1. Introduction
Respiration of citrus fruit after harvest consumes oxygen and produces carbon dioxide, the respiration reaction of which is conducted in the cell [
1,
2]. In the results, it is indicated a decrease in the oxygen concentration and an increase in the carbon dioxide concentration in the cell. Since gas diffusion between the outside and inside of the fruit is driven by the concentration gradient, as indicated by Fick’s first law of diffusion, oxygen diffuses from the outside to the inside of the fruit, and carbon dioxide diffuses from the inside to the outside [
1,
3,
4,
5,
6,
7]. However, gas diffusion is resisted by plant tissue construction of the fruit, such as the outer skin and inner skin of the fruit [
7,
8,
9,
10,
11,
12]. Thus, the internal oxygen and carbon dioxide gas concentrations are low and high, respectively, compared to the atmosphere because oxygen diffusion from outside to inside and carbon dioxide from inside to outside can be suppressed by the resistance generated from plant tissue construction [
3,
5,
7,
13,
14,
15,
16,
17]. Therefore, gas diffusion resistance is an important factor in understanding the internal gas component of the fruit and controlling the respiration of the fruit [
1].
Various cultivars of citrus fruit, which are cultivated even in Japan with more than a hundred varieties, have unique structures such as thick or slim outer skin. The outer skin in contact with the atmosphere may play an important role in resistance to gas diffusion between the outside and inside of the fruit [
1,
18]. However, the relationship between the thickness of the citrus fruit skin and gas diffusion resistance is unclear. Additionally, the number of stomates on the surface of the outer skin and void space and more specific construction may affect gas diffusion resistance [
7,
8,
12,
15,
17,
19,
20]. Moreover, it is unclear whether the specific construction of various citrus fruits affects the internal gas composition related to respiration.
In this study, it was investigated the gas diffusion resistance using a modified ethane efflux method and fruit tissue construction for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit, respectively. Additionally, the internal oxygen and carbon dioxide gas concentrations were investigated before and after storage at 5 and 25 °C to clarify the effect of the gas diffusion resistance on the internal gas components.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Plant Material
The citrus fruits used in this study was Citrus iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” and Citrus unshu “Nankan No.20” and Citrus spp. “Ehime Kashi No.28” and “Harehime” and “Kanpei” and “Setoka” and “Shiranuhi”. Seven cultivars of citrus fruits cultivated in Ehime were purchased in retail and stored at 10 °C until the experiment, which was utilized for the experiment within a week.
2.2. Measuring Gas Diffusion Resistance and Construction Characteristics for Cultivars of Citrus Fruit
2.2.1. Ethane Efflux Method for Calculation of Gas Diffusion Resistance
A modified ethane efflux method comprising an absorption process and an efflux process was performed using five samples for each of the citrus fruit cultivars to calculate the resistance to gas diffusion from the ethane effluence behavior in the effluence process according to the modified method of Dirpan
et al. (2016) [
11].
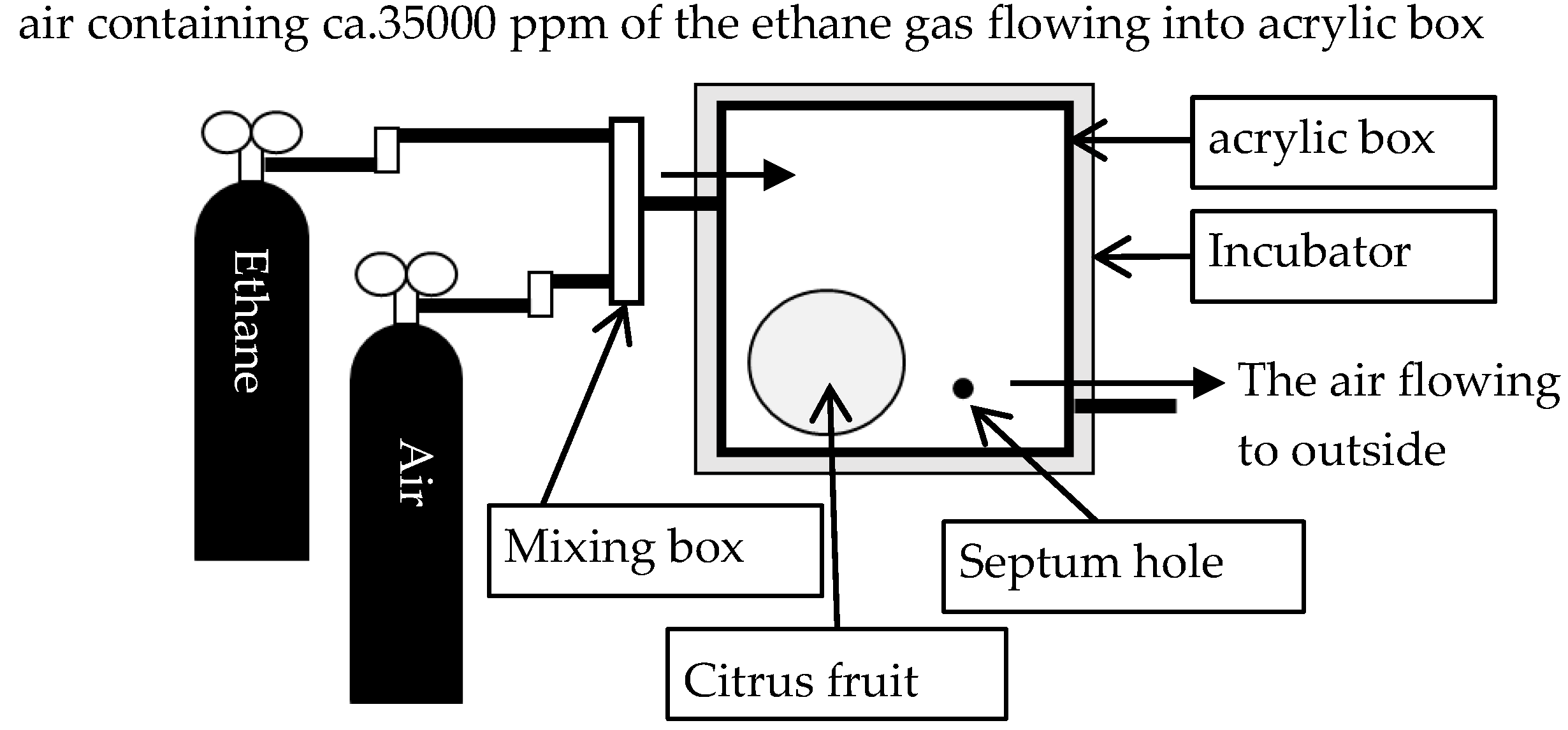
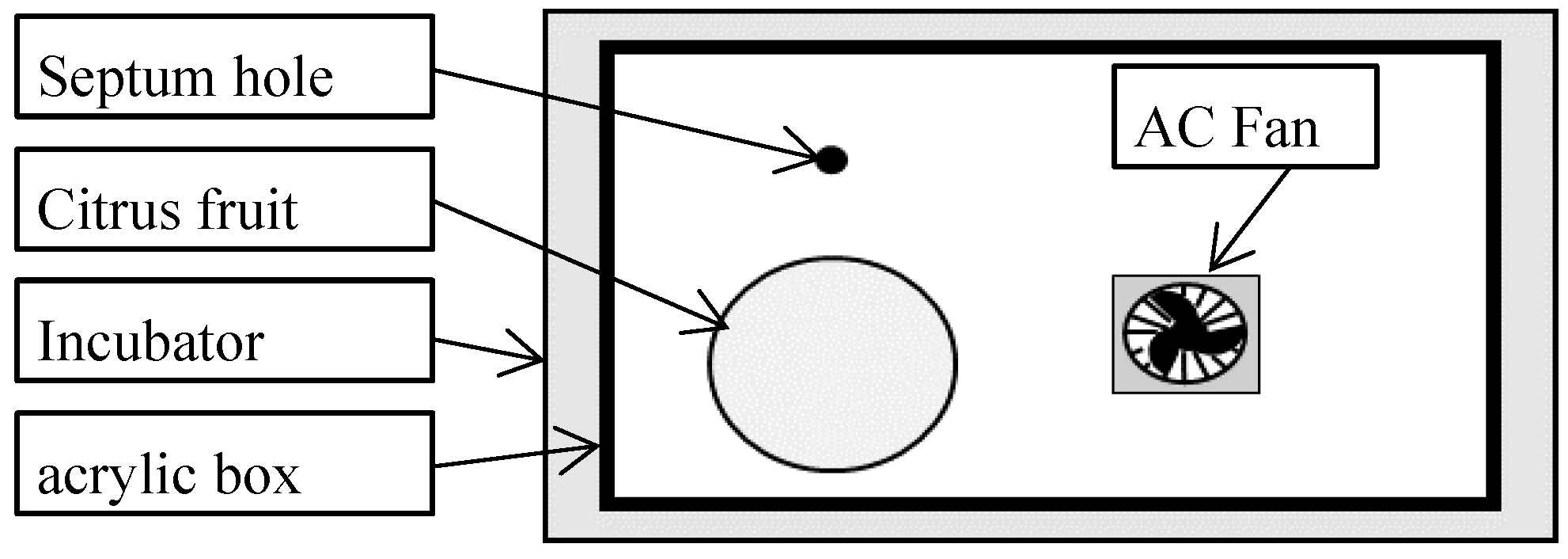
During the absorption process, it is shown as
Figure 1 that a single fruit was placed in an acrylic box with two vent holes and a septum hole at 20 °C maintained by an incubator, subsequently, a constant amount of air containing ca.35,000 ppm of ethane gas flowed through a mixing box into the box with two vent holes for 4 h to diffuse the ethane gas into the tissue of the fruit.
