1. What Are DNA Secondary Structures and How Do They Form?
Most deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA) exists in a conventional double stranded helical form (B-form DNA) in cells. However, vital cellular events in particular replication and transcription require the DNA duplex to unwound into a single-stranded form. This is when DNA has the maximal propensity to fold into non-canonical but stable secondary structures due to the presences of sequences of high repetitiveness or low complexity. The formation of such structures is also favoured by other variables and components such as, symmetry and the presence of other strands of nucleic acids. The prominent DNA secondary structures known and characterized are hairpins and cruciforms, that come into play in inverted and mirror repeat sequences. Other sequences that adopt secondary structures are tandem repeats: for instance, DNA sequences rich in Guanine tend to form G-quadruplexes while polypurine tracts may lead to triplex or hinged-DNA (H-DNA) formation [
1,
2].
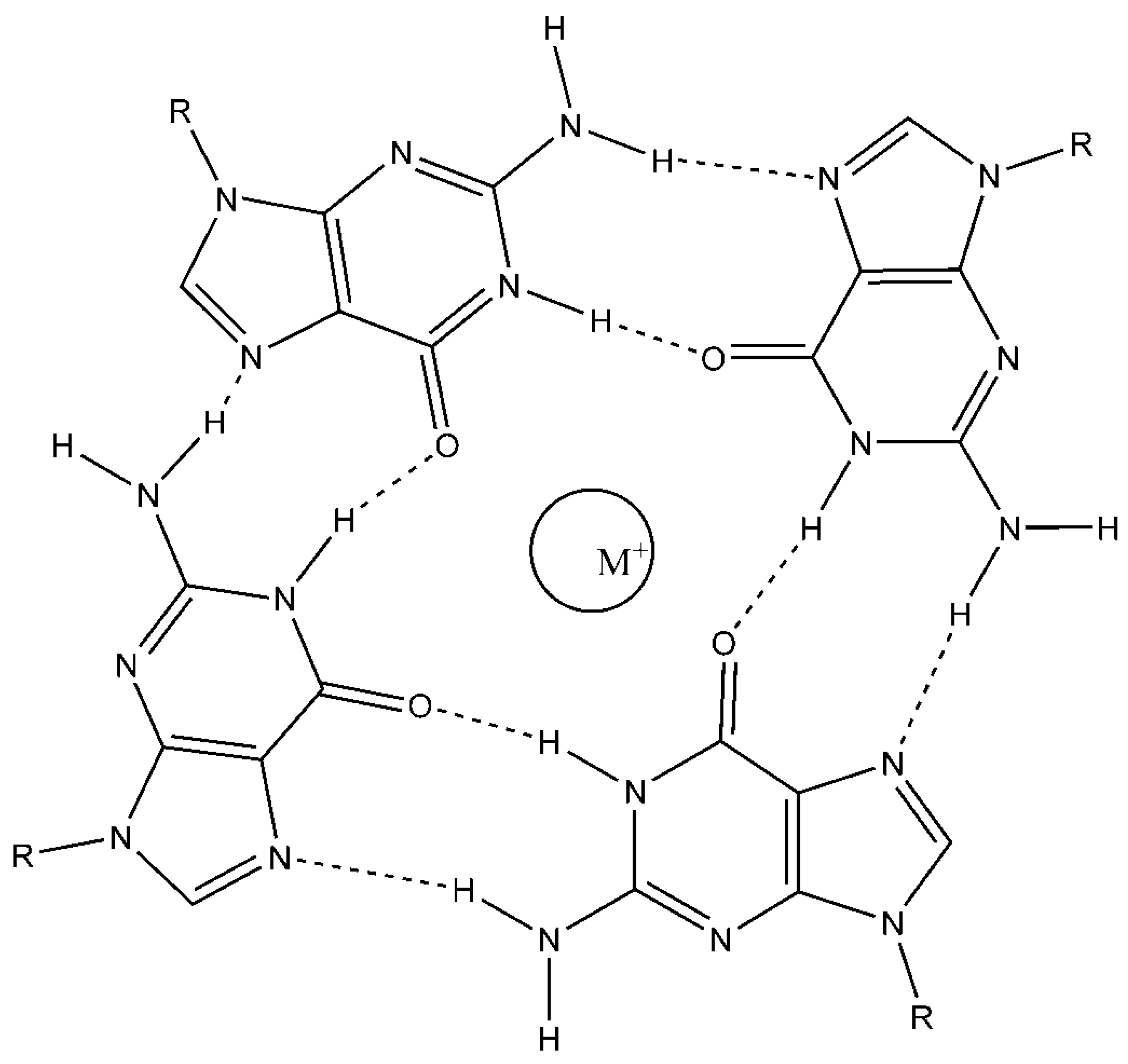
G4 secondary structures are formed due to the intrinsic ability of Guanine to engage in Hoogesteen hydrogen bonding which lets repetitive Guanines to form ring like structures often termed as G-quartets [
3]. The latter stack through pi–pi interactions giving rise to G4s [
4]. The prominent G4 known is tetramolecular which is formed from four strands of DNA (
Figure 1). Likewise, G4s can be bimolecular wherein two strands of DNA stack together. With regard to the DNA replication, a unimolecular G4 is highly relevant. Such a structure is formed due to the folding of a single DNA strand (
Figure 1). Many studies have defined a G4 consensus motif as G3–5N1–7G3–5N1–7G3–5N1–7G3–5, where N is any nucleotide [
5]. However, recent advances in G4 biology highlight that a wider range of sequences in which N can be larger than 7 and G of just 2, can make G4s and carry biological function [
6]. Consistent with this, different experimental procedures including a genome wide sequencing based assays estimate G4 DNA forming sequences to be evolutionarily conserved and have been reported to present in all kingdoms of life. Human genome has been reported to contain >700 000 G4 DNA forming sequences [
7]. Bacterial genomes including
Escherichia coli and pathogenic mycobacteria also possess ̴ 3,000 and ̴ 10,000 G4 DNA forming sequences, respectively [
8]. Intramolecular G4 structures are reported to showcase great topological diversity which is precisely dictated by the sequence of the G4 motif. This in turn influences the G quartet stack height and loop length enacted by non-participating nucleotide bases [
9]. Although known to exist for many years now, it is only lately that roles of G4 have been widely embraced. The G-rich sequences with high propensity to form G4 structures are abundantly present in transcription start sites, promoters, telomeres, immunoglobulin switch regions along with mitotic and meiotic double-strand breaks (DSBs). As such, some of the critical physiological roles played by G4s include the transcriptional regulation [
10], telomere maintenance [
11] and replication origin specification [
12]. Pertinently, unresolved G4 structures are known to block both DNA replication and transcription and thus, pose an increased risk of causing both genetic and epigenetic changes which may be potentially deleterious. Nonetheless, it is possible many sequences with the potential to form G4s do not have a cellular function or remain poorly studied.
A biggest factor aiding G4 formation is the unwinding of DNA double helix during DNA replication and transcription. The presence of single stranded DNA and a favourable G4 forming sequence like (G3N1)3G3 can form a stable G4 in vitro. However, in vivo, more factors need to be considered for the successful formation of G4s. These additional elements encompass the influence of neighboring DNA, the torsional and longitudinal forces exerted specifically on the DNA, and the indispensable roles played by DNA-binding proteins and nucleosomes.
Recent advances in G4 biology suggest G4 secondary structure forming sequences to be potential sites of mutagenesis. This is majorly due to the innate tendency of G4s to impede replication and partly due to the modulation of mutagenesis by external agents. Indeed, DNA secondary structure formation seems to have an obvious link with notable attributes of cancer genomes like variation in copy number, indels, translocation breakpoints and point mutations. This genetic instability of genome appears to be a manifestation of impediments in DNA replication by DNA secondary structures. Newer and more recent reports link G4 DNA sequences with epigenetic changes. This has made it increasingly important to decipher and develop a thorough understanding of DNA replication fork interactions with secondary structures formed in DNA.
