; Alshagadali, K.; Chaudhuri, S.R.; Saeed, A.; Dey, P. Chemically Defined Lactobacillus plantarum Cell-Free Metabolites Demonstrate Cytoprotection in HepG2 Cells through Nrf2-Dependent Mechanism. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sowah, S.A.; Milanese, A.; Schübel, R.; Wirbel, J.; Kartal, E.; Johnson, T.S.; Hirche, F.; Grafetstätter, M.; Nonnenmacher, T.; Kirsten, R.; et al. Calorie restriction improves metabolic state independently of gut microbiome composition: a randomized dietary intervention trial. Genome Med. 2022, 14, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chambers, E.S.; Preston, T.; Frost, G.; Morrison, D.J. Role of Gut Microbiota-Generated Short-Chain Fatty Acids in Metabolic and Cardiovascular Health. Curr. Nutr. Rep. 2018, 7, 198–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schugar, R.C.; Shih, D.M.; Warrier, M.; Helsley, R.N.; Burrows, A.; Ferguson, D.; Brown, A.L.; Gromovsky, A.D.; Heine, M.; Chatterjee, A.; et al. The TMAO-Producing Enzyme Flavin-Containing Monooxygenase 3 Regulates Obesity and the Beiging of White Adipose Tissue. Cell Rep. 2017, 19, 2451–2461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Yang, N.; Zan, M.; Zhang, L.; Ding, W. Potential novel biomarkers in small intestine for obesity/obesity resistance revealed by multi-omics analysis. Lipids Heal. Dis. 2022, 21, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamazaki, T.; Yamada, S.; Ohshio, K.; Sugamata, M.; Morita, Y. Lactobacillus paracasei KW3110 Prevents Inflammatory-Stress-Induced Mitochondrial Dysfunction in Mouse Macrophages. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ezzine, C.; Loison, L.; Montbrion, N.; Bôle-Feysot, C.; Déchelotte, P.; Coëffier, M.; Ribet, D. Fatty acids produced by the gut microbiota dampen host inflammatory responses by modulating intestinal SUMOylation. Gut Microbes 2022, 14, 2108280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, R.; Hong, J.; Xu, X.; Feng, Q.; Zhang, D.; Gu, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhao, S.; Liu, W.; Wang, X.; et al. Gut microbiome and serum metabolome alterations in obesity and after weight-loss intervention. Nat. Med. 2017, 23, 859–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ley, R.E., et al., Microbial ecology: human gut microbes associated with obesity. Nature 2006. 444(7122): p. 1022-3.
- Sze, M.A.; Schloss, P.D. Looking for a Signal in the Noise: Revisiting Obesity and the Microbiome. mBio 2016, 7, e01018-16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santacruz, A.; Collado, M.C.; García-Valdés, L.; Segura, M.T.; Martín-Lagos, J.A.; Anjos, T.; Martí-Romero, M.; Lopez, R.M.; Florido, J.; Campoy, C.; et al. Gut microbiota composition is associated with body weight, weight gain and biochemical parameters in pregnant women. Br. J. Nutr. 2010, 104, 83–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaźmierczak-Siedlecka, K., et al., Next-generation probiotics - do they open new therapeutic strategies for cancer patients? Gut Microbes 2022. 14(1): p. 2035659.
