Submitted:
16 September 2024
Posted:
17 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
| Pathology | Color and Appearance | Growth Rate | Area of Predicilition | Associated with Pain | Average age | Male or Female Predominance |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Superficial acral fibromyxoma | Firm flesh colored mass | Slow-growing; around 3 to 30 years | Fingers and toes | Painless | Mean age of 43 (4-86) | Male |
| Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans | pink-to-skin-color plaque that slowly grows into a painless to painful polypoid to multinodular mass | Slow-growing | Trunk | Painless | Present in all ages; Commonly seeen between ages 20-50 | Male |
| Sclerosing perineuroma | Soft grey colored lesion with thickened collagen patterns | Slow growing ~10 years | Extremeties | Painless | Young adults | Male |
| Acquired digital fibrokeratoma | Benign fibrous flesh colored-yellow textureed tumor around 3-5 mm | Growth for several months then with growth phase for several weeks | Fingers and toes | Painless | Adults between the age of 12-70 | Slight predominance in males |
| Myxoid neurofibroma | Skin colored nodular plaque | Slow growing from months to years | Face, shoulders, arms, periungual and in the fee | Painless | Young adults | No gender predominance |
| Superficial angiomyxoma | red-to-pink or skin-colored papule, nodule, or papule | Light to skin colored nodule with a translucent surface | scalp and neck | Painless | Middle aged adults | Male |
| Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma | Light tan smooth colored tumor | Slow | shoulders, trunk, and thigh | Painless | Median age of 33 years | Male |
| Pathology | Positive Immunohistochemical Stains | Negative Immunohistochemica Stains |
|---|---|---|
| Superficial acral fibromyxoma | CD34 CD99 Nestin Vimentin |
Keratin Claudin-1 Glial fibrillary acidic protein MUC4 AE1/AE3 Cam5.2 STAT6 S100 HMB-45 |
| Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans | Vimentin Nestin CD34 |
EMA |
| Sclerosing perineuroma | EMA Vimentin Collagen IV Claudin-1 |
S100 |
| Acquired digital fibrokeratoma | FXIIIA | EMA S100 |
| Myxoid neurofibroma | S100 Mucin |
- |
| Superficial angiomyxoma | CD34 | S-100 Smooth muscle actin |
| Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma | MUC4 | - |
Objective
Methods
Results
Epidemiology
Clinical Presentation
Pathogenesis
Imaging
Macroscopic Examination
Microscopic Examination
Immunohistochemistry
Differential Diagnosis
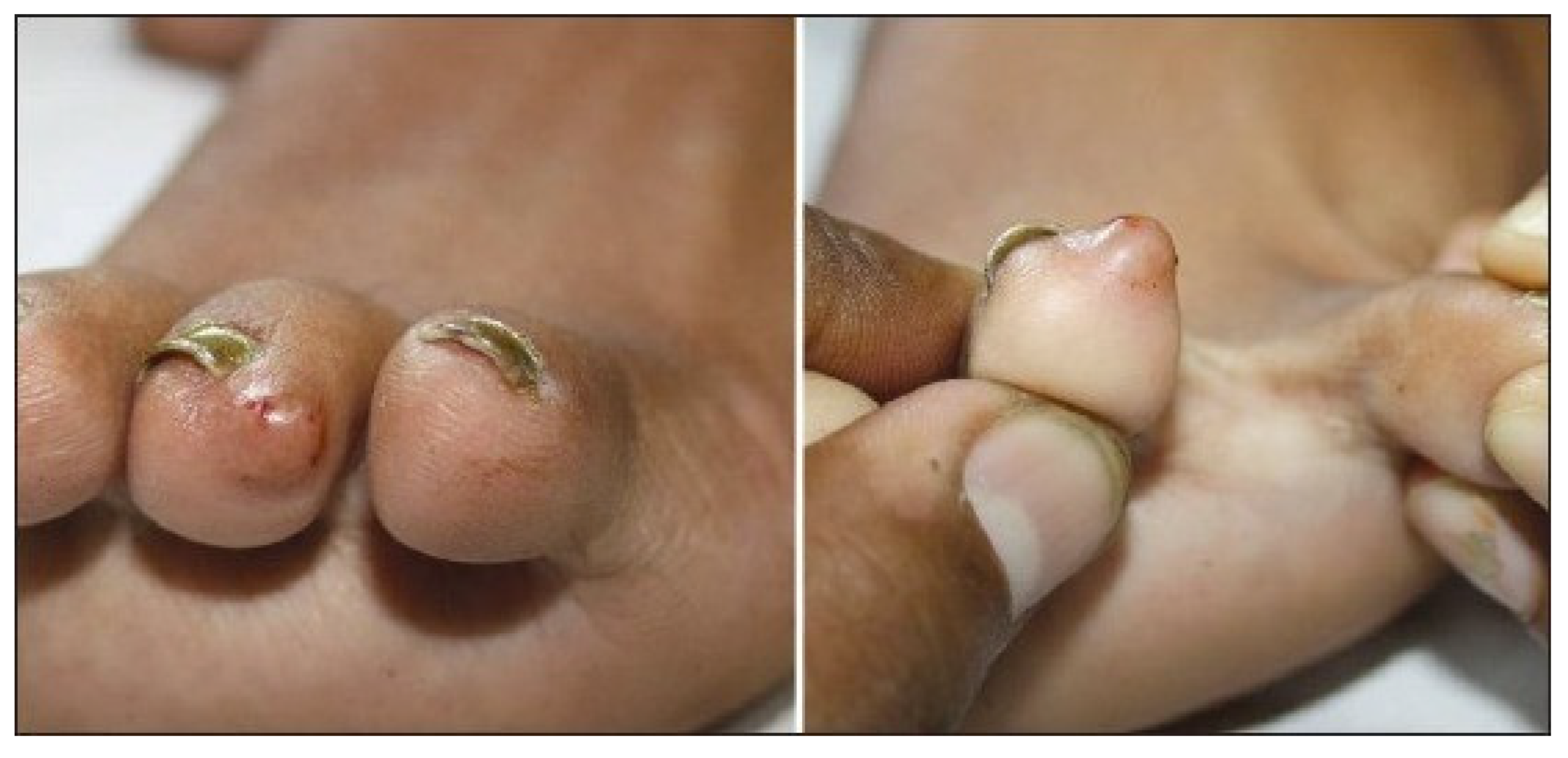
Treatment
