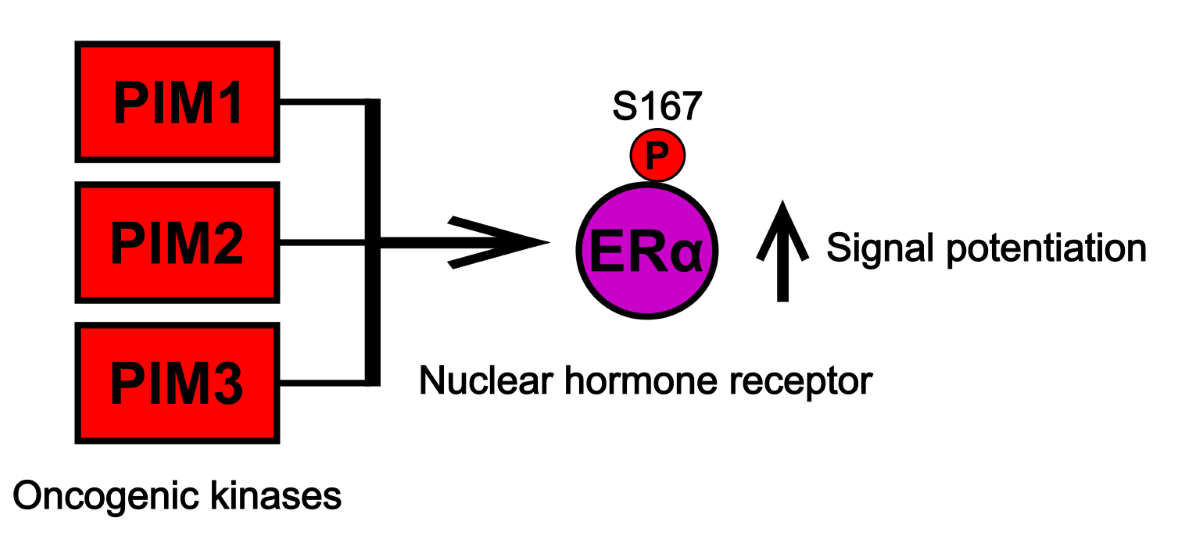
1. Introduction
The proviral integration site for Moloney murine leukemia virus (PIM) kinase family consists of three serine/threonine kinases, PIM1, PIM2 and PIM3. PIM substrates identified by us and others include multiple types of proteins, such as the transcription factors NFATC1 [
1], RUNX1 [
2] and FOXP3 [
3], the cell surface signaling proteins Notch1 [
4] and Notch3 [
5], the metabolic enzymes GSK3B [
3], LKB1 [
6] and LDHA [
7], the translational inhibitor AKT1S1 [
8], the pro-apoptotic protein BAD [
9], the chemokine receptor CXCR4 [
10], and the CAPZ actin capping proteins [
11]. Effects of PIM-dependent phosphorylation depend both on the substrate and the physiological context, but multiple studies, including our own, have shown that via phosphorylation, PIMs enhance cancer cell survival and motility in both hematologic and solid cancers, such as breast and prostate cancer [
12]. Moreover, PIMs promote chemo- and radioresistance of cancer cells [
13,
14,
15], suggesting that PIM inhibition may restore therapy sensitivity. Despite a slight reduction in size, triple knockout (TKO) mice lacking expression of all PIM family members are viable and fertile [
16], suggesting that PIMs would be a rational pharmacological target in cancer, with a favorable safety profile. However, while PIM inhibition has proven to be well-tolerated in patients, their efficacy in clinical trials has been underwhelming [
17], prompting a shift of interest towards the idea of using PIM inhibitors in combination with other treatments [
18].
Estrogen signaling via estrogen receptor α (ERα) is essential for female reproductive maturation and the development of female secondary sex characteristics, but some breast tumors exploit the receptor for growth and progression [
19]. Approximately 80% of breast tumors express ERα [
20]. These ERα-expressing (ER+) tumors can usually be treated effectively with endocrine therapies that work by blocking ERα signaling [
19]. However, the efficacy of estrogen blockers is limited in some patients due to intrinsic or acquired therapy resistance. There are numerous reports highlighting the relevance of genetics [
21,
22,
23], epigenetics [
24,
25], the cistrome [
26,
27,
28,
29,
30,
31] and DNA damage repair [
32] in therapy-resistant tumors, while other studies have pointed to mechanisms involving signal rewiring [
33,
34,
35,
36,
37,
38,
39] and post-translational modifications (PTMs) [
40,
41,
42,
43,
44]. Endocrine therapy resistance is therefore complex and the molecular mechanisms that facilitate this phenotype appear to be context-dependent and should be handled on a case-by-case basis.
In MCF-7 luminal A breast cancer cells, PIM1 [
4,
45] and PIM3 [
4] expression is upregulated in response to stimulation with estradiol. PIM1 depletion through RNA silencing has been shown to reduce the proliferative capacity of these cells and increase apoptosis [
45]. In our previous study, we did not observe any major difference between the proliferation rates of wild-type (WT) MCF-7 cells and their CRISPR-edited TKO derivatives lacking expression of all three PIM kinases [
6]. Even though it is known that ERα regulates PIM1 and PIM3 expression, and that PIMs can function as oncoproteins in ER+ breast cancer cells, an unaddressed question is whether PIMs regulate the ERα signaling axis itself, as a feedback mechanism or otherwise. Furthermore, links between endocrine therapy resistance and PIMs have remained unexplored. Here we present data to demonstrate that ERα is a novel PIM substrate phosphorylated at serine-167. This site has previously been shown to be targeted by several kinases including RSK [
46,
47], AKT [
48], CK2 [
49], p70S6K [
42], IKKε [
43] and, Aurora-A [
44]. Loss of PIM expression or activity drastically reduces ERα signaling capacity, although this may also depend on factors other than serine-167 phosphorylation. Moreover, we did not find any evidence that PIMs, or phosphorylation at serine-167, would protect cells from the antiproliferative effects of antiestrogens. By contrast, expression of PIM proteins and phosphorylation of ERα were diminished in tamoxifen-resistant cells.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell culture, treatments, and transfections
MCF-7 and T-47D breast cancer cells and PC-3 prostate cancer cells were obtained from American Type Culture Collection (Manassas, VA, USA). MCF-7 cells were grown in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium, high glucose (DMEM) (Gibco™ #11965092; Thermo Fisher Scientific, Waltham, MA, USA), and T-47D and PC-3 cells in RPMI-1640 medium (Sigma-Aldrich, St. Louis, MI, USA). Both media were supplemented with L-glutamine, 10% fetal bovine serum (FBS), and penicillin/streptomycin. RPMI-1640 medium was further supplemented with MEM Non-Essential Amino Acids (Gibco™, #11140050; Thermo Fisher Scientific) and sodium pyruvate (Gibco™, #11360070; Thermo Fisher Scientific). Phenol red-free DMEM, high glucose (PRF-DMEM) (Gibco™ #21063029; Thermo Fisher Scientific), supplemented with charcoal stripped FBS (Gibco™ #A3382101; Thermo Fisher Scientific), L-glutamine, and penicillin/streptomycin, served as estrogen-deprivation medium. To stimulate or inhibit estrogen signaling, culture medium was supplemented with β-estradiol (#E2758; Sigma-Aldrich) or 4-hydroxytamoxifen (#T176, Sigma-Aldrich), respectively, from stock solutions dissolved in ethanol. PIMi (an unpublished and patented pan-PIM inhibitor, the name and structure of which has not yet been disclosed) and AZD1208 (a well-characterized pan-PIM inhibitor, AstraZeneca, Cambridge, UK) were solubilized in DMSO and used to inhibit PIM activity. MCF-7 and PC-3 cells were transfected with the FuGENE® HD Transfection Reagent (#E2311; Promega, Madison, WI, USA) and T-47D cells with the jetPEI® DNA transfection reagent (#101000053; Polyplus, Illkirch-Graffenstaden, France) according to the manufacturer’s protocols with transfection reagent to DNA ratios of 3:1.
