1. Introduction
Diabetes Mellitus (DM) affects around 530 million adults worldwide. The global prevalence is 10.5% among adults, with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) corresponding to around 98% of them [
1]. Within the UK, the estimated prevalence of T2DM is 4.7 million, accounting for 7.4% of the population [
2]. The rise in type 2 diabetes (T2DM) prevalence among young people in the UK affects the choice of long-term management, with around £10.7 billion spent on treating diabetes and its complications annually [
3]. The majority of the cost is directed to the treatment of the complications and associated morbidities. One of the closely associated comorbidities of T2DM is obesity. Around 65% of adults in the UK are overweight or obese, with the prevalence increasing [
3,
4,
5,
6]. The social annual cost to the UK is estimated to be £58 billion, corresponding to 3% of gross domestic product (GDP) [
7].
Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA), such as Exenatide, Liraglutide, Dulaglutide, and Semaglutide, are considered an evolution in the treatment of T2DM. They are involved in glucose metabolism by mimicking the action of the natural GLP-1 hormone. They also promote insulin secretion and inhibit glucagon secretion, hindering gastric motility [
8]. GLP-1 RAs were initially introduced as a second- or third-line treatment for diabetic patients who failed to achieve the therapeutic goal with metformin, sulfonylureas, or dipeptidyl peptidase–4 (DPP-4) inhibitors [
9]. During the previous decades, a paradigm shift in diabetes management has occurred with a focus on treating or avoiding complications [
10]. GLP-1 RAs showed cardiovascular and renal benefits and weight reduction effects beyond their glycemic control effect, which led to gaining prominence in the diabetes guidelines [
11,
12]. For example, in the 2022 American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines of standards of care in diabetes, GLP-1 RAs benefits make them a preferred choice in T2DM for patients with additional or at risk for complications such as atherosclerotic cardiovascular disease, chronic kidney disease, and obesity [
13]. The European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD) has endorsed these guidelines, and together, they published a consensus report [
14]. In addition, studies revealed that T2DM patients prefer GLP-1 RAs over other antidiabetic medications, especially the less frequent dosing formulations [
15]. Therefore, an increased demand for GLP-1 RAs is expected.
Several challenges face this demand, including high costs, limited insurance coverage, and shortages. Starting in 2022, the GLP-1 RA faced a global shortage due to prescribing surge, manufacturing constraints, and spiked off-label use. The European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the Heads of Medicines Agencies (HMA) have set recommendations via the Executive Steering Group on Shortages and Safety of Medicinal Products (MSSG) to monitor and implement plans for mitigating the shortages. In the United Kingdom (UK), a safety alert has been issued by the National Health Service (NHS), emphasizing prescribing GP-1 RAs for their licensed indications to overcome the global shortage.
Understanding the prescribing trends for GLP-1 RAs and the factors that affect them is crucial for providing insights about the integration of guidelines into clinical practice. It also assists future policy decisions to optimize the treatment of DM and obesity. Studies on the prescribing trends of GLP-1 RAs have been conducted in some counties [
16,
17,
18]. None of these studies investigated the effect of the most recent guidelines or stock shortages on the prescribing trend. Similarly, no study describes the effect of these factors on the prescribing trends of GLP-1 RAs in the UK. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the change in prescribing trends after both the ADA 2022 guidelines and the NHS shortage alert.
2. Materials and Methods
Study Design
This study investigated the GLP-1 RA prescribing trends in the UK from January 2018 to May 2024 using a repeated cross-sectional methodology. Due to data constraints, analysis for England commenced in July 2019, while for Wales, it began in April 2018. The study focused on the following GLP-1 RAs: Dulaglutide (BNF code: 0601023AQ), Exenatide (BNF code: 0601023Y0), Liraglutide (BNF code: 0601023AB), Lixisenatide (BNF code: 0601023AI), Semaglutide (BNF code: 0601023AW), and Tirzepatide (BNF code: 0601023AZ).
