Submitted:
12 September 2024
Posted:
13 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patient Selection
2.2. Statistical Analysis
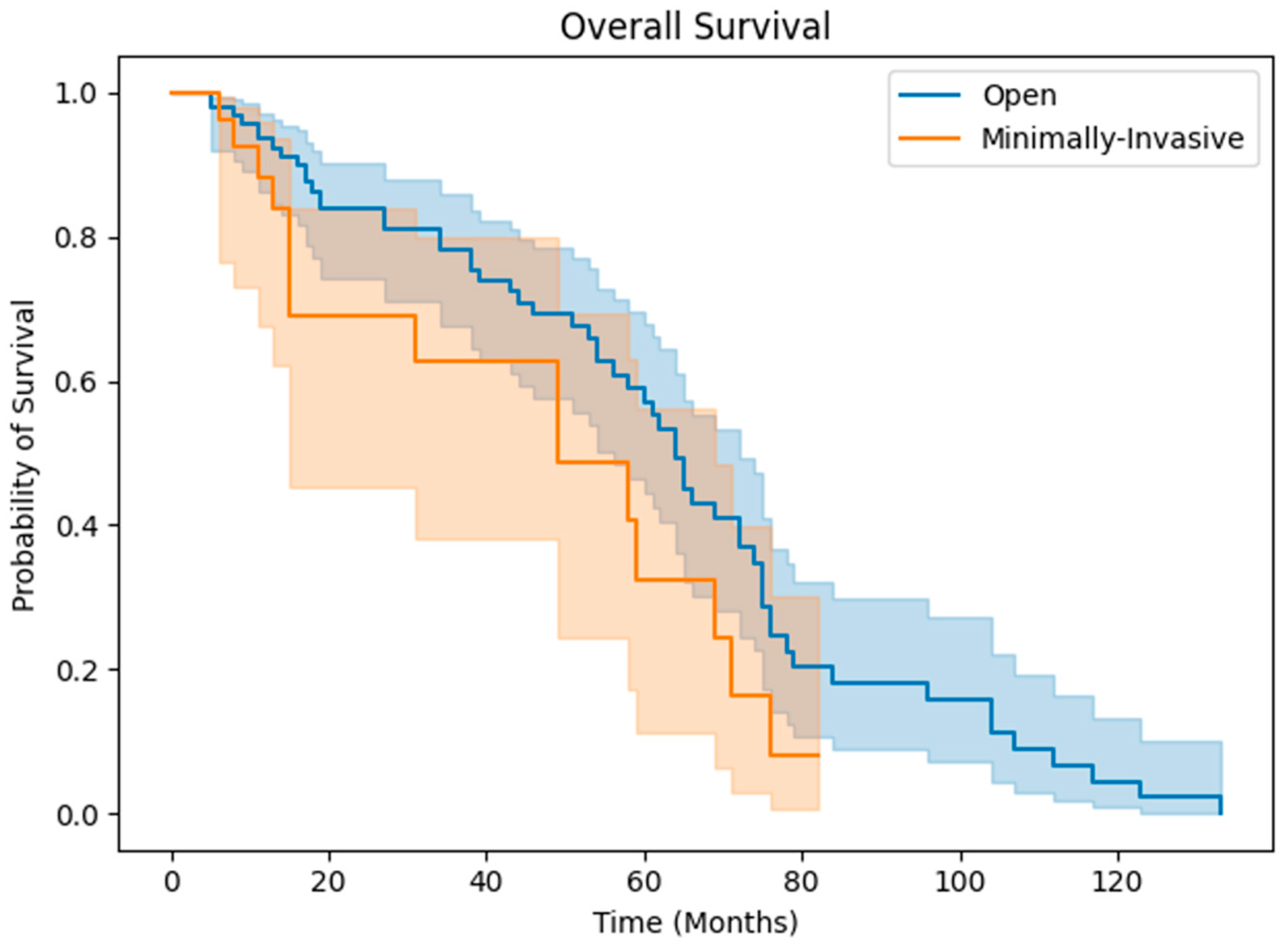
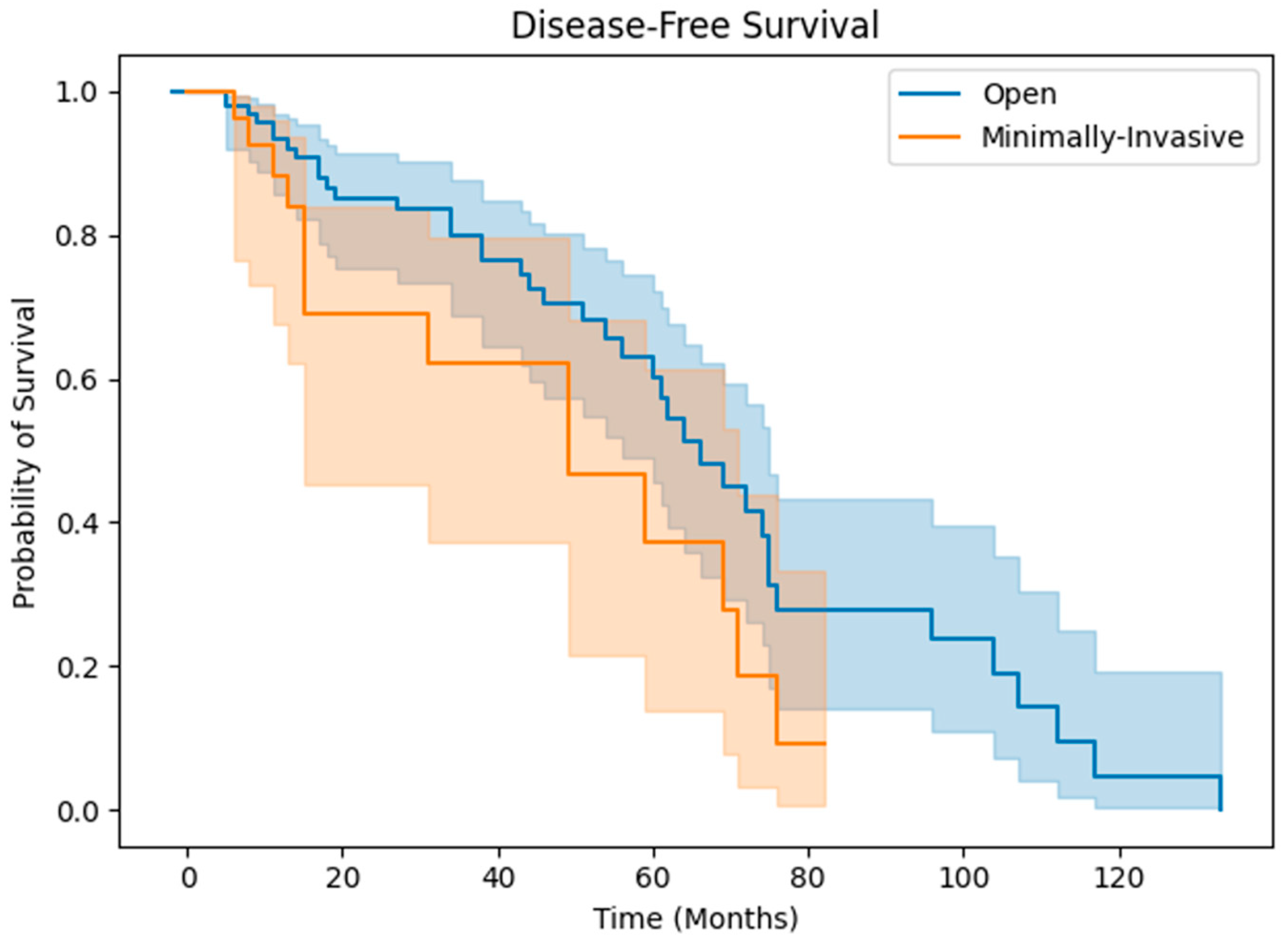
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
3.2. Clinical Outcomes
4. Discussion
Limitations
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Polyzos SA, Chrysavgis L, Vachliotis ID, Chartampilas E, Cholongitas E. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease and hepatocellular carcinoma:Insights in epidemiology, pathogenesis, imaging, prevention and therapy. Semin Cancer Biol. 2023 Aug;93:20-35. [CrossRef]
- Rumgay H, Arnold M, Ferlay J, Lesi O, Cabasag CJ, Vignat J, Laversanne M, McGlynn KA, Soerjomataram I. Global burden of primary liver cancer in 2020 and predictions to 2040. J Hepatol. 2022 Dec;77(6):1598-1606. [CrossRef]
- Villanueva A. Hepatocellular Carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2019;380(15):1450-1462. [CrossRef]
- European Association for the Study of the Liver. Electronic address: easloffice@easloffice.eu; European Association for the Study of the Liver. EASL Clinical Practice Guidelines: Management of hepatocellular carcinoma [published correction appears in J Hepatol. 2019 Apr;70(4):817. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2019.01.020]. J Hepatol. 2018;69(1):182-236. [CrossRef]
- Forner A, Reig M, Bruix J. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Lancet. 2018;391(10127):1301-1314. [CrossRef]
- Gordan J.D., Kennedy E.B., Abou-Alfa G.K., Beg M.S., Brower S.T., Gade T.P., Goff L., Gupta S., Guy J., Harris W.P., et al. Systemic Therapy for Advanced Hepatocellular Carcinoma: ASCO Guideline. J. Clin. Oncol. 2020;38:4317–4345. [CrossRef]
