Submitted:
11 September 2024
Posted:
11 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
- Why should SMEs make use of cloud computing to perform their business functions?
- What potential and future expectations do cloud computing services present on SMEs?
- What is the impact of utilizing cloud computing services on the business performance of SMEs?
- What are the costs involved in using cloud computing technology and how does it affect a company's budget?
- What business operations are affected by the adaptation of cloud computing and what are the most impacted business operations?
1.2. Rationale
1.3. Objectives
- To assess the embracement rate of cloud computing among SMEs.
- Understanding how extensive cloud computing is among the SME sectors as well as the factors affecting adoption rate.
- Analyzing the influence of cloud computing on the operating performance of SMEs, examining how it impacts scalability, efficiency, and business processes.
- Determining financial performance advancements in SMEs due to the adoption of cloud computing.
- Evaluating cloud computing's role in improving innovation and competitive advantage of SMEs.
- Identifying barriers and difficulties faced by SMEs in implementing and adopting cloud computing solutions.
- Exploring the long-term impact of cloud computing among SMEs.
1.4. Research Contribution
- We furnish a thorough analysis of cloud computing, centring on the integration of cloud services, data storage, and computing power. This analysis underscores the cost-effectiveness, reliability, and scalability benefits of cloud computing, offering crucial insights for informed decision-making and promoting the adoption of these technologies among SMEs.
- We consolidate existing research on cloud computing and identify gaps in the literature, particularly regarding the successful adoption and integration of cloud services by various SMEs. By addressing these gaps, we highlight areas needing further research and innovation, thereby advancing the field of cloud computing and ensuring improved performance and competitiveness of SMEs.
1.5. Research Novelty
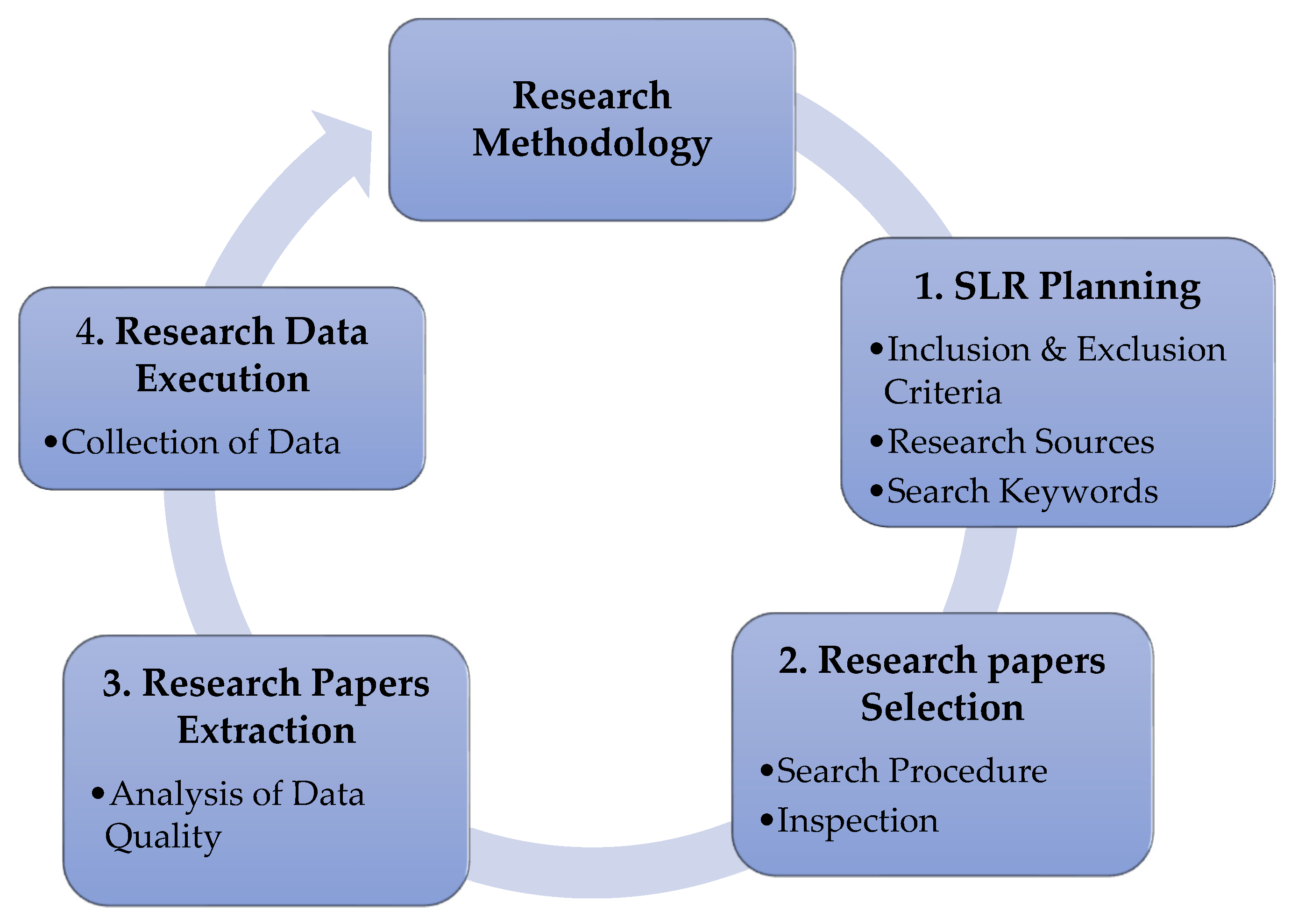
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Data Items
2.6.1. Data Collection Method
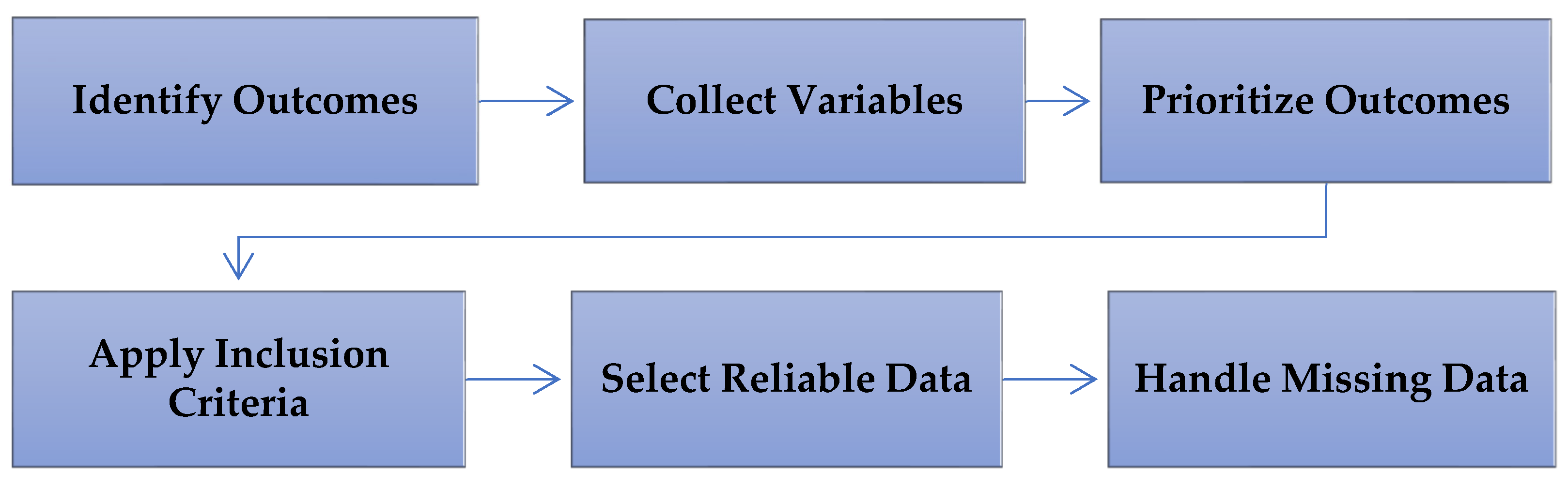
2.6.2. Variable Data Collection
- The journals: title, year, online database, and journal name.
- The study: sample characteristics and geographic location.
- The participants: research design, type of study, sample size, and sample characteristics.
- The research design and features: data collection methods and research design.
- The intervention: technology provider, IT performance metrics, and technology implementation model.
| Criteria | Description |
