Submitted:
13 September 2024
Posted:
16 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. Electricity Market Liberalization
2.2. Servitization
2.3. Performance Evaluation System Satisfaction
2.4. Literature Review Summary
3. Research and Data Methodology
3.1. Research Subjects
3.2. Ethical Approval
3.3. Research Methods
3.4. Data Collection
4. Data Analysis
4.1. Open Coding
4.2. Axial Coding
4.3. Selective Coding
4.4. Theoretical Saturation Test
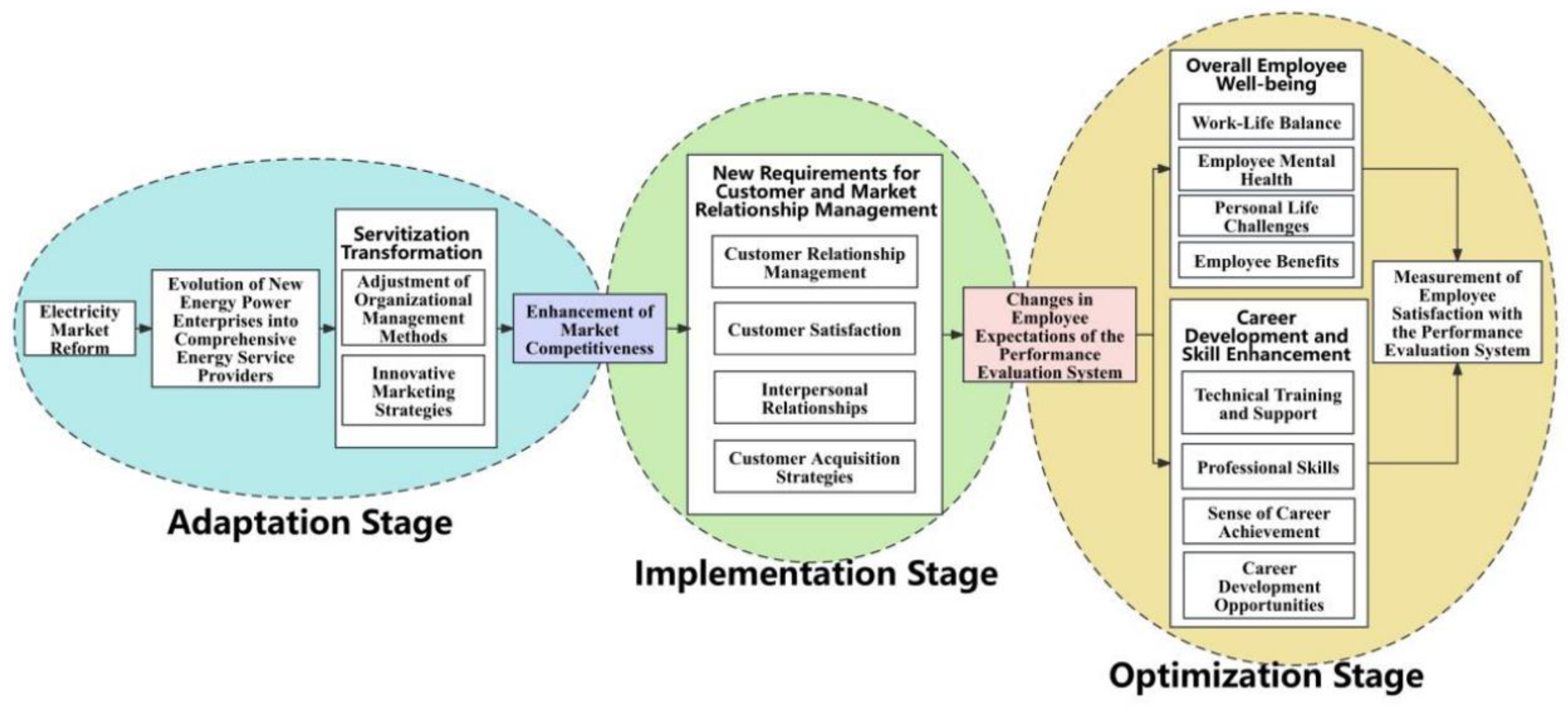
5. Model Analysis
5.1. Adaptation Stage
5.2. Implementation Stage
5.3. Optimization Stage
5.4. Model Application and Practical Guidance
6. Conclusions and Discussion
6.1. Conclusions
6.2. Discussion
6.3. Research Limitations and Future Directions
References
- Deng, Jing, et al. Can Carbon Neutrality Commitment Contribute to the Sustainable Development of China’s New Energy Companies? Sustainability 2022, 14, 11308. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Xiufeng, et al. “How do environmental technology standards affect the green transformation? new evidence from China.” International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health 19.10 (2022): 5883. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Hongye, et al. “Power market reform in China: Motivations, progress, and recommendations.” Energy Policy 145 (2020): 111717. [CrossRef]
- Sadjadi, Ebrahim Navid, and Roemi Fernández. “Relational marketing promotes sustainable consumption behavior in renewable energy production.” Sustainability 15.7 (2023): 5714. [CrossRef]
- Baines, Tim, et al. “Framing the servitization transformation process: A model to understand and facilitate the servitization journey.” International Journal of Production Economics 221 (2020): 107463. International Journal of Production Economics 221 (2020). [CrossRef]
- Kowalkowski, Christian, Heiko Gebauer, and Rogelio Oliva. “Service growth in product firms: Past, present, and future.” Industrial marketing management 60 (2017): 82-88. [CrossRef]
- Jang, Soojeen, Yanghon Chung, and Hosung Son. “Employee participation in performance measurement system: focusing on job satisfaction and leadership.” International Journal of Productivity and Performance Management 72.7 (2023): 2119-2134. [CrossRef]
- Dangol, Pooja. “Role of performance appraisal system and its impact on employees motivation.” Quantitative Economics and Management Studies 2.1 (2021): 13-26. [CrossRef]
- Joskow, Paul L. “Lessons learned from electricity market liberalization.” The Energy Journal 29.2_suppl (2008): 9-42. [CrossRef]
- Borenstein, Severin, and James Bushnell. “The US electricity industry after 20 years of restructuring.” Annu. Rev. Econ. 7.1 (2015): 437-463. [CrossRef]
- Green, Richard. “Market power mitigation in the UK power market.” Utilities Policy 14.2 (2006): 76-89. [CrossRef]
