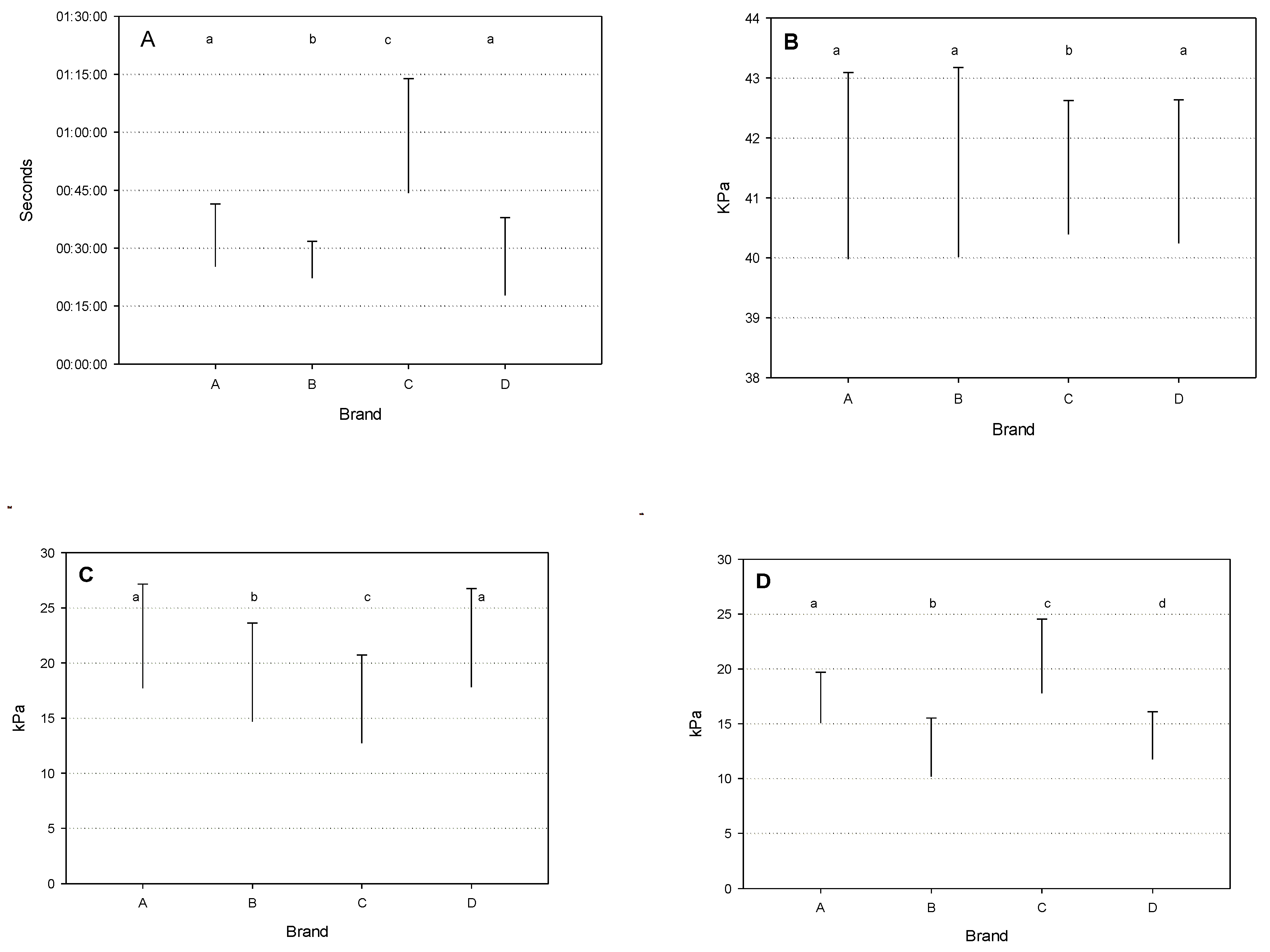1. Introduction
Automatic Milking Systems (AMS) are significantly transforming the dairy sector and are either currently prevalent or soon will be in many countries compared to traditional milking methods [
1]. AMS enhance herd efficiency, primarily through increased yield per cow and reduced labor costs. Additionally, they positively impact both human and animal behavior and welfare [
2,
3,
4,
5].
This technology allows to have a fully automatized milking process by udder quarter. Obviously, different manufacturers developed different technologies to perform all the milking procedures, with potentially different outcomes, for what concern mainly the performances and the effects on udder health [
1].
