Submitted:
11 September 2024
Posted:
14 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Research Questions
- How does the integration of IT strategic planning with business methods impact the operational performance of SMEs?
- What are the key challenges faced by SMEs in incorporating IT strategic planning, and what strategies can be employed to overcome these obstacles?
- How do external factors such as market dynamics, regulatory changes, and technological advancements influence IT strategic planning in SMEs?
- How do SMEs measure the success of their IT strategic planning efforts, and what metrics or frameworks are most effective for this evaluation?
1.2. Rationale
1.3. Objectives
- Examine the impact of IT strategic alignment on the operational performance of SMEs — focusing on measurable outcomes such as reductions in operational costs and improvements in process efficiency, which were observed in the reviewed studies where SMEs successfully implemented cloud-based IT solutions.
- Identify the role of organizational culture in the effectiveness of IT strategic planning processes within SMEs— emphasizing how organizational readiness and employee involvement were shown to positively affect IT adoption success rates in several case studies.
- Analyze how external factors, such as marketplace dynamics and technological advancements, impact IT strategic planning — assessing their effect on key performance indicators such as market responsiveness and adaptability, as highlighted in studies that examined the effects of regulatory changes and technological shifts on SMEs.
- Determine the critical success factors that influence the effectiveness of IT strategic planning in improving SMEs’ competitive advantage — measuring outcomes like revenue growth and customer satisfaction, which were consistently linked to strategic IT investments in the reviewed literature.
- Evaluate the impact of IT governance frameworks on the alignment of IT strategic planning with business goals in SMEs — linking specific performance metrics, such as ROI and productivity gains, to governance models that were shown to be effective for SMEs in resource-constrained environments.
1.4. Research Contribution
- We investigate how IT strategic planning affects significant overall performance metrics in SMEs, including operational performance and marketplace competitiveness, with insights into optimizing IT investments.
- We find that overall performance metrics are suffering from IT strategic planning and give a structure for aligning IT initiatives with business targets; hence, improve IT management practices.
- Our study gives empirical and theoretical insights into what effect ITSP would have on SME performance by addressing gaps within the current literature.
- We recommend practical guidelines to enhance IT strategies, optimize resources, and enhance overall performance for assisting SMEs in attaining a competitive space.
- We define the outline of future research on IT strategic planning and SME overall performance, indicating directions for further research and innovation.
1.5. Research Novelty
- Unlike prior research, which often focuses on IT strategies in larger enterprises or provides fragmented insights, this study offers a systematic and in-depth analysis specifically tailored to SMEs. It evaluates how IT strategic planning directly impacts various performance metrics, such as operational efficiency, competitiveness, and financial sustainability, which have not been thoroughly explored in previous studies for the SME context.
- This study offers new empirical findings on the optimization of IT resources in SMEs. It goes beyond general recommendations by identifying specific strategies SMEs can implement to maximize limited resources while maintaining alignment with business goals. This fills a gap in existing literature, which typically focuses on resource optimization for larger enterprises without considering the distinctive constraints SMEs face.
- This research provides a detailed examination of external factors—such as market dynamics, regulatory changes, and technological advancements—that influence IT strategic planning in SMEs. By highlighting how these factors shape IT strategy development, the study offers new insights that SMEs can use to future-proof their IT strategies in a rapidly changing business environment.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Eligibility Criteria
2.2. Information Sources
2.3. Search Strategy
2.4. Selection Process
2.5. Data Collection Process
2.6. Data Items
2.6.1. Data Collection Method
2.6.2. Variable Data Collection
2.7. Study Risk of Bias Assessment
2.8. Effect Measures

2.9. Synthesis Methods
2.10. Reporting Bias Assessment
2.11. Certainty Assessment
3. Results
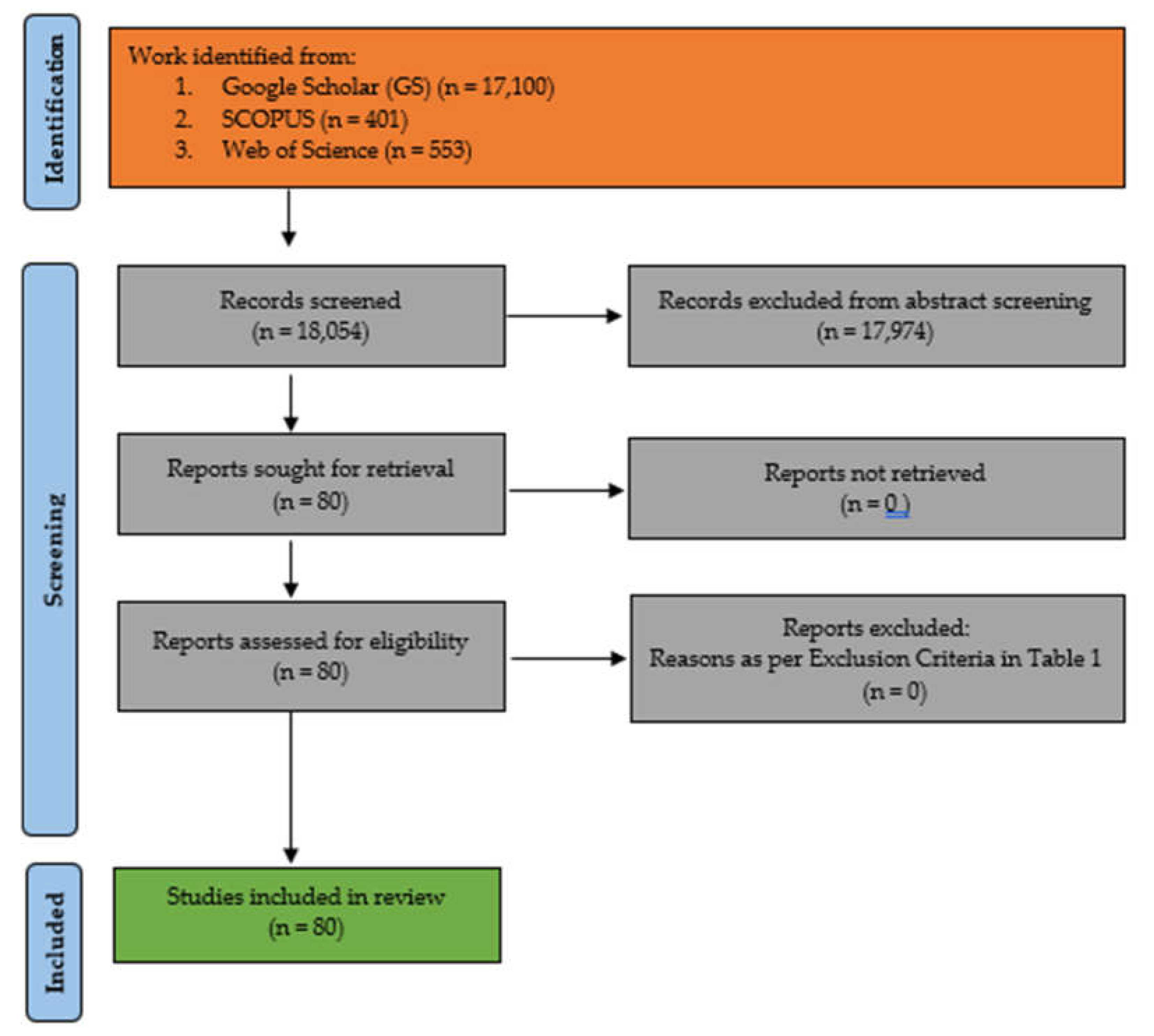
3.1. Study Selection
3.2. Study Characteristics
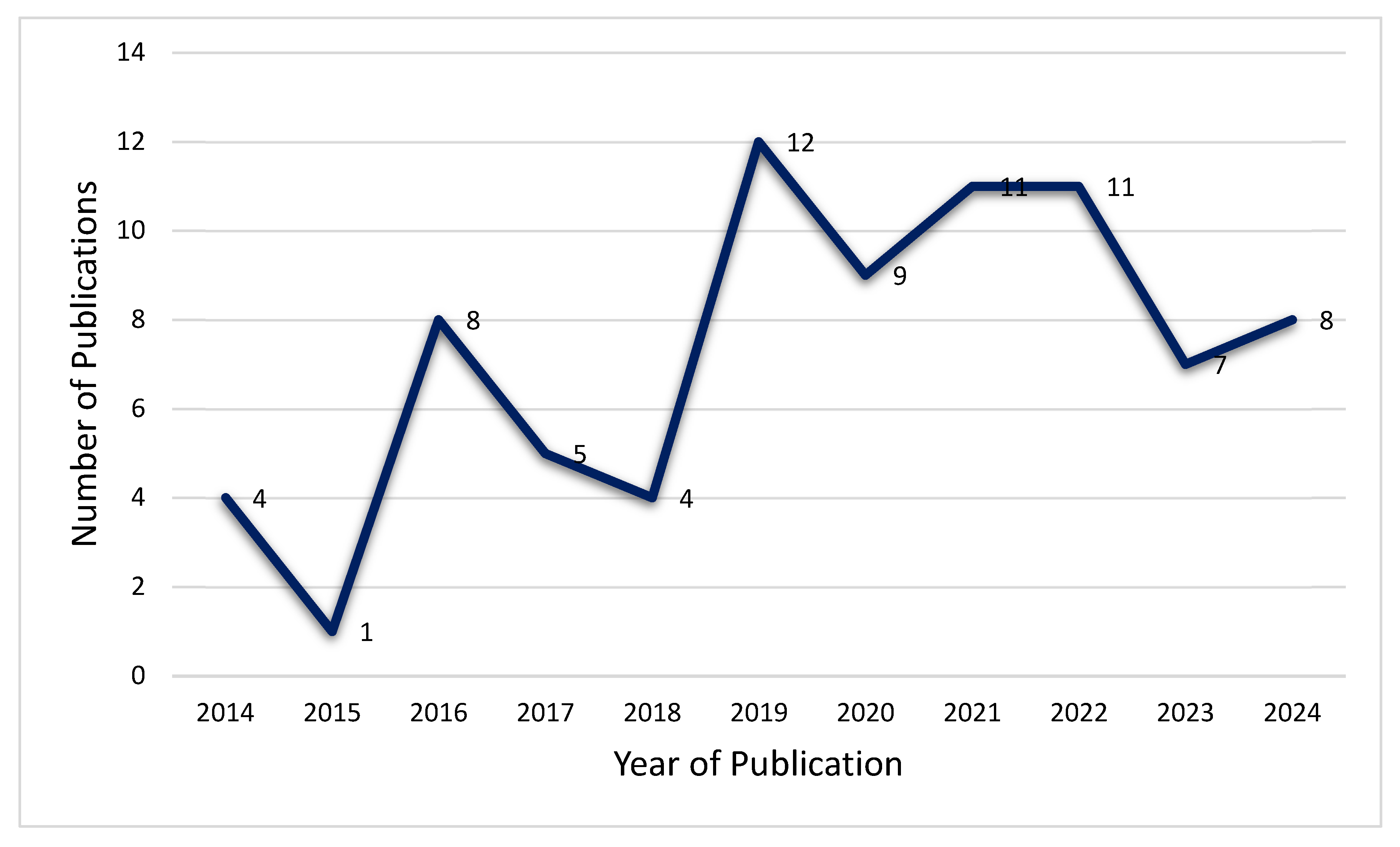

| Published Year | Book Chapter | Conference Paper | Journal | Dissertation | Thesis |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2014 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| 2015 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| 2016 | 1 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 2017 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 2018 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| 2019 | 0 | 6 | 5 | 1 | 0 |
| 2020 | 0 | 2 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 2021 | 1 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 1 |
| 2022 | 0 | 2 | 6 | 2 | 1 |
| 2023 | 0 | 0 | 7 | 0 | 0 |
| 2024 | 1 | 0 | 6 | 1 | 0 |

3.3. Risk of Bias in Studies
| Study | Sample Size | Long Term impacts on SMEs | Contribution |
|---|---|---|---|
| [43] | 245 | - | Study in Pakistan shows that IT strategic planning with a focus on goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management enhances alignment with business goals and resource efficiency; mixed methods with 245 samples demonstrates significant improvements in project success rates. |
| [44] | 235 | - | Research in Yemen highlights that strategic thinking and planning, along with human capital, mediate the relationship between strategic innovation and SME performance; quantitative study with 235 samples reveals improvements in strategic alignment. |
| [45] | 232 | - | Study in Kenya finds that effective risk management in IT strategic planning improves alignment with business goals and resource efficiency; quantitative approach with 232 samples underscores its impact on project success. |
| [46] | 612 | Competitive advantage | Analysis in Germany demonstrates that IT strategic planning focusing on resource allocation drives operational efficiency, revenue growth, and cost savings; quantitative study with 612 samples emphasizes the achievement of competitive advantage. |
| [47] | 390 | Competitive advantage | Research in Indonesia shows that strategic orientation and resource allocation contribute to competitive advantage; quantitative study with 390 samples highlights the importance of goal setting in SME performance. |
| [48] | - | Business sustainability | Study in Greece reveals that IT strategic planning incorporating goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management improves operational efficiency and cost savings; quantitative approach with 294 samples also highlights positive impacts on employee and customer satisfaction. |
| [49] | 294 | Competitive advantage | Greek study finds that IT strategic planning enhances alignment with business goals; quantitative study with 160 samples focuses on achieving competitive advantage with limited additional performance metrics. |
| [50] | 160 | - | Research in Indonesia emphasizes that integrating entrepreneurship orientation, IT, and strategic planning enhances competitive advantage and operational efficiency; quantitative study with 132 samples shows improvements in employee and customer satisfaction. |
| [51] | 132 | Competitive advantage | Study in Greece explores dimensions of success and performance in IT strategic planning; quantitative approach with two samples highlights the alignment with business goals and resource efficiency, though the limited sample size may affect generalizability. |
| [52] | - | Competitive advantage | Enhancing alignment with business goals and resource efficiency in Indonesian SMEs leads to increased operational efficiency, revenue growth, and cost savings, while improving employee and customer satisfaction. |
| [53] | 55 | Competitive advantage | Effective goal setting and resource allocation in Greece contribute to improved project success rates and competitive advantage through better alignment with business goals. |
| [54] | - | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | Strategic planning in South Africa positively impacts SME performance by improving alignment with business goals and resource efficiency, fostering competitive advantage. |
| [55] | 294 | Business sustainability | Comprehensive IT strategic planning in Greece boosts business sustainability and competitive advantage by enhancing alignment with business goals and resource efficiency. |
| [56] | - | Business sustainability | The development of IT strategy frameworks in Germany improves alignment with business goals, operational efficiency, and cost savings, supporting long-term business sustainability. |
| [57] | - | Competitive advantage | Identifying critical factors in Greece’s IT strategic planning phases contributes to business sustainability by focusing on goal setting and resource allocation. |
| [58] | 150 | Business sustainability | In the USA, hybrid IT strategy models that incorporate risk management and resource efficiency lead to revenue growth and customer satisfaction, contributing to business sustainability. |
| [59] | 100 | Competitive advantage | The application of TOGAF in South Africa enhances project success rates and cost savings, leading to increased employee satisfaction and competitive advantage. |
| [60] | - | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | The framework in Indonesia improves alignment with business goals and operational efficiency while supporting cost savings and competitive advantage through effective IT strategy development. |
| [61] | 160 | Business sustainability | Evaluating IT alignment and performance in Greece shows that goal setting and resource allocation improve operational efficiency and cost savings, contributing to business sustainability. |
