1. Introduction
Cervical cancer is 4th the most common cancer in women worldwide -
GLOBOCAN 2020 estimated that there were approximately 604 000 new cases of cervical cancer, with 342 000 deaths annually [
1]. Persistent infection with highly oncogenic HPV types is responsible for developing precancerous lesions and cervical cancer
. Additionally, HPV is responsible for forming many other HPV-related changes, including head and neck, vagina, vulva, penis, and anal cancers. HPV is an approximately 7,900 base pair double-stranded DNA virus with over 200 genotypes [
2,
3,
4]. The life cycle of HPV is directly related to the differentiation of keratinocytes. The critical event in the virus life cycle is the escalation of its replication associated with this differentiation. Due to the prevalence of HPV in the population (80-90%), the scientists are likely to discover even more associations of this pathogen with other diseases in the future. That is why it is so important to continue searching for diagnostic methods and validate the existing ones and use the best-known and the highest sensitivity and specificity methods for patients.
In histopathology, HPV DNA testing in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cervical tissue serves several essential purposes. Firstly, they might resolve diagnostic discrepancies in cervical intraepithelial neoplasia (CIN) patients. It aids in distinguishing between endocervical immature squamous metaplasia and high-grade dysplasia, as well as differentiating endocervical glandular reactive changes from glandular dysplasia. Secondly, risk assessment; the test provides valuable information for assessing the risk of CIN progression or disease recurrence in women who have undergone treatment for HSIL (CIN 2/3) or carcinoma. Ultimately, HPV DNA testing contributes crucial data in cervical cancer research, facilitating an understanding the virus’s role in disease development and progression. By employing HPV DNA testing in FFPE cervical tissue, medical professionals may enhance diagnostic accuracy, provide more personalized patient care, and contribute to advancing cervical cancer research. However, there are disadvantages to consider, that t
he assay requires highly trained laboratory personnel and strict laboratory conditions must be implemented to avoid contamination [
5,
6]
. As far as advantages connected with ISH over detecting HPV in tissue by PCR includes the lack of destroying the tissue, correlation with cytology results, the ability to test archival samples and identification of the HPV ISH result in the context of tissue morphology.
In recent years, ISH assays that use improved signal-detecting methods, such as the enzyme-categorized signal-detecting system, have shown a higher sensitivity [
7]. Inform HPV (Ventana Medical Systems), a commercially available ISH assay for HPV DNA testing, can be used in cytological and histological specimens [
8]. Recently, Inform HPV III, a new generation of ISH probe, became available for HPV DNA testing in tissue specimens. Knowing the efficacy of the ISH assay using the Inform HPV III probe in cervical tissue not only may allow for better use of ISH-based HPV DNA testing in tissue specimens but also could provide valuable information for the cytological application of ISH in LBC.
Therefore, in the present study, we aim to assess the association between HPV infection and an automatic signal detection of ISH for detecting HPV DNA using the Inform HPV II and HPV III probe in FFPE cervical tissue specimens with CINs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Design
We provide a prospective, ongoing 12-month, non-randomized study in patients reporting to the Individual Specialised Medical Practise in 2022–2023. Subjects attended the medical practise as part of in-depth diagnostics due to an abnormal cytological result or the presence of HPV 16, 18, and 31 in the cervical smear and histopathologically confirmed cervical intraepithelial neoplasia. The histopathologist re-verified the diagnosis and marked the places of CIN lesions on the formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded (FFPE) cervical tissues. The laboratory diagnostician prepared new slide preparations for ISH staining. In two cases, the final medical consensus did not confirm the diagnosis of CIN, therefore they were excluded from further analysis. The Poznan University of Medical Sciences Bioethical Committee approved the study protocol (540/22) on the 23rd of June 2022.
2.2. HPV Genotyping Test and LBC
We collected liquid-based cytology and molecular assessment samples with an endocervical Cyto-Brush preserved in BD SurePath ®. Then, the probes were passed to an independent, standardized laboratory. PCR was performed, followed by a DNA enzyme immunoassay and genotyping with a reverse hybridization line probe assay for HPV detection. The lab technicians performed sequence analysis to characterize HPV-positive samples. The molecular test detected the DNA of 37 HPV genotypes (6, 11, 16, 18, 26, 31, 33, 35, 39, 40, 42, 45, 51, 52, 53, 54, 55, 56, 58, 59, 61, 62, 64, 66, 67, 68, 69, 70, 71, 72, 73, 81, 82, 83, 84, IS39, and CP6108).
2.3. Colposcopy and Punch Biopsy
Further validation of abnormal screening results was performed on all patients with an abnormal smear: ASC-US, LSIL, HSIL, ASC-H; AGC; cervical cancer, a positive HPV test for types 16, 18, 31, and a clinically suspicious cervical image. Each colposcopy was performed by a specialist in gynecologic oncology with 10-year experience in SmartOPTIC colposcope. We performed a test with 5% aqueous solution of acetic acid and Schiller’s test with Lugol’s iodine in all included cases. The colposcopic images were evaluated according to Reid’s Colposcopic Index which assesses the color, lesion boundaries and surface, blood vessels and result of the iodine test. All colposcopic images were archived. The Polish Society of Colposcopy and Cervical Pathophysiology recommended the International Federation of Cervical Pathology and Colposcopy classification.
2.4. Immunohistochemistry
Serial 4-micrometre tissue sections were cut from the donor blocks containing cores of lesions and applied to special immunohistochemistry-coated slides. Two ISH probes: INFORM HPV II Family 6 Probe and INFORM HPV III Family 16 Probe (Ventana, Roche, Tucson, AZ) - were used to target the common HPV genotypes in cervical biopsy specimens. To demonstrate positive hybridization to low-risk genotypes 6 and 11 used the INFORM HPV II Family 6 Probe and the INFORM HPV III Family 16 Probe were used to demonstrate positive hybridization to the following genotypes: 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52, 56, 58 and 66.
Slides were stained on a fully automated immunohistochemistry slide stainer BenchMark ULTRA (Ventana, Roche, Tucson, AZ). Staining protocol parameters were based on HIER using CC2 (heating time 4+8+8 min. at 86°C), ISH-Protease 3 (780-4149) for 16 minutes, 12 min. of denaturation and 2 hours of hybridization with each ISH probe. To detect specific DNP labelled probes bounded to a target sequence, an indirect biotin-streptavidin system INFORM iView Blue + (760-097). Slides were then post-counterstained with Red Stain II (780-2218) for 4 min. Coverslips were passed through a series of alcohols and finally xylene before being mounted.