Milking represents one of the most important phases in milk production and therefore it is essential that the milker, the cow, and the machine are harmonized with each other. Indeed, the milking system can play a predisposing role in determining the development of mastitis, both due to action on the teats and as an active vehicle for the entry of pathogens into the udder [
2,
3,
4], on the other hand the manual operations of milking routine have a notable importance for the correct, quick and efficient emission of milk, and for keeping an appropriate hygiene [
5,
6,
7,
8,
9,
10]. Indeed, in conventional milking, for what concern the milk emission, the role of the individual milker [
11,
12,
13] is generally as strong as the role of the milking machine. Among the positive outcomes of the application of AMS, one of the most important is the standardization of the milking procedure from cleaning, through stimulation to the post-milking teat disinfection. The standardization of the milking procedure is different based on the equipment and manufacturer, although all of them do not require a human intervention, thus dramatically reducing the potential negative effects of the milker. However, the effects related to the machine components and settings still exist applying AMS, and they may affect both milk quality and udder health [
14,
15].
The AMS like the conventional milking machine, interact with cows with different genetic, anatomical, physiological and productive characteristics, with similar effects as conventional milking, although potentially of lower amplitude [
14,
16,
17].
An increasing number of studies have focused on the application of AMS since its commercial introduction in the 1990s, and most of these studies concern herd management, milk yield and quality, animal behavior, health and welfare, performance, and labor efficiency [
2,
4,
6,
7]. However, to the best of our knowledge, some aspects related to milk emission parameters (e.g. overmilking, vacuum fluctuations, bimodality) and the comparison between different AMS have not been generally considered in the current scientific literature [
18,
19].
The performance of the milking machine during milking, in both conventional and automated systems, can be evaluated using new generation flowmeters (dynamic testing). These procedures are currently applied to the dairy herds belonging to the Regional Association of Lombardy (ARAL) and to any dairy herd that requests this service. The availability of the data from these tests on AMS of different manufacturers and herds allowed to design a retrospective study aimed at describing and comparing the main parameters of milk emission for the different AMS manufacturers and the possible presence of factors associated with mastitis risk, as defined for conventional milking systems [
5,
20].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Herds and AMS
All the 776 herds with associated to the Regional Breeder Association of Lombardy (ARAL), having one or more AMS, and that received the dynamic testing during the year 2023 were considered. The characteristics of AMS present in Lombardy herds were summarized in
Table 1. Among the six distinct brands, only four had at least 400 quarter dynamic test results, therefore only these latter ones were furthermore considered in the statistical analysis.
2.2. Milking Dynamic Control
The Milking Control Service (SCM) provided by ARAL includes periodic inspection of the milking system and its components, through mechanical tests and flow meter measurements as required by the ISO 3918-5707-6690- UNI 11008 and ICAR standards.
Dynamic control involves checking the system and the routine during milking, with the aim of identifying the critical points of the process and with the analysis of the measurements and recorded data, providing indications and operational solutions to improve milking efficiency. The availability of new portable digital vacuum logger (VaDia™; Biocontrol, Rakkestad, NO) allows to assess the milking process at quarter level, a feature essential when AMS are involved.
Indeed, VaDia™ logger presents four vacuum recording channels, allowing to record the vacuum dynamics in four distinct points of the milking unit. Vacuum recordings were performed continuously from unit attachment until the units were removed. All vacuum recordings were downloaded to a computer and analyzed with the VaDia Suite™ software (Biocontrol, Rakkestad, Norway). The graphic analysis of the vacuum recordings performed by the software under the supervision of the ARAL milking specialist allows to identify several parameters which were described in
Table 2, following producers definition.
Among the several parameters available, we selected the ones that, in our opinion, better describe milking performance: milking duration (MD; min); milk let down (MLD, sec); average milk flow (AMG; L/min); mean vacuum during milking (MVT, kPa); mean vacuum at peak (MVP, kPa). Moreover, parameters related to mastitis risks were also considered: overmilking (OMD, sec); mean overmilking vacuum (MOV, kPa); mouthpiece chamber vacuum (MPC, kPa); delta vacuum fluctuations (DVF, kPa; measured by the difference between maximum and minimum vacuum level observed during the single milking); bimodality (BIM, N), and irregular vacuum fluctuations (IVC, N).