After 4 h, it is shown as
Figure 2 the fruit was transferred to an acrylic box with a septum hole for the effluence process, and the box was closed immediately. Subsequently, the internal ethane gas absorbed to the fruit was diffused to the headspace in a closed box at 20 °C maintained by incubator. An alternating current fan was placed in a closed box to ensure uniform ethane gas concentration in the headspace.
The gas in each of the boxes for absorption and effluence process was sampled by a syringe passing a needle through a septum, whose role was to increase the gas tightness of the boxes at the time of the gas sampling. The sampling gas of 0.5 ml in the syringe was used to analyze the ethane gas concentration. The ethane gas concentration was analyzed by gas chromatography (model GC-2014; Shimadzu, Japan) coupled with a flame ionization detector (FID) and a 200 × 0.3 cm I.D. stainless steel column containing activated alumina 80/100 mesh. Nitrogen gas was used as the carrier gas for gas chromatography. The injector, column, and detector temperatures for gas chromatography were 80, 70, and 90 °C, respectively.
2.2.2. Measuring Construction Characteristics
After the effluence process, the volume, stomatal density, surface area, outer skin thickness, and void ratio of the same fruits were measured. The fruit volume (
) was determined by measuring the buoyant force on the fruit in water. The stomatal density on the outer skin was measured by microscopic observation of the fruit outer skin surface of three samples that were transferred on instant adhesive using Suzuki's universal micro-printing (Sump) method. The surface area of the fruits was measured by measuring the dimensions of the outer skin of the fruits. The outer skin of the fruit was cut and photographed using a digital camera. The dimensions of the outer skin on the picture used as the surface dimension of the citrus fruit (
) were measured using Image J. Additionally, the thickness of the cut outer skin was measured at three locations on the equatorial plane using a digital caliper. The void ratio of the fruits was calculated from the volume (
), weight (
), and real density (
) of the fruits using Eq. (1). Real density (
) was measured using a pycnometer filled with fruits minced by a juicer.
Additionally, the void volume in citrus fruit (
) was calculated as the apparent citrus fruit volume (
) minus the true volume, which was the weight (
) divided by the real density (
), as shown in Eq. (2).
Table 1 shows the weight (
), apparent volume (
), internal void volume (
), and surface dimension (
) of all cultivars of citrus fruits.
2.2.3. Calculation of Gas Diffusion Resistance
A formula for calculating an external concentration of ethane gas in the effluence process was derived from differential equation of Fick’s first law of diffusion as shown in Eq. (3).
where
and
is the diffusion rate of ethane gas and the ethane gas diffusion kinetic constant.
is ethane gas concentration difference between the inside and outside of the citrus fruit, where the gradient (
) fluctuates according to the beginning of the effluence process.
The differential equation of Eq. (3) was solved as shown in Eq. (4).
where
is the ethane gas concentration sampling from the headspace of the closed box of the effluence process at each of the time, which can be calculated from the saturated ethane gas concentration in the headspace (
), time (
), and ethane gas diffusion kinetic constant (
). The saturated ethane gas concentration in the headspace (
) can be calculated by dividing the total amount of ethane gas absorbed into the void space of fruits inside the absorption process by the total volume of the headspace in the closed box (
) and void in citrus fruit (
) as shown in Eq. (5).
where
is internal gas concentration in the fruits at beginning of the effluence process, which is equivalent to external gas concentration in the box at end of the absorption process. The total amount of ethane gas absorbed into the fruits until end of the absorption process was calculated by multiplying the ethane gas concentration in the box at end of the absorption process with void in the fruit (
). The void volume in citrus fruit (
) was used as shown in 2.2.2, and the volume of the headspace in the closed box (
) was used as the total volume of the box inside minus the volume of the alternating current fan and the fruit.
The ethane gas diffusion kinetic constant (
) was calculated from the least-square method approximating between the calculation result in Eq. (4) (
) and the experimental result of the ethane gas concentration during the diffusion experiment. The resistance to gas diffusion was calculated using the ethane gas diffusion kinetic constant (
), void volume in citrus fruit (
), volume of headspace in the closed box (
), and surface dimension of the citrus fruit (
), as shown in Eq. (6).
2.3. Measurement of Internal Gas Components Related to the Respiration for Cultivars of Citrus Fruit
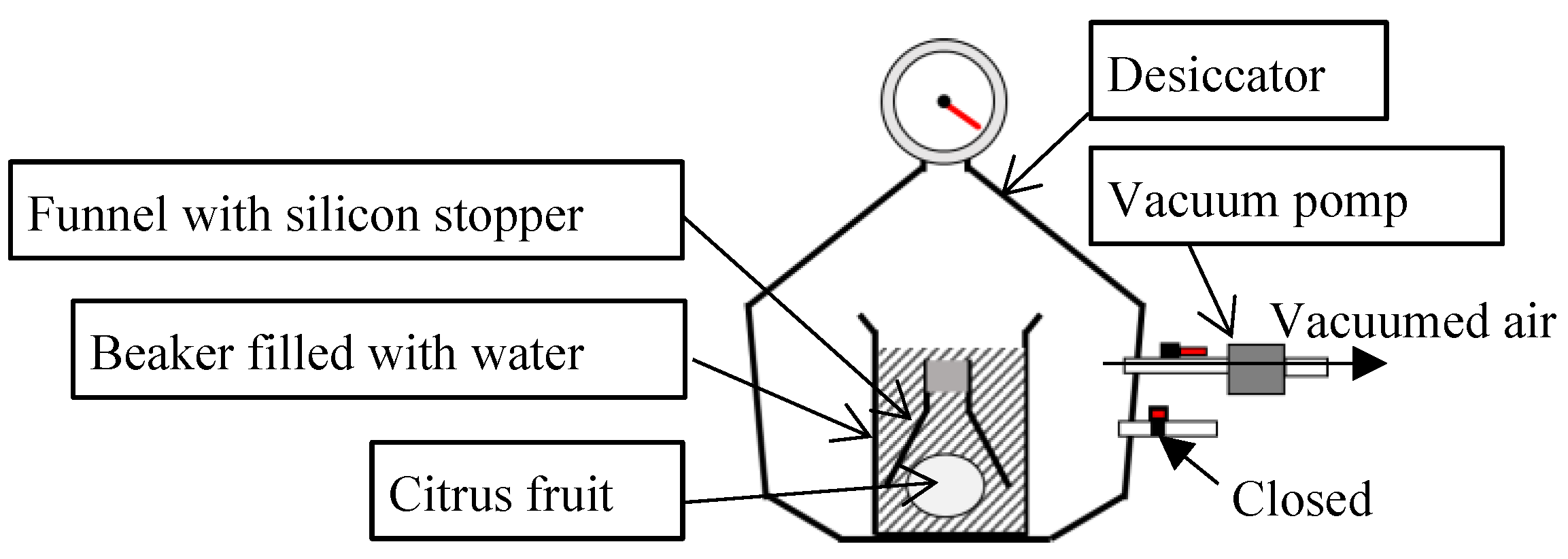
The internal gas component related with respiration was investigated using another five fruits of the citrus cultivars, respectively. After one night of storage at 10 °C, the samples stored at 10 °C or 25 °C for several weeks were used to extract the internal gas of the fruits. It is shown as
Figure 3 that the internal gas was extracted under vacuum. Each of the fruits was placed in a beaker filled with water. To collect internal gas after vacuum, a funnel filled with water and covered with a silicon stopper was placed above the fruit. The beaker was placed in a desiccator, and the air in the desiccator was vacuumed at –0.08 MPa for 1 min using an air compressor. After the vacuum, the collected gas at the top of the funnels was sampled using a syringe passing a needle through the silicon stopper.