| [62] | - | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | The empirical study in Malaysia identifies success factors and barriers in IT implementation, supporting business sustainability and competitive advantage through effective resource allocation. |
| [63] | - | - | Exploring strategy implementation in agritourism SMEs in Greece reveals the use of information systems for better strategic outcomes, though specific contributions are not detailed. |
| [64] | - | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | The framework in Australia demonstrates that aligning IT capabilities with business goals and focusing on project success rates enhance operational efficiency, employee satisfaction, and business sustainability. |
| [65] | 294 | Business sustainability | Leveraging artificial neural network models in Greece improves alignment with business goals and resource efficiency, leading to better operational efficiency and competitive advantage. |
| [66] | - | Business sustainability | Improving business competitiveness in Indonesian public hospitals through strategic IT planning enhances alignment with business goals and operational efficiency. |
| [67] | - | Competitive advantage | Recommendations for IT strategy in Indonesian IT companies improve alignment with business goals and resource efficiency, supporting long-term business sustainability. |
| [68] | - | Business sustainability | External environmental scanning in Malaysian SMEs enhances alignment with business goals, contributing to business sustainability |
| [69] | 106 | Business sustainability | Study in Croatia highlights that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, and project success rates; quantitative approach with 106 samples validates the impact on SME performance. |
| [70] | 130 | Competitive advantage | Research in Ecuador shows that integrating goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management enhances alignment with business goals and project success rates; qualitative study with 130 samples highlights resource efficiency. |
| [71] | 200 | Competitive advantage | Study in Ghana reveals that goal setting in IT strategic planning positively affects alignment with business goals and project success rates; qualitative approach with two hundred samples emphasizes resource efficiency. |
| [72] | 223 | Competitive advantage | Analysis in Canada demonstrates that risk management in IT strategic planning supports alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, and project success rates; qualitative study with 223 samples emphasizes its impact on SME performance. |
| [73] | 150 | Business sustainability | Research in Peru highlights that risk management in IT strategic planning contributes to alignment with business goals and project success rates; qualitative approach with 150 samples supports resource efficiency. |
| [74] | 25 | Competitive advantage | Study in South Africa shows that risk management in IT strategic planning enhances alignment with business goals and project success rates; qualitative study with twenty-five samples emphasizes resource efficiency. |
| [75] | 160 | Competitive advantage | Research in Greece highlights that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management contribute to alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, operational efficiency, revenue growth, cost savings, employee satisfaction, business sustainability, and competitive advantage; quantitative study with 160 samples. |
| [76] | - | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | Study in Greece explores strategic alignment and information systems success, emphasizing employee satisfaction; quantitative approach with unspecified samples. |
| [77] | 23 | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | Research in the USA shows that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage; qualitative study with twenty-three samples. |
| [78] | 150 | Competitive advantage | Study in Canada highlights that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning enhance alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, operational efficiency, revenue growth, employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction, business sustainability, and competitive advantage; mixed methods with 150 samples. |
| [79] | 214 | Competitive advantage | Analysis in China reveals that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning drive alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage; mixed methods with 214 samples. |
| [80] | 588 | Competitive advantage | Research in Canada highlights that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning contribute to alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, and competitive advantage; quantitative study with 588 samples. |
| [81] | - | Competitive advantage | Study in South Korea emphasizes goal setting and risk management in IT strategic planning, leading to alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, operational efficiency, cost savings, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage; qualitative approach with unspecified samples. |
| [82] | 250 | Competitive advantage | Research in South Korea shows that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning enhance alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, operational efficiency, revenue growth, employee satisfaction, business sustainability, and competitive advantage; quantitative study with 250 samples. |
| [83] | 100 | Business sustainability | Study in Egypt highlights that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, operational efficiency, revenue growth, employee satisfaction, business sustainability, and competitive advantage; quantitative approach with one hundred samples. |
| [84] | 164 | Competitive advantage | Research in Malaysia reveals that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning support alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, and operational efficiency; mixed methods with 164 samples. |
| [85] | 294 | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | Study in Greece demonstrates that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management contribute to alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, operational efficiency, revenue growth, and competitive advantage; quantitative study with 294 samples. |
| [86] | - | Competitive advantage | Research in Italy highlights that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning led to alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, and competitive advantage; quantitative approach with unspecified samples. |
| [87] | 588 | Competitive advantage | Study in Canada shows that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning enhance alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage; quantitative study with 588 samples. |
| [88] | 132 | Competitive advantage | Research in China reveals that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning drive alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, operational efficiency, revenue growth, employee satisfaction, and competitive advantage; quantitative study with 132 samples. |
| [89] | 75 | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | Analysis in Ethiopia highlight’s goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning, supporting alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, operational efficiency, revenue growth, employee satisfaction, and business sustainability; mixed methods with seventy-five samples. |
| [90] | 206 | Competitive Advantage, Long-term Sustainability | Study in Canada shows that resource allocation in IT strategic planning improves alignment with business goals and resource efficiency; mixed methods with 206 samples |
| [91] | - | Business sustainability, Competitive Advantage | Analysis in South Africa shows that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT governance contribute to alignment with business goals, improved operational efficiency, cost savings, employee satisfaction, and business sustainability; qualitative study. |
| [92] | 4 | Effective IT Management | Study in Canada reveals that goal setting and resource allocation enhance alignment with business goals, project success rates, and operational efficiency, leading to competitive advantage; qualitative study with four samples. |
| [93] | 315 | Effective IT Governance Practices, Differences by Firm Size and Location | Analysis in Oman indicates that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, and project success rates, leading to operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage; mixed methods with 315 samples. |
| [94] | - | SME IT Governance Baseline | Study in the USA shows that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning support alignment with business goals, improving operational efficiency and revenue growth, enhancing competitive advantage; qualitative study. |
| [95] | Enhances theories of knowledge management and organizational innovations | Study in Saudi Arabia demonstrates that goal setting and resource allocation enhance alignment with business goals and resource efficiency, supporting business sustainability and competitive advantage; qualitative study. | |
| [96] | - | Strategic Alignment, Competitive Advantage | Analysis in Denver, USA reveals that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT governance improve IT-business alignment, governance effectiveness, and risk mitigation, leading to operational efficiency and competitive advantage; qualitative study. |
| [97] | - | Enhanced operational efficiency | Study in Slovenia highlights that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT governance enhance alignment with business goals, leading to operational efficiency, cost savings, and competitive advantage; qualitative study. |
| [98] | - | Competitive advantage, sustainability | Research in Brazil shows that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT governance mechanisms contribute to effective IT management, operational efficiency, and employee satisfaction; qualitative study. |
| [99] | 67 | Competitive Advantage, Innovation | Study in South Africa reveals that IT strategic investments, roles, and responsibilities in IT governance improve IT management and effectiveness, with differences noted by firm size and location; qualitative study with sixty-seven samples. |