- Llovet J.M., Kelley R.K., Villanueva A., Singal A.G., Pikarsky E., Roayaie S., Lencioni R., Koike K., Zucman-Rossi J., Finn R.S. Hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers. 2021;7:6. [CrossRef]
- Sapisochin G., Bruix J. Liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Outcomes and novel surgical approaches. Nat. Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017;14:203–217. [CrossRef]
- Vitale A., Trevisani F., Farinati F., Cillo U. Treatment of Hepatocellular Carcinoma in the Precision Medicine Era: From Treatment Stage Migration to Therapeutic Hierarchy. Hepatology. 2020;72:2206–2218. [CrossRef]
- Di Sandro S., Benuzzi L., Lauterio A., Botta F., De Carlis R., Najjar M., Centonze L., Danieli M., Pezzoli I., Rampoldi A., et al. Single Hepatocellular Carcinoma approached by curative-intent treatment: A propensity score analysis comparing radiofrequency ablation and liver resection. Eur. J. Surg. Oncol. 2019;45:1691–1699. [CrossRef]
- Vogel A., Martinelli E., ESMO Guidelines Committee Updated treatment recommendations for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) from the ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines. Ann. Oncol. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Reich H, McGlynn F, DeCaprio J, Budin R. Laparoscopic excision of benign liver lesions. Obstet Gynecol. 1991;78(5 Pt 2):956-958.
- Wakabayashi G., Cherqui D., Geller D.A., Buell J.F., Kaneko H., Han H.S., Asbun H., O’Rourke N., Tanabe M., Koffron A.J., et al. Recommendations for laparoscopic liver resection: A report from the second international consensus conference held in Morioka. Ann. Surg. 2015;261:619–629. [CrossRef]