2. G4 DNA Interferes with Both Leading and Lagging Strand Synthesis
The replication of the lagging strand occurs in a discontinuous manner, resulting in this DNA strand being in a single-stranded state for a longer period compared to the leading strand. This makes many to think that lagging strand should intrinsically be more prone to G4 secondary structure formation [
13]. However, lagging strand is believed to be coated with a single strand DNA binding protein RPA which should effectively counter G4 formation [
14]. Nevertheless, a well-known lagging strand sequence (TTAGGG) which has a great potential to form G4 is seen in telomeres, probably explaining why the progression of the replication fork through telomeric repeats is slow and susceptible to instability [
13]. Pertinently, an important study regarding yeast replication demonstrates that G4s on lagging strand delay replication rates in the absence of G4 resolving PIF1 helicase [
15].
Advances in G4 biology strongly and unambiguously suggest the formation of G4s on the leading strand template which tend to stay unless resolved by helicases and other involved factors that resolve G4s. Interestingly, the G4-forming human minisatellite CEB1 exhibits greater tolerability on leading strand template in yeast, but demonstrates high genetic instability with either the G4-stabilising molecules or genetic PIF1 inactivation [
16]. Similarly many other studies have demonstrated that G4s impede with leading strand replication if cells lack G4 unwinding helicases such as, FANCJ [
17], BLM [
18] and WRN [
19] or G4 stabilising ligands are used to stabilise G4s in cells [
20].
3. Transcription Encourages G4 Formation in Genome
The process of transcription requires DNA to unwind to let RNA polymerase synthesise RNA. However, the DNA only partially unwinds during the course of transcription
The single-stranded bubble created by RNAPII is relatively small, typically around eight nucleotides in size, and is well shielded by the RNAPII complex. As a result, it is less prone to the formation of G-quadruplex structures, which contributes to its stability [
21]
. The only way a G4 can be formed during transcription progression is when RNAPII pauses which can extend the transcription bubble and let the exposed single-stranded DNA form G4s [
22].
When DNA strands segregate under these circumstances, the nascent RNA can hybridize with the template DNA. This prevents the coding DNA strand from reannealing and leads to the formation of a three-strand structure known as an R-loop. These R-loops tend to promote and support the formation of secondary structures [
23]. Transcription tends to generate negatively supercoiled DNA and in the highly transcribed genes supercoiling can exceed to an extent where an elongating polymerase can no longer counteract it. This leads to the generation of constitutive net negative helicity which causes transient denaturation of the DNA [
24] generating transcription-associated single-stranded ‘bubbles’ [
25]. Although transient, these bubbles may facilitate mutagenesis by activation induced deaminase (AID) and promote the formation of DSBs by forming excessive R-loops [
26].
4. G4 Formation Is Countered Directly and Indirectly during Replication
The factors known to hinder the formation of secondary structures can be classified into two groups: those that promote B-DNA formation and those that actively dismantle secondary structures, pushing the DNA back to its B-form. As mentioned earlier, the formation of secondary structures is aided by single-stranded DNA. Therefore, factors that reduce the exposure of single-stranded DNA indirectly decrease the probability of G-quadruplexes forming. For instance, PrimPol-mediated repriming of DNA synthesis after a block in leading strand polymerase [
27]. Proteins binding to single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) reduce its ability to form secondary structures. Additionally, these proteins can cause already formed G-quadruplexes (G4s) to become more relaxed or unwind, as exemplified by RPA [
14,
28], REV1 [
29] and a few of the ATP-dependent helicases including BLM and DHX36 proposed to have ATP-independent mechanisms to unfold G4s [
30]. Coordinating with these indirect or ATP-independent measures, numerous enzymatic activities have been implicated in effectively unwinding G-quadruplex structures. This includes the activities of DNA polymerases and helicases, which play a crucial role in managing secondary structure formation.
5. Replisome Encounters G4s That May Be Pre-Formed
Antibodies specific to G4s detect signals in non-S phase cells which suggests replisome encounters pre-formed G4s [
31]. Such encounters should first see the structure meet with replicative CMG helicases which unwinds the duplex DNA for replication. Recent advances in this field have tried to understand how pre-formed G4s are dealt by replisome. To understand this a good knowledge of CMG helicases is required. As regards to the structure of CMG helicase, it is well established that this ATP dependent enzyme is made up of the heterohexamer MCM2–7, which is the core motor of the helicase, along with Cdc45 and the GINS compl
ex [
32,
33]. Given that a pre-shaped G4 will incite nearby strand separation, it appears possible that a lagging strand G4 may only go round the helicase and not enter the central channel. This can be viewed as practically equivalent to the conduct of the replisome when it experiences a tethered streptavidin molecule on the lagging strand. Nevertheless, this capacity of CMG to cross lagging strand G4s isn’t just a uninvolved component of the complex as, without the accessory protein MCM10, lagging strand G4s do slow down the helicase prompting the suggestion that MCM10 is required to drive a conformational change in CMG to make it tolerant to a lagging strand secondary structures [
34].
It would be intriguing to investigate whether MCM10 is necessary for CMG (Cdc45-Mcm2-7-GINS) to navigate through G-quadruplex structures on the lagging strand. After passing the helicase, the G4 structure is likely to encounter the single-strand binding protein RPA (Replication Protein A). Notably, RPA has the capability to resolve G4 structures on its own, ensuring that the extension of the lagging strand during replication is not obstructed [
35].
The fate of a G-quadruplex (G4) structure on the leading strand during replication is not well-documented. There is no direct evidence suggesting that the translocation of the CMG (Cdc45-Mcm2-7-GINS) complex unwinds G4 structures on the leading strand. However, it is plausible that an advancing helicase could potentially disrupt such structures as it progresses along the DNA. It’s plausible that if the CMG complex doesn’t directly unwind G4 structures, the G4 could potentially pass through the channel of the MCM hexamer. Initially, at the point of assembly on DNA before origin activation, the channel of the MCM double hexamer allows double-stranded DNA [
36], which is approximately 2 nm (20 Å) in diameter, to pass through. However, at the origin, the MCM hexamers are oriented head-to-head and expel the lagging strand as they are converted to the active CMG complex, which proceeds along the leading strand template [
33]. The cryo-EM structure of the S. cerevisiae CMG complex reveals that while the opening of the channel into the N-terminus of MCM remains around 2 nm wide, there is a noticeable constriction deeper into the channel. The initial constrictions are formed by intrusions from the OB domains of MCM2 and MCM7 [
37]. Towards the C-terminus, the channel constricts progressively as the winged helix domain of MCM5 narrows it down to 1 nm, which may not be sufficient to accommodate dsDNA [
37]. However, despite this narrowing, CMG is capable of translocating on a duplex, indicating that the inner channel can indeed accommodate duplex DNA [
38]. Interestingly, the diameter of G-quadruplex structures is commonly larger than that of duplex DNA, ranging between 2.4 and 2.8 nm [
39]. Therefore, it seems unlikely that most G4s would be able to pass through the channel of the active helicase without some form of assistance.
6. Formation of G4s within the Replisome
Unwinding of DNA fundamentally creates an open door for secondary structure development. In this manner, the activity of the CMG helicase could, in essence, advance secondary structure development afterward. While the presence of RPA on the lagging strand should counter the likelihood of secondary structure arrangement, there is right now no proof that RPA ties to the main (leading) strand during an unperturbed replication event. Besides, regardless of the significant ongoing advances in the structure of the yeast replisome, neither the exact way or degree of the leading strand between the helicases and polymerase is known [
40]. Indeed, the length of the single-stranded DNA (ssDNA) region between the helicase and polymerase can vary significantly, affecting the dynamics of DNA polymerase movement differently from those influencing the replicative helicase. In extreme cases where the leading strand polymerase is stalled, the helicase can continue unwinding the parental duplex for a considerable distance, a phenomenon known as helicase-polymerase uncoupling. This results in the broader deposition of RPA [
41] along the ssDNA region. It is
reasonable to expect that continuous fluctuations in DNA synthesis speed, influenced by factors like DNA sequence and nucleotide availability, can cause temporary variations in leading strand exposure. This may be enough to allow secondary structure formation within the replisome. This aligns with a model where increased ssDNA length between the helicase and polymerase promotes G4 structure formation, posing a significant hindrance to DNA synthesis [
42].
