1. Introduction
Oral biofilms are biological communities formed on the tooth surface by oral microorganisms, causing oral diseases such as dental caries and periodontal disease. As oral microorganisms metabolize nutrients remaining in the oral cavity after eating, biofilms are formed by adhesion, proliferation, and aggregation on the tooth surface [
1,
2]. When this biofilm is formed, the microorganisms within it are resistant to antibacterial substances, giving them an opportunity to survive in the oral cavity for a long time [
3,
4]. In recent years, aspiration pneumonia as a cause of death, has surpassed cerebrovascular diseases [
5]. Oral and pharyngeal microorganisms are considered the causative agents of pneumonia [
6]. In developed countries, the ratio of elderly people is increasing due to the declining birth rate and aging population, and the number of bedridden elderly people is increasing [
7]. These bedridden elderly people have an increased number of opportunistic pathogens such as
Staphylococcus aureus and
Candida albicans in their oral biofilms [
7,
8].
S. aureus, also detected in the oral cavity, has been reported as a cause of infective endocarditis and pneumonia [
9,
10]. In addition,, immunocompromised hosts, such as those with diabetes and HIV-positive patients, are infected by
S. aureus and are at risk for the development of systemic diseases.
Salt (NaCl and KCl) is used to flavor food, and it is also an essential mineral component necessary for the maintenance of cells in the human body. Ethnic groups in many countries effectively utilize salt in their diets. NaCl exhibits bactericidal properties when it reaches a certain concentration. In the days when there was no toothpaste, NaCl was used directly to brush the teeth. However, recent research has reported that NaCl promotes biofilm formation [
11]. Salt is sometimes used in oral rinses and toothpastes to remove accumulated oral biofilms [
12]. It has been reported that this biofilm formation is promoted in media containing a certain concentration of NaCl [
13]. This phenomenon is considered dependent on salt concentration but a detailed mechanism has not been clarified. This may be associated with the ability of
S. aureus to survive under harsh conditions, including salinity, as it is a salt-resistant bacterium.
The biofilm formed by
S. mutans, a pathogen of dental caries
, is constructed of insoluble and soluble glucans induced by the principal enzymes GtfB and GtfC under sucrose-containing conditions [
14]. GtfB and GtfC are important virulence factors that strongly adhere to oral bacteria, aggregating and generating acidic conditions [
15,
16]. Gram-negative and Gram-positive bacteria usually produce membrane vesicles (MVs) during growth. Nucleotides, proteins, lipids, lipopolysaccharides (LPS), peptide glycans (PG), lipoproteins, and enzymes such as GTFs, which are toxic factors (toxins), are associated with MVs [
17,
18]. MVs are produced abundantly by bacteria in natural environments and promote bacteria and their interactions with their growth environment [
19]. Therefore, MVs play an important role in communication between bacterial cells and are responsible for microbial interactions in host cells [
20,
21,
22,
23]. MVs, including GtfC, promote the glucan-dependent formation of biofilms by the initial oral colonizers on tooth surfaces and which are employed for cell-to-cell communication and transition from nonvirulent to new pathogenic bacteria [
16,
24,
25,
26].
Extracellular DNA contributes to the development of biofilm formation and plays an important role in bacterial adhesion and aggregation on surfaces in the initial stage of biofilm formation [
27,
28]. Previous reports have shown that the absence of glucan and the presence of eDNA induce significant
S. mutans biofilm formation on human saliva-coated hydroxyapatite disks under raffinose-supplemented conditions [
16,
29]. eDNA may be required for the initial attachment and colonization of
S. aureus on the surface and for biofilm formation by a mixture of
S. aureus and other bacterial species.
Various important factors such as MVs, glucan, and eDNA contribute to biofilm formation and may affect the biofilm formation of S. aureus and mixed species of S. aureus and S. mutans under high-salinity conditions. The purpose of this study was to clarify how MVs, glucan and eDNA contribute to the biofilm formation of S. aureus and mix species and to elucidate the role of factors associated with harsh conditions, including NaCl. The study of NaCl under high-salinity conditions is important for the development of biofilm for patients with infectious diseases caused by S. aureus in elderly immunocompromised hosts.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Bacterial Strains and Culture Conditions
The bacterial strains
S. aureus cowan I,
S. mutans UA159 [
24],
S. mutans UA159 and
gtfBC mutant (
gtfBC-) [
25] were maintained and cultured in brain-heart infusion broth (BHI,
including 0.086 M NaCl) (Becton Dickinson and Company, Franklin Lakes, NJ) at 37 °C in an atmosphere containing 5% CO
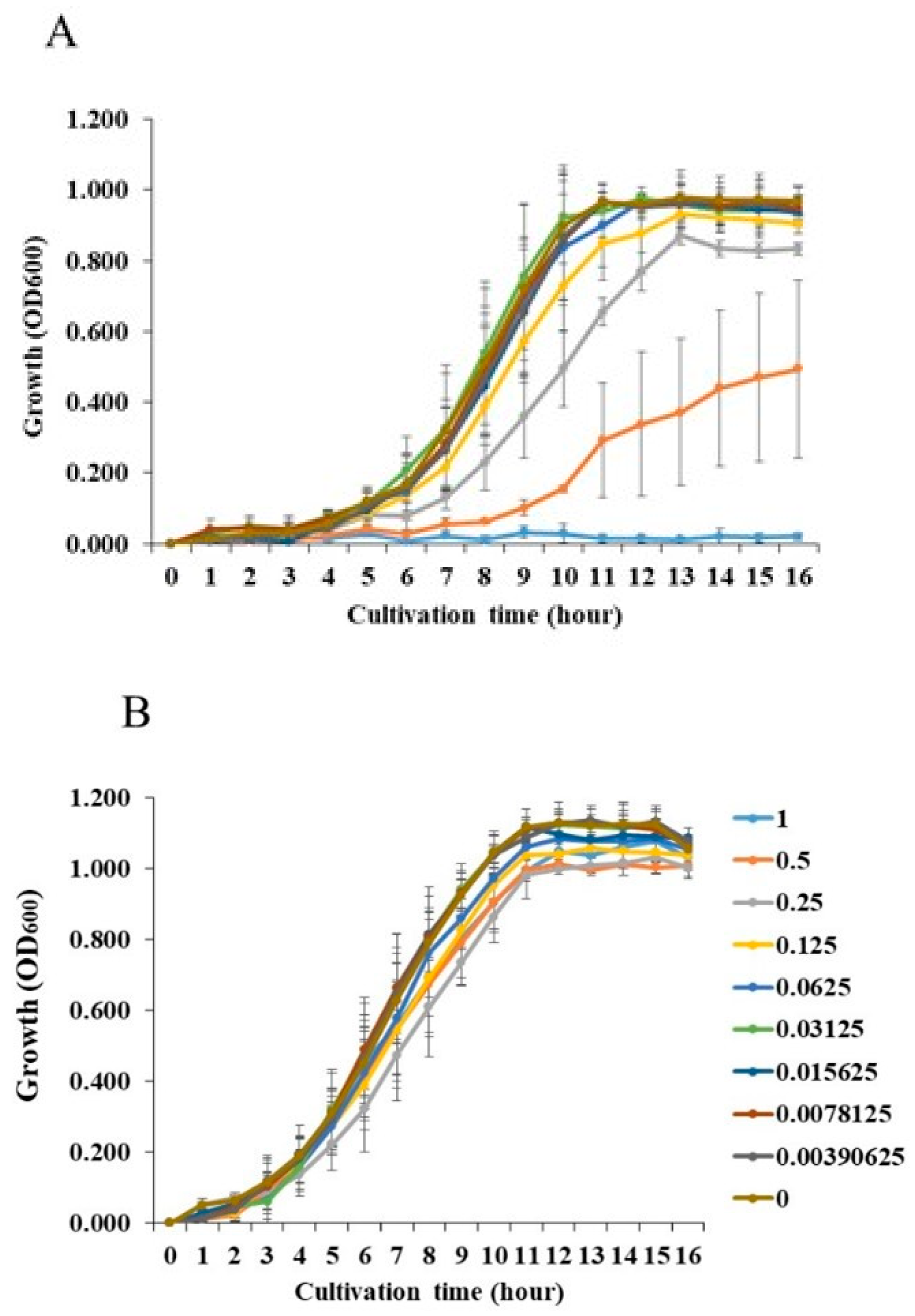
2 (gas pack: Mitsubishi Gas Chemical Co., Inc., Japan). These prepared cells were used in the experiments. The growth of