The sampling gas of 0.5 ml in the syringe was used for the analysis of oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations. The oxygen and carbon dioxide concentrations were analyzed using a gas chromatograph (model GC-8A; Shimadzu, Japan) coupled with a thermal conductivity detector (TCD) and a 1.8 m × ϕ1/4 O.D. stainless steel column WG-100. Helium gas was used as the carrier gas for gas chromatography. The temperatures of the injector and column used for gas chromatography were 80 °C and 50 °C, respectively.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
All experimental results were expressed as mean ± standard deviation using data of five samples, respectively. Comparing among experimental results, statistical significance was verified by Tukey-Kramer’s method (p < 0.05).
3. Results and Discussions
3.1. Gas Diffusion Resistance for 7 Citrus Fruit Cultivars
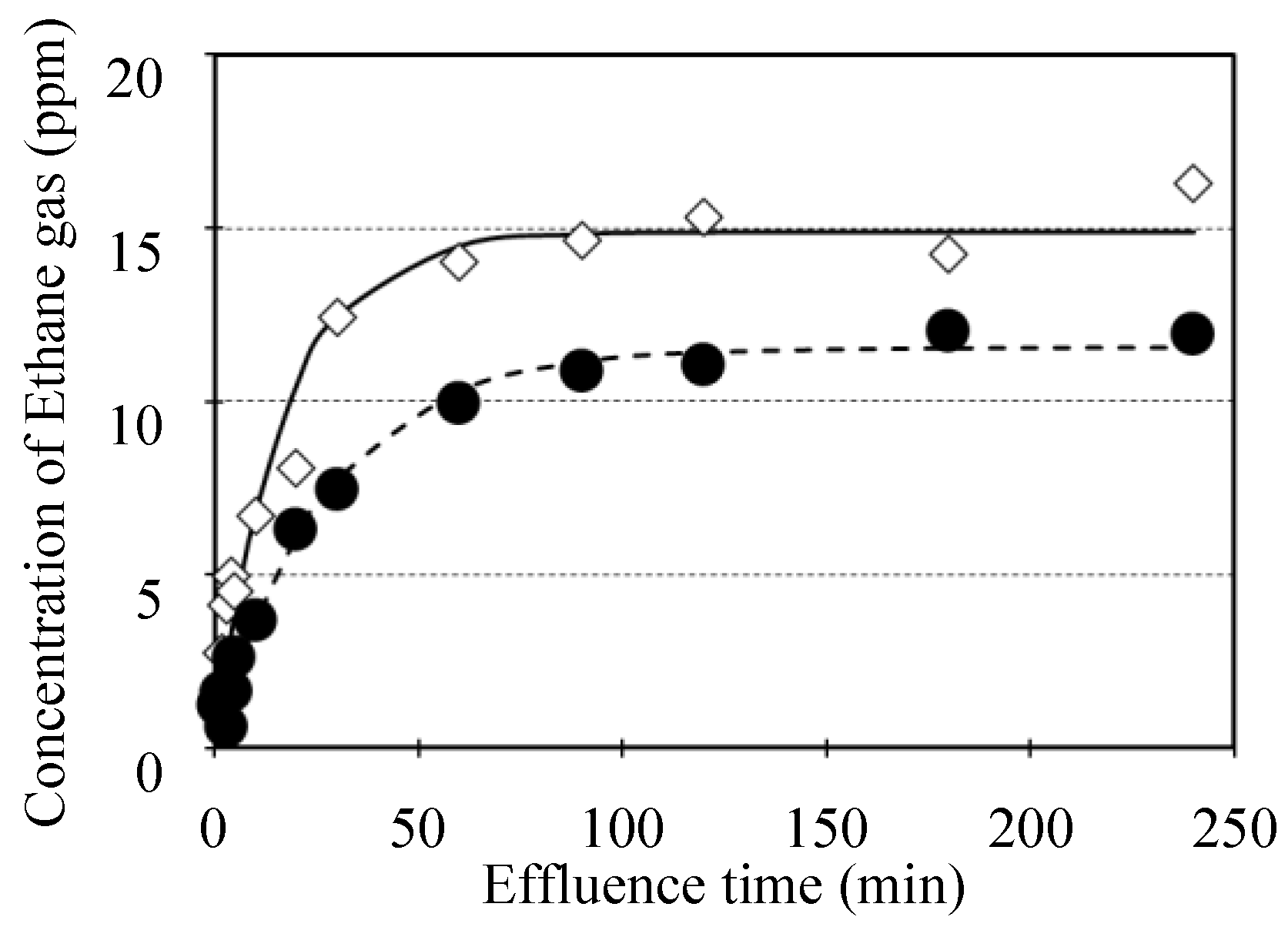
Figure 4 shows the ethane gas concentration in the closed box during the effluence process for
C. spp “
Shiranui” and
“Ehime Kashi No.28” of citrus fruits, which was example results of minimum and maximum gas resistance cultivars. In all of samples, a rapid effluence of the ethane gas from the fruits was observed at initial period of the process, while the effluence was suppressed secondly. Finally, an equilibrium of the gas concentration was observed in each of samples. On the other hands, effluence behavior of the ethane gas was differed to the cultivars considerably. These differences could be resulted from the gas resistance of each of the cultivars. Thus, the resistance to gas diffusion between fruit inside and atmosphere was calculated from the approximation between calculating formula (Eq. (4)) and the experimental results of the external ethane gas concentration as shown in section of 2.2, respectively.