7. G4 Biology Can Be Targeted in Therapeutics Intervention
Advances in G4 biology suggest they are intricately related with processes and control components that are significant for the biology and malignancy of cancer cells. These roles encompass telomere biology, replication, transcriptional regulation, and genome stability. Additionally, G-quadruplex (G4) motifs are disproportionately present in genes that promote cancer, and data indicates a higher prevalence of G4 structures in malignant states compared to normal states. This highlights G4s as potential targets for cancer treatment. Currently, the G4 ligand CX-5461 is undergoing human clinical trials for breast cancer patients with BRCA1/2 germline mutations. Furthermore, G4 ligands have shown synergy with DNA damaging therapies in ATR-X-deficient glioma cell models. They have also been effectively used in combination with inhibitors targeting key proteins involved in the DNA repair pathway. For instance, Pyridostatin synergizes with NU7441, an inhibitor of DNA-PK, a critical kinase in the non-homologous end joining (NHEJ) pathway. Similarly, the combination of RHPS4 and the PARP1 inhibitor GPI 15427 resulted in a 50% reduction in HT29 colon tumor xenograft growth, compared to 2% and 30% reductions with GPI 15427 and RHPS4 alone, respectively.
Another way is to target G4-containing genes engaged with malignant growth and control their transcription. The gene expression of individual genes has been regulated with small molecule inhibitors, it is sane to accept that most G4 ligands would bind to different G4s and conceivably regulate expression of many genes. This approach can influence and affect many pathways significant for cancer progression. A proof of this concept is the global transcriptional profiling of human pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) cell lines treated with the G4 ligand CM03 which demonstrate global downregulation of numerous G4-containing genes. An analysis of the downregulated genes revealed G-quadruplex (G4)-containing genes linked to pathways crucial for pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) progression. Notably, CM03 reduced tumor growth in PDAC xenografts and KPC mouse models at feasible doses without evident toxicity.
Thus, it is possible that a specific G4 ligand may bring about a distinct profile of affected genes for proteins engaged many pathways, appropriate for targeting malignant growths. As such, global transcriptional profiling of cancer cells supplemented with G4 ligands may help identify the affected pathways and recognize tumours most appropriate for testing efficacy. A thorough understanding of the pathways influenced by G4 ligands may ultimately provide a rationale to consider combination treatment opportunities with other available medications.
8. G4 DNA Can Potentially Be Targeted against Parasitic Adversaries
DNA damage in cells is a well known phenomenon. Due to DNA damage the replication fork stalls, this is when helicases come into the picture to remodel the stalled forks for the replication to proceed. A mycobacterial helicase DinG known to resolve DNA secondary structures in vitro also remodels stalled forks to replication by potential ‘chicken foot structure’ formation to enable replication recovery [
43]. Likewise, RuvAB, RecG, and UvrD helicases remodel stalled replication forks to restart the abortative replication in
E. coli [
43,
44,
45]. Notably, DinG from mycobacteria also tends to unwind HJ substrates, which demonstrates its involvement in recombinational repair possibly through its branch migration activity [
43]. Intrestingly,
M. tuberculosis genome doesn’t code for either RecQ and Pif1 helicases, suggesting that DinG in may be the only helicase to processes G4 structures
in vivo [
43]. Because DinG resolves G4s readily, and processes stalled replication fork or HJ structures only in high concentration it is possible that this helicase is the prominent G4 resolving enzyme in Mycobacteria whose genome is highly GC-rich with over 10,000 G-rich sequences that can form G4 structures [
43].
Many groups have reported the existence of G4 structures in the promoter regions of
M. tuberculosis [
8,
43,
46]. The genes that are encoded by the
mce1R operon play a crucial role in the persistence of
M. tuberculosis in the murine model. [
47] It is now known that G-rich sequences occurring in the promoter region of the
mce1R gene fold into canonical G4 structures. In other words, G4 structure formation may be a key component of the regulation of
mce1R expression. Similarly, genes encoding PE_PGRS have G-rich promoters that form G4 structures. Importantly, PE_PGRS family proteins appear to be exclusive to the genome of mycobacteria and are highly expressed in the pathogenic mycobacteria [
48]. Such proteins aid
M. tuberculosis in the persistence of infection and pathogenesis [
49]. The other gene carrying a G-rich promoter and forms G4 structures is
moeB1 [
43]. This gene is crucial for the survival of pathogenic mycobacteria as it encodes an enzyme needed for molybdopterin synthesis. Molybdopterin itself acts as a cofactor for many crucial enzymatic reactions whose disruption leads to growth attenuation of
M. tuberculosis grown in macrophages. This suggests G4 DNA structures may be important for the regulation of crucial genes such as, moeB1—a potential molecular target for novel therapeutics [
43].
As such the abundance of G4-forming sequences in
M. tuberculosis may assume importance for developing novel therapeutics. The sensitivity of
M. tuberculosis H37Ra cells to G4-specific ligand TMPyP4, and the demonstration of reduced growth support the view that G4 structures can be targeted for new drug design against pathogenic species that cause tuberculosis [
50]. However, identifying pathogenic genes that contain G4 structures in their promoters, and are essential for virulence, infection, pathogenicity and survival in host remains a therapeutic mainstay. Another important attribute of drug discovery aiming G4 structures is inhibitor specificity, thus, new inhibitors found should specifically target pathogenic G4 structures and not of the host.
9. Structure Based Drug Design—A Potential Way Forward
Structure-based drug design has emerged as one of the most powerful methods in the field of drug discovery. Indeed, a combination of chemistry and structure-based design has a potential to lead the synthesis of both compound libraries against a molecular target and direct the discovery of a drug lead or pro-drug with high affinity (preferably in nano or picomolar) for the target [
51]. Through time-consuming and cumbersome, this method has had many success stories over the past many decades [
51].
The entire structure-based m drug design is iterative goes through many cycles before a optimized lead goes into stage -I clinical trials. First cycle begins with the cloning, expression, purification and structure determination of the target protein or nucleic acid by one of three key techniques: X-ray crystallography, NMR, AI based modelling or high resolution Cryo-EM that has elevated the prospects and promises of drug discovery. Utilizing computer algorithms, compounds or their fragments are taken from databases and positioned into catalytic site or substrate binding site of the target structure. These compounds are then scored and ranked depending upon their steric and electrostatic interactions with the target site, and the best compounds are tested biochemically. In the second cycle, structure determination of the molecular target in complex with a promising lead from the first cycle is carried out. This is apparently done with a compound showing best potency in vitro to uncover lead binding sites for further optimization to obtain selectivity and potency. Subsequent cycles incorporate a combination of approaches, such as, synthesis of the optimized lead, structure determination of the new target: lead complex, and further enhancement of the lead compound potency [
51]. After many cycles of the drug design process, the optimized lead typically shows many-fold improvement in binding, specificity and potency.
A key facet of finding a suitable target for drug discovery is to select a target which is present in the adversary and absent in the host or a target which is present in both but structurally different to enable its drug targeting with small molecules that target the parasitic form and not the host form of target. Given that bacteria such as,
Mycobacterium tuberculosis have evolved differently than humans, the enzymes encoded by them find orthologs in human host but tend to be structurally different due to differences in the mechanism of action or structural differences brought about by key amino acid differences. Such key amino acid differences tend to shape the catalytic pocket of orthologous protein differently and in turn, aiding new inhibitor design. As parasitic G4 biology and the helicases encoded by parasitic organisms tend to harbour key structural differences, new inhibitor discovery targeting key parasitic proteins becomes inevitable. A significant feature of helicases is their essentiality for the parasite which makes them suitable for drug targeting. One such helicase is the DinG of
M. tuberculosis which not only shows structure specific helicase activity but may have potential roles in restarting stalled replication and recombinational repair [
43]. Targeting this enzyme with new small molecule pro-drugs assumes significance as prokaryotic genomes including
M. tuberculosis doesn’t encode RecQ and Pif1 helicases. This makes DinG a sole helicase to resolve G4 structures in vivo and a potential validate candidate for drug design.
