Submitted:
13 September 2024
Posted:
17 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Concept of Brain Plasticity
1.2. Different Types of Plasticity
2. Neuroanatomic and Neurophysiologic Bases of Brain Plasticity
2.1. Plasticity in the Periphery and at the Centrum of the Brain
2.2. Natural Plasticity in Different Functional Areas
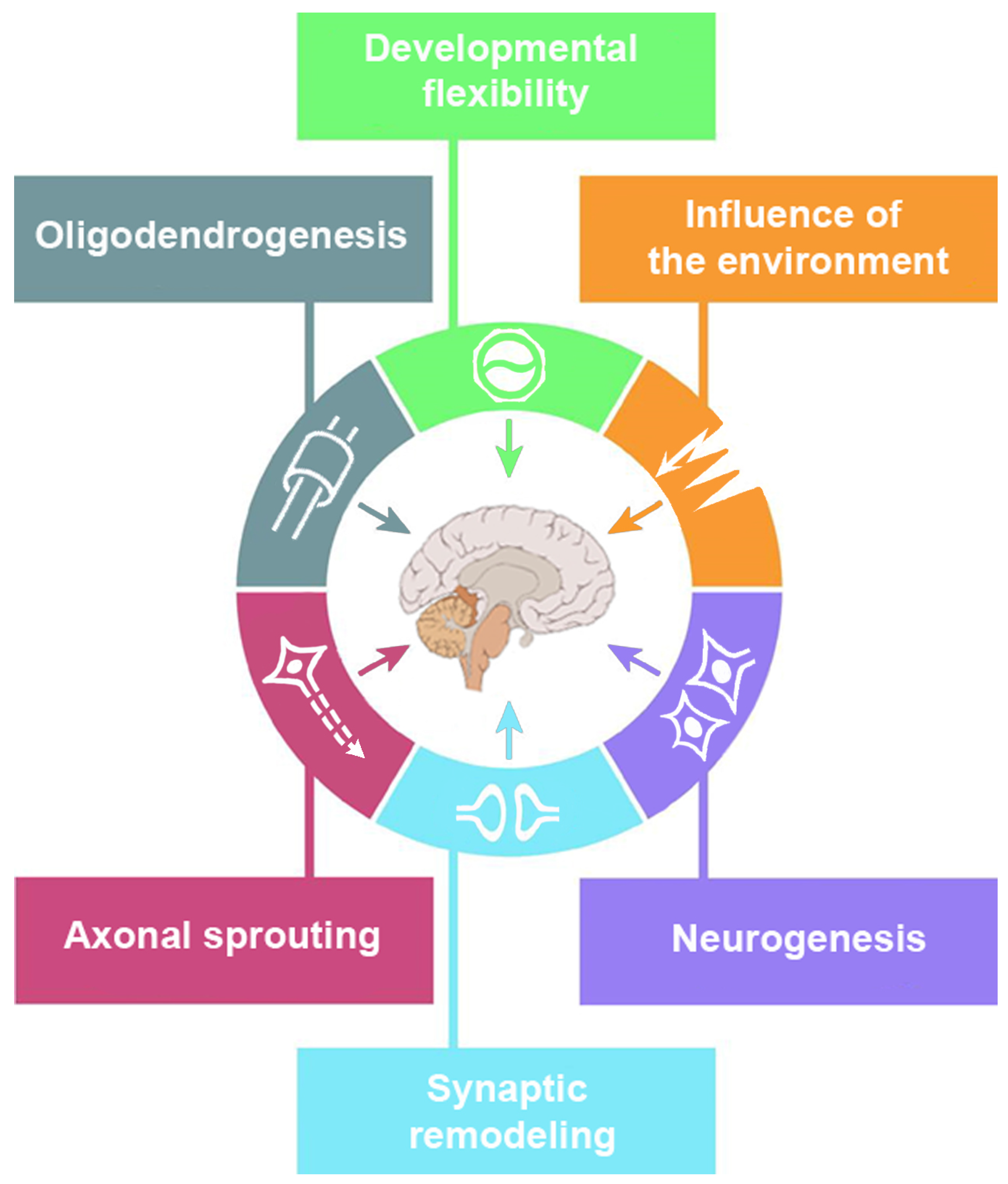
3. Pathophysiological Mechanisms Underlying Cerebral Plasticity
3.1. Plasticity Mechanisms at Microlevel
3.2. Plasticity Mechanisms at Macrolevel
4. Modulation of Experience-Dependent Change
4.1. Sex Hormones
4.2. Neurodevelopment and Brain Plasticity in Childhood
4.3. Brain Plasticity in Adulthood
5. Non-Coding RNAs in Brain Plasticity
6. Implications for Medical Practice
6.1. Pharmacology
6.2. Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation
6.3. Surgery
6.4. Transplantation
Conclusion
- The brain is a dynamic construct that changes structurally and/or functionally and constitutes interactive distributed glial-neuro-synaptic networks. Behavioral consequences of the changes may vary as a function of their effective connectivity, but the overall system remains stable due to homeostatic plasticity.
- A new insight into the concept of brain plasticity will provide perspectives on functional recovery following brain damage. The knowledge of this phenomenon will enable physicians to exploit cerebral plastic potential and regulate eloquent networks with timely interventions. Future studies will reveal pathophysiologic mechanisms of brain plasticity at microscopic and macroscopic levels, which will advance rehabilitation strategies and improve the quality of life in neurological diseases.
- Non-coding RNAs are optimal candidates for elucidating the molecular pathways underlying the phenomenon of brain plasticity. The candidates may signal the development of various neuropsychiatric disorders comprising schizophrenia, addiction, and fear-related anxiety disorders. The diversity of ncRNAs and their association with neurodegenerative diseases render them particularly interesting targets for new therapeutic approaches. New RNA-based therapeutics can arise from new data on the ncRNA regulation and the downstream effects of their interactions.
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
Patients and Public Involvement
Ethics and Dissemination
Abbreviations
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AMPA | -amino-3-hydroxy-5-methyl-4-isoxazolepropionic acid |
| BP | brain plasticity |
| BDNF | brain-derived neurotrophic factor |
| circRNA | circular RNA |
| ELAVL | embryonic lethal, abnormal vision, Drosophila-like |
| eRNA | enhancer RNA |
| FAT3 | FAT atypical cadherin 3 |
| GABA | gamma-aminobutyric acid |
| GAS5 | growth arrest specific 5 |
| HOTAIR | HOX transcript antisense RNA |
| Igfbp2 | insulin like growth factor binding protein 2 |
| lincRNA | long intergenic non-coding RNA |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| MALAT1 | metastasis associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1 |
| mRNA | messengerRNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| piRNA | Piwi-interacting RNA |
| RMST | rhabdomyosarcoma 2 associated transcript |
| RNA | ribonucleic acid |
| TMS | transcranial magnetic stimulation |
| XIST | X inactive specific transcript |
| yRNA | Y RNA |
Glossary
References
- Johnston, M.V. Clinical disorders of brain plasticity. Brain and Development 2004, 26, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H. Brain plasticity: from pathophysiological mechanisms to therapeutic applications. Journal of clinical neuroscience 2006, 13, 885–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolb, B.; Gibb, R. Brain plasticity and behaviour in the developing brain. Journal of the Canadian Academy of Child and Adolescent Psychiatry 2011, 20, 265. [Google Scholar]
- Fischer, T.M.; Blazis, D.E.; Priver, N.A.; Carew, T.J. Metaplasticity at identified inhibitory synapses in Aplysia. Nature 1997, 389, 860–865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Forrest, M.P.; Parnell, E.; Penzes, P. Dendritic structural plasticity and neuropsychiatric disease. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2018, 19, 215–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nature Porfolio. Spine Plasticity — Nature, Subjects, 2024. [Online; accessed 22-June-2024].