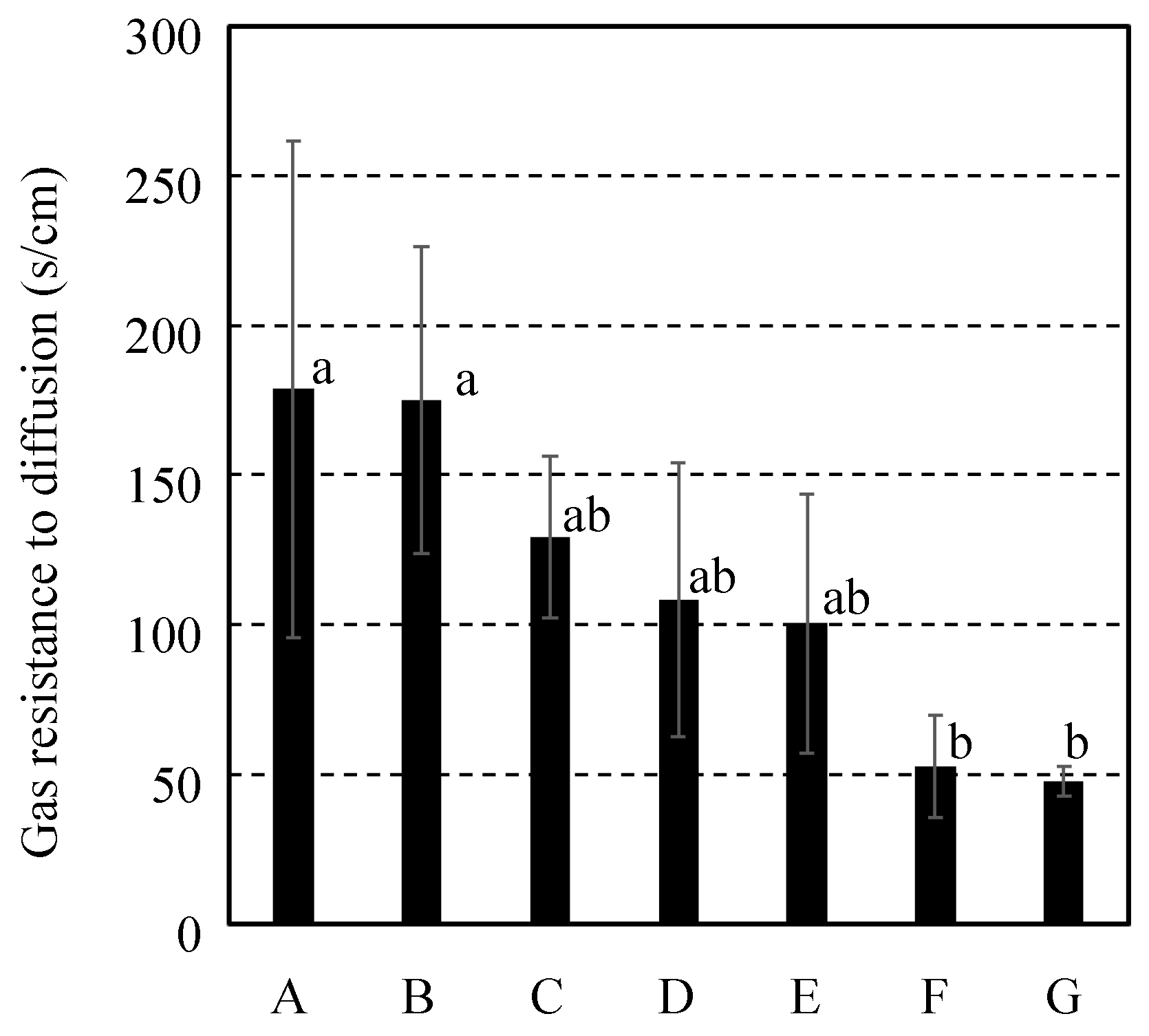
Figure 5 shows the resistance to gas diffusion between fruit inside and atmosphere using a calculation from each result of the ethane gas diffusion experiments for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit. The gas diffusion resistance was 178.8±82.8 s/cm for
Citrus spp “Shiranui” and 175.1±51.1 s/cm for
C. unshu “Nankan No.20” and 129.2±27.1 s/cm for
C. spp “Harehime” and 108.4±45.8 s/cm for
C. iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” and 100.6±43.2 s/cm for
C. spp “Setoka” and 52.7±17.2 s/cm for
C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” and 47.9±5.0 s/cm for
C. spp “Kanpei”. Although all cultivars of the fruits were grouped into the genus Citrus, each citrus fruit cultivar had a different resistance to gas diffusion. Considering that each of the cultivars of citrus fruit construction varied, the fruits constructions might affect the gas diffusion resistance of each cultivar. Thus, it was compared among gas diffusion resistance and the fruits construction.
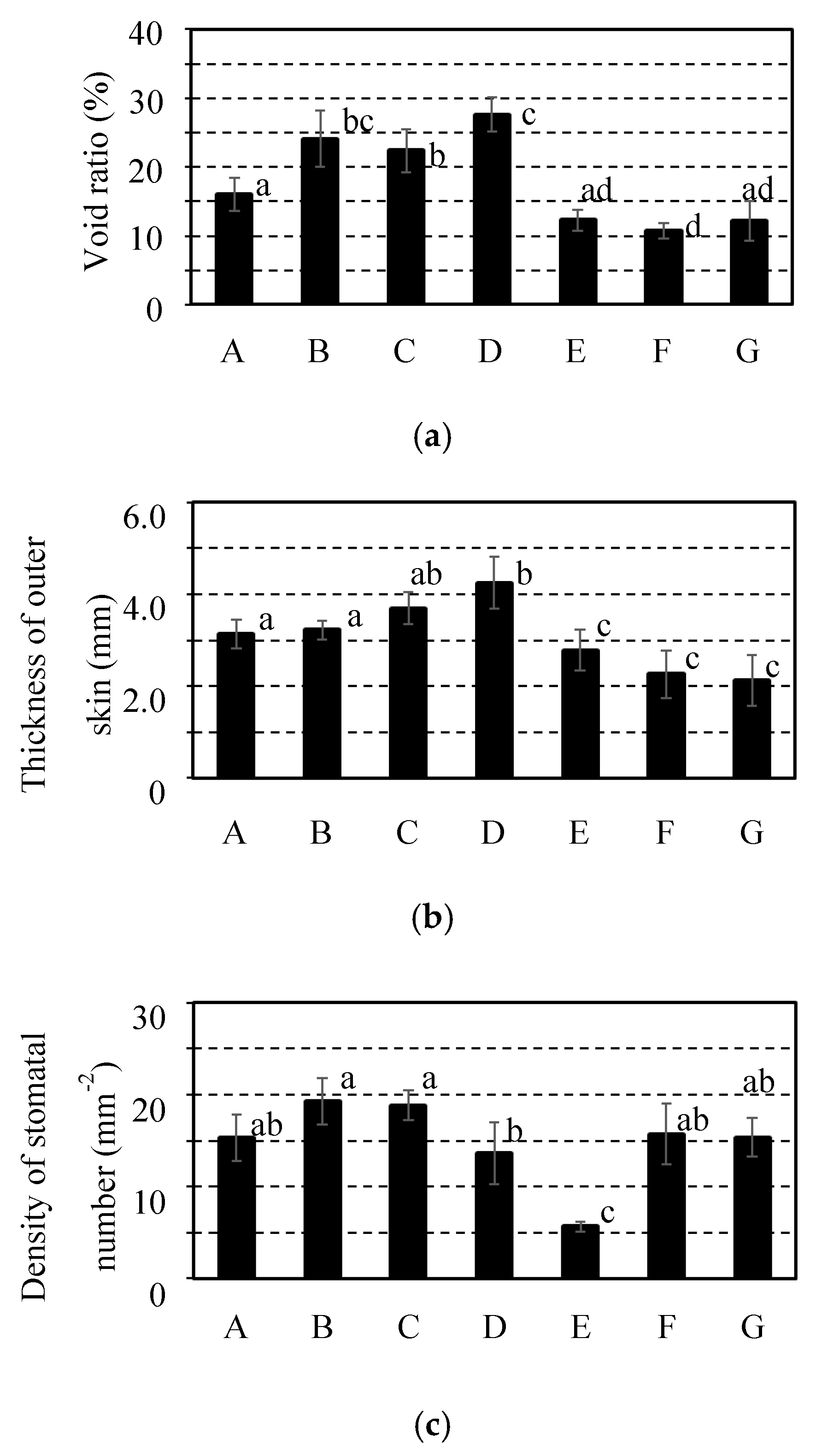
Figure 6 shows the void ratio of fruit inside, outer skin thickness, and stomatal number density for each of the seven fruit cultivars. These were investigated the same fruits after experiment of the gas diffusion resistance. The void of the fruit inside is a route for gas diffusion in the fruit inside [
1,
18]. Therefore, the gas diffusion resistance of the fruit inside might increase according to a decrease in the void ratio of the fruit inside. However, the cultivars of citrus fruit with lower gas diffusion resistance such as
C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” and
C. spp “Kanpei” had a low ratio of void for fruit inside as shown in
Figure 6(a). From this result, it was speculated that the void ratio for the fruits inside has no considerable effect on the gas diffusion resistance between the fruit inside and the atmosphere, which was similarly reported for Japanese pear cultivars [
12].