There are many reports now which suggest G4 binding ligands can increase the vulnerability of pathogenic bacteria and de-escalate their growth and sustenance abilities in host. Therefore, conceiving a combinatorial approach involving the use of both potent and specific G4 ligands and small molecule inhibitors targeting key pathogenic helicases may emerge as a key therapeutic strategy to cause effective elimination of pathogenic bacteria such as, M. tuberculosis.
10. Key Helicases Involved in G4 Processing
Helicases are ATP dependent molecular motors that unwind DNA and RNA double helices during vital cellular processes such as, replication, transcription, recombination and repair etc. Genes encoding helicases when mutated are connected to a few human ailments, some with attributes of neurological issues, quickened ageing and expanded danger of malignant growth advancement [
52]. Helicases play critical roles in different pathways and, until this point, no helicase is exclusively committed to G4 disruption only. Some of the important helicases and their known functions are summarized in the subsequent sections of this article.
10.1. Superfamily 1: DNA2 and PIF1
10.1.1. DNA2
DNA2 carries ssDNA endonuclease activity on both 5′ and 3′ single-stranded overhangs and a 5′-3′ helicase activity [
53,
54]. DNA2 characterized from human and yeast sources is known to bind to and unwind telomeric G4s in vitro and in the presence of RPA, to which the enzyme binds [
55]. Upon decline of DNA2 protein levels, defects in telomere replication and genetic aberrations occur in mouse cells, yet its importance for G4 resolution in vivo remains largely unknown [
56].
10.1.2. PIF1
The PIF1 family of enzymes are 5′-3′ helicases which unwind G4 structures. These enzymes are are largely conserved from bacteria to humans. P1F1 is not a processive helicases, but it traps a melted G4 in unfolded state by binding to the single-stranded DNA [
57,
58]. PIF1 characterized from human and yeast sources takes part in G4 metabolism at both nuclear (mainly telomeric) and mitochondrial genomes [
59], with the last prevailing as mitochondrial dysfunction in PIF1 mutants [
60]. Alternatively, it is well established that processing of G4 by Pif1 is essential to safeguard replication fork movement and supress chromosome breakage in both budding and fission yeast [
61,
62]. Pif1 is also know to partner with replication fork components and associate with PCNA to ensure effective replication through G4s. However, it remains ambiguous as to whether Pif1 works transcendently on the leading or lagging strand, while, it is understood that loss of Pif1 fuels hereditary precariousness brought about by leading strand G4s [
62]. Besides, it is now known that that general fork delay at a G4 is expanded without Pif1 when the G4 is on the lagging strand [
15]. The prompt clarification for this error is indistinct, and the two prospects are not fundamentally unrelated yet there doesn’t appear to be a straightforward connection between fork delay and the induction of hereditary unsteadiness.
10.2. The Superfamily 2 RecQ-Like Helicases: BLM and WRN
RecQ helicases are ubiquitous proteins encompassing a core domain of about 450 amino acids which includes a conserved DExH box unwinding with a 3′-5′ polarity. Human genome encodes five RecQ helicases, two of which are reported to have important roles in G4 digestion, BLM and WRN mutated in Bloom’s condition [
63] and Werner’s disorder [
64], respectively. ATP-subordinate G4 resolution by RecQ helicases is very well understood and includes DNA binding to the RecQ C-terminal domain (RQC), which is responsible for the recognition of DNA structures [
65]. Structure of a bacterial RecQ bound to a G4 gives a significant mechanistic information of this enzyme which can improve our mechanistic understanding of RecQ family of helicases. The structure highlights that guanine explicit pocket (GSP) sequesters dG from the end of G4 in a way that would not be fit with its participation in a folded G4 highlighting that the enzyme may be specific in its binding to a folded G4 and evicts out a guanine at the base of the structure. Whenever performed successively, this activity would destabilize the structure [
66].
10.2.1. BLM
BLM is reported to be the first human helicase [
67] to resolve G4s. Characterization of BLM function in vitro suggests this helicase binds to and unwinds multi-stranded intermolecular G4s over duplex DNA and extended substrates like twofold Holliday junctions [
65]. This helicase requires a short 30 single-strand overhang so as to stack onto DNA for G4 unwinding and the nearness of a G4 inside 6 nt of the finish of this tail represses its G4 unwinding activity [
67,
68]. It is interesting that BLM is less active on more physiologically applicable intramolecular G4s and its action is repressed by G4 binding ligands, which trap this protein in a state where it hydrolyses ATP yet can’t unwind G4s [
69,
70]. BLM destabilizes G4s both actively and passively. The active or ATP-dependent resolution of intramolecular G4s emerges by the protein pulling in single-stranded DNA nearby the structure [
71]. Unlike PIF1, BLM separates from the DNA, if it is unable to unwind G4s [
72]. Multiple experiments conducted in vivo also support BLM assuming a significant role in the processing of G4s. In fact, BLM homolog HIM-6 from
C. elegans limits G-tract deletions without the FANCJ homolog dog-1 [
73]. Another in vivo proof that BLM assumes a strong role in countering G4 formation stems from an inquisitively reliable element of cells lacking BLM and WRN helicases: dysregulated gene expression of gene sequences harbouring G4s motifs at or in the vicinity of their transcription start sites (TSS). This phenomenon can be explained with following reasons (i) Genes harbouring G4 forming sequences in the promoter region may witness altered gene expression due to persistent G4 formation (ii) In dysregulated genes, G4s can also be formed downstream of TSS which may cause altered expression via epigenetic instability [
19]. Because of the nature of telomere repeat TTAGGG, telomeres have the highest density of potential G4-enacting sequences in the genome thus; it is obvious that helicases with potential to resolve G4s like BLM assume a significant role in the telomere upkeep. BLM helicase interacts with an OB fold-bearing telomeric single-strand binding protein called POT1 [
74], and BLM deficient mouse cells are disabled in correct replication of G4-framing telomeric sequences, bringing about expanded telomeric instability [
75].
10.2.2. WRN
WRN is a unique G4 resolving helicase as along with its 3′-5′ helicase activity, this enzyme also exhibits exonuclease and single-strand annealing activities [
76]. This helicases is known to resolve many secondary structures including G4s and can act on its substrates both in ATP-dependent and independent ways, requiring a short 30 ssDNA tail and is invigorated by RPA [
77,
78]. Notably, WRN has been reported to physically associate with BLM and work in collaboration
in vivo [
79]. Intriguingly, WRN and BLM also display extensive functional redundancy to keep up G4 dependent epigenetic and transcriptional stability [
19]. And Like BLM helicase, WRN assumes a significant role at telomeres. WRN also associates with pol δ and this interaction appears to empower pol δ to replicate through G4s, indicating that WRN could assume a role in telomeric lagging strand replication [
80]. This is substantiated by the essentiality of WRN for the replication of a (TTAGGG)6 telomeric repeat where its absence leads to large recurring deletions and rearrangements [
81], and the inability of WRN-deficient to retain G-rich telomere lagging strand [
82]. Further control of WRN at telomeres probably originates from explicit associations with telomeric proteins and the shelter in complex proteins, which manage WRN’s catalytic roles on telomeric D-loops. The role of WRN at the telomeres and its connect to forestalling ageing is underscored by observation that telomerase-deficient mice with short telomeres that are also devoid of WRN show dysfunctional telomeres and high degree of chromosomal instability.
10.3. The Superfamily 2 Fe-S Helicases
Fe-S helicases are present in many known proteins involved in DNA metabolism [
83] and carry iron-sulphur clusters as protein co-factors which are implicated to have vital roles in protein folding and domain stabilisation [
84]. These Fe-S helicases include RTEL1, DDX11, FANC and XPD helicases, all of which have a tendency to unwind G4s
in vitro.