S. aureus and
S. mutans was measured as turbidity in BHI with and without various concentrations of NaCl by absorbance at 600 nm.
2.2. Human Saliva Collection
S. mutans was cultivated in 1,000 ml of BHI broth at 37 °C overnight in an atmosphere containing 5% CO
2. The preparation of MVs was performed as described previously with some modifications [
16]. The culture supernatants were separated with centrifugation (6,000 ×
g for 20 min) and concentrated to >50 kDa (Amicon Ultra 4, Merck kGaA, Darmstadt, Germany or VIVASPIN 20, Sartorius, Stone House, United Kingdom). Briefly, the concentrated MVs were filtered through polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filter membranes (Merck kGaA) with pore sizes of 0.45 and 0.22 μm. The MV samples were ultracentrifuged (150,000 ×
g at 4 °C for 2 h) and the pellets resuspended in 200 μl of sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.2). The suspended samples were called MVs and were used for the following experiments. The MV protein concentration was determined using a Bio-Rad protein assay kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., CA). GTFs are mainly expressed in MVs [
26].
2.3. Extraction of MVs
S. mutans was cultivated in 1,000 ml of BHI broth (control,
pH 7.4); BHI broth, pH 6.0, prepared with HCl (HC), lactic acid (LA) and acetic acid (AA), separately; and BHI broth, pH 8.0, prepared with NaOH (NO) at 37°C overnight in an atmosphere containing 5% CO
2. The initial cell densities was 1.5 x 10
8 and the final cell densities was 1.5 x 10
11 in 1000 ml. The preparation of MVs was performed as described previously with some modifications [
11]. Culture supernatants were separated by centrifugation (6,000 ×
g for 20 min) and concentrated to >50 kDa by centrifugal filtration (Amicon Ultra 4, Merck kGaA, Darmstadt, Germany or VIVASPIN 20, Sartorius, Stone House, United Kingdom). Briefly, the concentrated MVs were filtered through polyvinylidene difluoride (PVDF) filter membranes (Merck kGaA) with pore sizes of 0.45 and 0.22 μm. The MV samples were centrifuged (150,000 ×
g for 2 h) by a Beckman SW 41 Ti swinging bucket rotor using a Beckman optima L-90k ultracentrifuge (Beckman Coulter, South Kraemer Boulevard, CA), and the pellets were suspended in sterile phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; pH 7.2). The samples were also ultracentrifuged (150,000×
g at 4°C for 2 h), and the pellets were resuspended in 200 μl of sterile PBS as the sample. The suspended samples were called MVs and were used for the following experiments. The MV protein concentration was determined using a Bio-Rad Protein Assay kit (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Inc., CA).
2.4. Biofilm Formation Assay
Biofilms from each strain were developed in 96-well polystyrene microtiter plates (Sumitomo Bakelite) previously coated with human saliva. Biofilm formation assays were performed using a modified procedure [
30]. Overnight cultures of
S. aureus cowan I,
S. mutans UA159, and
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- in BHI broth were inoculated at a ratio of 1:100 in 200 µl of tryptic soy broth (TSB,
including 0.086 M NaCl) with 0.25% sucrose (TSBs) or 0.25% glucose (TSBg) with and without 0.25 μg/ml of MVs and with various concentrations of NaCl. This concentration of MVs was confirmed for the activity to the development of biofilm formation by previous paper [
31]. Single cultures of
S. aureus and
S. mutans, and mixed bacterial cultures of
S. aureus and
S. mutans UA159 or UA159.
gtfBC- were tested under various concentrations of NaCl. TSBs and TSBg was used to observe the glucan-dependent and -independent biofilm formation, respectively. To observe the contribution of extracellular DNA (eDNA) to MV-dependent biofilm formation, 50 units/ml DNase I (Roche Applied Science, Mannheim, Germany) were added to the biofilm formation assay under 0.25 M NaCl conditions. The plates were incubated at 37 °C in 5% CO
2 aerobic conditions for 16 h. After incubation, the planktonic cells were removed by washing with distilled water (DW) and the adherent cells were stained with 0.25% safranin for 15 min to determine the level of biofilm formation [
30]. After washing twice with DW, safranin was extracted from the biofilms with 70% (vol/vol) ethanol. Biofilm formation was quantified by measuring the absorbance of the stained biofilms at 492 nm.
2.5. Observations of Live Cells and Glucan in Biofilm Formation
Biofilms were stained with the FilmTracer Live/Dead Biofilm Viability Kit (Molecular Probes, Inc., Eugene, OR), with SYTO 9 and propidium iodide added to the biofilms at a final concentration of 5 µM, respectively. The glucan-dependent polysaccharides were labeled with an Alexa Fluor 647-dextran conjugate (Molecular Probes, Invitrogen Corp., Carlsbad, CA) (Koo, et al., 2010) for red fluorescence, while the nucleic acids in the bacterial cells were labeled with SYTO 9 to produce green fluorescence.
The biofilms were incubated with the dyes at room temperature for 20–40 min before being imaged using an LSM700 Meta NLO confocal laser scanning microscopy (CLSM) system (Carl Zeiss Inc., Jena, Germany). The biofilms were observed using CLSM, and two-dimensional (2D) images were acquired with a Plan-Apochromat 10x/0.45M27 lens objective. Confocal images of biofilm formation were evaluated using ZEN (Carl Zeiss) analysis software.
2.6. Statistical Analysis
Biofilm formation levels are expressed as mean ± standard deviation (SD). In the biofilm assay the statistical significance of differences between the bacteria with and without various concentrations of NaCl was determined using one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni correction (IBM SPSS statistics 24, IBM Corporation, Armonk, NY). A p value less than 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All experiments were repeated independently three times.