2.2. DNA Constructs
The pEGFP-PIM1 vector expressing GFP-tagged mouse PIM1, the pcDNA™3.1/V5-His-C and pGEX-6P-1 vectors expressing human PIMs, and the pGEX-6P-1 vector expressing mouse Notch1 intracellular domain (ICD) have been described previously [
4]. pEGFP-C1-Erα was a kind gift from Michael Mancini [50}, (Addgene plasmid # 28230;
http://n2t.net/addgene:28230; RRID:Addgene_28230) and was used for subcloning the human
ESR1 coding sequence (CDS) into pFLAG-CMV-2 (Sigma-Aldrich) and the N-terminal fragment of the human
ESR1 CDS (residues 1 – 184) into pGEX-6P-1 (GE Healthcare Life Sciences, Little Chalfont, UK) or pRSFDuet™-1 (Merck Millipore, Burlington, MA, USA). Site-directed mutagenesis of serine-167 to either alanine (SA) or glutamic acid (SE) was achieved by using Ultra Pfu DNA Polymerase (Stratagene, San Diego, CA, USA) according to the manufacturer’s protocol. The primers used for subcloning and mutagenesis are described in
Supplementary Tables 1 and
2, respectively. The 3X ERE TATA luc reporter construct was a kind gift from Donald McDonnell [
51] (Addgene plasmid # 11354;
http://n2t.net/addgene:11354; RRID:Addgene_11354). The pSV-β-galactosidase plasmid was purchased from Promega.
2.3. Recombinant Protein Production in Escherichia Coli
pGEX-6P-1 plasmids (expressing GST-PIMs, GST-ERα
184 or GST-Notch1-ICD) and pRSFDuet™-1 plasmid (expressing His-ERα
184) were transformed into BL21
E. coli and cultured overnight in Lysogeny broth at +30°C. The following day, when the optical density of the culture at 600 nm wavelength (OD
600) reached approximately of 0.6, 250 µM isopropyl-β-d-galactosidase (Sigma-Aldrich) was added to induce recombinant protein expression, and the bacteria were cultured for another 4 h (GST-PIMs) or 24 h (GST-ERα
184, His-ERα
184, GST-Notch1-ICD). The steps for isolating and purifying GST- and His-tagged recombinant proteins from the bacterial cultures have been described previously [
11].
2.4. Western Blotting
Cells were lysed for 10 min in ice-cold buffer containing 50 mM Tris–HCl, pH 8.0, 150 mM NaCl, 2 mM EDTA, 1% NP-40, 5 mM NaF, 10 mM β-glycerophosphate, 1 mM Na3VO4, 1 mM PMSF, 2 μg/ml leupeptin, aprotinin and pepstatin A. The cell lysates were scraped from the wells, transferred to Eppendorf tubes, and sonicated with a Branson Sonifier 450 probe sonicator for 10 seconds. Lysates were then centrifuged at 21,000 x g for 10 seconds and supernatants were collected. The protein concentrations of these lysates were determined using Pierce™ BCA Protein Assay Kit (#23228; Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Protein aliquots (20–90 μg) were separated by SDS/PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membranes (Merck Millipore). The membranes were incubated overnight at +4°C with primary antibodies. Secondary antibody staining was performed for 30 min at RT with HRP-linked secondary antibodies. Antibody details can be found in Supplementary Table 3. For immunoprecipitation of Flag-tagged proteins, lysate aliquots containing 1 mg of protein were incubated with 10 μL of anti-Flag® M2 affinity agarose gel (#A2220; Sigma-Aldrich). After 1 h incubation with rotation at +4°C, the samples were washed three times with lysis buffer. For western blotting, non-reducing 2X Laemmli sample buffer was added to the samples which were then heated for 10 min at +95°C prior to gel loading. Chemiluminescence was detected by Clarity or Clarity Max ECL western blotting substrates (#1705061/#1705062; Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA). Results were visualized with the ChemiDoc™ MP Imaging System (Bio-Rad) and analyzed with ImageJ (Wayne Rasband, National Institutes of Health, Bethesda, MD, USA).
2.5. In Vitro Kinase Assays
In vitro kinase assays were performed as described previously [
52], but without radioactivity. In brief, 0.5 – 1.0 μg aliquots of kinase and substrate proteins were incubated together per reaction. The samples were then separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred onto PVDF membranes. The membranes were probed with the sequence-specific RXXS*/T* phospho-antibody at +4°C overnight followed by HRP-linked secondary antibody staining for 30 min at RT. Antibody details can be found in
Supplementary Table 3. Chemiluminescence was detected as above for western blotting. Total protein levels were assessed afterwards by Ponceau S staining.
2.6. Luciferase Assays
The 3X ERE TATA luc reporter construct was transfected into cells together with the pSV-β-galactosidase plasmid. The luciferase values obtained were normalized according to β-galactosidase activity. Assays were performed using a Luciferase Assay System kit (#E1500; Promega) following the manufacturer’s instructions. Shortly, cell lysates were mixed with either D-luciferin for 5 minutes or ortho-nitrophenyl-β-galactoside (ONPG) for 30 minutes, after which bioluminescence or absorbance at 420 nm wavelength were measured with the EnSpire® Multimode Plate Reader (PerkinElmer, Turku, Finland).
2.7. Quantitative PCR
The NucleoSpin RNA kit (#740955.50; Macherey-Nagel, Düren, Germany) was used to isolate RNA from cell populations, following which complementary DNA (cDNA) samples were synthesized using a SensiFAST cDNA Synthesis Kit (#BIO-65054; Meridian Bioscience, Cincinnati, OH, USA). Quantitative PCR (qPCR) reaction mixtures were prepared with 5× HOT FIREPol EvaGreen qPCR Mix Plus (#08-24-0000S; Solis BioDyne, Tartu, Estonia) according to the manufacturer's instructions. The primer sequences for detection of ESR1, TFF1, XBP1, RET, and GAPDH (a housekeeping gene control) transcripts are described in Supplementary Table 4.
2.8. Viability Assays
To determine cell viability, MTT assays were performed as described previously [
53]. Briefly, cells cultured in 96-well plates were incubated for 4 h with 0.5 mg/ml 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyl tetrazolium bromide (MTT) reagent at +37°C. The resulting formazan crystals were solubilized by addition of 0.04 M HCl in isopropanol followed by mixing. Alternatively, alamarBlue™ assays were performed using the alamarBlue™ Cell Viability Reagent (#DAL1025; Thermo Fisher Scientific) according to the manufacturer’s instructions. Briefly, cells cultured in 96-well plates were incubated for 4 h with alamarBlue™ reagent at +37°C. For both MTT and alamarBlue™ assays, absorbance at 570 nm, serving as an index of cell viability, was measured using the EnSpire® Multimode Plate Reader.
2.9. Statistical Analysis and Figure Preparation
GraphPad Prism 6.0 (GraphPad Software, Boston, MA, USA) was used to prepare charts and results were analyzed by Student’s t-test. Where statistically significant difference was detected (p < 0.05), this was marked by *, with error bars signifying SEM. Inkscape was used for figure preparation.