- Parida, Vinit, David Sjödin, and Wiebke Reim. “Reviewing literature on digitalization, business model innovation, and sustainable industry: Past achievements and future promises.” Sustainability 11.2 (2019): 391. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Qianchun, et al. “Analysis of China’s Electricity Market Under the New Round of Reform.” Annual Report on China’s Petroleum, Gas and New Energy Industry (2022–2023). Singapore: Springer Nature Singapore, 2024. 359-372. [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Yuk-shing, Man-kit Chung, and Kam-pui Tsang. “Electricity Market Reforms for Energy Transition: Lessons from China.” Energies 16.2 (2023): 905. [CrossRef]
- Vandermerwe, Sandra, and Juan Rada. “Servitization of business: Adding value by adding services.” European management journal 6.4 (1988): 314-324. [CrossRef]
- Baines, Tim, et al. “Servitization: revisiting the state-of-the-art and research priorities.” International Journal of Operations & Production Management 37.2 (2017): 256-278. [CrossRef]
- Pei-Ju, Yu, Chen Shin-Horng, and Wen Pei-Chang. “A Study on Modes of the Servitization of Manufacturing.” Tai Da Guan Li Lun Cong 25.1 (2014): 325. [CrossRef]
- Brax, Saara A., et al. “Service modularity and architecture–an overview and research agenda.” International Journal of Operations & Production Management 37.6 (2017): 686-702. [CrossRef]
- Li, Jing Hua, et al. “An empirical study of servitization paradox in China.” The Journal of High Technology Management Research 26.1 (2015): 66-76. [CrossRef]
- Lindhult, Erik, et al. “Value logics for service innovation: practice-driven implications for service-dominant logic.” Service business 12 (2018): 457-481. [CrossRef]
- Singh, Mahendra, et al. “Servitization of energy sector: Emerging service business models and startup’s participation.” Energies 15.7 (2022): 2705. [CrossRef]
- Xie, Jifei, Lulu Ma, and Jiamin Li. “Servitization, Digitalization or Hand in Hand: A Study on the Sustainable Development Path of Manufacturing Enterprises.” Sustainability 15.13 (2023): 10644. [CrossRef]
- Locke, Edwin A. “What is job satisfaction?.” Organizational behavior and human performance 4.4 (1969): 309-336. [CrossRef]
- Judge, Timothy A., et al. “The job satisfaction–job performance relationship: A qualitative and quantitative review.” Psychological bulletin 127.3 (2001): 376. [CrossRef]
- Dasanayaka, Chamila H., et al. “The impact of the performance appraisal process on job satisfaction of the academic staff in higher educational institutions.” Education Sciences 11.10 (2021): 623. [CrossRef]
- Memon, Aftab Hameed, et al. “Relationship between Job Satisfaction and Employee Performance in the Construction Industry of Pakistan.” Sustainability 15.11 (2023): 8699. [CrossRef]
