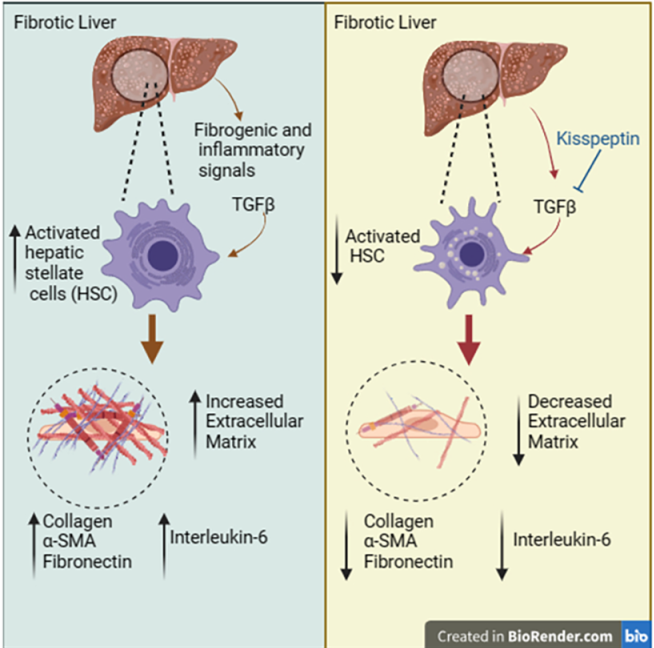
The peptide hormone kisspeptin attenuates liver steatosis, metabolic dysfunction-associated stea-tohepatitis (MASH) and fibrosis in mouse models, by signaling via the kisspeptin 1 receptor (KISS1R). However, whether kisspeptin impacts fibrogenesis in the human liver is not known. We investigated the impact of a potent kisspeptin analog (KPA) on fibrogenesis using human precision cut liver slices (hPCLS) from fibrotic livers from male patients, in human hepatic stellate cells (HSCs), LX-2 and in primary mouse HSCs. In hPCLS, 48 h and 72 h of KPA (3 nM, 100 nM) treatment decreased collagen secretion, and lowered expression of fibrogenic and inflammatory markers. Immunohistochemical studies revealed that KISS1R is expressed and localized to HSCs in MASH/fibrotic livers. In HSCs, KPA treatment reduced transforming growth factor beta (TGFb)-induced expression of fibrogenic and inflammatory markers, in addition to decreasing TGFb induced collagen secretion, cell migration, proliferation and colony formation. Mechanistically, KISS1R signaling downregulated TGFb signaling by decreasing SMAD2/3 phosphorylation, via activation of protein-phosphatases PP2A, that dehosphorylates SMAD 2/3. This study revealed for the first time that kisspeptin reverses human hepatic fibrogenesis thus identifying it as a new therapeutic target to treat hepatic fibrosis.