3. Results
3.1. Estrogen Receptor α is a Novel PIM Substrate
As we and others had previously observed that PIM expression can be enhanced by treatment with estradiol [
4,
45], we wanted to determine whether PIMs, in turn, regulate ERα activity. We first overexpressed Flag-tagged ERα in wild-type (WT) MCF-7 breast cancer cells, PC-3 prostate cancer cells or their CRISPR-edited triple knockout (TKO) derivatives, which lack expression of all three PIM family members, and which have been previously prepared and characterized by us [
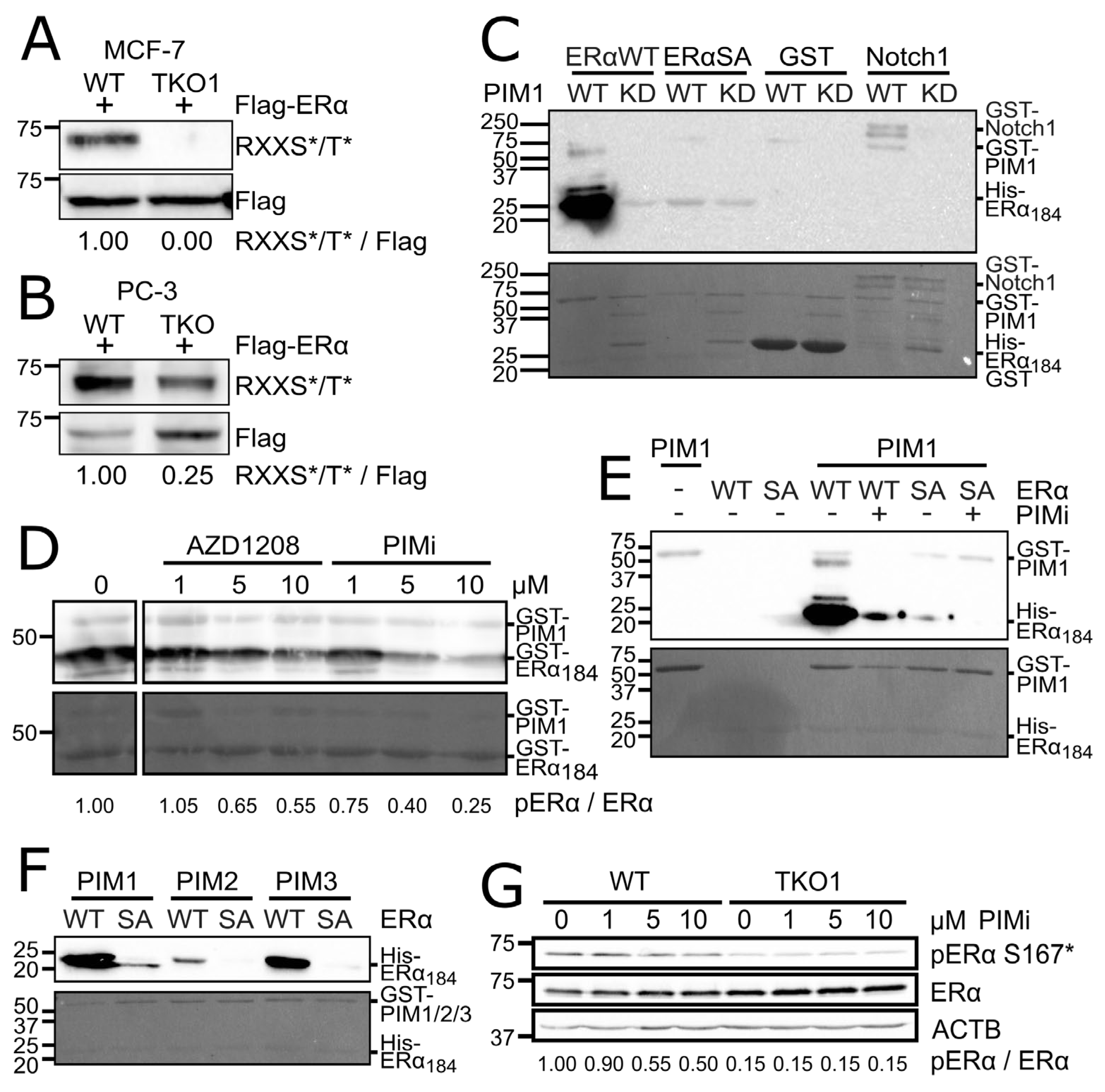
6]. Flag-tagged ERα was then immunoprecipitated and the phosphorylation level of the protein was determined using a phosphospecific antibody that recognizes phosphorylated amino acids within the consensus sequence of RXXS*/T* resembling a PIM target site. In both MCF-7 and PC-3 TKO derivatives, the level of ERα phosphorylation was drastically reduced as compared to WT cells (
Figure 1A-B), suggesting that ERα is a PIM substrate.
We then checked for such serines or threonines in ERα that aligned with the RXXS*/T* antibody target sequence. We found five such sites (S154, S167, S236, S338, and S518), and compared their preceding sequences to the PIM consensus phosphorylation sequences. These have been reported to contain K/R-K/R-R-L-S*/T*-X, where X represents an amino acid with a small chain [
54], or R-X-R-H-X-S*, where X represents any amino acid [
55]. Despite the lack of direct matches to either sequence, serine-167 (S167) within the sequence RERLAS*TND drew our interest, owing to its match at all but leucine-165, and it being an established phosphorylation site for several kinases [
42,
43,
44,
46,
47,
48,
49]. S167 sits in the N-terminal activation function-1 (AF-1) domain of the receptor. We therefore cloned the ERα N-terminal domain, consisting of amino acids 1-184 (ERα
184) into GST- and His-tagged bacterial expression vectors. We also used site-directed mutagenesis to generate a serine-167 to alanine (SA) phosphodeficient mutant of His-tagged ERα
184. We subsequently carried out
in vitro kinase assays on combinations of ERα
184 and PIMs, along with appropriate controls or pharmacological PIM inhibition.
PIM1 phosphorylated ERα
184 far more strongly than Notch1-ICD, a known PIM substrate [
4] that served as a positive control (
Figure 1C). Phosphorylation was disrupted by using the SA mutant instead of WT or kinase-deficient (KD) PIM1 in place of WT (
Figure 1C), or the PIM-selective small molecule inhibitors AZD1208 and PIMi (
Figure 1D-E). PIMi refers to an unpublished, but patented compound, which in our hands has behaved similarly to several previously characterized PIM-inhibitors, including AZD1208 (
Supplementary Figure 1). Furthermore, all PIM kinase family members were able to phosphorylate WT ERα
184, but not SA (
Figure 1F), although PIM2 was less active than PIM1 and PIM3 in this assay. To prove that PIMs also phosphorylate ERα when expressed at endogenous levels, we used an ERα S167* phosphospecific antibody and observed that phosphorylation of its target site was reduced in MCF-7 cells lacking PIMs, or in response to PIM inhibition (
Figure 1G).
3.2. PIM Kinases Enhance ERα Signaling
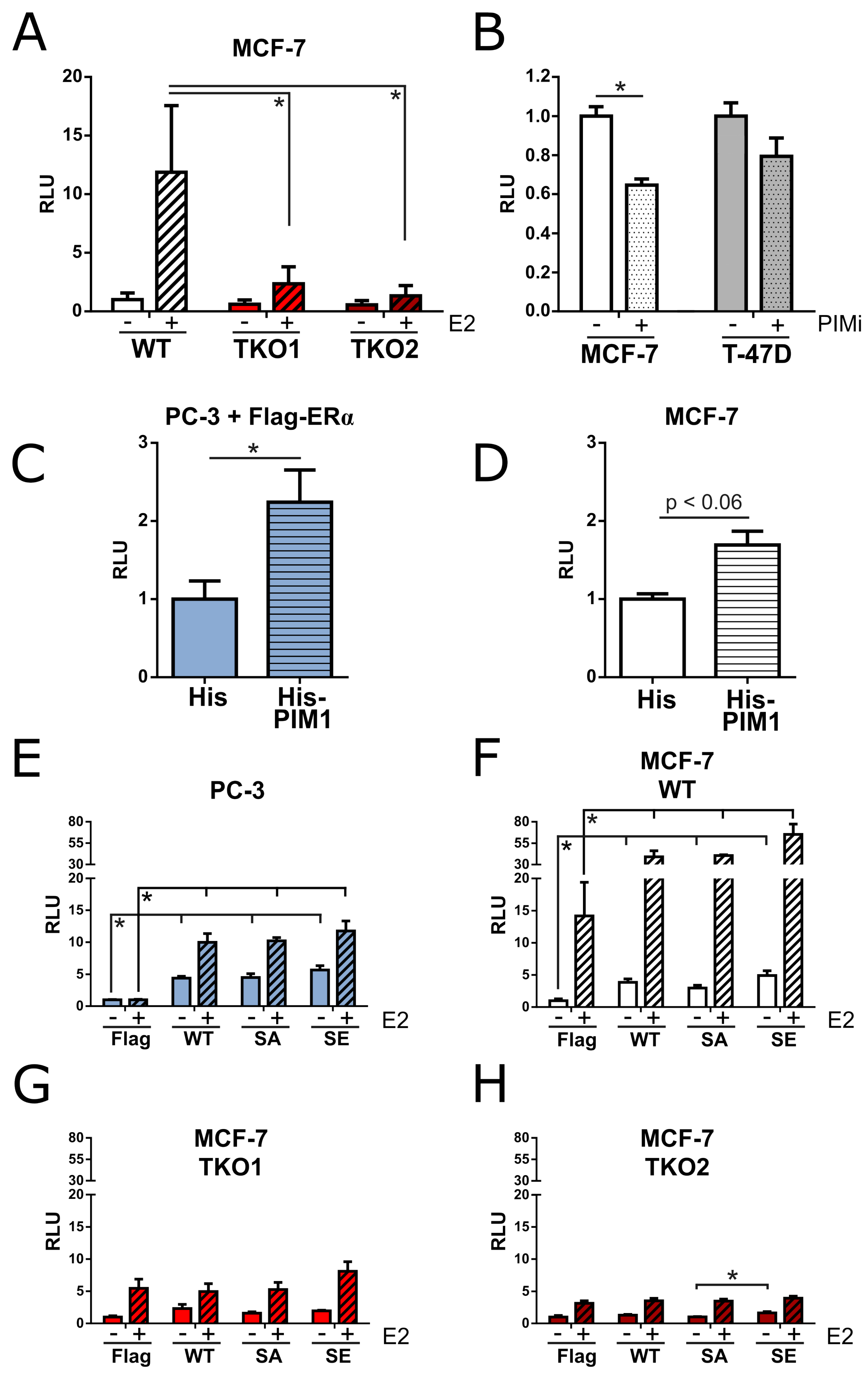
To determine how PIMs influence ERα signaling, we performed luciferase assays on the lysates of cells that had been transfected with estrogen-inducible luciferase and constitutively expressed β-galactosidase reporter constructs. We subsequently compared the ERα activity in WT and TKO MCF-7 cells and observed a dramatic decrease in cells lacking PIMs, both in the absence and especially in the presence of estradiol (