2.2. Data Recording and Statistical Analysis
Data were collected in a database with Excel™ (Microsoft USA), and the statistical analyses were performed using the appropriate procedures of SPSS 29.0.1 (IBM Corp, USA).
Milk quality data were analyzed by a generalized linear model as follows:
where Y = dependent variables (milking parameters); µ = general mean; Bj = effect of brand (j = A,B,C,D); Mk = effect of milk yield (j = <2.5 L; 2.6-3.5 L; 3.6-4.5 L; >4.5 L).
The association between bimodality or irregular vacuum fluctuation with brand and milk yield was assessed using a binomial logistic regression model.
3. Results
3.1. Data Description
A total of 4878 dynamic tests of single quarter milkings were performed on cows from 48 different dairy herds. For the purpose of this study, only AMS with at least 400 useful recordings were considered. Therefore, only four of the six different AMS brands available in Lombardy were considered.
The analysis of the frequency of the different brands and milk yield showed significant differences (
Table 3). Brand A had a low frequency of records in low yielding quarters, significantly different from the frequencies observed for all the other yield classes. The records in the highest yield class had the highest frequency among all the other classes. Brand B showed a linear distribution of the records among the yield classes, but the frequency of the lowest yield class was significantly higher than the other classes. Brand C showed a trend with a consistent and significant increase of the frequencies as milk yield increased. Brand D had the highest frequency of records in the <2.50 Kg class among all brands, and it was significantly different from all the other yield classes.
3.2. Main Milking Parameters
The results of the analysis of the influence of the brand, milk yield and their interaction on the variance of the main milking parameters were reported in
Table 4. The results showed that all the factors considered, except milk yield for MLD, had a significant influence on the variability of the factors considered. The models showed a R
2 in the range of 20-30%, except for MLD, suggesting, as expected, an important influence of AMS on the milking emission curves.
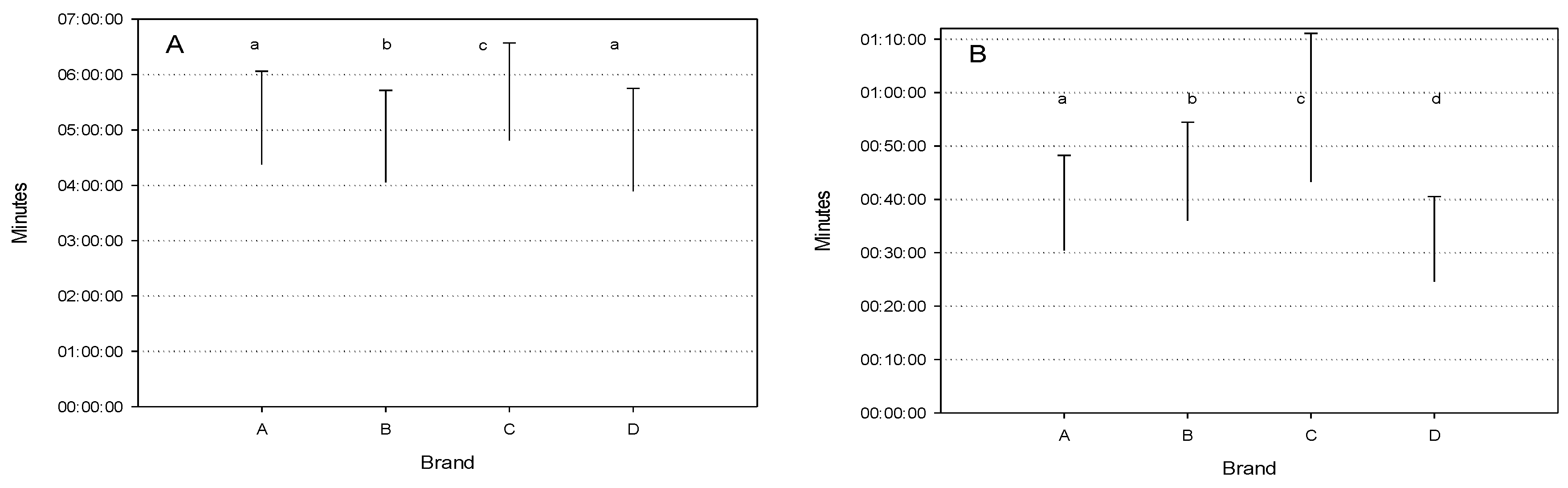
Figure 1 describes the mean values of the five factors considered classified by brand. The means for MLD and for MVP were always significantly different among brands, with significant differences mainly between brand C and D when compared to the other two brands. For all the other parameters the differences among the brands were numerically less evident, but it should be noted that MD was significantly longer for brand C, which is probably associated to the longer MLD time.