- Bagante F, Spolverato G, Strasberg SM, et al. Minimally Invasive vs. Open Hepatectomy: a Comparative Analysis of the National Surgical Quality Improvement Program Database. J Gastrointest Surg. 2016;20(9):1608-1617. [CrossRef]
- Cho JY, Han HS, Yoon YS, Shin SH. Feasibility of laparoscopic liver resection for tumors located in the posterosuperior segments of the liver, with a special reference to overcoming current limitations on tumor location. Surgery. 2008;144(1):32-38. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen KT, Marsh JW, Tsung A, Steel JJL, Gamblin TC, Geller DA. Comparative Benefits of Laparoscopic vs Open Hepatic Resection: A Critical Appraisal. Arch Surg. 2011;146(3):348–356. [CrossRef]
- Simillis C., Constantinides V.A., Tekkis P.P., Darzi A., Lovegrove R., Jiao L., Antoniou A. Laparoscopic versus open hepatic resections for benign and malignant neoplasms—A meta-analysis. Surgery. 2007;141:203–211. [CrossRef]
- Morino M., Morra I., Rosso E., Miglietta C., Garrone C. Laparoscopic vs. open hepatic resection: A comparative study. Surg. Endosc. 2003;17:1914–1918. [CrossRef]
- Dagher I., Di Giuro G., Dubrez J., Lainas P., Smadja C., Franco D. Laparoscopic versus open right hepatectomy: A comparative study. Am. J. Surg. 2009;198:173–177. [CrossRef]
- Xiong J.J., Altaf K., Javed M.A., Huang W., Mukherjee R., Mai G., Sutton R., Liu X.B., Hu W.M. Meta-analysis of laparoscopic vs. open liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J. Gastroenterol. 2012;18:6657–6668. [CrossRef]
- Tsung A, Geller DA, Sukato DC, et al. Robotic versus laparoscopic hepatectomy: a matched comparison. Ann Surg. 2014;259(3):549-555. [CrossRef]
- Vigano` L, Ferrero A, Amisano M, Russolillo N, Capussotti L (2013) Comparison of laparoscopic and open intraoperative ultrasonography for staging liver tumours. Br J Surg 100:535–542.