Figure 2A). Following this, we explored the effects of PIM inhibition on basal ERα activity in MCF-7 cells or in T-47D cells, which represent another line of luminal A breast cancer cells. Basal ERα activity was significantly decreased in inhibitor-treated MCF-7 cells, while a smaller and statistically insignificant decrease was observed in T-47D cells (
Figure 2B). This difference may be explained by lower levels of PIMs in T-47D as compared to MCF-7 cells [
5]. ERα-naïve PC-3 cells were included in subsequent experiments, as there was limited interference from endogenous ERα signaling in these cells. In PC-3 cells, we could potentiate luciferase activity by co-transfecting PIM1 along with ERα (
Figure 2C). Likewise, in MCF-7 cells with endogenous ERα signaling, overexpression of PIM1 enhanced luciferase activity (
Figure 2D). We subsequently overexpressed ERα WT, SA, serine-167 to glutamic acid (SE) phosphomimicking mutant or the Flag vector control in PC-3 cells, in MCF-7 WT cells, and in two independent MCF-7 TKO cell clones, and measured luciferase activity in the absence or presence of estradiol to see if there was any difference between phosphomutants (
Figure 2E-H). As expected, estradiol potentiated luciferase activity in all cases, except for control-transfected PC-3 cells. Interestingly, the ERα-dependent luciferase activities remained even lower in the two MCF-7 TKO cell clones than in the ERα-naïve PC-3 cells, irrespective of the transfected constructs. While lack of the PIM target site in the SA mutant did not reduce luciferase activity in either MCF-7 or PC-3 cells as compared to WT ERα, the SE mutant was slightly more potent.
We next performed quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qPCR) assays with MCF-7 WT and TKO cells to see how the absence of PIMs influences the expression levels of
TFF1,
RET and
XBP1, which are all ERα-regulated genes [
56,
57,
58,
59] (
Figure 3A). We observed that in TKO cells, mRNA levels for all these genes were downregulated in comparison to WT cells, most notably for
TFF1, so we decided to validate this finding by western blotting. Indeed, the TFF1 protein levels were substantially reduced in TKO cells as compared to WT cells (
Figure 3B). Moreover, PIM overexpression increased TFF1 expression in cells cultured in estrogen-deprived conditions (
Figure 3C). This was most noticeable in PIM1-overexpressing cells and not observed in estradiol-treated cells, where basal PIM expression most likely was sufficient to support estrogen-dependent ERα activity.
3.3. PIM Overexpression Does Not Protect Cells from Tamoxifen
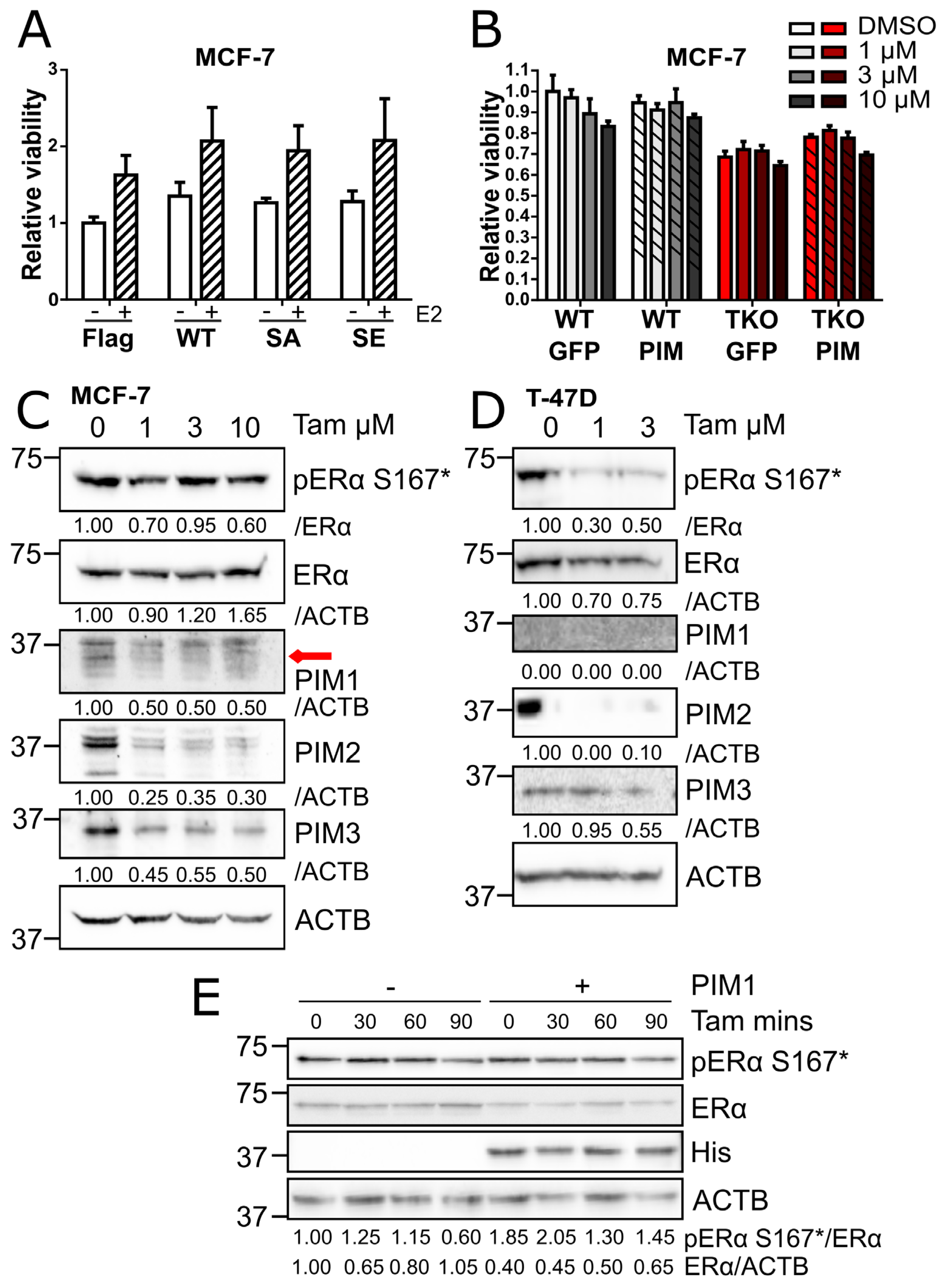
We then wanted to determine whether PIMs influence cellular responses to tamoxifen or estrogen deprivation. We first performed MTT-based viability assays with MCF-7 cells overexpressing WT ERα or the SA or SE phosphomutants. These cells had been cultured in the absence or presence of 10 nM estradiol for 4 days. Although ERα overexpression led to a modest, but statistically insignificant increase in viability under both conditions, cells expressing the SA and SE phosphomutants proved to be equally viable (
Figure 4A). We then overexpressed PIM1 in MCF-7 WT and TKO cells to see whether this would protect cells against tamoxifen-induced reduction in cell viability. While PIM1 overexpression slightly enhanced the viability of TKO cells, there was no statistically significant improvement in the relative viability of WT or TKO cells treated with tamoxifen as compared to cells overexpressing the vector control (
Figure 4B).