The GLM analysis of the influence of the interaction of milk yield and brand was reported in
Table 5. When considering the MD, as expected, an increasing trend was observed across milk yield and among all the brands, but significant differences were also observed among the brands within each yield class. In fact, brand D had the shortest MD among all the brands and yields. Similarly, the MLD time was shorter for brand D, but significant differences among brands were consistent only in the highest milk class. It should be noted that MLD time was shorter for brands A and D in the lowest yield classes, with an increasing trend for brand A, but not any other brands. This was confirmed by the mean MLD values in the different milk yield classes, which showed that the increasing trend in the mean values was not as great as for MD. These results suggest that the interaction of the AMS with the cows and the teat stimulation process play an important role, as also observed in conventional milking [
21].
As expected, average milk flow increased with increasing milk yield. Statistical differences were observed mainly in the highest yield classes, with the highest means for brands A and D. Although brands C had the longest MD and MLD, they also had the highest AMF, suggesting that a longer milking process, in this case, does not affect AMF.
Mean vacuum during milking and at peak flow were both in the acceptable range of 36.4-39.5 kPa. However, there were significant differences among brands and yield. Brand D had the highest values for both measurements with significant differences from the other brands. This result, which is associated with the shorter MD and MLD observed, suggests that the higher vacuum applied in these AMS results in a shortening of MD and MLD.
3.3. Parameters Associated with Mastitis Risk
The analysis of the factors influencing the variability of the four parameters that are considered as potential mastitis risk factors were summarized in
Table 6. Brand and its interaction with milk yield were always statistically significant and the corresponding GLM models showed relatively high R
2 for OMD and for DVF.
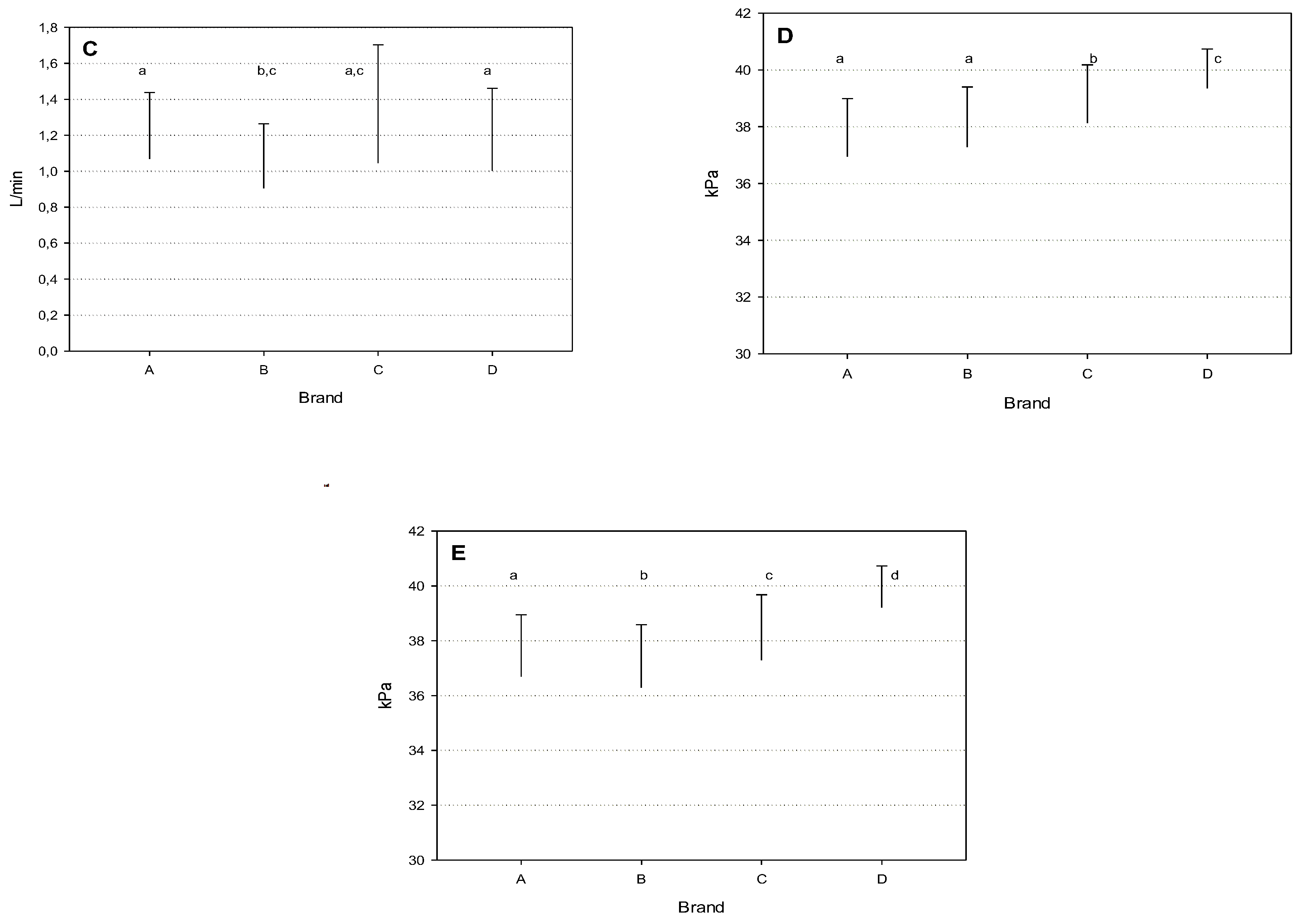
The OMD was significantly higher for brand C (
Figure 2, A), while it was very similar for the other brands, while the MOV was around 40 kPa for all the four brands, although a significantly higher mean value was observed for brand C (figure 2, B).
The AMS of the same brand showed a significantly lower vacuum level in the MPC (
Figure 2, C), while the DVF (
Figure 2, D) was significantly different among all the brands, with the lowest mean value for brand B and the highest for brand C.
The analysis of the interactions between brand and milk yield for the four parameters considered showed some interesting results (