| Title | Provide a short and descriptive title of the paper or study |
| Year | Indicate the year the research was published. |
| Online Database | List where the study was found (e.g., Google Scholar, SCOPUS, Web of Science). |
| Journal Name | Provide the name of the journal or source of publication. |
| Research Type | Identify the type of research (e.g., article, conference paper, dissertation). |
| #Cites | Number of citations the paper has received. |
| Industry Context | Specify the industry in which the study was conducted (e.g., manufacturing, agriculture). |
| Geographic Location | Mention the country or region the research is based in. |
| Economic Context | Note whether the research is from a developed or developing country. |
| Types of Cloud Computing Services | List the services discussed (e.g., IaaS, PaaS, SaaS). |
| Cloud Deployment Model | Indicate the deployment model (e.g., public, private, hybrid cloud). |
| Technology Providers | Mention cloud providers involved (e.g., AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud). |
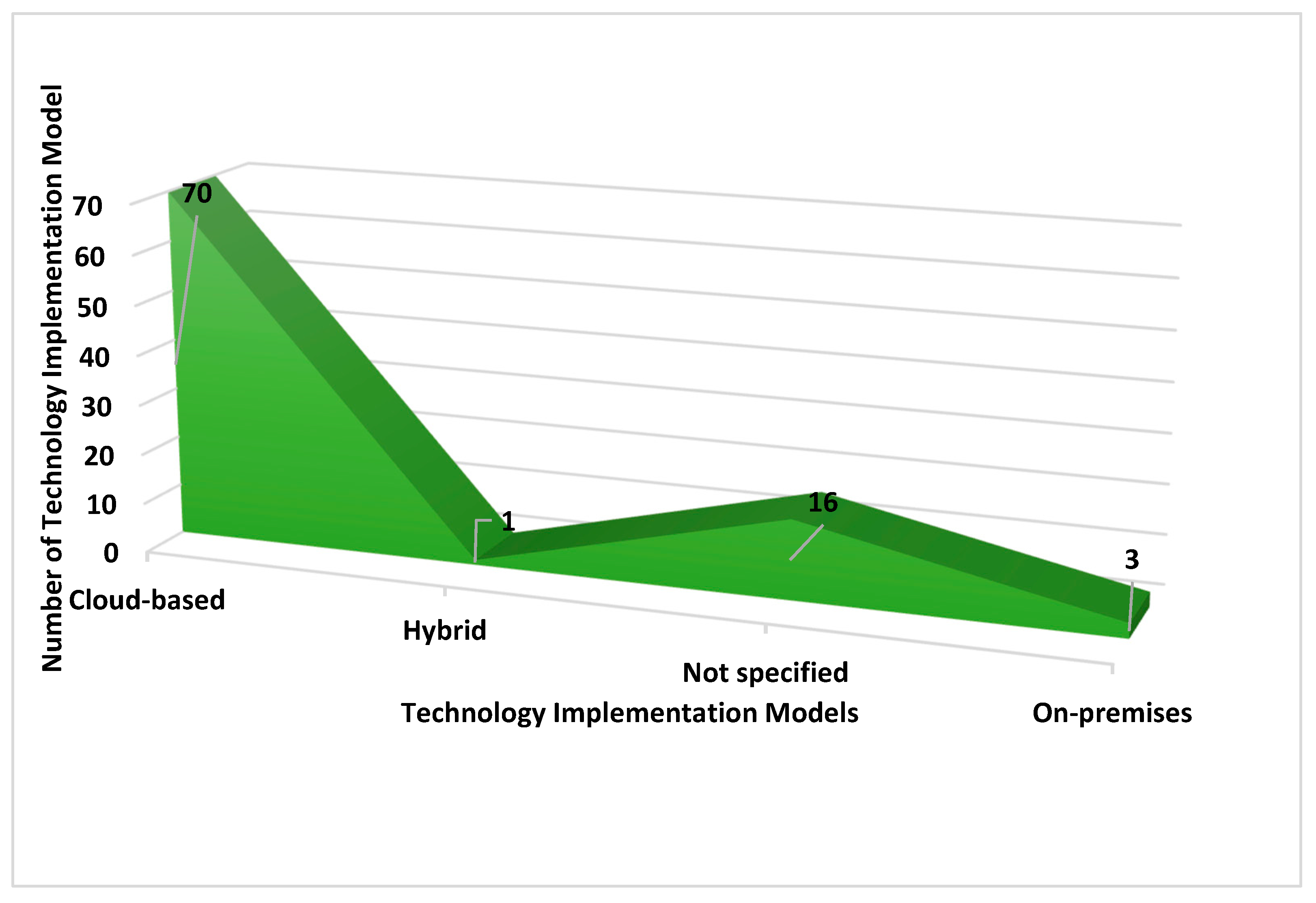
| Technology Implementation Model | Identify the model used (e.g., on-premises, cloud-based, hybrid). |
| Research Design | Describe the research design (e.g., case study, survey). |
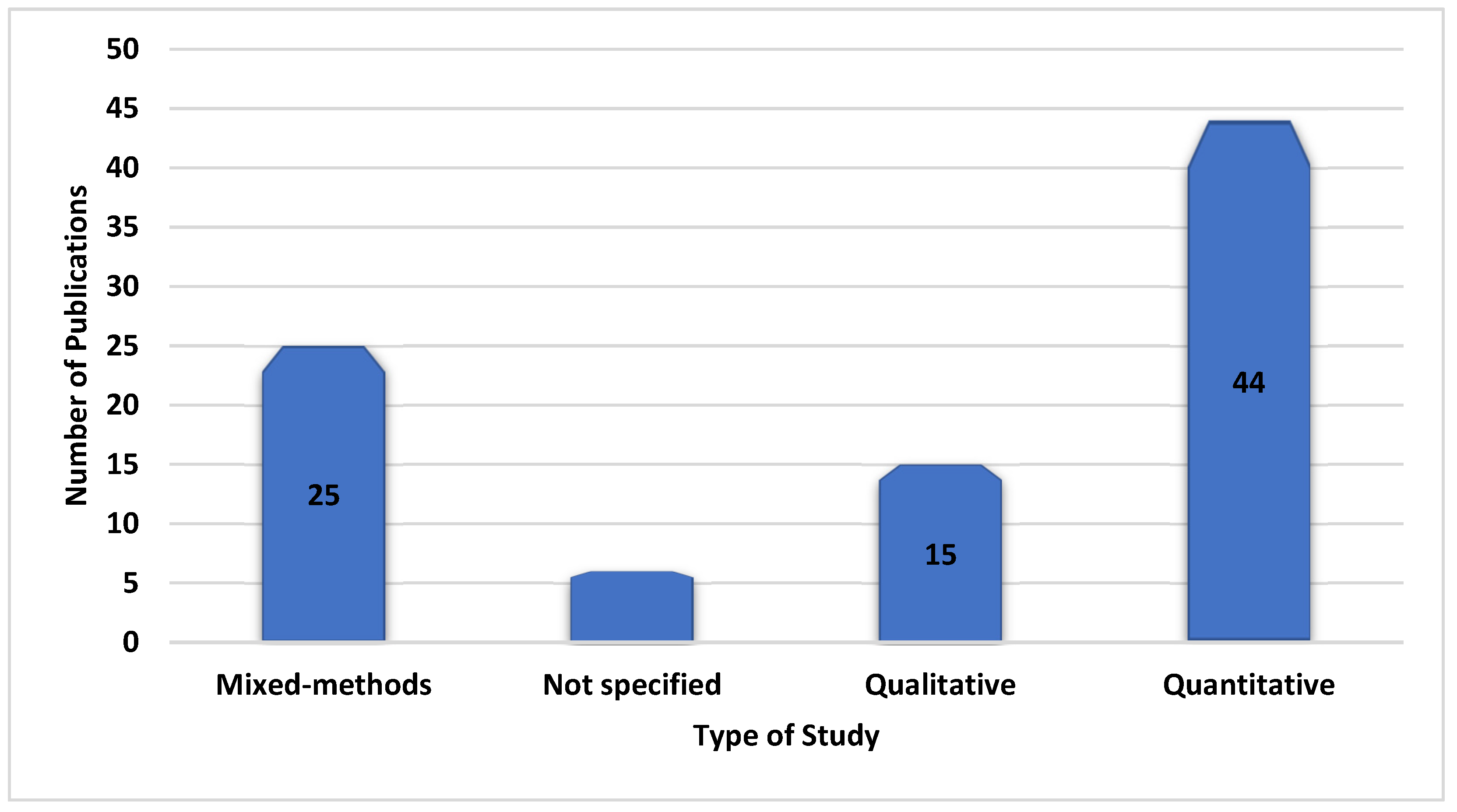
| Type of Study | Indicate whether the study is quantitative, qualitative, or mixed methods. |
| Sample Size | Number of SMEs or participants involved in the study. |
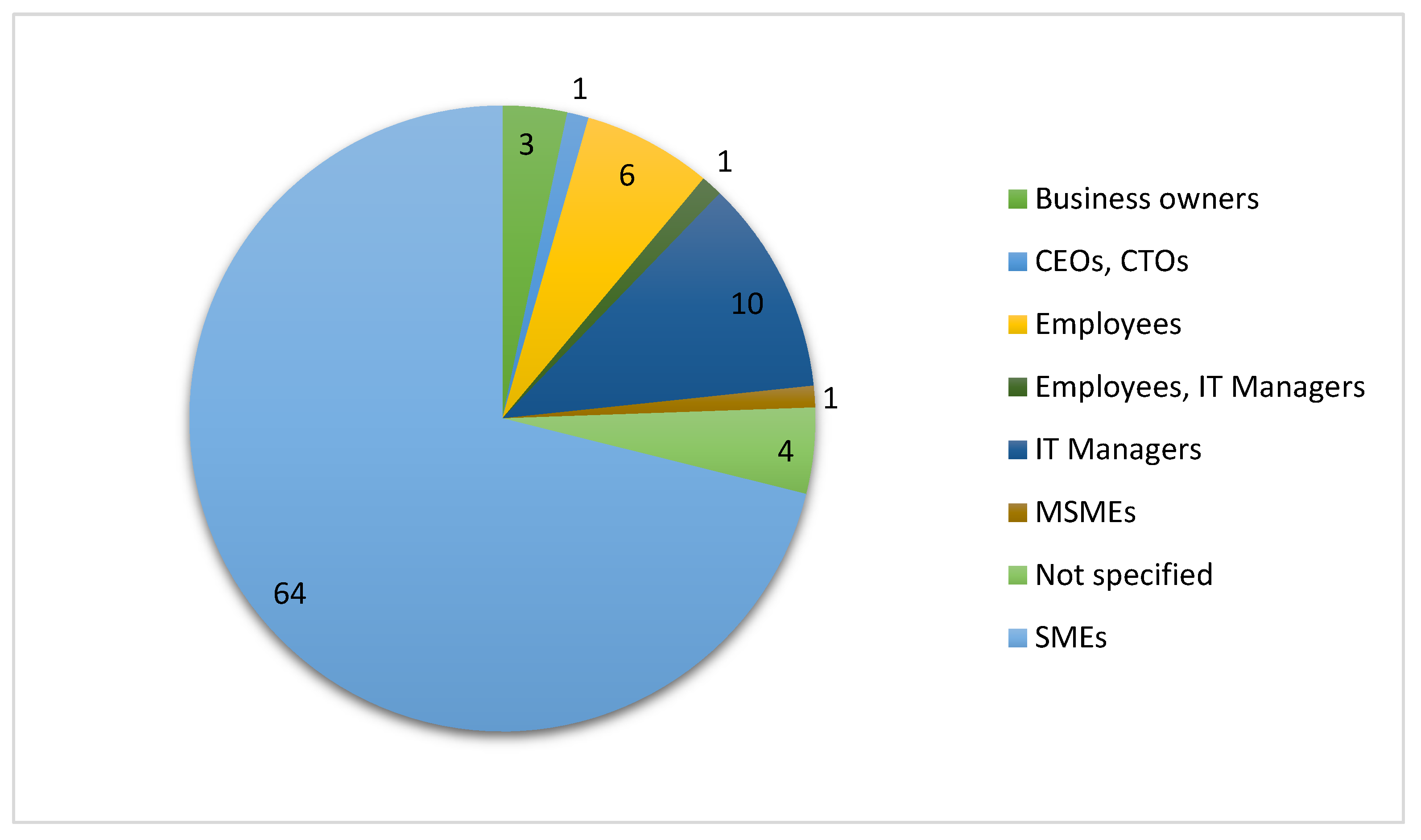
| Sample Characteristics | Define who the participants are (e.g., IT managers, business owners). |
| Data Collection Methods | Describe how the data was collected (e.g., interviews, surveys). |
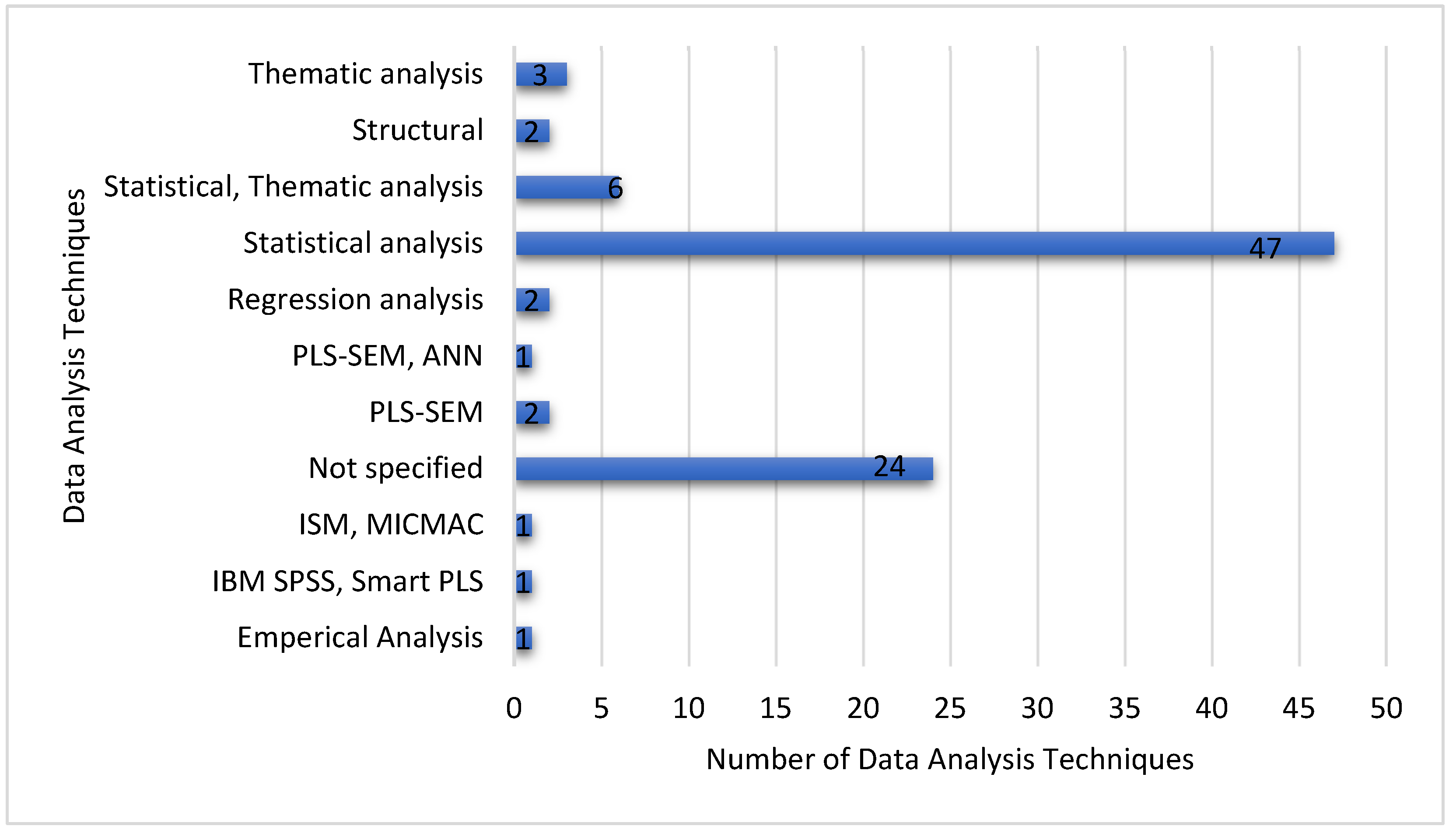
| Data Analysis Techniques | Identify how the data was analyzed (e.g., statistical analysis, thematic analysis). |
| IT Performance Metrics | Specify metrics such as system uptime, scalability, or data security. |
| Business Performance Metrics | Mention operational metrics like efficiency, cost savings, or revenue growth. |
| Organizational Outcomes | List outcomes such as employee satisfaction or customer satisfaction. |
| Long-Term Impacts | Identify long-term benefits like business sustainability or competitive advantage. |
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
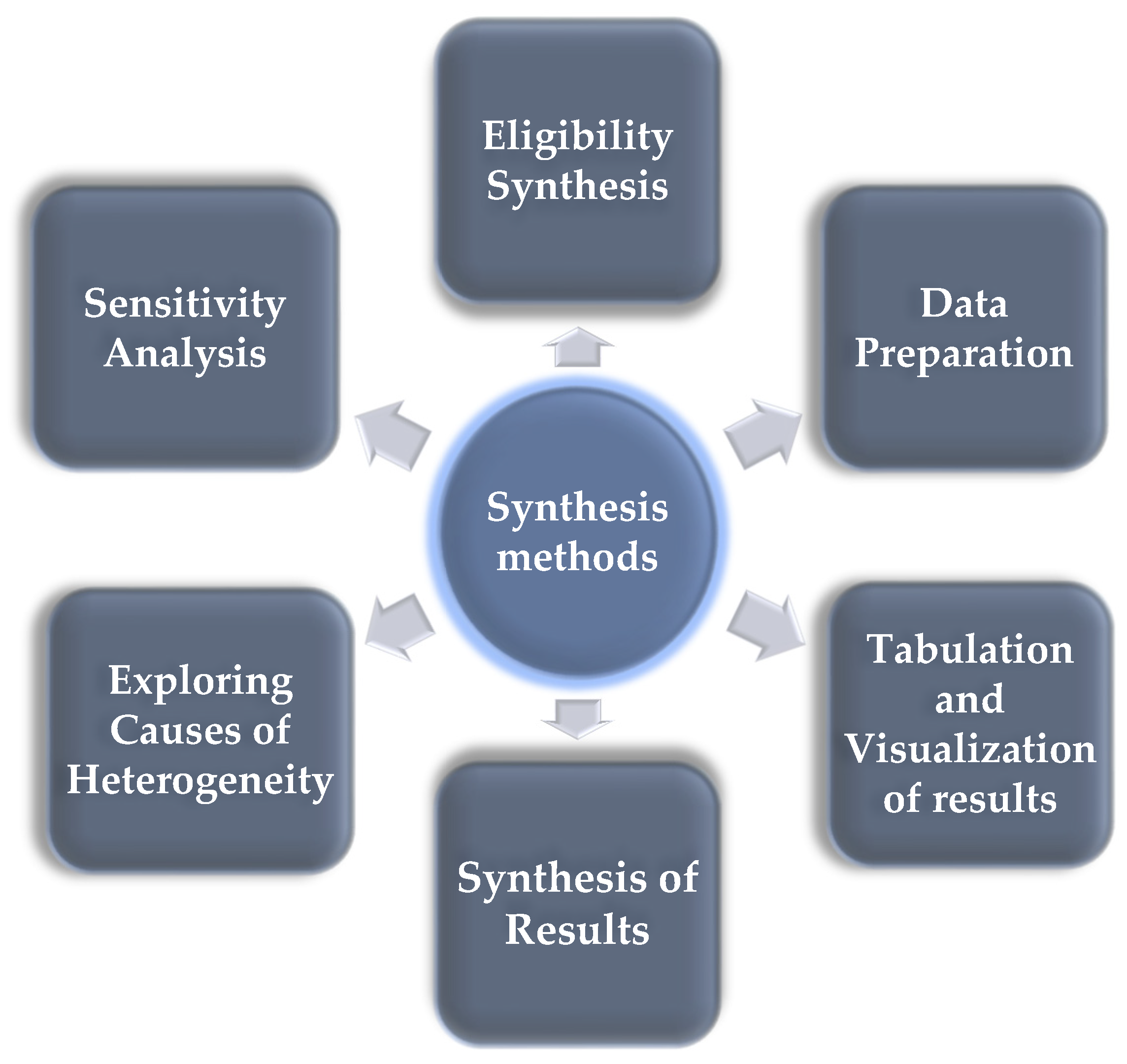
2.8. Synthesis Methods
2.9. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.11. Certainty Assessment
3. Results
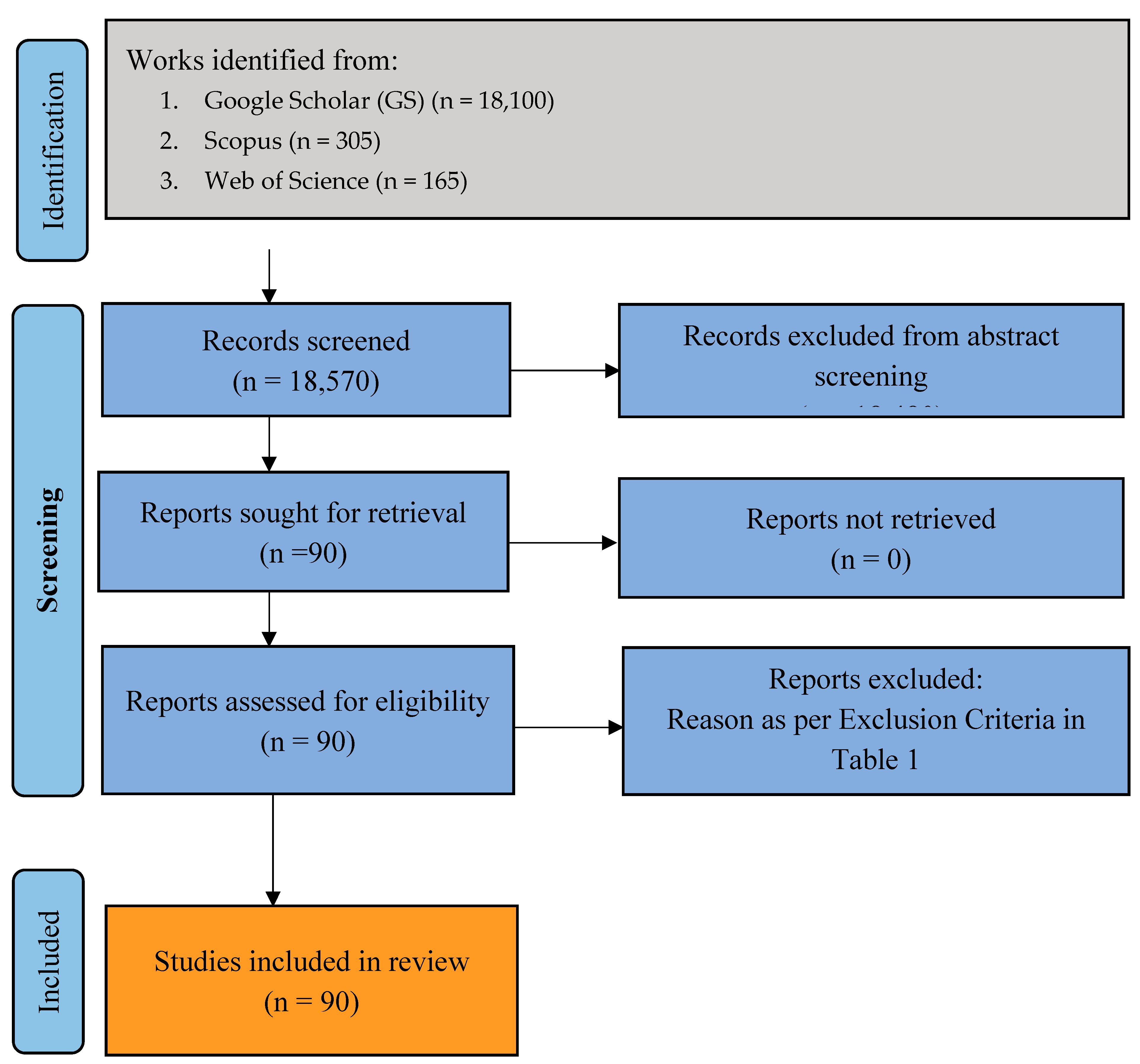
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
3.4. Results of Individual Studies
3.5. Results of Syntheses
3.6. Reporting Biases
3.7. Certainty of Evidence
4. Discussion
- RQ1: Why should SMEs make use of cloud computing to perform their business functions?
