Submitted:
11 September 2024
Posted:
11 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
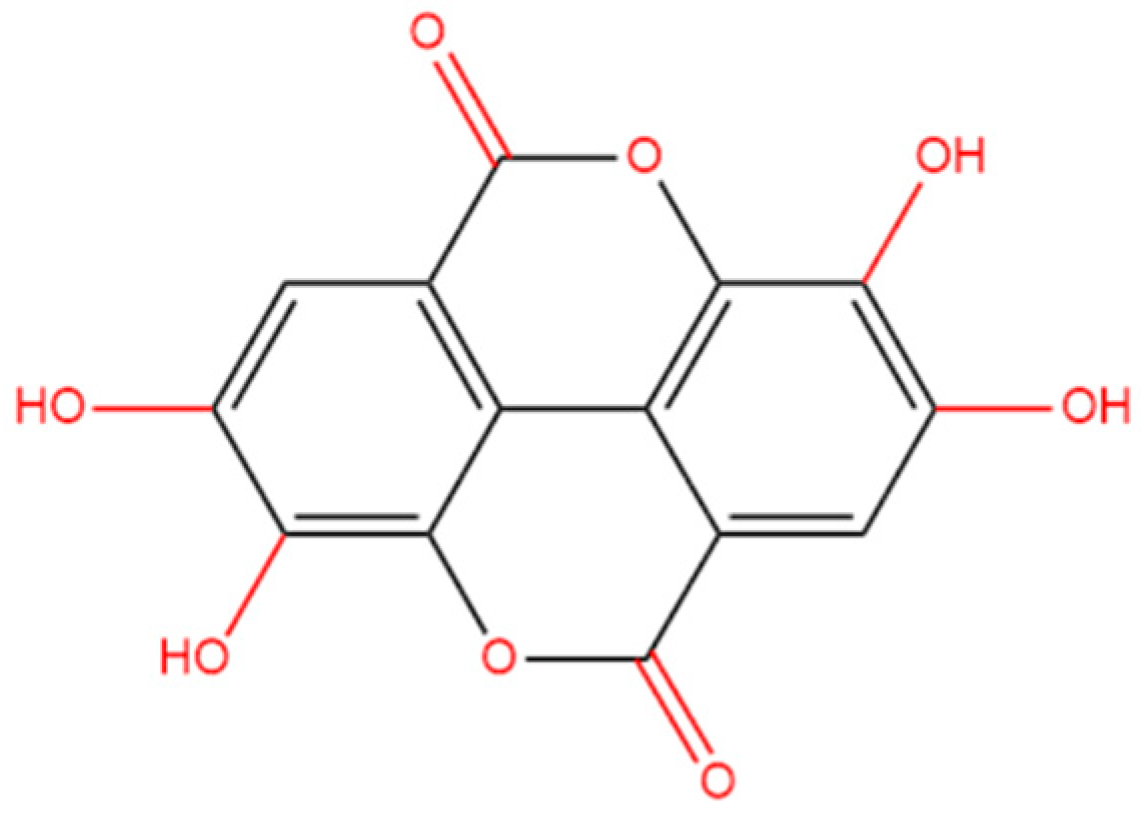
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemical and Reagents
2.2. Cell Viability and Treatment
2.3. Measurement of Cell Viabilities
2.4. LDH Measurement
2.5. Measurement of Cell Apoptosis
2.6. Measurement of Intracellular ROS Levels and Oxidative Stress Biomarkers
2.7. Measurement of Mitochondrial ROS
2.9. Western Blotting
2.10. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
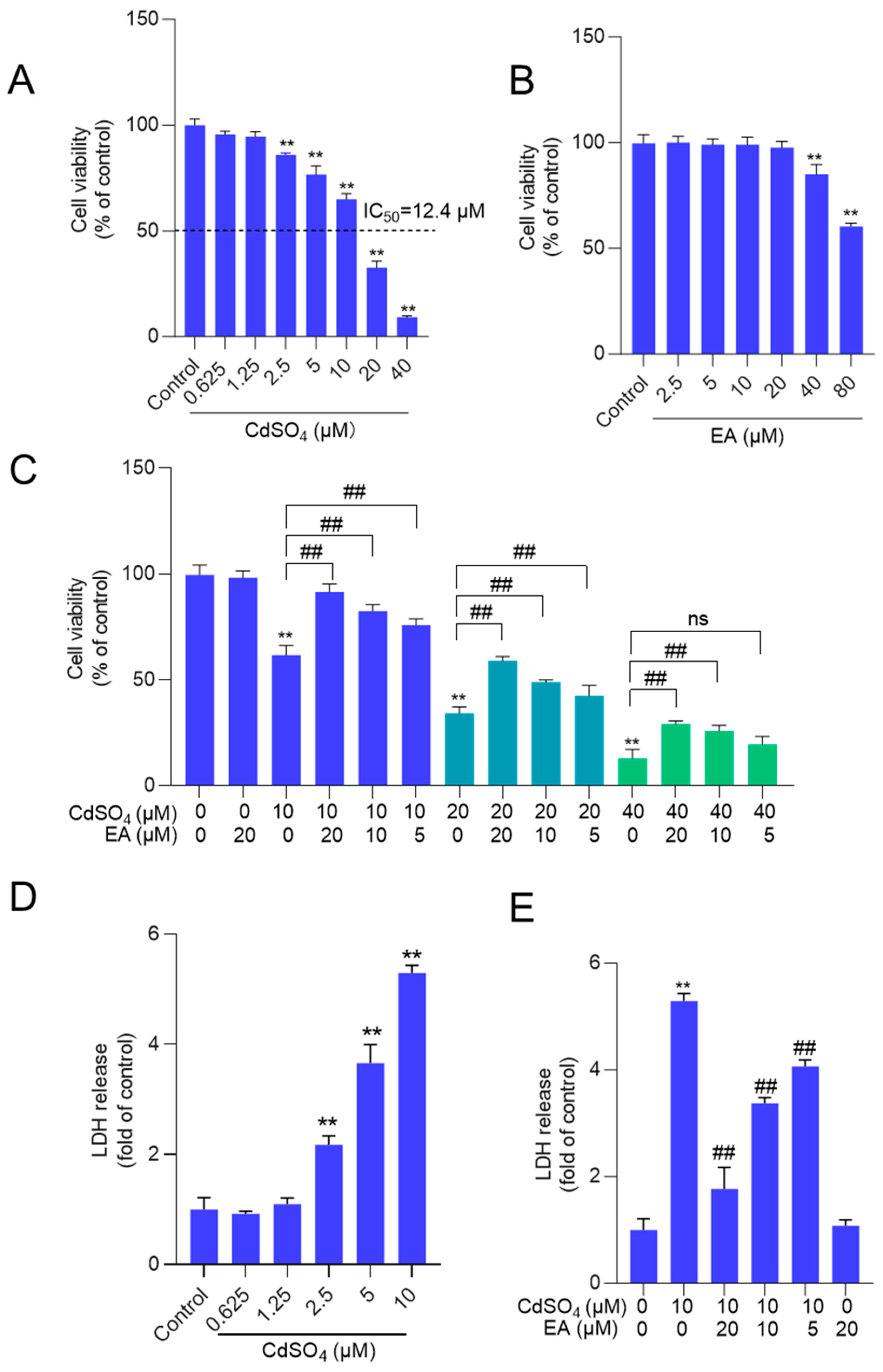
3.1. EA Supplementation Attenuates CdSO4-Induced Loss of Cell Viability and the Release of LDH in HT22 Cells
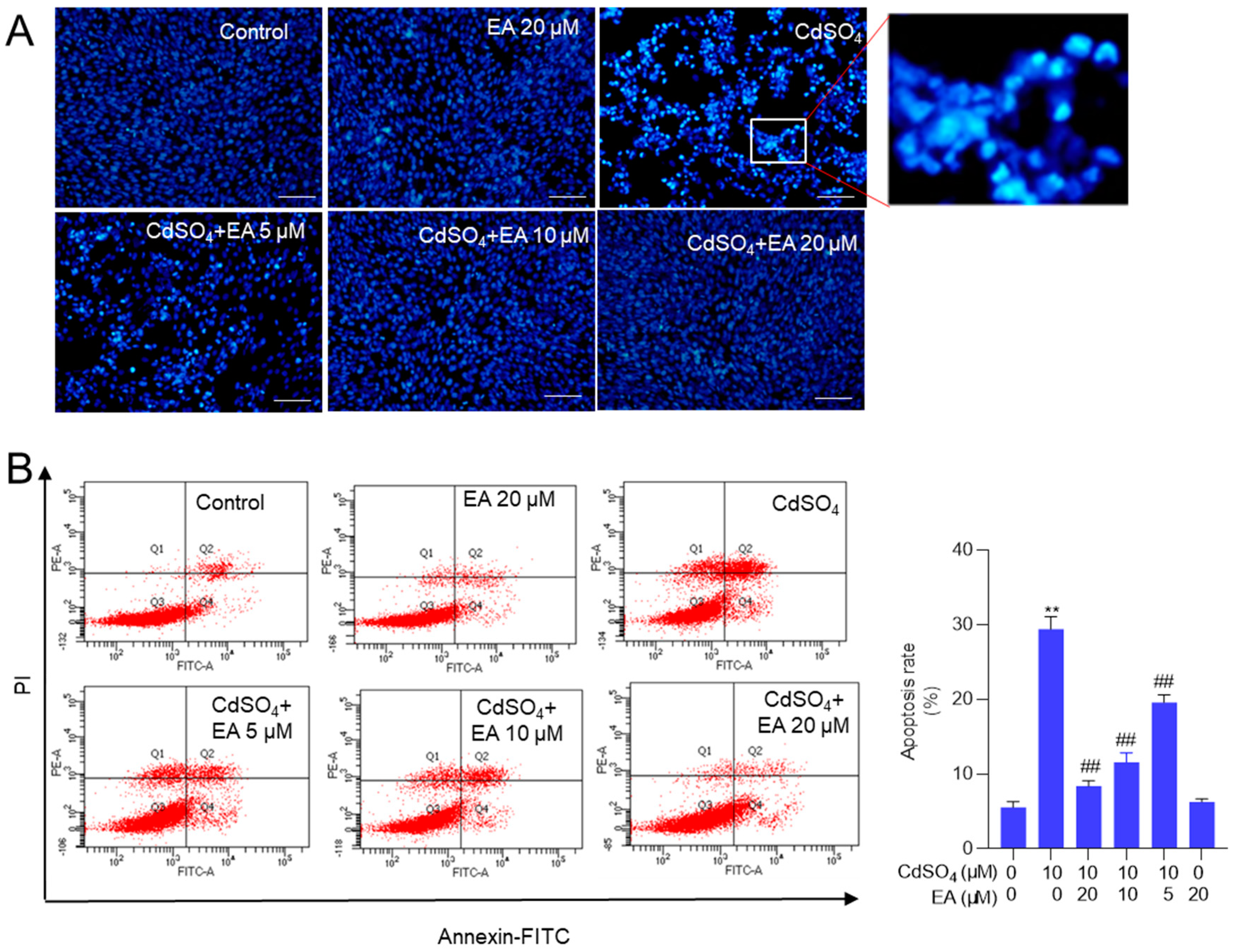
3.2. EA Supplementation Ameliorates CdSO4-Induced Cell Apoptosis in HT22 Cells
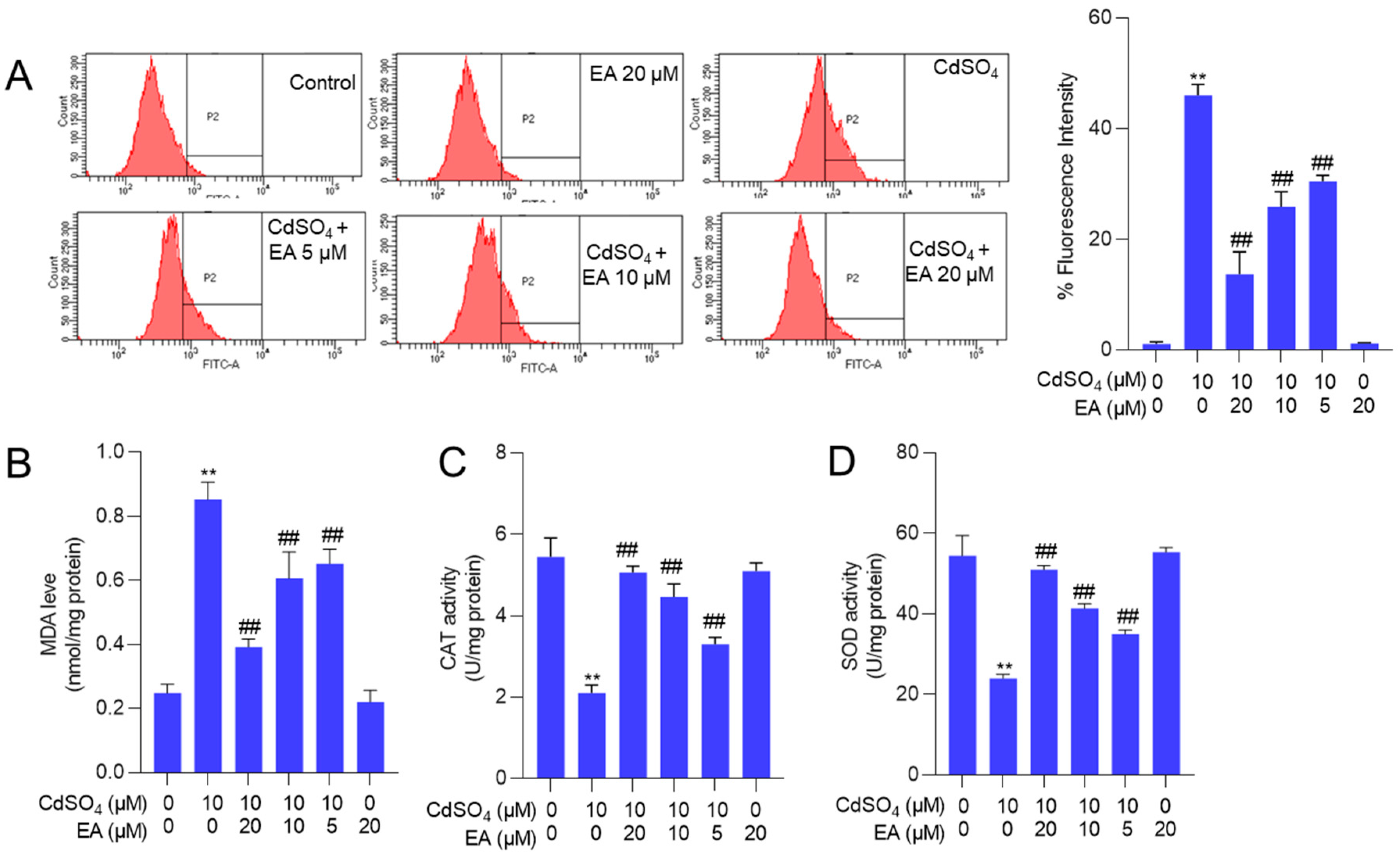
3.3. EA Supplementation Attenuates CdSO4-Induced ROS Production and Oxidative Stress Damage in HT22 Cells
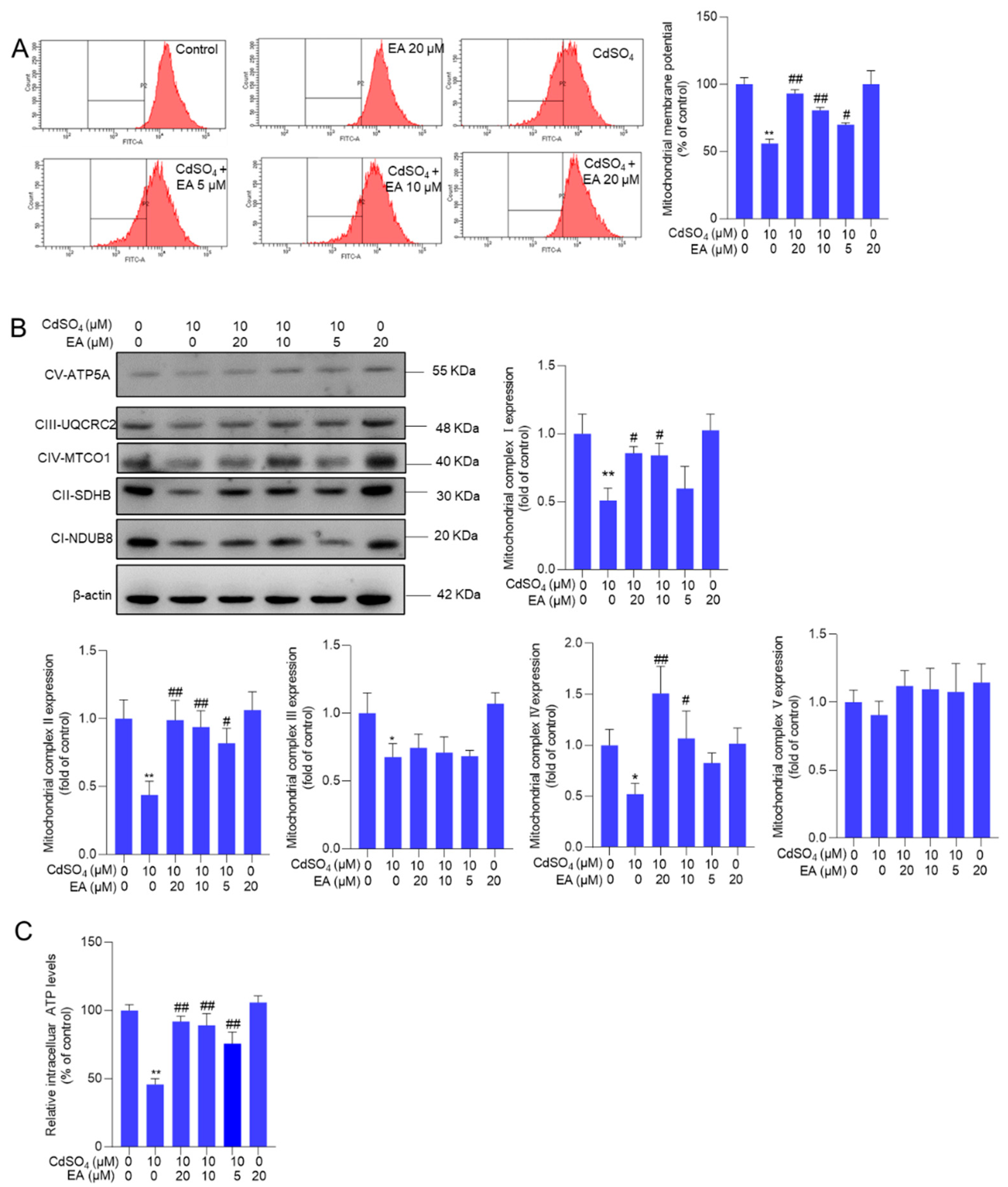
3.4. EA supplementation Attenuates CdSO4-Caused Mitochondrial Dysfunction
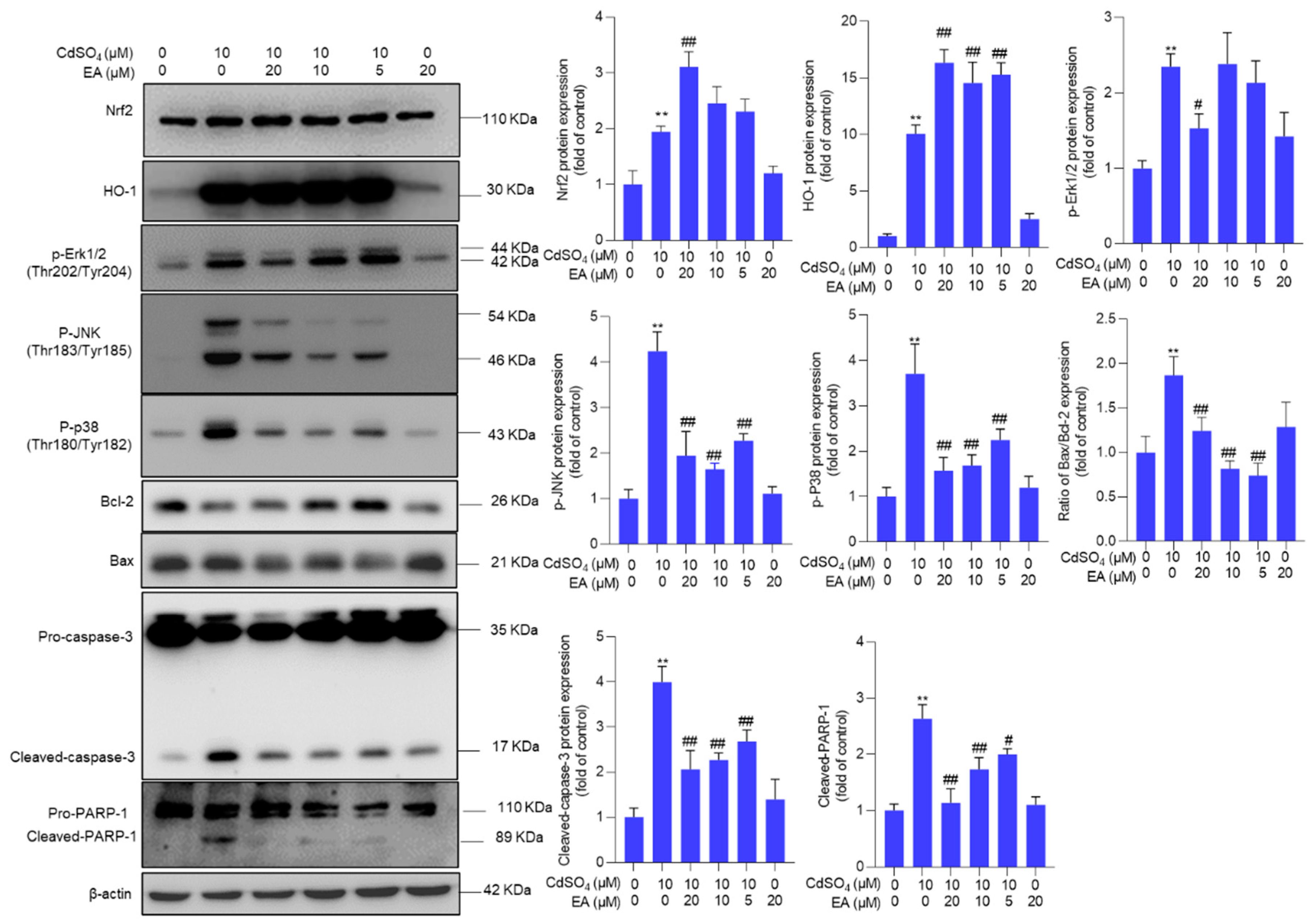
3.5. EA Supplementation Upregulates the Expression of Nrf2, HO-1, and Bcl-2 Proteins and Downregulates the Expression of Bax, p-JNK, p-p38, and p-ERK Proteins
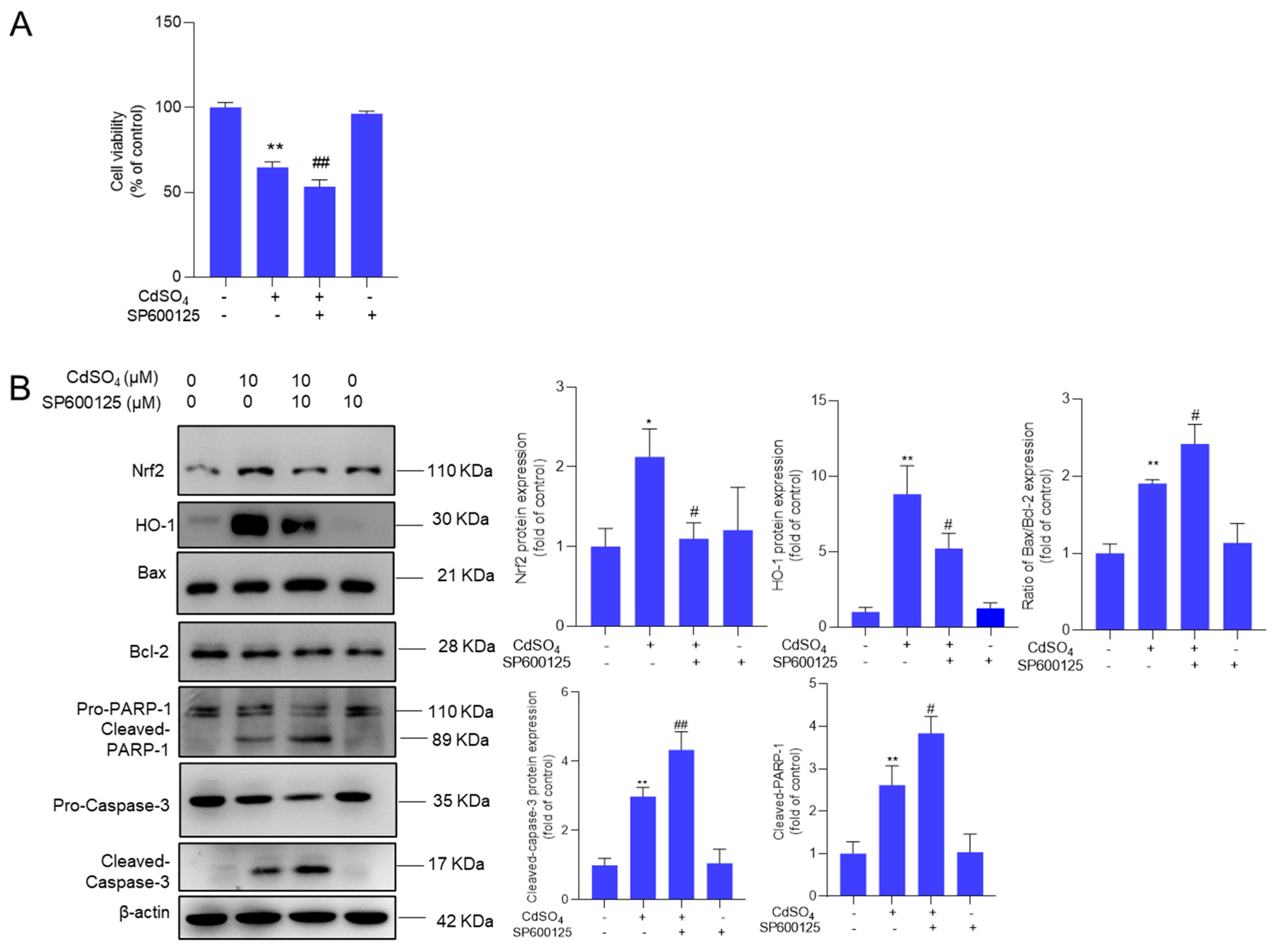
3.6. Pharmacological Inhibition of JNK Promotes CdSO4-Induced Cytotoxicity
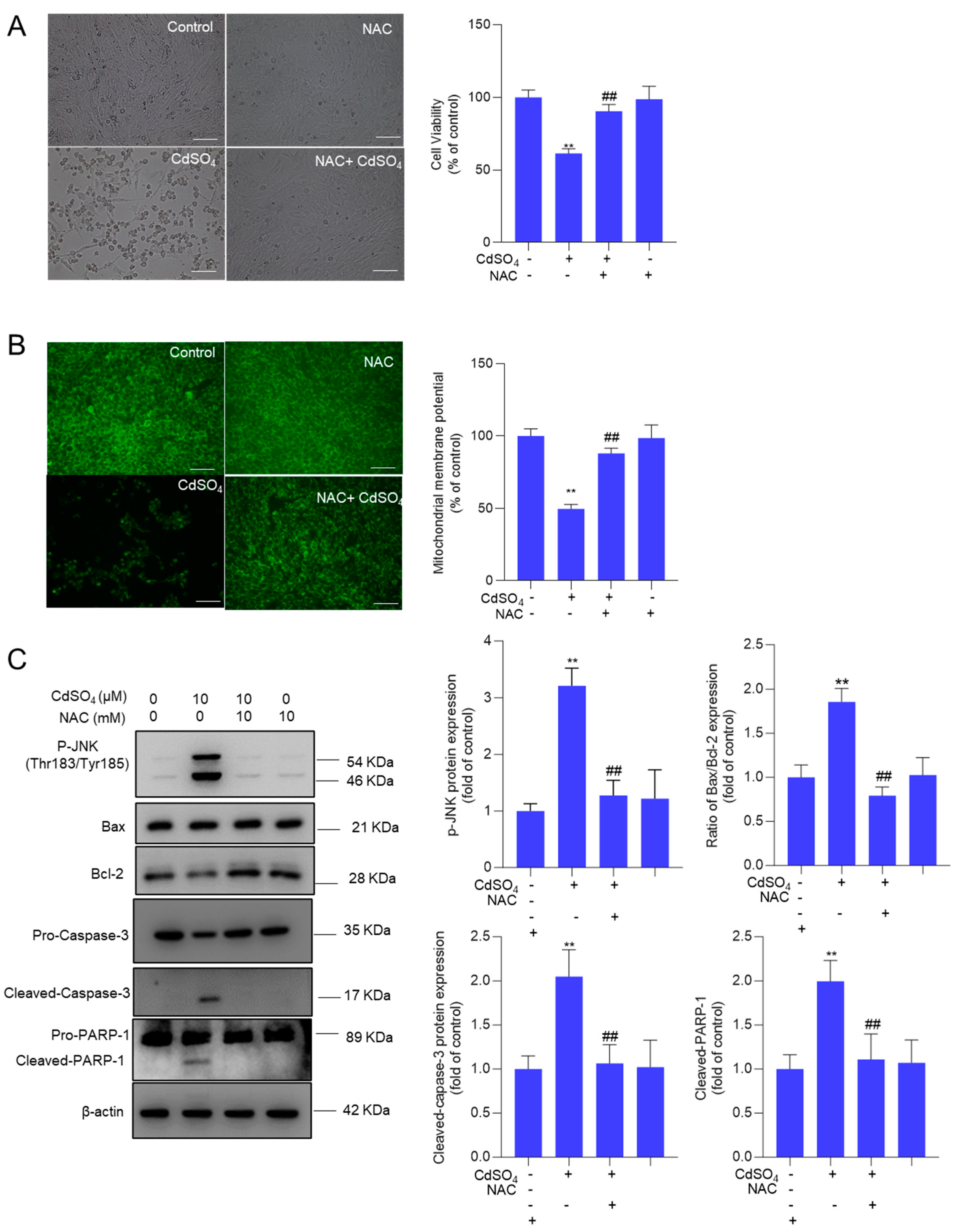
3.7. NAC Supplementation Attenuates CdSO4-Induced Cytotoxicity and the Activation of JNK and Mitochondrial Apoptotic Pathway
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflict of interest
References
- Deng, P.; Zhang, H.; Wang, L.; Jie, S.; Zhao, Q.; Chen, F.; Yue, Y.; Wang, H.; Tian, L.; Xie, J.; et al. Long-term cadmium exposure impairs cognitive function by activating lnc-Gm10532/m6A/FIS1 axis-mediated mitochondrial fission and dysfunction. Sci Total Environ 2023, 858, 159950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Chen, Z.; Song, W.; Hong, D.; Huang, L.; Li, Y. A review on Cadmium Exposure in the Population and Intervention Strategies Against Cadmium Toxicity. Bulletin of environmental contamination and toxicology 2021, 106, 65–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tinkov, A.A.; Gritsenko, V.A.; Skalnaya, M.G.; Cherkasov, S.V.; Aaseth, J.; Skalny, A.V. Gut as a target for cadmium toxicity. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987) 2018, 235, 429–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xie, D.; Yan, J.