Data collection was conducted using publicly accessible resources. Prescribing data for England were retrieved from OpenPrescribing.net [
19], for Wales from NHS Wales Shared Services Partnership's Prescribing Data Extracts [
20], for Scotland from Public Health Scotland's Monthly Prescribing Activity data [
21], and for Northern Ireland from the GP Prescribing Data available on Open Data Northern Ireland [
22]. All the data utilized in this study are openly available under the Open Government Licence (OGL) and did not require ethical approval. This study only examined prescriptions written by general practitioners (GPs) in community settings; prescriptions from hospitals or other healthcare facilities were not included.
Prevalence Calculation
To determine the prevalence of GLP-1 agonist prescriptions, the number of prescriptions per month was divided by the respective country’s population for that month and then multiplied by 100,000, yielding a standardized prescription rate per 100,000 individuals. Population data were obtained from official government websites. However, due to the unavailability of population data for Scotland and Northern Ireland for the years 2023 and 2024, as well as for all four countries in 2024, population figures for these periods were projected by applying the growth rate observed in the previous year.
Statistical Analysis
An analysis was conducted using AutoRegressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) models with exogenous variables to assess the prescribing trends of GLP-1 receptor agonists throughout the United Kingdom. The investigation used monthly prescription data spanning several years and included Dulaglutide, Exenatide, Liraglutide, Lixisenatide, and Semaglutide. The statistical analysis tables did not include tirzepatide because of its recent approval and the scarcity of prescription data. However, it was retained in the figure for the sake of completeness.
The dependent variable was the monthly prescriptions written for each medicine per 100,000 persons. Exogenous variables comprised Northern Ireland, Scotland, and Wales country-specific indicators, with England serving as the reference group. The analysis also accounted for a baseline trend representing prescribing behavior before the 2022 ADA guidelines, incorporating a six-month lag to reflect changes in practice up to June 2022. A binary variable marked the period from July 2022 onwards, capturing the influence of the ADA guidelines. Additionally, the analysis included a trend for the period following the ADA guidelines and a binary variable from July 2023 onwards, when a shortage of GLP-1 receptor agonists was observed. A post-shortage trend was also modeled.