3. Results
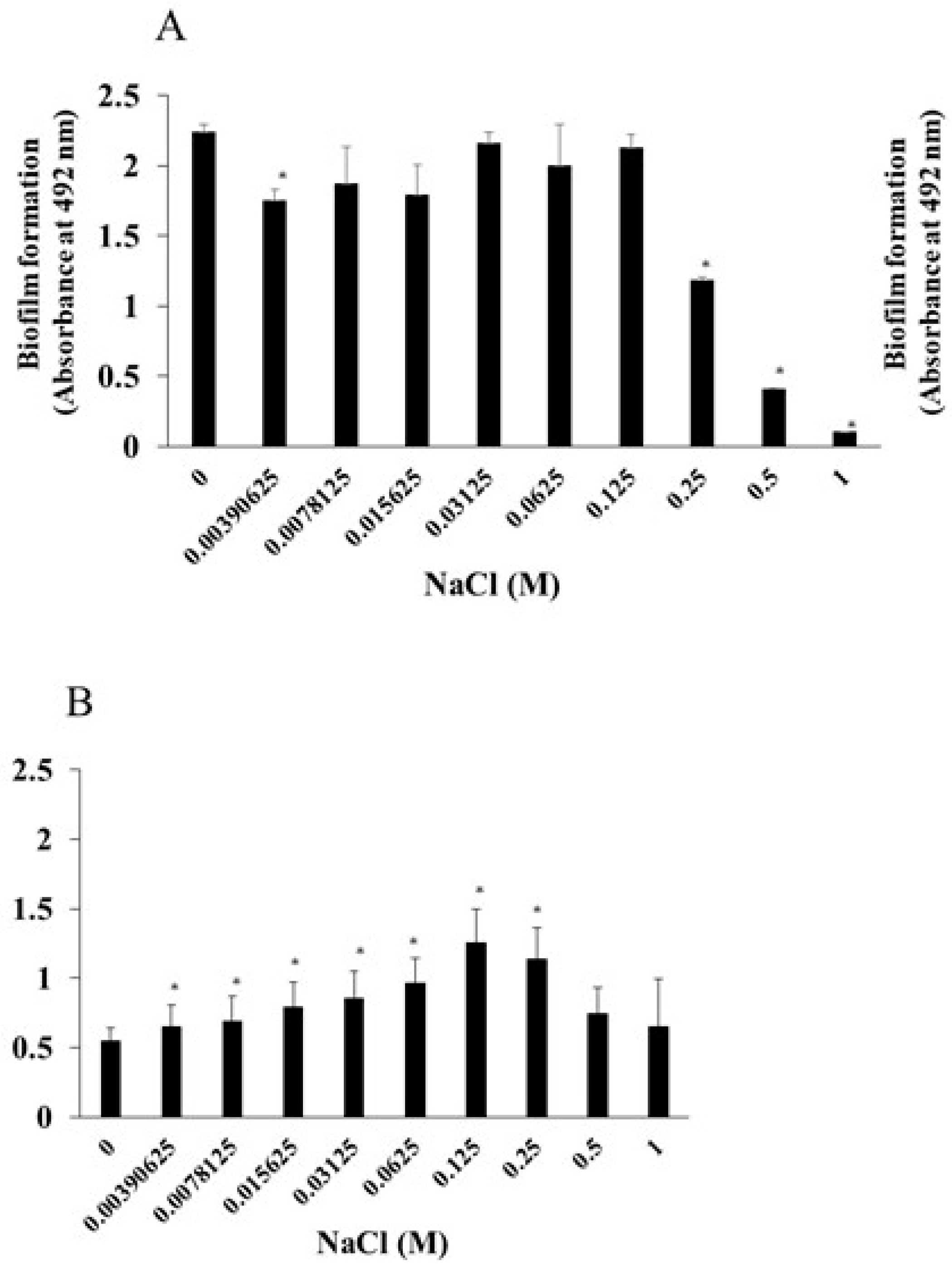
3.2. Effects of NaCl on the Biofilm Formation of Mixed Bacteria
As a next step, bacterial mixtures of
S. aureus and
S. mutans were used for the biofilm formation assay in the presence of NaCl. TSB with sucrose or glucose was used for cultivation to determine the effects of NaCl on mixed-species biofilms of
S. aureus and
S. mutans in which glucan is contained or not.
S. aureus was mixed with
S. mutans or
S. mutans UA159
gtfBC- lacking GtfB and GtfC, which are enzymes for synthesizing insoluble glucan, and applied to human saliva-coated 96-well microtiter plates in TSBs or TSBg containing various concentrations of NaCl. More than 0.125 M NaCl significantly inhibited the biofilm formation of mixed bacteria (
S. mutans and
S. aureus) in TSBs (
Figure 3A). In contrast, biofilm formation was significantly greater with 0.015625 M, 0.03125 M and 0.065 M NaCl than with 0 M NaCl in TSBg (
Figure 3A). More than 0.5 M NaCl significantly decreased biofilm formation by mixed bacteria in TSBg. To completely eliminate water-insoluble glucan synthesis,
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- was used instead of
S. mutans UA159. The biofilm formation of mixed bacteria (
S. aureus and
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC-) gradually increased in a NaCl concentration-dependent manner and peaked at 0.25 M NaCl in TSBs (
Figure 3B). However, greater than 0.5 M NaCl significantly inhibited biofilm formation compared with 0 M NaCl. Moreover, biofilm formation significantly increased at 0.0078125–0.0625 M NaCl in TSBg. Therefore, in the absence of glucan, 0.25 M NaCl significantly induced the biofilm formation of single
S. aureus and mixed bacteria of
S. aureus and
S. mutans in TSBs (
Figure 2B and
Figure 3B).