- Gomaa, E.Z. Human gut microbiota/microbiome in health and diseases: a review. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2020, 113, 2019–2040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suez, J.; Zmora, N.; Segal, E.; Elinav, E. The pros, cons, and many unknowns of probiotics. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 716–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McFarland, L.V.; Evans, C.T.; Goldstein, E.J.C. Strain-Specificity and Disease-Specificity of Probiotic Efficacy: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. (Lausanne) 2018, 5, 124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben Othman, M.; Sakamoto, K. Effect of inactivated Bifidobacterium longum intake on obese diabetes model mice (TSOD). Food Res. Int. 2020, 129, 108792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, N.; Yang, C.; Liang, X.; Cao, K.; Xie, J.; Luo, Q.; Luo, H. Mesoporous silica nanoparticle-encapsulated Bifidobacterium attenuates brain Aβ burden and improves olfactory dysfunction of APP/PS1 mice by nasal delivery. J. Nanobiotechnology 2022, 20, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.-Y.; Qiu, H.-M.; Yang, Y.; Han, Y.-Y. Analysis of risk factors for carotid intima-media thickness in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Western China assessed by logistic regression combined with a decision tree model. Diabetol. Metab. Syndr. 2020, 12, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruby, A.; Hu, F.B. The Epidemiology of Obesity: A Big Picture. PharmacoEconomics 2014, 33, 673–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, B.; Bai, Y.; Tong, F.; Yan, J.; Zhang, R.; Zhong, Y.; Tan, H.; Ma, X. Glycoursodeoxycholic acid regulates bile acids level and alters gut microbiota and glycolipid metabolism to attenuate diabetes. Gut Microbes 2023, 15, 2192155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chang, C.-J.; Lin, C.-S.; Lu, C.-C.; Martel, J.; Ko, Y.-F.; Ojcius, D.M.; Tseng, S.-F.; Wu, T.-R.; Chen, Y.-Y.M.; Young, J.D.; et al. Ganoderma lucidum reduces obesity in mice by modulating the composition of the gut microbiota. Nat. Commun. 2015, 6, 7489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, N.Y.; Shin, M.J.; Youn, G.S.; Yoon, S.J.; Choi, Y.R.; Kim, H.S.; Gupta, H.; Han, S.H.; Kim, B.K.; Lee, D.Y.; et al. Lactobacillus attenuates progression of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by lowering cholesterol and steatosis. Clin. Mol. Hepatol. 2021, 27, 110–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharifi-Rad, J.; Rodrigues, C.F.; Stojanović-Radić, Z.; Dimitrijević, M.; Aleksić, A.; Neffe-Skocińska, K.; Zielińska, D.; Kołożyn-Krajewska, D.; Salehi, B.; Prabu, S.M.; et al. Probiotics: Versatile Bioactive Components in Promoting Human Health. Medicina 2020, 56, 433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gong, H.; Gao, H.; Ren, Q.; He, J. The abundance of bifidobacterium in relation to visceral obesity and serum uric acid. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Engevik, M.A.; Luk, B.; Chang-Graham, A.L.; Hall, A.; Herrmann, B.; Ruan, W.; Endres, B.T.; Shi, Z.; Garey, K.W.; Hyser, J.M.; et al. Bifidobacterium dentium Fortifies the Intestinal Mucus Layer via Autophagy and Calcium Signaling Pathways. mBio 2019, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rustanti, N.; Murdiati, A.; Juffrie, M.; Rahayu, E.S. Effect of Probiotic Lactobacillus plantarum Dad-13 on Metabolic Profiles and Gut Microbiota in Type 2 Diabetic Women: A Randomized Double-Blind Controlled Trial. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 1806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riveros, N.F.H.; García-Corredor, L.; Martínez-Solare, M.; González-Clavijo, A. Effect of Bifidobacterium Intake on Body Weight and Body Fat in Overweight and Obese Adult Subjects: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. J. Am. Nutr. Assoc. 2024, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borgeraas, H., et al., Effects of probiotics on body weight, body mass index, fat mass and fat percentage in subjects with overweight or obesity: a systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Obes Rev 2018. 19(2): p. 219-232.
- Minami, J.; Iwabuchi, N.; Tanaka, M.; Yamauchi, K.; Xiao, J.-Z.; Abe, F.; Sakane, N. Effects of Bifidobacterium breve B-3 on body fat reductions in pre-obese adults: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Biosci. Microbiota, Food Health 2018, 37, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dixon, A.E.; Subramanian, M.; DeSarno, M.; Black, K.; Lane, L.; Holguin, F. A pilot randomized controlled trial of pioglitazone for the treatment of poorly controlled asthma in obesity. Respir. Res. 2015, 16, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.K., et al., Body Fat Reduction Effect of Bifidobacterium breve B-3: A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo Comparative Clinical Trial. Nutrients 2023. 15(1): p. 28.
- Agius, R.; Pace, N.P.; Fava, S. Reduced leukocyte mitochondrial copy number in metabolic syndrome and metabolically healthy obesity. Front. Endocrinol. 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tiderencel, K.A.; Hutcheon, D.A.; Ziegler, J. Probiotics for the treatment of type 2 diabetes: A review of randomized controlled trials. Diabetes/Metabolism Res. Rev. 2019, 36, e3213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaiyasut, C.; Sivamaruthi, B.S.; Lailerd, N.; Sirilun, S.; Thangaleela, S.; Khongtan, S.; Bharathi, M.; Kesika, P.; Saelee, M.; Choeisoongnern, T.; et al. Influence of Bifidobacterium breve on the Glycaemic Control, Lipid Profile and Microbiome of Type 2 Diabetic Subjects: A Preliminary Randomized Clinical Trial. Pharmaceuticals 2023, 16, 695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, N.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; Druart, C.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Cani, P.D.; Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.d.L.; Delzenne, N.M. Functional Effects of EPS-Producing Bifidobacterium Administration on Energy Metabolic Alterations of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, H.; Liu, Q.; Hu, H.; Jiang, Y.; Shao, W.; Wang, Q.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, A. Berberine ameliorates blockade of autophagic flux in the liver by regulating cholesterol metabolism and inhibiting COX2-prostaglandin synthesis. Cell Death Dis. 2018, 9, 824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyu, M.; Su, C.-C.; Miyagi, M.; Yu, E.W. Simultaneous solving high-resolution structures of various enzymes from human kidney microsomes. Life Sci. Alliance 2022, 6, e202201580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pi-Sunyer, F.X., Health implications of obesity. The American Journal of Clinical Nutrition 1991. 53(6): p. 1595S-1603S.