Each medication was analyzed using an ARIMA (p, d, q) model, where 'p' denotes the autoregressive term, 'd' indicates the differencing needed to achieve stationarity, and 'q' represents the moving average term. The models were fitted using the Seasonal ARIMA with exogenous factors (SARIMAX) function from the ‘statsmodels’ library, which allowed for the inclusion of the specified exogenous variables. The resulting coefficients and their associated 95% confidence intervals were reported. Model performance was assessed using the Akaike Information Criterion (AIC) and the Bayesian Information Criterion (BIC) to balance model fit and complexity. The Durbin-Watson statistic was used to check for autocorrelation in the residuals. Data cleaning and management were performed using Excel, while R was employed to run the statsmodels function and conduct the statistical analysis.
3. Results
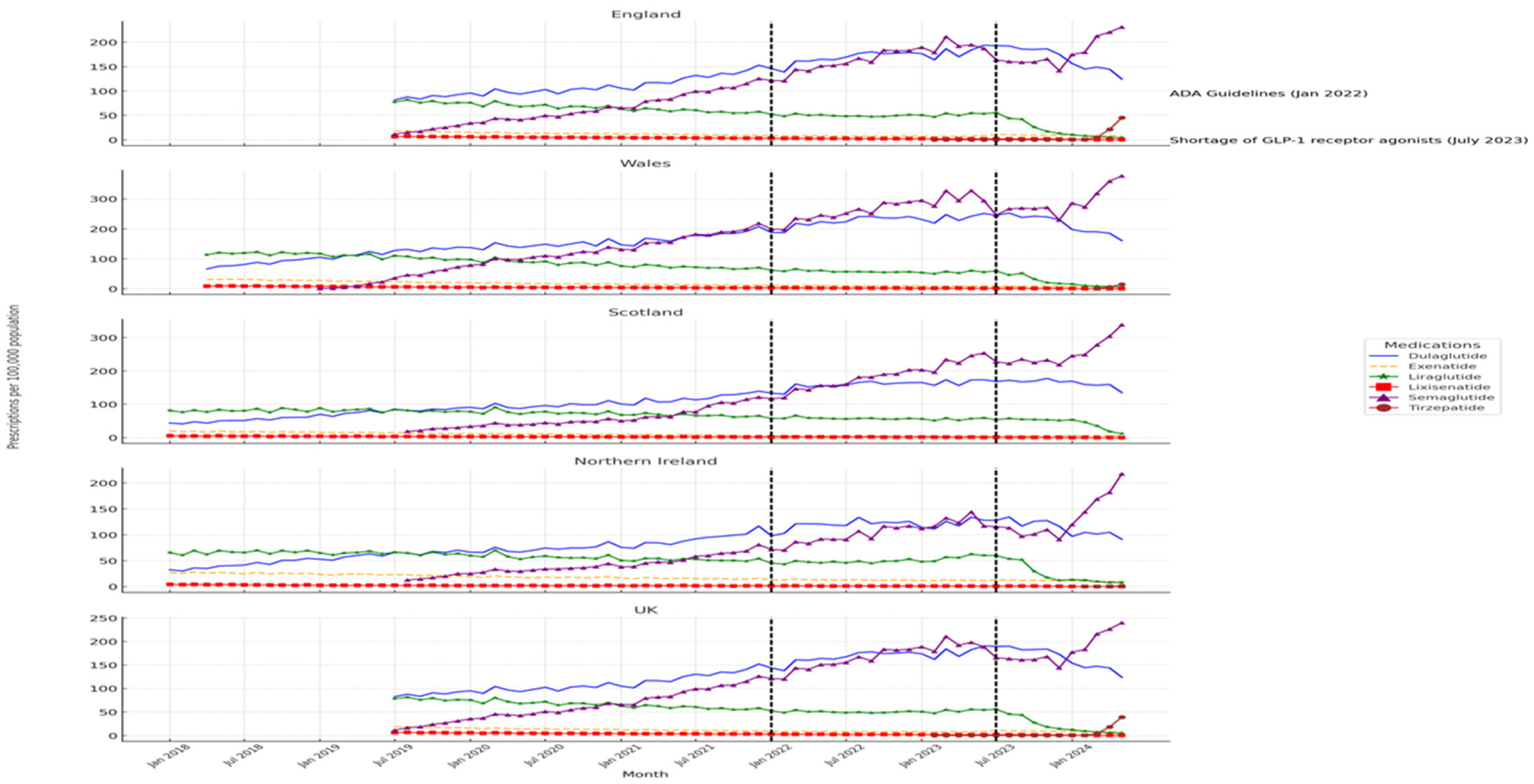
Prescription patterns for GLP-1 receptor agonists vary significantly across UK regions, as detailed in
Table 1. Wales reports the highest average prescription rates for most GLP-1 RAs, including Semaglutide (179.52 per 100,000 population) and Dulaglutide (168.98 per 100,000 population). England shows moderate prescription rates, while Scotland and Northern Ireland generally have lower rates. Scotland leads in Exenatide prescriptions (17.4 per 100,000 population) despite lower overall usage of other GLP-1 RAs.
Figure 1 illustrates temporal trends in GLP-1 RAs prescriptions, highlighting the effects of the ADA guideline update in January 2022 and the medication shortage in July 2023. Wales experienced the most significant increase in prescriptions following the ADA guidelines, especially for Semaglutide and Dulaglutide, with Semaglutide usage further surging during the shortage. In contrast, Scotland and Northern Ireland showed more muted responses, with Scotland even recording a decline in certain prescriptions, such as Liraglutide, post-shortage.
The ARIMA models (
Table 2,
Figure 2, and
Figure 3) provide deeper insights into these trends, capturing regional effects and temporal events' impact. Significant coefficients are reported with their 95% confidence intervals (CI95%).