Table 7). The OMD was significantly longer in the higher yield class. This result is probably influenced by the values observed for brand C AMS which had values almost double of those of the other brands. On the other hand, brand D AMS showed the shortest mean values, with a decreasing trend with increasing milk yield. This pattern was not observed for any of the other brands.
Mean vacuum during overmilking was not overly different among brands and milk yield classes, although some statistically significant differences can be observed. On the contrary, MPC were relatively similar among milk yield classes, but differed among brands, being particularly low for brand C VMS. In addition, MPC were higher for brands A and D, when compared to the other brands.
The greatest variation was observed for DVF, which was significantly different among brands and for all the yield classes. An increasing trend was observed among the milk yield classes with the highest level in the >4.5 Kg class. Overall, the lowest values were observed for brands B and D, with mean values significantly lower than those observed for brands A and D VMS.
3.4. Frequencies of Bimodality and Irregular Vacuum Fluctuations
The VaDia™ tools applied during milking also allow the assessment of two of the main risk factors for mastitis: bimodality and irregular vacuum fluctuations [
22,
23,
24,
25].
The patterns of BIM among brands and milk yield classes were shown in
Figure 3, while
Table 8 reports the results of the logistic regression analysis estimating the odds ratios for BIM based on brand and yield.
The overall trend showed that, as expected, the frequency of BIM decreases with increasing milk yield, and this observation was confirmed by statistical analysis with a significant protective (values <1) odds ratios when compared to the frequency of BIM with <2.5 Kg class. Large differences in the frequency of bimodality were observed among brands, with apparently lower values for brand A when compared to the other brands. However, statistical analysis did not confirm this observation.
Indeed, only in the case of brand D, a significant odd ratio was observed and its value <1 indicates that the risk of BIM for this latter brand is reduced when compared to brand A. This result supports previous observations on MLD, being the shortest among all the brands for all the milk yield classes.
The same analysis applied to IVF showed that AMS of brand C had the highest frequency with values close to 80%, while in all the other cases the values were around or below 40%. The statistical analysis showed that the odds ratio was <1 for all the yield classes >2.5 Kg, confirming previous observation on BIM. When the brands were considered, the results confirmed that the odds ratio for IVF was very high and significant for brand C, when compared to brand A, while it was below 1 when brands B and C were compared to brand A. This different pattern may be explained by previous observations on MLD, OMD, DVF values, which were always significantly higher for brand C VMS.