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, H.; Nie, G.; Zhu, X.; Li, X. Cadmium exacerbates liver injury by remodeling ceramide metabolism: Multiomics and laboratory evidence. Sci Total Environ 2024, 923, 171405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, C.; Yu, D.; He, Z.; Bao, L.; Feng, L.; Chen, L.; Liu, Z.; Hu, X.; Zhang, N.; Wang, T.; et al. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-mediated autophagy activation is involved in cadmium-induced ferroptosis of renal tubular epithelial cells. Free radical biology & medicine 2021, 175, 236–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qu, Z.; Liu, L.; Wu, X.; Guo, P.; Yu, Z.; Wang, P.; Song, Y.; Zheng, S.; Liu, N. Cadmium-induced reproductive toxicity combined with a correlation to the oogenesis process and competing endogenous RNA networks based on a Caenorhabditis elegans model. Ecotoxicology and environmental safety 2023, 268, 115687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Y.; Yao, W.; Ba, Q.; Wang, H. Effects of Cadmium Exposure on the Immune System and Immunoregulation. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 695484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, J.Y.; Min, K.B. Blood cadmium levels and Alzheimer's disease mortality risk in older US adults. Environmental health : a global access science source 2016, 15, 69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Abel, G.M.; Storm, D.R.; Xia, Z. Adolescent cadmium exposure impairs cognition and hippocampal neurogenesis in C57BL/6 mice. Environmental toxicology 2022, 37, 335–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Zhang, L.; Abel, G.M.; Storm, D.R.; Xia, Z. Cadmium Exposure Impairs Cognition and Olfactory Memory in Male C57BL/6 Mice. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2018, 161, 87–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Wu, Y.; Zhou, X.; Liang, C.; Ma, Y.; Yuan, Q.; Wu, Z.; Hao, X.; Zhu, X.; Li, X.; et al. Cadmium exposure induced neuronal ferroptosis and cognitive deficits via the mtROS-ferritinophagy pathway. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987) 2024, 349, 123958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Branca, J.J.V.; Pacini, A.; Gulisano, M.; Taddei, N.; Fiorillo, C.; Becatti, M. Cadmium-Induced Cytotoxicity: Effects on Mitochondrial Electron Transport Chain. Frontiers in cell and developmental biology 2020, 8, 604377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, S.; Xu, M.; Zhang, W.; Song, R.; Zou, H.; Gu, J.; Liu, X.; Bian, J.; Liu, Z.; Yuan, Y. Cadmium induces mitochondrial dysfunction via SIRT1 suppression-mediated