Submitted:
13 September 2024
Posted:
17 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
1.1. Emergence of Data-Driven Healthcare
1.2. Relevance for Mental Health
1.3. Predictive Modelling Using Machine Learning
1.4. Social Media and Internet Data Exploration
1.5. Smartphone Sensing for Just-In-Time Adaptive Interventions
1.6. Purpose of the Study
1.7. Research Questions
1.8. Aims and Objectives
- To analyze how predictive modeling using machine learning can help detect early signs of deteriorating mental health.
- To evaluate ways of mining social media and internet data to understand population-level trends and behavior patterns related to mental illnesses.
- To assess current applications and challenges of data-driven technologies in mental healthcare.
- Examine the potential of smartphone sensors and JITAI for real-time symptom monitoring, identification of high-risk situations and delivery of timely interventions.
- Understand ethical challenges around data privacy, algorithmic bias and informed consent in mental health applications.
2. Literature Review on Data-Driven Approaches to Tackling Mental Health
2.1. Predictive Modelling Using Machine Learning
2.2. Predictive Modeling for Early Detection
2.3. Data-Driven Architecture for Integrated Care
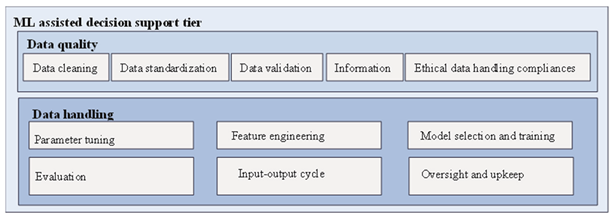
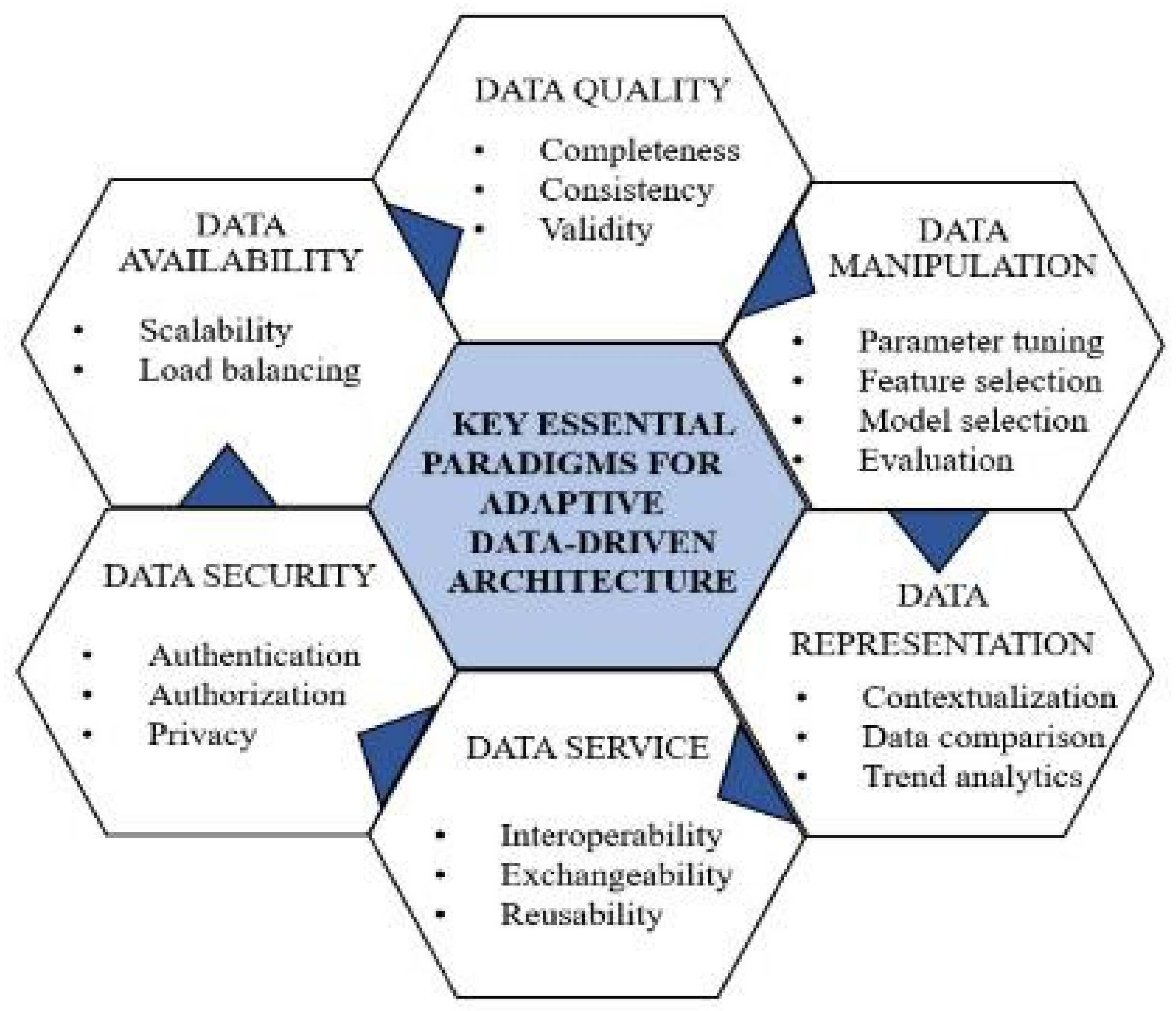
2.4. Social Media and Internet Data Exploration
2.5. Smartphone Sensing for Just-In-Time Adaptive Interventions
2.6. Chatbots and Conversational Agents
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Literature Search
3.2. Inclusion and Exclusion Criteria