- Wikipedia contributors. Homeostatic plasticity — Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, 2024. [Online; accessed 22-June-2024].
- Kujala, T.; Alho, K.; Näätänen, R. Cross-modal reorganization of human cortical functions. Trends in neurosciences 2000, 23, 115–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimojo, S.; Shams, L. Sensory modalities are not separate modalities: plasticity and interactions. Current opinion in neurobiology 2001, 11, 505–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bavelier, D.; Neville, H.J. Cross-modal plasticity: where and how? Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2002, 3, 443–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rioult-Pedotti, M.S.; Friedman, D.; Donoghue, J.P. Learning-induced LTP in neocortex. science 2000, 290, 533–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephan, K.E.; Friston, K.J. Analyzing effective connectivity with functional magnetic resonance imaging. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews: Cognitive Science 2010, 1, 446–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Rosa, C.; Parolisi, R.; Bonfanti, L. Brain structural plasticity: from adult neurogenesis to immature neurons. Frontiers in neuroscience 2020, 14, 512123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sale, A.; Berardi, N.; Maffei, L. Environment and brain plasticity: towards an endogenous pharmacotherapy. Physiological reviews 2014, 94, 189–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mandolesi, L.; Gelfo, F.; Serra, L.; Montuori, S.; Polverino, A.; Curcio, G.; Sorrentino, G. Environmental factors promoting neural plasticity: insights from animal and human studies. Neural plasticity 2017, 2017, 7219461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buttelmann, F.; Karbach, J. Development and plasticity of cognitive flexibility in early and middle childhood. Frontiers in psychology 2017, 8, 258078. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stampanoni Bassi, M.; Iezzi, E.; Gilio, L.; Centonze, D.; Buttari, F. Synaptic plasticity shapes brain connectivity: implications for network topology. International journal of molecular sciences 2019, 20, 6193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, M.; Zheng, B. Axon plasticity in the mammalian central nervous system after injury. Trends in neurosciences 2014, 37, 583–593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marshall, K.L.; Farah, M.H. Axonal regeneration and sprouting as a potential therapeutic target for nervous system disorders. Neural Regeneration Research 2021, 16, 1901–1910. [Google Scholar]
- El Waly, B.; Macchi, M.; Cayre, M.; Durbec, P. Oligodendrogenesis in the normal and pathological central nervous system. Frontiers in neuroscience 2014, 8, 87323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fletcher, J.L.; Makowiecki, K.; Cullen, C.L.; Young, K.M. Oligodendrogenesis and myelination regulate cortical development, plasticity and circuit function. Seminars in cell & developmental biology. Elsevier, 2021, Vol. 118, pp. 14–23.
- Scott, H. Brain Plasticity Influencing Phantom Limb and Prosthetics. Outstanding Honors Theses 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Duffau, H. New insights into functional mapping in cerebral tumor surgery: study of the dynamic interactions between the lesion and the brain. Focus on Brain Mapping Research 2006, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Kolb, B.; Whishaw, I.Q. Brain plasticity and behavior. Annual review of psychology 1998, 49, 43–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johnston, M.V.; Nishimura, A.; Harum, K.; Pekar, J.; Blue, M.E. Sculpting the developing brain. Advances in pediatrics 2001, 48, 1–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gould, E.; Reeves, A.J.; Graziano, M.S.; Gross, C.G. Neurogenesis in the neocortex of adult primates. Science 1999, 286, 548–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenough, W.T. Structural correlates of information storage in the mammalian brain: a review and hypothesis. Trends in Neurosciences 1984, 7, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenough, W.T.; Hwang, H.; Gorman, C. Evidence for active synapse formation or altered postsynaptic metabolism in visual cortex of rats reared in complex environments. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 1985, 82, 4549–4552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, A.M.; Greenough, W.T. Differential rearing effects on rat visual cortex synapses. I. Synaptic and neuronal density and synapses per neuron. Brain research 1985, 329, 195–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jacobs, B.; Schall, M.; Scheibel, A.B. A quantitative dendritic analysis of Wernicke’s area in humans. II. Gender, hemispheric, and environmental factors. Journal of Comparative Neurology 1993, 327, 97–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purpura, D.P. Dendritic spine" dysgenesis" and mental retardation. Science 1974, 186, 1126–1128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikipedia contributors. Neuroplasticity — Wikipedia, The Free Encyclopedia, 2024. [Online; accessed 24-June-2024].