- Vuong, Thu Doan Ngoc, and Loi Tan Nguyen. “The key strategies for measuring employee performance in companies: a systematic review.” Sustainability 14.21 (2022): 14017. [CrossRef]
- Arcelay, Irene, et al. “Definition of the future skills needs of job profiles in the renewable energy sector.” Energies 14.9 (2021): 2609. [CrossRef]
- Glaser, Barney, and Anselm Strauss. Discovery of grounded theory: Strategies for qualitative research. Routledge, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Gioia, Dennis A., Kevin G. Corley, and Aimee L. Hamilton. “Seeking qualitative rigor in inductive research: Notes on the Gioia methodology.” Organizational research methods 16.1 (2013): 15-31. [CrossRef]
- Ni, Guodong, et al. “Influence mechanism of organizational flexibility on enterprise competitiveness: The mediating role of organizational innovation.” Sustainability 13.1 (2020): 176. [CrossRef]
- Perona, Marco, Nicola Saccani, and Andrea Bacchetti. “Research vs. practice on manufacturing firms’ servitization strategies: A gap analysis and research agenda.” Systems 5.1 (2017): 19. [CrossRef]
- Peco-Torres, Francisco, Ana I. Polo-Peña, and Dolores M. Frías Jamilena. “Antecedents and consequences of strategic online-reputation management: moderating effect of online tools.” Journal of Hospitality and Tourism Technology 14.3 (2023): 384-400. [CrossRef]
- Štverková, Hana, and Michal Pohludka. “Quality Management for Assurance Value of the Customer in Industry 4.0 Times.” Quality Management, Value Creation, and the Digital Economy. Routledge, 2023. 129-141. [CrossRef]
- Geissinger, Andrea, et al. “Social media analytics for innovation management research: A systematic literature review and future research agenda.” Technovation 123 (2023): 102712. [CrossRef]
- Rabetino, Rodrigo, et al. “Guest editorial: servitization 2.0: evaluating and advancing servitization-related research through novel conceptual and methodological perspectives.” International Journal of Operations & Production Management 41.5 (2021): 437-464. [CrossRef]
- Bustinza, Oscar F., et al. “Make-or-buy configurational approaches in product-service ecosystems and performance.” Journal of Business Research 104 (2019): 393-401. [CrossRef]
- Malik, Nida. “Organizations Should Maintain Employee’s Work-Life Balance.” JOURNAL OF ECONOMICS, FINANCE AND MANAGEMENT STUDIES. https://api. semanticscholar. org/CorpusID 261012371 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Wood, Alex J. “Powerful times: Flexible discipline and schedule gifts at work.” Work, Employment and Society 32.6 (2018): 1061-1077. [CrossRef]
- Skinner, Natalie, and Janine Chapman. “Work-life balance and family friendly policies.” Evidence Base: a journal of evidence reviews in key policy areas 4 (2013): 1-25. Available online: https://search.informit.org/doi/10.3316/informit.254936331381144.