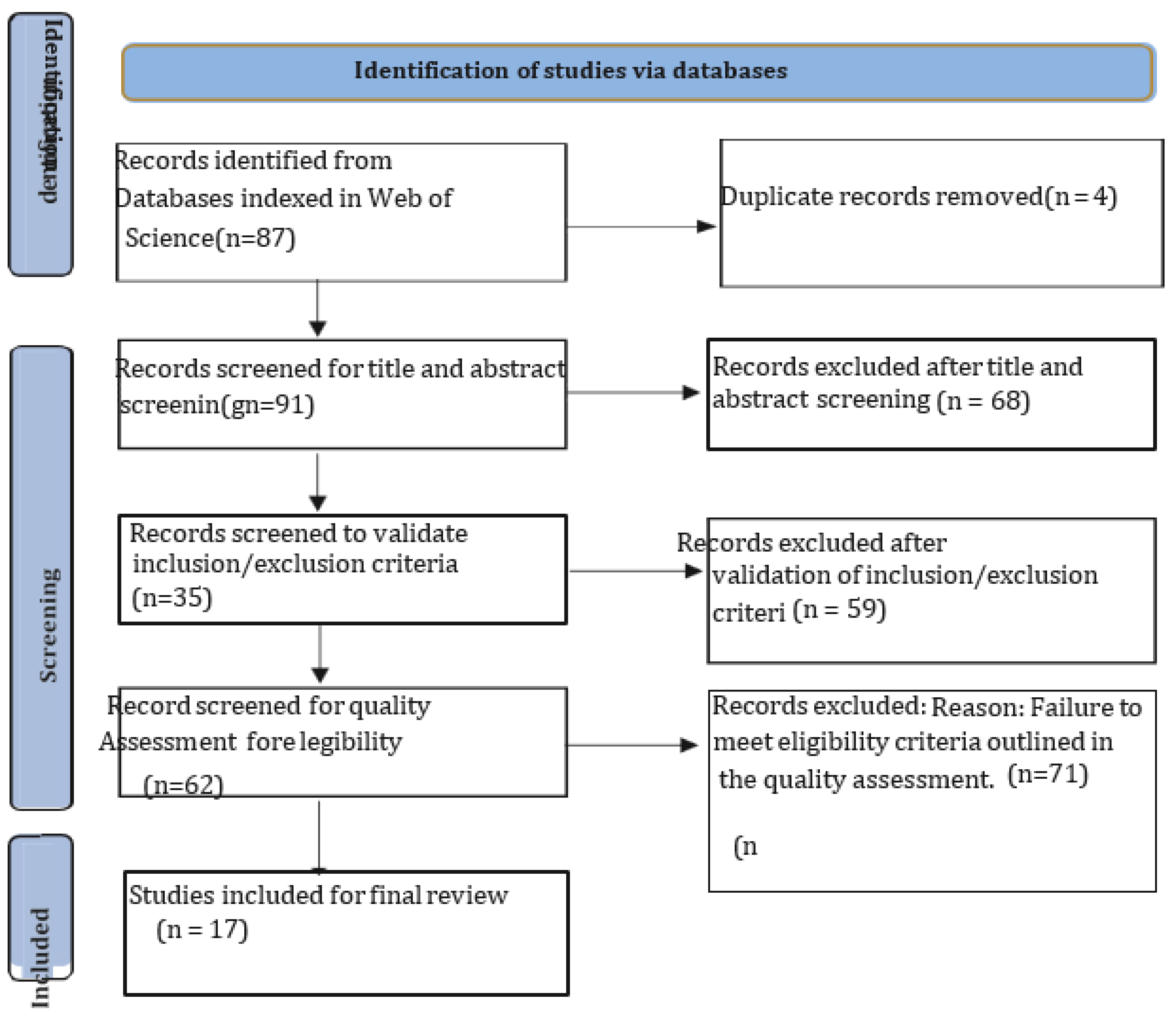
3.3. Screening and Selection
3.4. Data Extraction
3.5. Data Synthesis
4. Results and Discussions
4.1. Predictive Modelling for Early Detection
4.1.1. Smartphone Sensing for Symptom Monitoring
4.1.2. Social Media Analytics for Population Monitoring
4.2. Integration within Clinical Services
4.3. Policy Frameworks and Ethical Considerations
4.4. Challenges to Clinical Integration
4.4.1. Interoperability and Integration Challenges
4.4.2. Usability and Acceptability Challenges
4.4.3. Technology Adoption Barriers
4.4.4. Ensuring Appropriate Human Oversight
4.5. Innovation through Multidisciplinary Partnerships
4.6. Legal and Ethical Considerations
4.7. Future Directions
5. Conclusion
References
- Aggarwal R, Girdhar N. 2022. Machine learning role in cognitive mental health analysis amid Covid-19 crisis: a critical study. In: 2022 International Conference on Machine Learning, Big Data, Cloud and Parallel Computing, COM-IT-CON 2022.
- Aggarwal, S., Saluja, S., Gambhir, V., Gupta, S., & Satia, S. P. S. (2020). Predicting likelihood of psychological disorders in PlayerUnknown’s Battlegrounds (PUBG) players from Asian countries using supervised machine learning. Addictive Behaviors, 101, 106132.
- Aldabbas H, Albashish D, Khatatneh K, Amin R. 2022. An architecture of IoT-aware healthcare smart system by leveraging machine learning. International Arab Journal of Information Technology 19(2):160–172. [CrossRef]
- Berrouiguet, S., Barrigón, M. L., Castroman, J. L., Courtet, P., Artés-Rodríguez, A., & Baca-García, E. (2019). Combining mobile-health (mHealth) and artificial intelligence (AI) methods to avoid suicide attempts: the Smartcrises study protocol. BMC Psychiatry, 19(1), 277.