- Nudo, R.J.; Wise, B.M.; SiFuentes, F.; Milliken, G.W. Neural substrates for the effects of rehabilitative training on motor recovery after ischemic infarct. Science 1996, 272, 1791–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Georgopoulos, A.P. News in motor cortical physiology. News Physiol Sci 1999, 14, 64–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanes, J.N.; Schieber, M.H. Orderly somatotopy in primary motor cortex: does it exist? NeuroImage 2001, 13, 968–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karni, A.; Meyer, G.; Rey-Hipolito, C.; Jezzard, P.; Adams, M.M.; Turner, R.; Ungerleider, L.G. The acquisition of skilled motor performance: fast and slow experience-driven changes in primary motor cortex. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America 1998, 95, 861–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hlustik, P.; Solodkin, A.; Gullapalli, R.; Noll, D.C.; Small, S.L. Hand motor skill learning generalizes anatomically and behaviorally. NeuroImage 2000, 11, S866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pesenti, M.; Thioux, M.; Seron, X.; De Volder, A. Neuroanatomical substrates of arabic number processing, numerical comparison, and simple addition: a PET study. Journal of cognitive neuroscience 2000, 12, 461–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ganis, G.; Keenan, J.P.; Kosslyn, S.M.; Pascual-Leone, A. Transcranial magnetic stimulation of primary motor cortex affects mental rotation. Cerebral cortex (New York, N.Y. : 1991) 2000, 10, 175–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Laubach, M.; Wessberg, J.; Nicolelis, M.A. Cortical ensemble activity increasingly predicts behaviour outcomes during learning of a motor task. Nature 2000, 405, 567–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salenius, S.; Hari, R. Synchronous cortical oscillatory activity during motor action. Current opinion in neurobiology 2003, 13, 678–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchel, C.; Coull, J.; Friston, K.J. The predictive value of changes in effective connectivity for human learning. Science 1999, 283, 1538–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, F.G.; Gerloff, C. Coherence of sequential movements and motor learning. Journal of clinical neurophysiology : official publication of the American Electroencephalographic Society 1999, 16, 520–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffau, H.; Capelle, L.; Sichez, N.; Denvil, D.; Lopes, M.; Sichez, J.P.; Bitar, A.; Fohanno, D. Intraoperative mapping of the subcortical language pathways using direct stimulations. An anatomo-functional study. Brain 2002, 125, 199–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Gatignol, P.; Mandonnet, E.; Peruzzi, P.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N.; Capelle, L. New insights into the anatomo-functional connectivity of the semantic system: A study using cortico-subcortical electrostimulations. Brain 2005, 128, 797–810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McClelland, J.L.; Rogers, T.T. The parallel distributed processing approach to semantic cognition. Nature reviews neuroscience 2003, 4, 310–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatten, M.E. New directions in neuronal migration. Science 2002, 297, 1660–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gandolfo, F.; Li, C.S.; Benda, B.; Schioppa, C.P.; Bizzi, E. Cortical correlates of learning in monkeys adapting to a new dynamical environment. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2000, 97, 2259–2263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Laubach, M.; Wessberg, J.; Nicolelis, M.A. Cortical ensemble activity increasingly predicts behaviour outcomes during learning of a motor task. Nature 2000, 405, 567–571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lamprecht, R.; LeDoux, J. Structural plasticity and memory. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2004, 5, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Byrne, J.H. Synapses Plastic plasticity. Nature 1997, 389, 791–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buonomano, D.V.; Merzenich, M.M. Cortical plasticity: from synapses to maps. Annual review of neuroscience 1998, 21, 149–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aroniadou, V.A.; Keller, A. Mechanisms of LTP induction in rat motor cortex in vitro. Cerebral cortex 1995, 5, 353–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Braunewell, K.H.; Manahan-Vaughan, D. Long-term depression: a cellular basis for learning? Reviews in the Neurosciences 2001, 12, 121–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fischer, T.M.; Blazis, D.E.; Priver, N.A.; Carew, T.J. Metaplasticity at identified inhibitory synapses in Aplysia. Nature 1997, 389, 860–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, S.J.; Grimwood, P.D.; Morris, R.G. Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annual review of neuroscience 2000, 23, 649–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martin, S.J.; Grimwood, P.D.; Morris, R.G. Synaptic plasticity and memory: an evaluation of the hypothesis. Annual review of neuroscience 2000, 23, 649–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widrow, B.; Kim, Y.; Park, D.; Perin, J.K. Nature’s learning rule: The Hebbian-LMS algorithm. In Artificial Intelligence in the Age of Neural Networks and Brain Computing; Elsevier, 2024; pp. 11–40.
- Cruikshank, S.J.; Weinberger, N.M. Evidence for the Hebbian hypothesis in experience-dependent physiological plasticity of neocortex: a critical review. Brain Research Reviews 1996, 22, 191–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kilgard, M.P.; Merzenich, M.M. Cortical map reorganization enabled by nucleus basalis activity. Science 1998, 279, 1714–1718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andres, F.G.; Gerloff, C. Coherence of sequential movements and motor learning. Journal of clinical neurophysiology 1999, 16, 520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blitz, D.M.; Foster, K.A.; Regehr, W.G. Short-term synaptic plasticity: a comparison of two synapses. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2004, 5, 630–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malenka, R.C.; Nicoll, R.A. Silent synapses speak up. Neuron 1997, 19, 473–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ridding, M.; Brouwer, B.; Miles, T.; Pitcher, J.; Thompson, P. Changes in muscle responses to stimulation of the motor cortex induced by peripheral nerve stimulation in human subjects. Experimental brain research 2000, 131, 135–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fields, R.D.; Stevens-Graham, B. New insights into neuron-glia communication. Science 2002, 298, 556–562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haydon, P.G. GLIA: listening and talking to the synapse. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2001, 2, 185–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trachtenberg, J.T.; Chen, B.E.; Knott, G.W.; Feng, G.; Sanes, J.R.; Welker, E.; Svoboda, K. Long-term in vivo imaging of experience-dependent synaptic plasticity in adult cortex. Nature 2002, 420, 788–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanco, T.L.; Greenough, W.T. Physiological consequences of morphologically detectable synaptic plasticity: potential uses for examining recovery following damage. Neuropharmacology 2000, 39, 765–776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- by Synaptic, H.D.I. Rapid Dendritic Morphogenesis in CA1. Cold Spring Harb. Symp. Quant. Biol, 1987, Vol. 52, p. 825.
- Poo, M.m. Neurotrophins as synaptic modulators. Nature reviews neuroscience 2001, 2, 24–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turrigiano, G.G.; Nelson, S.B. Homeostatic plasticity in the developing nervous system. Nature reviews neuroscience 2004, 5, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selzer, M.E. Promotion of axonal regeneration in the injured CNS. The Lancet Neurology 2003, 2, 157–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ullian, E.M.; Sapperstein, S.K.; Christopherson, K.S.; Barres, B.A. Control of synapse number by glia. science 2001, 291, 657–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shao, Y.; McCarthy, K.D. Plasticity of astrocytes. Glia 1994, 11, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langle, S.L.; Poulain, D.A.; Theodosis, D.T. Neuronal–glial remodeling: a structural basis for neuronal–glial interactions in the adult hypothalamus. Journal of physiology-Paris 2002, 96, 169–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Couldwell, W.T.; Simard, M.F.; Song, H.; Lin, J.H.; Nedergaard, M. Direct gap junction communication between malignant glioma cells and astrocytes. Cancer research 1999, 59, 1994–2003. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Steindler, D.A.; Pincus, D.W. Stem cells and neuropoiesis in the adult human brain. The Lancet 2002, 359, 1047–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanai, N.; Tramontin, A.D.; Quinones-Hinojosa, A.; Barbaro, N.M.; Gupta, N.; Kunwar, S.; Lawton, M.T.; McDermott, M.W.; Parsa, A.T.; Manuel-García Verdugo, J.; others. Unique astrocyte ribbon in adult human brain contains neural stem cells but lacks chain migration. Nature 2004, 427, 740–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pincus, D.; Harrison-Restelli, C.; Barry, J.; Goodman, R.; Fraser, R.; Nedergaard, M.; Goldman, S. In vitro neurogenesis by adult human epileptic temporal neocortex. Clinical neurosurgery 1997, 44, 17–25. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Roy, N.S.; Wang, S.; Jiang, L.; Kang, J.; Benraiss, A.; Harrison-Restelli, C.; Fraser, R.A.; Couldwell, W.T.; Kawaguchi, A.; Okano, H.; others. In vitro neurogenesis by progenitor cells isolated from the adult human hippocampus. Nature medicine 2000, 6, 271–277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nunes, M.C.; Roy, N.S.; Keyoung, H.M.; Goodman, R.R.; McKhann, G.; Jiang, L.; Kang, J.; Nedergaard, M.; Goldman, S.A. Identification and isolation of multipotential neural progenitor cells from the subcortical white matter of the adult human brain. Nature medicine 2003, 9, 439–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gross, C.G. Neurogenesis in the adult brain: death of a dogma. Nature Reviews Neuroscience 2000, 1, 67–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magavi, S.S.; Macklis, J.D. Induction of neuronal type-specific neurogenesis in the cerebral cortex of adult mice: manipulation of neural precursors in situ. Developmental brain research 2002, 134, 57–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, D.K.; Botez, M. Diaschisis and neurobehavior. Canadian journal of neurological sciences 1998, 25, 5–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seitz, R.J.; Azari, N.P.; Knorr, U.; Binkofski, F.; Herzog, H.; Freund, H.J. The role of diaschisis in stroke recovery. Stroke 1999, 30, 1844–1850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Sichez, J.P.; Lehéricy, S. Intraoperative unmasking of brain redundant motor sites during resection of a precentral angioma: evidence using direct cortical stimulation. Annals of neurology 2000, 47, 132–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H. Acute functional reorganisation of the human motor cortex during resection of central lesions: a study using intraoperative brain mapping. Journal of Neurology, Neurosurgery & Psychiatry 2001, 70, 506–513. [Google Scholar]
- Rijntjes, M.; Weiller, C. Recovery of motor and language abilities after stroke: the contribution of functional imaging. Progress in neurobiology 2002, 66, 109–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krainik, A.; Duffau, H.; Capelle, L.; Cornu, P.; Boch, A.L.; Mangin, J.F.; Le Bihan, D.; Marsault, C.; Chiras, J.; Lehéricy, S. Role of the healthy hemisphere in recovery after resection of the supplementary motor area. Neurology 2004, 62, 1323–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Levänen, S.; Jousmäki, V.; Hari, R. Vibration-induced auditory-cortex activation in a congenitally deaf adult. Current Biology 1998, 8, 869–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, D.S.; Lee, J.S.; Oh, S.H.; Kim, S.K.; Kim, J.W.; Chung, J.K.; Lee, M.C.; Kim, C.S. Cross-modal plasticity and cochlear implants. Nature 2001, 409, 149–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rossini, P.M.; Dal Forno, G. Integrated technology for evaluation of brain function and neural plasticity. Physical medicine and rehabilitation clinics of North America 2004, 15, 263–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luders, E.; Gaser, C.; Jancke, L.; Schlaug, G. A voxel-based approach to gray matter asymmetries. Neuroimage 2004, 22, 656–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josse, G.; Mazoyer, B.; Crivello, F.; Tzourio-Mazoyer, N. Left planum temporale: an anatomical marker of left hemispheric specialization for language comprehension. Cognitive Brain Research 2003, 18, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sluming, V.; Barrick, T.; Howard, M.; Cezayirli, E.; Mayes, A.; Roberts, N. Voxel-based morphometry reveals increased gray matter density in Broca’s area in male symphony orchestra musicians. Neuroimage 2002, 17, 1613–1622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hutchinson, S.; Lee, L.H.L.; Gaab, N.; Schlaug, G. Cerebellar volume of musicians. Cerebral cortex 2003, 13, 943–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackay, C.E.; Roberts, N.; Mayes, A.R.; Downes, J.J.; Foster, J.K.; Mann, D. An exploratory study of the relationship between face recognition memory and the volume of medial temporal lobe structures in healthy young males. Behavioural Neurology 1998, 11, 3–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maguire, E.A.; Gadian, D.G.; Johnsrude, I.S.; Good, C.D.; Ashburner, J.; Frackowiak, R.S.; Frith, C.D. Navigation-related structural change in the hippocampi of taxi drivers. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2000, 97, 4398–4403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paus, T.; Zijdenbos, A.; Worsley, K.; Collins, D.L.; Blumenthal, J.; Giedd, J.N.; Rapoport, J.L.; Evans, A.C. Structural maturation of neural pathways in children and adolescents: in vivo study. Science 1999, 283, 1908–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Draganski, B.; Gaser, C.; Busch, V.; Schuierer, G.; Bogdahn, U.; May, A. Changes in grey matter induced by training. Nature 2004, 427, 311–312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraska, J.M. Sex differences in dendritic response to differential experience in the rat visual cortex. Brain Research 1984, 295, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JURASKA, J.M. Sex differences in developmental plasticity of behavior and the brain. Developmental neuropsychobiology 1986, 409–422. [Google Scholar]
- Juraska, J.M.; Fitch, J.M.; Henderson, C.; Rivers, N. Sex differences in the dendritic branching of dentate granule cells following differential experience. Brain research 1985, 333, 73–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Juraska, J.M. The structure of the rat cerebral cortex: Effects of gender and the environment. 1990.
- Coleman, P.; Buell, S. Regulation of dendritic extent in developing and aging brain. Synaptic plasticity 1985, 311–333. [Google Scholar]
- Duque, A.; Arellano, J.I.; Rakic, P. An assessment of the existence of adult neurogenesis in humans and value of its rodent models for neuropsychiatric diseases. Molecular psychiatry 2022, 27, 377–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raff, M.C.; Barres, B.A.; Burne, J.F.; Coles, H.S.; Ishizaki, Y.; Jacobson, M.D. Programmed cell death and the control of cell survival: lessons from the nervous system. Science 1993, 262, 695–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Johansson, B.B. Brain plasticity in health and disease. The Keio journal of medicine 2004, 53, 231–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Charykova, I.; Gorkom, K.N.V.; Zaki, N.; Almansoori, T.M.; Baylis, G.; Ljubisavljevic, M.; Belghali, M. Predicting age from behavioral test performance for screening early onset of cognitive decline. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2021, 13, 661514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Gorkom, K.N.V.; Zaki, N.; Almansoori, T.M.; Al Zahmi, F.; Ljubisavljevic, M.R.; Belghali, M. Proportional changes in cognitive subdomains during normal brain aging. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2021, 13, 673469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Smetanina, D.; Simiyu, G.L.; Uzianbaeva, L.; Neidl-Van Gorkom, K.; Zaki, N.; Charykova, I.; Al Koteesh, J.; Almansoori, T.M.; others. Brain morphometry and cognitive performance in normal brain aging: age-and sex-related structural and functional changes. Frontiers in aging neuroscience 2022, 13, 713680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belghali, M.; Statsenko, Y.; Laver, V. Stroop switching card test: brief screening of executive functions across the lifespan. Aging, Neuropsychology, and Cognition 2022, 29, 14–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Uzianbaeva, L.; Gorkom, K.; Belghali, M.; Charykova, I.; others. Correlation between lifelong dynamics of psychophysiological performance and brain morphology. ESNR 2021. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 41–42. [Google Scholar]
- Habuza, T.; Statsenko, Y.; Uzianbaeva, L.; Gorkom, K.; Zaki, N.; Belghali, M.; others. Models of brain cognitive and morphological changes across the life: machine learning-based approach. ESNR 2021. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 10–26226. [Google Scholar]
- Uzianbaeva, L.; Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Gorkom, K.; Belghali, M.; Charykova, I.; others. Effects of sex age-related changes in brain morphology. ESNR 2021. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 42–43. [Google Scholar]
- Gorkom, K.; Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Uzianbaeva, L.; Belghali, M.; Charykova, I.; others. Comparison of brain volumetric changes with functional outcomes in physiologic brain aging. ESNR 2021. Neuroradiology 2021, 63, 43–44. [Google Scholar]
- Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Charykova, I.; Gorkom, K.; Zaki, N.; Almansoori, T.; Ljubisavljevic, M.; Szolics, M.; Al Koteesh, J.; Ponomareva, A.; others. AI models of age-associated changes in CNS composition identified by MRI. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2021, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habuza, T.; Zaki, N.; Statsenko, Y.; Elyassami, S. MRI and cognitive tests-based screening tool for dementia. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2021, 429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsenko, Y.; Habuza, T.; Gorkom, K.N.V.; Zaki, N.; Almansoori, T.M. Applying the inverse efficiency score to visual–motor task for studying speed-accuracy performance while aging. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2020, 12, 574401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habuza, T.; Zaki, N.; Statsenko, Y.; Alnajjar, F.; Elyassami, S. Predicting the diagnosis of dementia from MRI data: added value to cognitive tests. The 7th Annual International Conference on Arab Women in Computing in Conjunction with the 2nd Forum of Women in Research, 2021, pp. 1–7.