- RQ2: What potential and future expectations do cloud computing services present on SMEs?
- RQ3: What is the impact of utilizing cloud computing services on the business performance of SMEs?
- RQ4: What are the costs involved in using cloud computing technology, and how does it affect a company's budget?
- RQ5: What business operations are affected by the adaptation of cloud computing, and what are the most impacted business operations?
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- A. Khayer, Md. S. Talukder, Y. Bao, and Md. N. Hossain, “Cloud computing adoption and its impact on SMEs’ performance for cloud supported operations: A dual-stage analytical approach,” Technology in Society, vol. 60, no. 1, p. 101225, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- T. Vasiljeva, S. Shaikhulina, and K. Kreslins, “Cloud Computing: Business Perspectives, Benefits and Challenges for Small and Medium Enterprises (Case of Latvia),” Procedia Engineering, vol. 178, pp. 443–451, 2017. [CrossRef]
- T. Vasiljeva, S. Shaikhulina, and K. Kreslins, “Cloud Computing: Business Perspectives, Benefits and Challenges for Small and Medium Enterprises (Case of Latvia),” Procedia Engineering, vol. 178, pp. 443–451, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Rawashdeh and B. Rawashdeh, “The effect cloud accounting adoption on organizational performance in SMEs,” International Journal of Data and Network Science, vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 411–424, 2023, Available: https://m.growingscience.com/beta/ijds/5801-the-effect-cloud-accounting-adoption-on-organizational-performance-in-smes.html.
- M. Skafi, M. Yunis, and A. Zekri, “Factors Influencing SMEs’ Adoption of Cloud Computing Services in Lebanon: An Empirical Analysis Using TOE and Contextual Theory,” IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 1–1, 2020. [CrossRef]
- A. Khayer, Md. S. Talukder, Y. Bao, and Md. N. Hossain, “Cloud computing adoption and its impact on SMEs’ performance for cloud supported operations: A dual-stage analytical approach,” Technology in Society, vol. 60, no. 1, p. 101225, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Shetty, J.P. and Panda, R. (2021). An overview of cloud computing in SMEs. Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research. [CrossRef]
- W. N. Picoto, N. F. Crespo, and F. K. Carvalho, “The influence of the technology-organization-environment framework and strategic orientation on cloud computing use, enterprise mobility, and performance,” Review of Business Management, vol. 23, no. 2, pp. 278–300, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- E. A. Odero, “Framework for Adoption of Cloud Computing by Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises in Meru County.,” repository.kemu.ac.ke, Mar. 01, 2021. http://repository.kemu.ac.ke/handle/123456789/1129.
- S. Gamache, Georges Abdul-Nour, and C. Baril, “Evaluation of the influence parameters of Industry 4.0 and their impact on the Quebec manufacturing SMEs: The first findings,” vol. 7, no. 1, pp. 1771818–1771818, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- S. A. Qalati, L. W. Yuan, M. A. S. Khan, and F. Anwar, “A mediated model on the adoption of social media and SMEs’ performance in developing countries,” Technology in Society, vol. 64, no. 64, p. 101513, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Nuskiya, Aliyar Fathima, “Factors influencing cloud computing adoption by SMEs in eastern region of Sri Lanka,” 248.66.13, 2017.
- F. Thabit, S. Alhomdy, and S. Jagtap, “Security analysis and performance evaluation of a new lightweight cryptographic algorithm for cloud computing,” Global Transitions Proceedings, vol. 2, no. 1, pp. 100–110, Jun. 2021. [CrossRef]
- J. Bhat, “Adoption of Cloud Computing by SMEs in India: A study of the Institutional Factors Completed Research Paper,” no. 1, 2013, Available: https://web.archive.org/web/20200318075740id_/https://aisel.aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?referer=&httpsredir=1&article=1884&context=amcis2013.
- N. Ahmad, Z. Liu, J. Wu, F. Alam, Muhammad Waqas, and X. Yi, “Examining the Employees Behavior Control in Cloud Computing Performance Through the Moderating Lenses of Transformational Leadership,” Lecture notes in business information processing, pp. 285–297, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Tomás, M. Thomas, and T. Oliveira, “Evaluating the impact of virtualization characteristics on SaaS adoption,” Enterprise Information Systems, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 259–278, Jul. 2017. [CrossRef]
- K. Y. Tan, “Determining factors for the adoption of cloud computing among small and medium-sized enterprises during the covid-19 pandemic - UTAR Institutional Repository,” Utar.edu.my, 2022. https://doi.org/4971/1/Final_Report_Tan_Keng_Yeng.pdf.
- N. Badie, A. R. C. Hussin, and A. H. Lashkari, “Cloud Computing Data Center Adoption Factors Validity By Fuzzy AHP,” International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 854–873, Sep. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Alexandru Bajenaru, “Software-as-a-Service and Cloud Computing, a solution for small and medium-sized companies,” Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Brasov. Series V: Economic Sciences, pp. 173–184, 2021, Accessed: Sep. 02, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://webbut.unitbv.ro/index.php/Series_V/article/view/7055.
- L. X. Fen and T. A. Ping, "Cloud Computing Adoption Among Malaysian SMEs Manufacturers: The Role of Relative Advantage, Complexity and Cybersecurity Readiness," 2024 2nd International Conference on Software Engineering and Information Technology (ICoSEIT), Bandung, Indonesia, 2024, pp. 336-341. [CrossRef]
- Alkawsi, G.A., Mahmood, A.K. and Baashar, Y.M. (2015). Factors influencing the adoption of cloud computing in SME: A systematic review. 2015 International Symposium on Mathematical Sciences and Computing Research (iSMSC). [CrossRef]
- Hasan, L., Zgair, L., Ngotoye, A., Hussain, H., Najmuldeen, C. and Hasan, M. (n.d.). A Review of the Factors that Influence the Adoption of Cloud Computing by Small and Medium Enterprises. [online]. [CrossRef]
- Fatema AlZayani, A. Hamdan, and Haneen Mohammad Shoaib, “The Impact of Smart Technologies on SME Sustainability: The Mediation Effect of Sustainability Strategy – Literature Review,” Internet of things, pp. 431–454, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Salleh, N.A., Hussin, H., Suhaimi, Mohd.A. and Md Ali, A. (2018). A Systematic Literature Review of Cloud Computing Adoption and Impacts among Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs). [online] IEEE Xplore. [CrossRef]
- Priyadarshinee, P., Jha, M.K., Raut, R.D. and Kharat, M.G. (2016). Risk analysis in adoption of cloud computing in SMEs - a literature review. International Journal of Business Information Systems, 23(1), p.54. [CrossRef]
- Rai, R., Sahoo, G. and Mehfuz, S. (2015). Exploring the factors influencing the cloud computing adoption: a systematic study on cloud migration. SpringerPlus, 4(1). [CrossRef]
- Alouane, M. and El Bakkali, H. (2015). Security, privacy and trust in cloud computing: A comparative study. [online] IEEE Xplore. [CrossRef]
- Alouane, M. and El Bakkali, H. (2015). Security, privacy and trust in cloud computing: A comparative study. [online] IEEE Xplore. [CrossRef]
- Setiyani, L., Makluf, L. and Suherman, Y. (2020). Utilization Analysis of Cloud Computing on SMEs : Systematic Review. International Journal of Applied Business and Information Systems, [online] 4(1), pp.93–99. [CrossRef]
- Rahmat Oriza and Maulidar (2024). Adoption and Impact of Cloud Computing in Small and Medium Enterprises A Systematic Review. Journal Informatic, Education and Management (JIEM), [online] 6(2), pp.8–15. [CrossRef]
- Hartono, I.K., Inayatulloh and Alianto, H. (2020). Improving SMEs Knowledge and Performance With Cloud Computing CSF Approach : Systematic Literature Review. 2020 International Conference on Information Management and Technology (ICIMTech). [CrossRef]
- Alrababah, Z. (2023). BARRIERS TO CLOUD COMPUTING ADOPTION AMONG SMEs IN THE MIDDLE EAST: A SYSTEMATIC REVIEW. [online] 101(17). Available at: https://www.jatit.org/volumes/Vol101No17/10Vol101No17.pdf [Accessed 12 Aug. 2024].
- Durao, F., Carvalho, J.F.S., Fonseka, A. and Garcia, V.C. (2014). A systematic review on cloud computing. The Journal of Supercomputing, 68(3), pp.1321–1346. [CrossRef]
- Maina Lawan, M., Oduoza, C. and Buckley, K. (2021). A Systematic Review of Cloud Computing Adoption by Organisations. International Journal of Industrial and Manufacturing Systems Engineering, 6(3), p.39. [CrossRef]
- M’rhaouarh, I., Okar, C., Namir, A. and Chafiq, N. (2018). Cloud Computing adoption in developing countries: A systematic literature review. [online] IEEE Xplore. [CrossRef]
- Ainayah Syifa Hendri and Endah Sudarmilah (2024). Unraveling Evolution and Trends of Information Technology Adoption in SMEs: a Systematic Review. [online]. [CrossRef]
- N. A. Salleh, H. Hussin, Mohd. A. Suhaimi, and A. Md Ali, “A Systematic Literature Review of Cloud Computing Adoption and Impacts among Small Medium Enterprises (SMEs),” IEEE Xplore, Jul. 01, 2018. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/document/8567134?arnumber=8567134.
- R. F. El-Gazzar, “A Literature Review on Cloud Computing Adoption Issues in Enterprises,” Creating Value for All Through IT, pp. 214–242, 2014. [CrossRef]
- I. Mikkonen and I. Khan, “Cloud computing : SME company point of view,” Theseus.fi, 2016, doi: urn:ISBN:978-80-89306-32-9.
- D. Widyastuti and I. Irwansyah, “Benefits And Challenges Of Cloud Computing Technology Adoption In Small And Medium Enterprises (SMEs),” Bandung Creative Movement (BCM), vol. 4, no. 1, Mar. 2018, Available: https://openlibrarypublications.telkomuniversity.ac.id/index.php/bcm/article/view/5905.
- S. R. Tehrani and F. Shirazi, “Factors Influencing the Adoption of Cloud Computing by Small and Medium Size Enterprises (SMEs),” Lecture Notes in Computer Science, pp. 631–642, 2014. [CrossRef]
- Z. H. Pathan, Z. Jianqiu, U. Akram, Z. Latif, M. K. Khan, and M. Z. Tunio, “Essential factors in cloud-computing adoption by SMEs,” Human Systems Management, vol. 36, no. 4, pp. 261–275, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Amini, “The Factors that Influence on Adoption of Cloud Computing for Small and Medium Enterprises,” Ssrn.com, 2014. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=2635479.
- D. Kumar, H. V. Samalia, and P. Verma, “Factors Influencing Cloud Computing Adoption by Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs) in India,” Pacific Asia Journal of the Association for Information Systems, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 25–48, 2017. [CrossRef]
- A. Khayer, N. Jahan, Md. N. Hossain, and Md. Y. Hossain, “The adoption of cloud computing in small and medium enterprises: a developing country perspective,” VINE Journal of Information and Knowledge Management Systems, vol. 51, no. 1, pp. 64–91, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Vasiljeva, T., Shaikhulina, S. and Kreslins, K. (2017). Cloud Computing: Business Perspectives, Benefits and Challenges for Small and Medium Enterprises (Case of Latvia). Procedia Engineering, 178, pp.443–451. [CrossRef]
- Al-Sharafi, M.A., Arshah, R.A., Abu-Shanab, E.A. and Alajmi, Q. (2019). The Effect of Sustained Use of Cloud-Based Business Services on Organizations’ Performance: Evidence from SMEs in Malaysia. 2019 5th International Conference on Information Management (ICIM). [CrossRef]
- A. H. N. Kariyawasam, "Analysing the impact of cloud-based accounting on business performance of SMEs," The Business & Management Review, vol. 10, no. 4, pp. 37-44, 2019.