- Canzian, L., & Musolesi, M. (2015). Trajectories of depression: Unobtrusive monitoring of depressive states by means of smartphone mobility traces analysis. In Proceedings of the 2015 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing (pp. 1293-1304).
- Chawla, N. V., & Davis, D. A. (2013). Bringing big data to personalized healthcare: A patient-cantered framework.
- Journal of General Internal Medicine, 28(Suppl 3), S660-S665.
- Dao, B., Nguyen, T., Venkatesh, S., & Phung, D. (2016). Effect of social capital on emotion, language style and latent topics in online depression community. In Proceedings of the IEEE RIVF International Conference on Computing & Communication Technologies, Research, Innovation, and Vision for the Future (RIVF) (pp. 61-66). Hanoi, Vietnam. [CrossRef]
- De Choudhury, M., Counts, S., & Horvitz, E. (2013). Social media as a measurement tool of depression in populations. In Proceedings of the 5th Annual ACM Web Science Conference (pp. 47-56).
- Dias, L., & Barbosa, J. (2019). Towards a ubiquitous care model for patients with anxiety disorders. In Proceedings of the 25th Brazillian Symposium on Multimedia and the Web (pp. 141-144).
- Ferrario, M. A., Simm, W., Gradinar, A., Forshaw, S., Smith, M. T., Lee, T., Smith, I., & Whittle, J. (2017). Computing and mental health: intentionality and reflection at the click of a button. In Proceedings of the 11th EAI International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (pp. 1-10).