- Cho JY, Han HS, Yoon YS, Shin SH (2008) Experiences of laparoscopic liver resection including lesions in the posterosuperior segments of the liver. Surg Endosc 22:2344–2349. [CrossRef]
- Giulianotti PC, Coratti A, Sbrana F, et al. Robotic liver surgery: results for 70 resections. Surgery. 2011;149(1):29-39. [CrossRef]
- Morise Z. Current status of minimally invasive liver surgery for cancers. World J. Gastroenterol. 2022;28:6090–6098. [CrossRef]
- Takahara T, Wakabayashi G, Beppu T, et al. Long-term and perioperative outcomes of laparoscopic versus open liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma with propensity score matching: a multi-institutional Japanese study. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Sci. 2015;22(10):721-727. [CrossRef]
- Haney CM, Studier-Fischer A, Probst P, et al. A systematic review and meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials comparing laparoscopic and open liver resection. HPB (Oxford). 2021;23(10):1467-1481. [CrossRef]
- Endo Y, Tsilimigras DI, Munir MM, et al. Textbook outcome in liver surgery: open vs minimally invasive hepatectomy among patients with hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastrointest Surg. 2024;28(4):417-424. [CrossRef]
- Okinaga H, Yasunaga H, Hasegawa K, Fushimi K, Kokudo N. Short-Term Outcomes following Hepatectomy in Elderly Patients with Hepatocellular Carcinoma: An Analysis of 10,805 Septuagenarians and 2,381 Octo- and Nonagenarians in Japan. Liver Cancer. 2018;7(1):55-64. [CrossRef]
- Wabitsch S, Haber PK, Ekwelle N, et al. Minimally Invasive Liver Surgery in Elderly Patients-A Single-Center Experience. J Surg Res. 2019;239:92-97. [CrossRef]
- Chan AC, Poon RT, Cheung TT, et al. Laparoscopic versus open liver resection for elderly patients with malignant liver tumors: a single-center experience. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014;29(6):1279-1283. [CrossRef]
- Demiselle J, Duval G, Hamel JF, et al. Determinants of hospital and one-year mortality among older patients admitted to intensive care units: results from the multicentric SENIOREA cohort. Ann Intensive Care. 2021;11(1):35. Published 2021 Feb 17. [CrossRef]
- Duarte VC, Coelho FF, Valverde A, et al. Minimally invasive versus open right hepatectomy: comparative study with propensity score matching analysis. BMC Surg. 2020;20(1):260. Published 2020 Oct 30. [CrossRef]
- Yoon YI, Kim KH, Kang SH, et al. Pure Laparoscopic Versus Open Right Hepatectomy for Hepatocellular Carcinoma in Patients With Cirrhosis: A Propensity Score Matched Analysis. Ann Surg. 2017;265(5):856-863. [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Cecilia D, Cipriani F, Shelat V, et al. Laparoscopic Versus Open Liver Resection for Colorectal Metastases in Elderly and Octogenarian Patients: A Multicenter Propensity Score Based Analysis of Short- and Long-term Outcomes. Ann Surg. 2017;265(6):1192-1200. [CrossRef]
- Clavien PA, Lesurtel M, Bossuyt PM, et al. Recommendations for liver transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an international consensus conference report. Lancet Oncol. 2012;13(1):e11-e22. [CrossRef]