10.3.1. FANCJ
FANCJ, also known as BRIP1 and BACH1 is an ATP-dependent 5′-3′ helicase which unwinds DNA duplex, branched DNA structures, D-loops and many forms of G4s which tend to be its more favourable substrates [
85,
86]. This helicase is mutated in an uncommon subtype of Fanconi Anemia [
87]. Notwithstanding its helicase core that ties with and translocates along ssDNA, FANCJ additionally has a G4 recognition site [
88]. Like other known G4 disturbing helicases, it requires a short ssDNA tail for ideal G4 unwinding activity and is invigorated by RPA [
85]. FANCJ has been reported to associate with the elongating replication fork [
89] and with telomeres [
90]. With respect to PIF1, there is proof for FANCJ working on both leading and lagging strands. Worms lacking FANCJ orthologue dog-1 possess deletions in G4 motifs that can possibly enact G4 structures during lagging strand replication [
73]. Apparently, in chicken DT40 cells, FANCJ smothers the development of G4 structures on the leading strand template [
19]. This capacity of FANCJ to oversee G4s at the fork assumes a significant importance in the potential of cells to sustain chromatin states through replication [
19,
91]. Besides, FANCJ resolves G4s independent of the canonical FA pathway. Moreover, deficiency of FANCA or FANCD2 doesn’t prompt affectability to the G4 ligand telomestatin in human cells [
92], and the G4-subordinate instability of expression of the BU-1 locus of DT40 seen in FANCJ-deficient cells isn’t seen in a FANCC mutant [
19]. Similarly, the tenacious fork stalling that happens during replication of a G4-containing plasmid in a FANCJ-depleted Xenopus egg extract isn’t seen following depletion of FANCD2 [
93]. In any case, the double mutant of FANCJ and FANCD2 shows a higher mutation rate at G4 motifs than a single FANCJ mutant in
C. elegans, indicating that these proteins may assume distinct roles to encourage G4 resolution [
94].
10.3.2. DDX11
DDX11 is also known as CHLR1 and is reported to be essential [
95]. Mutations of this gene lead to a rare inheritable disorder called Warsaw Breakage Syndrome which is characterized by retarded growth, microcephaly, cochlear abnormalities and abnormal skin pigmentation [
96]. This helicase resolves G4s [
97] along with other DNA structures such as, D-loops [
98] and triplex DNA [
99] in an ATP dependent manner [
98]. DDX11 exhibits high homology with the helicase core of FANCJ, yet the two helicases tend to have different G4 substrate preferences. While unlike DDX11, FANCJ tends to be proficient against unimolecular G4 [
97], DDX11 prefers intermolecular G4 substrates for unwinding [
97], which has a potential but unproven relevance in the origin of prominent phenotypes due to its inactivation and defects in sister chromatid cohesion [
97,
98]. DDX11 has been shown to interact with eurokaryotic replisomes core component, the Timeless [
100], and has been implicated to place it in right orientation to disrupt G4s that tend to abrogate the progression of the replicative polymerases.
10.3.3. RTEL1
RTEL1 or Regulator of telomere prolongation helicase 1 assumes a vital role in the maintenance of telomere. It exhibits 5′-3′ helicase activity to catalyze ATP-dependent resolution of an intramolecular G4 framed by the human telomeric repeat. Without RTEL1, telomeric D-loops (T-loops) are not effectively resolved during replication, bringing about loss of telomeric sequence [
75]. Besides, RTEL1 stifles telomeric instability due to G4s as the delicacy of telomere without RTEL1 is limitlessly expanded when BLM is also evacuated or G4s are ligand stabilised [
75]. As T-circles are known to shield telomeres from de-stabilizing events, the biochemical action of RTEL1 is in line with an anticipated capacity of this helicase to encourage the replication of the 30 G-rich overhang [
101]. Notably, the deficiency of RTEL1 proves fatal, possibly due to the undermined telomere lengthening in ES cells [
102]. Meanwhile, RTEL1 also assumes a roles in the non-telomeric DNA replication. It interacts with PCNA to bind to the replisome. Loss of interaction between RTEL1 and PCNA prompts diminished replication fork speed and expanded fork instability.
10.3.4. XPD/ERCC2
XPD or ERCC2 helicase is one of the members of the TFIIH complex, and is reported to have roles in nucleotide excision repair (NER) and basal transcription [
103]. While as, XPD first binds to and then unwinds G4 secondary structures, other member of the TFIIH complex called XPB only binds G4 DNA [
104]. Notably, the binding sites of XPD and XPB overlap with G4 motifs suggesting that TFIIH is recruited to G4 structures. Besides, the binding sites of XPD and XPB are often located near TSS of highly expressed genes whose in vivo importance remains largely unknown.
10.4. The Superfamily 2 DEAD-Box Helicases: DHX36
DHX36 is also known as RHAU/G4-Resolvase 1 and DHX9, and was firstly distinguished as a RNA helicase. It was reported to be recruited to an AU-rich element in the urokinase plasminogen activator messenger RNA (mRNA), henceforth given the name RHAU. This enzyme acts to promote the deadenylation of mRNA and mRNA decay by exosome [
105]. This gene sequence coding for this helicase is considered essential and implicated in embryogenesis [
106]. It was subsequently recognized to predominantly resolve G4 structures in HeLa cell lysate [
107]. DHX36 exhibits specificity for parallel G4s resolving both unimolecular and tetramolecular structures in an ATP-dependent manner [
108,
109]. It has an amazingly high affinity for both DNA and RNA G4s which is interceded to a greater degree by a 13 amino acid N-terminal motif, the DHX36 specific motif (DSM), and to some extent by contacts made by the C-terminal OB fold domain [
30].
There are reports of DHX36 acting on its substrates in ATP independent manner as well [
30,
110]. Crystal structure of Bos taurus DHX36 bound to the MYC promoter G4 affirms its mode of binding to be identical to numerous G4 ligands wherein DSM enacts a flat, non-polar surface which connects with the top quartet of G4 [
30].
The energy originating from nucleic acid binding is transduced by the helicase into a coordinated pulling power emerging from the rotation of C-terminal domain and opening of the core of helicase enzyme. This outcomes in the parallel G4 substrate being resolved consecutively by each nucleotide in turn without the requirement for ATP hydrolysis, giving additional proof for the occurrence and significance of ATP-independent methods of G4 destabilization. Notably, the hydrolysis of ATP is required for the release of the substrate and when the enzyme is bound to ADP or the non-hydrolysable analogue AMP-PNP which tends to stabilize G4 structures against mechanical unwinding [
111]. This signifies that a helicase can display opposing activities by causing both G4 unwinding up and stabilisation.
10.4.1. DHX9
DHX9 is also referred to as a Nuclear DNA helicase or RNA helicase A is has emerged as a physiologically important DNA G4 resolving helicase [
112] and is reported to associate with PCNA [
113], WRN [
114] along with the topoisomerase II [
115]. As such DHX9 has a role in DNA replication and appears to be an essential helicase as fibroblast cells lacking DHX9 demonstrate significant replication defects and p53-dependent senescence [
116].
11. Helicases Connect Translocation along DNA with Protein Displacement
Helicases are important enzymes in nucleic acid metabolism for their role in unwinding and remodelling of nucleic acids—DNA and RNA by using ATP to power their directional translocation [
117]. Nonetheless, nucleic acids are bound by proteins thus strand separation can be accomplished once the interactions between nucleic acids and bound proteins are nullified [
118]. Helicases are equipped with the ability to act through chemo-mechanical pushing for protein displacement along DNA [
119]. In fact, the translocation along DNA is coupled to protein dislodging and helicases appear to have developed mechanisms to encourage this coupling. Indeed, the protein-DNA complexes are obstructions to DNA replication, creating a need for accessory replicative helicases that guide fork development along protein-bound DNA [
120]. Rep is the accessory helicase in
Escherichia coli, translocating 3′-5′ along ssDNA and likely operates on the leading strand template at the replication fork to help protein dislodging in front of the fork [
121]. This activity is encouraged by interaction between the Rep C-terminus and the 5′-3′ replicative helicase DnaB [
121].