2.5. Light Microscopy Techniques for Cell Imaging
Photographs of the tissue slides were taken, using an Olympus BX 43 light microscope with an XC 30 digital camera (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). Magnification was set at 400X. Based on the obtained images from the light microscope, a semi-quantitative analysis of immunopositive cells was performed. Calculations were made using the Olympus cellSens commercial software. Phase analysis of immunohistochemically stained tissue microarrays was undertaken, including automatic signal detection of objects based on their color, shade intensity or shape. In this case, the color criterion—the blue of the cell nuclei due to the ISH reaction —was selected. The computer program automatically classified cells based on predefined threshold values. The data were exported to MS Excel files and used for further statistical analyses [
9].
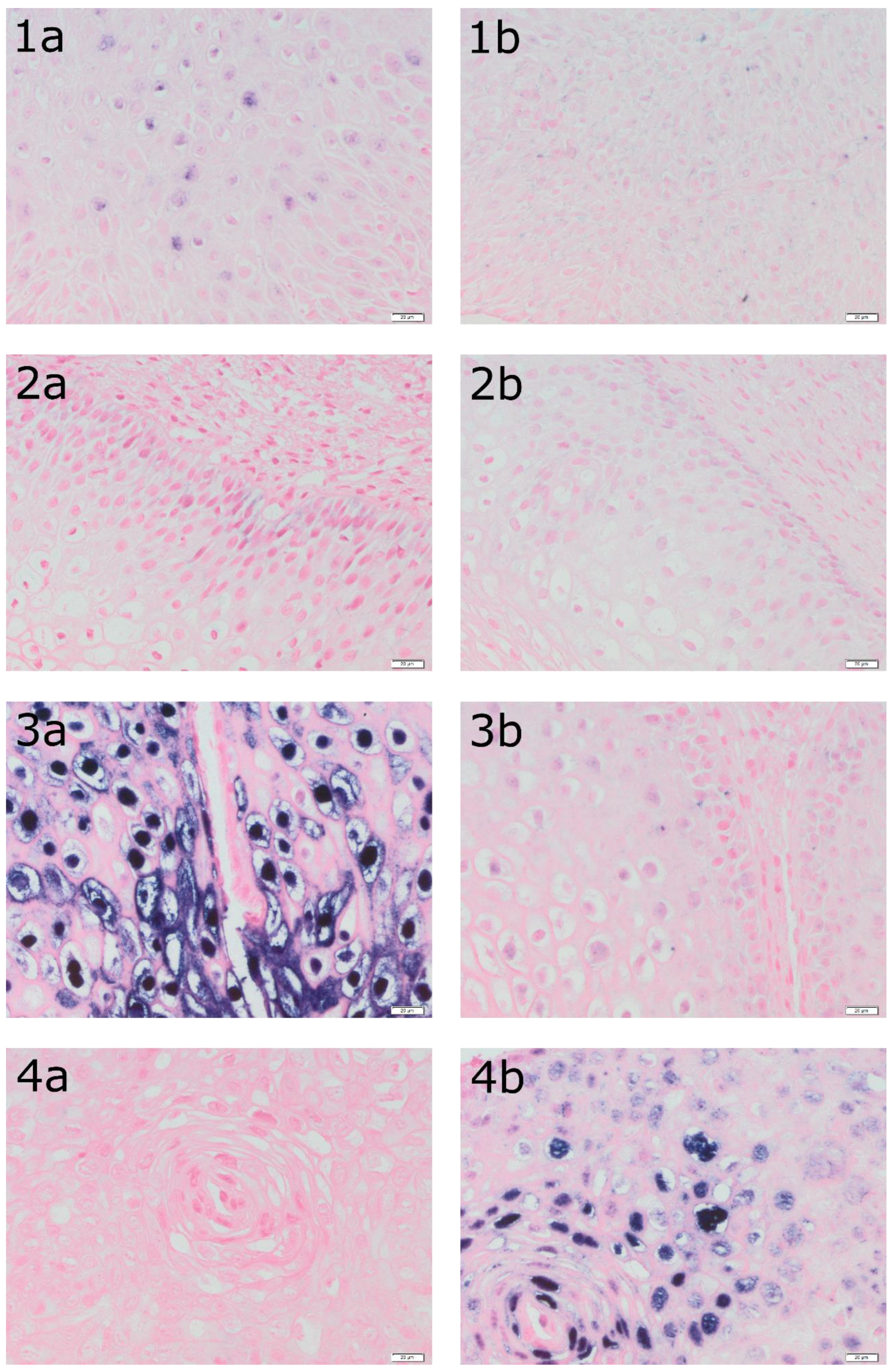
Figure 1 presents a detection of HPV DNA (in situ hybridization: a – ISH HPV II and ISH b – HPV III) in epithelial cells in the tissue of four patients.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Analysis was conducted with statistical software R, version R4.1.2. All calculations assumed a significance level of α = 0.05. Nominal variables were presented as n and %, quantitative ones as median with quartiles 1 and 3. The normality of the variables distributions was analyzed with Shapiro-Wilk’s test and further verified with skewness and kurtosis. All tests that were used in the analysis were non-parametric – to compare the level of ISH II and the level of ISH III between groups, Mann-Whitney’s U test or Kruskal-Wallis test were conducted (depending on the number of groups). Spearman correlation analysis was used to analyze the dependency between two quantitative variables. The Kappa coefficient was used to determine the agreement between CIN1, CIN2 and CIN3 with HPV outcomes (positive/negative). We assessed the sensitivity, specificity, PPV (positive predictive value), NPV (negative predictive value) and accuracy with a 95% confidence interval of diagnostic abilities of LBC result, ISH and HPV outcomes for CIN2 + CIN3 as well as for ISH II for HPV 6 or 11 and ISH III for HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52, 56, 58, 66.
3. Results
The patients in the study ranged from 18 to 79 years, with a mean age of 33. A study group characteristic is shown in
Table 1.
Figure 1 shows a detection of HPV DNA in epithelial cells in the tissue of four patients with histopathologically confirmed LSIL. The tissue from patient 1 was determined as ASC-US in LBC while the genotype of the HPV was negative. In turn, the tissue of patient 2 belongs to ASC-US while the genotype of the HPV was positive for 51. The tissue from patient 3 was classified as ASC-US in LBC and was positive for HPV 16 and 56. Finally, tissue from patient 4 was classified as ASC-H and was positive for HPV 82.