oxidative stress in neuronal cells. Environmental toxicology 2023, 38, 743–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.; Ikram, M.; Muhammad, T.; Park, J.; Kim, M.O. Caffeine Modulates Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress, Neuroinflammation, and Cognitive Impairments by Regulating Nrf-2/HO-1 In Vivo and In Vitro. Journal of clinical medicine 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chandler, J.D.; Wongtrakool, C.; Banton, S.A.; Li, S.; Orr, M.L.; Barr, D.B.; Neujahr, D.C.; Sutliff, R.L.; Go, Y.M.; Jones, D.P. Low-dose oral cadmium increases airway reactivity and lung neuronal gene expression in mice. Physiological reports 2016, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al Olayan, E.M.; Aloufi, A.S.; AlAmri, O.D.; El-Habit, O.H.; Abdel Moneim, A.E. Protocatechuic acid mitigates cadmium-induced neurotoxicity in rats: Role of oxidative stress, inflammation and apoptosis. Sci Total Environ 2020, 723, 137969. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Al-Assaf, A.H.; Alqahtani, A.M.; Alshatwi, A.A.; Syed, N.A.; Shafi, G.; Hasan, T.N. Mechanism of cadmium induced apoptosis in human peripheral blood lymphocytes: the role of p53, Fas and Caspase-3. Environmental toxicology and pharmacology 2013, 36, 1033–1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.H.; Sim, Y.; Hwang, J.H.; Kwun, I.S.; Lim, J.H.; Kim, J.; Kim, J.I.; Baek, M.C.; Akbar, M.; Seo, W.; et al. Ellagic Acid Prevents Binge Alcohol-Induced Leaky Gut and Liver Injury through Inhibiting Gut Dysbiosis and Oxidative Stress. Antioxidants (Basel) 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, A.; Singh, A.K.; Kumar, R.; Jamieson, S.; Pandey, A.K.; Bishayee, A. Neuroprotective Potential of Ellagic Acid: A Critical Review. Advances in nutrition (Bethesda, Md.) 2021, 12, 1211–1238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Y.Z.; Zhu, G.F.; Zheng, C.Q.; Li, J.J.; Sheng, S.; Li, D.D.; Wang, G.Q.; Zhang, F. Ellagic acid protects dopamine neurons from rotenone-induced neurotoxicity via activation of Nrf2 signalling. J Cell Mol Med 2020, 24, 9446–9456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goudarzi, M.; Amiri, S.; Nesari, A.; Hosseinzadeh, A.; Mansouri, E.; Mehrzadi, S. The possible neuroprotective effect of ellagic acid on sodium arsenate-induced neurotoxicity in rats. Life sciences 2018, 198, 38–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, C.; Ciccotosto, G.D.; Cappai, R.; Tang, S.; Li, D.; Xie, S.; Xiao, X.; Velkov, T. Curcumin Attenuates Colistin-Induced Neurotoxicity in N2a Cells via Anti-inflammatory Activity, Suppression of Oxidative Stress, and Apoptosis. Mol Neurobiol 2018, 55, 421–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Li, M.; Sun, T.