Whereas, the cultivars of citrus fruit with lower gas diffusion resistance such as
C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” and
C. spp “Kanpei” had a slim outer skin thickness in comparison with the other cultivars as shown in
Figure 6(b). The outer skin of horticultural produce is the outermost construction separating the fruit inside and the atmosphere and plays a major role in the barrier to gas exchange [
1,
18]. It was reported on apple by Schotsmans
et al. (2004) [
18] that the cultivar of
“Jonica” with a thin outer skin thickness (20 μm) had a higher gas diffusion resistance than
“Braeburn” with a slim thickness of outer skin (14 μm) [
15]. Additionally, the gas diffusion resistance was increased by coating the surface of fruits with wax even for a thickness of ca. 0.8 × 10
–2 mm [
21]. Therefore, differences in outer skin thickness between 2.1–4.2 mm for citrus fruits could have a considerable effect on the gas diffusion resistance for each cultivar.
However, the citrus fruits of
C. spp “Setoka” with the outer skin thickness equivalent to that of
C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” and
C. spp “Kanpei” had a higher gas diffusion resistance than these cultivars of fruit. Focusing on the density of stomatal number on the outer skin surface, that for the citrus fruits of
C. spp “Setoka” was less than that for fruits of the other cultivars with significance as shown in
Figure 3(c) (
p <0.05). Since a stoma is a route for gas diffusion between the fruit inside and the atmosphere [
1,
18], the stomatal number density could affect the gas diffusion resistance. Therefore, although the citrus fruits of
C. spp “Setoka” had a slim thickness of the outer skin, high gas diffusion resistance for the citrus fruits of
C. spp “Setoka” might be induced by the low density of stomatal number compared to that of
C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” and
C. spp “Kanpei”.
From these results, resistance to gas diffusion between the fruit inside and the atmosphere could be generated from multiple constructions of citrus fruits, such as outer skin thickness and stomatal number density.
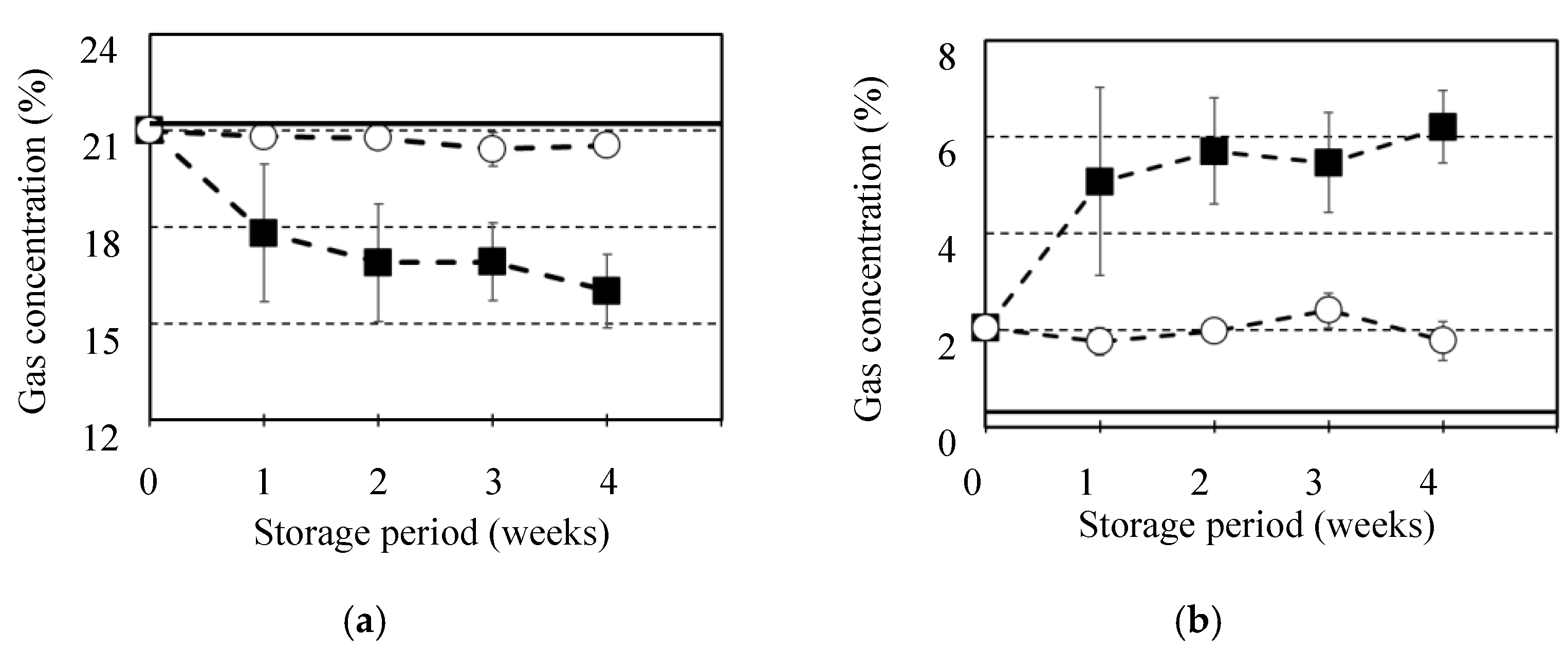
3.2. Fluctuation of Internal Gas Concentration in the Fruits of Citrus unshu “Nankan 20 gou” during Storage
Figure 7 shows the gas concentration of O
2 and CO
2 in the fruits of
C. unshu “Nankan 20 gou” stored at 10 °C or 25 °C for 4 weeks. The atmospheric gas concentration in laboratory room for control was 0.3±0.0 % for CO
2 and 21.2±1.6 % for O
2. While, in the fruits even before the storage, gas concentration was 2.0±0.2 % for CO
2 and 21.0±0.2 % for O
2. Therefore, it was clear that the CO
2 gas concentrations inside the fruits might be constantly higher than those in the atmosphere. When the fruits were stored at 10 °C for 4 weeks, the gas concentration was 1.8±0.4 % for CO
2 and 20.5±0.2 % for O
2, which was observed slight fluctuation of the internal gas concentrations during the storage. However, at 25 °C, the fluctuation in the gas concentration during the storage time was considerable. After the storage of 4 weeks, the CO
2 gas concentration increased to 6.2±0.8 % and O
2 decreased to 16.0±1.1 %. A fruit constantly undergoes respiration, and its respiration results in the O
2 consumption and CO
2 synthesis in the fruits. Normally, gases transport between the atmosphere and the fruit inside for supply of O
2 gas and effusion of CO
2 gas conducted passing through the outer skin and the other construction. When the gas concentration fluctuation induced by respiration of fruits is not considerable, gas exchange can result in maintenance of gas concentrations during storage such as stored at 10 °C. However, if respiration is activated by the high storage temperature, supply and effusion of the gases can be conducted insufficiently, which can result in a decrease in O
2 and an increase in CO
2 of the internal gas concentration. The internal gas concentration of fruit can be determined by the balance between its respiration and gas exchange [
1]. As a result of the balance, comparing with the pre-storage gas concentration of the fruits, storage at 10 °C maintained the gas concentration, while storage at 25 °C induced a decrease in O
2 and an increase in CO
2. Additionally, in visible observation, it seemed that the amount of gas extracted by the vacuum from the fruit stored at 10 °C was constant regardless of the storage period, while that at 25 °C decreased with extension of the storage period, which was reported a similar observation that the internal gas amount of the onion bulb decreased with an increase in storage temperature [
17]. Therefore, as observed at 25 °C, active respiration could cause not only fluctuations of the gas concentration but also a decrease in the gaseous amount in the fruit.