| [100] | - | Enhanced IT Governance, Strategic Alignment | Analysis in the UK shows that IT governance frameworks contribute to the development of digital capabilities and firm innovation, enhancing overall firm performance; mixed methods study. |
| [101] | 100 | Business sustainability | Research in the UK reveals that IT strategic planning incorporating goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management improves operational efficiency, revenue growth, and employee satisfaction; quantitative study with one hundred samples demonstrates alignment with business goals. |
| [102] | 50 | Competitive advantage | Study in South Korea highlights that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning drive project success rates, revenue growth, and customer satisfaction; qualitative approach with fifty samples emphasizes alignment with business goals. |
| [103] | 75 | Business sustainability | Analysis in the UK shows that goal setting and risk management in IT strategic planning enhance alignment with business goals, operational efficiency, and revenue growth; mixed methods with seventy-five samples highlight employee satisfaction. |
| [104] | 40 | Competitive advantage | Research in Tunisia demonstrates that resource allocation and risk management in IT strategic planning contribute to cost savings and employee satisfaction; qualitative study with forty samples supports resource efficiency. |
| [105] | 120 | Competitive advantage | Study in Canada reveals that goal setting and risk management in IT strategic planning improve project success rates, operational efficiency, and revenue growth; quantitative study with 120 samples highlights customer satisfaction. |
| [106] | 150 | Competitive advantage | Research in Zimbabwe shows that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning enhance alignment with business goals and employee satisfaction; quantitative approach with 150 samples emphasizes revenue growth. |
| [107] | 50 | Business sustainability | Study in Taiwan highlights that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning contribute to alignment with business goals, operational efficiency, and revenue growth; quantitative approach with fifty samples supports customer satisfaction. |
| [108] | 100 | Business sustainability | Analysis in the UK demonstrates that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals, project success rates, and revenue growth; quantitative study with one hundred samples. |
| [109] | 50 | Competitive advantage | Research in the USA shows that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning enhance alignment with business goals, project success rates, and operational efficiency; mixed methods with fifty samples highlight employee satisfaction. |
| [110] | 10 | Competitive advantage | Study in the UK reveals that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning contribute to revenue growth, cost savings, and employee satisfaction; qualitative approach with ten samples emphasizes alignment with business goals. |
| [111] | 50 | Competitive advantage | Research in Canada highlights that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals and project success rates; quantitative study with fifty samples supports customer satisfaction. |
| [112] | 8 | Competitive advantage | Analysis in the UK shows that goal setting, resource allocation, and risk management in IT strategic planning drive revenue growth and employee satisfaction; qualitative study with eight samples emphasizes alignment with business goals. |
| [113] | 120 | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | Study in the UK reveals that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning enhance alignment with business goals, operational efficiency, and employee satisfaction; quantitative study with 120 samples. |
| [114] | 80 | - | Research in South Korea highlights that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals, operational efficiency, and employee satisfaction; quantitative study with eighty samples |
| [115] | 150 | Competitive advantage | Study in Greece highlights that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning improve alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, project success rates, revenue growth, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage; quantitative study with 150 samples. |
| [116] | 60 | Business sustainability, Competitive advantage | Research in the USA shows that goal setting in IT strategic planning enhances alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, operational efficiency, customer satisfaction, and competitive advantage; qualitative study with sixty samples. |
| [117] | 100 | Competitive advantage | Study in New Zealand demonstrates that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning support alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, revenue growth, cost savings, employee satisfaction, and competitive advantage; quantitative approach with one hundred samples. |
| [118] | 85 | Competitive advantage | Analysis in Zimbabwe reveals that goal setting and resource allocation in IT strategic planning drive alignment with business goals, resource efficiency, revenue growth, cost savings, employee satisfaction, and competitive advantage; mixed methods with eighty-five samples. |
| [119] | - | Competitive positioning in the business community | Research in Canada highlights the role of goal setting and risk management in IT governance within steering committees, contributing to employee satisfaction, competitive advantage, and business sustainability; qualitative study. |
| [120] | 80 | Business Sustainability | Addressing challenges in IT strategic planning in South Korea with COBIT and cloud-based solutions improves alignment with business goals and operational efficiency, supporting business sustainability. |
| [121] | 50 | Business Sustainability | In Australia, focusing on goal setting and resource allocation enhances resource efficiency and revenue growth, contributing to business sustainability. |
| Ref. | Selection (0-4 stars) | Comparability (0-2 stars) | Outcome/Exposure (0-3 stars) | Total Stars | Quality Rating |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [68,104,122] | ★★ | ★★ | ★ | 5 | Low Quality |
| [44,61,64,71,72,81,83,84,86,88,93,97,100,102,107,111,113,114,116] | ★★★ | ★ | ★★ | 6 | Medium Quality |
| [46,48,50,52,54,56,58,60,63,66,69,74,76,78,79,80,85,89,92,98,103,105,108,110,118,121] | ★★★ | ★★ | ★★ | 7 | Moderate Quality |
| [47,49,51,53,55,57,59,62,67,75,82,87,90,91,94,95,99,109,115,119,120] | ★★★★ | ★ | ★★★ | 8 | High Quality |
| [43,45,65,70,73,77,96,101,106,112,117] | ★★★★ | ★★ | ★★★ | 9 | High Quality |


3.4. Results of Individual Studies

3.5. Results of Syntheses

3.6. Reporting Biases

3.7. Certainty of Evidence

4. Discussion
Q1. How does integrating IT strategic planning with business methods impact SMEs’ operational performance?
Q2. What are the significant challenges faced by SMEs in incorporating IT strategic planning, and what techniques can be employed to overcome these obstacles?
Q3. How does the resource constraint of SMEs affect the efficacy of IT strategic planning, and what resource optimization techniques can be employed?
Q4. What roles do external factors such as market dynamics, regulatory adjustments, and technological advancements play in shaping the IT strategic planning process of SMEs?
Q5. How do SMEs measure the success of their IT strategic planning efforts, and what metrics or frameworks are best for this evaluation?
4. Practical Recommendations
| Framework Component | Description | Key Actions | Example from Study |
|---|---|---|---|
| IT Alignment with Business Goals | Ensuring that IT investments support key business objectives like customer service and operational efficiency. | - Conduct business needs analysis.- Align IT projects with business metrics. | SMEs in Pakistan used CRM tools to enhance customer service and project success [43]. |
| Resource Optimization | Maximizing the impact of IT investments while minimizing resource waste. | - Use cloud-based solutions.- Implement IT resource tracking tools.- Review IT spending. | German SMEs optimized resources by adopting cloud services, resulting in cost savings [46]. |
| Adaptation to External Factors | Adjusting IT strategies in response to market, regulatory, and technological changes. | - Monitor external trends.- Implement compliance tools.- Adopt new technologies gradually. | UK SMEs adopted automated compliance tools to meet GDPR requirements [58]. |
| Performance Measurement | Tracking financial and operational metrics to evaluate the success of IT investments. | - Define KPIs.- Use data analytics to monitor performance.- Review IT outcomes regularly. | Greek SMEs measured IT success through metrics like customer satisfaction and revenue growth [48]. |
| Continuous Improvement | Regularly updating IT strategies to incorporate new technologies and align with business growth. | - Conduct annual reviews.- Incrementally adopt scalable technologies.- Encourage innovation. | Greek SMEs gradually adopted AI tools to improve customer satisfaction [48]. |
| SME Name | Industry | IT/AI Solution | Results Achieved | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| KLM Royal Dutch Airlines | Aviation | AI-powered chatbot (BlueBot) for customer service | Handled 60% of queries without human intervention, improved overall customer experience | [121] |
| UPS | Logistics | AI-powered logistics platform (ORION) for delivery optimization | Reduced travel distance, resulting in cost savings and environmental benefits | [121] |
| Manufacturing SME (Unnamed) | Manufacturing | AI for predictive maintenance and quality control | 20% reduction in delivery times and enhanced product quality | [122] |
| Retail SME (Unnamed) | Retail | AI-driven analytics for personalized marketing | 25% increase in sales within one quarter | [122] |
| IBM Watson Health | Healthcare | AI for medical image analysis and patient data management | Improved diagnostic accuracy and personalized treatment plans | [123] |
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tshienda, H. The Effects of Strategic Planning on the Performance of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) in the Cape Metropole; Master’s Thesis, Cape Peninsula University of Technology, Faculty of Business and Management Science, Cape Town, South Africa, 2024. Available online: https://etd.cput.ac.za/bitstream/20.500.11838/3504/1/Tshienda_Hugor_213128810.pdf (accessed on 12 August 2024).