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Shen, Z.; Velkov, T.; Tang, S.; Shen, J. Colistin-induced pulmonary toxicity involves the activation of NOX4/TGF-β/mtROS pathway and the inhibition of Akt/mTOR pathway. Food Chem Toxicol 2022, 163, 112966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tang, S.; Velkov, T.; Shen, J.; Dai, C. Copper exposure induces mitochondrial dysfunction and hepatotoxicity via the induction of oxidative stress and PERK/ATF4 -mediated endoplasmic reticulum stress. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987) 2024, 352, 124145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ben, P.; Zhang, Z.; Xuan, C.; Sun, S.; Shen, L.; Gao, Y.; Cao, X.; Zhou, Y.; Lan, L.; Yin, Z.; et al. Protective Effect of L-Theanine on Cadmium-Induced Apoptosis in PC12 Cells by Inhibiting the Mitochondria-Mediated Pathway. Neurochemical research 2015, 40, 1661–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fotakis, G.; Timbrell, J.A. In vitro cytotoxicity assays: comparison of LDH, neutral red, MTT and protein assay in hepatoma cell lines following exposure to cadmium chloride. Toxicology letters 2006, 160, 171–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Chu, Y.; Cao, J.; Yang, Z.; Guo, X.; Wang, Z. T-2 toxin induces apoptosis, and selenium partly blocks, T-2 toxin induced apoptosis in chondrocytes through modulation of the Bax/Bcl-2 ratio. Food Chem Toxicol 2006, 44, 567–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Guo, X.; Pang, Q.; Wu, S.; Wu, C.; Xu, P.; Bai, Y. The role of mitochondria in T-2 toxin-induced human chondrocytes apoptosis. PLoS One 2014, 9, e108394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mokhtari, Z.; Seyedhashemi, E.; Eftekhari, M.; Ghasemi, S.; Sabouri, A.; Abbaszadeh-Goudarzi, K.; Abuali, M.; Azimi, H.; Kesharwani, P.; Pourghadamyari, H.; et al. Enhancement of cisplatin-induced apoptosis by saffron in human lung cancer cells. Journal of trace elements in medicine and biology : organ of the Society for Minerals and Trace Elements (GMS) 2023, 79, 127229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, T.; Yan, L.; Wang, L.; Sun, J.; Qu, H.; Ma, Y.; Song, R.; Tong, X.; Zhu, J.; Yuan, Y.; et al. VPS41-mediated incomplete autophagy aggravates cadmium-induced apoptosis in mouse hepatocytes. Journal of hazardous materials 2023, 459, 132243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, L.; Shang, X.J.; Lv, L.