To see whether acquired tamoxifen resistance is associated with increased or decreased PIM expression levels, we cultured MCF-7 and T-47D cells in media containing different concentrations of tamoxifen for 3 months. MCF-7 cells acquired resistance at 1, 3, and 10 µM, while no T-47D cells survived continuous culturing at 10 µM, leaving us with cell populations resistant to either 1 or 3 µM. Protein levels of PIM family members were diminished in resistant cells and the level of ERα S167 phosphorylation was also reduced (
Figure 4C-D). A shorter treatment with tamoxifen for up to 90 minutes was also enough to substantially reduce ERα S167 phosphorylation in cells overexpressing PIM1, where the basal phosphorylation levels however were higher (
Figure 4E). Thus, we obtained no evidence to suggest that PIM kinases contribute to acquisition of tamoxifen resistance in ER+ luminal A breast cancer cells.
4. Discussion
Post-translational modifications modulate ERα signaling output, and in doing so can influence the physiology of body tissues and pathophysiology of disease states. To date, twenty-seven distinct phosphorylation sites have been identified on ERα [
60]. The most studied of these are S118 and S167, and numerous studies have explored the link between phosphorylation of these residues and patient responses to endocrine therapy [
61].
Here we show, to our knowledge, the first piece of evidence that ERα is a PIM substrate, and that PIM-dependent phosphorylation occurs at the broadly known ERα phosphosite S167 in the N-terminal AF-1 activation domain. PIMs therefore join the company of several S167-targeting kinases such as RSK [
46,
47], AKT [
48], CK2 [
49], p70S6K [
42], IKKε [
43], Aurora-A [
44]. ERα in turn joins the growing list of substrates that can be phosphorylated by both PIMs and AKTs, the functional roles of which overlap in many contexts [
12,
62]. We performed
in vitro kinase assays to show that all three PIM family members can phosphorylate S167. Furthermore, we present evidence that PIMs also phosphorylate ERα in mammalian cells. We observed that lack of expression or activity of PIMs in MCF-7 cells drastically reduces S167 phosphorylation, suggesting that PIMs play a more dominant role in regulating ERα activity in this cell line as compared to other S167-phosphorylating kinases. Indeed, in MCF-7-based TKO cells lacking all three PIM family members, the mRNA and protein expression levels of several ERα target genes, particularly
TFF1 were remarkably reduced. These results align well with the previous finding that the ERα S167A phosphomutant binds more weakly to the promoter of
TFF1 than the wild-type protein [
63]. Furthermore, several reports have indicated that ERα S167A displays reduced transcriptional activity in BHK cells [
46,
47], COS-1 cells [
48], HeLa cells [
63], and MCF-10A cells [
43], and that ERα transcriptional activity can be enhanced by overexpression of S167-phosphorylating kinases such as AKT in COS-1 cells [
48], p70S6K in HEK293E cells [
42], and IKKϵ in MCF-7 cells [
43]. In accordance with this, we report here that in PC-3 and MCF-7 cells, PIM overexpression increases ERα transcriptional activity.
Data from our luciferase assays indicate that the phosphomimicking S167E mutant of ERα is slightly more active than WT and S167A, but this difference was in most cases statistically insignificant. It is somewhat surprising that the SE mutant is not a more potent activator of the ERα pathway, given how much ERα activity is increased by overexpression of S167-phosphorylating kinases. Perhaps the phosphomimicking glutamic acid residue is an inadequate mimetic of the phosphorylated serine. Nonetheless, it remains possible that PIMs also influence ERα via mechanisms other than S167 phosphorylation. As our data on PIM-mediated phosphorylation of S167 primarily rely on the usage of an RXXS*/T* phosphospecific antibody, we cannot rule out the possibility that PIMs also phosphorylate ERα at other sites. While there are five RXXS/T sites within ERα: S154, S167, S236, S338, and S518, only S154 and S167 are located in the N-terminus of ERα (1-184) used in the in vitro kinase assays. Our data indicate that S154 is not a PIM target site, but the other sites have not been investigated. Nevertheless, it seems unlikely that they would be targeted given that the sequences preceding them align less well with the PIM consensus sequence as compared to S167.
The effect of PIMs in cells that have been treated with tamoxifen was limited in our experiments. While basal ERα S167 phosphorylation is elevated in cells overexpressing PIM, tamoxifen treatment reduces S167 phosphorylation at a similar rate as in control cells. Furthermore, PIM overexpression did not offer any protection to cells treated with tamoxifen. ERα overexpression leads to a modest increase in viability of cells cultured in estrogen-starved conditions, but this is independent from ERα S167 phosphorylation status. These findings suggest that in 2D in vitro models, PIMs offer little advantage to cells in the context of estrogen deprivation or ERα blockade. These findings are consistent with our in-house tamoxifen-resistant cell lines, in which expression of all PIM kinase family members was downregulated, suggesting that the cells have not been rewired to utilize PIMs as part of a therapy-escape mechanism. Nonetheless, it would be of interest to examine patient data to determine whether there are any links between PIM expression in luminal A tumors and de novo resistance.
In broader terms, the role of S167 in tamoxifen resistance has been difficult to determine, with patient data often seeming to contradict those from cell-based studies. For example, several cell-based studies have suggested that phosphorylation at S167 is positively associated with endocrine therapy resistance [
43,
44,
48,
64]. Conversely, in one study using MCF-7 cell derivatives with stable expression of ERα S167A, the cells were equally viable to WT cells following treatment with estradiol or antiestrogens [
65], which is in line with what we observed. In patients, data from one study indicated that phosphorylation at S118, but not S167, correlates with resistance to tamoxifen [
41]. Indeed, other patient-based studies have even highlighted S167 phosphorylation as a positive prognostic marker in metastatic breast cancer patients treated with aromatase inhibitors [
66] and in postmenopausal breast cancer patients on endocrine therapies [
67], and as a predictor of positive response to endocrine therapies in patients with metastatic breast cancer [
68]. Furthermore, in another study S167 phosphorylation was linked to low tumor grade, improved relapse-free survival, and overall survival, suggesting that the activity of kinases that phosphorylate S167 correlates with better prognoses [
69].
ERα activity is known to regulate PIM expression [
4,
45], and our study has demonstrated that PIMs in turn influence ERα activity, which hints at a system of signaling feedback between these two proteins, the depth and complexity of which was beyond the scope of this study. The influence of PIMs on ERα involves, but is not limited to, phosphorylation on S167 in the AF-1 domain. In the future, studying the effects of S167A at an endogenous level would be highly informative, and could offer higher fidelity over the experiments performed with overexpressed phosphomutants. Indeed, given the positive results that have been reported in patients treated with various kinase inhibitors in combination with antiestrogens [
70,
71,
72,
73,
74], it seems likely that when the activity of certain kinases is enriched, it provides luminal A breast cancer cells with a means to escape endocrine therapies.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on
Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, W.B.E. and P.J.K.; investigation, W.B.E., K.L.M. and I.L.; writing-original draft preparation, W.B.E.; writing-review and editing, P.J.K., C.M.S., W.B.E. and K.L.M.; supervision, P.J.K. and C.M.S.; funding acquisition, W.B.E. and C.M.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This study was financially supported by the Drug Research Doctoral Programme of the University of Turku, the Ida Montin Foundation, the K. Albin Johansson foundation, the Magnus Ehrnrooth Foundation, the Maud Kuistila Foundation, the Paulo Foundation, the Cancer Society of Southwest Finland, the Turku University Foundation, and the University of Turku joint research grant fund for scientific research on cancer to WBE, and The Cancer Foundation Finland to CMS.