- Song, Q.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Wei, H.; Liang, W.; Zhou, Y.; Ding, Y.; Ji, F.; Cheung, A.H.-K.; Wong, N.; et al. Bifidobacterium pseudolongum-generated acetate suppresses non-alcoholic fatty liver disease-associated hepatocellular carcinoma. J. Hepatol. 2023, 79, 1352–1365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, P.J.; Lapworth, A.L.; An, J.; Wang, L.; McGarrah, R.W.; Stevens, R.D.; Ilkayeva, O.; George, T.; Muehlbauer, M.J.; Bain, J.R.; et al. Branched-chain amino acid restriction in Zucker-fatty rats improves muscle insulin sensitivity by enhancing efficiency of fatty acid oxidation and acyl-glycine export. Mol. Metab. 2016, 5, 538–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colom-Pellicer, M.; Rodríguez, R.M.; Soliz-Rueda, J.R.; de Assis, L.V.M.; Navarro-Masip, .; Quesada-Vázquez, S.; Escoté, X.; Oster, H.; Mulero, M.; Aragonès, G. Proanthocyanidins Restore the Metabolic Diurnal Rhythm of Subcutaneous White Adipose Tissue According to Time-Of-Day Consumption. Nutrients 2022, 14, 2246. [CrossRef]
- Guo, M., et al., Lactobacillus rhamnosus GG ameliorates osteoporosis in ovariectomized rats by regulating the Th17/Treg balance and gut microbiota structure. Gut Microbes 2023. 15(1): p. 2190304.
- He, H. , et al., Arabinogalactan, Bifidobacterium longum, and Faecalibacterium prausnitzii improve insulin resistance in high-fat diet-induced C57BL/6J mice. eFood 2022. 3(1-2): p. e1.
- Desbonnet, L.; Garrett, L.; Clarke, G.; Bienenstock, J.; Dinan, T.G. The probiotic Bifidobacteria infantis: An assessment of potential antidepressant properties in the rat. J. Psychiatr. Res. 2008, 43, 164–174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vallianou, N.; Stratigou, T.; Christodoulatos, G.S.; Tsigalou, C.; Dalamaga, M. Probiotics, Prebiotics, Synbiotics, Postbiotics, and Obesity: Current Evidence, Controversies, and Perspectives. Curr. Obes. Rep. 2020, 9, 179–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salazar, N.; Neyrinck, A.M.; Bindels, L.B.; Druart, C.; Ruas-Madiedo, P.; Cani, P.D.; Reyes-Gavilán, C.G.d.L.; Delzenne, N.M. Functional Effects of EPS-Producing Bifidobacterium Administration on Energy Metabolic Alterations of Diet-Induced Obese Mice. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 1809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Z. and V.B. Kraus, Does lipopolysaccharide-mediated inflammation have a role in OA? Nat Rev Rheumatol 2016. 12(2): p. 123-9.