S. aureus was inoculated with S. mutans UA159 or S. mutans UA159.gtfBC- in TSBs or TSBg with various concentration of NaCl in the biofilm formation assay. The data indicate the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate a significant difference between the two groups (*: p < 0.05, NaCl vs no NaCl).
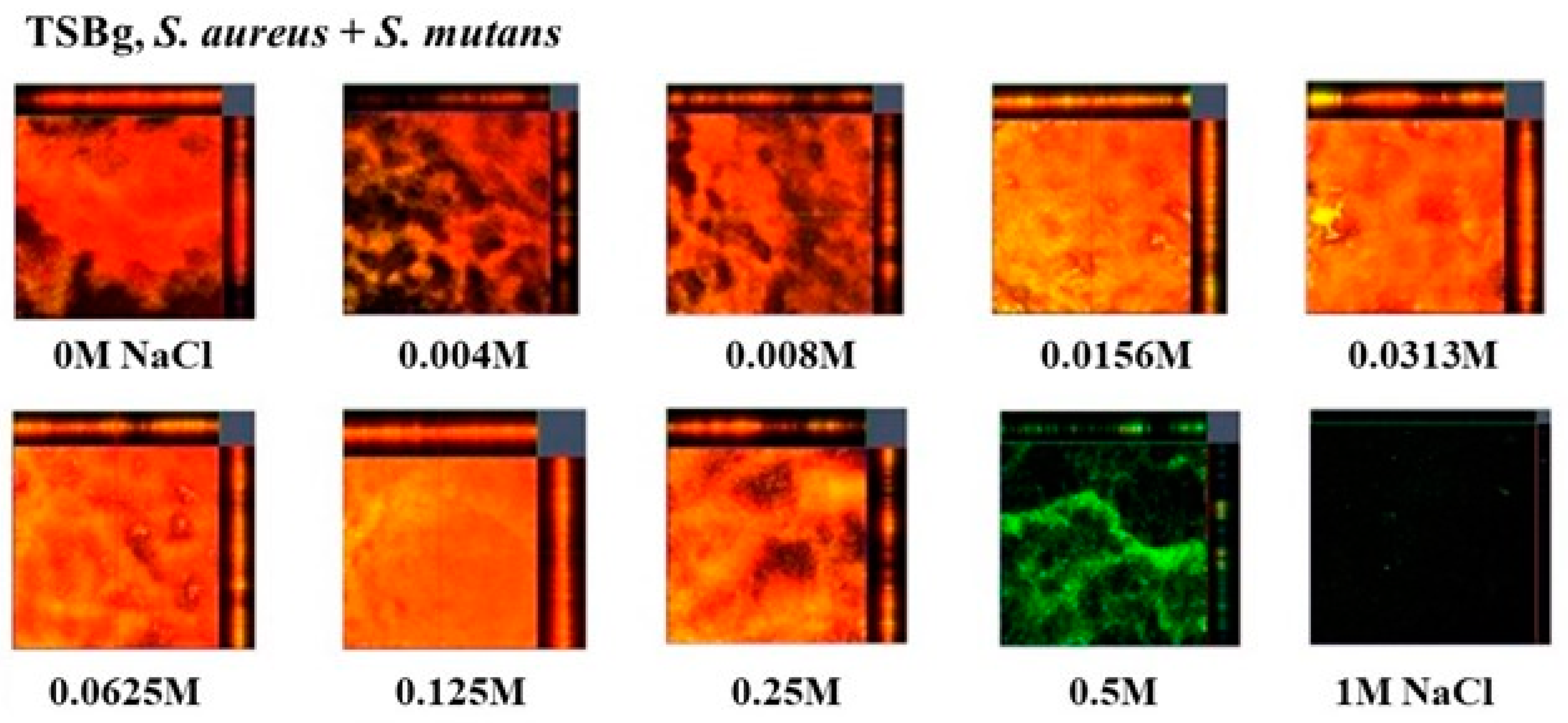
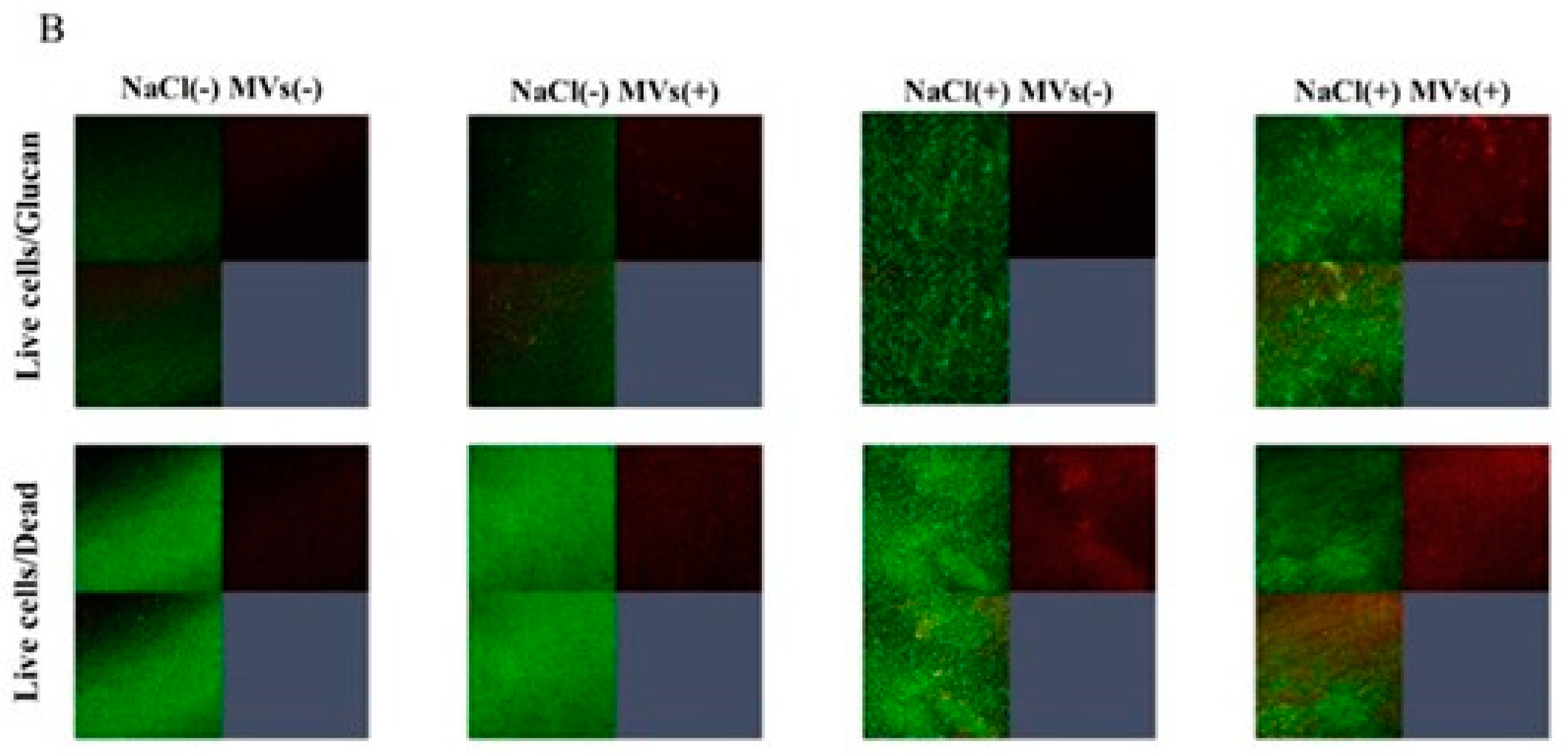
To observe live and dead cells in the biofilms of mixed bacteria of
S. aureus and
S. mutans, a live/dead staining assay was performed in TSBg. Red indicates dead cells, and green indicates live cells. Dead cells were observed in the biofilm formation of mixed bacteria in the presence of 0–0.25 M NaCl (
Figure 4). However, live cells were mainly observed at 0.5 M NaCl. Live and dead cells were not observed at 1 M NaCl. These results indicate that 0.004M-0.25 M NaCl induces dead cell-dependent biofilm formation of mixed bacteria in the condition without glucan. High concentrations (> 0.5 M) inhibited the growth of
S. mutans (
Figure 1A) and did not induce dead cell-dependent biofilm formation in mixtures of
S. aureus and
S. mutans.
S. aureus was inoculated with S. mutans UA159 or S. mutans UA159.gtfBC- in TSBs or TSBg with various concentration of NaCl in the biofilm formation assay. The data indicate the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate a significant difference between the two groups (*: p < 0.05, NaCl vs no NaCl).
3.3. Effects of MVs on the Biofilm Formation
MVs are important for the development of
S. mutans biofilms because MVs are associated with GTFs and induce soluble and insoluble glucan-dependent biofilm formation (Senpuku, et al., 2019). To determine whether MVs with GTFs affect the biofilm formation of
S. aureus, 0.25 μg/ml MVs from
S. mutans were added to
S. aureus in a biofilm formation assay in the presence of 0.25 M NaCl, which was selected to induce highest biofilm in TSBs (
Figure 3B).