Data Availability Statement
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
We thank Ronja Mehtonen, Tytti Uurasmaa and Francisco Sáez González (University of Turku) for their technical assistance during this project. We would also like to thank Pirkko Härkönen, Niina Santio, and Eeva Rainio (University of Turku) for helpful discussions.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Aho, T.L.T.; Sandholm, J.; Peltola, K.J.; Ito, Y.; Koskinen, P.J. Pim-1 kinase phosphorylates RUNX family transcription factors and enhances their activity. BMC Cell Biol 2006, 7, 21. [CrossRef]
- Rainio, E.-M.; Sandholm, J.; Koskinen, P.J. Cutting Edge: Transcriptional activity of NFATc1 is enhanced by the Pim-1 kinase. J Immunol 2002, 168, 1524–1527. [CrossRef]
- Santio, N.M.; Salmela, M.; Arola, H.; Eerola, S.K.; Heino, J.; Rainio, E.M.; Koskinen, P.J. The PIM1 kinase promotes prostate cancer cell migration and adhesion via multiple signaling pathways. Exp Cell Res 2016, 342, 113-124. [CrossRef]
- Santio, N.M.; Landor, S.K.-J.; Vahtera, L.; Ylä-Pelto, J.; Paloniemi, E.; Imanishi, S.Y.; Corthals, G.; Varjosalo, M.; Manoharan, G.B.; Uri, A.; et al. Phosphorylation of Notch1 by Pim kinases promotes oncogenic signaling in breast and prostate cancer cells. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 43220–43238. [CrossRef]
- Landor, S.K.J.; Santio, N.M.; Eccleshall, W.B.; Paramonov, V.M.; Gagliani, E.K.; Hall, D.; Jin, S.B.; Dahlström, K.M.; Salminen, T.A.; Rivero-Müller, A.; et al. PIM-induced phosphorylation of Notch3 promotes breast cancer tumorigenicity in a CSL-independent fashion. J Biol Chem 2021, 296:100593. [CrossRef]
- Mung, K.L.; Eccleshall, W.B.; Santio, N.M.; Rivero-Müller, A.; Koskinen, P.J. PIM kinases inhibit AMPK activation and promote tumorigenicity by phosphorylating LKB1. Cell Commun Signal 2021, 19(1):68. [CrossRef]
- Mung, K.L.; Meinander, A.; Koskinen, P.J. PIM kinases phosphorylate lactate dehydrogenase A at serine 161 and suppress its nuclear ubiquitination. FEBS J 2023, 290(9):2489-2502. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Beharry, Z.M.; Harris, T.E.; Lilly, M.B.; Smith, C.D.; Mahajan, S.; Kraft, A.S. PIM1 protein kinase regulates PRAS40 phosphorylation and mTOR activity in FDCP1 cells. Cancer Biol Ther 2009, 8(9):846-53. [CrossRef]
- Aho, T.L.T.; Sandholm, J.; Peltola, K.J.; Mankonen, H.; Lilly, M.; Koskinen, P.J. Pim-1 kinase promotes inactivation of the pro-apoptotic Bad protein by phosphorylating it on the Ser112 gatekeeper site. FEBS Lett 2004, 571, 43-49,. [CrossRef]
- Grundler, R.; Brault, L.; Gasser, C.; Bullock, A.N.; Dechow, T.; Woetzel, S.; Pogacic, V.; Villa, A.; Ehret, S.; Berridge, G.; et al. Dissection of PIM serine/threonine kinases in FLT3-ITD-induced leukemogenesis reveals PIM1 as regulator of CXCL12-CXCR4-mediated homing and migration. J Exp Med 2009, 206(9):1957-70. [CrossRef]
- Santio, N.M.; Vainio, V.; Hoikkala, T.; Mung, K.L.; Lång, M.; Vahakoski, R.; Zdrojewska, J.; Coffey, E.T.; Kremneva, E.; Rainio, E.M.; et al. PIM1 accelerates prostate cancer cell motility by phosphorylating actin capping proteins. Cell Commun Signal 2020, 18(1):121. [CrossRef]
- Santio, N.M.; Koskinen, P.J. PIM Kinases: From survival factors to regulators of cell motility. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 2017, 93, 74–85.
- Zemskova, M.; Sahakian, E.; Bashkirova, S.; Lilly, M. The PIM1 kinase is a critical component of a survival pathway activated by docetaxel and promotes survival of docetaxel-treated prostate cancer cells. J Biol Chem 2008, 283(30): 20635–20644. [CrossRef]
- Peltola, K.; Hollmen, M.; Maula, S.M.; Rainio, E.; Ristamäki, R.; Luukkaa, M.; Sandholm, J.; Sundvall, M.; Elenius, K.; Koskinen, P.J.; et al. Pim-1 kinase expression predicts radiation response in squamocellular carcinoma of head and neck and is under the control of Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor. Neoplasia 2009, 11(7): 629–636. [CrossRef]
- Marayati, R.; Stafman, L.L.; Williams, A.P.; Bownes, L. V.; Quinn, C.H.; Aye, J.M.; Stewart, J.E.; Yoon, K.J.; Anderson, J.C.; Willey, C.D.; et al. PIM kinases mediate resistance to cisplatin chemotherapy in hepatoblastoma. Sci Rep 2021, 11(1):5984. [CrossRef]
- Mikkers, H.; Nawijn, M.; Allen, J.; Brouwers, C.; Verhoeven, E.; Jonkers, J.; Berns, A. Mice deficient for all PIM Kinases display reduced body size and impaired responses to hematopoietic growth factors. Mol Cell Biol 2004, 24, 6104–6115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cortes, J.; Tamura, K.; DeAngelo, D.J.; de Bono, J.; Lorente, D.; Minden, M.; Uy, G.L.; Kantarjian, H.; Chen, L.S.; Gandhi, V.; et al. Phase I Studies of AZD1208, a proviral integration Moloney virus kinase inhibitor in solid and haematological cancers. Br J Cancer 2018, 118, 1425–1433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luszczak, S.; Kumar, C.; Sathyadevan, V.K.; Simpson, B.S.; Gately, K.A.; Whitaker, H.C.; Heavey, S. PIM kinase inhibition: Co-targeted therapeutic approaches in prostate cancer. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2020, 5, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clusan, L.; Ferrière, F.; Flouriot, G.; Pakdel, F. A basic review on estrogen receptor signaling pathways in breast cancer. Int J Mol Sci 2023, 24(7): 6834. [CrossRef]
- American Cancer Society. Breast Cancer Facts and Figures 2022–2024. Available online: https://www.cancer.org/content/dam/cancer-org/research/cancer-facts-and-statistics/breast-cancer-facts-and-figures/2022-2024-breast-cancer-fact-figures-acs.pdf (accessed on 23 August 2024).
- Pejerrey, S.M.; Dustin, D.; Kim, J.A.; Gu, G.; Rechoum, Y.; Fuqua, S.A.W. The impact of ESR1 mutations on the treatment of metastatic breast cancer. Horm Cancer 2018, 9(4): 215–228.