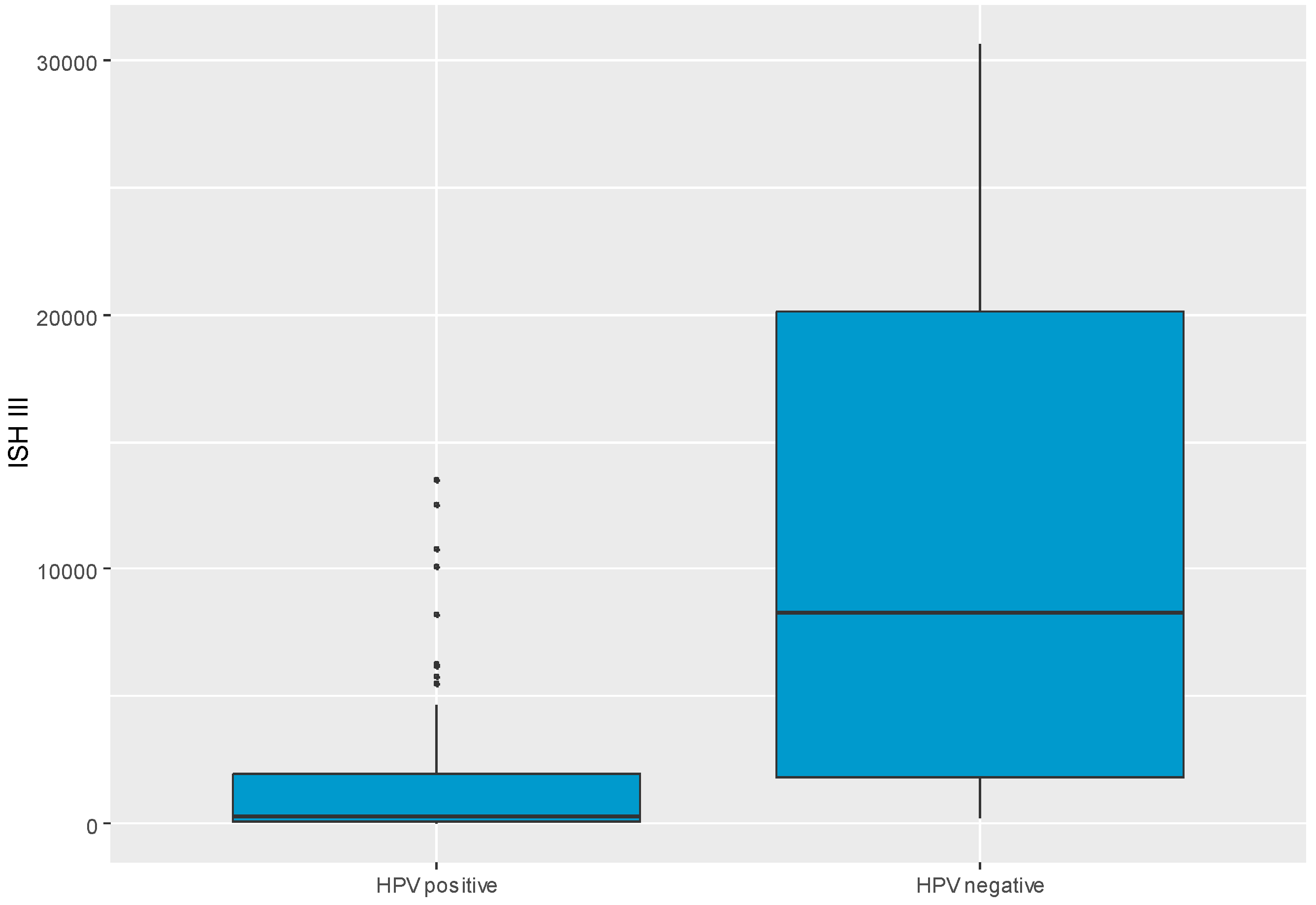
Table 2 shows the relationships of ISH II levels to various variables, but no statistically significant associations were observed. A significant relation was confirmed between ISH III level and HPV outcome (positive/negative). Patients with positive HPV outcomes had significantly lower ISH III levels, MD = -7961.82 CI
95 [-17230.00; -199.21], p = 0.005. ISH III level split into HPV groups was visualized in
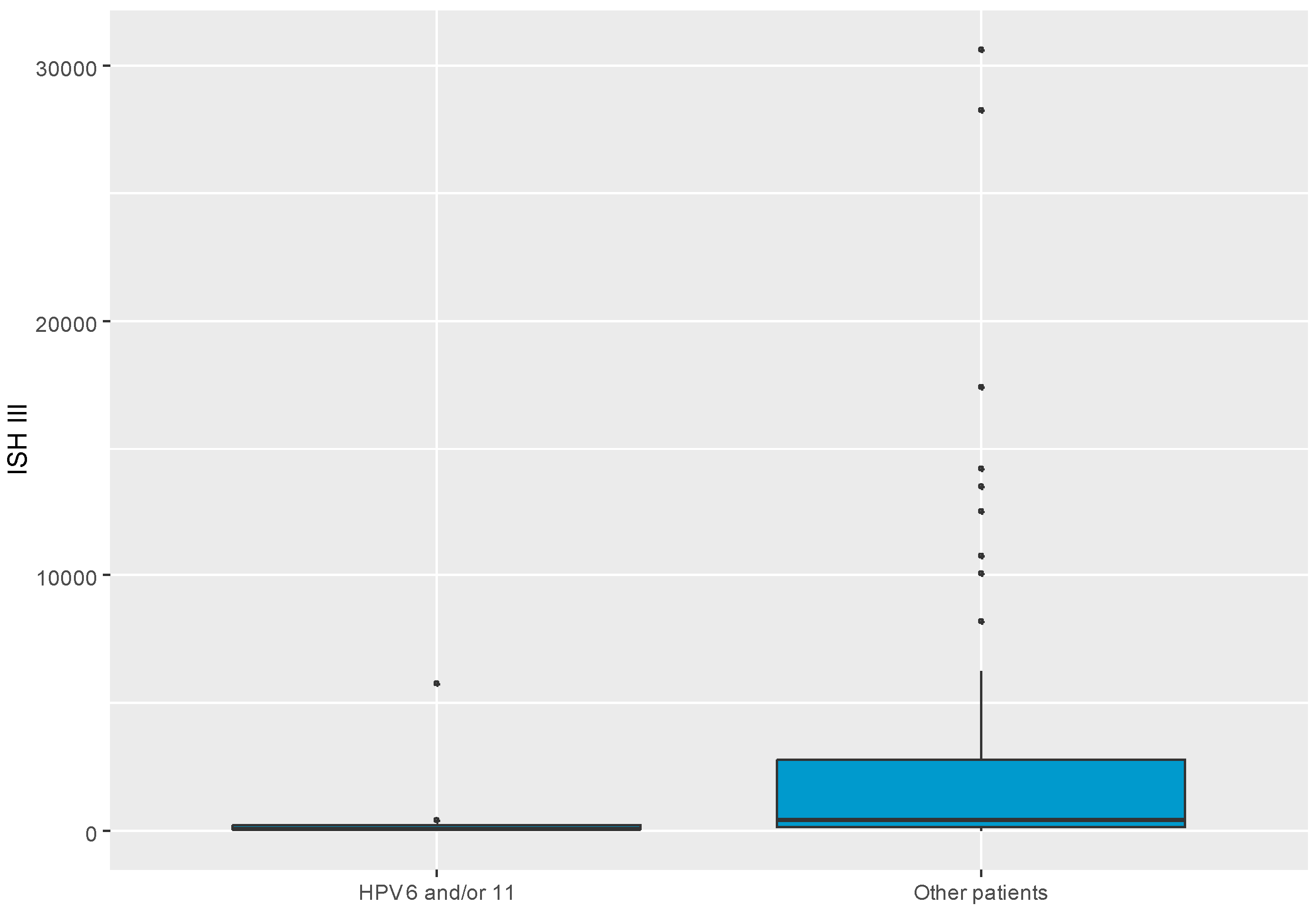
Figure 2. Also, there was a significant difference in ISH III levels between groups with HPV genotypes of 6 and/or 11 and other patients. Patients with HPV genotype 6 and/or 11 had significantly lower ISH III levels than others, MD = -317.05 CI
95 [-1972.19; -13.71], p = 0.037. ISH III level in split to HPV 6 and/or 11 group and other patients was visualized as presented in
Figure 3. No other relations with ISH III were found significant, as shown in
Table 3.