- Trigueros-Preciado, S., Pérez-González, D. and Solana-González, P. (2013). Cloud computing in industrial SMEs: identification of the barriers to its adoption and effects of its application. Electronic Markets, [online] 23(2), pp.105–114. [CrossRef]
- Carcary, D.M., Doherty, D.E. and Conway, G. (2014). The Adoption of Cloud Computing by Irish SMEs an Exploratory Study. Electronic Journal of Information Systems Evaluation, [online] 17(1), pp.pp3-14–pp3-14. Available at: https://academic-publishing.org/index.php/ejise/article/view/191.
- Hassan, H., Mohd, Khairudin, N. and Adon, I. (2017). Factors Influencing Cloud Computing Adoption in Small Medium Enterprises - UUM Repository. Uum.edu.my. [online]. [CrossRef]
- Safari, F., Safari, N., Hasanzadeh, A. and Ghatari, A.R. (2015). Factors affecting the adoption of cloud computing in small and medium enterprises. International Journal of Business Information Systems, 20(1), p.116. [CrossRef]
- Assante, D., Castro, M., Hamburg, I. and Martin, S. (2016). The Use of Cloud Computing in SMEs. Procedia Computer Science, [online] 83, pp.1207–1212. [CrossRef]
- Abubakar, A.D., Bass, J.M. and Allison, I. (2014). Cloud Computing: Adoption Issues for Sub-Saharan African SMEs. The Electronic Journal of Information Systems in Developing Countries, 62(1), pp.1–17. [CrossRef]
- Kaplancalı, U.T. and Akyol, M. (2021). Analysis of Cloud Computing Usage on Performance: The Case of Turkish SMEs. Proceedings, 74(1), p.11. [CrossRef]
- Dincă, V.M., Dima, A.M. and Rozsa, Z. (2019). DETERMINANTS OF CLOUD COMPUTING ADOPTION BY ROMANIAN SMES IN THE DIGITAL ECONOMY. Journal of Business Economics and Management, 20(4), pp.798–820. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, H. (2017). Organisational factors affecting cloud computing adoption in small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in service sector. Procedia Computer Science, 121, pp.976–981. [CrossRef]
- Anon, (n.d.). The impact of SMEs in the global economy – iQualify UK – Modern British Education. [online] Available at: https://iqualifyuk.com/the-impact-of-smes-in-the-global-economy/.
- Tutunea, M.F. (2014). SMEs’ Perception on Cloud Computing Solutions. Procedia Economics and Finance, 15, pp.514–521. [CrossRef]
- Narwane, V.S., Raut, R.D., Mangla, S.K., Gardas, B.B., Narkhede, B.E., Awasthi, A. and Priyadarshinee, P. (2020). Mediating role of cloud of things in improving performance of small and medium enterprises in the Indian context. Annals of Operations Research. [CrossRef]
- R. Otuka, D. Preston, and E. Pimenidis, "The use and challenges of cloud computing services in SMEs in Nigeria," in Proceedings of the European Conference on Information Management, Reading, UK, Sep. 2014, p. 325.
- Mohlameane, M. and Ruxwana, N. (2020). Exploring the impact of cloud computing on existing South African regulatory frameworks. SA Journal of Information Management, 22(1). [CrossRef]
- Gong, C., Liu, J., Zhang, Q., Chen, H. and Gong, Z. (2010). The Characteristics of Cloud Computing. [online] IEEE Xplore. [CrossRef]
- Sunyaev, A. (2020). Cloud Computing. Internet Computing, 1(1), pp.195–236.
- R. Sandu, E. Gide, and S. Karim, "The impact of innovative strategies to influence the adoption of cloud-based service success in Indian small and medium enterprises (SMEs)," *International Journal of Arts & Sciences*, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 403-413, 2017.
- Ming, C.F., On, C.K., Rayner, A., Guan, T.T. and Patricia, A. (2018). The Determinant Factors Affecting Cloud Computing Adoption by Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in Sabah, Malaysia. Journal of Telecommunication, Electronic and Computer Engineering (JTEC), [online] 10(3-2), pp.83–88. Available at: https://jtec.utem.edu.my/jtec/article/view/4716.
- E. Doherty, M. Carcary, and G. Conway, "Migrating to the cloud: Examining the drivers and barriers to adoption of cloud computing by SMEs in Ireland: an exploratory study," Journal of Small Business and Enterprise Development, vol. 22, no. 3, pp. 512-527, 2015.
- Hamada, M., Lobiyal, D.K. and Yamin, M. (2015). Tamil Nadu (INDIA) AI and Innovative Learning Technologies. [online] 7(1). Available at: http://bvicam.in/INDIACom/BJIT/downloads/BIJIT%20-%20Complete%20Issue%2013.pdf#page=71.
- A. D. Abubakar, A. Abubakar, and J. Bass, "Cloud computing: Adoption issues for Sub-Saharan Africa SMEs.
- Safari, F., Safari, N., Hasanzadeh, A. and Ghatari, A.R. (2015). Factors affecting the adoption of cloud computing in small and medium enterprises. International Journal of Business Information Systems, 20(1), p.116. [CrossRef]
- Prihatiningtias, Y.W. and Wardhani, M.R. (2021). Understanding the effect of sustained use of cloud-based point of sales on SMEs performance during covid-19 pandemic. The Indonesian Accounting Review, 11(1), p.33. [CrossRef]
- B. M. R. Wilson, B. Khazaei, and L. Hirsch, "Enablers and barriers of cloud adoption among Small and Medium Enterprises in Tamil Nadu," in 2015 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing in Emerging Markets (CCEM), Bangalore, India, Nov. 2015, pp. 140-145.
- E. Gide and R. Sandu, "A study to explore the key factors impacting on cloud based service adoption in Indian SMEs," in 2015 IEEE 12th International Conference on e-Business Engineering, Beijing, China, Oct. 2015, pp. 387-392.
- M. Ramasamy and J. Periasamy, "Explore the impact of cloud computing on ERP systems used in small and medium enterprises," Int. J., vol. 5, 2017.
- Sajay K R and S. S. Babu, "A study of cloud computing environments for High Performance applications," 2016 International Conference on Data Mining and Advanced Computing (SAPIENCE), Ernakulam, India, 2016, pp. 353-359. [CrossRef]
- D. Kumar and H. V. Samalia, "Investigating Factors Affecting Cloud Computing Adoption by SMEs in Himachal Pradesh," 2016 IEEE International Conference on Cloud Computing in Emerging Markets (CCEM), Bangalore, India, 2016, pp. 9-16. [CrossRef]
- “Cloud Computing,” Google Books, 2024. https://books.google.co.za/books?hl=en&lr=&id=GaN41KF7hvgC&oi=fnd&pg=PP1&dq=Cloud+computing:+Methodology (accessed Sep. 04, 2024).
- R. D. Raut, B. B. Gardas, M. K. Jha, and P. Priyadarshinee, “Examining the critical success factors of cloud computing adoption in the MSMEs by using ISM model,” The Journal of High Technology Management Research, vol. 28, no. 2, pp. 125–141, 2017. [CrossRef]
- C. Chan, O. Liu, and R. Szeto, “Developing Information Sharing Model Using Cloud Computing and Smart Devices for SMEs Supply Chain,” International Journal of Information Systems and Supply Chain Management, vol. 10, no. 3, pp. 44–64, Jul. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. Jha and A. Kathuria, “Association for Information Systems Association for Information Systems AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) AIS Electronic Library (AISeL) AMCIS 2022 Proceedings SCUIDT-Strategic and Competitive Uses of Information and Digital Technologies Aug 10th, 12:00 AM Size Matters for Cloud Capability and Performance Size Matters for Cloud Capability and Performance.” Accessed: Sep. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://core.ac.uk/download/pdf/529573645.pdf.
- J. Zhao, L. Zhang, and Y. Zhao, “Informatization of Accounting Systems in Small- and Medium-Sized Enterprises Based on Artificial Intelligence-Enabled Cloud Computing,” Computational Intelligence and Neuroscience, vol. 2022, pp. 1–9, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- J. Deng, “The Informatization of Small and Medium-Sized Enterprises Accounting System Based on Sensor Monitoring and Cloud Computing,” Mobile Information Systems, vol. 2022, pp. 1–13, May 2022. [CrossRef]
- L. Yen Ling, M. Ehsan Rana and Q. Al Maatouk, "Critical Review of Design Considerations in Forming a Cloud Infrastructure for SMEs," 2022 International Conference on Decision Aid Sciences and Applications (DASA), Chiangrai, Thailand, 2022, pp. 1537-1543. [CrossRef]
- S. Bhagat and P. Gupta, “A Survey on Scalable Resource Allocation in Cloud Computing,” Lecture notes in electrical engineering, pp. 401–414, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- A. Gui, Y. Fernando, M. S. Shaharudin, M. Mokhtar, I. G. M. Karmawan, and Suryanto, “Drivers of Cloud Computing Adoption in Small Medium Enterprises of Indonesia Creative Industry,” JOIV : International Journal on Informatics Visualization, vol. 5, no. 1, p. 69, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Goyal and A. Sharma, "Enhancing Hybrid Encryption Techniques for Secured Data Processing for Small Medium Enterprises in cloud," 2021 IEEE International Conference on Technology, Research, and Innovation for Betterment of Society (TRIBES), Raipur, India, 2021, pp. 1-5. [CrossRef]
- Muhammad, Noor, Muslihah Wook, Mohd Nazri Ismail, and T. Mohd, “The Mediating Role of Cloud Computing and Moderating Influence of Digital Organizational Culture Towards Enhancing SMEs Performance,” Lecture notes in computer science, pp. 447–458, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Mujinga, "Cloud Computing Inhibitors Among Small and Medium Enterprises," 2020 3rd International Conference on Intelligent Sustainable Systems (ICISS), Thoothukudi, India, 2020, pp. 1385-1391. [CrossRef]
- M. Attaran and J. Woods, “Cloud computing technology: improving small business performance using the Internet,” Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, vol. 31, no. 6, pp. 495–519, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- N. Sandu and E. Gide, "A Model for Successful Adoption of Cloud-Based Services in Indian SMEs," 2019 7th International Conference on Future Internet of Things and Cloud (FiCloud), Istanbul, Turkey, 2019, pp. 169-174. [CrossRef]
- J. P. Shetty and R. Panda, “An overview of cloud computing in SMEs,” Journal of Global Entrepreneurship Research, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- L. Rajabion, "Application and Adoption of Big Data Technologies in SMEs," 2018 International Conference on Computational Science and Computational Intelligence (CSCI), Las Vegas, NV, USA, 2018, pp. 1133-1135. [CrossRef]
- S. J. E. Taylor et al., “The CloudSME simulation platform and its applications: A generic multi-cloud platform for developing and executing commercial cloud-based simulations,” Future Generation Computer Systems, vol. 88, pp. 524–539, Nov. 2018. [CrossRef]
- X. V. Wang, L. Wang, and R. Gördes, “Interoperability in cloud manufacturing: a case study on private cloud structure for SMEs,” International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, vol. 31, no. 7, pp. 653–663, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- S. H. Kim, S. Y. Jang, and K. H. Yang, “Analysis of the Determinants of Software-as-a-Service Adoption in Small Businesses: Risks, Benefits, and Organizational and Environmental Factors,” Journal of Small Business Management, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 303–325, Nov. 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. Khayer, Md. S. Talukder, Y. Bao, and Md. N. Hossain, “Cloud computing adoption and its impact on SMEs’ performance for cloud supported operations: A dual-stage analytical approach,” Technology in Society, vol. 60, no. 1, p. 101225, Feb. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Al-Mutawa, B. and Saeed Al Mubarak, M.M. (2024), "Impact of cloud computing as a digital technology on SMEs sustainability", Competitiveness Review, Vol. 34 No. 1, pp. 72-91. [CrossRef]
- Asiaei, A. and Ab. Rahim, N.Z. (2019), "A multifaceted framework for adoption of cloud computing in Malaysian SMEs", Journal of Science and Technology Policy Management, Vol. 10 No. 3, pp. 708-750. [CrossRef]
- “Factors Influencing Cloud Computing Adoption by SMEs in the Czech Republic: An Empirical Analysis Using Technology-Organization-Environment Framework,” Acta Informatica Pragensia, vol. 12, no. 2, pp. 296–310, 2023, Accessed: Sep. 04, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.ceeol.com/search/article-detail?id=1211714.
- Lu, Q., Chen, J., Song, H. and Zhou, X. (2022), "Effects of cloud computing assimilation on supply chain financing risks of SMEs", Journal of Enterprise Information Management, Vol. 35 No. 6, pp. 1719-1741. [CrossRef]
- Subramanian, G., Patil, B.T. and Gardas, B.B. (2021), "Evaluation of enablers of cloud technology to boost industry 4.0 adoption in the manufacturing micro, small and medium enterprises", Journal of Modelling in Management, Vol. 16 No. 3, pp. 944-962. [CrossRef]
- M. Carcary, E. Doherty, G. Conway, and S. McLaughlin, “Cloud Computing Adoption Readiness and Benefit Realization in Irish SMEs—An Exploratory Study,” Information Systems Management, vol. 31, no. 4, pp. 313–327, Oct. 2014. [CrossRef]
- M. Skafi, M. M. Yunis and A. Zekri, "Factors Influencing SMEs’ Adoption of Cloud Computing Services in Lebanon: An Empirical Analysis Using TOE and Contextual Theory," in IEEE Access, vol. 8, pp. 79169-79181, 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. A. Al-Sharafi, M. Iranmanesh, M. Al-Emran, A. I. Alzahrani, F. Herzallah, and N. Jamil, “Determinants of cloud computing integration and its impact on sustainable performance in SMEs: An empirical investigation using the SEM-ANN approach,” Heliyon, vol. 9, no. 5, p. e16299, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- K. Mousa, Z. Zhang, E. Sumarliah, and I. K. A. Hamdan, “The Impact of Cloud Computing Adoption on Firm Performance Among SMEs in Palestine: A Machine Learning Approach,” International Journal of Intelligent Information Technologies (IJIIT), vol. 20, no. 1, pp. 1–24, Jan. 2024. [CrossRef]
- A. F. Ali, A. A. Hassan, H. O. Abdullahi, and R. H. Abdulah, “Analyzing the factors influencing the adoption of cloud computing by SMEs using the SEM approach - SIMAD University Research Repository,” Simad.edu.so, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Hosseini, G. Fallon, V. Weerakkody, and U. Sivarajah, “Cloud computing utilization and mitigation of informational and marketing barriers of the SMEs from the emerging markets: Evidence from Iran and Turkey,” International Journal of Information Management, vol. 46, pp. 54–69, Jun. 2019. [CrossRef]
- M. Chen, H. Wang, Y. Liang, and G. Zhang, “Net and configurational effects of determinants on cloud computing adoption by SMEs under cloud promotion policy using PLS-SEM and fsQCA,” vol. 8, no. 3, pp. 100388–100388, Jul. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Fakieh, B., Blount, D. Y. & Busch, D. P., “Success in the Digital Economy: Cloud Computing”, SMEs and the Impact to National Productivitiy. Auckland, New Zealand, 25th Australasian Conference on Information Systems,2014.