- Cetindamar Kozanoglu, Dilek, and Babak Abedin. “Understanding the role of employees in digital transformation: conceptualization of digital literacy of employees as a multi-dimensional organizational affordance.” Journal of Enterprise Information Management 34.6 (2021): 1649-1672. [CrossRef]
- Ismail, Hussein Nabil, and Nazha Gali. “Relationships among performance appraisal satisfaction, work–family conflict and job stress.” Journal of management & organization 23.3 (2017): 356-372. [CrossRef]
| Category | Item | Number of Participants | Proportion (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | 82 | 66% |
| Female | 43 | 34% | |
| Age Group | 20-30years old | 66 | 53% |
| 30-40years old | 52 | 41% | |
| 40-50years old | 7 | 6% | |
| Above 50 years old | 0 | 0% | |
| Education Level | Doctoral | 0 | 0% |
| Master’s | 7 | 6% | |
| Bachelor’s | 92 | 74% | |
| Associate’s | 26 | 20% | |
| Job Level | Senior Leadership | 2 | 2% |
| Department Manager | 9 | 7% | |
| Department Staff | 114 | 91% |
| Initial Categories | Original Data |
|---|---|
| Work-life balance | “In our marketing department, you have to be on call even after hours. We start at 8:30 AM, and although our official workday ends at 5:30 PM, many of us continue working beyond that” |
| Career development opportunities | “I have been with the company for two months and feel quite fulfilled. I have been thinking about my career growth and future direction. Our manager often discusses our plans and ideas, which I find motivating despite the inevitable challenges.” |
| Customer relationship management | “When talking to clients, I noticed significant differences. For instance, one client, a leader in a listed company, has a remarkable depth of understanding and ability to grasp the essence of matters, which highlighted the gap between us.” |
| Context of market-oriented reforms | “Our products are simple, characterized by the attributes of the store. Under the 3060 renewable energy development backdrop, our leading department focuses on continuous construction of new power generation units.” |
| Employee mental health | “I have been in marketing since 2017 before our department was established in 2021. Unlike other roles where you might have regular hospital visits or childcare responsibilities, our job does not easily accommodate such personal time.” |
| Technical training and support | “Technical skills are crucial., especially in our trading center. Your sales price depends on your judgment and forecasts, along with communication with peers.” |
| Organizational management style | “Starting as a sales intern involves supporting sales staff, handling orders, and daily administrative tasks, which might differ from one’s expectations of a marketing role.” |
| Career achievement | “Our peak sales period is from October to December each year, preparing for the next year’s market. Initially, the targets from headquarters might seem daunting, but our excellent leadership makes the process manageable.” |
| Interpersonal communication | “The main difference lies in interaction. While production deals with machinery, marketing involves much human interaction, requiring higher interpersonal skills.” |
| Sales strategies | “Our marketing center focuses on market development, finding clients to purchase our power, followed by trading center activities to manage transactions.” |
| Employee benefits | “Both men and women are equally assigned tasks, but considering women’s additional family responsibilities, a more accommodating work arrangement for women would be beneficial.” |
| Customer satisfaction | “Our clients are mostly enterprises with high-level decision-making needs. It is essential to visit these companies, understand their power needs from their perspective, and address their core requirements.” |
| Personal life challenges | “Our industry is predominantly male, which creates challenges, especially for personal issues. Unlike sectors with a balanced gender ratio, here men often face difficulties in resolving personal matters.” |
| Professional skills | “Both technical and sales skills are crucial in our field. Despite focusing on trading, we continuously engage in customer development, highlighting the importance of diverse skills.” |
| Innovation capability | “Given the unique nature of electricity as a policy-driven commodity, it is vital to stay updated with regulations and continuously learn and adapt to changes.” |
| Major Category | Initial Category | Category Connotation |
|---|---|---|
| Work-life balance | Work-Life Balance | The indistinguishability between work and life, arrangements for work during and after office hours |
| Employee Mental Health | Psychological support and care, attending to employees’ family responsibilities | |
| Personal Life Challenges | Inclusivity in work arrangements, especially for female employees, balancing life and work | |
| Employee Benefits | Health and welfare benefits, working conditions, and employee welfare policies | |