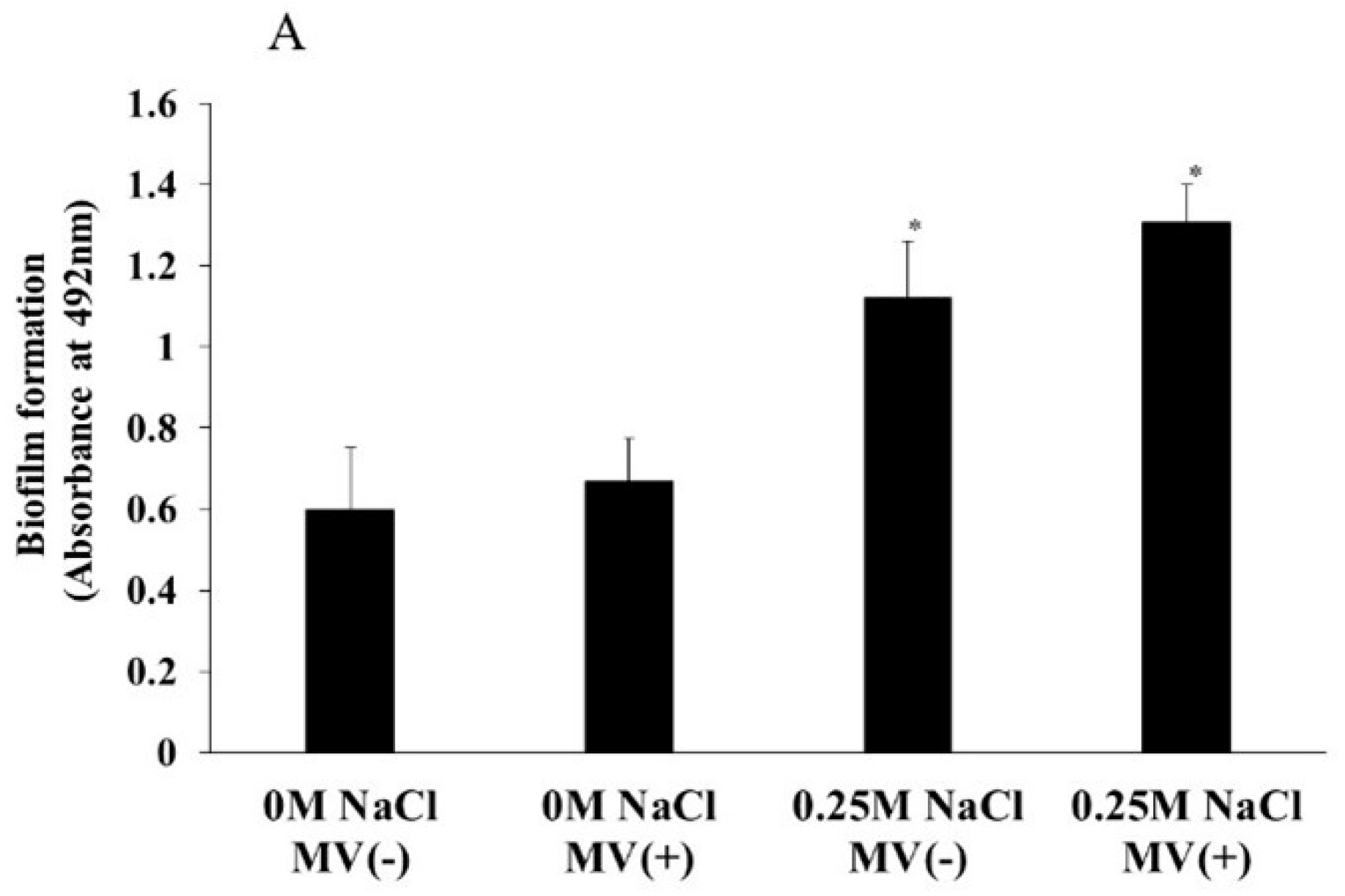
S. aureus biofilm formation was significantly increased by the addition of 0.25 NaCl. The addition of MVs slightly up-regulated the biofilm formation levels in 0.25 M NaCl, but the difference was not significant (
Figure 5A). To observe glucan formation in the biofilm formation assay using
S. aureus with MVs in TSB conditions with 0.25 M NaCl, Alexa Fluor 647-dextran conjugates were added to the assay mixture, and the results were compared with those obtained without MVs. Glucan formation was clearly observed after the addition of MVs in the presence of 0.25 M NaCl (
Figure 5B). Therefore, slight upregulation of the biofilm might be dependent on the presence of glucan in the mixture of
S. aureus and MVs rather than on biofilm formation in the absence of MVs. Compared with those in the absence of 0.25 M NaCl, biofilm formation increased, and the number of dead cells in the presence of 0.25 M NaCl increased (
Figure 5AB). Glucose combines with dead cells and may induce biofilm formation.
S. aureus was inoculated in TSBs with and without 0.25M NaCl in the biofilm formation assay with and without MVs from S. mutans (A). The data indicate the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. The asterisks indicate a significant difference between the two groups (*: p < 0.05, NaCl vs no NaCl). These biofilm formations were observed in confocal microscope (B). Representative data from more than three independent experiments were presented in the pictures.
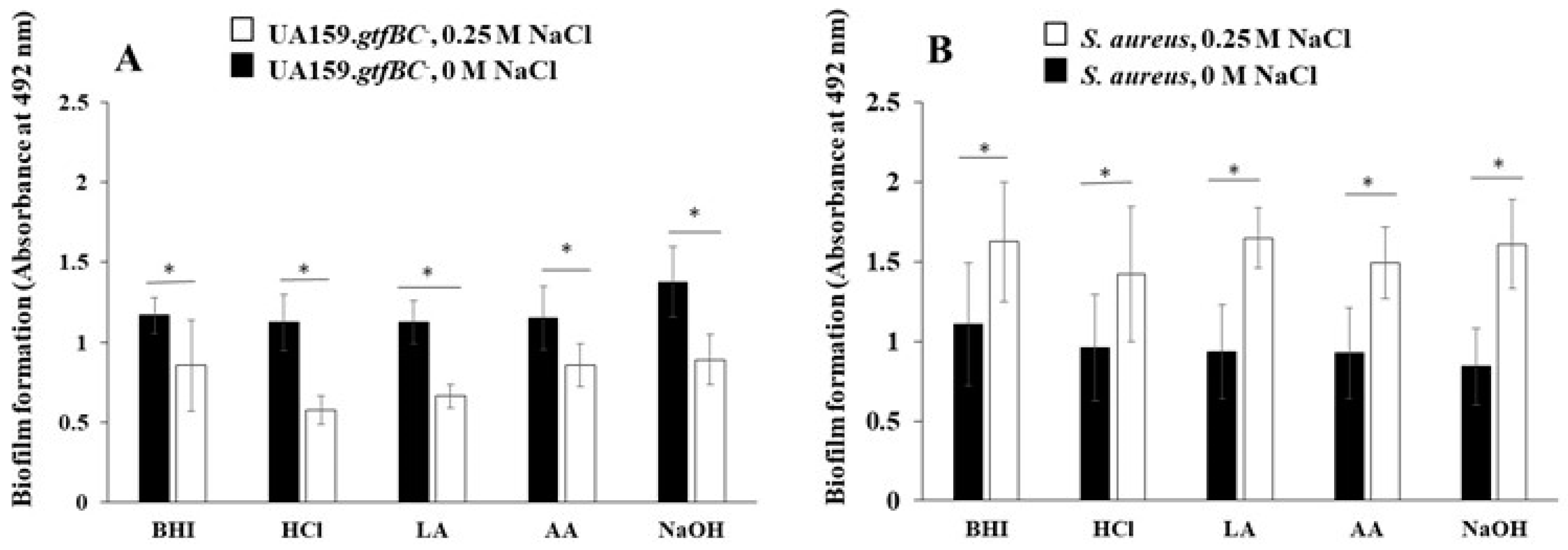
MVs acquired in the culture of
S. mutans with an initial pH of 8.0 increased the expression of
gtfB and
gtfC in the culture of
S. mutans and the protein levels of GtfB and GtfC in the MVs were comparable to those in the control (pH 7.2)[
31]. At pH 6.0, controlled using acetic acid, the protein expression of GtfC in MVs was greater than those at pH 6.0, controlled using HCl and lactic acid. To observe different volumes of GtfB and GtfC in MVs, MVs were collected from BHI broth (pH 6.0) prepared with HCl (HC), lactic acid (LA) or acetic acid (AA), and from BHI broth (pH 8.0), prepared using NaOH (NO) were added to the biofilm formation assay using
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- and
S. aureus in 0 and 0.25 M NaCl, respectively. The addition of NaCl inhibited the biofilm formation of
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- with MVs (
Figure 6A) but enhanced the biofilm formation of
S. aureus with MVs (
Figure 6B). The effect of NaCl on biofilms of
S. aureus was greater than the effects of different amounts of Gtfs, and the different volumes of GtfB and GtfC in MVs did not affect