Conclusions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sundaramurthy, N.; Parthasarathy, J.; Mahipathy, S.R.; Durairaj, A.R. Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma: A Rare Entity—A Case Report. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016, 10, PD03–PD05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kura, M.M.; Jindal, S.R. Solitary superficial acral angiomyxoma: an infrequently reported soft tissue tumor. Indian J Dermatol. 2014, 59, 529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crepaldi, B.E.; Soares, R.D.; Silveira, F.D.; Taira, R.I.; Hirakawa, C.K.; Matsumoto, M.H. Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma: Literature Review. Rev Bras Ortop (Sao Paulo). 2019, 54, 491–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fetsch, J.F.; Laskin, W.B.; Miettinen, M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: a clinicopathologic and immunohistochemical analysis of 37 cases of a distinctive soft tissue tumor with a predilection for the fingers and toes. Hum Pathol. 2001, 32, 704–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ashby-Richardson, H.; Rogers, G.S.; Stadecker, M.J. (2011). Superficial acral fibromyxoma: an overview. Archives of pathology & laboratory medicine, 1066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawaya, J.L.; Khachemoune, A. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. International Journal of Dermatology 2015, 54, 499–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, J.H.; Ro, J.Y. The 2020 WHO Classification of Tumors of Soft Tissue: Selected Changes and New Entities. Adv Anat Pathol. 2021, 28, 44–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hollmann, T.J.; Bovée, J.V.; Fletcher, C.D. Digital fibromyxoma (superficial acral fibromyxoma): a detailed characterization of 124 cases. The American journal of surgical pathology 2012, 36, 789–798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hwang, Y.J.; Lee, H.W.; Lee, I.S.; Jung, S.G.; Lee, H.K. Superficial angiomyxoma of the posterior neck. Arch Craniofac Surg. 2021, 22, 62–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Agaimy, A.; Michal, M.; Giedl, J.; Hadravsky, L.; Michal, M. Superficial acral fibromyxoma: clinicopathological, immunohistochemical, and molecular study of 11 cases highlighting frequent Rb1 loss/deletions. Human pathology 2017, 60, 192–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bindra, J.; Doherty, M.; Hunter, J.C. Superficial acral fibromyxoma. Radiology case reports 2015, 7, 751. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brooks, J.; Ramsey, M.L. Dermatofibrosarcoma Protuberans. [Updated 2022 Nov 12]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. 5133. [Google Scholar]