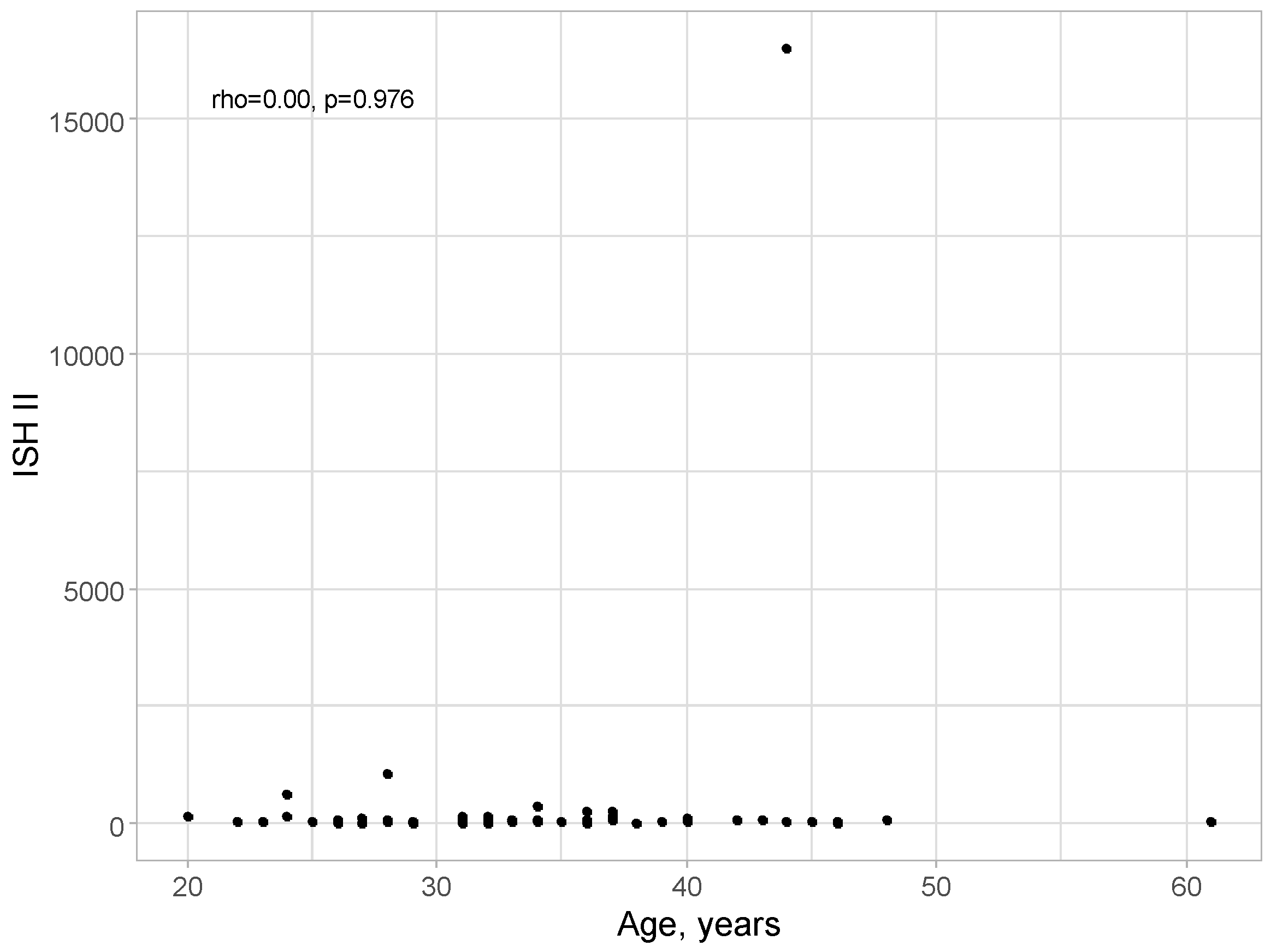
No correlation was detected between age and ISH II level: rho = 0.00; p = 0.976, as presented in
Figure 4.
A positive correlation of minor strength was detected between age and ISH III level: rho = 0.23; p = 0.049, as shown in
Figure 5.
With increasing age, there are higher levels of ISH III; however, the strength of this relationship is not high.