- Jeselsohn, R.; Bergholz, J.S.; Pun, M.; Cornwell, M.; Liu, W.; Nardone, A.; Xiao, T.; Li, W.; Qiu, X.; Buchwalter, G.; et al. Allele-specific chromatin recruitment and therapeutic vulnerabilities of ESR1 activating mutations. Cancer Cell 2018, 33(2):173-186. [CrossRef]
- Lei, J.T.; Shao, J.; Zhang, J.; Iglesia, M.; Chan, D.W.; Cao, J.; Anurag, M.; Singh, P.; He, X.; Kosaka, Y.; et al. Functional annotation of ESR1 gene fusions in estrogen receptor-positive breast cancer. Cell Rep 2018, 7;24(6):1434-1444. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Gerrard, D.L.; Wang, J.; Li, T.; Yang, Y.; Fritz, A.J.; Rajendran, M.; Fu, X.; Schiff, R.; Lin, S.; et al. Temporal dynamic reorganization of 3D chromatin architecture in hormone-induced breast cancer and endocrine resistance. Nat Commun 2019, 10(1):1522. [CrossRef]
- Achinger-Kawecka, J.; Valdes-Mora, F.; Luu, P.L.; Giles, K.A.; Caldon, C.E.; Qu, W.; Nair, S.; Soto, S.; Locke, W.J.; Yeo-Teh, N.S.; et al. Epigenetic reprogramming at estrogen-receptor binding sites alters 3D chromatin landscape in endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Nat Commun 2020, 11(1):320. [CrossRef]
- Xu, G.; Chhangawala, S.; Cocco, E.; Razavi, P.; Cai, Y.; Otto, J.E.; Ferrando, L.; Selenica, P.; Ladewig, E.; Chan, C.; et al. ARID1A determines luminal identity and therapeutic response in estrogen-receptor-positive breast cancer. Nat Genet 2020, 52(2):198-207. [CrossRef]
- Nagarajan, S.; Rao, S. V.; Sutton, J.; Cheeseman, D.; Dunn, S.; Papachristou, E.K.; Prada, J.E.G.; Couturier, D.L.; Kumar, S.; Kishore, K.; et al. ARID1A influences HDAC1/BRD4 activity, intrinsic proliferative capacity and breast cancer treatment response. Nat Genet 2020, 52(2):187-197. [CrossRef]
- Hurtado, A.; Holmes, K.A.; Ross-Innes, C.S.; Schmidt, D.; Carroll, J.S. FOXA1 is a key determinant of estrogen receptor function and endocrine response. Nat Genet 2011, 43(1): 27–33. [CrossRef]
- Ross-Innes, C.S.; Stark, R.; Teschendorff, A.E.; Holmes, K.A.; Ali, H.R.; Dunning, M.J.; Brown, G.D.; Gojis, O.; Ellis, I.O.; Green, A.R.; et al. Differential oestrogen receptor binding is associated with clinical outcome in breast cancer. Nature 2012, 481(7381): 389–393. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Jeselsohn, R.; Pereira, R.; Hollingsworth, E.F.; Creighton, C.J.; Li, F.; Shea, M.; Nardone, A.; De Angelis, C.; Heiser, L.M.; et al. FOXA1 overexpression mediates endocrine resistance by altering the ER transcriptome and IL-8 expression in ER-positive breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2016, 113(43):E6600-E6609. [CrossRef]
- Fu, X.; Pereira, R.; De Angelis, C.; Veeraraghavan, J.; Nanda, S.; Qin, L.; Cataldo, M.L.; Sethunath, V.; Mehravaran, S.; Gutierrez, C.; et al. FOXA1 upregulation promotes enhancer and transcriptional reprogramming in endocrine-resistant breast cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 2019, 116(52):26823-26834. [CrossRef]
- Haricharan, S.; Punturi, N.; Singh, P.; Holloway, K.R.; Anurag, M.; Schmelz, J.; Schmidt, C.; Lei, J.T.; Suman, V.; Hunt, K.; et al. Loss of Mutl disrupts CHK2-dependent cell-cycle control through CDK4/6 to promote intrinsic endocrine therapy resistance in primary breast cancer. Cancer Discov 2017, 7(10):1168-1183. [CrossRef]
- Frogne, T.; Benjaminsen, R. V.; Sonne-Hansen, K.; Sorensen, B.S.; Nexo, E.; Laenkholm, A.V.; Rasmussen, L.M.; Riese, D.J.; De Cremoux, P.; Stenvang, J.; et al. Activation of ErbB3, EGFR and Erk is essential for growth of human breast cancer cell lines with acquired resistance to fulvestrant. Breast Cancer Res Treat 2009, 114(2):263-75. [CrossRef]
- McClaine, R.J.; Marshall, A.M.; Wagh, P.K.; Waltz, S.E. Ron receptor tyrosine kinase activation confers resistance to tamoxifen in breast cancer cell lines. Neoplasia 2010, 12(8): 650–658. [CrossRef]
- Turner, N.; Pearson, A.; Sharpe, R.; Lambros, M.; Geyer, F.; Lopez-Garcia, M.A.; Natrajan, R.; Marchio, C.; Iorns, E.; Mackay, A.; et al. FGFR1 amplification drives endocrine therapy resistance and is a therapeutic target in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2010, 70(5):2085-94. [CrossRef]
- Fox, E.M.; Miller, T.W.; Balko, J.M.; Kuba, M.G.; Sánchez, V.; Smith, R.A.; Liu, S.; González-Angulo, A.M.; Mills, G.B.; Ye, F.; et al. A kinome-wide screen identifies the insulin/IGF-I receptor pathway as a mechanism of escape from hormone dependence in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2011, 71(21):6773-84. [CrossRef]
- Kirkegaard, T.; Witton, C.J.; McGlynn, L.M.; Tovey, S.M.; Dunne, B.; Lyon, A.; Bartlett, J.M.S. AKT activation predicts outcome in breast cancer patients treated with tamoxifen. J Pathol 2005, 207(2):139-46. [CrossRef]
- Miller, T.W.; Hennessy, B.T.; González-Angulo, A.M.; Fox, E.M.; Mills, G.B.; Chen, H.; Higham, C.; García-Echeverría, C.; Shyr, Y.; Arteaga, C.L. Hyperactivation of Phosphatidylinositol-3 Kinase promotes escape from hormone dependence in estrogen receptor-positive human breast cancer. J Clin Invest 2010, 120(7):2406-13. [CrossRef]
- Staka, C.M.; Nicholson, R.I.; Gee, J.M.W. Acquired resistance to oestrogen deprivation: role for growth factor signalling kinases/oestrogen receptor cross-talk revealed in new MCF-7X model. Endocr Relat Cancer 2005, 12 Suppl 1:S85-97. [CrossRef]
- Likhite, V.S.; Stossi, F.; Kim, K.; Katzenellenbogen, B.S.; Katzenellenbogen, J.A. Kinase-specific phosphorylation of the estrogen receptor changes receptor interactions with ligand, deoxyribonucleic acid, and coregulators associated with alterations in estrogen and tamoxifen activity. Mol Endocrinol 2006, 20(12):3120-32. [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Cui, Y.K.; Huang, W.H.; Man, K.; Zhang, G.J. Chen, M.; Cui, Y.K.; Huang, W.H.; Man, K.; Zhang, G.J. Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor α at serine 118 is correlated with breast cancer resistance to tamoxifen. Oncol Lett 2013, 6(1): 118–124. [CrossRef]
- Yamnik, R.L.; Digilova, A.; Davis, D.C.; Brodt, Z.N.; Murphy, C.J.; Holz, M.K. S6 kinase 1 regulates estrogen receptor α in control of breast cancer cell proliferation. J Biol Chem 2009, 284(10): 6361-9. [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.-P.; Shu, S.-K.; Esposito, N.N.; Coppola, D.; Koomen, J.M.; Cheng, J.Q. IKKϵ Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor α Ser-167 and contribution to tamoxifen resistance in breast cancer. J Biol Chem 2016, 285(6): 3676–3684. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.Q.; Guo, J.P.; Yang, H.; Kanai, M.; He, L.L.; Li, Y.Y.; Koomen, J.M.; Minton, S.; Gao, M.; Ren, X.B.; et al. Aurora-A Is a determinant of tamoxifen sensitivity through phosphorylation of ERα in breast cancer. Oncogene 2014, 33(42):4985-96. [CrossRef]
- Malinen, M.; Jääskeläinen, T.; Pelkonen, M.; Heikkinen, S.; Väisänen, S.; Kosma, V.M.; Nieminen, K.; Mannermaa, A.; Palvimo, J.J. Proto-oncogene PIM-1 is a novel estrogen receptor target associating with high grade breast tumors. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2013, 365(2), 270–276. [CrossRef]
- Joel, P.B.; Smith, J.; Sturgill, T.W.; Fisher, T.L.; Blenis, J.; Lannigan, D.A. Pp90 Rsk1 regulates estrogen receptor-mediated transcription through phosphorylation of Ser-167. Mol Cell Biol 1998, 18(4): 1978–1984. [CrossRef]
- Clark, D.E.; Poteet-Smith, C.E.; Smith, J.A.; Lannigan, D.A. Rsk2 allosterically activates estrogen receptor α by docking to the hormone-binding domain. EMBO J 2001, 20(13):3484-94. [CrossRef]