- Jeon, M.S.; Choi, Y.Y.; Mo, S.J.; Ha, J.H.; Lee, Y.S.; Lee, H.U.; Park, S.D.; Shim, J.-J.; Lee, J.-L.; Chung, B.G. Contributions of the microbiome to intestinal inflammation in a gut-on-a-chip. Nano Converg. 2022, 9, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, Y.; Han, X.; Fang, J.; Jiang, H. Role of dietary amino acids and microbial metabolites in the regulation of pig intestinal health. Anim. Nutr. 2021, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hooper, L.V.; Wong, M.H.; Thelin, A.; Hansson, L.; Falk, P.G.; Gordon, J.I. Molecular Analysis of Commensal Host-Microbial Relationships in the Intestine. Science 2001, 291, 881–884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Project | Unit | BBr60 (33) | Placebo (32) | P value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Woman | - | 24 (72.7%) | 19 (59.4%) | 0.255 |
| Man | - | 9 (27.3%) | 13 (40.6%) | |
| Age | year | 27.88±8.65 | 30.38±8.45 | 0.150 |
| Weight | kg | 90.86 ± 10.45 | 93.56 ± 12.04 | 0.251 |
| BMI | kg/m2 | 30.80 ± 3.21 | 31.96 ± 2.95 | 0.068 |
| FP | % | 36.57 ± 6.77 | 38.91 ± 5.69 | 0.203 |
| WHR | % | 0.99 ± 0.05 | 1.01 ± 0.05 | 0.500 |
| FBG | mg/dL | 6.27±0.87 | 5.87±0.45 | 0.120 |
| TC | mg/dL | 4.31±0.90 | 4.82±0.94 | 0.058 |
| TG | mg/dL | 2.13±1.78 | 1.62±0.71 | 0.345 |
| HDL-C | mg/dL | 1.15±0.27 | 1.29±0.31 | 0.484 |
| LDL-C | mg/dL | 2.26±0.63 | 2.62±0.62 | 0.970 |
| ALT | IU/L | 39.27±26.55 | 41.53±21.84 | 0.618 |
| AST | IU/L | 61.18±58.70 | 49.56±17.88 | 0.969 |
| TP | g/L | 74.45±9.70 | 72.47±3.46 | 0.787 |
| ALB | g/L | 47.76±3.93 | 47.41±3.07 | 0.905 |
| GLB | g/L | 26.70±7.28 | 25.06±3.05 | 0.697 |
| A/G | - | 1.90±0.41 | 1.92±0.29 | 0.273 |
| TB | mg/dL | 13.58±6.58 | 17.38±14.83 | 0.453 |
| BUN | mg/dL | 4.48±1.24 | 4.65±1.26 | 0.846 |
| UA | mg/dL | 427.09±76.69 | 433.59±103.49 | 0.069 |
| CRE | mg/dL | 76.48±14.80 | 71.16±15.77 | 0.543 |
| Variables | BBr60 (n=33) | Placebo (n=32) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before (0 week) |
After (12 week) |
p-Value | Before (0 week) |
After (12 week) |
p-Value | ||
| Weight (kg) | 90.86±10.45 | 86.19±9.82 | <0.0001 | 93.56±12.04 | 90.74±12.77 | 0.0006 | 0.114 |
| Weight (12-0 week) | -4.67±4.40 | -2.82±4.17 | 0.047 | ||||
| BMI (kg/m²) | 30.80±3.21 | 29.32±3.63 | <0.0001 | 31.96±2.95 | 31.03±3.49 | 0.0019 | 0.057 |
| BMI (12-0 week) | -1.49±1.37 | -0.93±1.55 | 0.135 | ||||
| BFP (%) | 36.57±6.77 | 34.54±7.50 | <0.0001 | 38.91±5.69 | 37.11±6.70 | 0.0003 | 0.150 |
| BFP (12-0 week) | -2.03±2.54 | -1.80±2.47 | 0.684 | ||||
| WHR (%) | 0.99±0.05 | 0.96±0.04 | <0.0001 | 1.01±0.05 | 0.98±0.05 | <0.0001 | 0.149 |
| WHR (12-0 week) | -0.036±0.03 | -0.038±0.03 | 0.821 | ||||
| Variables | BBr60 (n=33) | Placebo (n=32) | p-Value | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Before (0 week) |
After (12 week) |
p-Value | Before (0 week) |
After (12 week) |
p-Value | ||
| FBG, mg/dL | 5.87±0.45 | 5.26±0.57 | <0.0001 | 6.27±0.87 | 5.69±0.86 | <0.0001 | 0.0381 |
| TC, mg/dL | 4.31±0.90 | 4.38±0.75 | 0.618 | 4.82±0.94 | 4.55±0.90 | 0.0058 | 0.4181 |
| TG, mg/dL | 2.13±1.78 | 1.98±1.12 | 0.8566 | 1.62±0.71 | 2.09±1.34 | 0.0984 | 0.9870 |
| HDL-C, mg/dL | 1.15±0.27 | 1.45±0.28 | <0.0001 | 1.29±0.31 | 1.47±0.26 | 0.0071 | 0.7589 |
| LDL-C, mg/dL | 2.26±0.63 | 1.44±0.52 | <0.0001 | 2.62±0.62 | 1.57±0.53 | <0.0001 | 0.3483 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