Meanwhile there appears to be a direct relationship between helicases catalyzed DNA unwinding and protein displacement. While as the 2B subdomain is not essential for DNA unwinding, lack of this subdomain in RepΔ2B inhibits protein displacement from DNA within the setting of both ssDNA and dsDNA [
122]. Besides, RepΔ2B can’t also work as an accessory replicative helicase. Therefore, regardless of whether or not DNA is being unwound, the presence of 2B subdomain is critical for proficient coupling of translocation with protein displacement. In fact, helicases have developed specific structural highlights to upgrade nucleoprotein disruption alongside duplex DNA unwinding [
122]. Considering the omnipresence of proteins bound to DNA inside cells, similar structural highlights may be present in other prominent helicases to guarantee that protein-bound DNA is resolved adequately whenever necessary.
12. In Conclusion
The extension of G4 biology work from in vitro to in vivo has improved our understanding regarding the importance of G4 structures in biological systems and in health and disease. It is now fairly clear that G4 DNA structure has numerous biological function and right now it appears many of these functions may still be unknown and would need more studies to develop a thorough and mechanistic understanding of how G4 structures influence crucial biological process such as, replication, transcription and DNA repair. Given the importance of G4 structures in critical biological process, it may be feasible to target G4s as molecular targets to develop novel therapeutics against many parasitic adversaries.
Funding
No funding support was used to produce this article
References
- Mirkin, S. M. Expandable DNA repeats and human disease. Nature 447, (2007). [CrossRef]
- Wickramasinghe, C. M., Arzouk, H., Frey, A., Maiter, A. & Sale, J. E. Contributions of the specialised DNA polymerases to replication of structured DNA. DNA Repair 29, (2015). [CrossRef]
- GELLERT, M., LIPSETT, M. N. & DAVIES, D. R. Helix formation by guanylic acid. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 48, (1962).
- Sundquist, W. I. & Klug, A. Telomeric DNA dimerizes by formation of guanine tetrads between hairpin loops. Nature 342, (1989). [CrossRef]
- Huppert, J. L. & Balasubramanian, S. Prevalence of quadruplexes in the human genome. Nucleic Acids Research 33, (2005). [CrossRef]
- Wang, L., Wang, Q. M., Wang, Y. R., Xi, X. G. & Hou, X. M. DNA-unwinding activity of Saccharomyces cerevisiae Pif1 is modulated by thermal stability, folding conformation, and loop lengths of G-quadruplex DNA. Journal of Biological Chemistry 293, (2018).
- Chambers, V. S. et al. High-throughput sequencing of DNA G-quadruplex structures in the human genome. Nature Biotechnology 33, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P. et al. G-quadruplex structures in bacteria: Biological relevance and potential as an antimicrobial target. Journal of Bacteriology 203, (2021). [CrossRef]
- Burge, S., Parkinson, G. N., Hazel, P., Todd, A. K. & Neidle, S. Quadruplex DNA: Sequence, topology and structure. Nucleic Acids Research 34, (2006).
- Siddiqui-Jain, A., Grand, C. L., Bearss, D. J. & Hurley, L. H. Direct evidence for a G-quadruplex in a promoter region and its targeting with a small molecule to repress c-MYC transcription. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 99, (2002). [CrossRef]
- Smith, J. S. et al. Rudimentary G-quadruplex-based telomere capping in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology 18, (2011). [CrossRef]
- Valton, A. L. et al. G4 motifs affect origin positioning and efficiency in two vertebrate replicators. EMBO Journal 33, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Ding, H. et al. Regulation of murine telomere length by Rtel: An essential gene encoding a helicase-like protein. Cell 117, (2004).
- Safa, L. et al. 5′ to 3′ unfolding directionality of DNA secondary structures by replication protein A: G-quadruplexes and duplexes. Journal of Biological Chemistry 291, (2016).
- Dahan, D. et al. Pif1 is essential for efficient replisome progression through lagging strand G-quadruplex DNA secondary structures. Nucleic Acids Research 46, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Lopes, J. et al. G-quadruplex-induced instability during leading-strand replication. EMBO Journal 30, (2011). [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, D. et al. Determinants of G quadruplex-induced epigenetic instability in REV 1-deficient cells . The EMBO Journal 33, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Sarkies, P., Reams, C., Simpson, L. J. & Sale, J. E. Epigenetic Instability due to Defective Replication of Structured DNA. Molecular Cell 40, (2010). [CrossRef]
- Sarkies, P. et al. FANCJ coordinates two pathways that maintain epigenetic stability at G-quadruplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Research 40, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Guilbaud, G. et al. Local epigenetic reprogramming induced by G-quadruplex ligands. Nature Chemistry 9, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Kireeva, M. L., Komissarova, N., Waugh, D. S. & Kashlev, M. The 8-nucleotide-long RNA:DNA hybrid is a primary stability determinant of the RNA polymerase II elongation complex. Journal of Biological Chemistry 275, (2000). [CrossRef]
- Gómez-González, B. & Aguilera, A. Activation-induced cytidine deaminase action is strongly stimulated by mutations of the THO complex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 104, (2007). [CrossRef]
- Daniels, G. A. & Lieber, M. R. RNA: DNA complex formation upon transcription of immunoglobulin switch regions: Implications for the mechanism and regualtion of class switch recombination. Nucleic Acids Research 23, (1995). [CrossRef]
- Kouzine, F., Sanford, S., Elisha-Feil, Z. & Levens, D. The functional response of upstream DNA to dynamic supercoiling in vivo. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology 15, (2008). [CrossRef]
- Jeon, J. H., Adamcik, J., Dietler, G. & Metzler, R. Supercoiling induces denaturation bubbles in circular DNA. Physical Review Letters 105, (2010). [CrossRef]
- Parsa, J. Y. et al. Negative supercoiling creates single-stranded patches of DNA that are substrates for AID-mediated mutagenesis. PLoS Genetics 8, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Sekibo, D. A. T. & Fox, K. R. The effects of DNA supercoiling on G-quadruplex formation. Nucleic Acids Research 45, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Audry, J. et al. RPA prevents G-rich structure formation at lagging-strand telomeres to allow maintenance of chromosome ends . The EMBO Journal 34, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Eddy, S. et al. Human Rev1 polymerase disrupts G-quadruplex DNA. Nucleic Acids Research 42, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. C. et al. Structural basis of G-quadruplex unfolding by the DEAH/RHA helicase DHX36. Nature 558, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Biffi, G., Tannahill, D., McCafferty, J. & Balasubramanian, S. Quantitative visualization of DNA G-quadruplex structures in human cells. Nature Chemistry 5, (2013). [CrossRef]
- Moyer, S. E., Lewis, P. W. & Botchan, M. R. Isolation of the Cdc45/Mcm2-7/GINS (CMG) complex, a candidate for the eukaryotic DNA replication fork helicase. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 103, (2006).
- Noguchi, Y. et al. Cryo-EM structure of Mcm2-7 double hexamer on DNA suggests a lagging-strand DNA extrusion model. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Langston, L. D. et al. Mcm10 promotes rapid isomerization of CMG-DNA for replisome bypass of lagging strand DNA blocks. eLife 6, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Salas, T. R. et al. Human replication protein A unfolds telomeric G-quadruplexes. Nucleic Acids Research 34, (2006). [CrossRef]
- Evrin, C. et al. A double-hexameric MCM2-7 complex is loaded onto origin DNA during licensing of eukaryotic DNA replication. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 106, (2009). [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Z. et al. Structure of the eukaryotic replicative CMG helicase suggests a pumpjack motion for translocation. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology 23, (2016). [CrossRef]
- Langston, L. & O’Donnell, M. Action of CMG with strand-specific DNA blocks supports an internal unwinding mode for the eukaryotic replicative helicase. eLife 6, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Amrane, S. et al. Formation of pearl-necklace monomorphic G-quadruplexes in the human CEB25 minisatellite. Journal of the American Chemical Society 134, (2012). [CrossRef]
- O’Donnell, M. E. & Li, H. The ring-shaped hexameric helicases that function at DNA replication forks. Nature Structural and Molecular Biology 25, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Zou, L. & Elledge, S. J. Sensing DNA damage through ATRIP recognition of RPA-ssDNA complexes. Science 300, (2003).