- Gutierrez, A., Boukrami, E. and Lumsden, R. (2015), "Technological, organisational and environmental factors influencing managers’ decision to adopt cloud computing in the UK", Journal of Enterprise Information Management, Vol. 28 No. 6, pp. 788-807. [CrossRef]
- A. Rawashdeh, B. S. Rawashdeh, and E. Shehadeh, “The Determinants of Cloud Computing Vision and Its Impact on Cloud Accounting Adoption in SMBs,” Human Behavior and Emerging Technologies, vol. 2023, p. e8571227, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- P.-F. Hsu, S. Ray, and Y.-Y. Li-Hsieh, “Examining cloud computing adoption intention, pricing mechanism, and deployment model,” International Journal of Information Management, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 474–488, Aug. 2014. [CrossRef]
- G. Mwansa, “Promoting adoption and utilization of cloud computing services for agile software developers,” Journal on Innovation and Sustainability RISUS, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. Mihoci, “Exploring the Challenges Faced by Small and Medium Sized Enterprises When Adapting to Technological Change - University of Twente Student Theses,” Utwente.nl, 2022. https://doi.org/91762.
- S. J. E. Taylor et al., "Enabling Cloud-Based Computational Fluid Dynamics With a Platform-as-a-Service Solution," in IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics, vol. 15, no. 1, pp. 85-94, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- S. Gupta and S. C. Misra, "Moderating Effect of Compliance, Network, and Security on the Critical Success Factors in the Implementation of Cloud ERP," in IEEE Transactions on Cloud Computing, vol. 4, no. 4, pp. 440-451, 1 Oct.-Dec. 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Balina, D. Baumgarte, and E. Salna, “Cloud Based Cross-system Integration for Small and Medium-sized Enterprises,” Procedia Computer Science, vol. 104, pp. 127–132, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Y. Huo, J. Xiong, Q. You, Z. Guo, and H. Xiang, “A personalized method of cloud manufacturing service customization,” International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing, vol. 34, no. 4, pp. 440–454, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- C. Yoon, K. Lee, B. Yoon, and O. Toulan, “Typology and Success Factors of Collaboration for Sustainable Growth in the IT Service Industry,” Sustainability, vol. 9, no. 11, p. 2017, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Ranjan, J. Kolodziej, L. Wang and A. Y. Zomaya, "Cross-Layer Cloud Resource Configuration Selection in the Big Data Era," in IEEE Cloud Computing, vol. 2, no. 3, pp. 16-22, May-June 2015. [CrossRef]
- L. X. Fen and T. A. Ping, "Cloud Computing Adoption Among Malaysian SMEs Manufacturers: The Role of Relative Advantage, Complexity and Cybersecurity Readiness," 2024 2nd International Conference on Software Engineering and Information Technology (ICoSEIT), Bandung, Indonesia, 2024, pp. 336-341. [CrossRef]
- A. Hussain, A. Shahzad, and R. Hassan, “Organizational and Environmental Factors with the Mediating Role of E-Commerce and SME Performance,” Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Complexity, vol. 6, no. 4, p. 196, Dec. 2020. [CrossRef]
- H. M. Sabi, F.-M. E. Uzoka, K. Langmia, and F. N. Njeh, “Conceptualizing a model for adoption of cloud computing in education,” International Journal of Information Management, vol. 36, no. 2, pp. 183–191, Apr. 2016. [CrossRef]
- P. Priyadarshinee, R. D. Raut, M. K. Jha, and B. B. Gardas, “Understanding and predicting the determinants of cloud computing adoption: A two staged hybrid SEM - Neural networks approach,” Computers in Human Behavior, vol. 76, pp. 341–362, Nov. 2017. [CrossRef]
- J. Oredo and D. Dennehy, “Exploring the Role of Organizational Mindfulness on Cloud Computing and Firm Performance: The Case of Kenyan Organizations,” Information Systems Frontiers, Nov. 2022. [CrossRef]
- S. Ali Qalati, W. Li, N. Ahmed, M. Ali Mirani, and A. Khan, “Examining the Factors Affecting SME Performance: The Mediating Role of Social Media Adoption,” Sustainability, vol. 13, no. 1, p. 75, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Nidhi Shridhar Natrajan, Rinku Sanjeev, and Rishabh Upendra Jain, “Sustainability in small and medium enterprises: A circular economy approach using cloud computing,” Business Strategy & Development, vol. 7, no. 2, Apr. 2024. [CrossRef]
- N. Kshetri, “Cloud Computing in the Global South: drivers, effects and policy measures,” Third World Quarterly, vol. 32, no. 6, pp. 997–1014, Jul. 2011. [CrossRef]
- H. Zhang and Mohammadi Alireza, “A Study on Technology Application and Performance of Small and Medium-sized Enterprises in the Context of Cloud Computing Application - A Case Study of Hotel Industry in Henan, China,” Journal of Sustainable Business and Economics, vol. 7, no. 2, pp. 69–75, 2023. [CrossRef]
- A. ALHAMMADI, C. STANIER, and A. EARDLEY, “The Determinants of Cloud Computing Adoption in Saudi Arabia,” eprints.staffs.ac.uk, Aug. 13, 2015. https://eprints.staffs.ac.uk/2774/.
- N. Ahmad, Z. Liu, J. Wu, F. Alam, Muhammad Waqas, and X. Yi, “Examining the Employees Behavior Control in Cloud Computing Performance Through the Moderating Lenses of Transformational Leadership,” Lecture notes in business information processing, pp. 285–297, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Tomás, M. Thomas, and T. Oliveira, “Evaluating the impact of virtualization characteristics on SaaS adoption,” Enterprise Information Systems, vol. 12, no. 3, pp. 259–278, Jul. 2017. [CrossRef]
- K. Y. Tan, “Determining factors for the adoption of cloud computing among small and medium-sized enterprises during the covid-19 pandemic - UTAR Institutional Repository,” Utar.edu.my, 2022. https://doi.org/4971/1/Final_Report_Tan_Keng_Yeng.pdf.
- N. Badie, A. R. C. Hussin, and A. H. Lashkari, “Cloud Computing Data Center Adoption Factors Validity By Fuzzy AHP,” International Journal of Computational Intelligence Systems, vol. 8, no. 5, pp. 854–873, Sep. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Alexandru Bajenaru, “Software-as-a-Service and Cloud Computing, a solution for small and medium-sized companies,” Bulletin of the Transilvania University of Brasov. Series V: Economic Sciences, pp. 173–184, 2021, Accessed: Sep. 02, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://webbut.unitbv.ro/index.php/Series_V/article/view/7055.
- Bhat, “Adoption of Cloud Computing by SMEs in India: A study of the Institutional Factors Completed Research Paper,” no. 1, 2013, Available: https://web.archive.org/web/20200318075740id_/https://aisel.aisnet.org/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?referer=&httpsredir=1&article=1884&context=amcis2013.

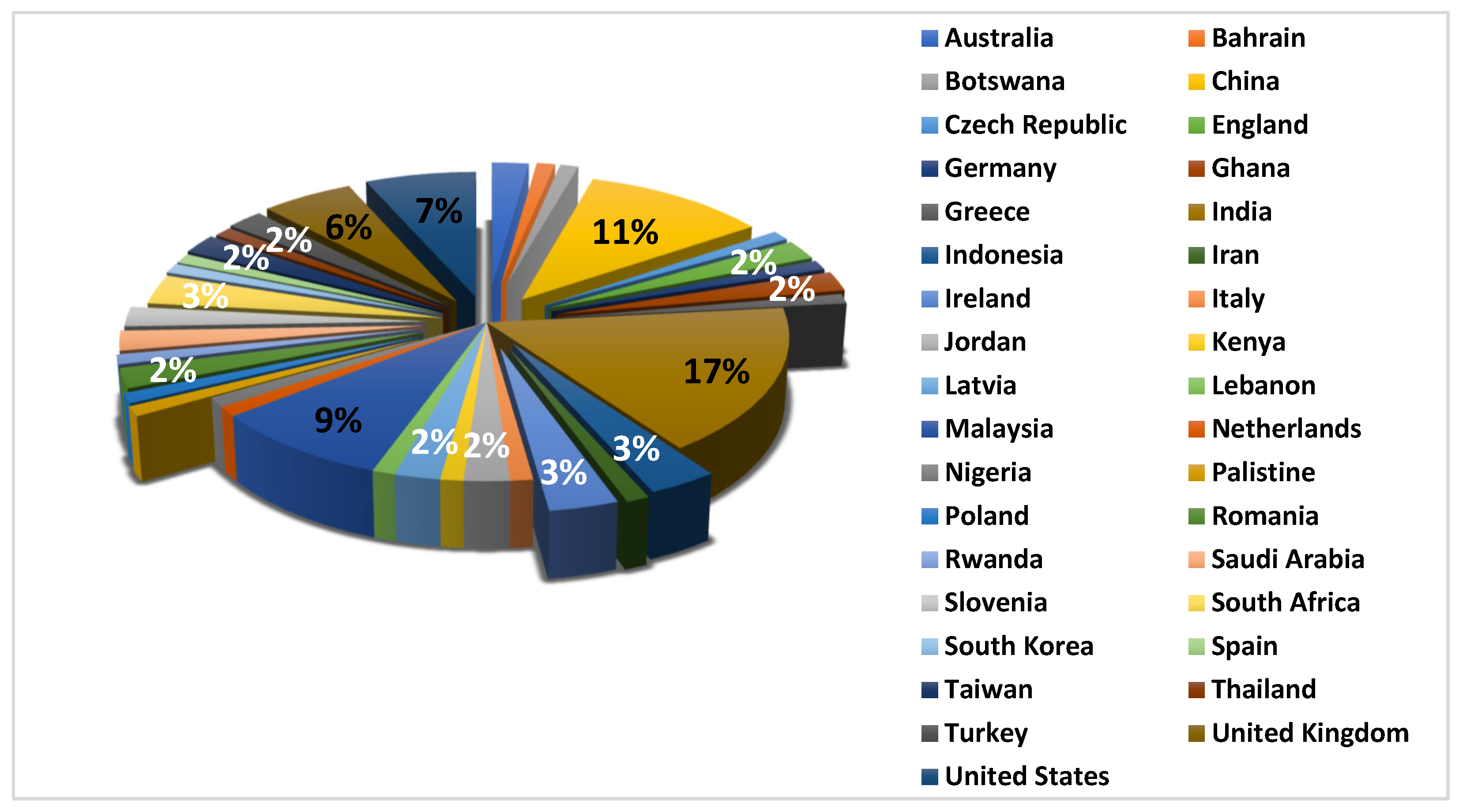
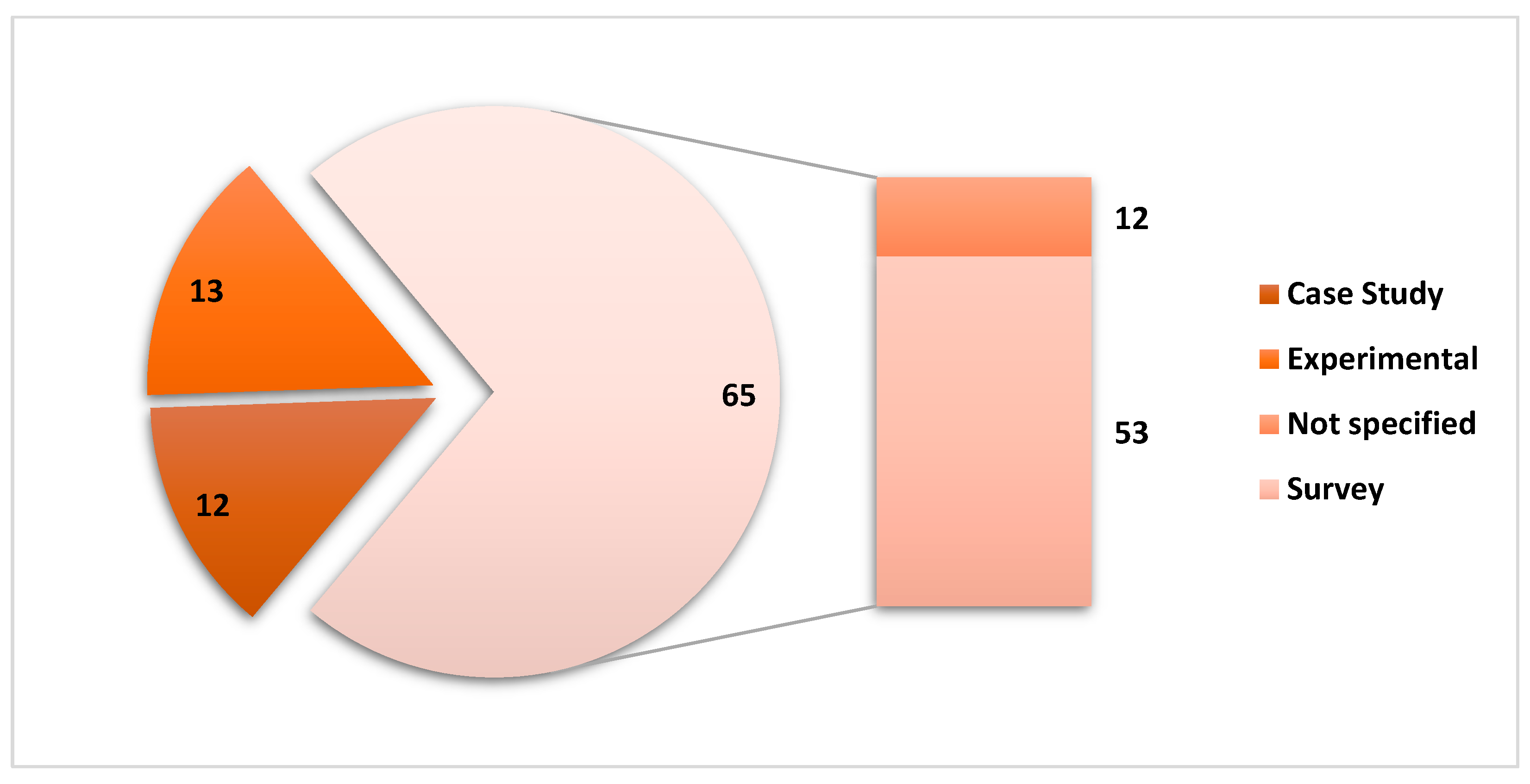
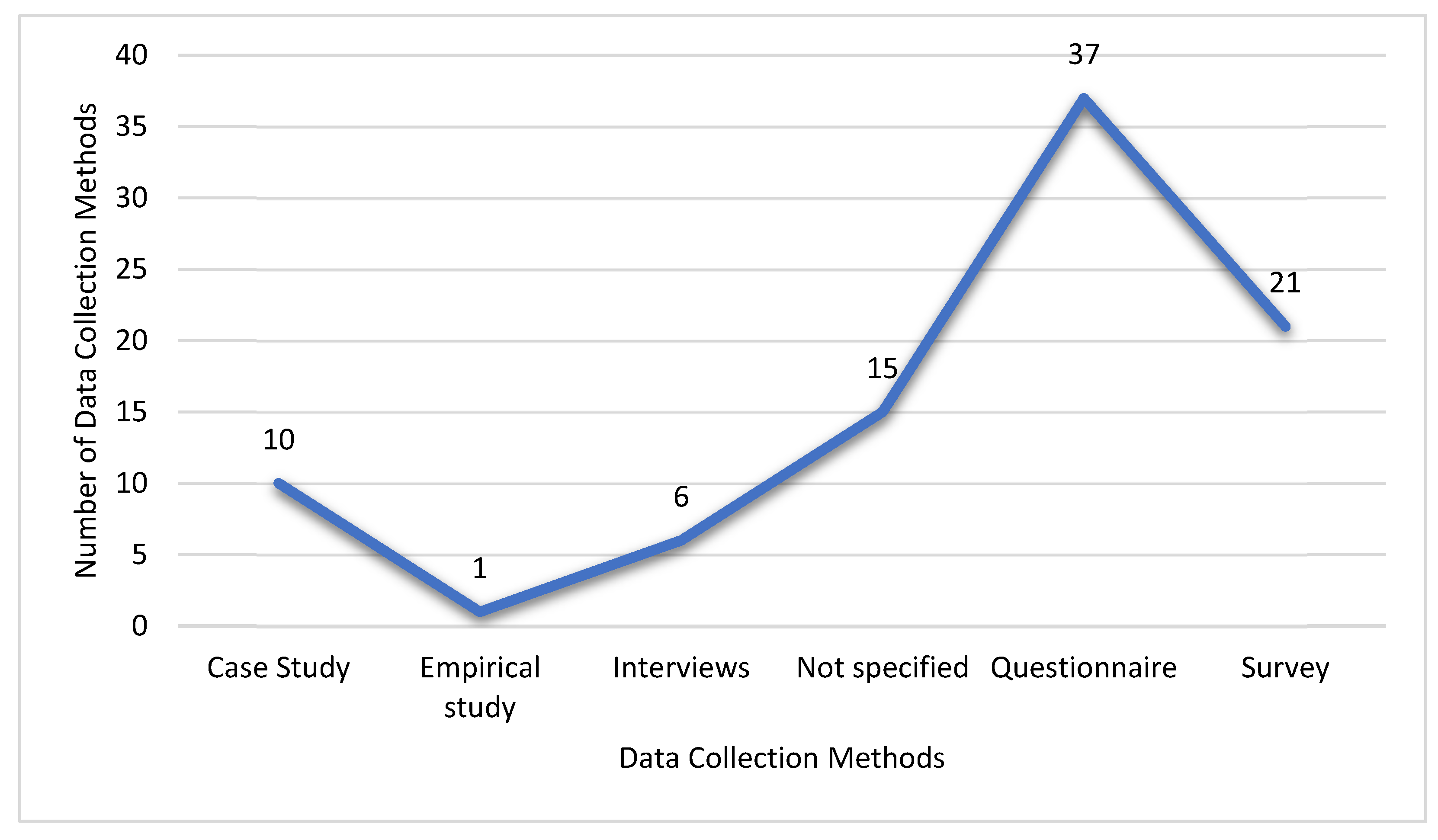
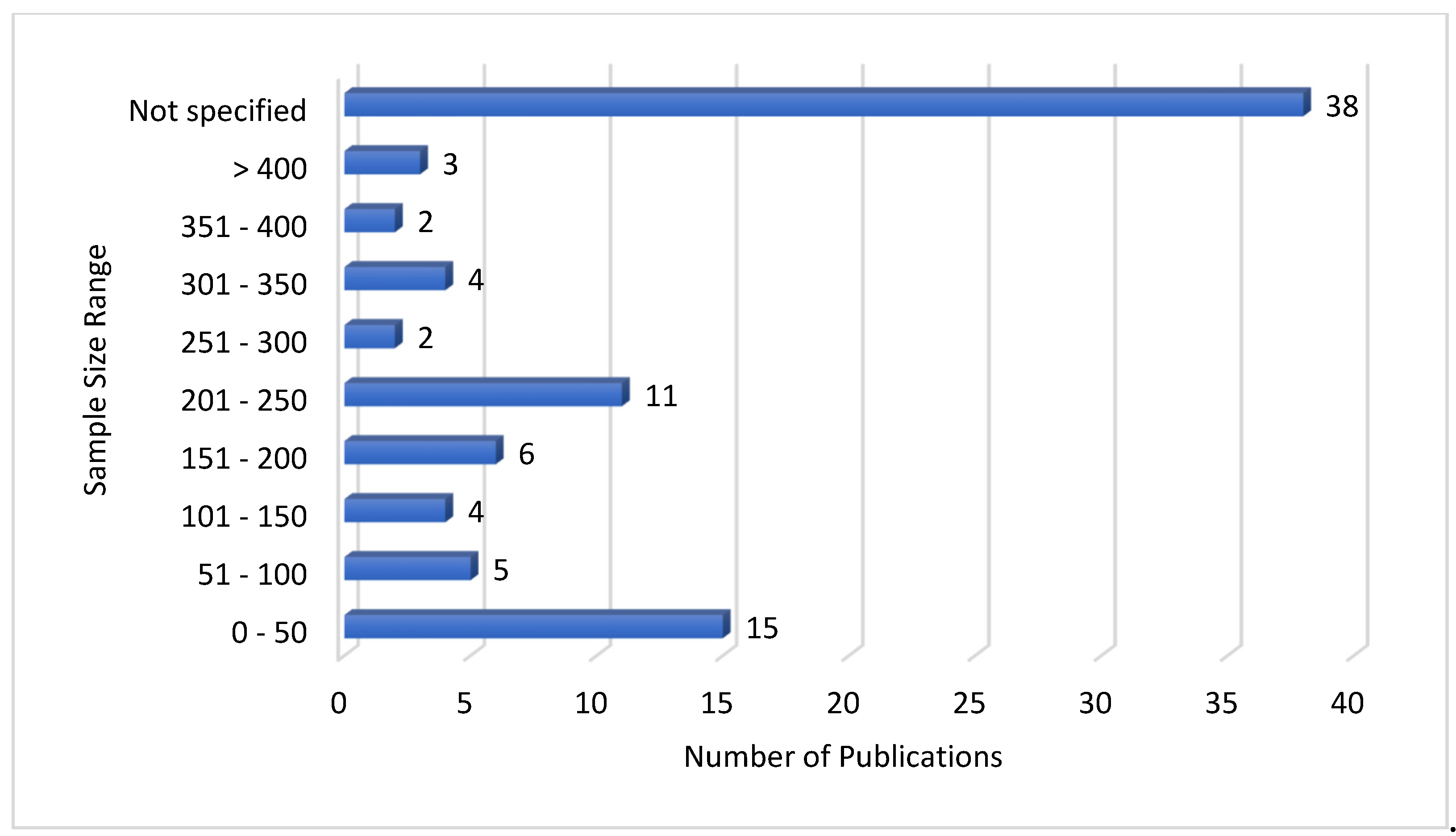
| Ref. | Cites | Year | Contribution | Pros | Cons |
| [21] | 35 | 2014 | Reviews cloud computing endorsement in SMEs, highlighting key risks and issues. | Exhaustive review concentrating on the risk analysis. | Restricted research of non-risk factors of adoption of cloud computing on SMEs. |
| [22] | 25 | 2014 | Evaluate cloud adoption in SMEs, emphasizing operational, technical, and organizational gaps. | Determine key endorsement factors; extensive literature review. | Limited by geography, scope; SME adoption model coverage and lacks institutional theory. |
| [23] | 18 | 2015 | Provides a systematic review of cloud computing adoption in SMEs, focusing on risk analysis and proposing a future research agenda. | Offers a structured literature overview, emphasizes critical risk issues, and provides clear future research directions. | Limited to articles up to 2016, focuses primarily on risk analysis, and may introduce subjective bias and limited scope. |
| [24] | 53 | 2015 | Reviews factors affecting cloud computing adoption and suggests a hypothetical model. | Specify key factors viz. management support, cost, ease of use, security, and usefulness. | Lacks practical validation, and limited focus on technical aspects. |
| [25] | 20 | 2015 | Evaluate cloud computing adoption in SMEs, highlighting adoption issues and future research on post-adoption impacts. | Determines research gaps and proposes to focus on the performance of SMEs. | Restricted focus on post-adoption problems. |
| [26] | 21 | 2016 | Risk assessment in cloud computing adoption. | Addresses crucial risk factors, improving decision-making for the adoption of cloud. | Lacks organizational perspective; restricted to technical issues. |
| [27] | 91 | 2016 | Factors affecting SME processes in cloud computing. | Emphasizes scalability as a key factor, providing a foundation for future performance. | Focuses on cloud adoption without integrating other crucial adoption factors like cost and security. |
| [28] | 49 | 2016 | Review on C-KMS in processes of SME KM. | Demonstrate a detailed review of recent developments. | Focuses on databases less KM processes. |
| [29] | 36 | 2017 | Privacy, trust, and security in cloud computing. | Extensive analysis of key concerns of cloud computing. | Focusing more on technical issues, and less on a holistic approach to adoption factors. |
| [30] | 3 | 2017 | Review of types of cloud computing supporting SMEs. | Furnish a list of solutions of cloud for SMEs. | Restricted to 12 articles, specific focus. |
| [31] | 0 | 2017 | Examines adoption of cloud computing among SMEs. | Emphasizes benefits like scalability and efficiency. | Limited focus on integration and security. |
| [32] | 7 | 2017 | Reviews factors affecting successful cloud computing in SMEs. | Emphasizes benefits like flexibility and efficiency. | Limited focus on precise difficulties. |
| [33] | 1 | 2018 | Classifies barriers to cloud computing. | Insights review using PRISMA, several databases. | Limited infrastructure issues and awareness. |