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, J.; Quan, C.; Shi, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, L. Cadmium-induced apoptosis of Leydig cells is mediated by excessive mitochondrial fission and inhibition of mitophagy. Cell Death Dis 2022, 13, 928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arab, H.H.; Gad, A.M.; Fikry, E.M.; Eid, A.H. Ellagic acid attenuates testicular disruption in rheumatoid arthritis via targeting inflammatory signals, oxidative perturbations and apoptosis. Life sciences 2019, 239, 117012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aslan, A.; Hussein, Y.T.; Gok, O.; Beyaz, S.; Erman, O.; Baspinar, S. Ellagic acid ameliorates lung damage in rats via modulating antioxidant activities, inhibitory effects on inflammatory mediators and apoptosis-inducing activities. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 2020, 27, 7526–7537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardah, M.T.; Eid, N.; Kitada, T.; Haque, M.E. Ellagic Acid Prevents α-Synuclein Aggregation and Protects SH-SY5Y Cells from Aggregated α-Synuclein-Induced Toxicity via Suppression of Apoptosis and Activation of Autophagy. Int J Mol Sci 2021, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Li, J.; Tang, S.; Li, J.; Xiao, X. Colistin-induced nephrotoxicity in mice involves the mitochondrial, death receptor, and endoplasmic reticulum pathways. Antimicrob Agents Chemother 2014, 58, 4075–4085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, H.; Gu, R.; Ouyang, H.; Wang, L.; Shi, S.; Ji, Y.; Bao, B.; Liao, G.; Xu, B. Cadmium exposure induces osteoporosis through cellular senescence, associated with activation of NF-κB pathway and mitochondrial dysfunction. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987) 2021, 290, 118043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyun, M.; Kim, H.; Kim, J.; Lee, J.; Lee, H.J.; Rathor, L.; Meier, J.; Larner, A.; Lee, S.M.; Moon, Y.; et al. Melatonin protects against cadmium-induced oxidative stress via mitochondrial STAT3 signaling in human prostate stromal cells. Communications biology 2023, 6, 157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Firdaus, F.; Zafeer, M.F.; Waseem, M.; Anis, E.; Hossain, M.M.; Afzal, M. Ellagic acid mitigates arsenic-trioxide-induced mitochondrial dysfunction and cytotoxicity in SH-SY5Y cells. Journal of biochemical and molecular toxicology 2018, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Jian, T.; Wu, Y.; Zuo, Y.; Li, J.; Lv, H.; Ma, L.; Ren, B.; Zhao, L.; Li, W.; et