3.3. Comparison of Internal Gas Concentration among 7 Cultivars of Citrus Fruits
In the fruits of C. unshu “Nankan 20 gou,” considerable fluctuation of gas concentration was not observed after longer storage than 2 weeks at 25 °C. Thus, the citrus fruits were utilized after 2 weeks of storage to compare the internal gas concentrations among the cultivars.
Figure 5,
Figure 6, and
Figure 7 shows the internal gas concentrations of the fruit which were utilized before storage and after storage at 10 °C and 25 °C for 2 weeks. In the pre-stored fruits for all of the cultivars, gas concentrations of 2.0–3.0 % for CO
2 and 19.4–20.1 % for O
2, as shown in
Figure 5. In the fruits stored at 10 °C, gas concentrations of 2.0–2.9 % for CO
2 and 19.5–20.8 % for O
2 are shown in
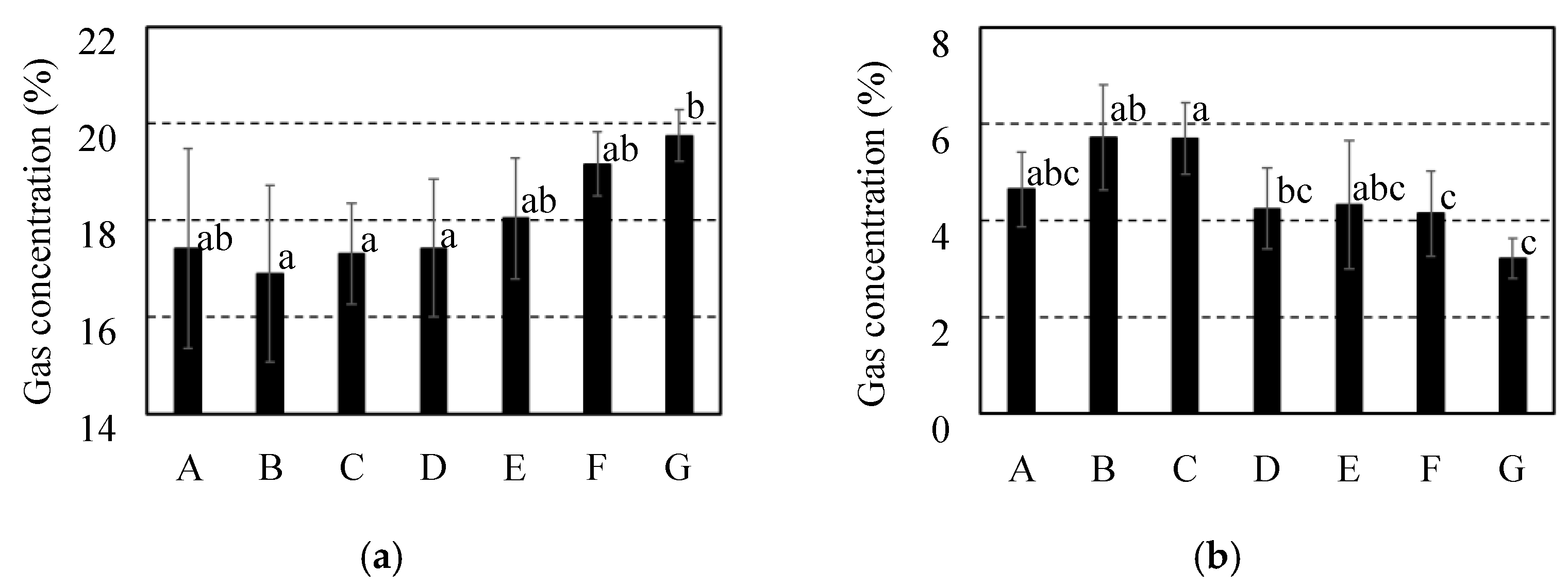
Figure 6. Comparing the internal gas concentration of the fruits before and after storage at 10 °C, in all of the cultivars, no considerable effect of storage on the internal gas concentrations of the fruits was observed. After storage at 25 °C, an increase in CO
2 concentration and a decrease in O
2 concentration were observed compared to pre-stored fruits in all of the cultivars, as shown in
Figure 7. Therefore, besides the fruits of
C. unshu “
Nankan 20 gou”, fluctuations in the internal gas concentrations could be affected by active respiration at 25 °C in all of the cultivars. Additionally, focusing on the difference in the internal gas concentration among the cultivars, a significant difference was observed in the stored fruits at 25 °C, in contrast with comparing with the pre-stored fruits and the stored fruits at 10 °C. With the increase in the gas diffusion resistance of the cultivars fruits, it was tended that the CO
2 concentration increased and the O
2 concentration decreased after storage at 25 °C. When active respiration induced fluctuation of the internal gas concentration, high gas diffusion resistance of the fruits could limit the gas exchange between the atmosphere and the inside of the fruits, which could maintain fluctuated internal gas concentration [
10]. Therefore, one of the factors resulting in an increase in CO
2 concentration and a decrease in O
2 concentration after storage at 25 °C may be the high gas diffusion resistance of the fruits.
Figure 8.
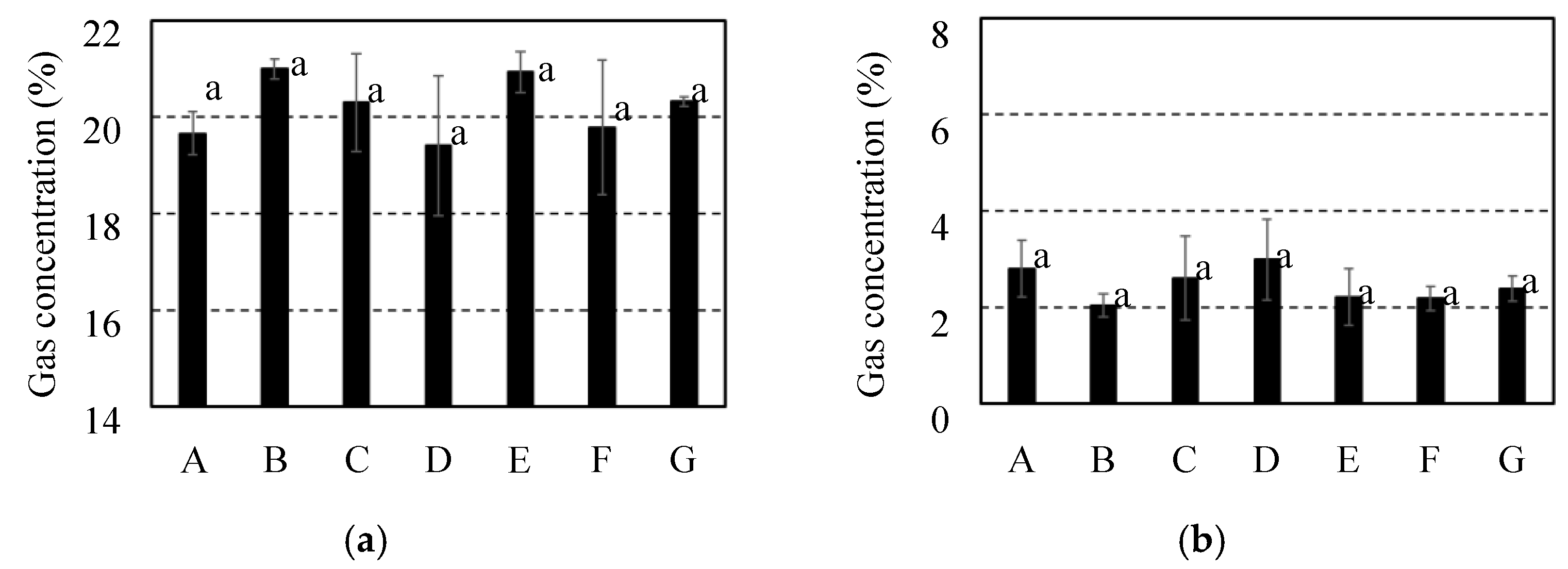
Internal gas concentration for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit before storage. It was investigated each of gas concentrations for (a) O2 and (b) CO2. It was indicated C. spp “Shiranui” as “A” and C. unshu “Nankan No.20” as “B” and C. spp “Harehime” as “C” and C. iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” as “D” and C. spp “Setoka” as “E” and C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” as “F” and C. spp “Kanpei” as “G”. Results and error bar were shown by mean values and standard deviation of 5 samples (n=5). Significant difference of the gas diffusion resistance among all breeds of citrus fruit was evaluated by Tukey-Kramer’s method (p<0.05). The different letters indicate a significant difference.