- “Strategic Information Systems Planning: SMEs Performance outcomes,” ResearchGate, Jun. 2016. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/320960932_Strategic_Information_Systems_Planning_SMEs_Performance_outcomes (accessed Aug. 10, 2024).
- Auka and, J. Chepngeno, “R M B R Effects of Strategic Planning on Performance of Medium Sized Enterprises in Nakuru Town,” International Review of Management and Business Research, vol. 5, no. 1, 2016, Available: https://www.irmbrjournal.com/papers/1455102998.pdf (accessed Aug. 10, 2024).
- “(PDF) Relationship Between Strategic Planning and SME Success: Empirical Evidence from Thailand,” ResearchGate. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/229046574_Relationship_Between_Strategic_Planning_and_SME_Success_Empirical_Evidence_from_Thailand (accessed Aug. 10, 2024).
- “The effect of innovation and strategic planning on enhancing organizational performance of Dubai Police,” Emerald logo Discover Journals, Feb. 25, 2020. https://www.emerald.com/insight/content/doi/10.1108/INMR-06-2018-0039/full/html (accessed Aug. 10, 2024).
- Carrasco-Carvajal, D. García-Pérez-de-Lema, and M. Castillo-Vergara, “Impact of innovation strategy, absorptive capacity, and open innovation on SME performance: A Chilean case study,” Journal of Open Innovation: Technology, Market, and Com-plexity, vol. 9, no. 2, p. 100065, Jun. 2023, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joitmc.2023.100065 (accessed Aug. 10, 2024).
- “Strategic Planning and SMEs Performance a Developing Country’s Perspective,” ResearchGate, Dec. 2019. https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338751336_Strategic_Planning_and_SMEs_Performance_A_Developing_Country%27s_Perspective (accessed Aug. 10, 2024).
- Strategic planning pillar. Accessed: Oct. 12, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://emt.gartnerweb.com/ngw/globalassets/en/insights/strategic-planning/2023/it-strategic-planning-pillar-page.
- Five-steps-of-strategic-planning-process. Accessed: Aug. 12, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://bscdesigner.com/wp-content/uploads/2019/06/five-steps-of-strategic-planning-process.
- “A comprehensive guide for conducting a rigorous systematic literature review,” www.linkedin.com. https://www.linkedin.
- “Opportunities and Challenges for Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs) - International Trade Council,” Sep. 12, 2022. https://tradecouncil.
- H. Yahaya and G. Nadarajah, “Determining key factors influencing SMEs’ performance: A systematic literature review and experts’ verification,” Cogent Business & Management, vol. 10, no. 3, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Gagan Deep Sharma, S. Kraus, A. Talan, M. Srivastava, and C. Theodoraki, “Navigating the storm: the SME way of tackling the pandemic crisis,” Small Business Economics, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- D.-Y. Lin, S. N. Rayavarapu, K. Tadjeddine, and R. Yeoh, “Helping small and medium-size enterprises thrive | McKinsey,” www.mckinsey.com, Jan. 26, 2022. https://www.mckinsey.com/industries/public-sector/our-insights/beyond-financials-helping-small-and-medium-size-enterprises-thrive.
- Drechsler and S. Weißschädel, “An IT strategy development framework for small and medium enterprises,” Information Systems and e-Business Management, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 93–124, May 2017. [CrossRef]
- Corient Business Solutions, “Strategic Business Planning for SME’s Businesses: Building a Path to Success,” Medium, Oct. 20, 2023. https://medium.com/@Corientbs/strategic-business-planning-for-smes-businesses-building-a-path-to-success-84beb1656d92 (accessed Sep. 06, 2024).
- C. A. Maritan and G. K. Lee, “Resource Allocation and Strategy,” Journal of Management, vol. 43, no. 8, pp. 2411–2420, Oct. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Mishrif and A. I. Khan, “Technology adoption as survival strategy for small and medium enterprises during COVID-19,” Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, vol. 12, no. 1, Aug. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Hansson and B. F. Abrantes, “Strategic Adaption (Capabilities) and the Responsiveness to COVID-19’s Business Environmental Threats,” Studies on entrepreneurship, structural change and industrial dynamics, pp. 1–23, Jan. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Ghobakhloo and S. H. Tang, “Information system success among manufacturing SMEs: case of developing countries,” Information Technology for Development, vol. 21, no. 4, pp. 573–600, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- N. AlQershi, “Strategic thinking, Strategic planning, Strategic Innovation and the Performance of SMEs: the Mediating Role of Human Capital,” Management Science Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 1003–1012, 2021. [CrossRef]
- N. AlQershi, “Strategic thinking, Strategic planning, Strategic Innovation and the Performance of SMEs: the Mediating Role of Human Capital,” Management Science Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 1003–1012, 2021. [CrossRef]
- P. Gatukui, Candidate, and P. Katuse, “A REVIEW OF SMEs STRATEGIC PLANNING FOR GROWTH AND SUSTAINABILITY IN KENYA: ISSUES AND CHALLENGES,” International Journal of Social Sciences and Entrepreneurship, vol. 1, 2014, Available: https://www.ijsse.org/articles/ijsse_v1_i10_26_41.
- D. Sornette, “Power laws without parameter tuning: An alternative to self-organized criticality,” Physical Review Letters, vol. 72, no. 14, pp. 2306–2306, Apr. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Waiganjo, D. Godinic, and O. Bojan, “Strategic Planning and Sustainable Innovation During the COVID-19 Pandemic: A Literature Review,” International Journal of Innovation and Economic Development, vol. 7, no. 5, pp. 52–59, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Ali, “Strategic planning–organizational performance relationship: Perspectives of previous studies and literature re-view,” International Journal of Healthcare Management, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 8–24, Sep. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Moeuf, R. Pellerin, S. Lamouri, S. Tamayo-Giraldo, and R. Barbaray, “The industrial management of SMEs in the era of Industry 4.0,” International Journal of Production Research, vol. 56, no. 3, pp. 1118–1136, Sep. 2017.
- S. K. N. Gamage, E. Ekanayake, G. Abeyrathne, R. Prasanna, J. Jayasundara, and P. Rajapakshe, “A Review of Global Challenges and Survival Strategies of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs),” Economies, vol. 8, no. 4, p. 79, Oct. 2020, Available: https://www.mdpi.com/2227-7099/8/4/79.
- T. Yangailo and M. Mpundu, “Identifying Research Gaps in Literature related to studies of Strategic Planning on Competitive Advantage: A Systematic Review of Literature,” International Journal of Applied Research in Business and Management, vol. 4, no. 2, pp. 47–70, Aug. 2023, Accessed: Aug. 12, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.ijarbm.org/issues/ijarbm-volume-4-issue-2/identifying-research-gaps-in-literature-related-to-studies-of-strategic-planning-on-competitive-advantage-a-systematic-review-of-literature/.
- R. Prasanna, J. Jayasundara, S. K. Naradda Gamage, E. Ekanayake, P. Rajapakshe, and G. Abeyrathne, “Sustainability of SMEs in the Competition: A Systemic Review on Technological Challenges and SME Performance,” Journal of Open Innovation: Tech-nology, Market, and Complexity, vol. 5, no. 4, p. 100, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Klewitz and E. G. Hansen, “Sustainability-oriented innovation of SMEs: a systematic review,” Journal of Cleaner Production, vol. 65, no. 1, pp. 57–75, Feb. 2014. [CrossRef]
- Q. S. Awang Ali, M. H. Hanafiah, and S. H. Mogindol, “Systematic literature review of Business Continuity Management (BCM) practices: Integrating organisational resilience and performance in Small and medium enterprises (SMEs) BCM framework,” International Journal of Disaster Risk Reduction, vol. 99, p. 104135, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Mbuyisa and A. Leonard, “The Role of ICT Use in SMEs Towards Poverty Reduction: A Systematic Literature Review,” Journal of International Development, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 159–197, Nov. 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. Mellett and E. O’Brien, “Irish SMEs and e-learning implementation: The strategic innovative approach,” British Journal of Educational Technology, vol. 45, no. 6, pp. 1001–1013, Sep. 2014. [CrossRef]
- F. Akbar, A. Omar, F. Wadood, and S. N. A. Al-Subari, “The Importance of SMEs, and Furniture Manufacturing SMEs in Malaysia: A Review of Literature,” papers.ssrn.com, Dec. 25, 2017.
- L. K. Kidombo, “Strategic Planning Among Small and Medium Enterprises in Nairobi County,” Uonbi.ac.ke, 2014, http://hdl.handle.net/11295/79912.
- K. Miller, R. McAdam, and M. McAdam, “A systematic literature review of university technology transfer from a quadruple helix perspective: toward a research agenda,” R&D Management, vol. 48, no. 1, pp. 7–24, Jul. 2016. [CrossRef]
- S. K. N. Gamage, E. Ekanayake, G. Abeyrathne, R. Prasanna, J. Jayasundara, and P. Rajapakshe, “A Review of Global Challenges and Survival Strategies of Small and Medium Enterprises (SMEs),” Economies, vol. 8, no. 4, p. 79, Oct. 2020.
- T. TCHOUWO, D. POULIN, and S. VEILLEUX, “UNDERSTANDING THE SPECIFIC CHARACTERISTICS AND DETER-MINANTS OF OPEN INNOVATION IN SMALL AND MEDIUM-SIZED ENTERPRISES: A SYSTEMATIC LITERATURE REVIEW,” International Journal of Innovation Management, p. 2150063, Mar. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Mory-Alvarado, C. Juiz, B. Bermejo, and M. Campoverde-Molina, “Green IT in small and medium-sized enterprises: A systematic literature review,” Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, vol. 39, p. 100891, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- “Digital Transformation of SMEs: The Role of Entrepreneurial Persistence and Market Sensing Dynamic Capability | IEEE Journals & Magazine | IEEE Xplore,” ieeexplore.ieee.org. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/10018086.
- M. Parkin, F. Bray, J. Ferlay, and P. Pisani, “Global Cancer Statistics, 2002,” CA: A Cancer Journal for Clinicians, vol. 55, no. 2, pp. 74–108, Mar. 2014, https://doi.org/10.3322/canjclin.55.2.74., opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) deny re-possibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content.