- Heise D, Bednarsch J, Kroh A, et al. Operative Time, Age, and Serum Albumin Predict Surgical Morbidity After Laparoscopic Liver Surgery. Surg Innov. 2021;28(6):714-722. [CrossRef]
- Chen J, Li H, Liu F, Li B, Wei Y. Surgical outcomes of laparoscopic versus open liver resection for hepatocellular carcinoma for various resection extent. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(12):e6460. [CrossRef]
- Choi GH, Kim DH, Kang CM, et al. Is preoperative transarterial chemoembolization needed for a resectable hepatocellular carcinoma?. World J Surg. 2007;31(12):2370-2377. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Q, Tuo F, Li R, et al. Transarterial Chemoembolization Combined With Hepatectomy for the Treatment of Intermediate-Stage Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Front Oncol. 2020;10:578763. Published 2020 Nov 4. [CrossRef]
- Lin CW, Chen YS, Lo GH, et al. Comparison of overall survival on surgical resection versus transarterial chemoembolization with or without radiofrequency ablation in intermediate stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a propensity score matching analysis. BMC Gastroenterol. 2020;20(1):99. Published 2020 Apr 10. [CrossRef]
- Bruix J, Llovet JM, Castells A, et al. Transarterial embolization versus symptomatic treatment in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: results of a randomized, controlled trial in a single institution. Hepatology. 1998;27(6):1578-1583. [CrossRef]
- Bernardi L, Balzano E, Roesel R, et al. Concomitant training in robotic and laparoscopic liver resections of low-to-intermediate difficulty score: a retrospective analysis of the learning curve. Sci Rep. 2024;14(1):3595. Published 2024 Feb 13. [CrossRef]
- Endo T, Morise Z, Katsuno H, et al. Caudal Approach to Laparoscopic Liver Resection-Conceptual Benefits for Repeated Multimodal Treatment for Hepatocellular Carcinoma and Extended Right Posterior Sectionectomy in the Left Lateral Position. Front Oncol. 2022;12:950283. Published 2022 Jul 11. [CrossRef]
- Cho JY, Han HS, Choi Y, et al. Association of Remnant Liver Ischemia With Early Recurrence and Poor Survival After Liver Resection in Patients With Hepatocellular Carcinoma. JAMA Surg. 2017;152(4):386-392. [CrossRef]
- Fukumori D, Tschuor C, Penninga L, Hillingsø J, Svendsen LB, Larsen PN. Learning curves in robot-assisted minimally invasive liver surgery at a high-volume center in Denmark: Report of the first 100 patients and review of literature. Scand J Surg. 2023;112(3):164-172. [CrossRef]
| Characteristics | Open (n=109) | Minimally-Invasive (n=29) | P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sex, n (%) | 0.112 | ||
| Male | 72 (66.1) | 24 (82.8) | |
| Female | 37 (33.9) | 5 (17.2) | |
| Age (year), mean (SD) | 60.1 (13.4) | 66.9 (12.1) | 0.015 |
| Race, n (%) | 0.070 | ||
| White | 46 (42.2) | 14 (48.3) | |
| Black | 49 (45.0) | 11 (37.9) | |
| Asian | 14 (12.8) | 2 (6.9) | |
| Hispanic | 0 (0) | 1 (3.4) | |