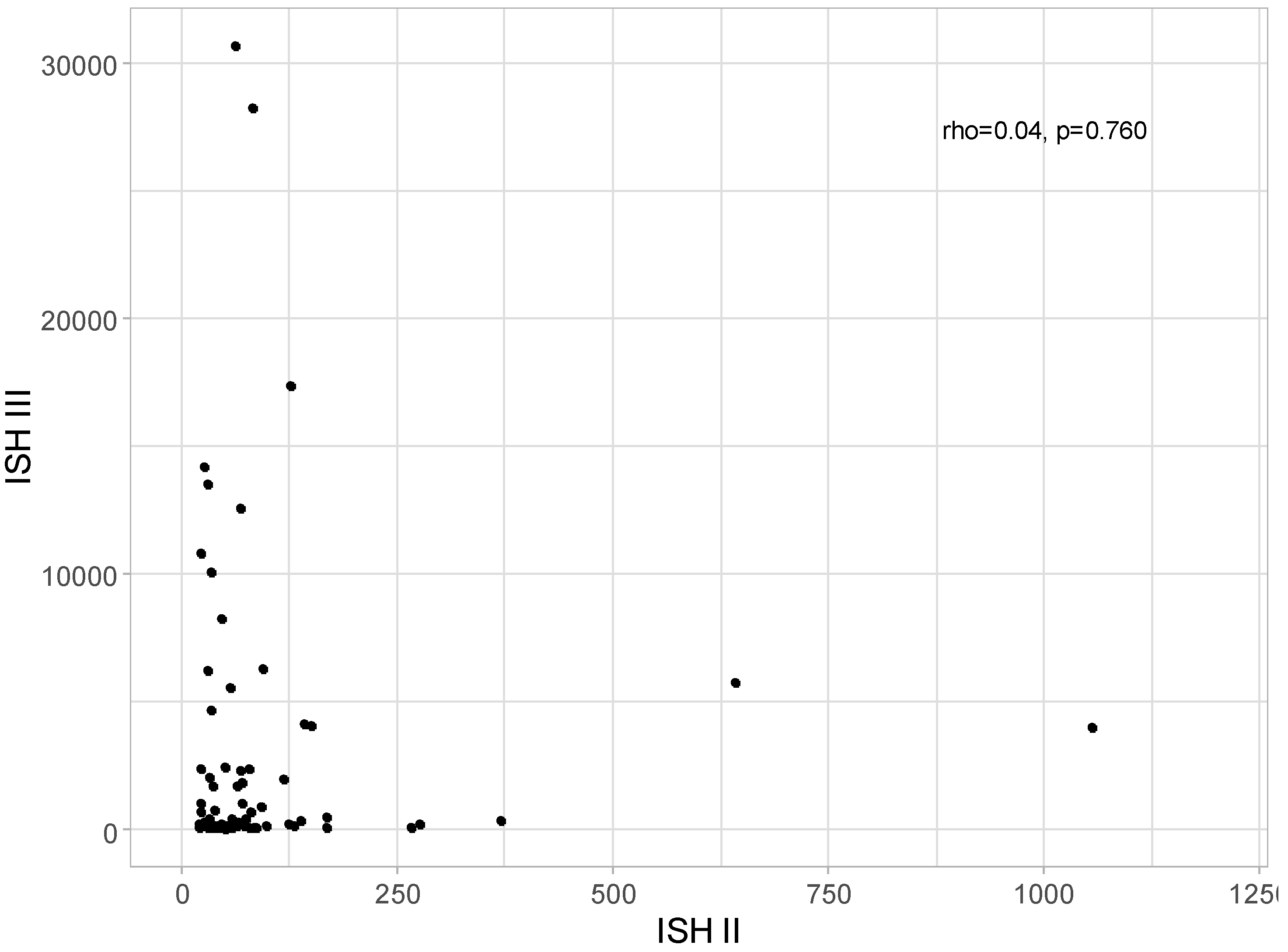
No correlation was detected between ISH II and ISH III levels: rho = 0.04; p = 0.760, as presented in
Figure 6.
Kappa coefficients were calculated to understand the level of agreement between CIN1, CIN2 and CIN3 outcomes with HPV outcome (positive/negative) as presented in
Table 4.
Table 5 compares the value and usefulness of various diagnostic methods in detecting CIN 2+ lesions. In the case of cytological smears, the specificity of CIN 2+ detection increased from the diagnosis of LSIL (46.67%), through ASC-H (86.67%) to the diagnosis of HSIL (96.67%). However, in the case of ASC-US diagnosis with low sensitivity, a relatively high specificity was achieved - 76.67%. This result supports the unquestionable necessity of extending diagnostics with HPV DNA molecular testing and cervical biopsy. The sensitivity of HPV testing in detecting CIN 2+ lesions reached the level of 95.24% - higher than any cytological result - which proves the superiority of this test over LBC. We are unable to assess the sensitivity of ISH since only histopathological materials with a positive reaction to both ISH II and ISH III were collected for the examination; as shown in
Table 6 and
Table 7.
4. Discussion
Our study was intended to assess the usefulness of the automatic signal detection of ISH assay using the Inform HPV II and HPV III in diagnosing cervical intraepithelial lesions in formalin-fixed, paraffin-embedded tissues. Additionally, we aimed to describe the sensitivity and specificity of LBC, and HPV DNA testing in relation to automatic signal detection of ISH assay. The main results indicate a significant association between ISH III level and HPV outcome in a study group. Patients with positive HPV results from cervical swab had significantly lower ISH III levels. This observation may be explained by the fact that the precancerous lesions of the cervix were caused by transient HPV infection or the low level of HPV ISH resulting from the lack of ongoing virus replication. However, we cannot quite correlate this result as we did not assess the number of virus copies in the tissue.
Furthermore, low ISH III levels with a positive HPV test result indicate a much higher HPV DNA value of the cervical smear as it provides a large amount of relevant material. Positive results of automatic signal detection of ISH may also be related to artifacts on the slide preparation, lack of an appropriate amount of tissue material in the preparation or contamination related to the preparation of the preparation - coming from the person preparing it. However, it seems to us that the assessment of HPV in the tissue by automatic signal detection of ISH may serve other potentially HPV-related cancers, e.g., head and neck cancers or
oropharyngeal squamous cell carcinoma (OPSCC).
Currently, there is no clear consensus on the gold standard for HPV testing in OPSCC. Multimodality testing could help to reliably identify patients with transcriptionally active high-risk HPV-positive. Due to this reason researchers from Naples, Italy conducted a study of HPV RNA ISH and p16 IHC on the same slide to detect simultaneously HPV E6/E7 transcripts and p16INK4a overexpression. They revealed that the multiplex HPV RNA ISH /p16 IHC results in the series of both cervical cancers and the oral- oropharyngeal cancers were fully concordant with the previous results achieved through the classic p16 IHC and HPV RNA scope carried out on two different slides [
10]
.
Sheng et al. conducted a study where ISH used a probe targeting multiple hrHPV subtypes, PCR, genotyping, and p16 IHC were performed on specimens from 27 cases of AIS and CA. A total of 63% of the AIS and CA specimens were HPV-ISH positive in this study. These results confirm that HPV infection occurs in cervical glandular neoplasia with relatively high frequency. HPV DNA was detected in 67% of cases by PCR. Furthermore, 74% of cases were positive for HPV following HPV genotyping analysis. Combining the results of HPV-ISH and HPV - PCR/ genotyping, 22 AIS and CA cases (81.5%) were considered HPV-positive. When two cases of clear cell adenocarcinoma, in which HPV is generally regarded as negative, HPV was detected in 88% of cases of cervical glandular neoplasia [
11]. In our study, all samples were also ISH-positive, but HPV was negative in 8/72 patients (10.8%). Additionally, Tase et al. detected HPV DNA in 42.5% of FFPE sections from CA cases using ISH with mixed probes [
12]. However, using RNR-RNA ISH, Milde-Langosch et al. found HPV-16 and -18 E6/E7 oncogene expressions in 62.3% of FFPE sections from adenocarcinoma cases [
13].
ISH assay can be used in tissue material and thin-layer cytological swabs. A study conducted by Samama B. et al. on thin-layered Pap smears showed that the rate of HPV detection increased with the severity of cytology result. They revealed DNA HPV 14% in minor cellular changes, 55% in AS-CUS, 95% in LSIL, and up to 100% in HSIL and carcinoma. High-risk HPV types were mainly present, alone or associated with low-risk HPV types, whatever the cytological findings. The researchers found a good correlation between ISH and the Hybrid Capture II test results with cervical smears. By using the HC test as the reference method, the sensitivity of the ISH protocol was 87.5% and the specificity 96% [
14].