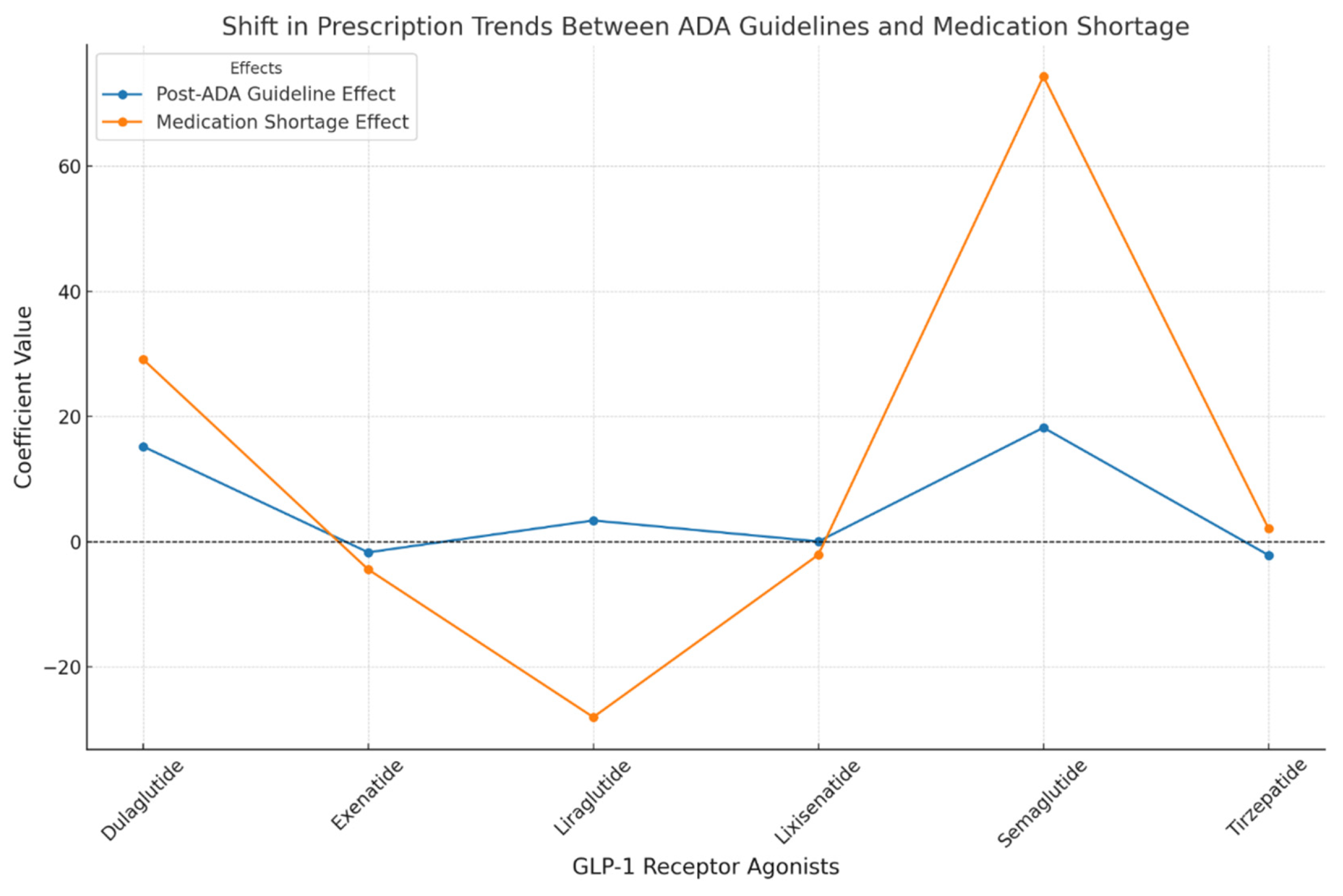
The analysis of GLP-1 RAs prescribing across different regions in the UK revealed notable variations. In Scotland, Dulaglutide usage was significantly lower compared to England, with a coefficient of -39.94 (CI95%: [-42.56, -37.32]). Conversely, Wales exhibited a marked increase in prescribing relative to England, with a coefficient of 40.81 (CI95%: [38.29, 43.33]), indicating a substantial difference. Northern Ireland, on the other hand, showed a modest decrease with a coefficient of -11.08 (CI95%: [-13.52, -8.64]). For Liraglutide, effect was more significant in Wales, with a coefficient of 18.87 (CI95%: [16.59, 21.15]). Semaglutide prescribing was particularly higher in Wales, reflected in a coefficient of 69.80 (CI95%: [67.12, 72.48]), while Scotland reported lower prescribing with a coefficient of -32.42 (CI95%: [-34.50, -30.34]). Northern Ireland displayed a slight positive coefficient of 9.00 (CI95%: [6.85, 11.15]) for Semaglutide.