S. aureus biofilm formation.
3.4. Effects of eDNA on the Biofilm Formation
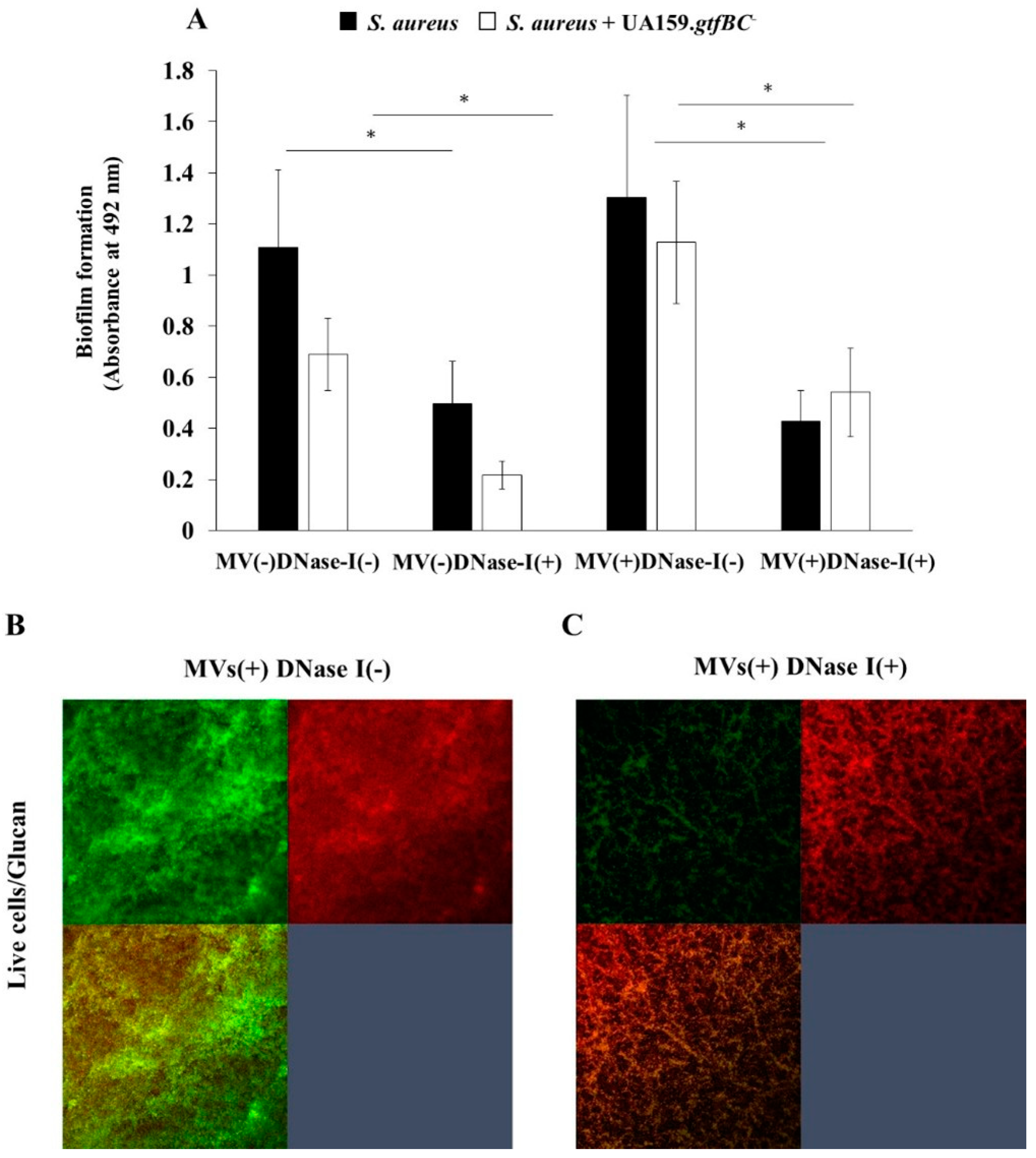
To clarify the effects of eDNA on biofilm formation, DNase I was added to the biofilm formation assay using
S. aureus only and mixed
S. aureus and
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- biofilms with and without MVs from
S. mutans in the presence of 0.25 M NaCl (
Figure 7). The biofilm formation of
S. aureus only and the mixed-species biofilms of
S. aureus and
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- was significantly inhibited by DNase I. The biofilm formation of the mixed-species biofilms of
S. aureus and
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- was upregulated by the addition of MVs, and the upregulated biofilm was significantly inhibited by DNase I (
Figure 7A). To confirm glucan formation in the mixed biofilm of
S. aureus and
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC-, an Alexa Fluor 647-dextran conjugate was added to the biofilm formation assay with MVs in the presence of 0.25 M NaCl. Glucan formation was observed, and the live cells were inhibited by the addition of DNase I biofilm and were observed with confocal microscopy (
Figure 7B). Therefore, eDNA principally contributes to the formation of mixed species biofilms under saline conditions.
4. Discussion
The biofilm formation of
S. aureus single and mixed species
, which are anti-salt resistant bacteria, was increased by the addition of 0.25 M NaCl.
When 0.25 M NaCl is added to TSB with 0.25% sucrose containing 0.086 M NaCl, the final concentration of NaCl is 0.335 M. The physiological concentration of human body salt is 0.154 M NaCl, which is used as a fluid infusion. An increase in the concentration of NaCl to physiological concentrations stimulated eDNA-dependent biofilm formation in
S. aureus in vitro. High salinity might increase density and viscosity [
32]. This may be due to the ability of these cells to survive under high-salinity conditions. In hypersaline solutions, high viscosity and density result in a reduced settling velocity of suspended particles such as MVs. The slower settling of MVs may result in increased turbidity for
S. aureus and increased efficiency of aggregation transport in mixed species biofilm formation. Moreover, fructan, which
S. mutans produces in the presence of sucrose, may affect biofilm formation because it enhances the viscosity of eDNA solutions and is necessary for biofilm formation by
Bacillus subtilis [
33] and
S. mutans [
29]. The bacterial cells are hypothesized to aggregate due to the increased viscosity of the cells in the presence of eDNA and fructan and the high-salinity conditions.
S. mutans produces three types of GTF: GTF-I, encoded by
gtfB; GTF-SI, encoded by
gtfC; and GTF-S, encoded by
gtfD [
34,
35]. In the presence of sucrose, polysaccharide synthesized by GTF-I is composed of insoluble glucan (rich in α1.3 linkages) on the bacterial surface, and insoluble glucan is thought to derive from bacterial aggregation [
14,
15]. Furthermore, GTF-SI, attached to the surface of a tooth covered with a salivary pellicle, produces insoluble and soluble glucan (rich in α1.3 and α1.6 linkages). Aggregated bacteria, guided by insoluble glucan, attach to the tooth surface and fusible glucan.
S. aureus interacts as an opportunistic pathogen and associates with oral biofilms in the oral cavity. However, it does not contain glucan-binding proteins (gbps) such as the gbps of
S. mutans [
14,
36]. Soluble and insoluble glucans might not affect the adherence and aggregation of
S. aureus preferentially because
S. aureus differs from
S. mutans in various ways. However, MVs with GTFs slightly enhanced the biofilm formation of
S. aureus only and mixed species of
S. aureus and
S. mutans UA159.
gtfBC- under high-salinity conditions. MVs from
S. mutans are associated mainly with GtfC [
27], and these biofilms are upregulated by both soluble and insoluble glucans on MVs. Larger amounts of Gtfs were loaded on MVs acquired at pH 8.0, controlled with NaOH [
31]. At pH 6.0, controlled with acetic acid, the protein expression of GtfC in MVs was greater than at pH 6.0, controlled with both HCl and lactic acid [
31].
The acetic acid
group induced different phenotypes of Gtf expression and different activities in oral bacteria biofilms. However, different volumes of GtfB and GtfC in MVs did not affect
S. aureus biofilm formation. Therefore, the presence of both soluble and insoluble glucans might support the physical adherence and aggregation of
S. aureus stimulated by excess salt in 0.25 M NaCl, whereas the difference of volume between soluble and insoluble glucans did not affect biofilm formation.