- K. Yang and L. I. Meho, “Citation Analysis: A Comparison of Google Scholar, Scopus, and Web of Science,” Proceedings of the American Society for Information Science and Technology, vol. 43, no. 1, pp. 1–15, Oct. 2007, https://doi.org/10.1002/meet.14504301185.Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) deny responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions, or products referred to in the content.
- Haleem and M. Jehangir, “Strategic Planning and SMEs Performance A Developing Country’s Perspective,” Journal of Business and Economics, vol. 11, no. 2, Dec. 2019, Accessed: Sep. 06, 2024. [Online]. Available: https://www.researchgate.net/publication/338751336_Strategic_Planning_and_SMEs_Performance_A_Developing_Country’s_Perspective.
- N. AlQershi, “Strategic thinking, Strategic planning, Strategic Innovation and the Performance of SMEs: the Mediating Role of Human Capital,” Management Science Letters, vol. 11, no. 3, pp. 1003–1012, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Rachadaporn Pinrattananont, “Strategic IT alignment and organization performance: A resource-based view,” Rmutt.ac.th, 2015, http://www.repository.rmutt.ac.th/dspace/handle/123456789/2941.
- M. L. & N. Omrani, “SME Internationalization: the Impact of Information Technology and Innovation,” ideas.repec.org, 2020, [Online]. Available: https://ideas.repec.org/a/spr/jknowl/v11y2020i2d10.1007_s13132-018-0576-3.html#:~:text=The%20results%20show%20that%20IT%20has%20no%20direct,the%20level%20of%20IT%2C%20can%20improve%20SME%20internationalization.
- H. Pratono, “Strategic orientation and information technological turbulence,” Business Process Management Journal, vol. 22, no. 2, pp. 368–382, Apr. 2016, 10.1108/bpmj-05-2015-0066.
- Kitsios and M. Kamariotou, “Decision support systems and strategic planning: information technology and SMEs’ performance,” International Journal of Decision Support Systems, vol. 3, no. 1/2, p. 53, 2018. [CrossRef]
- Φ. Κίτσιος et al., “Strategic planning and information systems in small-medium enterprises: dimensions of success and performance,” 2022. https://dspace.lib.uom.gr/handle/2159/27283.
- “Strategic Planning and Information Systems Success: Evaluation in Greek SMES,” IEEE Conference Publication | IEEE Xplore, Jul. 01, 2019. https://ieeexplore.ieee.org/abstract/document/8808050?
- Anis, B. Christiananta, and L. Ellitan, “THE EFFECT OF ENTREPRENEURSHIP ORIENTATION, INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY, STRATEGIC PLANNING TO COMPETITIVE ADVANTAGES WITH BUSINESS PERFORMANCE AS INTERVENING VARIABLES: EMPIRICAL STUDY FOOD PROCESSING SMEs IN NORTH SULAWESI.,” International Journal of Advanced Research, vol. 6, no. 1, pp. 236–242, Jan. 2018. [CrossRef]
- L. Ellitan, “The Importance of Entrepreneurship and Information Technology for SMEs Strategic Planning,” Int. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev., vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1004-1009, Jun. 2021. Available: https://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd42479.pdf.
- M. Kamariotou and F. Kitsios, “An Empirical Evaluation of Strategic Information Systems Planning Phases in SMEs: Determinants of Effectiveness,” Proc. 6th Int. Symp. and 28th Nat. Conf. Operational Research, Thessaloniki, Greece, pp. 67-72, June 2017.
- shienda, Hugor Tshienda, “The effects of strategic planning on the performance of small and medium enterprises (SMEs) in the Cape Metropole,” Cput.ac.za, 2021, http://hdl.handle.net/20.500.11838/3504.
- Kitsios and M. Kamariotou, “Information Systems Strategy and Strategy-as-Practice: Planning Evaluation in SMEs,” Proc. of Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 2019), Cancun, Mexico, pp. 1-10, Aug. 2019. [Online]. Available: https://aisel.aisnet.org/amcis2019/strategic_uses_it/strategic_uses_it/3/.
- Drechsler and S. Weißschädel, “An IT strategy development framework for small and medium enterprises,” Information Systems and e-Business Management, vol. 16, no. 1, pp. 93–124, May 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. Kamariotou and F. Kitsios, “Critical Factors of Strategic Information Systems Planning Phases in SMEs,” Information Systems, pp. 503–517, 2019. [CrossRef]
- Yahaya and G. Nadarajah, “Determining key factors influencing SMEs’ performance: A systematic literature review and experts’ verification,” Cogent Business & Management, vol. 10, no. 3, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Pai, “An empirical study of the relationship between knowledge sharing and IS/IT strategic planning (ISSP),” Management Decision, vol. 44, no. 1, pp. 105–122, Jan. 2006. [CrossRef]
- Burhanudin and S. M. Isa, “Strategic Planning of Information System and Information Technology in Small and Medium Enterprises with Reference to PT. Giri Artha Sejahtera,” Int. J. Small Medium Enterprises Bus. Sustain., vol. 4, no. 1, pp. 86-114, Mar. 2019.
- M. Kamariotou and F. Kitsios, “Evaluating IT alignment and performance in SMEs using Multivariate Regression Analysis,” in Proc. 19th Int. Conf. Electronic Business (ICEB), Newcastle, UK, pp. 222-230, 2019. [Online]. Available: https://www.scopus.com/record/display.uri?eid=2-s2.0-85082619074&origin=resultslist.
- R. Hamdan, J. H. Yahaya, A. Deraman, and Y. Y. Jusoh, “The success factors and barriers of information technology implementation in small and medium enterprises: an empirical study in Malaysia,” International Journal of Business Information Systems, vol. 21, no. 4, p. 477, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Kamariotou and F. Kitsios, “How Managers Use Information Systems for Strategy Implementation in Agritourism SMEs,” Information, vol. 11, no. 6, p. 331, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- M. Kamariotou and Fotis Kitsios, “Information systems and strategy-as-practice in the digital era: an artificial neural network model for SMEs,” Operational research, vol. 24, no. 3, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- F. Kitsios and M. Kamariotou, “Information systems and strategy-as-practice in the digital era: an...,” in Proc. of Americas Conference on Information Systems (AMCIS 2019), Cancun, Mexico, 2019.
- M. R. Bintang Janaputra, F. Samopa, and R. Ambarwati Sukmono, “Strategic Planning IS/IT TO Improve Business Competitiveness in Public Hospital,” Kinetik: Game Technology, Information System, Computer Network, Computing, Electronics, and Control, pp. 83–92, Feb. 2021. [CrossRef]
- P.G. Pakusadewa, E. Suryani, R. Ambarwati, and M. R. Bintang, “Selection of Information System Strategy Recommendations in Information Technology Company,” www.atlantis-press.com, May 10, 2021. https://www.atlantis-press.com/proceedings/iconbmt-20/125956361 (accessed Mar. 26, 2024).
- Donkor, G. N. A. Donkor, and C. K. Kwarteng, “Strategic planning and performance of SMEs in Ghana,” Asia Pacific Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 62–76, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Klačmer Čalopa, “Business owner and manager’s attitudes towards financial decision-making and strategic planning: Evidence from Croatian SMEs,” Management: Journal of Contemporary Management Issues, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 103–116, Jun. 2017. [CrossRef]
- R. Aman, “ISSN 1390-3837, UPS-Ecuador, No. 17, julio-diciembre 2012, pp. 51-68 En la lengua del Otro: la Unión Europea y el diálogo intercultural como instrumento de exclusión,” Universitas, no. 17, p. 51, Dec. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Donkor, G. N. A. Donkor, and C. K. Kwarteng, “Strategic planning and performance of SMEs in Ghana,” Asia Pacific Journal of Innovation and Entrepreneurship, vol. 12, no. 1, pp. 62–76, Apr. 2018. [CrossRef]
- Raymond, F. Bergeron, A.-M. Croteau, and S. Uwizeyemungu, “Determinants and outcomes of IT governance in manufacturing SMEs: A strategic IT management perspective,” International Journal of Accounting Information Systems, vol. 35, p. 100422, Dec. 2019. [CrossRef]
- Ríos-Ríos, F. Ochoa-Paredes, M. Vargas-Tasayco, Y. Uribe-Fernández, and A. Chaman- Bardalez, “Flexible strategic planning for the financial management of MSES-2019,” International Journal of ADVANCED AND APPLIED SCIENCES, vol. 10, no. 2, pp. 1–6, Feb. 2023. [CrossRef]
- M. Mathu, “The information technology role in supplier-customer information-sharing in the supply chain management of South African small and medium-sized enterprises,” South African Journal of Economic and Management Sciences, vol. 22, no. 1, Mar. 2019. [CrossRef]
- F. C. Kitsios and M. Kamariotou, “Digital Business Strategy and Information Systems Planning: Determinants of Success,” in Proc. 14th European Conf. Innovation and Entrepreneurship (ECIE19), Kalamata, Greece, vol. 1, pp. 514-521, Sept. 2019. 10.34190/ECIE.19.134.
- M. Kamariotou and Fotis Kitsios, “Strategic alignment and Information Systems success: Towards an evaluation model for firm performance,” AIS Electronic Library (AISeL), 2022. https://aisel.aisnet.org/ukais2022/9/ (accessed Sep. 06, 2024).
- Howe, “The Impact of Strategic Planning in Small Business: Empirical Evidence From East Tennessee,” Scholars Crossing, 2022. https://digitalcommons.liberty.edu/doctoral/3708/ (accessed Jun. 11, 2023).