al. Ellagic acid ameliorates oxidative stress and insulin resistance in high glucose-treated HepG2 cells via miR-223/keap1-Nrf2 pathway. Biomed Pharmacother 2019, 110, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, L.; Mehmood, A.; Soliman, M.M.; Iftikhar, A.; Iftikhar, M.; Aboelenin, S.M.; Wang, C. Protective Effects of Ellagic Acid Against Alcoholic Liver Disease in Mice. Front Nutr 2021, 8, 744520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.N.; Koren, S.A.; Wojtovich, A.P. Mitochondrial complex I ROS production and redox signaling in hypoxia. Redox Biol 2023, 67, 102926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dröse, S. Differential effects of complex II on mitochondrial ROS production and their relation to cardioprotective pre- and postconditioning. Biochim Biophys Acta 2013, 1827, 578–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Khodaei, F.; Rashedinia, M.; Heidari, R.; Rezaei, M.; Khoshnoud, M.J. Ellagic acid improves muscle dysfunction in cuprizone-induced demyelinated mice via mitochondrial Sirt3 regulation. Life sciences 2019, 237, 116954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vercellino, I.; Sazanov, L.A. The assembly, regulation and function of the mitochondrial respiratory chain. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology 2022, 23, 141–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolin, M.S. Evidence for novel aspects of Nox4 oxidase regulation of mitochondrial function and peroxide generation in an endothelial cell model of senescence. The Biochemical journal 2013, 452, e1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okoye, C.N.; MacDonald-Jay, N.; Kamunde, C. Effects of bioenergetics, temperature and cadmium on liver mitochondria reactive oxygen species production and consumption. Aquatic toxicology (Amsterdam, Netherlands) 2019, 214, 105264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Adiele, R.C.; Stevens, D.; Kamunde, C. Differential inhibition of electron transport chain enzyme complexes by cadmium and calcium in isolated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) hepatic mitochondria. Toxicological sciences : an official journal of the Society of Toxicology 2012, 127, 110–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, C.F.; Latorre-Muro, P.; Puigserver, P. Mechanisms of mitochondrial respiratory adaptation. Nature reviews. Molecular cell biology 2022, 23, 817–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, J.; Zhang, C.; Sun, Y.C.; Zhang, Q.; Lv, M.W.; Guo, K.; Li, J.L. Cadmium