In the vaccination against HPV era and the era of changes in sexual habits, we are looking for new diagnostic methods to facilitate the identification of patients with real progression of HSIL lesions towards cancer, regardless of the number of obstetric history. In the diagnosis of SIL changes, the identification of E6 E7 transcripts based on mRNA tests is already used [
15,
16,
17], and population-based preventive vaccinations against HPV in each age group may influence the occurrence of specific types of HPV and reduce the number of persistent virus infections [
18]. Additionally, researchers are looking for new diagnostic methods in patients with persistent HR HPV infection after preventive vaccinations, who may have a higher risk of developing epithelial changes towards HSIL and cervical cancer. Molecular methods such as mRNA, methylation or ISH may be used in laryngology or in men - in swabs from under the foreskin of penile. This is associated with a significantly lower concentration of HPV particles in secretions [
10,
19]
.
Concluding, the interpretation of a positive or negative ISH test must be guided in the context of clinical history and morphology and supplemented by appropriate control slide studies and other diagnostic tests. Responsibility for the use of probes, reagents, and methods for preparing stained slides rests with the collaboration of the histopathologist and clinician.
5. Conclusions
Automatic signal detection of ISH assay is not particularly applicable to cervical tissue material. A more useful method of confirming the presence of HPV in the cervix is the HPV test with genotyping, as it allows for collecting a larger amount of material from the cervical disc and canal. The interpretation of a positive or negative ISH test must be guided in the context of clinical history and morphology. It should be treated with due care and interpreted by the clinician in consultation with the histopathologist. The future use of automated algorithms based on AI facilitating the identification of morphological changes in epithelial cells of the HSIL or LSIL type with simultaneous intensity of staining will influence the parameters of the diagnosis of pre-cancerous changes in the cervix.
Author Contributions
Conceptualisation, D.P., P.K and M.P.; methodology, D.P. and J.Ż.; software, D.P. and S.M.-K.; validation, D.P. and S.M.-K.; formal analysis, D.P., S.M.-K. and M.P.; investigation, D.P., M.P., S.M.-K., M.K., M.d.M. and J.Ż.; resources, D.P., M.P. and P.K.; data curation, D.P., S.M.-K. and M.P.; writing—original draft preparation, D.P., S.M.-K. and M.P.; writing—review and editing, D.P., S.M.-K., R.J. and M.P.; visualisation, M.d.M. and M.K.; supervision, J.Ż. and R.J.; project administration, D.P. and M.P.; funding acquisition, D.P. and M.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and approved by the Institutional Review Board of the Poznan University of Medical Sciences (protocol number 540/22) on the 23rd of June 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
All source data is available at the corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
In this section, you can acknowledge any support given which is not covered by the author contribution or funding sections. This may include administrative and technical support, or donations in kind (e.g., materials used for experiments).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin. 2021 May;71(3):209-249. Epub 2021 Feb 4. PMID: 33538338. [CrossRef]
- Fitzpatrick MB, Hahn Z, Mandishora RSD, et al. Whole-Genome Analysis of Cervical Human Papillomavirus Type 35 from rural Zimbabwean Women. Sci Rep. 2020;10(1). [CrossRef]
- de Sanjosé S, Alemany L, Castellsagué X, Bosch FX. Human papillomavirus vaccines and vaccine implementation. Women’s Health. 2008;4(6). [CrossRef]
- Chen Z, Schiffman M, Herrero R, et al. Evolution and taxonomic classification of human papillomavirus 16 (HPV16)-related variant genomes: HPV31, HPV33, HPV35, HPV52, HPV58 and HPV67. PLoS One. 2011;6(5). [CrossRef]
- Cohen C, Lawson D, Jiang J, Siddiqui MT. Automated in situ hybridization for human papilloma virus. Appl Immunohistochem Mol Morphol. 2014 Sep;22(8):619-22. PMID: 24897064. [CrossRef]
- Lodde M, Mian C, Mayr R, Comploj E, Trenti E, Melotti R, Campodonico F, Maffezzini M, Fritsche HM, Pycha A. Recurrence and progression in patients with non-muscle invasive bladder cancer: prognostic models including multicolor fluorescence in situ hybridization molecular grading. Int J Urol. 2014 Oct;21(10):968-72. Epub 2014 Jun 19. PMID: 24947145. [CrossRef]
- Ishida M, Ohashi S, Kizaki Y, Naito J, Horiguchi K, Harigaya T. Expression profiling of mouse placental lactogen II and its correlative genes using a cDNA microarray analysis in the developmental mouse placenta. J Reprod Dev. 2007 Feb;53(1):69-76. Epub 2006 Oct 24. PMID: 17062983. [CrossRef]
- Guo M, Gong Y, Deavers M, Silva EG, Jan YJ, Cogdell DE, Luthra R, Lin E, Lai HC, Zhang W, Sneige N. Evaluation of a commercialized in situ hybridization assay for detecting human papillomavirus DNA in tissue specimens from patients with cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and cervical carcinoma. J Clin Microbiol. 2008 Jan;46(1):274-80. Epub 2007 Oct 31. PMID: 17977987; PMCID: PMC2224284. [CrossRef]
- Chalcarz, M.; Z˙ urawski, J. Injection of Aquafilling® for Breast Augmentation Causes Inflammatory Responses Independent of Visible Symptoms. Aesthet. Plast. Surg. 2021, 45, 481–490.
- Zito Marino F, Ronchi A, Stilo M, Cozzolino I, La Mantia E, Colacurci N, Colella G, Franco R. Multiplex HPV RNA in situ hybridization/p16 immunohistochemistry: a novel approach to detect papillomavirus in HPV-related cancers. A novel multiplex ISH/IHC assay to detect HPV. Infect Agent Cancer. 2020 Jul 14;15:46. PMID: 32684947; PMCID: PMC7362547. [CrossRef]
- Sheng Z, Minato H, Sasagawa T, et al. Detection of high-risk human papillomavirus subtypes in cervical glandular neoplasia by in situ hybridization. Int J Clin Exp Pathol. 2013;6(10).
- Tase T, Okagaki T, Clark BA, et al. Human Papillomavirus Types and Localization in Adenocarcinoma and Adenosquamous Carcinoma of the Uterine Cervix: A study by in Situ DNA Hybridization. Cancer Res. 1988;48(4).