- V. Dutot, F. Bergeron, and A. Calabrò, “The impact of family harmony on family SMEs’ performance: the mediating role of information technologies,” Journal of Family Business Management, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Y. Wang, S. Shi, S. Nevo, S. Li, and Y. Chen, “The interaction effect of IT assets and IT management on firm performance: A systems perspective,” International Journal of Information Management, vol. 35, no. 5, pp. 580–593, Oct. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Raymond, S. Uwizeyemungu, B. Fabi and J. St-Pierre, “IT Capability Configurations for Innovation: An Empirical Study of Industrial SMEs,” 2014 47th Hawaii International Conference on System Sciences, Waikoloa, HI, USA, 2014, pp. 3939-3948. [CrossRef]
- Lacina, Libor Mesicek, H. Ko, and Sung Bum Pan, “Case Study: Continual Evaluation of IT Process Portfolio in SME based on Val IT 2.0,” Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- ang, M. Singh, Z. Pita, and I. Storey, “The Relationship between Strategic Information Systems Planning Facilitators and the Success of South Korean Organisations,” AIS Electronic Library (AISeL), 2015. https://aisel.aisnet.org/pacis2015/185/#:~:text=By%20surveying%20a%20random%20sample%20of%20SISP%20experts (accessed Sep. 06, 2024).
- Makhloufi, N. Azbiya Yaacob, A. A. Laghouag, A. Ali Sahli, and F. Belaid, “Effect of IT capability and intangible IT resources on sustainable competitive advantage: Exploring moderating and mediating effect of IT flexibility and core competency,” Cogent Business & Management, vol. 8, no. 1, p. 1935665, Jan. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. Kamariotou and Fotis Kitsios, “Information systems and strategy-as-practice in the digital era: an artificial neural network model for SMEs,” Operational research, vol. 24, no. 3, Jun. 2024. [CrossRef]
- Frigerio, M. Martinez, Mario Pezzillo Iacono, F. Rajola, and T. Jacks, “Information Technology Issues in Italy,” World Scientific-Now Publishers series in business, pp. 195–207, Apr. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Raymond, S. Uwizeyemungu, B. Fabi, and J. St-Pierre, “IT capabilities for product innovation in SMEs: a configurational approach,” Information Technology and Management, vol. 19, no. 1, pp. 75–87, Jun. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Yu and T. Moon, “Influence of Competitor, Customer Orientation and IT Competence on Marketing Performance in Chinese SMEs,” Journal of Information Systems, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 131–153, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- R. Ahmed, “Assessing Business and Information Technology Alignment Maturity: The Case of Commercial Banks in Ethiopia,” M.S. thesis, School of Information Science, Addis Ababa University, Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, Dec. 2017.
- L’Écuyer and L. Raymond, “Enabling the HR function of industrial SMEs through the strategic alignment of e-HRM: a configurational analysis,” Journal of Small Business & Entrepreneurship, pp. 1–33, Aug. 2020. [CrossRef]
- Olutoyin and S. Flowerday, “Successful IT governance in SMES: An application of the Technology–Organisation–Environment theory,” SA Journal of Information Management, vol. 18, no. 1, May 2016. [CrossRef]
- Pelletier and L. Raymond, “Investigating the strategic IT alignment process with dynamic capabilities view: A multiple case study,” Information & Management, p. 103819, May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Zighan and S. Ruel, “SMEs’ resilience from continuous improvement lenses,” Journal of Entrepreneurship in Emerging Economies, vol. ahead-of-print, no. ahead-of-print, Nov. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Baporikar, “Information and Communication Technology for SMEs’ Competitiveness,” International Journal of Strategic Information Technology and Applications, vol. 7, no. 3, pp. 41–55, Jul. 2016. [CrossRef]
- Boamah-Abu and M. Kyobe, “IT Governance Practices of SMEs in South Africa and the Factors Influencing Their Effectiveness,” Advances in human resources management and organizational development book series, pp. 188–207, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Jabr, “John A. Long - Publications List,” Publicationslist.org, vol. 14, no. 6, 2021.
- Levstek, A. Pucihar, and T. Hovelja, “Towards an Adaptive Strategic IT Governance Model for SMEs,” Journal of Theoretical and Applied Electronic Commerce Research, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 230–252, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- C. C. da Silva, J. S. Dornelas, and M. A. V. Araújo, “Strategic role of IT and IT governance mechanisms for the context of small and medium enterprises,” REGEPE - Revista de Empreendedorismo e Gestão de Pequenas Empresas, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Boamah-Abu and M. Kyobe, “IT Governance Practices of SMEs in South Africa and the Factors Influencing Their Effectiveness,” Advances in human resources management and organizational development book series, pp. 188–207, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- Khalil.S and Belitski, M (2020), “Dynamic capabilities for firm performance under the information technology governance framework”, Europe an Business Review, Vol. 32 No. 2, pp. 129-157. [CrossRef]
- Schubert, J. Unlocking growth in small and medium-size enterprises. McKinsey & Company. 2020. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Omar, F. Wadood, and S. N. A. Al-Subari, “The Importance of SMEs, and Furniture Manufacturing SMEs in Malaysia: A Review of Literature,” papers.ssrn.com, Dec. 25, 2017. https://papers.ssrn.com/sol3/papers.cfm?abstract_id=3110311 L. Ellitan, “The Importance of Entrepreneurship and Information Technology for SMEs Strategic Planning,” Int. J. Trend Sci. Res. Dev., vol. 5, no. 4, pp. 1004-1009, Jun. 2021. Available: https://www.ijtsrd.com/papers/ijtsrd42479.pdf.
- Bermejo, and M. Campoverde-Molina, “Green IT in small and medium-sized enterprises: A systematic literature review,” Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, vol. 39, p. 100891, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Fatimatuz Zahro, M. Fikri, Muhammad Dumairy Priyanto, Gg Faniru Pakuning Desak, and Meta Amalya Dewi, “Strategic Planning For Information Systems Optimization Of Vocational Higher Education Facilities And Infrastructures At The Ministry Of Education, Culture, Research And Technology (E-Sarpras),” Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Adomako, J. Amankwah-Amoah, F. Donbesuur, M. Ahsan, A. Danso, and M. Uddin, “Strategic agility of SMEs in emerging economies: Antecedents, consequences and boundary conditions,” International Business Review, p. 102032, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Dong, L., Neufeld, D. and Higgins, C. (2009). Top Management Support of Enterprise Systems Implementations, Journal of Information Technology 24 (1): 55–80.
- Fotis Kitsios and M. Kamariotou, “Strategic IT Alignment and Business Performance in SMEs: An Empirical Investigation,” Lecture notes in business information processing, pp. 113–123, Jan. 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. Bellamy, N. Amoo, K. Mervyn, and J. Hiddlestone-Mumford, “The use of strategy tools and frameworks by SMEs in the strategy formation process,” International Journal of Organizational Analysis, vol. 27, no. 2, pp. 337–367, Apr. 2019. [CrossRef]
- “International Journal of Advanced Research,” International Journal of Advanced Research, 2019. http://www.journalijar.com/.
- Mory-Alvarado, C. Juiz, B. Bermejo, and M. Campoverde-Molina, “Green IT in small and medium-sized enterprises: A systematic literature review,” Sustainable Computing: Informatics and Systems, vol. 39, p. 100891, Sep. 2023. [CrossRef]
- Sam Saguy, “Food SMEs’ open innovation: Opportunities and challenges,” Elsevier eBooks, pp. 39–52, Jan. 2022. [CrossRef]
- Huebner and S. Flessa, “Strategic management in healthcare: A call for long-term and systems-thinking in an uncertain system,” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, vol. 19, no. 14, 2022. [CrossRef]
- W. Li, K. Liu, M. Belitski, A. Ghobadian, and N. O’Regan, “E-Leadership through Strategic Alignment: An Empirical Study of Small- and Medium-sized Enterprises in the Digital Age,” Journal of Information Technology, vol. 31, no. 2, pp. 185–206, Jun. 2016.
- H. Yahaya and G. Nadarajah, “Determining key factors influencing SMEs’ performance: A systematic literature review and experts’ verification,” Cogent Business & Management, vol. 10, no. 3, Nov. 2023. [CrossRef]
- R. I. Williams, A. Smith, J. R. Aaron, S. C. Manley, and W. C. McDowell, “Small business strategic management practices and performance: A configurational approach,” Economic Research-Ekonomska Istraživanja, vol. 33, no. 1, pp. 1–19, Oct. 2019. [CrossRef]
- VMware (2013). IT: time to take the lead in creating business value with enterprise social networks. White Paper. [WWW document] www.vmware.com/files/pdf/socialcast/vmw-enterprise-social-network-value-whitepaper.pdf (accessed 7 September 2024).
- Muhammad Awais, Ali et al., Muhammad Sajid Khattak, Muhammad Irfanullah Arfeen, Muhammad, and A. Syed, “Strategic Flexibility and Organizational Performance: Mediating Role of Innovation,” SAGE Open, vol. 13, no. 2, Apr. 2023. [CrossRef]
- S. Reiche and Carl Henning Reschke, “THE ROLE OF STRATEGIC PLANNING IN SMEs: LITERATURE REVIEW AND IMPLICATIONS,” Academia.edu, 2015. https://www.academia.edu/3055123/THE_ROLE_OF_STRATEGIC_PLANNING_IN_SMEs_LITERATURE_REVIEW_AND_IMPLICATIONS .
- Yunis, A. Tarhini, and A. Kassar, “The role of ICT and innovation in enhancing organizational performance: The catalysing effect of corporate entrepreneurship,” Journal of Business Research, vol. 88, pp. 344–356, Jul. 2018, Available: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0148296317305246.
- Khalil.S and Belitski, M (2020), “Dynamic capabilities for firm performance under the information technology governance framework”, Europe an Business Review, Vol. 32 No. 2, pp. 129-157. [CrossRef]
- Albaz, A.; Dondi, M.; Rida, T.; Schubert, J. Unlocking growth in small and medium-size enterprises. McKinsey & Company. 2020. Available online: https://www.mckinsey.com (accessed on 10 September 2024).
- Yassin, M. Case Studies: SMEs Successfully Implementing AI Solutions – Insights and Outcomes. ProfileTree. 2024. Available online: https://www.profiletree.com (accessed on 9 September 2024).