| [34] | 230 | 2018 | Reviews challenges, gaps, and advances in cloud computing. | A thorough review of current developments. | Limited to security and privacy. |
| [35] | 1 | 2020 | Examine HPC SME cloud contracts. | Furnish guidelines and guidance for contract management and negotiation. | Narrows topic with restricted extensive applicability. |
| [36] | 4 | 2020 | Review cloud computing in developing countries. | Determine key endorsement factors and specific advantages to developing countries. | Limited to developing countries. |
| [37] | 0 | 2020 | Carry out SLR and bibliometric review on IT adoption. | Highlights crucial improvement in publications. | May lack detailed IT implementation. |
| [38] | 50 | 2020 | Offers a systematic literature review on cybersecurity risk management in SMEs. | Highlights major perspectives in cybersecurity risk management using NVivo software. | Limited to 15 out of 50 papers, may not capture all relevant studies. |
| [39] | 17 | 2021 | Explains SMEs' benefits from cloud computing and key adoption factors | Identifies cost-effectiveness, flexibility, and scalability as primary benefits of cloud computing for SMEs. | Relies on a small sample size of six SMEs. |
| [40] | 36 | 2022 | Explores Indonesian SMEs' views on cloud computing benefits, challenges, and business impact. | Highlights cloud computing benefits for SMEs. | Points out concerns over security and limited infrastructure. |
| [41] | 7 | 2022 | Examines Indonesian SMEs' views on cloud computing benefits. | Highlights cost savings and improved communication as key benefits of cloud computing for SMEs. | Limited to security and infrastructure. |
| [42] | 108 | 2023 | Evaluate cloud computing suitability for Indian SMEs using a tested conceptual framework. | Highlights cost savings, scalability, and improved disaster recovery for SMEs. | Focus on only 121 manufacturing SMEs, which may limit generalizability. |
| [43] | 42 | 2024 | Identifies key factors in Pakistani SMEs' cloud adoption using the TEO framework. | Highlights six positive factors and validates them with robust statistical methods. | Relies on data from a limited sample of 103 SMEs. |
| [44] | 162 | 2024 | Reviews cloud computing adoption issues, classifies key factors and suggests a research agenda. | Identifies major adoption challenges and offers a future research agenda for cloud computing adoption. | May not cover all recent developments or emerging trends in cloud computing. |
| Proposed systematic review | Evaluates the impact of cloud computing on SME performance, highlighting key benefits such as cost savings, scalability, and enhanced operational efficiency. Examining factors influencing cloud adoption. | Offers a comprehensive understanding by identifying critical predictors of cloud adoption and assessing their impact. The review highlights research gaps and provides valuable guidance for researchers to enhance cloud adoption in SMEs. | |||
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
| Topic | Articles focusing on Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SME's Performance | Articles not related to Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SME's Performance |
| Research Framework | This article must include a research framework or methodology for Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SME's Performance | Articles lacking a clear research framework related to Evaluating the Impact of Cloud Computing on SME's Performance |
| Language | Must be written in English | Articles published in languages other than English |
| Period | Articles between 2014 and 2024 | Articles outside 2014 and 2024 |
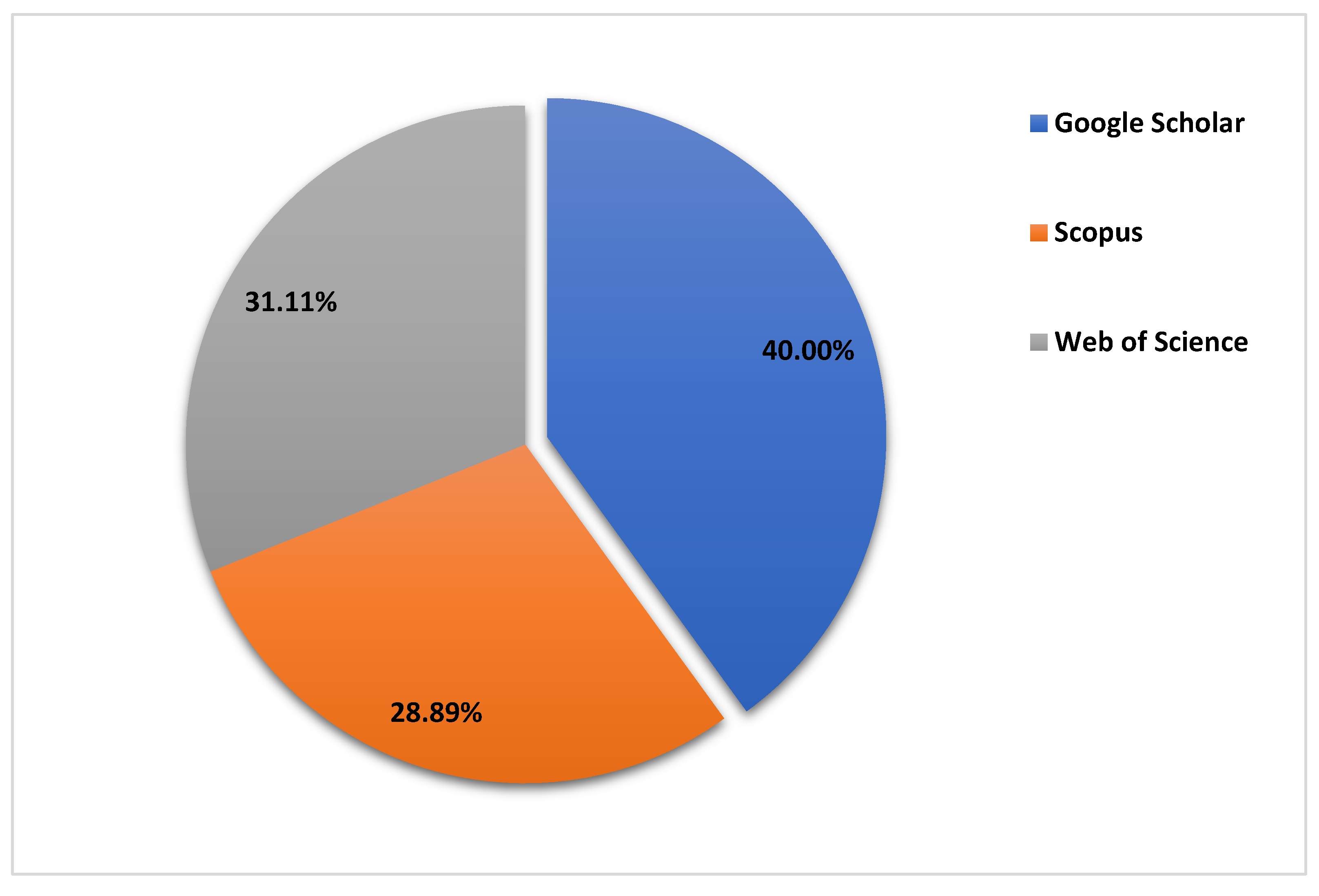
| No. | Online Repository | Number of results |
| 1 | Google Scholar | 18 100 |
| 2 | Web of Science | 165 |
| 3 | Scopus | 305 |
| Total | 18 570 |
| Step | Description | Details |
| Risk of bias tool | Customized Cochrane's Risk of Bia’s tool tailored to mixed-method studies | Based on the Cochrane tool adapted to cloud computing research |
| Bias domains | Five distinct bias domains used for evaluation | (1) Data privacy, (2) Economic benefits, (3) Data analysis techniques, (4) Software architecture, (5) Policy and operational issues |
| Bias classification | Studies classified into risk levels based on assessment | Low, Moderate, High, or unclear |
| Consensus process | Discrepancies resolved through discussions | A fourth author was consulted to settle disagreements |
| Outcome | Ensured a thorough, reliable evaluation of risk across all studies | Provided clarity on the impact of cloud computing on SMEs' performance |
| Synthesis step | Description | Methods applied |
| Eligibility synthesis | Evaluation of studies based on emphasis on cloud computing and alignment with review objectives | Tabulation |
| Data preparation for synthesis | Preparation of data for synthesis, including conversion to uniform scales and handling of missing data | Standardization, Multiple Imputation |
| Tabulation and visualization of results | Presentation of results in tables and graphical formats to highlight patterns and ensure transparency | Structured Tables, Forest Plots |
| Synthesis of results | Data aggregation using meta-analysis models to determine summary estimates and assess consistency across studies | Fixed-Effects Model, Random-Effects Model, Heterogeneity Tests |
| Exploring causes of heterogeneity | Examination of factors contributing to variability in outcomes through subgroup analysis and meta-regression | Subgroup Analysis, Meta-Regression |
| Sensitivity analyses | Testing the robustness of the synthesized results by excluding high-risk studies and using alternative models | Sensitivity Tests, Model Comparison |
| QA | Research Quality Assessment Questions |
| QA1 | Is the aim of the research explicitly stated? |
| QA2 | Does the research clearly specify the data collection methods? |
| QA3 | Is the impact of cloud computing on SMEs' performance clearly analyzed? |
| QA4 | Is there a clear and appropriate research methodology utilized in the study? |
| QA5 | Do the research findings contribute to the existing literature on the impact of cloud computing on SMEs? |
| Paper ID. | QA1 | QA2 | QA3 | QA4 | QA5 | Total | % |
| [46] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 60 |
| [47] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [48] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [49] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [50] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [51] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [52] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [53] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [54] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [55] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [56] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [57] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 4 | 80 |
| [58] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [59] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [60] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [61] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [62] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [63] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [64] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [65] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [66] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [67] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [68] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [69] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [70] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [71] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [72] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [73] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [74] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [75] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [76] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [77] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [78] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [79] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [80] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [81] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [82] | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 30 |
| [83] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [84] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 50 |
| [85] | 0.5 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 30 |
| [86] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [87] | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 | 20 |
| [88] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 60 |
| [89] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 50 |
| [90] | 1 | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 50 |
| [91] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 4 | 80 |
| [92] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [93] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 60 |
| [94] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [95] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [96] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [97] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [98] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 40 |
| [99] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [100] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [101] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [102] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [103] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [104] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 0 | 2.5 | 50 |
| [105] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [106] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [107] | 0.5 | 0 | 0.5 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 40 |
| [108] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 4 | 80 |