- Papadopoulou, C., Guilbaud, G., Schiavone, D. & Sale, J. E. Nucleotide Pool Depletion Induces G-Quadruplex-Dependent Perturbation of Gene Expression. Cell Reports 13, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Thakur, R. S. et al. Mycobacterium tuberculosis DinG is a structure-specific helicase that unwinds G4 DNA: Implications for targeting G4 DNA as a novel therapeutic approach. Journal of Biological Chemistry 289, (2014).
- Thakur, R. S. et al. Evidence for the role of Mycobacterium tuberculosis RecG helicase in DNA repair and recombination. FEBS Journal 280, (2013).
- Shukla, K., Thakur, R. S., Ganguli, D., Rao, D. N. & Nagaraju, G. Escherichia coli and Neisseria gonorrhoeae UvrD helicase unwinds G4 DNA structures. Biochemical Journal 474, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Zegeye, E. D., Balasingham, S. V., Laerdahl, J. K., Homberset, H. & Tønjum, T. Mycobacterium tuberculosis RecG binds and unwinds model DNA substrates with a preference for Holliday junctions. Microbiology (United Kingdom) 158, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Casali, N., White, A. M. & Riley, L. W. Regulation of the Mycobacterium tuberculosis mce1 operon. Journal of Bacteriology 188, (2006). [CrossRef]
- Delogu, G. et al. Rv1818c-encoded PE_PGRS protein of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is surface exposed and influences bacterial cell structure. Molecular Microbiology 52, (2004). [CrossRef]
- Copin, R. et al. Sequence diversity in the pe_pgrs genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis is independent of human T cell recognition. mBio 5, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S. K. et al. Characterization of G-Quadruplex Motifs in espB, espK, and cyp51 Genes of Mycobacterium tuberculosis as Potential Drug Targets. Molecular Therapy—Nucleic Acids 16, (2019). [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A. C. The process of structure-based drug design. Chemistry and Biology 10, (2003). [CrossRef]
- Brosh, R. M. DNA helicases involved in DNA repair and their roles in cancer. Nature Reviews Cancer 13, (2013). [CrossRef]
- Bae, S. H. et al. Dna2 of Saccharomyces cerevisiae possesses a single-stranded DNA- specific endonuclease activity that is able to act on double-stranded dna in the presence of ATP. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, (1998). [CrossRef]
- Budd, M. E. & Campbell, J. L. A yeast gene required for DNA replication encodes a protein with homology to DNA helicases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 92, (1995). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, C., Pourmal, S. & Pavletich, N. P. Dna2 nuclease-helicase structure, mechanism and regulation by Rpa. eLife 4, (2015).
- Lin, W. et al. Mammalian DNA2 helicase/nuclease cleaves G-quadruplex DNA and is required for telomere integrity. EMBO Journal 32, (2013). [CrossRef]
- Bochman, M. L., Sabouri, N. & Zakian, V. A. Unwinding the functions of the Pif1 family helicases. DNA Repair 9, (2010). [CrossRef]
- Byrd, A. K., Bell, M. R. & Raney, K. D. Pif1 helicase unfolding of G-quadruplex DNA is highly dependent on sequence and reaction conditions. Journal of Biological Chemistry 293, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Boulé, J. B. & Zakian, V. A. Roles of Pif1-like helicases in the maintenance of genomic stability. Nucleic Acids Research 34, (2006). [CrossRef]
- Bannwarth, S. et al. Inactivation of Pif1 helicase causes a mitochondrial myopathy in mice. Mitochondrion 30, (2016). [CrossRef]
- Ribeyre, C. et al. The yeast Pif1 helicase prevents genomic instability caused by G-quadruplex-forming CEB1 sequences in vivo. PLoS Genetics 5, (2009). [CrossRef]
- McDonald, K. R. et al. Pfh1 Is an Accessory Replicative Helicase that Interacts with the Replisome to Facilitate Fork Progression and Preserve Genome Integrity. PLoS Genetics 12, (2016). [CrossRef]
- Ellis, N. A. et al. The Bloom’s syndrome gene product is homologous to RecQ helicases. Cell 83, (1995). [CrossRef]
- Yu, C. E. et al. Positional cloning of the Werner’s syndrome gene. Science 272, (1996). [CrossRef]
- Huber, M. D., Lee, D. C. & Maizels, N. G4 DNA unwinding by BLM and Sgs1p: Substrate specificity and substrate-specific inhibition. Nucleic Acids Research 30, (2002). [CrossRef]
- Voter, A. F., Qiu, Y., Tippana, R., Myong, S. & Keck, J. L. A guanine-flipping and sequestration mechanism for G-quadruplex unwinding by RecQ helicases. Nature Communications 9, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Sun, H., Karow, J. K., Hickson, I. D. & Maizels, N. The Bloom’s syndrome helicase unwinds G4 DNA. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, (1998). [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q. et al. G-quadruplex formation at the 3′ end of telomere DNA inhibits its extension by telomerase, polymerase and unwinding by helicase. Nucleic Acids Research 39, (2011).
- Liu, J. Q., Chen, C. Y., Xue, Y., Hao, Y. H. & Tan, Z. G-quadruplex hinders translocation of BLM helicase on DNA: A real-time fluorescence spectroscopic unwinding study and comparison with duplex substrates. Journal of the American Chemical Society 132, (2010). [CrossRef]
- Li, J. L. et al. Inhibition of the Bloom’s and Werner’s syndrome helicases by G-quadruplex interacting ligands. Biochemistry 40, (2001). [CrossRef]
- Wu, W. Q., Hou, X. M., Li, M., Dou, S. X. & Xi, X. G. BLM unfolds G-quadruplexes in different structural environments through different mechanisms. Nucleic Acids Research 43, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Budhathoki, J. B., Stafford, E. J., Yodh, J. G. & Balci, H. ATP-dependent G-quadruplex unfolding by Bloom helicase exhibits low processivity. Nucleic Acids Research 43, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Youds, J. L., O’Neil, N. J. & Rose, A. M. Homologous recombination is required for genome stability in the absence of DOG-1 in Caenorhabditis elegans. Genetics 173, (2006). [CrossRef]
- Opresko, P. L. et al. POT1 stimulates RecQ helicases WRN and BLM to unwind telomeric DNA substrates. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280, (2005). [CrossRef]
- Vannier, J. B., Pavicic-Kaltenbrunner, V., Petalcorin, M. I. R., Ding, H. & Boulton, S. J. RTEL1 dismantles T loops and counteracts telomeric G4-DNA to maintain telomere integrity. Cell 149, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Shen, J. C. et al. Werner syndrome protein: I. DNA helicase and DNA exonuclease reside on the same polypeptide. Journal of Biological Chemistry 273, (1998).
- Brosh, R. M., Waheed, J. & Sommers, J. A. Biochemical characterization of the DNA substrate specificity of Werner syndrome helicase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, (2002). [CrossRef]
- Lee, M. et al. Multiple RPAs make WRN syndrome protein a superhelicase. Nucleic Acids Research 46, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Von Kobbe, C. et al. Colocalization, physical, and functional interaction between Werner and Bloom syndrome proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, (2002).
- Kamath-Loeb, A. S., Loeb, L. A., Johansson, E., Burgers, P. M. J. & Fry, M. Interactions between the Werner Syndrome Helicase and DNA Polymerase δ Specifically Facilitate Copying of Tetraplex and Hairpin Structures of the d(CGG)n Trinucleotide Repeat Sequence. Journal of Biological Chemistry 276, (2001).