Figure 8.
Internal gas concentration for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit before storage. It was investigated each of gas concentrations for (a) O2 and (b) CO2. It was indicated C. spp “Shiranui” as “A” and C. unshu “Nankan No.20” as “B” and C. spp “Harehime” as “C” and C. iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” as “D” and C. spp “Setoka” as “E” and C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” as “F” and C. spp “Kanpei” as “G”. Results and error bar were shown by mean values and standard deviation of 5 samples (n=5). Significant difference of the gas diffusion resistance among all breeds of citrus fruit was evaluated by Tukey-Kramer’s method (p<0.05). The different letters indicate a significant difference.
Figure 9.
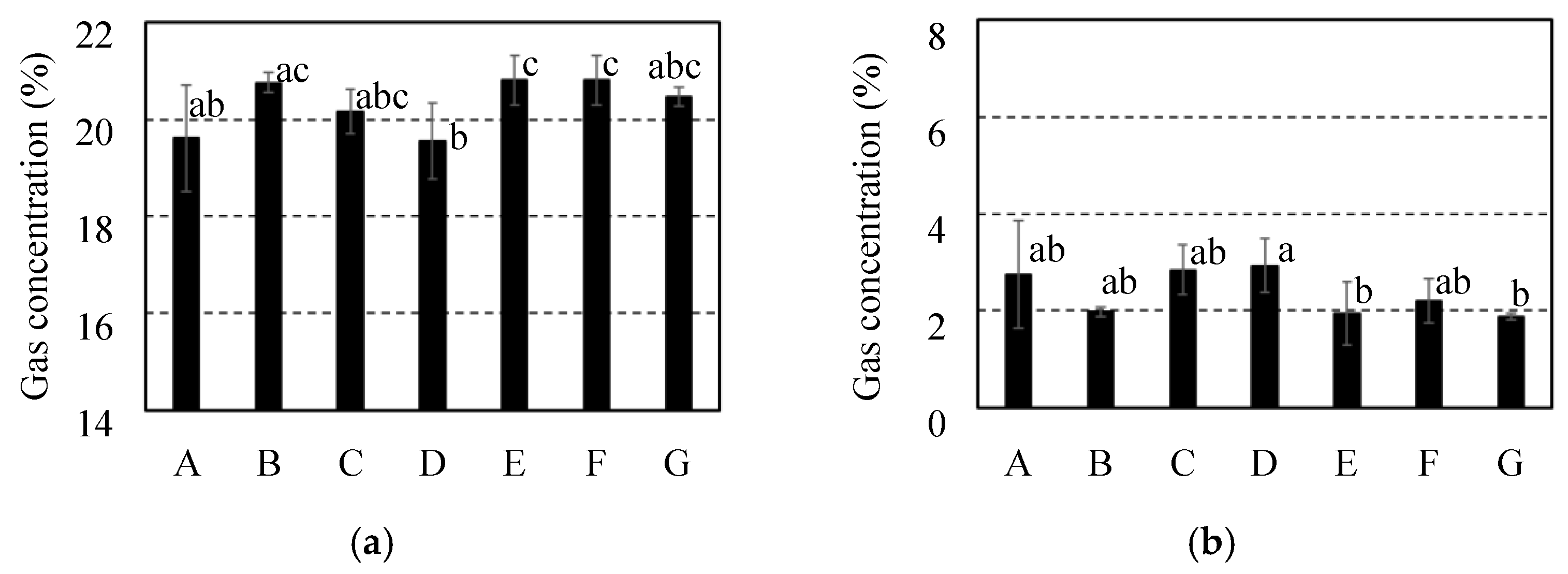
Internal gas concentration for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit after storage at 10 ºC for 2 weeks. It was investigated each of gas concentrations for (a) O2 and (b) CO2. It was indicated C. spp “Shiranui” as “A” and C. unshu “Nankan No.20” as “B” and C. spp “Harehime” as “C” and C. iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” as “D” and C. spp “Setoka” as “E” and C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” as “F” and C. spp “Kanpei” as “G”. Results and error bar were shown by mean values and standard deviation of 5 samples (n=5). Significant difference of the gas diffusion resistance among all breeds of citrus fruit was evaluated by Tukey-Kramer’s method (p<0.05). The different letters indicate a significant difference.
Figure 9.
Internal gas concentration for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit after storage at 10 ºC for 2 weeks. It was investigated each of gas concentrations for (a) O2 and (b) CO2. It was indicated C. spp “Shiranui” as “A” and C. unshu “Nankan No.20” as “B” and C. spp “Harehime” as “C” and C. iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” as “D” and C. spp “Setoka” as “E” and C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” as “F” and C. spp “Kanpei” as “G”. Results and error bar were shown by mean values and standard deviation of 5 samples (n=5). Significant difference of the gas diffusion resistance among all breeds of citrus fruit was evaluated by Tukey-Kramer’s method (p<0.05). The different letters indicate a significant difference.
Figure 10.
Internal gas concentration for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit after storage at 10 ºC for 2 weeks. It was investigated each of gas concentrations for (a) O2 and (b) CO2. It was indicated C. spp “Shiranui” as “A” and C. unshu “Nankan No.20” as “B” and C. spp “Harehime” as “C” and C. iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” as “D” and C. spp “Setoka” as “E” and C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” as “F” and C. spp “Kanpei” as “G”. Results and error bar were shown by mean values and standard deviation of 5 samples (n=5). Significant difference of the gas diffusion resistance among all breeds of citrus fruit was evaluated by Tukey-Kramer’s method (p<0.05). The different letters indicate a significant difference.
Figure 10.
Internal gas concentration for 7 cultivars of citrus fruit after storage at 10 ºC for 2 weeks. It was investigated each of gas concentrations for (a) O2 and (b) CO2. It was indicated C. spp “Shiranui” as “A” and C. unshu “Nankan No.20” as “B” and C. spp “Harehime” as “C” and C. iyo “Miyauchi iyokan” as “D” and C. spp “Setoka” as “E” and C. spp “Ehime Kashi No.28” as “F” and C. spp “Kanpei” as “G”. Results and error bar were shown by mean values and standard deviation of 5 samples (n=5). Significant difference of the gas diffusion resistance among all breeds of citrus fruit was evaluated by Tukey-Kramer’s method (p<0.05). The different letters indicate a significant difference.
Additional experiments were performed to investigate the role of the outer skin in the internal gas of citrus fruits since outer skin of thickness and stomatal number density in the citrus fruits affected the gas diffusion resistance considerably. In additional experiments, the fruits of C. unshu “Nankan 20 gou” after storage at 25 °C for 2 weeks were utilized to investigate the gas concentration in the fruits before and after peeling the outer skin flavedo. In visible observation, it seemed that the amount of extracted gas from the unpeeled fruit was approximately 20–30 ml while that from the peeled fruits was approximately 3–5 ml. Since the amount of the extracted gas was increased by the presence of the outer skin, the outer skin could play an important role in holding gases in the fruit. Additionally, the flesh part of the peeled fruits, called segments and vesicles, could contain a small amount of gas compared to the whole fruit.