| [109] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [110] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [111] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 40 |
| [112] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [113] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [114] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [115] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [116] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 60 |
| [117] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [118] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [119] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [120] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [121] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [122] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
| [123] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 80 |
| [124] | 1 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3 | 60 |
| [125] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [126] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 4 | 80 |
| [127] | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 90 |
| [128] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 80 |
| [129] | 1 | 0 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [130] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [131] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 100 |
| [132] | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 3 | 60 |
| [133] | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 50 |
| [134,135] | 1 | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 3.5 | 70 |
| [136] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100 |
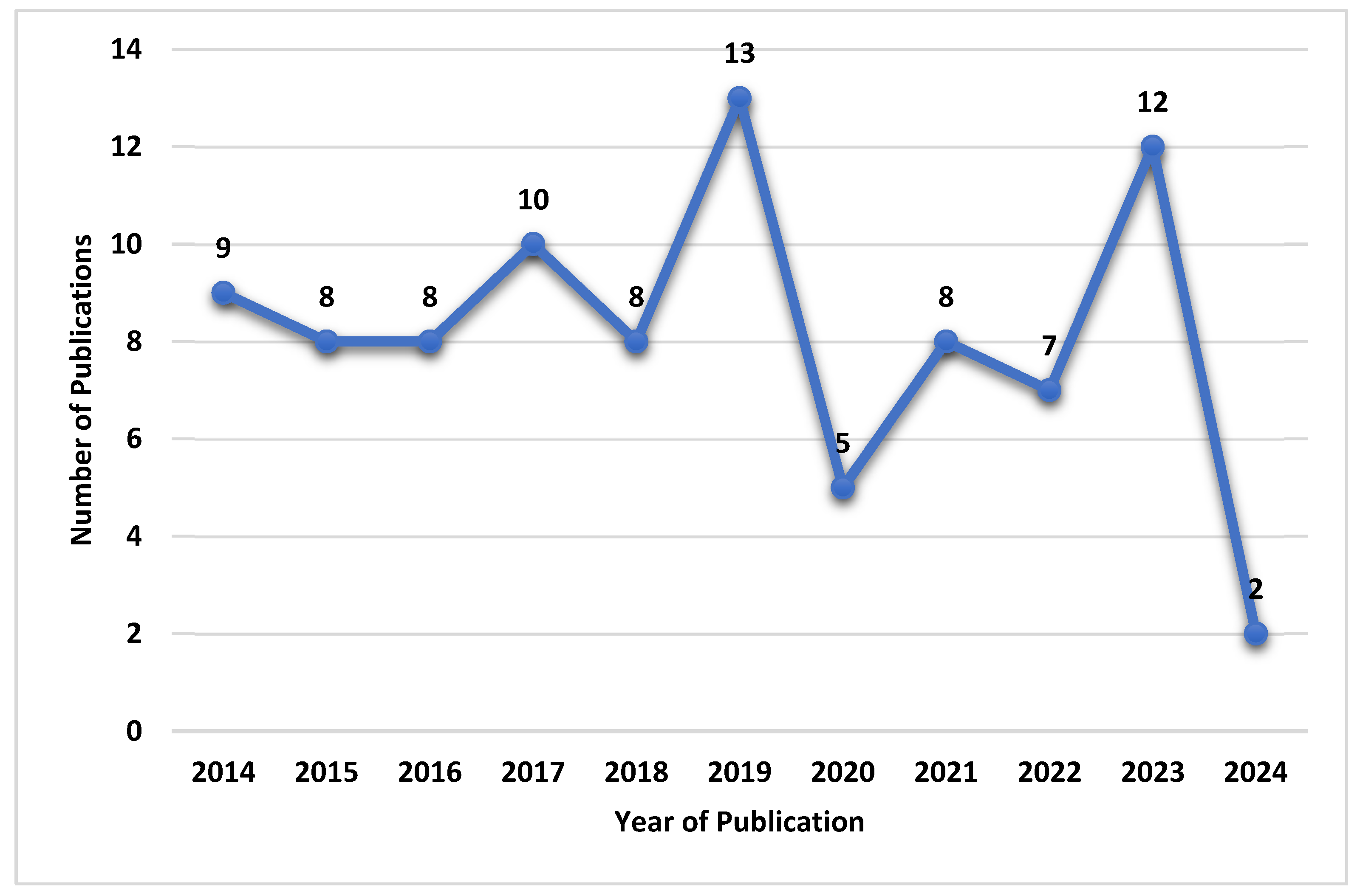
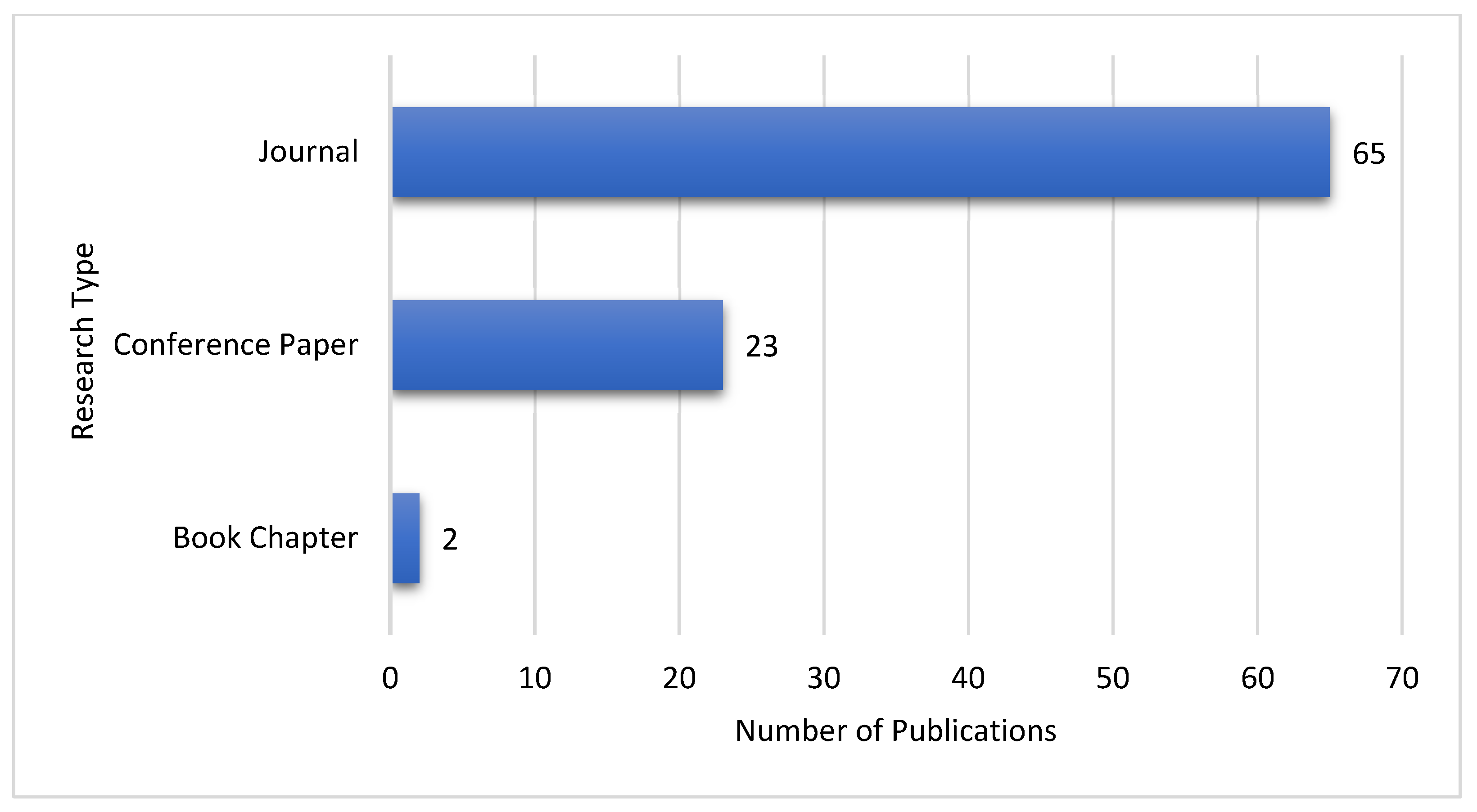
| Published Year | Book Chapter | Conference Paper | Journal |
| 2014 | 1 | 1 | 7 |
| 2015 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| 2016 | 0 | 5 | 3 |
| 2017 | 1 | 1 | 8 |
| 2018 | 0 | 1 | 7 |
| 2019 | 0 | 5 | 8 |
| 2020 | 0 | 1 | 4 |
| 2021 | 0 | 3 | 5 |
| 2022 | 0 | 3 | 4 |
| 2023 | 0 | 0 | 12 |
| 2024 | 0 | 0 | 2 |
| Study | Industry Context | Sample Size | Contributions |
| [46] | Transport | 86 | CC adoption in Latvian SMEs, its impact on business performance, and offers recommendations for SMEs, service providers, and government agencies. |
| [47] | Manufacturing | 415 | Cloud-based business services in Malaysian SMEs, analyzing their impact on financial and non-financial benefits, using PLS-SEM to evaluate organizational performance. |
| [48] | Finance | 50 | Cloud accounting on intellectual capital and business performance in Sri Lankan SMEs, using a quantitative approach to analyze relationships between these variables. |
| [49] | ICT | 30 | Factors influencing cloud computing adoption in SMEs within a developing economy, identifying key drivers, barriers, and influential factors, offering insights for service providers and policymakers. |
| [50] | ICT | 250 | Cloud computing adoption among Irish SMEs, revealing low migration rates and insufficient readiness assessments, and practical recommendations for successful cloud adoption. |
| [51] | ICT | 343 | Cloud computing adoption in Malaysian SMEs, finding that IT resources and external pressure significantly impact adoption. |
| [52] | Manufacturing | 200 | Cloud adoption model for SMEs based on the TOE framework and individual characteristics, identifying key factors like relative advantage, vendor support, and CEO trust. |
| [53] | ICT | 7 | The paper discusses the potential of cloud computing to enhance European SMEs' business efficiency, particularly through e-learning. |
| [54] | Finance | 12 | Cloud computing adoption by SMEs in sub-Saharan Africa, particularly in Nigeria. |
| [55] | ICT | 112 | Impact of cloud computing on business performance in Turkish SMEs, finding a positive effect on performance despite general reluctance. |
| [56] | Accounting | 198 | Cloud computing adoption in Romanian SMEs, identifying key influencing factors such as managerial knowledge and perceived costs. |
| [57] | Manufacturing | 90 | IT resources significantly impact cloud computing adoption in Malaysian SMEs, while top management support and employee knowledge do not. |
| [58] | ICT | 470 | SMEs' role in national economies and how cloud computing boosts their productivity and global competitiveness. |
| [59] | Finance | 14 | SMEs' perceptions of cloud computing solutions and their benefits, focusing on Romania's North-West region. It assesses awareness levels and provides insights for both IT solution providers and SMEs. |
| [60] | Manufacturing | 120 | The study examines how the cloud of things impacts performance in Indian SMEs, analyzing factors such as security, ease of use, and top management support. |
| [61] | Manufacturing | 7 | Cloud computing boosts Nigerian SMEs' efficiency but faces adoption challenges. The study aims to develop a framework for evaluating and improving cloud services for SMEs. |
| [62] | - | - | Cloud computing addresses key challenges for South African SMEs, including red tape and IT costs. A Cloud Adoption Framework, based on the TOE model, is proposed to enhance SME survival rates. |
| [63] | Marketing | 372 | Examines determinants of cloud computing adoption in SMEs and measures its impact on firm performance by enhancing organizational agility. |
| [64] | Manufacturing | 317 | Determinants of cloud adoption in Indian SMEs validated, showing the impact on economic performance. |
| [65] | ICT | 305 | SMEs include relative advantage, compatibility, complexity, cost savings, and security, with adoption depending on relative advantage, compatibility, cost, and security. |
| [66] | Manufacturing | 170 | SMEs in Sabah, Malaysia, while a relative advantage, competitive pressure, and external support do not significantly impact adoption. |
| [67] | ICT | 95 | Cost benefits drive cloud adoption in Irish SMEs, but service availability concerns limit uptake. |
| [68] | ICT | 80 | Cloud computing offers affordable solutions for SMEs, particularly in developing countries like Saudi Arabia, based on a comprehensive survey of small businesses on the West Coast. |
| [69] | - | 11 | Cloud computing adoption strategies for Sub-Saharan African SMEs identified key factors: setting goals, creating a roadmap, and tailoring strategies to enhance growth and customer experience. |
| [70] | Manufacturing | 300 | Cloud-based ERP adoption in Penang SMEs: Top management support positively impacts the manufacturing sector; other factors show no significant effect. |
| [71] | Manufacturing | 9 | Positive impact on SMEs' non-financial performance; negative impact on financial performance. |
| [72] | ICT | 36 | Cost benefits and scalability drive adoption; barriers include broadband issues and vendor lock-in. TOE framework identifies key enablers and organizational factors. |
| [73] | - | - | Key factors include cost reduction, security, and management support; Diffusion of Innovation (DOI) and Technology Organization and Environment (TOE) theories frame the study. |
| [74] | ICT | - | Indian SMEs face challenges and costs; this paper reviews ERP deployment models, and cost factors, and presents a framework for evaluating cloud-based ERP feasibility. |
| [75] | ICT | - | SMEs can overcome high costs and resource limitations; and explore HPC requirements, cluster-based applications, Google's HPC Cloud, and vendor performance. |
| [76] | Manufacturing | 100 | Key factors influencing adoption to aid in expanding cloud use among SMEs. |
| [77] | ICT | - | Cloud computing methodologies examine various systems and discuss applications to highlight their transformative impact on technology and business operations. |
| [78] | Manufacturing | - | The study identifies key factors for cloud computing adoption in Indian MSMEs, highlighting 'previous technological experience' as crucial. |
| [79] | Manufacturing | - | Cloud computing and smart device model to enhance inventory management in fashion SMEs. |
| [80] | Manufacturing | 30 | Examines cloud computing adoption predictors in SMEs using SEM and ANN, highlighting server location and management support as key factors. |
| [81] | ICT | 387 | The study investigates cloud computing adoption's impact on SME sustainability. |
| [82] | Business & Economics | 209 | Influence of cloud computing adoption in Malaysian SMEs. It finds data security, technology readiness, and top management support as key predictors, with adoption intention mediating the relationship between these factors and actual usage. |
| [83] | ICT | 335 | The study identifies relative advantage, competitive pressure, compatibility, and industry pressure as key factors in cloud computing adoption among Czech SMEs. |
| [84] | ICT | 273 | The study examines how cloud computing assimilation reduces supply chain financing risks for SMEs. |
| [85] | Business & Economics | 14 | Factors affecting cloud technology implementation for Industry 4.0 in MSMEs. System integration, project management, and competitive pressure. |
| [86] | ICT | 20 | The study tests existing cloud computing adoption models for suitability in Irish SMEs and finds they are inadequate. |
| [87] | ICT | 230 | Cloud computing adoption in Lebanese SMEs using the TOE framework: technological and organizational factors positively impact adoption, while poor infrastructure and lack of government support hinder it. |
| [88] | ICT | 415 | Integration enhances environmental, financial, and social performance, offering practical insights for policymakers and managers. |
| [89] | ICT | 415 | The study finds that perceived benefit and upper management support drive cloud computing adoption in Palestinian SMEs, which in turn enhances performance. |
| [90] | - | 147 | Cloud computing impacts SMEs and large firms in India, finding SMEs benefit more due to better business scalability. |