| Other | 0 (0) | 1 (3.4) | |
| WBC (x109/L), mean (SD) | 6.8 (2.4) | 5.8 (2.0) | 0.059 |
| PLT (x109/L), n (%) | 0.828 | ||
| <225 | 72 (66.1) | 20 (69.0) | |
| ≥225 | 37 (33.9) | 9 (31.0) | |
| ALT (U/L), n (%) | 0.648 | ||
| <80 | 76 (70.4) | 22 (75.9) | |
| ≥80 | 32 (29.6) | 7 (24.1) | |
| Serum Sodium (mmol/L), mean (SD) | 139.0 (3.1) | 140.0 (2.6) | 0.125 |
| Serum Creatinine (μmol/L), mean (SD) | 0.9 (0.3) | 1.0 (0.5) | 0.042 |
| TBIL (μmol/L), mean (SD) | 0.8 (0.7) | 0.8 (0.5) | 0.750 |
| INR, mean (SD) | 1.1 (0.3) | 1.1 (0.1) | 0.511 |
| AFP (ng/mL), mean (SD) | 0.039 | ||
| <200 | 76 (74.5) | 27 (93.1) | |
| ≥200 | 26 (25.5) | 2 (6.9) | |
| MELD-XI, mean (SD) | 8.7 (3.5) | 8.8 (2.8) | 0.852 |
| Cirrhosis, n (%) | 96 (88.1) | 23 (79.3) | 0.233 |
| Prior cancer, n (%) | 15 (13.8) | 5 (17.4) | 0.767 |
| Preoperative therapy, n (%) | 0.732 | ||
| No therapy | 79 (73.1) | 24 (82.8) | |
| TACE only | 19 (17.6) | 2 (6.9) | |
| RFA only | 3 (2.8) | 1 (3.4) | |
| Radiation only | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0) | |
| Resection only | 1 (0.9) | 0 (0) | |
| Combination | 5 (4.6) | 2 (6.9) | |
| Tumor number | 0.045 | ||
| ≤3 | 88 (80.7) | 28 (96.6) | |
| >3 | 21 (19.3) | 1 (3.4) | |
| Largest tumor size (cm) | 5.6 (4.3) | 4.3 (3.3) | 0.138 |
| Total tumor size (cm) | 7.3 (5.2) | 4.9 (4.1) | 0.031 |
| Tumor differentiation, n (%) | 0.372 | ||
| G1 | 11 (10.7) | 5 (19.2) | |
| G2 | 62 (60.2) | 16 (61.5) | |
| G3 | 30 (29.1) | 5 (19.2) | |
| Microvascular invasion, n (%) | 59 (54.1) | 10 (34.5) | 0.118 |
| Macrovascular invasion, n (%) | 29 (26.6) | 5 (17.2) | 0.460 |
| Lymphatic invasion, n (%) | 5 (4.6) | 1 (3.4) | 1.000 |
| Capsular invasion, n (%) | 69 (63.3) | 18 (62.1) | 0.643 |
| AJCC staging, n (%) | 0.159 | ||
| I-II | 78 (76.5) | 22 (91.7) | |
| III-IV | 24 (23.5) | 2 (8.3) |
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Sex (ref: female) | 0.602 | |||||
| Male | 1.137 | 0.701-1.845 | ||||
| Age (ref: <60) | 0.011 | 0.016 | ||||
| >=60 | 1.891 | 1.156-3.093 | 1.848 | 1.122-3.046 | ||
| WBC (ref: <3.5) | 0.350 | |||||
| >=3.5 | 0.615 | 0.222-1.704 | ||||
| PLT (ref: <225) | 0.778 | |||||
| >=225 | 0.933 | 0.577-1.510 | ||||
| ALT (ref: <80) | 0.634 | |||||
| >=80 | 0.870 | 0.492-1.541 | ||||
| TBIL (ref: <2) | 0.398 | |||||
| >=2 | 1.663 | 0.512-5.402 | ||||
| AFP (ref: <400) | 0.695 | |||||
| >=400 | 0.874 | 0.447-1.711 | ||||
| MELD-XI (ref: <15) | 0.710 | |||||
| >=15 | 1.250 | 0.385-4.051 | ||||
| Cirrhosis | 0.979 | |||||
| Present | 1.008 | 0.565-1.799 | ||||
| Prior TACE | 0.001 | 0.002 | ||||
| No | 0.393 | 0.221-0.698 | 0.398 | 0.222-0.712 | ||
| Prior RFA | 0.077 | |||||
| No | 0.276 | 0.066-1.150 | ||||
| Prior Resection | 0.291 | |||||
| No | 2.147 | 0.520-8.858 | ||||
| Resection Margin (ref: positive) | ||||||
| <10mm | 1.756 | 0.924-3.339 | 0.086 | |||
| >10mm | 1.204 | 0.610-2.379 | 0.593 | |||
| Surgical Technique (ref: open) | 0.072 | |||||
| Lap/Robotic | 1.703 | 0.953-3.044 | ||||
| Tumor Number (ref: <3) | 0.715 | |||||