- Francillette, Y., Bouchard, B., Boucher, E., Gaboury, S., Bernard, P., Romain, A. J., & Fournier, M. (2018). Development of an exergame on mobile phones to increase physical activity for adults with severe mental illness. In Proceedings of the 11th PErvasive Technologies Related to Assistive Environments Conference (pp. 241-248).
- Fulmer, R., Joerin, A., Gentile, B., Lakerink, L., & Rauws, M. (2018). Using psychological artificial intelligence (Tess) to relieve symptoms of depression and anxiety: randomized controlled trial. JMIR Mental Health, 5(4), e64.
- Gooding P, Kariotis T. 2021. Ethics and law in research on algorithmic and data-driven technology in mental health care: scoping review. JMIR Mental Health 8(6):e24668. [CrossRef]
- Gooding, P. (2018). A New Era for Mental Health Law and Policy: Supported Decision-Making and the UN Convention on the Rights of Persons with Disabilities. Cambridge University Press.
- Househ, M., Schneider, J., Ahmad, K., Alam, T., Al-Thani, D., Siddig, M. A., Alhamad, M., Moo-Young, J., & Saddik, B. (2019). An evolutionary bootstrapping development approach for a mental health conversational agent. Studies in Health Technology and Informatics, 262, 228-231.
- Joshi, D., Makhija, M., Nabar, Y., Nehete, N., & Patwardhan, M. (2018). Mental health analysis using deep learning for feature extraction. In Proceedings of the ACM India Joint International Conference on Data Science and Management of Data (pp. 356-359). Goa, India. [CrossRef]
- Joshi, D., Makhija, M., Nabar, Y., Nehete, N., & Patwardhan, M. (2018). Mental health analysis using deep learning for feature extraction. In Proceedings of the ACM India Joint International Conference on Data Science and Management of Data (pp. 356-359). Goa, India. [CrossRef]
- Kaur P, Sharma M, Mittal M. 2018. Big data and machine learning based secure healthcare framework. Procedia Computer Science 132(3):1049–1059. [CrossRef]
- Kraemer, H. C., & Freedman, R. (2014). Computer AIDS for the diagnosis of anxiety and depression. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 171(2), 134-136.
- Lahti, A. C. (2016). Making progress toward individualized medicine in the treatment of psychosis. The American Journal of Psychiatry, 173(1), 5-7.
- Leech, N. L., & Onwuegbuzie, A. J. (2011). Beyond constant comparison qualitative data analysis: Using NVivo.
- School Psychology Quarterly, 26(1), 70-84. [CrossRef]
- Li, A., Jiao, D., & Zhu, T. (2018). Detecting depression stigma on social media: A linguistic analysis. Journal of Affective Disorders, 232, 358-362. [CrossRef]
- Liu Y, Xie Y-N, Li W-G, He X, He H-G, Chen L-B, Shen Q. 2022. A machine learning-based risk prediction model for post-traumatic stress disorder during the COVID-19 pandemic. Medicina 58(12):1704. [CrossRef]
- Ma-Kellams, C., Or, F., Baek, J. H., & Kawachi, I. (2015). Rethinking suicide surveillance. Clinical Psychological Science, 4(3), 480-484.
- Mandryk, R. L., & Birk, M. V. (2019). The potential of game-based digital biomarkers for modeling mental health.
- JMIR Mental Health, 6(4), e13485.
- Marks, M. (2020). Emergent medical data: health information inferred by artificial intelligence. U.C. Irvine Law Review, 11, 995.
- McMullen TL, Mandl SR, Pratt MJ, Van CD, Connor BA, Levitt AF. 2022. The IMPACT Act of 2014: standardizing patient assessment data to support care coordination, quality outcomes, and interoperability. Journal of the American Geriatrics Society 70(4):975–980. [CrossRef]
- Meena V, Gorripatti M, Praba TS. 2021. Trust enforced computational offloading for health care applications in fog computing. Wireless Personal Communications 119(2):1369–1386. [CrossRef]
- Meng, H., Huang, D., Wang, H., Yang, H., AI-Shuraifi, M., & Wang, Y. (2013). Depression recognition based on dynamic facial and vocal expression features using partial least square regression. In Proceedings of the 3rd ACM International Workshop on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge (pp. 21-30).