- Milde-Langosch K, Riethdorf S, Kraus-Pöppinghaus A, Riethdorf L, Löning T. Expression of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p16MTS1, p21WAF1, and p27KIP1 in HPV-positive and HPV-negative cervical adenocarcinomas. Virchows Archiv. 2001;439(1). [CrossRef]
- Samama B, Plas-Roser S, Schaeffer C, Chateau D, Fabre M, Boehm N. HPV DNA detection by in situ hybridization with catalyzed signal amplification on thin-layer cervical smears. Journal of Histochemistry and Cytochemistry. 2002;50(10). [CrossRef]
- Pruski D, Millert-Kalinska S, Lewek A, Kedzia W. Sensitivity and specificity of HR HPV E6/E7 mRNA test in detecting cervical squamous intraepithelial lesion and cervical cancer. Ginekol Pol. 2019;90(2):66-71. PMID: 30860271. [CrossRef]
- Zappacosta R, Colasante A, Viola P, D’Antuono T, Lattanzio G, Capanna S, Gatta DM, Rosini S. Chromogenic in situ hybridization and p16/Ki67 dual staining on formalin-fixed paraffin-embedded cervical specimens: correlation with HPV-DNA test, E6/E7 mRNA test, and potential clinical applications. Biomed Res Int. 2013;2013:453606. Epub 2013 Nov 24. PMID: 24369532; PMCID: PMC3858005. [CrossRef]
- Hui C, Bai H, Liu J, Lu X, Wang S, Zhang Z, Jin M, Wang Y, Liu Y. Accuracy of HPV E6/E7 mRNA examination using in situ hybridization in diagnosing cervical intraepithelial lesions. Diagn Pathol. 2021 Feb 19;16(1):13. PMID: 33608003; PMCID: PMC7896359. [CrossRef]
- Pruski, D.; Millert-Kalińska, S.; Łagiedo, M.; Sikora, J.; Jach, R.; Przybylski, M. Effect of HPV Vaccination on Virus Disappearance in Cervical Samples of a Cohort of HPV-Positive Polish Patients. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 7592. [CrossRef]
- Takamoto D, Kawahara T, Kasuga J, Sasaki T, Yao M, Yumura Y, Uemura H. The analysis of human papillomavirus DNA in penile cancer tissue by in situ hybridization. Oncol Lett. 2018 May;15(5):8102-8106. Epub 2018 Mar 26. PMID: 29731917; PMCID: PMC5920620. [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Detection of HPV DNA (in situ hybridization: a – ISH HPV II and ISH b – HPV III) in epithelial cells in the tissue of the same patients (1 – LBC result: ASC-US, HPV negative, LSIL in biopsy; 2- LBC result: ASC-US, HPV 51 positive, LSIL in biopsy; 3 – LBC result: ASC-US, HPV 16, 56 positive, LSIL in biopsy; 4- LBC result: ASC-H, HPV 82 positive LSIL in biopsy). Magnification 400X. ISH analyses were performed using the INFORM HPV III Family 16 Probe for high-risk HPV (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, and 66) and the INFORM HPV II Family 6 probe for low-risk HPV (HPV 6 and 11) with the iVIEW Blue Plus Detection Kit Ventana detection system.
Figure 1.
Detection of HPV DNA (in situ hybridization: a – ISH HPV II and ISH b – HPV III) in epithelial cells in the tissue of the same patients (1 – LBC result: ASC-US, HPV negative, LSIL in biopsy; 2- LBC result: ASC-US, HPV 51 positive, LSIL in biopsy; 3 – LBC result: ASC-US, HPV 16, 56 positive, LSIL in biopsy; 4- LBC result: ASC-H, HPV 82 positive LSIL in biopsy). Magnification 400X. ISH analyses were performed using the INFORM HPV III Family 16 Probe for high-risk HPV (HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, and 66) and the INFORM HPV II Family 6 probe for low-risk HPV (HPV 6 and 11) with the iVIEW Blue Plus Detection Kit Ventana detection system.
Figure 2.
Boxplot chart visualizing level of ISH III in split to HPV positive and HPV negative groups. ISH- in situ hybridization.
Figure 2.
Boxplot chart visualizing level of ISH III in split to HPV positive and HPV negative groups. ISH- in situ hybridization.
Figure 3.
Boxplot chart visualizing level of ISH III in split to patients with HPV type 6 and/or 11 and other patients. ISH- in situ hybridization.
Figure 3.
Boxplot chart visualizing level of ISH III in split to patients with HPV type 6 and/or 11 and other patients. ISH- in situ hybridization.
Figure 4.
Scatter plot for age and ISH II level.
Figure 4.
Scatter plot for age and ISH II level.
Figure 5.
Scatter plot for age and ISH III level.
Figure 5.
Scatter plot for age and ISH III level.
Figure 6.
Scatter plot for ISH II and ISH III level (w/o one patient with ISH II = 16483,55).
Figure 6.
Scatter plot for ISH II and ISH III level (w/o one patient with ISH II = 16483,55).
Table 1.
Group characteristics.
Table 1.
Group characteristics.
| Characteristics |
Values |
| N |
72 |
| Age, years, Me (Q1; Q3) |
33.00 (28.75;37.00) |
| Histopathological diagnosis, n (%) |
|
| CIN1 |
28 (38.9) |
| CIN2 |
22 (30.6) |
| CIN3 |
20 (27.8) |
| No pathology |
2 (2.8) |
| ISH II, Me (Q1; Q3) |
58.45 (33.36;87.99) |
| ISH III, Me (Q1; Q3) |
375.60 (134.90;2400.16) |
| LBC result, n (%) |
|
| NILM |
3 (4.2) |
| AS-CUS |
11 (15.3) |
| LSIL |
32 (44.4) |
| ASC-H |
15 (20.8) |
| HSIL |
11 (15.3) |
| HPV, n (%) |
|
| Positive |
64 (88.9) |
| Negative |
8 (11.1) |
| HPV genotype, n (%)* |
|
| 6 or 11 |
8 (11.1) |
| Any of 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52, 56, 58, 66 |
53 (73.6) |
| Other positive |
22 (30.6) |
Table 2.
Comparison of ISH II level between selected groups.
Table 2.
Comparison of ISH II level between selected groups.
| Variables |
ISH II level |
MD (95% CI) |
p |
| LBC result |
|
|
|
| NILM |
79.12 (52.51;177.78) |
- |
- |
| AS-CUS |
63.55 (44.55;79.13) |
- |
0.786 |
| LSIL |
61.15 (35.89;92.27) |
| ASC-H |
50.77 (32.00;102.45) |
| HSIL |
46.81 (29.84;69.30) |
| HPV |
|
|
|
| yes |
52.28 (33.12;85.47) |
-28.24 (-88.01;3.05) |
0.072 |
| no |
80.52 (67.09;163.84) |
| HPV genotypes |
|
|
|
| 6 or 11 |
|
|
|
| yes |
48.76 (42.74;54.36) |
-14.66 (-34.26;17.44) |
0.809 |
| no |
63.42 (32.46;92.27) |
| Any of 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 66 |
|
|
|
| yes |
57.15 (31.72;86.34) |
-8.67 (-41.39;7.72) |
0.188 |
| no |
65.82 (47.26;115.24) |
| Histopathological diagnosis |
|
|
|
| CIN1 |
63.42 (36.07;85.47) |
11.14 (-16.15; -26.32) |
0.527 |
| CIN2 + CIN3 |
52.28 (35.59;71.45) |
Table 3.