4. Discussion
The increasing use of AMS in many countries represents a true revolution in the dairy industry, with positive implications for cows, farmers and, more generally, the sustainability of dairy herds [
8,
26]. These tools have standardized several aspects of milking, avoiding problems related to the behavior and performance of the milker, but not those related to the interaction between the cow and the milking machine. In addition, the performance of AMS from different manufacturers may differ and should be considered when adopting this technology.
The evaluation of the performance of a milking machine, whether automated or conventional, has improved in recent years thanks to the availability of new electronic vacuum meters that allow the evaluation of the milking of individual quarters for many different parameters, which is crucial when AMS are involved.
The availability of these new test tools, and in particular VaDia™, within a standardized evaluation procedure, makes it possible to describe the performance of a milking machine at quarter level, to identify the presence of potential risk factors for milk quality and udder health, and to compare the different machines [
27].
The analysis of nearly 5,000 milkings from four different AMS used in 48 Italian dairy herds has undoubtedly revealed new and, in some cases, unexpected results. One of these results showed that milking performance is influenced by the milk yield of each quarter. As such, this result was expected based on previous studies [
14,
28], and the knowledge based on conventional milking [
16,
17]. However, the significant interaction of milk yield classes with the four different AMS brands suggests that the expected milk yield per milking is a variable that needs to be considered when choosing which technology to purchase or when defining the number of milkings allowed daily for each cow. In fact, lower milk yield/milking is associated to higher MVT and MVP levels and to AMG, but also with higher frequency of BIM. The latter condition is one of the best-known risk factors for teat injuries and mastitis [
27,
29,
30].
The differences among manufacturers were also statistically significant when MLD, and, consequently, the MD were considered. These differences were found to be large among AMS and could affect both the efficiency of the whole milking, delaying cow trafficking, but also cow welfare leaving several cows standing in waiting for a free AMS [
31]. The difference among AMS brands in MLD may be explained by the different system of quarter pre-milking preparation, milking vacuum, and by the teat cup detachment setting [
32,
33,
34], but also by other factors such as pulsation rates and liner characteristics, which were not considered in this study.
The differences observed in the main milking parameters were also reflected in the parameters considered to predispose to the development of mastitis. Overmilking was observed in all AMS, although with different amplitude and with significant differences between manufacturers, and even though milking is independent for each quarter. This result was unexpected because the teats are milked separately, reducing the effect of conventional milking where cluster detachment is regulated by the quarter that maintains sufficient milk flow to keep the cluster on [
35]. The differences among brands were also unexpected, but they are supported by the different values of the milking parameters (e.g. MD, MLD, DVF) that were correlated with the OVD.
However, the most unexpected result was the presence of high frequencies of two important factors for mastitis risk (bimodality and irregular vacuum fluctuations) [
5,
27]. The absence of human intervention during milking, the standardized milking procedure, the presence of a stimulation phase, albeit with different methods, led to expect that these two factors should be observed with very low frequencies. On the contrary, bimodality was observed with a frequency ranging from 5 to 32%, and 3 out of 4 brands showed frequencies > 15%, a level considered as critical [
27,
29], when milk yield was <3.5 Kg/milking. In fact, a decrease in odds ratio values was observed with increasing milk yield. This result supports the previous observation on the need to consider the quarter milk yield as a critical factor and suggest that the individual milking frequency should be defined based on the expected yield which should be at least > 3.5 Kg/milking, on quarter bases.
The pattern for IVF was even worse with frequencies ranging from 18-79%. In this case the frequencies and the odds ratios decreased as the yield increased. Moreover, the AMS brand showed a greater role compared to BIM, with one of the brands being significantly associated with the presence of IVF. It should also be noted that the overall frequencies of IVF were higher when compared to conventional milking systems, probably because AMS have a more complex milking system, which may introduce additional points of potential vacuum instability.
the results of one of the few studies to compare different brands of AMS using dynamic testing under real-life conditions. It highlights the importance of such testing for evaluating AMS performance in the field and indicates that both AMS and conventional milking systems may pose risks for teat damage and mastitis. The study should be complemented with follow-up research to further investigate the relationship between milking parameters observed during dynamic testing and the incidence of mastitis or teat injuries.