The baseline trend analysis offered insights into the pre-existing trends before the influence of significant events like the ADA guideline update and medication shortages. Dulaglutide showed a positive baseline trend, with a coefficient of 14.36 (CI95%: [12.12, 21.60]), suggesting a steady increase in its prescribing over time. Semaglutide exhibited an even stronger baseline trend, indicated by a coefficient of 24.61 (CI95%: [22.05, 27.17]). In contrast, Liraglutide and Lixisenatide had either flat or negative baseline trends with coefficients of 2.02 (CI95%: [-0.53, 4.57]) and -2.31 (CI95%: [-4.57, 2.24]), respectively (
Table 2).
The post-ADA guideline effect, measured with a 6-month lag after January 2022, was most pronounced for Semaglutide, which saw a significant increase in prescribing, as indicated by a coefficient of 18.24 (CI95%: [15.95, 20.53]). Dulaglutide also experienced a notable increase, with a coefficient of 15.22 (CI95%: [12.97, 17.47]), while other drugs such as Exenatide showed minimal or negative changes (
Table 2).
Further analysis of the post-ADA trend highlighted ongoing influences from the guidelines on drug prescribing. Both Dulaglutide and Semaglutide exhibited positive trends; however, the confidence intervals included zero, indicating that these trends were not statistically significant. Liraglutide and Lixisenatide, in contrast, displayed minimal changes (
Table 2).
The medication shortage effect was another critical factor, particularly impacting Semaglutide, which saw a sharp increase of 74.36 (CI95%: [71.92, 76.80]). Dulaglutide also experienced a significant positive effect, with a coefficient of 29.14 (CI95%: [26.72, 31.56]), while Liraglutide encountered a substantial negative impact, with a coefficient of -28.02 (CI95%: [-30.41, -25.63]). The post-shortage trend analysis explored the long-term effects of the medication shortage on usage patterns. Semaglutide continued to exhibit a positive trend, with a coefficient of 27.3 (CI95%: [15.1, 39.6]). Dulaglutide and Liraglutide showed minimal or negative trends (
Table 2).
Lastly, the model quality was assessed using the Durbin-Watson statistic, AIC, and BIC. The Durbin-Watson statistics for all models were close to 2, indicating minimal autocorrelation in the residuals and suggesting that the models are well-specified. The AIC and BIC values varied, with Dulaglutide showing an AIC of 2526.57 and a BIC of 2566.71, indicating a relatively good model fit. Semaglutide, with an AIC of 2410.62 and a BIC of 2448.77, demonstrated a robust model with strong predictive power. These indicators confirm the adequacy of the models in capturing the underlying data structures, making them reliable tools for understanding trends and influences on GLP-1 receptor agonist usage across different regions and time periods.