- Digital Transformation Skills. Case Studies: IT and AI Transformations in Aviation and Logistics. 2024. Available online: https://www.digitaltransformationskills.com (accessed on 9 September 2024).
| Ref. | Cites | Year | Contribution | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [21] | 15 | 2014 | Explores the role of government policies in supporting SMEs during economic crises. | Advocates for government intervention to bolster SME resilience. | Implementation varies across regions; SMEs may still face barriers even with policy support. |
| [22] | 29 | 2014 | Discusses the importance of strategic planning in complex and uncertain environments, emphasizing its role in successful operations. | Highlights the necessity of strategic planning across contexts; extensive literature review. | Mixed results on the impact of planning on performance; lacks focus on SMEs. |
| [23] | 53 | 2014 | A holistic review of empirical studies of strategic planning and future research avenues. | Emphasizes the importance of strategic planning for business success; links planning to firm performance. | Mixed findings on the impact of strategic planning, especially in SMEs; limited focus on developing countries. |
| [24] | 84 | 2014 | Examines how SMEs apply strategic planning and its correlation with success, identifying informal planning practices. | Reviews key CSR themes in SMEs; offers a framework for future studies. | Limited studies on CSR in SMEs; potential bias in content analysis. |
| [25] | 91 | 2014 | Literature review on drivers of sustainable development of SMEs during the COVID-19 pandemic, offering crisis management strategies. | Highlights the importance of planning, cost-effective solutions, and collaboration with larger enterprises. | Focuses on SMEs, limiting generalizability to larger corporations. |
| [26] | 75 | 2016 | Reviews strategic planning frameworks applicable to SMEs. | Provides actionable frameworks for SMEs. | Frameworks may be too general for some SMEs. |
| [27] | 64 | 2016 | Reviews PMS in SMEs, highlighting their complexity and necessity for effective performance measurement. | Identifies specific challenges and evolution of PMS models; proposes a research agenda. | Limited empirical research; focuses on theoretical aspects. |
| [28] | 100 | 2016 | Examines global challenges affecting SMEs and proposes survival strategies. | Identifies eight global challenges and emphasizes the need for SMEs to engage with MNCs. | Complexity of global challenges may overwhelm SMEs. |
| [29] | 85 | 2017 | Analyzes the relationship between strategic planning and innovation in SMEs. | Strong empirical evidence supporting the claims. | May lack depth in qualitative insights. |
| [30] | 86 | 2017 | Reviews global challenges for SMEs, identifying survival strategies. | Acknowledges the vital contribution of SMEs to the global economy. | Lacks actionable solutions for the challenges faced by SMEs. |
| [31] | 59 | 2019 | Systematic literature review on new product development (NPD) processes in SMEs, focusing on open innovation. | Identifies NPD characteristics and collaboration opportunities; comprehensive analysis of ninety-nine articles. | May not cover all relevant issues; limited by the scope of reviewed literature. |
| [32] | 50 | 2020 | Examines barriers to effective strategic planning in SMEs. | Identifies common challenges faced by SMEs. | Solutions are often high-level and non-specific. |
| [33] | 50 | 2020 | Systematic review identifying research gaps in strategic planning and competitive advantage. | Provides a replicable methodology for future research. | Limited to English-language literature and three databases. |
| [34] | 83 | 2015 | Examines how and to what extent SMEs apply strategic planning, exploring correlations with corporate success. | Provides a systematic review of strategic planning in SMEs. | Limited focus on formal planning in SMEs. Limited comparison across different methodologies and regions. |
| [35] | 99 | 2021 | Systematic review on NPD processes in SMEs, emphasizing adaptation and collaboration. | Highlights the importance of planning for SME success; proposes future research directions. | May not represent all issues in NPD; limited to selected articles. |
| [36] | 80 | 2021 | Reviews the impact of strategic management on SME development, highlighting differences in planning approaches and contexts. | Provides insight into strategic management on SME development. | Lacks comparison across methodologies and regions. |
| [37] | 41 | 2021 | Explores strategic planning issues and challenges for SMEs in Kenya, emphasizing the importance of governance and planning. | Addresses the specific context of Kenyan SMEs and their challenges. | High failure rates of SMEs remain unaddressed. |
| [38] | 44 | 2021 | Systematic review on integrating sustainability in SMEs’ strategic planning; identifies gaps and suggests future research. | Emphasizes long-term value; proposes an integration framework. | Limited empirical studies; fragmented understanding. |
| [39] | 100 | 2021 | Discusses the role of strategic planning in enhancing SME performance. | Comprehensive overview of numerous studies. | Limited focus on specific industries. |
| [40] | 60 | 2022 | Evaluates the impact of strategic planning on the financial performance of SMEs. | Includes case studies highlighting success stories. | Limited geographical scope in case studies. |
| [41] | 85 | 2023 | Comprehensive framework for designing performance measurement systems (PMS) that align with organizational goals. | Emphasizes stakeholder needs and business dynamics. | Lacks empirical validation; broad scope may be too general for specific applications. |
| [42] | 106 | 2023 | Examines strategic planning in SMEs, focusing on the extent and correlation with corporate success. | Identifies key themes and research gaps; establishes a theoretical framework for future research. | Limited by survivor bias; lacks recent data from the last two decades. |
| Proposed systematic review | The reviewed papers highlight the essential role of IT strategic planning in enhancing SME performance. They show how aligning IT investments with business goals can improve efficiency, decision-making, and adaptability, thereby supporting long-term business success. | IT strategic planning offers significant benefits, including improved operational efficiency, better decision-making, and greater adaptability to market changes. It enables SMEs to manage resources more effectively and fosters innovation, contributing to overall business growth. | However, there are limitations, such as issues with generalizability due to small or industry-specific samples and methodological constraints. Some studies may not fully address the challenges SMEs face, such as limited resources and expertise. | ||
| Section # | Content Description | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 0. Abstract | A concise summary of the entire paper, including the research questions, methodology, key findings, and conclusions. | Provides a snapshot of the study’s importance, objectives, methods, and key insights, allowing readers to quickly assess the relevance of the research. |
| 1. Introduction | Introduces the concept of IT strategic planning and its importance to SMEs, including a review of relevant literature. | Establishes the foundational context, identifies gaps in current research, and justifies the need for a systematic review on this topic. |
| 1.1. Problem Statement | Specifies the problem being addressed: the lack of a comprehensive understanding of IT strategic planning’s impact on SME performance. | Clarifies the research problem and articulates the precise scope of investigation, providing focus for the entire study. |
| 1.2. Research Questions | Lists the research questions the systematic review seeks to address. | Directs the research by laying out specific questions that the study aims to answer, guiding the analysis and synthesis of the literature. |
| 1.3. Rationale | Explains why it is essential to study the impact of IT strategic planning on SMEs, considering their unique challenges such as resource constraints. | Justifies the study by linking the importance of IT strategic planning to SME success, sustainability, and competitiveness. It highlights gaps in existing research. |
| 2. Objectives | Describes the study’s primary goals: to explore the relationship between IT strategic planning and SME performance, identify challenges, and assess external factors like market dynamics and regulatory changes. | Defines the scope of the review, ensuring the research remains focused on specific, actionable outcomes. The objectives drive the structure of the analysis. |
| 3. Materials and Methods | Outlines the methodology used in the systematic review, including inclusion/exclusion criteria, databases searched, and data extraction processes. | Ensures the research is replicable, transparent, and systematic. Demonstrates the rigor of the study, enhancing the credibility of the findings. |
| 3.1. Eligibility Criteria | Provides detailed criteria for selecting studies for inclusion in the review, such as publication period (2014-2024), relevance, and peer-reviewed status. | Establishes the validity of the research by ensuring only relevant, high-quality studies are considered, strengthening the conclusions. |
| 3.2. Information Sources | Describes the databases used for literature searches (Google Scholar, Web of Science, SCOPUS) and how these sources contribute to the study’s comprehensiveness. | Ensures that a wide variety of studies are included, making the review comprehensive and reducing the risk of selection bias. |
| 3.3. Search Strategy | Details the specific search codes and keywords used to locate relevant studies. | Demonstrates a systematic and unbiased approach to gathering research materials, ensuring no relevant studies are missed. |
| 4. Results | Presents the findings from the systematic review, including the key trends in IT strategic planning and its impact on SMEs. Quantitative and qualitative findings are synthesized. | Highlights the core insights from the reviewed studies, providing evidence for the hypotheses and addressing the research questions. Offers practical examples of IT adoption and its outcomes in SMEs. |
| 4.1. Study Selection | Describes how studies were selected and the number of papers included after screening (e.g., 80 studies selected). | Ensures transparency in how the data was gathered and provides context for the breadth and depth of the review. |