| [91] | Accounting | - | Cloud computing into SME accounting systems improves management efficiency and economic settlements in China: risk management and secure network protections. |
| [92] | Finance | - | SME accounting system using cloud computing and sensor monitoring, resulting in a 13.84% increase in data accuracy and a 14.63% boost in processing efficiency compared to traditional systems. |
| [93] | - | - | Cloud strategies for SMEs focus on scalability, cost-effectiveness, performance, and efficiency. |
| [94] | ICT | - | The paper highlights the benefits of cloud over traditional methods for small and large enterprises. |
| [95] | ICT | - | Cloud adoption drivers for SMEs in Indonesia, using e-survey data analyzed with SPSS and Smart PLS. |
| [96] | - | - | The study proposes cryptographic mechanisms to ensure data uniqueness and security in cloud storage. |
| [97] | ICT | - | This study proposes a framework to explore how digital organizational culture impacts cloud computing adoption in SMEs. |
| [98] | - | - | It highlights security and privacy concerns as key inhibitors and aims to develop strategies to enhance cloud adoption. |
| [99] | ICT | 202 | SMEs in Kenya, despite their growth and potential benefits, are slow to adopt cloud computing. |
| [100] | ICT | - | This study evaluates cloud computing adoption among SMEs in Saudi Arabia. |
| [101] | Accounting | - | Cloud accounting adoption in SMEs, influenced by TOE factors, enhances organizational performance. |
| [102] | Agriculture | - | Exploring the impact of cloud computing on SMEs in Africa reveals enhanced operational efficiency, scalability, and cost savings. |
| [103] | ICT | 25 | Cloud computing adoption in Malaysian enterprises remains low. Key factors influencing adoption include security, top management support, cost savings, and competitive, and trading partner pressures. |
| [104] | Business & Economics | 197 | The model highlights critical factors and their impact on performance. |
| [105] | ICT | - | Cloud computing adoption in Somali SMEs is driven by cost savings, firm size, top management support, and regulatory support, while security concerns and competitive pressure are less significant. |
| [106] | Retail | 227 | This study examines how Cloud Computing Utilization (CCU) helps Emerging Market SMEs in Iran and Turkey overcome informational and marketing barriers. |
| [107] | Business & Economics | 203 | fsQCA reveals complex causations and configurations not captured by traditional methods, offering new theoretical and practical insights. |
| [108] | ICT | - | Cloud adoption in Botswana: recommendations for a tailored adoption framework are also provided. |
| [109] | ICT | 249 | This study investigates how technological, organizational, and environmental factors influence IT managers' decisions to adopt cloud computing in the UK. |
| [110] | Manufacturing | 200 | This study explores how technological, organizational, and environmental (TOE) factors influence cloud accounting adoption in SMEs, emphasizing the mediating role of a cloud computing vision. |
| [111] | ICT | 249 | Examines cloud computing adoption intentions, pricing strategies, and deployment models, highlighting factors that influence decision-making and implementation in organizations. |
| [112] | ICT | 36 | Promotes cloud computing adoption and use among agile software developers in South Africa, focusing on enhancing development efficiency and flexibility. |
| [113] | Engineering | - | Explores IT adoption in Indian SMEs, highlighting opportunities and challenges for enhancing business operations and growth. |
| [114] | Business & Economics | - | Examines how cloud computing technology enhances small business performance by leveraging internet-based solutions. |
| [115] | Finance | - | Explores the development and implementation of an intelligent ERP platform for SMEs utilizing cloud computing technology. |
| [116] | ICT | - | Proposes a model to enhance cloud-based service adoption in Indian SMEs, addressing key factors for successful implementation. |
| [117] | ICT | - | Analyzes opportunities for SMEs in leveraging cloud high-performance computing, highlighting potential benefits and strategies through a meta-analysis. |
| [118] | Engineering | - | Proposes a hybrid method to enhance the quality of service for SMEs facing availability constraints in cloud environments. |
| [119] | ICT | 216 | Explores how cloud computing impacts small businesses by enhancing flexibility, reducing costs, and improving efficiency. |
| [120] | ICT | - | Proposes a conceptual model to enhance performance and sustainability in SMEs using cloud computing technology. |
| [121] | Business & Economics | - | Develops a questionnaire to assess SMEs' ongoing use behaviour of cloud computing services, focusing on continuous engagement and satisfaction. |
| [122] | ICT | - | Examines how SMEs apply and adopt big data technologies, focusing on the benefits and challenges of integration into their operations. |
| [123] | Accounting | - | Analyzes the key factors influencing the adoption of SaaS ERP systems in SMEs and the challenges they face during implementation. |
| [124] | ICT | - | Evaluates the performance of enterprise cloud computing systems, focusing on efficiency, reliability, and cost-effectiveness. |
| [125] | ICT | - | Describes the Cloud SME platform as a versatile multi-cloud solution for creating and running commercial cloud-based simulations. |
| [126] | Engineering | - | Explores interoperability challenges in cloud manufacturing through a case study on a private cloud structure tailored for SMEs. |
| [127] | Business & Economics | 4 | Examines the adoption of cloud computing by an SME in a developing economy, highlighting challenges and strategies for reaching cloud-based solutions. |
| [128] | ICT | - | Explores how Platform-as-a-Service (PaaS) solutions enable cloud-based Computational Fluid Dynamics (CFD), enhancing flexibility and scalability for users. |
| [129] | Engineering | - | Examines how compliance, network, and security factors moderate the success of implementing Cloud ERP systems, highlighting their impact on critical success factors. |
| [130] | ICT | 208 | Explores how cloud-based cross-system integration enhances connectivity and efficiency for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). |
| [131] | Business & Economics | - | Analyzes the key factors influencing Software-as-a-Service (SaaS) adoption in small businesses, focusing on risks, benefits, and both organizational and environmental determinants. |
| [132] | ICT | 198 | Proposes a personalized approach to customizing cloud manufacturing services to better meet individual business needs and enhance service efficiency. |
| [133] | Engineering | - | Examines different collaboration types and success factors in the IT service industry that contribute to sustainable growth. |
| [134] | ICT | 127 | Introduces the PaaS port semantic model, an ontology designed to enhance semantic interoperability in platform-as-a-service (PaaS) marketplaces. |
| [135] | ICT | - | Explores strategies for selecting cloud resource configurations across multiple layers in the context of big data, focusing on optimizing performance and resource utilization. |
| [136] | Manufacturing | 20 | Offering flexible and scalable solutions, cloud technology enhances process efficiency, collaboration, and agility. |
| Ref. | Random Sequence Generation (Selection Bias) | Allocation Concealment (Selection Bias) | Blinding of Participants and Personnel (Performance Bias) | Blinding of Outcome Assessment (Detection Bias) | Incomplete Outcome Data (Attrition Bias) | Selective Reporting (Reporting Bias) | Other Bias | Overall Risk of Bias |
| [46] | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Moderate |
| [47] | High | Unclear | Low | High | Low | High | Low | High |
| [48] | Low | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [49] | Unclear | High | High | High | High | Unclear | High | High |
| [50] | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [51] | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low | Low |
| [52] | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Moderate |
| [53] | High | Low | Low | High | High | Unclear | High | High |
| [54] | Unclear | High | High | Low | Low | Low | Low | High |
| [55] | High | Low | Low | High | High | Low | High | High |
| [56] | High | Low | Unclear | High | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [57] | Low | Low | Low | High | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [58] | Low | Low | Unclear | High | Low | Low | High | Low |
| [59] | High | Low | Unclear | High | High | Low | High | High |
| [60] | Low | Low | Low | Low | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [61] | High | High | High | High | Low | Low | High | High |
| [62] | High | Low | Unclear | Low | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [63] | Low | Low | Low | High | High | Low | High | Low |
| [64] | Low | Low | Unclear | High | High | Low | High | Low |
| [65] | High | Low | High | High | High | Low | High | High |
| *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** | *** |
| [126] | Low | Low | Unclear | High | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [127] | Low | Low | Low | High | low | Low | High | Low |
| [128] | Low | Unclear | High | Unclear | High | Low | High | Low |
| [129] | Low | Low | Unclear | High | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [130] | Low | High | High | High | High | Low | High | High |
| [131] | Low | Unclear | Low | High | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [132] | Low | Unclear | Unclear | High | High | Low | High | Moderate |
| [133] | Low | Low | Low | High | High | Low | High | Low |
| [134] | High | High | Unclear | High | High | Low | High | High |
| [135] | High | Low | High | High | High | Low | High | High |
| [136] | Low | Low | High | Low | Low | Unclear | Low | Moderate |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