4. Discussion
This study offers a comprehensive analysis of the temporal and regional variations shifts in the prescribing patterns of GLP-1 receptor agonists across the United Kingdom. It mainly highlights the effect of ADA guidelines and drug shortages on these patterns. Semaglutide and dulaglutide were the most prescribed drugs during the study period. The results show a significant increase in prescriptions following the endorsement of ADA guidelines, particularly for Semaglutide, Dulaglutide, and Liraglutide. Their prescribing trends have been insignificantly increased. A study in the United States showed a fast increase in the prescribing rate of GLP-1 RAs in the period of 2012-2022 [
16]. Another study in Australia demonstrated a dramatic rise in GLP-1 RAs use from 2014 to 2022 [
23]. The observed rapid increase in prescribing represents an apparent shift in the prescribing pattern of this therapeutic category, which will probably continue to accelerate as data on potential cardiovascular advantages and weight loss outcomes become available. The analysis of the GIP/GLP-1 receptor agonist, Trizapatide, prescribing rate was restricted to a 12-month period. However, it seems that it will continue to accelerate with a surge compared to the other drugs. Regarding health outcomes, GLP-1 RAs are associated with control of blood glucose levels and reduced cardiovascular events and stroke, which could be translated into cost-saving benefits [
24]. A comparative meta-analysis showed that the GLP-1 RAs improved blood pressure, lipid, and glycemia profiles compared to insulins in T2DM patients [
25]. GLP-1 RAs may also help patients avoid surgical weight loss interventions and reduce their medical costs. During the study period, Lixisenatide was the least prescribed. This may be attributed to the more significant clinical benefits and reduced cost of Semaglutide compared to Lixisendatide [
26,
27]. In addition, the once-weekly regimen may contribute to patients' preferences for these drugs [
15]. This attribute may also be the drive behind slowing the prescribing rate of liraglutide over time.
In Wales, the GLP-1 RAs prescribing surpassed those of other regions, while in Scotland, there is a marked decrease in the prescribing rate. This could be explained by the marked increase in obesity rate among Wales adults compared to other regions [
28]. Another possible explanation is the higher prevalence of diabetes among the Walsh population compared to Scotland [
29,
30]. This approach in Scotland is aligned with the conservative recommendations to adopting GLP-1 RAs of NG28 NICE guidelines for diabetes [
31], where GLP-1 RAs remain a fourth line of treatment, which is much later in the treatment algorithm of the American guidelines of the ADA [
10]. Additionally, NG28 recommends discontinuation of GLP-1 RAs after six months if there is no significant reduction in the A1c and the weight [
31].
In July 2023, the NHS issued a safety alert regarding GLP-1 RAs shortages, requiring actions for clinicians and prescribers to emphasize prescribing these drugs in their licensed indications and forbidding the initiation of new patients on these drugs. The NHS also recommends against prescribing excessive GLP-1 RAs [
32]. After this safety alert, Liraglutide prescriptions were significantly reduced. Semaglutide and Dulaglutide prescriptions significantly increased, with an insignificant increase in prescribing rates. One possible explanation is that the NHS later issued an update that superseded the previous one but emphasized that the supply would continue to be limited until the end of 2024. However, the safety alert mentioned that Semaglutide tablets would be available in sufficient quantities. It is possible that the prescribers switched Liraglutide to alternatives like Semaglutide
Drug shortages are a significant problem in providing healthcare to the community [
33]. They have become a global phenomenon continuously rising [
29,
30,
31]. In the UK, the Department of Health and Social Care (DHSC) received 137 notifications of drug shortage on average each month in 2023 [
34]. The British Generic Manufacturers Association (BGMA) revealed that drug shortages have increased by 100% from January 2022 to January 2024 [
35]. These emphasize the need for informed decisions in accordance with the prescribing behaviors before and after issuing safety alerts.
Limitations: This study encountered several limitations. First, the data represents prescribing in community settings rather than hospital facilities, which may affect the comprehensiveness of the findings. The ARIMA models do not completely account for unpredicted drops and spikes because they rely on the stationarity assumption However, the use of ARIMA remains appropriate for the majority of our analysis, as the primary focus was on identifying underlying trends and patterns, rather than isolated anomalies. The recent introduction of Tirzepatide to the UK market limited the ability to evaluate its trends fully.