- Habuza, T.; Zaki, N.; Mohamed, E.A.; Statsenko, Y. Deviation from model of normal aging in alzheimer’s disease: Application of deep learning to structural MRI data and cognitive tests. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 53234–53249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsenko, Y.; Meribout, S.; Habuza, T.; Almansoori, T.M.; Gorkom, K.N.V.; Gelovani, J.G.; Ljubisavljevic, M. Patterns of structure-function association in normal aging and in Alzheimer’s disease: Screening for mild cognitive impairment and dementia with ML regression and classification models. Frontiers in Aging Neuroscience 2023, 14, 943566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smetanina, D.; Meribout, S.; Habuza, T.; Simiyu, G.; Ismail, F.; Zareba, K.; Gorkom, K.; Almansoori, T.; Gelovani, J.; Ljubisavljevic, M.; others. Reference curves of age-related volumetric changes in hippocampus and brain ventricles in healthy population. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2023, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meribout, S.; Habuza, T.; Smetanina, D.; Simiyu, G.; Ismail, F.; Gorkom, K.; Almansoori, T.; Gelovani, J.; Statsenko, Y.; Ljubisavljevic, M. Rate and onset of cognitive decline and cortical atrophy in normal and pathological ageing. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2023, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meribout, S.; Habuza, T.; Smetanina, D.; Simiyu, G.; Ismail, F.; Gorkom, K.; Almansoori, T.; Gelovani, J.; Statsenko, Y.; Ljubisavljevic, M. Functional changes in age-related neurocognitive slowing and disease-related cognitive decline: Evidence from global cognitive tests and psychophysiological tests. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2023, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Statsenko, Y.; Meribout, S.; Habuza, T.; Smetanina, D.; Simiyu, G.; Ismail, F.; Gorkom, K.; Almansoori, T.; Gelovani, J.; Ljubisavljevic, M. Structure-function association patterns of the brain in individuals with different level of cognitive impairment. Journal of the Neurological Sciences 2023, 455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spadaro, P.A.; Bredy, T.W. Emerging role of non-coding RNA in neural plasticity, cognitive function, and neuropsychiatric disorders. Frontiers in genetics 2012, 3, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kyzar, E.J.; Bohnsack, J.P.; Pandey, S.C. Current and future perspectives of noncoding RNAs in brain function and neuropsychiatric disease. Biological psychiatry 2022, 91, 183–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Earls, L.R.; Westmoreland, J.J.; Zakharenko, S.S. Non-coding RNA regulation of synaptic plasticity and memory: implications for aging. Ageing research reviews 2014, 17, 34–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keihani, S.; Kluever, V.; Fornasiero, E.F. Brain long noncoding RNAs: multitask regulators of neuronal differentiation and function. Molecules 2021, 26, 3951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ip, J.Y.; Sone, M.; Nashiki, C.; Pan, Q.; Kitaichi, K.; Yanaka, K.; Abe, T.; Takao, K.; Miyakawa, T.; Blencowe, B.J.; others. Gomafu lncRNA knockout mice exhibit mild hyperactivity with enhanced responsiveness to the psychostimulant methamphetamine. Scientific reports 2016, 6, 27204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Jin, T.; Cheng, X.; Qin, J.; Zhang, L.; He, H.; Xue, J.; Jin, G. GAS5 which is regulated by Lhx8 promotes the recovery of learning and memory in rats with cholinergic nerve injury. Life sciences 2020, 260, 118388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, L.; Zhuang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Li, X. Long non-coding RNA in neuronal development and neurological disorders. Frontiers in genetics 2019, 9, 436598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhan, A.; Soleimani, M.; Mandal, S.S. Long noncoding RNA (lncRNA): Functions in health and disease. Gene Regulation, Epigenetics and Hormone Signaling 2017, 169–208. [Google Scholar]
- Khalifa, F.N.; Hussein, R.F.; Mekawy, D.M.; Elwi, H.M.; Alsaeed, S.A.; Elnawawy, Y.; Shaheen, S.H. Potential role of the lncRNA. Molecular Biology Reports 2024, 51, 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Sim, S.E.; Lim, C.S.; Kim, J.I.; Seo, D.; Chun, H.; Yu, N.K.; Lee, J.; Kang, S.J.; Ko, H.G.; Choi, J.H.; others. The brain-enriched microRNA miR-9-3p regulates synaptic plasticity and memory. Journal of Neuroscience 2016, 36, 8641–8652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNeill, E.M.; Warinner, C.; Alkins, S.; Taylor, A.; Heggeness, H.; DeLuca, T.F.; Fulga, T.A.; Wall, D.P.; Griffith, L.C.; Van Vactor, D. The conserved microRNA miR-34 regulates synaptogenesis via coordination of distinct mechanisms in presynaptic and postsynaptic cells. Nature communications 2020, 11, 1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Song, J.; Ouyang, Y.; Han, Q.; Chen, W.; Zhao, X.; Xie, Y.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, W.; Fan, C. Advances in roles of miR-132 in the nervous system. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2017, 8, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xin, H.; Katakowski, M.; Wang, F.; Qian, J.Y.; Liu, X.S.; Ali, M.M.; Buller, B.; Zhang, Z.G.; Chopp, M. MicroRNA-17–92 cluster in exosomes enhance neuroplasticity and functional recovery after stroke in rats. Stroke 2017, 48, 747–753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, J.; Kim, S.N.; Liu, X.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, C.; Seo, J.S.; Kim, Y.; Sun, T. miR-17-92 cluster regulates adult hippocampal neurogenesis, anxiety, and depression. Cell reports 2016, 16, 1653–1663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, P.; Li, X.; Song, Z.; Wei, C.; Zhang, Q.; Luo, B.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Y.; others. Clinical and preclinical evaluation of miR-144-5p as a key target for major depressive disorder. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics 2023, 29, 3598–3611. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, C.; Yin, F.; Li, R.; Ruan, Q.; Meng, C.; Zhao, K.; Zhu, Q. MicroRNA-145-Mediated KDM6A Downregulation Enhances Neural Repair after Spinal Cord Injury via the NOTCH2/Abcb1a Axis. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021, 2021, 2580619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Zhao, J.; Chang, S.; Sun, Q.; Liu, N.; Dong, J.; Chen, Y.; Yang, D.; Ye, D.; Liu, X.; others. MicroRNA-153 improves the neurogenesis of neural stem cells and enhances the cognitive ability of aged mice through the notch signaling pathway. Cell Death & Differentiation 2020, 27, 808–825. [Google Scholar]