exposure triggers mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress in chicken (Gallus gallus) kidney via mitochondrial UPR inhibition and Nrf2-mediated antioxidant defense activation. Sci Total Environ 2019, 689, 1160–1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, M.; Jiang, Z.; Gu, P.; Guo, B.; Li, J.; Cheng, S.; Ba, Q.; Wang, H. Cadmium promotes colorectal cancer metastasis through EGFR/Akt/mTOR signaling cascade and dynamics. Sci Total Environ 2023, 899, 165699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C.; Sharma, G.; Liu, G.; Shen, J.; Shao, B.; Hao, Z. Therapeutic detoxification of quercetin for aflatoxin B1-related toxicity: Roles of oxidative stress, inflammation, and metabolic enzymes. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987) 2024, 345, 123474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, D.R.; Reed, J.C. Mitochondria and apoptosis. Science (New York, N.Y.) 1998, 281, 1309–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mashimo, M.; Onishi, M.; Uno, A.; Tanimichi, A.; Nobeyama, A.; Mori, M.; Yamada, S.; Negi, S.; Bu, X.; Kato, J.; et al. The 89-kDa PARP1 cleavage fragment serves as a cytoplasmic PAR carrier to induce AIF-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem 2021, 296, 100046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bello, M.; Morales-González, J.A. Molecular recognition between potential natural inhibitors of the Keap1-Nrf2 complex. International journal of biological macromolecules 2017, 105, 981–992. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Liu, Y.; Shen, Z.; Wang, S.; Wu, C.; Liu, D.; Tang, S.; Dai, C. Osthole ameliorates myonecrosis caused by Clostridium perfringens type A infection in mice. One Health Advances 2023, 1, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Li, C.; Xu, M.; Liu, Y.; Cong, M.; Liu, S. LncRNA MT1DP Aggravates Cadmium-Induced Oxidative Stress by Repressing the Function of Nrf2 and is Dependent on Interaction with miR-365. Adv Sci (Weinh) 2018, 5, 1800087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, X.; Xu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Mu, C.; Liu, P.; Li, J. The role of Nrf2 in mitigating cadmium-induced oxidative stress of Marsupenaeus japonicus. Environmental pollution (Barking, Essex : 1987) 2021, 269, 116112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Botchway, B.O.A.