Comparison of ISH III level between selected groups.
Table 3.
Comparison of ISH III level between selected groups.
| Variables |
ISH III level |
MD (95% CI) |
p |
| LBC result |
|
|
|
| NILM |
198.92 (127.20;220.16) |
- |
- |
| AS-CUS |
166.58 (147.58;2379.48) |
- |
0.828 |
| LSIL |
334.40 (122.33;2045.52) |
| ASC-H |
396.79 (215.43;3932.40) |
| HSIL |
1031.62 (135.07;6098.14) |
| HPV |
|
|
|
| positive |
318.25 (117.75;1954.46) |
-7961.82
(-17230.00;-199.21) |
0.005 |
| negative |
8280.07 (1805.37;20100.63) |
| HPV genotypes |
|
|
|
| 6 or 11 |
|
|
|
| yes |
110.96 (85.23;195.17) |
-317.05 (-1972.19;-13.71) |
0.037 |
| no |
428.01 (153.80;2828.15) |
| Any of 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 66 |
|
|
|
| yes |
346.67 (140.08;1997.89) |
-1660.38
(-4089.04;65.29) |
0.157 |
| no |
2007.05 (141.99;12071.24) |
| Histopathological diagnosis |
|
|
|
| CIN1 |
375.60 (137.87;3007.58) |
-338.61
(-929.97;516.39) |
0.812 |
| CIN2 + CIN3 |
714.21 (99.78;2757.10) |
Table 4.
Kappa coefficients for assessing agreement between CIN and HPV outcomes.
Table 4.
Kappa coefficients for assessing agreement between CIN and HPV outcomes.
| Variables |
HPV |
Kappa coefficient |
p |
| yes (n = 64) |
no (n = 8) |
| CIN1 |
|
|
|
|
| yes |
22 (34.4) |
6 (75.0) |
-0.14 |
0.917 |
| No |
42 (65.6) |
2 (25.0) |
| CIN2 |
|
|
|
|
| yes |
20 (31.2) |
2 (25.0) |
0.02 |
0.413 |
| No |
44 (68.8) |
6 (75.0) |
| CIN3 |
|
|
|
|
| yes |
20 (31.2) |
0 (0.0) |
0.09 |
0.132 |
| No |
44 (68.8) |
8 (100.0) |
Table 5.
Sensitivity and specificity of selected outcomes in CIN2 + CIN3.
Table 5.
Sensitivity and specificity of selected outcomes in CIN2 + CIN3.
| Variable |
CIN2 + CIN3 |
Sensitivity, % |
Specificity, % |
PPV, % |
NPV, % |
Accuracy, % |
Yes,
n = 42 |
No,
n = 30 |
Total,
n = 72 |
| ASC-US |
+ |
4 |
7 |
11 |
9.52 (2.66-22.62) |
76.67 (57.72-90.07) |
36.36 (15.51-64.01) |
37.70 (32.68-43.01) |
37.50 (26.32-48.68) |
| - |
38 |
23 |
61 |
| LSIL |
+ |
16 |
16 |
32 |
38.10 (23.57-54.36) |
46.67 (28.34-65.67) |
50.00 (37.51-62.49) |
35.00 (25.56-45.79) |
41.67 (30.28-53.05) |
| - |
26 |
14 |
40 |
| ASC-H |
+ |
11 |
4 |
15 |
26.19 (13.86-42.04) |
86.67 (69.28-96.24) |
73.33 (49.19-88.65) |
45.61 (40.03-51.31) |
51.39 (39.84-62.93) |
| - |
31 |
26 |
57 |
| HSIL |
+ |
10 |
1 |
11 |
23.81 (12.05-39.45) |
96.67 (82.78-99.92) |
90.91 (57.47-98.67) |
47.54 (43.04-52.08) |
54.17 (42.66-65.68) |
| - |
32 |
29 |
61 |
| ISH II |
+ |
42 |
30 |
72 |
100.00 (91.59-100.00) |
0.00 (0.00-11.57) |
58.33 (56.21-61.17) |
- |
58.33 (46.95-69.72) |
| - |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| ISH III |
+ |
42 |
30 |
72 |
100.00 (91.59-100.00) |
0.00 (0.00-11.57) |
58.33 (56.21-61.17) |
- |
58.33 (46.95-69.72) |
| - |
0 |
0 |
0 |
| HPV |
+ |
40 |
24 |
64 |
95.24 (83.84-99.42) |
20.00 (7.71-38.57) |
62.50 (57.92-66.87) |
75.00 (39.38-93.27) |
63.89 (52.79-74.98) |
| - |
2 |
6 |
8 |
| HPV 6 or 11 |
+ |
4 |
4 |
8 |
9.52 (2.66-22.62) |
86.67 (69.28-96.24) |
50.00 (21.34-78.66) |
40.62 (36.57-44.81) |
41.67 (30.28-53.05) |
| - |
38 |
26 |
64 |
| HPV group 2* |
+ |
35 |
18 |
53 |
83.33 (68.64-93.03) |
40.00 (22.66-59.40) |
66.04 (58.49-72.85) |
63.16 (43.37-79.33) |
65.28 (54.28-76.27) |
| - |
7 |
12 |
19 |
Table 6.
Sensitivity and specificity of ISH II in HPV 6 or 11.
Table 6.
Sensitivity and specificity of ISH II in HPV 6 or 11.
| Variable |
HPV 6 or 11 |
|
Sensitivity, % |
Specificity, % |
PPV, % |
NPV, % |
Accuracy, % |
Yes,
n = 8 |
No,
n = 64 |
Total,
n = 72 |
| ISH II |
+ |
8 |
64 |
72 |
100.00 (63.06-100.00) |
0.00 (0.00-5.60) |
11.11 (7.72-12.20) |
- |
11.11 (3.85-18.37) |
| - |
0 |
0 |
0 |
Table 7.
Sensitivity and specificity of ISH III in HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52, 56, 58, 66.
Table 7.
Sensitivity and specificity of ISH III in HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52, 56, 58, 66.
| Variable |
HPV 16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 45, 52, 56, 58, 66 |
Sensitivity, % |
Specificity, % |
PPV, % |
NPV, % |
Accuracy, % |
| Yes, n = 53 |
No, n = 19 |
Total, n = 72 |
| ISH III |
+ |
53 |
19 |
72 |
100.00 (93.28-100.00) |
0.00 (0.00-17.65) |
73.61 (72.03-77.08) |
- |
73.61 (63.43-83.79) |
| - |
0 |
0 |
0 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).