In the unpeeled fruits, it was observed that CO2 and O2 of the gas concentrations were 4.1±0.6% and 18.7±0.8 %. In the peeled fruits, it was observed that CO2 and O2 of the gas concentrations were 6.0±1.0% and 18.0±1.9 %. Although no difference in O2 concentration was observed, the CO2 concentration was higher in the unpeeled fruits than in the peeled fruits. Therefore, CO2 concentration could increase according to the depth of the fruit inside, although it was unclear why the effect of fruit depth on O2 concentration was not observed.
4. Conclusion
In this study, the gas diffusion resistance and internal gas concentration of seven citrus fruit cultivars were investigated. The results showed that the gas diffusion resistance of the seven cultivars varied according to the characteristics of fruit construction, such as the outer skin thickness and the stomatal number density. Although the internal gas concentration of the fruits was high CO2 concentration and low O2 concentration before storage, storage at 25 °C promoted an increase in CO2 concentration and a decrease in O2 concentration. Additionally, it was tended that the CO2 concentration increased and the O2 concentration decreased with an increase in the gas diffusion resistance of fruit cultivars. In addition, the outer skin of citrus fruit may play an important role in holding internal gases.
From these results, it was clarified that the internal gas concentration varied according to the gas diffusion resistance for each of the citrus fruits, which affected the respiration of citrus fruits. Considering that maintaining a level of high CO2 concentration and low O2 concentration of the fruits inside was observed even in the fruits with a minimum gas diffusion resistance such as C. spp “Kanpei,” it is possible that citrus fruit has a system that gas diffusion resistance self-controls internal gas concentration to suppress their respiration. Although this study clarified a clear relationship between the gas diffusion resistance and the construction characteristics of citrus fruits, the resistance of citrus fruit can be related to the outer skin thickness and stomatal number density. Therefore, if the construction characteristics of citrus fruits are modified by genome editing or bleeding, a new citrus fruit cultivar that is excellent in terms of self-controlling respiration may be created. To create this new citrus cultivar, further studies focusing on the relationship between the gas diffusion resistance and construction characteristics of citrus fruits are required.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.K.; methodology, M.K.; software, M.K.; validation, M.K.; formal analysis, M.K.; investigation, M.K.; resources, M.K.; data curation, M.K.; writing—original draft preparation, M.K.; writing—review and editing, M.K. and K.K.; visualization, M.K.; supervision, M.K.; project administration, M.K.; funding acquisition, M.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
I am grateful to Dr. Hikida Yoshio for their advice in the early stages of this work. I wish to thank four students, “Matsuzaka Ayane”, “Manabe Sota”, “Kanaoka Kohei” and “Makino Takumi” who studied in this work for their graduation thesis of Ehime University.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kader, A.A.; Saltveit, M.E. Chapter 2 Respiration and Gas Exchange. In Postharvest Physiology and Pathology of Vegetables; Bartz, J.A., Brecht, J.K., Eds.; CRC Press: Florida, U.S.A, 2002; pp. 7–29. [Google Scholar]
- Saltveit, M.E. Chapter 4 Respiratory Metabolism. In Postharvest Physiology and Biochemistry of Fruits and Vegetables; Yahia, E.M., Ed.; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, England, 2019; pp. 73–91. [Google Scholar]
- Hikida, Y.; Morimatsu, K. Prediction Method of O2 and CO2 Concentrations in the Intercellular Space of Fresh Produce. Mem. Coll. Agric. Ehime Univ. 2018, 62, 5–11. [Google Scholar]
- Ho, Q.T.; Verlinden, B.E.; Verboven, P.; Vandewalle, S.; Nicolaï, B.M. A permeation–diffusion–reaction model of gas transport in cellular tissue of plant materials. J. Exp. Bot. 2006, 57, 4215–4224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lammertyn, J.; Scheerlinck, N.; Jancsók, P.; Verlinden, B.E.; Nicolaï, B.M. A respiration-diffusion model for ‘Conference’ pears I: model development and validation. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2003, 30, 29–42. [Google Scholar]
- Nicolaï, B.M.; Hertog, M.L.A.T.M.; Ho, Q.T.; Verlinden, B.E.; Verboven, P. CHAPTER 5 Gas Exchange Modeling. In Modified and Controlled Atmosphere for the Storage, Transpiration and Packaging of Horticultural Commodities; Yahia, E.M., Ed.; CRC Press: Florida, U.S.A, 2009; pp. 93–110. [Google Scholar]
- Rajapakse, N.C.; Banks, N.H.; Hewett, E.W.; Cleland, D.J. Development of Oxygen Concentration Gradients in Flesh Tissues of Bulky Plant Organs. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1990, 115, 793–797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, N.H. Estimating skin resistance to gas diffusion in apples and potatoes. J. Exp. Bot. 1985, 36, 1842–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, A.C.; Yang, S.F. A Simple Method for the Determination of Resistance to Gas Diffusion in Plant Organs. Plant Physiol. 1982, 70, 21–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadzie, B.K.; Banks, N.H.; Cleland, D.J.; Hewett, E.W. ROLE OF SKIN RESISTANCE TO GAS DIFFUSION IN THE RESPONSE OF FRUITS TO MODIFIED ATMOSPHERES. ISHS Acta Hortic. 1993, 343, 129–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dirpan, A.; Hikida, Y.; Morimatsu, K. Improving the Measurement of Resistance to Gas Diffusion and the Resistance Characteristics in Citrus Iyo Fruit (Citrus iyoHort. ex Tanaka). Food Preserv. Sci. 2016, 42, 71–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezagah, M.E.; Ishida, S.; Tanaka, F.; Uchino, T.; Hamanaka, D.; Hikida, Y. Determination of Gas Diffusivity and Skin Resistance for Three Cultivars of Japanese Pear Using their Actual 3D Geometry. Env. Control Biol. 2013, 51, 193–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Banks, N.H.; Kays, S.J. Measuring Internal Gases and Lenticel Resistance to Gas Diffusion in Potato Tubers. J. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1988, 113, 577–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piga, A.; D'Aquino, S.; Agabbio, M. Evolution of respiration rate, internal CO2 or O2 and resistance to gas diffusion of anaerobic exposed and waxed ‘Miho’ satsuma fruits during market life. Adv. Hortic. Sci. 1998, 12, 132–137. [Google Scholar]
- Schotsmans, W.; Verlinden, B.E.; Lammertyn, J.; Nicolaï, B.M. The relationship between gas transport properties and the histology of apple. Sci. Food Agric. 2004, 84, 1131–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valle-Guadarrama, S.; Saucedo-Veloz, C.; Penña-Valdivia, C.B.; Corrales-García, J.J.E.; Chávez-Franco, S.H.; Espinosa-Solares, T. Skin Permeance and Internal Gas Composition in 'Hass' Avocado (Persea americana Mill.) Fruits. Food Sci. Technol. Int. 2002, 8, 365–373. [Google Scholar]
- Yoo, K.S.; Andersen, C.R.; Pike, L.M. Internal CO2 concentrations in onion bulbs at different storage temperatures and in response to sealing of the neck and base. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 1997, 12, 157–163. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, V.; Pandey, R. Role of internal atmosphere on fruit ripening and storability - a review. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2014, 51, 1223–1250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dirpan, A.; Hikida, Y. Effect of various citrus sizes on the resistance to gas diffusion. Procedia Environ. Sci. 2015, 28, 391–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, Q.T.; Schotsmans, W.; Ho, Q.T.; Verlinden, B.; Verboven, P.; Nicolai, B. Simultaneous measurement of neon diffusivity and skin resistance of ‘Braeburn’ and ‘Jonica’ apples. Postharvest Biol. Technol. 2008, 50, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hagenmaier, R.D.; Shaw, P.E. Gas Permeability of Fruit Coating Waxes. Am. Soc. Hortic. Sci. 1992, 117, 105–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).