- Midha S, Verma S, Kavita, Mittal M, Jhanjhi N, Masud M, A. AlZain M. 2023. A secure multi-factor authentication protocol for healthcare services using cloud-based SDN. CMCComputers Materials & Continua 74(2):3711–3726. [CrossRef]
- Mills, C., & Hilberg, E. (2018). The construction of mental health as a technological problem in India. Critical Public Health, 30(1), 41-52.
- Mukhiya SK, Lamo Y, Rabbi F. 2022. A reference architecture for data-driven and adaptive internet-delivered psychological treatment systems: software architecture development and validation study. JMIR Human Factors 9(2):e31029. [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, T. B., & Detsky, A. S. (2013). The inevitable application of big data to health care. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 309(13), 1351-1352.
- Newaz MT, Giggins H, Ranasinghe U. 2022. A critical analysis of risk factors and strategies to improve mental health issues of construction workers. Sustainability 14(20):13024. [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, H., Nguyen, V., Nguyen, T., Larsen, M., O’Dea, B., Nguyen, D., et al. (2018). Jointly predicting affective and mental health scores using deep neural networks of visual cues on the web. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Web Information Systems Engineering—WISE 2018 (pp. 100-110). Dubai, United Arab Emirates. [CrossRef]
- Nithya B, Ilango V. 2017. Predictive analytics in health care using machine learning tools and techniques. In: 2017 International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Control Systems (Iciccs). 492–499.
- Paes MR, Silva AC, Kowalski ICD, Nimtz MA, da Silav OBM, Paes RG. 2021. Mental health in a general hospital: perception of the nursing team. Revista De Pesquisa-Cuidado E Fundamental Online 13:1460–1466. [CrossRef]
- Parekh, Ruchit, and Charles Smith. “Innovative AI-driven software for fire safety design: Implementation in vast open structure.” World Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology and Sciences 12.2 (2024): 741-750.
- Patel HB, Gandhi S. 2018. A review on big data analytics in healthcare using machine learning approaches. In: 2018 2nd International Conference on Trends in Electronics and Informatics (ICOEI).
- Parekh, Ruchit. “Comparison Analysis of Construction Costs according to LEED and non-LEED Certified Educational Buildings.” Journal of Emerging Technologies and Innovative Research 11 (2024): b410-b417.
- Plaza AM, Diaz J, Perez J. 2018. Software architectures for health care cyber-physical systems: a systematic literature review. Journal of Software-Evolution and Process 30(7):22. [CrossRef]
- Parekh, Ruchit. “Automating the design process for smart building technologies.” World Journal of Advanced Research and Reviews 23.2 (2024): 1213-1234.
- Ray, A., Kumar, S., Reddy, R., Mukherjee, P., & Garg, R. (2019). Multi-level attention network using text, audio and video for depression prediction. In Proceedings of the 9th International on Audio/Visual Emotion Challenge and Workshop (pp. 81-88).
- Saeb, S., Zhang, M., Kwasny, M., Karr, C. J., Kording, K., & Mohr, D. C. (2015). The relationship between clinical, momentary, and sensor-based assessment of depression. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare (pp. 229-232).
- Shatte, A. B., Hutchinson, D. M., & Teague, S. J. (2019). Machine learning in mental health: A scoping review of methods and applications. Psychological Medicine, 49(9), 1426-1448. [CrossRef]
- Suganuma, S., Sakamoto, D., & Shimoyama, H. (2018). An embodied conversational agent for unguided internet- based cognitive behavior therapy in preventative mental health: feasibility and acceptability pilot trial. JMIR Mental Health, 5(3), e10454.
- Swain S, Patra MR. 2022. Analysis of depression, anxiety, and stress chaos among children and adolescents using machine learning algorithms. In: Panda M, ed. Communications in Computer and Information Science. Vol. 1737. Cham: Springer.
- ai, A. M., Albuquerque, A., Carmona, N. E., Subramanieapillai, M., Cha, D. S., Sheko, M., Lee, Y., Mansur, R., & McIntyre, R. S. (2019). Machine learning and big data: implications for disease modeling and therapeutic discovery in psychiatry. Artificial Intelligence in Medicine, 99, 101704.
- Thieme A, Belgrave D, Doherty G. 2020. Machine learning in mental health: a systematic review of the HCI literature to support the development of effective and implementable ML systems. ACM Transactions on Computer-Human Interaction 27(5):34. [CrossRef]
- Thorstad, R., & Wolff, P. (2019). Predicting future mental illness from social media: A big-data approach. Behavior Research Methods, 51(4), 1586-1600. [CrossRef]
- Torous, J., & Baker, J. T. (2016). Why psychiatry needs data science and data science needs psychiatry: Connecting with technology. JAMA Psychiatry, 73(1), 3-4.