5. Conclusions
Automatic milking systems are increasingly replacing conventional milking methods. These systems offer several significant advantages, including enhanced milk production, improved human and animal welfare, and overall herd sustainability. The results of the study indicate substantial differences among various AMS, suggesting that comparisons should be based on field data collected with dynamic testing. Findings also revealed that AMS do not always resolve certain milking process issues linked to mastitis risk, such as overmilking and bimodality, which are commonly observed in conventional milking systems. Although numerous studies have been conducted on AMS, there remains a need for dynamic testing under field conditions to evaluate their performance, identify issues that can be resolved through machine fine-tuning, thus mitigating the risk of teat impairment and mastitis.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.Z., S.M. and V.C.G.; methodology, A.Z, V.S.,F:Z.; software, S.M., D.D., V.C.G.; formal analysis, A.Z.,V.S., F.Z.; investigation, S.M., D.D., V.C.G.; data curation, S.M, V.C.G.; writing—original draft preparation, A.Z.,V.S., F.Z.; writing—review and editing, A.Z.,S.M.,V.C.G.;. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data is unavailable due to privacy restrictions.
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the ARAL Servizio Controllo Mungitrici technicians involved.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Sharipov, D.R.; Yakimov, O.A.; Gainullina, M.K.; Kashaeva, A.R.; Kamaldinov, I.N.; Iop. Development of automatic milking systems and their classification. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Engineering Studies and Cooperation in Global Agricultural Production, Azov Black Sea Engn Inst Zernograd, Zernograd, RUSSIA, Aug 27-28, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Hamann, J.; Burvenich, C.; Bramley, A.J.; Osteras, O.; Woolford, M.; Woyke, M.; Haider, W.; Mayntz, M.; Ledu, J. Teat tissue reactions to machine milking and new infection risk. Bulletin of the International Dairy Federation 1994, 297, 1-43.
- Zecconi, A.; Hamann, J. Interpretation of machine effects on bovine teat tissues defence mechanisms. Milchwissenschaft 2006, 61, 356-359.
- Zecconi, A. Contagious mastitis control. FIL-IDF Bulletin 2007, 416, 34-40.
- Hamann, J. Guidelines for the evaluation of the milking process. Bulletin of the International Dairy Federation 1997, 321, 26-30.
- Tancin, V.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Factors affecting milk ejection and removal during milking and suckling of dairy cows. Veterinarni Medicina 2001, 46, 108-118. [CrossRef]
- Martin, T.; Gasselin, P.; Hostiou, N.; Feron, G.; Laurens, L.; Purseigle, F.; Ollivier, G. Robots and transformations of work in farm: a systematic review of the literature and a research agenda. Agron. Sustain. Dev. 2022, 42, 20. [CrossRef]
- Bijl, R.; Kooistra, S.R.; Hogeveen, H. The Profitability of Automatic Milking on Dutch Dairy Farms. Journal of Dairy Science 2007, 90, 239-248. [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.A.; Siegford, J.M. The impact of automatic milking systems on dairy cow management, behavior, health, and welfare. Journal of Dairy Science 2012, 95, 2227-2247. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, B.G.; Herje, H.O.; Höva, J. Profitability on dairy farms with automatic milking systems compared to farms with conventional milking systems. International Food and Agribusiness Management Review 2019, 22, 215-228. [CrossRef]
- Múnera-Bedoya, O.D.; Cassoli, L.D.; Machado, P.F.; Cerón-Muñoz, M.F. Influence of attitudes and behavior of milkers on the hygienic and sanitary quality of milk. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0184640. [CrossRef]
- Dufour, S.; Fréchette, A.; Barkema, H.W.; Mussell, A.; Scholl, D.T. <em>Invited review:</em> Effect of udder health management practices on herd somatic cell count. Journal of Dairy Science 2011, 94, 563-579. [CrossRef]
- Tarabla, H.D.; Dodd, K. Associations between farmers’ personal characteristics, management practices and farm performance. British Veterinary Journal 1990, 146, 157-164. [CrossRef]
- Kuczaj, M.; Mucha, A.; Kowalczyk, A.; Mordak, R.; Czerniawska-Piatkowska, E. Relationships between Selected Physiological Factors and Milking Parameters for Cows Using a Milking Robot. Animals 2020, 10, 12. [CrossRef]
- Chikurtev, D.; Chikurteva, A.; Blagoeva, E. Technological Analysis of Types of Milking Systems and Robots: A Review. Cham, 2024; pp. 575-584.