The mature
S. aureus biofilm is sensitive to the external addition of DNase I, indicating that eDNA is a structural component of the biofilm matrix [
37]. Owing to the negative charge of the DNA polymer, eDNA may participate in the early adhesion stage and mature stage of biofilms as an electrostatic polymer and play a basic structural role in the structural integrity of biofilms [
38]. In this study, the biofilm formation of live bacterial cells was induced mainly by the presence of eDNA without the influence of glucan under high-salinity conditions in TSBg. NaCl conditions preferentially induce eDNA-dependent biofilm formation in live
S. aureus in different ways than glucan formation by
S. mutans MVs. The opportunity for and mechanisms by which
S. aureus produces DNA are unknown but are required when a single
S. aureus cell at an initial stage actually attaches to the surface in the absence of glucan.
Cyclic di-adenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is a recently discovered secondary messenger that is produced predominantly by Gram-positive bacteria [
39,
40,
41,
42]. c-di-AMP production is dispensable for the growth of
S. aureus in chemically defined media and in rich media supplemented with additional sodium or potassium chloride [
43].
These results reveal the influence of c-di-AMP on biofilms, which may play an important role in the persistence of S. aureus biofilm infection under high-salinity conditions [
44]
. The production of c-di-AMP promoted K+ and cell wall homeostasis, biofilm formation, and virulence but sensitized the cells to osmotic stress [
45,
46,
47]
. Elevated c-di-AMP concentrations may promote S. aureus biofilm formation under high-salinity conditions, as previously shown in several streptococci [
48,
49]
.
Compared with single-species
S. aureus biofilms, whole-body
S. mutans biofilms reduced the biofilm formation of mixed species of
S. aureus because the biofilm formation levels were reduced by mixing with
S. mutans. In contrast, MVs from
S. mutans slightly enhanced dead cell-dependent biofilm formation. Glucan formation by MVs might enhance the connective relationships between
S. aureus and dead cells in high salinity condition. In contrast, under conditions including glucose,
S. aureus may be able to attach to and colonize old biofilm that contain an accumulation of dead bacteria because dead cells do not produce antibacterial substances such as acids or bacteriocin [
7]. When the commensal bacteria in the oral cavity are living and colonized, opportunistic pathogens such as
S. aureus are less likely to colonize [
50]. This is also because young people with sufficient normal oral flora have a low incidence of
S. aureus infection.
5. Conclusions
The biofilm formation of S. aureus single and mixed species was increased in high salinity condition including NaCl. The intake of sucrose may be a risk factor for S. aureus infection in humans, who typically have high concentrations of NaCl, because Gtfs on MVs from S. mutans produce soluble and insoluble glucans. Therefore, to avoid infection by opportunistic pathogens such as S. aureus, sucrose and glucose intake possibly should be limited to maintain oral and systemic health.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.S., S.N.; Data curation, Y.I., H.K.; Funding acquisition, H.S; Investigation, Y.I., H.S., H.K.; Methodology, H.S., Y.I; Resources, Y.I., H.S.; Supervision, S.N., H.S.; Writing-original draft, H.K., H.S.; Writing-review and editing, H.S., S.N.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for the Development of Scientific Research (20K10286 and 24K02661) from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science, and Technology of Japan and the Research Grant of SoltScience Program.
Data Availability Statement
All data generated or analyzed during study are included in this published article.
Acknowledgments
We thank Kaori Ochiai who has supported secretary works for purchasing experimental items. This manuscript was edited by American Journal Experts (
https://www.aje.com).
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
References
- Loesche, W.J. Role of Streptococcus mutans in human dental decay. Microbiological. Review. 1986, 50, 353–380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamada, S.; Slade, H.D. Biology, immunology, and cariogenicity of Streptococcus mutans. Microbiological. Review. 1980, 44, 331–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costerton, J.W.; Stewart, P. S.; Greenberg, E.P. Bacterial biofilms: a common cause of persistent infections. Science. 1999, 284, 1318–1322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mirghani, R.; Saba, T.; Khaliq, H.; Mitchell, J.; Do, L.; Chambi, L.; Diaz, K.; Kennedy, T.; Alkassab, K.; Huynh, T.; Elmi, M.; Martinez, J.; Sawan, S; Rijal. G. Biofilms: Formation, drug resistance and alternatives to conventional approaches. AIMS Microbiology 2022, 8, 239–277.
- Mandell, L. A.; Niederman, M. S. Aspiration pneumonia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019, 380, 651–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoneyama, T.; Yoshida, M.; Matsui, T.; Sasaki, H. Oral care and pneumonia. Oral Care Working Group. Lancet. 1999, 354, 515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senpuku, H.; Sogame, A.; Inoshita, E.; Tsuha, Y.; Miyazaki, H.; Hanada. N. Systemic diseases in association with microbial species in oral biofilm from elderly requiring care. Gerontology 2003, 49, 301–309. [CrossRef]
- Tada, A.; Hanada, N. Opportunistic respiratory pathogens in the oral cavity of the elderly. FEMS Immunol. Med. Microbiol. 2010, 60, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Solh, A.A.; Pietrantoni, C.; Bhat, A.; Aquilina, A.T.; Okada, M.; Grover, V.; Gifford, N. Microbiology of severe aspiration pneumonia in institutionalized elderly. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2003, 167, 1650–1654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koukos, G.; Sakellari,D.; Arsenakis, M.; Tsalikis, L.; Slini, T.; Konstantinidis, A. Prevalence of Staphylococcus aureus and methicillin resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA) in the oral cavity. Arch. Oral Biol. 2015, 60, 1410–1415. [CrossRef]
- Lee, S., Choi, K-H., & Yoon, Y. Effect of NaCl on biofilm formation of the isolate from Staphylococcus aureus outbreak linked to ham. Kor. J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2014, 34, 257–261.
- Hoover, J.; Tovar, E.; Zlatnik, T.; Karunanayake, C. Efficacy of a rinse containing sea salt and lysozyme on biofilm and gingival health in a group of young adults: A pilot study. Int. J. Dent. 2017, 2017, 4056708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- O’Neill, E.; Pozzi, C.; Houston, P.; Smyth, D.; Humphreys, H.; Robinson, D.A.; O’Gara, J.P. Association between methicillin susceptibility and biofilm regulation in Staphylococcus aureus isolates from device-related infections. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 45, 1379–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bowen, W.; Koo, H. Biology of Streptococcus mutans-derived glucosyltransferases: role in extracellular matrix formation of cariogenic biofilms. Caries Res. 2011, 45, 69–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, H.; Xiao, J.; Klein, M. I.; Jeon, J. G. Exopolysaccharides produced by Streptococcus mutans glucosyltransferases modulate the establishment of microcolonies within multispecies biofilms, J. Bacteriol. 2010, 192, 3024–3032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senpuku, H.; Nakamura, T.: Iwabuchi, Y.; Hirayama, S.; Nakao, R.; Ohnishi, M. Effects of complex DNA and MVs with GTF extracted from Streptococcus mutans on the oral biofilm. Molecules. 2019, 24, 3131. [CrossRef]
- Bonnington, K.E.; Kuehn, M.J. Protein selection and export via outer membrane vesicles. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2014, 1843, 1612–1619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellis, T. N.; Kuehn, M. J. Virulence and immunomodulatory roles of bacterial outer membrane vesicles, Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2010, 74, 81–94.