| >3 | 1.174 | 0.496-2.779 | ||||
| Mean Largest Tumor Size (ref: <5) | 0.135 | |||||
| >=5 | 0.678 | 0.408-1.128 | ||||
| Mean Tumor Size (ref: <10) | 0.471 | |||||
| >=10 | 0.781 | 0.399-1.529 | ||||
| Microvascular Invasion | 0.315 | |||||
| Present | 0.786 | 0.492-1.257 | ||||
| Macrovascular Invasion | 0.349 | |||||
| Present | 0.744 | 0.400-1.382 | ||||
| Lymphatic Invasion | 0.731 | |||||
| Present | 0.706 | 0.097-5.142 | ||||
| Ductal Invasion | 0.714 | |||||
| Present | 0.870 | 0.411-1.838 | ||||
| AJCC Staging (ref: I-II) | 0.307 | |||||
| II-IV | 0.680 | 0.324-1.424 | ||||
| Univariate | Multivariate | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| HR | 95% CI | P-value | HR | 95% CI | P-value | |
| Sex (ref: female) | 0.635 | |||||
| Male | 1.150 | 0.646-2.049 | ||||
| Age (ref: <60) | 0.027 | 0.024 | ||||
| >=60 | 1.918 | 1.076-3.418 | 1.982 | 0.169-0.712 | ||
| WBC (ref: <3.5) | 0.302 | |||||
| >=3.5 | 0.533 | 0.162-1.759 | ||||
| PLT (ref: <225) | 0.643 | |||||
| >=225 | 0.876 | 0.500-1.534 | ||||
| ALT (ref: <80) | 0.606 | |||||
| >=80 | 0.834 | 0.418-1.663 | ||||
| TBIL (ref: <2) | 0.514 | |||||
| >=2 | 1.613 | 0.383-6.792 | ||||
| AFP (ref: <400) | 0.547 | |||||
| >=400 | 0.792 | 0.370-1.693 | ||||
| MELD-XI (ref: <15) | 0.745 | |||||
| >=15 | 0.719 | 0.098-5.263 | ||||
| Cirrhosis | 0.883 | |||||
| Present | 1.052 | 0.536-2.063 | ||||
| Prior TACE | 0.004 | 0.004 | ||||
| No | 0.360 | 0.178-0.727 | 0.347 | 0.169-0.712 | ||
| Prior RFA | 0.130 | |||||
| No | 0.216 | 0.030-1.572 | ||||
| Prior Resection | 0.269 | |||||
| No | 2.234 | 0.536-9.306 | ||||
| Resection Margin (ref: positive) | ||||||
| <10mm | 1.928 | 0.908-4.093 | 0.087 | |||
| >10mm | 1.135 | 0.485-2.657 | 0.770 | |||
| Surgical Technique (ref: open) | 0.060 | |||||
| Lap/Robotic | 1.815 | 0.975-3.379 | ||||
| Tumor Number (ref: <3) | 0.893 | |||||
| >3 | 0.931 | 0.330-2.631 | ||||
| Mean Largest Tumor Size (ref: <5) | 0.098 | |||||
| >=5 | 0.589 | 0.315-1.103 | ||||
| Mean Tumor Size (ref: <10) | 0.310 | |||||
| >=10 | 0.620 | 0.246-1.562 | ||||
| Microvascular Invasion | 0.405 | |||||
| Present | 0.794 | 0.461-1.366 | ||||
| Macrovascular Invasion | 0.590 | |||||
| Present | 0.824 | 0.407-1.667 | ||||
| Lymphatic Invasion | 0.756 | |||||
| Present | 0.730 | 0.100-5.335 | ||||
| Ductal Invasion | 0.728 | |||||
| Present | 0.858 | 0.362-2.033 | ||||
| AJCC Staging (ref: I-II) | 0.181 | |||||
| II-IV | 0.497 | 0.179-1.383 | ||||
| Open (n=109) | Minimally-Invasive (n=29) | P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| LOS (days), mean (STD) | 8.8 (5.7) | 5.4 (2.9) | 0.003 |
| Operation time (minutes), mean (STD) | 338.8 (129.1) | 261.0 (101.2) | 0.004 |
| Transfusion | 0.317 | ||
| Yes | 25 | 4 | |
| No | 82 | 25 | |
| Transfusion amount, median (IQR) | 1161.6 (788.4) | 700.0 (285.8) | 0.263 |
| Resection Margin | 0.392 | ||
| Negative <10mm, n (%) | 55 (54.5) | 11 (44.0) | |
| Negative >10mm, n (%) | 30 (29.7) | 11 (44.0) | |
| Positive, n (%) | 16 (15.8) | 3 (12.0) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