- Bruckmaier, R.M.; Wellnitz, O. Induction of milk ejection and milk removal in different production systems. Journal of Animal Science 2008, 86, 15-20. [CrossRef]
- Odorcic, M.; Rasmussen, M.D.; Paulrud, C.O.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Review: Milking machine settings, teat condition and milking efficiency in dairy cows. Animal 2019, 13, S94-S99. [CrossRef]
- Castro, A.; Pereira, J.M.; Amiama, C.; Bueno, J. Estimating efficiency in automatic milking systems. Journal of Dairy Science 2012, 95, 929-936. [CrossRef]
- Pezzuolo, A.; Cillis, D.; Marinello, F.; Sartori, L. Estimating efficiency in automatic milking systems. In Proceedings of the 16th International Scientific Conference on Engineering for Rural Development, Latvia Univ Agr, Fac Engn, Jelgava, LATVIA, May 24-26, 2017; pp. 736-741. [CrossRef]
- Goodger, W.J.; Galland, J.C.; Christiansen, V.E. Survey of milking management practices on large dairy dairies and their relationship to udder health and production variables. J Dairy Sci 1988, 71, 2535-2542. [CrossRef]
- Vetter, A.; van Dorland, H.A.; Youssef, M.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Effects of a latency period between pre- stimulation and teat cup attachment and periodic vacuum reduction on milking characteristics and teat condition in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Research 2014, 81, 107-112. [CrossRef]
- Tancin, V.; Ipema, B.; Hogewerf, P.; Macuhova, J. Sources of variation in milk flow characteristics at udder and quarter levels. Journal of Dairy Science 2006, 89, 978-988. [CrossRef]
- Zecconi, A.; Frosi, S.; Cipolla, M.; Gusmara, C. Effects of chronic mastitis and its treatment with ketoprofen on the milk ejection curve. Journal of Dairy Research 2018, 85, 50-52. [CrossRef]
- Erskine, R.J.; Norby, B.; Neuder, L.M.; Thomson, R.S. Decreased milk yield is associated with delayed milk ejection. Journal of Dairy Science 2019, 102, 6477-6484. [CrossRef]
- Besier, J.; Lind, O.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Dynamics of teat-end vacuum during machine milking: types, causes and impacts on teat condition and udder health - a literature review. J. Appl. Anim. Res. 2016, 44, 263-272. [CrossRef]
- Bach, A.; Cabrera, V. Robotic milking: Feeding strategies and economic returns. Journal of Dairy Science 2017, 100, 7720-7728. [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, S.; Pereira, G.; Bexiga, R. Bimodal milk flow and overmilking in dairy cattle: risk factors and consequences. Animal 2023, 17, 100716. [CrossRef]
- Aerts, J.; Sitkowska, B.; Piwczynski, D.; Kolenda, M.; Önder, H. The optimal level of factors for high daily milk yield in automatic milking system. Livest. Sci. 2022, 264, 10. [CrossRef]
- Tamburini, A.; Bava, L.; Piccinini, R.; Zecconi, A.; Zucali, M.; Sandrucci, A. Milk emission and udder health status in primiparous dairy cows during lactation. Journal of Dairy Research 2010, 77, 13-19. [CrossRef]
- Zucali, M.; Bava, L.; Sandrucci, A.; Tamburini, A.; Piccinini, R.; Dapra, V.; Tonni, M.; Zecconi, A. Milk flow pattern, somatic cell count and teat apex score in primiparous dairy cows at the beginning of lactation. Ital J Anim Sci 2009, 8, 103-111. [CrossRef]
- Jacobs, J.A.; Ananyeva K Fau - Siegford, J.M.; Siegford, J.M. Dairy cow behavior affects the availability of an automatic milking system. [CrossRef]
- Weiss, D.; Bruckmaier, R.M. Optimization of individual prestimulation in dairy cows. Journal of Dairy Science 2005, 88, 137-147. [CrossRef]
- Jago, J.G.; Davis, K.L.; Copeman, P.J.; Woolford, M.M. The effect of pre-milking teat-brushing on milk processing time in an automated milking system. Journal of Dairy Research 2006, 73, 187-192. [CrossRef]
- Lüdi, I.; Bruckmaier, R.M. The teat cup detachment level affects milking performance in an automatic milking system with teat cleaning and milking in the same teat cup. Journal of Dairy Research 2022, 89, 279-284. [CrossRef]
- Sandrucci, A.; Tamburini, A.; Bava, L.; Zucali, M. Factors affecting milk flow traits in dairy cows: Results of a field study. Journal of Dairy Science 2007, 90, 1159-1167. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).