- Biller, S.J.; Schubotz, F.; Roggensack, S.E.; Thompson, A.W.; Summons, R.E.; Chisholm, S.W. Bacterial vesicles in marine ecosystems. Science. 2014, 343, 183–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berleman, J.; Auer, M. The role of bacterial outer membrane vesicles for intra- and interspecies delivery, Environ Microbiol. 2013, 15, 347–354.
- Kuehn, M.J.; Kesty, N.C. Bacterial outer membrane vesicles and the host-pathogen interaction, Genes Development. 2005, 19, 2645–2655.
- Avila-Calderón, E.D.; Araiza-Villanueva, M.G.; Cancino-Diaz, J.C.: López-Villegas, E.O.; Sriranganathan, N.; Boyle, S.M.; Contreras-Rodríguez, A. Roles of bacterial membrane vesicles, Arch. Microbiol. 2015, 197, 1–10.
- Tashiro, Y.; Uchiyama, H.; Nomura, N. Multifunctional membrane vesicles in Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 14, 1349–1362. [Google Scholar]
- Lai, H.; White, J.; Roe, B.A.; Ferretti, J.J. Genome sequence of Streptococcus mutans UA159, a cariogenic dental pathogen. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002, 99, 14434–14439. [Google Scholar]
- Suzuki, Y.; Nagasawa, R.; Senpuku, H. Inhibiting effects of fructanase on competence-stimulating peptide-dependent quorum sensing system in Streptococcus mutans. J. Infect. Chemother. 2017, 23, 634–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Iwabuchi, Y.; Hirayama, S.; Narisawa, N.; Takenaga, F.; Nakao, R.; Senpuku, H. Roles of membrane vesicles from Streptococcus mutans for the induction of antibodies to glucosyltransferase in mucosal immunity. Microb. Pathog. 2020, 149, 104260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Sharma, P.K.; Busscher, H.J.; Van Der Mei, H.C.; Krom, B.P. Role of extracellular DNA in initial bacterial adhesion and surface aggregation. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2010, 76, 3405–3408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, T.; Sehar, S.; Manefield, M. The roles of extracellular DNA in the structural integrity of extracellular polymeric substance and bacterial biofilm development. Environ. Microbio.l Rep. 2013, 5, 778–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagasawa, R.; Sato, T.; Senpuku, H. Raffinose induces biofilm formation by Streptococcus mutans in low concentrations of sucrose by increasing production of extracellular DNA and fructan. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2017, 83, e00869-17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motegi, M.; Takagi, Y.; Yonezawa, H.; Kanada, N.; Terajima, J.; Watanabe, H.; Senpuku, H. Assessment of genes associated with Streptococcus mutans biofilm morphology. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 6277–6287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iwabuchi, Y.; Nakamura, T.; Kusumoto, Y.; Nakao, R.; Iwamoto, T.; Shinozuka, O.; Senpuku, H. Effects of pH on the properties of membrane vesicles including glucosyltransferase in Streptococcus mutans. Microorganisms. 2021, 9, 2308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weisbrod, N.; Yechieli,Y.; Shandalov, S.; Lensky, N. On the viscosity of natural hyper-saline solutions and its importance: The dead sea brines. J. Hydrol. 2016, 532, 46–51. [CrossRef]
- Dogsa, I.; Brloznik, M.; Stopar, D.; Mandic-Mulec, I. Exopolymer diversity and the role of levan in Bacillus subtilis biofilms. PLoS One 2013, 8, e62044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wexler, D.L.; Hudson, M.C.; Burne, R.A. Streptococcus mutans fructosyltransferase (ftf) and glucosyltransferase (gtfBC) operon fusion strains in continuous culture. Infect. Immun. 1993, 61, 1259–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fujiwara, T.; Terao, Y.; Hoshino, T.; Kawabata, S.; Ooshima, T.; Sobue, S.; Kimura, S.; Hamada, S. Molecular analyses of glucosyltransferase genes among strains of Streptococcus mutans. FEMS Microbiol. Letter. 1998, 161, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, D.J.; Akita, H.; King, W. F.; Taubman, M.A. Purification and antigenicity of a novel glucan-binding protein of Streptococcus mutans. Infect. Immuni. 1994, 62, 2545–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, E.E.; Rice, K.C.; Boles, B.R.; Endres, J.L.; Ranjit, D.; Chandramohan, L.; Tsang, L.H.; Smeltzer, M.S.; Horswill, A.R.; Bavles, K.W. Modulation of eDNA release and degradation affects Staphylococcus aureus biofilm maturation. PLoS One 2009, 4, e5822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Campoccia, D.; Montanaro, L.; Arciola, C.R. , Extracellular DNA (eDNA). A major ubiquitous element of the bacterial biofilm architecture. Int J Mol Sci. 2021, 22, 9100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, R.M.; Abbott, J.C.; Burhenne, H.; Kaever, V.; Gründling, A. c-di-AMP is a new second messenger in Staphylococcus aureus with a role in controlling cell size and envelope stress. PLoS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corrigan, R. M.; Gründling, A. Cyclic di-AMP: another second messenger enters the fray. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2013, 11(8), 513–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Römling, U. Great times for small molecules: c-di-AMP, a second messenger candidate in bacteria and archaea. Science Signaling. 2008, 1, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witte, G.; Hartung, S.; Büttner, K.; Hopfner, K.P. Structural biochemistry of a bacterial checkpoint protein reveals diadenylate cyclase activity regulated by DNA recombination intermediates. Mol. Cell. 2008, 30, 167–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeden, M.S.; Schuster, C.F.; Bowman, L.; Zhong, Q.; Williams, H.D.; Gründling, A. (2018). Cyclic di-adenosine monophosphate (c-di-AMP) is required for osmotic regulation in Staphylococcus aureus but dispensable for viability in anaerobic conditions. J. Biolog. Chem. 2018, 293, 3180–3200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huynh, N.; Luo, S.; Pensinger, D.; Sauer, J. D.; Tong, L.; Woodward, J.J. An HD-domain phosphodiesterase mediates cooperative hydrolysis of c-di-AMP to affect bacterial growth and virulence. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2015, 112, E747–756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, Y.; Helmann, J.D. Analysis of the role of Bacillus subtilis σ(M) in β-lactam resistance reveals an essential role for c-di-AMP in peptidoglycan homeostasis. Mol. Microbiol. 2012, 83, 623–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Yang, J.; Eisele, L.; Underwood, A.J.; Koestler, B.J.; Waters, C.M.; Metzger, D.W.; Bai. G. Two DHH subfamily 1 proteins in Streptococcus pneumoniae possess cyclic di-AMP phosphodiesterase activity and affect bacterial growth and virulence. J. Bacteriol. 2013, 195, 5123–5132. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jackson-Litteken, C.D.; Ratliff, C.T.; Kneubehl, A.R.; Siletti, C.; Pack, L.; RLan, R.; Huynh, T.N.; Lopez, J.E., Blevins, J.S. The diadenylate cyclase CdaA is critical for Borrelia turicatae virulence and physiology. Infect. Immun. 2021, 89, e00787-2089.
- Du, B.; Ji, W.; An, H.; Shi, Y.; Huang, Q.; Cheng, Y.; Fu, Q.; Wang, H.; Yan, Y.; Sun, J. Functional analysis of c-di-AMP phosphodiesterase, GdpP, in Streptococcus suis serotype 2. Microbiol.l Res. 2014, 169, 749–758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, X.; Zhang, Y.; Bai, G.; Zhou, X.; Wu, H. Cyclic di-AMP mediates biofilm formation. Mol. Microbiol. 2016, 99, 945–959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tada, A.; Senpuku, H.; Motozawa, Y.; Yoshihara, A.; Hanada, N.; Tanzawa, H. Association between commensal bacteria and opportunistic pathogens in the dental plaque of elderly individuals. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2006, 12, 776–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).