| 4.2. Study Characteristics | Summarizes the characteristics of the included studies, such as the type of research (journal articles, conference papers, etc.) and geographic distribution. | Provides context for the studies included, allowing readers to assess the relevance and generalizability of the findings. |
| 4.3. Key Findings | Presents the core outcomes of the review, such as the benefits of IT strategic planning in SMEs (e.g., operational efficiency, cost savings, and competitive advantage) and challenges (e.g., resource constraints). | Delivers the primary insights from the study, providing a foundation for further discussion and recommendations. Identifies patterns and gaps in the current literature. |
| 5. Discussion | Interprets the findings, discussing the significance of IT strategic planning in SMEs and how it addresses operational, financial, and strategic challenges. | Connects the review findings to the broader context of SME performance, making the results actionable for stakeholders. Highlights implications for future research and policy. |
| 5.1. Practical Recommendations | Provides actionable steps for SMEs to overcome challenges in IT strategic planning (e.g., cloud adoption, outsourcing IT services). | Offers real-world solutions for SMEs to enhance their performance through better IT planning. These recommendations are grounded in the systematic review’s findings, making them evidence based. |
| 6. Conclusions | Summarizes the main conclusions of the research, reiterating the importance of aligning IT strategies with business goals and addressing challenges like resource constraints. | Reinforces the significance of the study’s findings and calls for further research in areas where gaps still exist. Provides closure and a synthesis of the entire review. |
| 6.1. Future Research Directions | Suggests areas for further study, such as exploring IT governance frameworks in SMEs or the long-term impact of IT adoption. | Encourages future research to build upon the current review, addressing limitations and expanding the understanding of IT strategic planning in SMEs. |
| Criteria | Inclusion | Exclusion |
|---|---|---|
| Topic | Publications focusing The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SMEs Performance | Publications that do not relate to The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SMEs Performance |
| Research Framework | This article must include a research framework or methodology for The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SMEs Performance | Articles lacking clear research framework related to Evaluating The Impact of IT Strategic Planning Process on SMEs Performance |
| Language | Must be written in English | Articles published in languages other than English |
| Period | Articles between 2014 and 2024 | Articles outside 2014 and 2024 |
| No. | Online Repository | Number of results |
|---|---|---|
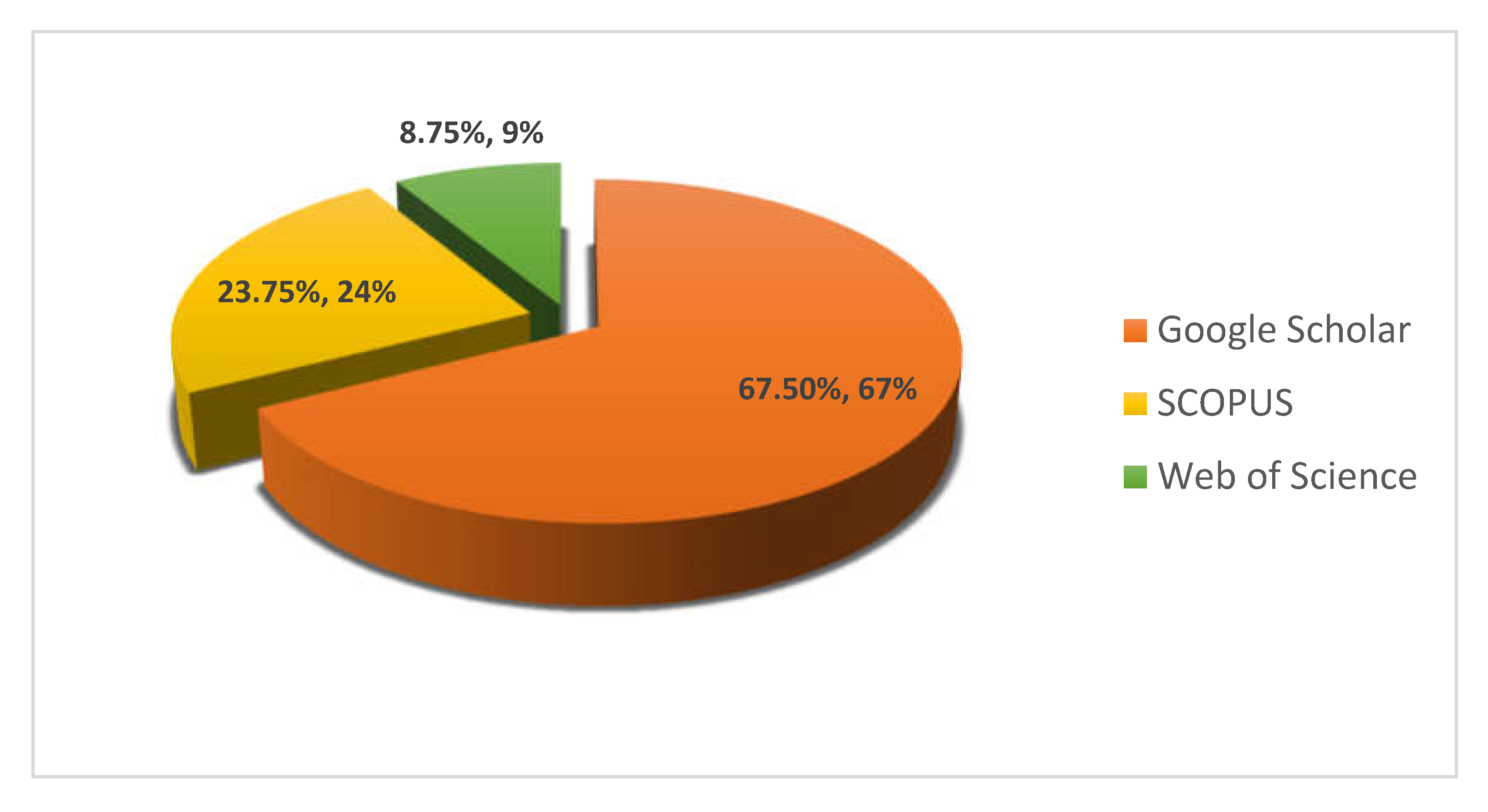
| 1 | Google Scholar | 570 |
| 2 | Web of Science | 22 |
| 3 | SCOPUS | 19 |
| Total | 611 |
| Criteria | Description |
|---|---|
| Title | The name of the study or article focusing on the influence of IT strategic planning on SME performance. |
| Year | The publication year of the study. |
| Online Database | The digital platform where the study is available (e.g., Google Scholar). |
| Journal Name | The name of the journal where the study was published. |
| Research Type | The format of the research (e.g., Article Journal, Conference Paper, Book Chapter, Dissertation). |
| # Cites | The number of times the study has been cited. |
| GSRank | The ranking or relevance based on Google Scholar metrics. |
| Discipline or Subject Area | The main academic area of focus (e.g., IT Strategic Planning, SME Performance, Business Strategy). |
| Industry Context | The industry where the IT strategic planning is applied (e.g., manufacturing, health, agriculture). |
| Geographic Location | The region or country where the study was conducted or focused. |
| Economic Context | The economic development of the region (e.g., Developed, Developing economies). |
| Components of IT Strategic Planning | Key elements of IT planning (e.g., goal setting, resource allocation, risk management). |
| IT Planning Frameworks | Specific frameworks used in the IT planning (e.g., COBIT, ITIL, TOGAF). |
| Technology Providers | The companies or vendors providing technology solutions. |
| Technology Implementation Model | The mode of technology implementation (e.g., on-premises, cloud-based, hybrid). |
| Research Design | The approach taken in the study (e.g., experimental, case study, survey). |
| Type of Study | The methodology used in the study (e.g., quantitative, qualitative, mixed methods). |
| Sample Size | The number of participants or data points in the study. |
| Sample Characteristics | The demographics or specifics of the participants (e.g., SMEs, IT managers, business strategists). |
| Data Collection Methods | Techniques used to gather data (e.g., interviews, surveys, observations, document analysis). |
| Data Analysis Techniques | The methods used for analyzing data (e.g., statistical analysis, thematic analysis). |
| IT Performance Metrics | Measurements of IT success (e.g., alignment with business goals, resource efficiency). |
| Business Performance Metrics | Indicators of business success (e.g., operational efficiency, revenue growth). |
| Organizational Outcomes | Effects on the organization (e.g., employee satisfaction, customer satisfaction). |
| Long-term Impacts | The sustained outcomes for the business (e.g., business sustainability, competitive advantage). |
| Step | Description | Details |
|---|---|---|
| Risk of Bias Tool | Newcastle-Ottawa Scale (NOS) tailored to non-randomized studies | Focused on the quality of study groups, group comparability, and outcome ascertainment |
| Bias Domains | Three critical domains were assessed | (1) Selection of study groups, (2) Comparability of groups, (3) Ascertainment of outcomes |
| Bias Classification | Studies classified into risk levels based on assessment | Low, Moderate, High, or Unclear risk of bias |
| Consensus Process | Discrepancies resolved through discussions | A fourth reviewer was consulted if consensus could not be reached among the three initial reviewers |
| Outcome | Provided thorough, reliable evaluation of bias | Ensured transparency in the risk of bias assessments and validity of the study findings on IT and SMEs |
| QA | Research Quality Assessment Questions |
|---|---|
| QA1 | Does the study clearly define the IT strategic planning process? |
| QA2 | Are the performance metrics used to measure SME success well-defined and relevant? |
| QA3 | Is there evidence of a robust methodology for data collection and analysis? |
| QA4 | Does the research account for potential biases and limitations in its findings? |
| QA5 | How well does the study relate its findings to existing literature and theoretical frameworks? |
| Ref. | QA1 | QA2 | QA3 | QA4 | QA5 | Total | % grading |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1,4,13,15,17,20,23,25,40,62] | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 2.5 | 50% |
| [3,7,11,41,44,47,57,65,66,75,76] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 3 | 60% |
| [8,9,10,19,26,30,31,38,45,46,48,49,52,53,54,55,56,59,60,64,73,74,79] | 1 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 0.5 | 1 | 3.5 | 70% |
| [2,14,18,24,27,28,29,32,33,34,35,36,37,39,50,51,58,61,80] | 0.5 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 4 | 80% |
| [5,6,16,21,42,68,71] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 0.5 | 4.5 | 90% |
| [12,22,43,63,67,69,70,72,77,78] | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 5 | 100% |
| Challenge | Recommendation | Proposed Actionable Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Limited Financial Resources | Prioritize cloud-based solutions to offer flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. | - Shift non-critical IT functions to cloud-based platforms to reduce upfront hardware costs.- Use pay-as-you-go models to match the company’s growth stage and avoid large initial investments. |
| Lack of Technical Expertise | Leverage outsourced IT services by partnering with third-party providers for IT support. | - Engage with managed IT service providers to handle technical tasks such as cybersecurity and data management.- Conduct periodic reviews of outsourced services to ensure alignment with business goals. |
| Resource Optimization | Implement IT Resource Planning tools using software to track and optimize resource usage. | - Adopt project management and IT resource allocation tools (e.g., Trello, Asana) to track project timelines and resources.- Regularly assess IT asset utilization to reduce inefficiencies. |
| Adapting to Market Dynamics | Focus on Agile IT Strategies like implementing flexible IT plans that can adapt to market changes. | - Incorporate agile methodologies to quickly adjust IT infrastructure to market trends.- Regularly update IT plans based on current business performance and external market signals. |
| Technology Integration | Adopt scalable technologies that can grow with the business. | - Start with basic versions of essential technologies (e.g., CRM, ERP) and upgrade as the business expands.- Regularly review emerging technologies (e.g., AI, blockchain) for potential future integration. |
| Employee Training and Retention | Develop continuous IT Training programs to build internal capabilities for IT strategy execution. | - Organize regular IT training for employees to improve internal expertise.- Utilize free or low-cost online training platforms like Coursera, Udemy, and LinkedIn Learning to keep staff up to date. |
| Compliance and Regulatory Changes | Automate Compliance Monitoring by using softwares to track regulatory compliance. | - Invest in compliance monitoring tools that automatically update according to changes in regulations.- Train staff on the latest regulatory requirements and cybersecurity best practices. |
| Innovation and Competitiveness | Utilize data analytics by invest in data-driven decision-making to stay competitive. | - Implement affordable data analytics tools (e.g., Power BI, Tableau) to track key performance indicators.- Use predictive analytics for demand forecasting and identifying market trends. |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