- Tuli, A., Singh, P., Sood, M., Deb, K. S., Jain, S., Jain, A., Wason, M., Chadda, R., & Verma, R. (2016). Harmony: close knitted mHealth assistance for patients, caregivers and doctors for managing SMIs. In Proceedings of the 2016 ACM International Joint Conference on Pervasive and Ubiquitous Computing: Adjunct (pp. 1144-1152).
- Tummers J, Tobi H, Catal C, Tekinerdogan B. 2021. Designing a reference architecture for health information systems. Bmc Medical Informatics and Decision Making 21. [CrossRef]
- Upadhyay S, Kumar M, Upadhyay A, Verma S, Kavita Kaur M, Abu Khurma R, Castillo PA. 2023. Challenges and limitation analysis of an IoT-dependent system for deployment in smart healthcare using communication standards features. Sensors 23. [CrossRef]
- Vaishali Narayanrao P, Lalitha Surya Kumari P. 2020. Analysis of machine learning algorithms for predicting depression. In: 2020 International Conference on Computer Science, Engineering and Applications, ICCSEA, Vol. C7, 9132963.
- van den Bergh D, Bogaerts S, Spreen M, Flohr R, Vandekerckhove J, Batchelder WH, Wagenmakers EJ. 2020. Cultural consensus theory for the evaluation of patients’ mental health scores in forensic psychiatric hospitals. Journal of Mathematical Psychology 98(1):102383. [CrossRef]
- Vinci ALT, Rijo RPCL, Marques JMdA, Alves D. 2016. Proposal of an evaluation model for mental health care networks using information technologies for its management. Procedia Computer Science 100:826–831. [CrossRef]
- Wahle, F., Kowatsch, T., Fleisch, E., Rufer, M., & Weidt, S. (2016). Mobile sensing and support for people with depression: A pilot trial in the wild. JMIR mHealth and uHealth, 4(3), e111.
- Wang, R., Wang, W., Aung, M. H., Ben-Zeev, D., Brian, R., Campbell, A. T., Choudhury, T., Hauser, M., Kane, J., Scherer.
- E. A., & Walsh, M. (2018). Predicting symptom trajectories of schizophrenia using mobile sensing. GetMobile: Mobile Computing and Communications, 22(2), 32-37.
- Weber, G. M., Mandl, K. D., & Kohane, I. S. (2014). Finding the missing link for big biomedical data. The Journal of the American Medical Association, 311(24), 2479-2480.
- Wilton R. 2017. Trust and ethical data handling in the healthcare context. Health and Technology 7(4):569–578. [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization. (2022). Mental disorders. Available at https://www.who.int/newsroom/fact- sheets/detail/mental-disorders.
- Wshah, S., Skalka, C., & Price, M. (2019). Predicting posttraumatic stress disorder risk: A machine learning approach. JMIR Mental Health, 6(7), e13946.
- Wu, P., Koh, J., & Chen, A. (2019). Event detection for exploring emotional upheavals of depressive people. In Proceedings of the 34th ACM/SIGAPP Symposium on Applied Computing (pp. 2086-2095). Limassol Cyprus. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, D., Luo, J., Silenzio, V., Zhou, Y., Hu, J., Currier, G., & Kautz, H. (2015). Tackling Mental Health by Integrating Unobtrusive Multimodal Sensing. In Proceedings of the Twenty-Ninth AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence (pp. 1401-1408).
- Zhou, T., Hu, G., & Wang, L. (2019). Psychological disorder identifying method based on emotion perception over social networks. International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health, 16(6), 953. [CrossRef]
| User layer | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Public health organization epidemiological review | Evaluation and care instruments | Report and data visualization | |
| Therapist and client communication | Scheduling and referral | Trend analytics | |
| Protection tier | |||
| Permission-based entry regulation | Data anonymization | Mental health regulatory compliance | |
| Multifactor authentication | Audit logs and monitoring | Fraud analytics | |
| Scalable service layer | |||
| Auto-scaling infrastructure | Geo-proximity routing | Data sharding | |
| API Integration | Interoperability standards | Platform agonistic compatibility | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