| Career Development and Skill Enhancement | Career Development Opportunities | Individual development paths, regular communication with management about career goals and progress |
| Sense of Career Achievement | Impact of role transitions on personal growth and character, challenges, and achievements in meeting career goals | |
| Professional Skills | Enhancement and application of professional skills, support for obtaining relevant professional certifications | |
| Technical Training and Support | Providing technical training and support, adapting to and applying new technologies | |
| Customer and Market Relations | Customer Relationship Management | Managing and maintaining customer relationships, impact of customer interactions on employees |
| Customer Satisfaction | Understanding and meeting customer needs, managing and improving customer feedback | |
| Customer Acquisition Strategies | Strategies for market development and customer acquisition, transaction and contract management | |
| Interpersonal Relationships | Building and maintaining relationships with customers and colleagues, teamwork, and cross-departmental collaboration | |
| Organizational Management and Market Context | Market Reform Background | Impact of electricity market reform, strategic adjustments of enterprises in the context of market reform |
| Organizational Management Methods | Management approaches and decision-making transparency, sales cycle, and management rhythm | |
| Innovation Capability | Innovative marketing strategies in the market, ability to respond to market demands |
| Typical Structural Relationship | Relationship Connotation | |
|---|---|---|
| Adaptation Stage | China’s Electricity market reform → Corresponding increase in service-oriented job demands | China’s electricity market reform signifies a shift from a traditional., government-controlled model to a more open and competitive market environment. As a result, new energy power enterprises are evolving from traditional energy suppliers to providers of integrated energy solutions, thereby increasing the demand for service-oriented roles. |
| Service-oriented job demand increase → Enterprise servitization transformation | As the demand for service-oriented roles increases, enterprises need to adjust their service models to meet market demands better. This necessitates innovation in service delivery methods and improvements in service quality to adapt to the continually evolving market environment. | |
| Enterprise servitization transformation → Adjusting organizational management and adapting to market background | In the process of servitization transformation, enterprises must adjust their organizational management structures to adapt to the new market context. This includes optimizing internal management processes and enhancing organizational flexibility to better respond to market changes and customer needs. | |
| Implementation Stage | Adjusting organizational management and adapting to market background → Enhancing enterprise competitiveness | Adjusting organizational management structures and processes enhances enterprise efficiency and agility, thereby boosting competitiveness and positioning the enterprise advantageously in a highly competitive market. |
| Enhancing enterprise competitiveness → New requirements for customer and market relationship management | As enterprise competitiveness improves, customers’ and the market’s expectations also rise. Enterprises need to manage customer and market relationships better to maintain and enhance customer satisfaction and market share. | |
| New requirements for customer and market relationship management → Expectations for employee performance evaluation systems | New customer and market management requirements increase the workload and changes in job content, leading to new expectations for employee performance evaluation systems. Enterprises need to develop more comprehensive and fair performance evaluation systems to motivate employees to serve customer and market needs better. | |
| Optimization Stage | Expectations for employee performance evaluation systems → Overall employee well-being | Employees’ expectations of the performance evaluation system typically reflect their pursuit of a favorable work environment and work-life balance, which are crucial to their overall well-being. To enhance employee satisfaction with the performance evaluation system, enterprises need to create a positive work environment and pay attention to the quality of employees’ lives. |
| Expectations for employee performance evaluation systems → Career development and skill enhancement | Employees expect a fair and transparent performance evaluation system and seek opportunities for career development and skill enhancement through their work. Enterprises should provide training and development opportunities to help employees improve their skills and achieve career growth, thereby increasing their satisfaction with the performance evaluation system. | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