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, X. Ellagic acid activates the Keap1-Nrf2-ARE signaling pathway in improving Parkinson's disease: A review. Biomed Pharmacother 2022, 156, 113848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, X.; Fu, M.; Bi, R.; Zheng, X.; Fu, B.; Tian, S.; Liu, C.; Li, Q.; Liu, J. Cadmium induced BEAS-2B cells apoptosis and mitochondria damage via MAPK signaling pathway. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Huang, S. Cadmium activates the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) pathway via induction of reactive oxygen species and inhibition of protein phosphatases 2A and 5. Free radical biology & medicine 2008, 45, 1035–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Liu, L.; Luo, Y.; Huang, S. MAPK and mTOR pathways are involved in cadmium-induced neuronal apoptosis. J Neurochem 2008, 105, 251–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Chang, J.; Yang, C.; Zhang, T.; Chen, X.; Shi, R.; Liang, Y.; Xia, Q.; Ma, S. Genome-wide CRISPR-Cas9 screening in Bombyx mori reveals the toxicological mechanisms of environmental pollutants, fluoride and cadmium. Journal of hazardous materials 2021, 410, 124666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.R.; Ma, H.; Zou, Z.Y.; He, K.; Xiao, Y.B.; Wang, Y.; Feng, M.; Ye, X.L.; Li, X.G. Activation of Akt and JNK/Nrf2/NQO1 pathway contributes to the protective effect of coptisine against AAPH-induced oxidative stress. Biomed Pharmacother 2017, 85, 313–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tasaki, M.; Umemura, T.; Maeda, M.; Ishii, Y.; Okamura, T.; Inoue, T.; Kuroiwa, Y.; Hirose, M.; Nishikawa, A. Safety assessment of ellagic acid, a food additive, in a subchronic toxicity study using F344 rats. Food Chem Toxicol 2008, 46, 1119–1124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heilman, J.; Andreux, P.; Tran, N.; Rinsch, C.; Blanco-Bose, W. Safety assessment of Urolithin A, a metabolite produced by the human gut microbiota upon dietary intake of plant derived ellagitannins and ellagic acid. Food Chem Toxicol 2017, 108, 289–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ardah, M.T.; Bharathan, G.; Kitada, T.; Haque, M.E. Ellagic Acid Prevents Dopamine Neuron Degeneration from Oxidative Stress and Neuroinflammation in MPTP Model of Parkinson's Disease. Biomolecules 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baluchnejadmojarad, T.; Rabiee, N.; Zabihnejad, S.; Roghani, M. Ellagic acid exerts protective effect in intrastriatal 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinson's disease: Possible involvement of ERβ/Nrf2/HO-1 signaling. Brain Res 2017, 1662, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