- Del Val, C.; Díaz de la Guardia-Bolívar, E.; Zwir, I.; Mishra, P.P.; Mesa, A.; Salas, R.; Poblete, G.F.; de Erausquin, G.; Raitoharju, E.; Kähönen, M. ; others. Gene expression networks regulated by human personality. Molecular Psychiatry 2024, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Seeler, S.; Andersen, M.S.; Sztanka-Toth, T.; Rybiczka-Tešulov, M.; van den Munkhof, M.H.; Chang, C.C.; Maimaitili, M.; Venø, M.T.; Hansen, T.B.; Pasterkamp, R.J.; others. A circular RNA expressed from the FAT3 locus regulates neural development. Molecular Neurobiology 2023, 60, 3239–3260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, M.; Wu, C.; Yu, R.; Cheng, Y.; Tang, Z.; Wu, B.; Fu, J.; Tan, W.; Zhou, Q.; Zhu, Z.; others. A novel circular RNA, circIgfbp2, links neural plasticity and anxiety through targeting mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress-induced synapse dysfunction after traumatic brain injury. Molecular Psychiatry 2022, 27, 4575–4589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, N.; Liu, J.; Peng, Z.; Zhang, R.; Ni, R.; Li, R.; Wu, J.; Liu, Z.; Pan, B. Identification of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA networks to explore the molecular mechanism and immune regulation of postoperative neurocognitive disorder. Aging (Albany NY) 2022, 14, 8374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoudi, E.; Fitzsimmons, C.; Geaghan, M.P.; Shannon Weickert, C.; Atkins, J.R.; Wang, X.; Cairns, M.J. Circular RNA biogenesis is decreased in postmortem cortical gray matter in schizophrenia and may alter the bioavailability of associated miRNA. Neuropsychopharmacology 2019, 44, 1043–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brookes, E.; Alan Au, H.Y.; Varsally, W.; Barrington, C.; Hadjur, S.; Riccio, A. A novel enhancer that regulates Bdnf expression in developing neurons. bioRxiv 2021. pp. 2021–11. [Google Scholar]
- Cajigas, I.; Chakraborty, A.; Swyter, K.R.; Luo, H.; Bastidas, M.; Nigro, M.; Morris, E.R.; Chen, S.; VanGompel, M.J.; Leib, D.; others. The Evf2 ultraconserved enhancer lncRNA functionally and spatially organizes megabase distant genes in the developing forebrain. Molecular cell 2018, 71, 956–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvageau, M.; Goff, L.A.; Lodato, S.; Bonev, B.; Groff, A.F.; Gerhardinger, C.; Sanchez-Gomez, D.B.; Hacisuleyman, E.; Li, E.; Spence, M.; others. Multiple knockout mouse models reveal lincRNAs are required for life and brain development. elife 2013, 2, e01749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chanda, K.; Mukhopadhyay, D. LncRNA Xist, X-chromosome instability and Alzheimer’s disease. Current Alzheimer Research 2020, 17, 499–507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasethupathy, P.; Antonov, I.; Sheridan, R.; Frey, S.; Sander, C.; Tuschl, T.; Kandel, E.R. A role for neuronal piRNAs in the epigenetic control of memory-related synaptic plasticity. Cell 2012, 149, 693–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zuo, L.; Wang, Z.; Tan, Y.; Chen, X.; Luo, X. piRNAs and their functions in the brain. International journal of human genetics 2016, 16, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qiu, W.; Guo, X.; Lin, X.; Yang, Q.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Y.; Zuo, L.; Zhu, Y.; Li, C.S.R.; Ma, C.; others. Transcriptome-wide piRNA profiling in human brains of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiology of aging 2017, 57, 170–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheckel, C.; Drapeau, E.; Frias, M.A.; Park, C.Y.; Fak, J.; Zucker-Scharff, I.; Kou, Y.; Haroutunian, V.; Ma’ayan, A.; Buxbaum, J.D.; others. Regulatory consequences of neuronal ELAV-like protein binding to coding and non-coding RNAs in human brain. Elife 2016, 5, e10421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, Z.; Batagov, A.O.; Schinelli, S.; Wang, J.; Wang, Y.; El Fatimy, R.; Rabinovsky, R.; Balaj, L.; Chen, C.C.; Hochberg, F.; others. Coding and noncoding landscape of extracellular RNA released by human glioma stem cells. Nature communications 2017, 8, 1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haack, F.; Trakooljul, N.; Gley, K.; Murani, E.; Hadlich, F.; Wimmers, K.; Ponsuksili, S. Deep sequencing of small non-coding RNA highlights brain-specific expression patterns and RNA cleavage. RNA biology 2019, 16, 1764–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zimmer-Bensch, G. Emerging roles of long non-coding RNAs as drivers of brain evolution. Cells 2019, 8, 1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, D.; Prasanth, K.V.; Tripathi, V.; Colasse, S.; Nakamura, T.; Xuan, Z.; Zhang, M.Q.; Sedel, F.; Jourdren, L.; Coulpier, F.; others. A long nuclear-retained non-coding RNA regulates synaptogenesis by modulating gene expression. The EMBO journal 2010, 29, 3082–3093. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, V.; Ellis, J.D.; Shen, Z.; Song, D.Y.; Pan, Q.; Watt, A.T.; Freier, S.M.; Bennett, C.F.; Sharma, A.; Bubulya, P.A.; others. The nuclear-retained noncoding RNA MALAT1 regulates alternative splicing by modulating SR splicing factor phosphorylation. Molecular cell 2010, 39, 925–938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, W.S.; Zhao, Q.; Bademosi, A.; Gormal, R.S.; Gong, H.; Marshall, P.R.; Periyakaruppiah, A.; Madugalle, S.U.; Zajaczkowski, E.L.; Leighton, L.J.; others. Fear extinction is regulated by the activity of long noncoding RNAs at the synapse. Nature Communications 2023, 14, 7616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, T.X.; Rothenberg, M.E. MicroRNA. Journal of allergy and clinical immunology 2018, 141, 1202–1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Starega-Roslan, J.; Krol, J.; Koscianska, E.; Kozlowski, P.; Szlachcic, W.J.; Sobczak, K.; Krzyzosiak, W.J. Structural basis of microRNA length variety. Nucleic acids research 2011, 39, 257–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fiore, R.; Siegel, G.; Schratt, G. MicroRNA function in neuronal development, plasticity and disease. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA)-Gene Regulatory Mechanisms 2008, 1779, 471–478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martins, H.C.; Schratt, G. MicroRNA-dependent control of neuroplasticity in affective disorders. Translational Psychiatry 2021, 11, 263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Constantin, L. Circular RNAs and neuronal development. Circular RNAs: Biogenesis and Functions 2018, 205–213. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, T.K.; Hemberg, M.; Gray, J.M.; Costa, A.M.; Bear, D.M.; Wu, J.; Harmin, D.A.; Laptewicz, M.; Barbara-Haley, K.; Kuersten, S.; others. Widespread transcription at neuronal activity-regulated enhancers. Nature 2010, 465, 182–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arner, E.; Daub, C.O.; Vitting-Seerup, K.; Andersson, R.; Lilje, B.; Drabløs, F.; Lennartsson, A.; Rönnerblad, M.; Hrydziuszko, O.; Vitezic, M.; others. Transcribed enhancers lead waves of coordinated transcription in transitioning mammalian cells. Science 2015, 347, 1010–1014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gray, J.M.; Kim, T.K.; West, A.E.; Nord, A.S.; Markenscoff-Papadimitriou, E.; Lomvardas, S. Genomic views of transcriptional enhancers: essential determinants of cellular identity and activity-dependent responses in the CNS. Journal of Neuroscience 2015, 35, 13819–13826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roberts, T.C.; Morris, K.V.; Wood, M.J. The role of long non-coding RNAs in neurodevelopment, brain function and neurological disease. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2014, 369, 20130507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gu, S.; Xie, R.; Liu, X.; Shou, J.; Gu, W.; Che, X. Long coding RNA XIST contributes to neuronal apoptosis through the downregulation of AKT phosphorylation and is negatively regulated by miR-494 in rat spinal cord injury. International journal of molecular sciences 2017, 18, 732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aravin, A.; Gaidatzis, D.; Pfeffer, S.; Lagos-Quintana, M.; Landgraf, P.; Iovino, N.; Morris, P.; Brownstein, M.J.; Kuramochi-Miyagawa, S.; Nakano, T.; others. A novel class of small RNAs bind to MILI protein in mouse testes. Nature 2006, 442, 203–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girard, A.; Sachidanandam, R.; Hannon, G.J.; Carmell, M.A. A germline-specific class of small RNAs binds mammalian Piwi proteins. Nature 2006, 442, 199–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Betel, D.; Sheridan, R.; Marks, D.S.; Sander, C. Computational analysis of mouse piRNA sequence and biogenesis. PLoS computational biology 2007, 3, e222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xerri, C.; Zennou-Azogui, Y. Influence of the postlesion environment and chronic piracetam treatment on the organization of the somatotopic map in the rat primary somatosensory cortex after focal cortical injury. Neuroscience 2003, 118, 161–177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goldstein, L.B. Neuropharmacology of TBI-induced plasticity. Brain injury 2003, 17, 685–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Plewnia, C.; Hoppe, J.; Cohen, L.G.; Gerloff, C. Improved motor skill acquisition after selective stimulation of central norepinephrine. Neurology 2004, 62, 2124–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loubinoux, I.; Pariente, J.; Boulanouar, K.; Carel, C.; Manelfe, C.; Rascol, O.; Celsis, P.; Chollet, F. A single dose of the serotonin neurotransmission agonist paroxetine enhances motor output: double-blind, placebo-controlled, fMRI study in healthy subjects. NeuroImage 2002, 15, 26–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dam, M.; Tonin, P.; De Boni, A.; Pizzolato, G.; Casson, S.; Ermani, M.; Freo, U.; Piron, L.; Battistin, L. Effects of fluoxetine and maprotiline on functional recovery in poststroke hemiplegic patients undergoing rehabilitation therapy. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 1996, 27, 1211–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sawaki, L.; Boroojerdi, B.; Kaelin-Lang, A.; Burstein, A.H.; Bütefisch, C.M.; Kopylev, L.; Davis, B.; Cohen, L.G. Cholinergic influences on use-dependent plasticity. Journal of neurophysiology 2002, 87, 166–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ziemann, U.; Lönnecker, S.; Steinhoff, B.J.; Paulus, W. The effect of lorazepam on the motor cortical excitability in man. Experimental brain research 1996, 109, 127–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walker-Batson, D.; Curtis, S.; Natarajan, R.; Ford, J.; Dronkers, N.; Salmeron, E.; Lai, J.; Unwin, D.H. A double-blind, placebo-controlled study of the use of amphetamine in the treatment of aphasia. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 2001, 32, 2093–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bragoni, M.; Altieri, M.; Di Piero, V.; Padovani, A.; Mostardini, C.; Lenzi, G.L. Bromocriptine and speech therapy in non-fluent chronic aphasia after stroke. Neurological sciences : official journal of the Italian Neurological Society and of the Italian Society of Clinical Neurophysiology 2000, 21, 19–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kessler, J.; Thiel, A.; Karbe, H.; Heiss, W.D. Piracetam improves activated blood flow and facilitates rehabilitation of poststroke aphasic patients. Stroke; a journal of cerebral circulation 2000, 31, 2112–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, S.; Rossini, P.M. TMS in cognitive plasticity and the potential for rehabilitation. Trends in cognitive sciences 2004, 8, 273–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stefan, K.; Kunesch, E.; Cohen, L.G.; Benecke, R.; Classen, J. Induction of plasticity in the human motor cortex by paired associative stimulation. Brain : a journal of neurology 2000, 123 Pt 3, 572–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveri, M.; Bisiach, E.; Brighina, F.; Piazza, A.; La Bua, V.; Buffa, D.; Fierro, B. rTMS of the unaffected hemisphere transiently reduces contralesional visuospatial hemineglect. Neurology 2001, 57, 1338–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brighina, F.; Bisiach, E.; Oliveri, M.; Piazza, A.; La Bua, V.; Daniele, O.; Fierro, B. 1 Hz repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation of the unaffected hemisphere ameliorates contralesional visuospatial neglect in humans. Neuroscience Letter 2003, 336, 131–3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mottaghy, F.M.; Hungs, M.; Brügmann, M.; Sparing, R.; Boroojerdi, B.; Foltys, H.; Huber, W.; Töpper, R. Facilitation of picture naming after repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. Neurology 1999, 53, 1806–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grafman, J.; Wassermann, E. Transcranial magnetic stimulation can measure and modulate learning and memory. Neuropsychologia 1999, 37, 159–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boylan, L.S. Enhancing analogic reasoning with rTMS over the left prefrontal cortex. Neurology 2001, 57, 1349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evers, S.; Böckermann, I.; Nyhuis, P.W. The impact of transcranial magnetic stimulation on cognitive processing: an event-related potential study. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 2915–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, L.; Siebner, H.R.; Rowe, J.B.; Rizzo, V.; Rothwell, J.C.; Frackowiak, R.S.J.; Friston, K.J. Acute remapping within the motor system induced by low-frequency repetitive transcranial magnetic stimulation. The Journal of neuroscience : the official journal of the Society for Neuroscience 2003, 23, 5308–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canavero, S.; Bonicalzi, V.; Paolotti, R.; Castellano, G.; Greco-Crasto, S.; Rizzo, L.; Davini, O.; Maina, R. Therapeutic extradural cortical stimulation for movement disorders: a review. Neurological research 2003, 25, 118–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsubokawa, T.; Katayama, Y.; Yamamoto, T.; Hirayama, T.; Koyama, S. Chronic motor cortex stimulation in patients with thalamic pain. Journal of neurosurgery 1993, 78, 393–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canavero, S.; Bonicalzi, V. Extradural cortical stimulation for central pain. Acta neurochirurgica. Supplement 2007, 97, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Benabid, A. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease. Current opinion in neurobiology 2003, 13, 696–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lozano, A.M.; Dostrovsky, J.; Chen, R.; Ashby, P. Deep brain stimulation for Parkinson’s disease: disrupting the disruption. The Lancet. Neurology 2002, 1, 225–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Capelle, L.; Lopes, M.; Faillot, T.; Sichez, J.P.; Fohanno, D. The insular lobe: physiopathological and surgical considerations. Neurosurgery 2000, 47, 801–10, discussion 810–1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Bauchet, L.; Lehéricy, S.; Capelle, L. Functional compensation of the left dominant insula for language. Neuroreport 2001, 12, 2159–2163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Denvil, D.; Capelle, L. Absence of movement disorders after surgical resection of glioma invading the right striatum. Journal of neurosurgery 2002, 97, 363–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Duffau, H.; Capelle, L.; Denvil, D.; Sichez, N.; Gatignol, P.; Lopes, M.; Mitchell, M.C.; Sichez, J.P.; Van Effenterre, R. Functional recovery after surgical resection of low grade gliomas in eloquent brain: hypothesis of brain compensation. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry 2003, 74, 901–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Capelle, L.; Denvil, D.; Gatignol, P.; Sichez, N.; Lopes, M.; Sichez, J.P.; Van Effenterre, R. The role of dominant premotor cortex in language: a study using intraoperative functional mapping in awake patients. NeuroImage 2003, 20, 1903–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Khalil, I.; Gatignol, P.; Denvil, D.; Capelle, L. Surgical removal of corpus callosum infiltrated by low-grade glioma: functional outcome and oncological considerations. Journal of neurosurgery 2004, 100, 431–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duffau, H.; Denvil, D.; Capelle, L. Long term reshaping of language, sensory, and motor maps after glioma resection: a new parameter to integrate in the surgical strategy. Journal of neurology, neurosurgery, and psychiatry 2002, 72, 511–6. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Naeser, M.A.; Palumbo, C.L.; Helm-Estabrooks, N.; Stiassny-Eder, D.; Albert, M.L. Severe nonfluency in aphasia. Role of the medial subcallosal fasciculus and other white matter pathways in recovery of spontaneous speech. Brain : a journal of neurology 1989, 112 Pt 1, 1–38. [Google Scholar]
- Holodny, A.I.; Schwartz, T.H.; Ollenschleger, M.; Liu, W.C.; Schulder, M. Tumor involvement of the corticospinal tract: diffusion magnetic resonance tractography with intraoperative correlation. Journal of neurosurgery 2001, 95, 1082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peraud, A.; Meschede, M.; Eisner, W.; Ilmberger, J.; Reulen, H.J. Surgical resection of grade II astrocytomas in the superior frontal gyrus. Neurosurgery 2002, 50, 966–75, discussion 975–7. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Duffau, H. Intraoperative cortico–subcortical stimulations in surgery of low-grade gliomas. Expert review of neurotherapeutics 2005, 5, 473–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Döbrössy, M.D.; Dunnett, S.B. The influence of environment and experience on neural grafts. Nature reviews. Neuroscience 2001, 2, 871–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachoud-Lévi, A.C.; Rémy, P.; Nguyen, J.P.; Brugières, P.; Lefaucheur, J.P.; Bourdet, C.; Baudic, S.; Gaura, V.; Maison, P.; Haddad, B.; Boissé, M.F.; Grandmougin, T.; Jény, R.; Bartolomeo, P.; Dalla Barba, G.; Degos, J.D.; Lisovoski, F.; Ergis, A.M.; Pailhous, E.; Cesaro, P.; Hantraye, P.; Peschanski, M. Motor and cognitive improvements in patients with Huntington’s disease after neural transplantation. Lancet 2000, 356, 1975–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lindvall, O. Stem cells for cell therapy in Parkinson’s disease. Pharmacological research : the official journal of the Italian Pharmacological Society 2003, 47, 279–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchan, A.M.; Warren, D.; Burnstein, R. Transplantation of cultured human neuronal cells for patients with stroke. Neurology 2001, 56, 821–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| No | Name (acronym) | Molecular species | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | long non-coding RNA (lncRNA) |
Gomafu, GAS5, MALAT1, HOTAIR | [131,132,133,134,135] |
| 2 | microRNA (miRNA) | miR-9, miR-34, miR-132 | [136,137,138] |
| miR-17-92 cluster | [139,140] | ||
| miR-144-5p, miR-145, miR-153 | [141,142,143] | ||
| hsa-miR-1-3p, hsa-miR-335-5p, hsa-miR-34a-5p |
[144] | ||
| 3 | circular RNA (circRNA) | ciRS-7, circRMST, circFAT3 | [145] |
| circIgfbp2 | [146] | ||
| nearly 1167 cerebral circRNAs | [147] | ||
| cirC_0000400, cirC_0000331, cirC_0000406, cirC_0000798 |
[148] | ||
| 4 | enhancer RNA (eRNA) | Bdnf-Enhg1, Bdnf-Enhg2 | [149] |
| Evf2 | [150] | ||
| 5 | long intergenic non-coding RNA (lincRNA) |
linc-Brn1b | [151] |
| Xist | [152] | ||
| 6 | Piwi-interacting RNA (piRNA) |
list of 1251 brain-specific piRNAs piR-hsa-1281, piR-hsa-1280, piR-hsa-1282, piR-hsa-27492 |
[153,154,155] |
| 7 | Y RNA (yRNA) | nELAVL/Y RNA complex hY1, hY4, hY5 |
[156,157,158] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