- Neff, R. , Collins, R., & Backes, F. Dermatofibrosarcoma protuberans: A rare and devastating tumor of the vulva. Gynecologic oncology reports, 2019; 29, 9–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengot-Carbo, M.; Millán, F.; Sanjuan, J.; Quecedo, E.; Gimeno, E. Sclerosing perineurioma: case report and literature review. Dermatol Online J. 2014, 20, 13030/qt92s86728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fetsch, J.F.; Miettinen, M. Sclerosing perineurioma: a clinicopathologic study of 19 cases of a distinctive soft tissue lesion with a predilection for the fingers and palms of young adults. Am J Surg Pathol. 1997, 21, 1433–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhat, W.; Akhtar, S.; Teoh, V.; Bourke, G. Sclerosing perineuroma in paediatric fingers: a rare distinct and under-recognised entity. J Plast Reconstr Aesthet Surg. 2014, 67, 1161–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tancredi, A.; Graziano, P.; Dimitri, L.; Impagnatiello, E.; Taurchini, M. Left Supraclavicular Swelling: Sclerosing Perineurioma. Eurasian J Med. 2018, 50, 47–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tabka, M.; Litaiem, N. Acquired Digital Fibrokeratoma. [Updated 2022 May 1]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan-. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih. 1 May 5451. [Google Scholar]
- Ali, M.; Mbah, C.A.; Alwadiya, A.; Nur, M.M.; Sunderamoorthy, D. Giant fibrokeratoma, a rare soft tissue tumor presenting like an accessory digit, a case report and review of literature. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2015, 10, 187–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Ponce-Olivera, R.M.; Tirado-Sanchez, A.; Peniche-Castellanos, A.; Peniche-Rosado, J.; Mercadillo-Perez, P. Myxoid neurofibroma: an unusual presentation. Indian J Dermatol. 2008, 53, 35–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calonje, E.; Guerin, D.; McCormick, D.; Fletcher, C.D. Superficial angiomyxoma: clinicopathologic analysis of a series of distinctive but poorly recognized cutaneous tumors with tendency for recurrence. Am J Surg Pathol. 1999, 23, 910–917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, M.; Fisher, C.; Thway, K. Low-grade fibromyxoid sarcoma: Clinical, morphologic and genetic features. Ann Diagn Pathol. 2017, 28, 60–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hashimoto, K.; Nishimura, S.; Oka, N.; Tanaka, H.; Kakinoki, R.; Akagi, M. Aggressive superficial acral fibromyxoma of the great toe: A case report and mini-review of the literature. Mol Clin Oncol. 2018, 9, 310–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [PubMed Central]
- Hankinson, A.; Holmes, T.; Pierson, J. Superficial Acral Fibromyxoma (Digital Fibromyxoma): A Novel Treatment Approach Using Mohs Micrographic Surgery for a Recurrence-Prone Digital Tumor. Dermatol Surg. 2016, 42, 897–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