- Campbell, R.A.; Bhat-Nakshatri, P.; Patel, N.M.; Constantinidou, D.; Ali, S.; Nakshatri, H. Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase/AKT-mediated activation of estrogen receptor α: A new model for anti-estrogen resistance. J Biol Chem 2001, 276(13):9817-24. [CrossRef]
- Arnold, S.F.; Obourn, J.D.; Jaffe, H.; Notides, A.C. Serine 167 is the major estradiol-induced phosphorylation site on the human estrogen receptor. Mol Endocrinol 1994, 8(9):1208-14. [CrossRef]
- Stenoien, D.L.; Mancini, M.G.; Patel, K.; Allegretto*, E.A.; Smith, C.L.; Mancini, M.A. Subnuclear trafficking of estrogen receptor-α and steroid receptor coactivator-1. Mol Endocrinol 2000, 14(4):518-34. [CrossRef]
- Hall, J.M.; McDonnel, D.P. The estrogen receptor β-isoform (ERβ) of the human estrogen receptor modulates ERα transcriptional activity and is a key regulator of the cellular response to estrogens and antiestrogens. Endocrinology 1999, 140(12):5566-78. [CrossRef]
- Kiriazis, A.; Vahakoski, R.L.; Santio, N.M.; Arnaudova, R.; Eerola, S.K.; Rainio, E.M.; Aumüller, I.B.; Yli-Kauhaluoma, J.; Koskinen, P.J. Tricyclic benzo[Cd]azulenes selectively inhibit activities of Pim kinases and restrict growth of Epstein-Barr virus-transformed cells. PLoS One 2013, 8(2):e55409. [CrossRef]
- Santio, N.M.; Vahakoski, R.L.; Rainio, E.M.; Sandholm, J.A.; Virtanen, S.S.; Prudhomme, M.; Anizon, F.; Moreau, P.; Koskinen, P.J. Pim-selective inhibitor DHPCC-9 reveals Pim kinases as potent stimulators of cancer cell migration and invasion. Mol Cancer 2010, 9:279. [CrossRef]
- Palaty, C.K.; Clark-lewis, I.; Leung, D.; Pelech, S.L. Phosphorylation site substrate specificity determinants for the Pim-1 proto-oncogene-encoded protein kinase. Biochem Cell Biol 1997, 75(2):153–162. [CrossRef]
- Peng, C.; Knebel, A.; Morrice, N.A.; Li, X.; Barringer, K.; Li, J.; Jakes, S.; Werneburg, B.; Wang, L. Pim kinase substrate identification and specificity. J Biol Chem 2007, 141, 353–362. [CrossRef]
- Masiakowski, P.; Breathnach, R.; Bloch, J.; Gannon, F.; Krust, A.; Chambon, P. Cloning of cDNA sequences of hormone-regulated genes from the MCF-7 human breast cancer cell line. Nucleic Acids Res 1982, 10(24):7895-903. [CrossRef]
- Boulay, A.; Breuleux, M.; Stephan, C.; Fux, C.; Brisken, C.; Fiche, M.; Wartmann, M.; Stumm, M.; Lane, H.A.; Hynes, N.E. The Ret receptor tyrosine kinase pathway functionally interacts with the ERα pathway in breast cancer. Cancer Res 2008, 68(10):3743-51. [CrossRef]
- Bertucci, F.; Houlgatte, R.; Benziane, A.; Granjeaud, S.; Adélaïde, J.; Tagett, R.; Loriod, B.; Jacquemier, J.; Viens, P.; Jordan, B.; et al. Gene expression profiling of primary breast carcinomas using arrays of candidate genes. Hum Mol Genet 2000, 9(20):2981-91. [CrossRef]
- Creighton, C.J.; Cordero, K.E.; Larios, J.M.; Miller, R.S.; Johnson, M.D.; Chinnaiyan, A.M.; Lippman, M.E.; Rae, J.M. Genes regulated by estrogen in breast tumor cells in vitro are similarly regulated in vivo in tumor xenografts and human breast tumors. Genome Biol 2006, 7(4):R28. [CrossRef]
- Hornbeck, P. V.; Zhang, B.; Murray, B.; Kornhauser, J.M.; Latham, V.; Skrzypek, E. PhosphoSitePlus, 2014: mutations, PTMs and recalibrations. Nucleic Acids Res 2015, 43(Database issue):D512-20. [CrossRef]
- Anbalagan, M.; Rowan, B.G. Estrogen receptor alpha phosphorylation and its functional impact in human breast cancer. Mol Cell Endocrinol 2015, 418(3):264-72.
- Warfel, N.A.; Kraft, A.S. PIM kinase (and Akt) biology and signaling in tumors. Pharmacol Ther 2015, 151: 41-49.
- Shah, Y.M.; Rowan, B.G. The Src kinase pathway promotes tamoxifen agonist action in Ishikawa endometrial cells through phosphorylation-dependent stabilization of estrogen receptor (Alpha) promoter interaction and elevated steroid receptor coactivator 1 activity. Mol Endocrinol 2005, 19: 732–748. [CrossRef]
- Pardeshi, J.; McCormack, N.; Gu, L.; Ryan, C.S.; Schröder, M. DDX3X Functionally and physically interacts with estrogen receptor-alpha. Biochim Biophys Acta Gene Regul Mech 2022, 1865(2):194787. [CrossRef]
- Huderson, B.P.; Duplessis, T.T.; Williams, C.C.; Seger, H.C.; Marsden, C.G.; Pouey, K.J.; Hill, S.M.; Rowan, B.G. Stable Inhibition of Specific Estrogen Receptor α(ERα) Phosphorylation confers increased growth, migration/invasion, and disruption of estradiol signaling in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. Endocrinology 2012, 153(9):4144-59. [CrossRef]
- Motomura, K.; Ishitobi, M.; Komoike, Y.; Koyama, H.; Nagase, H.; Inaji, H.; Noguchi, S. Expression of estrogen receptor beta and phosphorylation of estrogen receptor alpha serine 167 correlate with progression-free survival in patients with metastatic breast cancer treated with aromatase inhibitors. Oncology 2010, 79(1-2):55-61. [CrossRef]
- Ishida, N.; Baba, M.; Hatanaka, Y.; Hagio, K.; Okada, H.; Hatanaka, K.C.; Togashi, K.; Matsuno, Y.; Yamashita, H. PIK3CA mutation, reduced AKT serine 473 phosphorylation, and increased ERα serine 167 phosphorylation are positive prognostic indicators in postmenopausal estrogen receptor-positive early breast cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9(25):17711-17724. [CrossRef]
- amashita, H.; Nishio, M.; Kobayashi, S.; Ando, Y.; Sugiura, H.; Zhang, Z.; Hamaguchi, M.; Mita, K.; Fujii, Y.; Iwase, H. Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor α serine 167 is predictive of response to endocrine therapy and increases postrelapse survival in metastatic breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res 2005, 7(5):R753-64. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, J.; Sarwar, N.; Peston, D.; Kulinskaya, E.; Shousha, S.; Coombes, R.C.; Ali, S. Phosphorylation of estrogen receptor-α at Ser167 is indicative of longer disease-free and overall survival in breast cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13(19):5769-76. [CrossRef]
- Smyth, L.M.; Batist, G.; Meric-Bernstam, F.; Kabos, P.; Spanggaard, I.; Lluch, A.; Jhaveri, K.; Varga, A.; Wong, A.; Schram, A.M.; et al. Selective AKT Kinase inhibitor capivasertib in combination with fulvestrant in PTEN-mutant ER-positive metastatic breast cancer. NPJ Breast Cancer 2021, 7(1):44. [CrossRef]
- Hortobagyi, G.N.; Stemmer, S.M.; Burris, H.A.; Yap, Y.-S.; Sonke, G.S.; Hart, L.; Campone, M.; Petrakova, K.; Winer, E.P.; Janni, W.; et al. Overall survival with ribociclib plus letrozole in advanced breast cancer. New Engl J Med 2022, 386(10):942-950. [CrossRef]
- Johnston, S.R.D.; Toi, M.; O’Shaughnessy, J.; Rastogi, P.; Campone, M.; Neven, P.; Huang, C.S.; Huober, J.; Jaliffe, G.G.; Cicin, I.; et al. Abemaciclib plus endocrine therapy for hormone receptor-positive, HER2-negative, node-positive, high-risk early breast cancer (MonarchE): Results from a preplanned interim analysis of a randomised, open-label, phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol 2023, 24(1):77-90. [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, K.; Niikura, N.; Kikawa, Y.; Oba, M.; Kobayashi, K.; Tada, H.; Ozaki, S.; Toh, U.; Yamamoto, Y.; Tsuneizumi, M.; et al. Fulvestrant plus palbociclib in advanced or metastatic hormone receptor-positive/human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-negative breast cancer after fulvestrant monotherapy: Japan Breast Cancer Research Group-M07 (FUTURE Trial). Breast Cancer Res Treat 2023, 199(2):253-263. [CrossRef]
- Riemsma, R.; Forbes, C.A.; Amonkar, M.M.; Lykopoulos, K.; Diaz, J.R.; Kleijnen, J.; Rea, D.W. Systematic review of lapatinib in combination with letrozole compared with other first-line treatments for hormone receptor positive(HR+) and HER2+ advanced or metastatic breast cancer(MBC). Curr Med Res Opin 2012, 28(8):1263-79.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).