- Damerla, R. R. et al. Werner syndrome protein suppresses the formation of large deletions during the replication of human telomeric sequences. Cell Cycle 11, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Crabbe, L., Verdun, R. E., Haggblom, C. I. & Karlseder, J. Defective telomere lagging strand synthesis in cells lacking WRN helicase activity. Science 306, (2004). [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y. & Brosh, R. M. DNA helicase and helicase-nuclease enzymes with a conserved iron-sulfur cluster. Nucleic Acids Research 40, (2012). [CrossRef]
- White, M. F. & Dillingham, M. S. Iron-sulphur clusters in nucleic acid processing enzymes. Current Opinion in Structural Biology 22, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R. et al. FANCJ (BACH1) helicase forms DNA damage inducible foci with replication protein a and interacts physically and functionally with the single-stranded DNA-binding protein. Blood 110, (2007). [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y., Shin-ya, K. & Brosh, R. M. FANCJ Helicase Defective in Fanconia Anemia and Breast Cancer Unwinds G-Quadruplex DNA To Defend Genomic Stability. Molecular and Cellular Biology 28, (2008). [CrossRef]
- Levitus, M. et al. The DNA helicase BRIP1 is defective in Fanconi anemia complementation group J. Nature Genetics 37, (2005). [CrossRef]
- Wu, C. G. & Spies, M. G-quadruplex recognition and remodeling by the FANCJ helicase. Nucleic Acids Research 44, (2016). [CrossRef]
- Alabert, C. et al. Nascent chromatin capture proteomics determines chromatin dynamics during DNA replication and identifies unknown fork components. Nature Cell Biology 16, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Déjardin, J. & Kingston, R. E. Purification of Proteins Associated with Specific Genomic Loci. Cell 136, (2009). [CrossRef]
- Schwab, R. A., Nieminuszczy, J., Shin-ya, K. & Niedzwiedz, W. FANCJ couples replication past natural fork barriers with maintenance of chromatin structure. Journal of Cell Biology 201, (2013). [CrossRef]
- London, T. B. C. et al. FANCJ is a structure-specific DNA helicase associated with the maintenance of genomic G/C tracts. Journal of Biological Chemistry 283, (2008). [CrossRef]
- Castillo Bosch, P. et al. FANCJ promotes DNA synthesis through G-quadruplex structures . The EMBO Journal 33, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Youds, J. L. et al. DOG-1 Is the Caenorhabditis elegans BRIP1/FANCJ Homologue and Functions in Interstrand Cross-Link Repair . Molecular and Cellular Biology 28, (2008).
- Inoue, A. et al. Loss of ChlR1 helicase in mouse causes lethality due to the accumulation of aneuploid cells generated by cohesion defects and placental malformation. Cell Cycle 6, (2007). [CrossRef]
- Alkhunaizi, E. et al. Warsaw breakage syndrome: Further clinical and genetic delineation. American Journal of Medical Genetics, Part A 176, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Bharti, S. K. et al. Specialization among iron-sulfur cluster helicases to resolve G-quadruplex DNA structures that threaten genomic stability. Journal of Biological Chemistry 288, (2013). [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y., Sommers, J. A., Khan, I., De Winter, J. P. & Brosh, R. M. Biochemical characterization of Warsaw breakage syndrome helicase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 287, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Guo, M. et al. A distinct triplex DNA unwinding activity of ChlR1 helicase. Journal of Biological Chemistry 290, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Calì, F., Bharti, S. K., Perna, R. Di, Brosh, R. M. & Pisani, F. M. Tim/Timeless, a member of the replication fork protection complex, operates with the Warsaw breakage syndrome DNA helicase DDX11 in the same fork recovery pathway. Nucleic Acids Research 44, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Porreca, R. M. et al. Human RTEL1 stabilizes long G-overhangs allowing telomerase-dependent over-extension. Nucleic Acids Research 46, (2018). [CrossRef]
- Uringa, E. J. et al. RTEL1 contributes to DNA replication and repair and telomere maintenance. Molecular Biology of the Cell 23, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Cleaver, J. E., Lam, E. T. & Revet, I. Disorders of nucleotide excision repair: The genetic and molecular basis of heterogeneity. Nature Reviews Genetics 10, (2009). [CrossRef]
- Gray, L. T., Vallur, A. C., Eddy, J. & Maizels, N. G quadruplexes are genomewide targets of transcriptional helicases XPB and XPD. Nature Chemical Biology 10, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Tran, H., Schilling, M., Wirbelauer, C., Hess, D. & Nagamine, Y. Facilitation of mRNA Deadenylation and Decay by the Exosome-Bound, DExH Protein RHAU. Molecular Cell 13, (2004). [CrossRef]
- Lai, J. C. et al. The DEAH-box helicase RHAU is an essential gene and critical for mouse hematopoiesis. Blood 119, (2012). [CrossRef]
- Vaughn, J. P. et al. The DEXH protein product of the DHX36 gene is the major source of tetramolecular quadruplex G4-DNA resolving activity in HeLa cell lysates. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280, (2005). [CrossRef]
- Chen, M. C., Murat, P., Abecassis, K., Ferre-D’Amare, A. R. & Balasubramanian, S. Insights into the mechanism of a G-quadruplex-unwinding DEAH-box helicase. Nucleic Acids Research 43, (2015). [CrossRef]
- Gueddouda, N. M., Mendoza, O., Gomez, D., Bourdoncle, A. & Mergny, J. L. G-quadruplexes unfolding by RHAU helicase. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta—General Subjects 1861, (2017).
- Tippana, R., Hwang, H., Opresko, P. L., Bohr, V. A. & Myong, S. Single-molecule imaging reveals a common mechanism shared by G-quadruplex-resolving helicases. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 113, (2016). [CrossRef]
- You, H., Lattmann, S., Rhodes, D. & Yan, J. RHAU helicase stabilizes G4 in its nucleotide-free state and destabilizes G4 upon ATP hydrolysis. Nucleic Acids Research 45, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, P. & Grosse, F. Human DHX9 helicase preferentially unwinds RNA-containing displacement loops (R-loops) and G-quadruplexes. DNA Repair 10, (2011). [CrossRef]
- Ohta, S., Shiomi, Y., Sugimoto, K., Obuse, C. & Tsurimoto, T. A proteomics approach to identify proliferating cell nuclear antigen (PCNA)-binding proteins in human cell lysates: Identification of the human CHL12/RFCs2-5 complex as a novel PCNA-binding protein. Journal of Biological Chemistry 277, (2002).
- Friedemann, J., Grosse, F. & Zhang, S. Nuclear DNA helicase II (RNA helicase A) interacts with Werner syndrome helicase and stimulates its exonuclease activity. Journal of Biological Chemistry 280, (2005). [CrossRef]
- Zhou, K. et al. RNA helicase A interacts with dsDNA and topoisomerase II. Nucleic Acids Research 31, (2003).
- Lee, T. et al. Suppression of the DHX9 helicase induces premature senescence in human diploid fibroblasts in a p53-dependent manner. Journal of Biological Chemistry 289, (2014). [CrossRef]
- Lee, J. Y. & Yang, W. UvrD Helicase Unwinds DNA One Base Pair at a Time by a Two-Part Power Stroke. Cell 127, (2006). [CrossRef]
- Mackintosh, S. G. & Raney, K. D. DNA unwinding and protein displacement by superfamily 1 and superfamily 2 helicases. Nucleic Acids Research 34, (2006). [CrossRef]
- Terakawa, T., Redding, S., Silverstein, T. D. & Greene, E. C. Sequential eviction of crowded nucleoprotein complexes by the exonuclease RecBCD molecular motor. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 114, (2017). [CrossRef]
- Ivessa, A. S. et al. The Saccharomyces cerevisiae Helicase Rrm3p Facilitates Replication Past Nonhistone Protein-DNA Complexes. Molecular Cell 12, (2003). [CrossRef]
- Guy, C. P. et al. Rep Provides a Second Motor at the Replisome to Promote Duplication of Protein-Bound DNA. Molecular Cell 36, (2009). [CrossRef]
- Brüning, J. G., Howard, J. A. L., Myka, K. K., Dillingham, M. S. & McGlynn, P. The 2B subdomain of Rep helicase links translocation along DNA with protein displacement. Nucleic Acids Research 46, (2018). [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).