Ethical considerations: Data collection was conducted using publicly accessible resources and openly available under the Open Government Licence (OGL) and did not require ethical approval for use.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.I. and K.O.; methodology, , A.I. and K.O.; validation, K.O.; formal analysis, K.O.; investigation, , A.I. and K.O.; data curation, , A.I. and K.O.; writing—original draft preparation, , A.I. and K.O.; writing—review and editing, , A.I. and K.O.; project administration, A.I.; funding acquisition, A.I. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors extend their appreciation to the Deanship of Research and Graduate Studies at King Khalid University for funding this work through Large Research Project under grant number RGP2/391/45.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable. This study was based on publicly available, anonymised data sets, and it did not use human individuals or personally identifying information. As a result, Institutional Review Board approval was not required.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The study's data analysis is based solely on publicly available sources. Prescribing data for England were sourced from OpenPrescribing.net, data for Wales from NHS Wales Shared Services Partnership's Prescribing Data Extracts, data for Scotland from Public Health Scotland's Monthly Prescribing Activity data, and data for Northern Ireland from the GP Prescribing Data available on Open Data Northern Ireland. All data utilized are available under the Open Government Licence (OGL) and can be accessed directly through these platforms.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- International Diabetes Federation, Diabetes Atlas 2021. Available online: https://diabetesatlas.org/atlas/tenth-edition/ (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Down, S. NICE type 2 diabetes management guidance: What's new? Journal of Diabetes Nursing 2022, 26. [Google Scholar]
- Hex, N.; MacDonald, R.; Pocock, J.; Uzdzinska, B.; Taylor, M.; Atkin, M.; Wild, S.H.; Beba, H.; Jones, R. Estimation of the direct health and indirect societal costs of diabetes in the UK using a cost of illness model. Diabet Med 2024, 41, e15326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Health, D.o. Health survey Northern Ireland: first results 2022/23. Available online: https://www.health-ni.gov.uk/sites/default/files/publications/health/hsni-trend-tables-22-23.xlsx (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Welsh Government. National Survey for Wales headline results: April 2022 to March 2023. Available online: https://www.gov.wales/national-survey-wales-headline-results-april-2022-march-2023-html (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Obesity In Scotland: Prevalence, Causes and Impact. Available online: https://www.obesityactionscotland.org/media/235lfdxq/prevalence_causes__impact_1920_data_f_2023_updated_version.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Economics, F. Estimating the full costs of obesity. Available online: https://www.frontier-economics.com/media/hgwd4e4a/the-full-cost-of-obesity-in-the-uk.pdf (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Drucker, D.J. Biological actions and therapeutic potential of the glucagon-like peptides. Gastroenterology 2002, 122, 531–544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Association, A.D. Standards of medical care in diabetes--2012. Diabetes Care 2012, 35 Suppl 1, S11–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Boer, I.H.; Khunti, K.; Sadusky, T.; Tuttle, K.R.; Neumiller, J.J.; Rhee, C.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Rossing, P.; Bakris, G. Diabetes Management in Chronic Kidney Disease: A Consensus Report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and Kidney Disease: Improving Global Outcomes (KDIGO). Diabetes Care 2022, 45, 3075–3090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ussher, J.R.; Drucker, D.J. Glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonists: cardiovascular benefits and mechanisms of action. Nat Rev Cardiol 2023, 20, 463–474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michos, E.D.; Bakris, G.L.; Rodbard, H.W.; Tuttle, K.R. Glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists in diabetic kidney disease: A review of their kidney and heart protection. Am J Prev Cardiol 2023, 14, 100502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Association, A.D. Abridged for Primary Care Providers. Clin Diabetes 2022, 40, 10–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davies, M.J.; Aroda, V.R.; Collins, B.S.; Gabbay, R.A.; Green, J.; Maruthur, N.M.; Rosas, S.E.; Del Prato, S.; Mathieu, C.; Mingrone, G.; et al. Management of hyperglycaemia in type 2 diabetes, 2022. A consensus report by the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the European Association for the Study of Diabetes (EASD). Diabetologia 2022, 65, 1925–1966. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thieu, V.T.; Robinson, S.; Kennedy-Martin, T.; Boye, K.S.; Garcia-Perez, L.E. Patient preferences for glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor-agonist treatment attributes. Patient Prefer Adherence 2019, 13, 561–576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watanabe, J.H.; Kwon, J.; Nan, B.; Reikes, A. Trends in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor agonist use, 2014 to 2022. J Am Pharm Assoc (2003) 2024, 64, 133–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fadini, G.P.; Frison, V.; Rigato, M.; Morieri, M.L.; Simioni, N.; Tadiotto, F.; D'Ambrosio, M.; Paccagnella, A.; Lapolla, A.; Avogaro, A. Trend 2010-2018 in the clinical use of GLP-1 receptor agonists for the treatment of type 2 diabetes in routine clinical practice: an observational study from Northeast Italy. Acta Diabetol 2020, 57, 367–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nishimura, R.; Kato, H.; Kisanuki, K.; Oh, A.; Hiroi, S.; Onishi, Y.; Guelfucci, F.; Shimasaki, Y. Treatment patterns, persistence and adherence rates in patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan: a claims-based cohort study. BMJ Open 2019, 9, e025806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett Institute for Applied Data Science, U.o.O. OpenPrescribing.net. Available online: https://openprescribing.net/ (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Partnership, N.W.S.S. General Practice Prescribing Data Extract. Available online: https://nwssp.nhs.wales/ourservices/primary-care-services/general-information/data-and-publications/prescribing-data-extracts/general-practice-prescribing-data-extract/ (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- https://publichealthscotland.scot/. Available online: https://publichealthscotland.scot/publications/monthly-prescribing-activity-data/monthly-prescribing-activity-data-data-for-may-2024/dashboard/ (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Prescribing Data available on Open Data Northern Ireland. Available online: https://www.data.gov.uk/dataset/a7b76920-bc0a-48fd-9abf-dc5ad0999886/gp-prescribing-data (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Lin, J.; Pearson, S.A.; Greenfield, J.R.; Park, K.H.; Havard, A.; Brieger, D.; Day, R.O.; Falster, M.O.; de Oliveira Costa, J. Trends in use of sodium-glucose co-transporter 2 inhibitors (SGLT2i) and glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1RA) in Australia in the era of increased evidence of their cardiovascular benefits (2014-2022). Eur J Clin Pharmacol 2023, 79, 1239–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldenberg, R.M.; Cheng, A.Y.Y.; Fitzpatrick, T.; Gilbert, J.D.; Verma, S.; Hopyan, J.J. Benefits of GLP-1 (Glucagon-Like Peptide 1) Receptor Agonists for Stroke Reduction in Type 2 Diabetes: A Call to Action for Neurologists. Stroke 2022, 53, 1813–1822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abd El Aziz, M.S.; Kahle, M.; Meier, J.J.; Nauck, M.A. A meta-analysis comparing clinical effects of short- or long-acting GLP-1 receptor agonists versus insulin treatment from head-to-head studies in type 2 diabetic patients. Diabetes Obes Metab 2017, 19, 216–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ericsson, Å.; Fridhammar, A. Cost-effectiveness of once-weekly semaglutide versus dulaglutide and lixisenatide in patients with type 2 diabetes with inadequate glycemic control in Sweden. J Med Econ 2019, 22, 997–1005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gæde, P.; Johansen, P.; Tikkanen, C.K.; Pollock, R.F.; Hunt, B.; Malkin, S.J.P. Management of Patients with Type 2 Diabetes with Once-Weekly Semaglutide Versus Dulaglutide, Exenatide ER, Liraglutide and Lixisenatide: A Cost-Effectiveness Analysis in the Danish Setting. Diabetes Ther 2019, 10, 1297–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bone, J. A third of adults in Wales live with obesity, according to new analysis.
- Government, W. New approach to tackle diabetes and improve care unveiled. 2024.
- UK, D. Diabetes Care in Scotland. 2024. Available online: https://www.diabetes.org.uk/support-for-you/diabetes-uk-in-your-area/scotland/diabetes-care-in -scotland (accessed on 1 September 2024).
- Fisher, M. Guidelines on the Management of Type 2 Diabetes. Journal of Diabetes and Endocrine Practice 2022, 5, 135–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iacobucci, G. UK clinics told to stop prescribing antidiabetes drugs for weight loss, after shortages. BMJ 2023, 382, 1693. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krisl, J.C.; Fortier, C.R.; Taber, D.J. Disruptions in the supply of medications used in transplantation: implications and management strategies for the transplant clinician. Am J Transplant 2013, 13, 20–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wickware, C. Medicines shortages reported to government increase by almost 70% since 2021.
- Boffey, D. NHS medicines shortage putting lives at risk, pharmacists warn.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).