1. Introduction
In recent decades, factors such as globalization, urbanization, aging populations, and shifts in health policies have contributed to the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, now the leading cause of death worldwide [
1,
2]. Among these, chronic respiratory diseases (CRDs), such as asthma and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) are particularly concerning due to their high mortality and morbidity rates [
1,
3]. These conditions not only significantly reduce patients’ quality of life but also place a substantial economic burden on healthcare systems, with global costs projected to reach
$47 trillion by 2030 [
1,
4,
5]. This economic impact reflects both direct healthcare costs and a 20% increase in Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) since 1990 [
6].
Asthma and COPD are the most prevalent CRDs, affecting approximately 262 million and 212 million people globally, respectively [
7]. The severity of these diseases is reflected in alarming statistics: over 1,000 people die from asthma daily, and COPD-related deaths have increased by 26% since 1990, now accounting for 3.3 million deaths annually, making COPD the fourth leading cause of death worldwide [
8,
9,
10,
11]. Managing the complex needs of patients with CRDs, particularly those with asthma, COPD and overlapping features of asthma and COPD (asthma-COPD overlap syndrome or ACOS), poses a significant challenge in medical practice. Inadequate diagnosis and misdiagnosis of asthma and COPD are common in primary care settings, often leading to suboptimal treatment and poor disease control [
12,
13,
14,
15].
Given these challenges, primary care plays a crucial role in managing chronic conditions. Effective primary care can enhance prevention strategies, improve treatment outcomes, and reduce the strain on secondary healthcare services [
6,
14,
16]. Strong primary care systems can meet the clinical needs of most patients efficiently, whereas weak or inadequate systems are associated with higher risks of hospitalization and complications [
2,
17]. However, a significant proportion of asthma and COPD patients still do not achieve effective disease control. Approximately 45.1% of asthma patients and 63.2% of COPD patients have uncontrolled disease, highlighting the need for more comprehensive evaluation and management strategies [
18,
19,
20,
21,
22].
Recent advancements in Spain, such as the implementation of Electronic Health Records (EHR) in the
Sistema Nacional de Salud (SNS), offer a promising tool to improve healthcare delivery by reducing unnecessary procedures and ensuring timely access to updated clinical information across any regional health service [
23,
24]. EHRs provide a valuable opportunity to develop preclinical tools capable of screening patients at risk of poorer health outcomes more effectively. Such tools would allow healthcare professionals to prioritize patients with more severe prognoses and optimize the allocation of medical resources.
Therefore, in this study, we propose the use of predictive clinical variables derived from EHR data to assess the control of chronic respiratory diseases, such as asthma and COPD. This novel approach aims to provide an effective preclinical screening of these patients, potentially enhancing disease management in primary care without increasing the demand for care.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Overview
Seleida is a multicenter, observational, non-interventional study designed to identify clinical variables that could predict poor control of asthma and COPD using EHR data. Data were randomly selected from digital clinical records of primary care centers in Seville and Valencia. The project was approved from the Ethics Committee of Valencia (CEIm 132.22, approval date March 06, 2023) and was registered in the Portal de Ética de la Investigación Biomédica de Andalucía through the Sistema de Información de los Comités de Ética de la Investigación (1140-N-23, approval date September 12, 2023), with the endorsement of the SEMERGEN Research Department (2023-00035, approval date June 06, 2023).
2.2. Data Source and Patient Selection
Patient data were anonymously extracted from the digital clinical history of the Spanish SNS between 01 May 2024 and 31 July 2024. Each patient was assigned with a unique code to ensure confidentiality and protection of their personal data.
2.2.1. Inclusion Criteria
The study included patients aged between 18 to 80 years with a confirmed clinical and/or spirometric diagnosis of asthma and those aged 40 to 80 years with a diagnosis of COPD, all registered in the SNS as of December 31, 2023. Furthermore, patients without a formal diagnosis recorded in the EHR, but who had received treatment for asthma or COPD for a minimum of three months per year over the preceding two years, were also considered eligible for inclusion.
2.2.2. Exclusion Criteria
For the asthma cohort, patients classified at step 6 according to the treatment scale outlined in version 5.4 of the Guía Española para el Manejo del Asma (GEMA) [
25] were excluded. Exclusion criteria applicable to both asthma and COPD cohorts included patients with a diagnosis of active cancer or those receiving palliative care, those undergoing biologic therapy, pregnant patients, and individuals with concurrent diagnoses of asthma and COPD or ACOS. Additionally, patients with conditions such as rheumatic diseases or other pathologies requiring regular systemic corticosteroid use, bedridden patients, and those participating in clinical trials were also excluded. These criteria were implemented to minimize the potential of confounding factors that could affect the control of respiratory diseases or the response to treatment, thereby ensuring a more homogeneous study population. To avoid selection bias, patients were selected from groups not assigned to the authors.
2.2.3. Variables Collected
Clinical variables were extracted from EHRs to identify effective predictors of poorly controlled asthma or COPD. These variables included relevant demographic and anthropometric data (age, gender, height, weight and body mass index [BMI]), comorbidities and treatable traits that may affect respiratory disease control (smoking habit, obesity; sleep apnea; rhinitis or chronic rhinosinusitis, nasosinusal polyposis; drug, environmental and food allergies; bronchiectasis; gastroesophageal reflux; ischemic heart disease; heart failure; arrhythmias; hypercholesterolemia; hypertriglyceridemia; hypertension, patients undergoing non-cardiovascular β2 blockers or angiotensin-converting enzyme [ACE] inhibitors treatment; diabetes mellitus, patients undergoing glucagon-like peptide-1 [GLP1] agonists or sodium-glucose cotransporter-2 [SGLT2] inhibitors treatment, anxious-depressive disorder; anemia; osteoporosis; chronic kidney disease or peripheral arterial disease), as well as disease history (current treatment, number of daily inhalations; measurement of rescues with short-acting β-agonists [SABA], short-acting muscarinic antagonists [SAMA; Ipratropium Bromide]; days without treatment due to lack of prescription or dispensing; exacerbations in the last year; visits to the emergency department or physician’s office in the last year due to asthma or COPD; oral or parenteral corticosteroid therapy expressed as number of regimens and as equivalent doses of prednisone in the last year; antibiotics used for treating bronchitis or exacerbations expressed as number of courses and as number of days of treatment in the last year and eosinophilia). For both asthma and COPD, two additional variables were recorded: the province of origin and an identification number, which ensured patient anonymity. Additionality, asthma patients’ data were collected for the following variables: assessment of asthma severity (treatment step according to GEMA 5.4 [
25]) and current treatment with inhaled corticosteroids (IC)-formoterol combinations (treatment, number of canisters and doses of each canister, and number of daily inhalations). In the case of COPD, data were collected on the ABE classification defined by the 2024 version of Global Initiative for Chronic Obstructive Lung Disease (GOLD) [
26] and the number of severe exacerbations (with hospital admission) in the last year.
The control variable was calculated for all patients based on a selection of parameters collected in the current evidence.
2.3. Model and Calculating Predictions
Current clinical characterization of asthma control is well-defined, being based on three key areas: current symptoms, recent lung function, and exacerbations in the past year [
25]. In contrast, the 2021 update of the Spanish COPD guideline (GesEPOC) proposes a control tool that has not yet achieved a broad international consensus [
27]. Both approaches (asthma and COPD) have significant limitations in preclinical primary care studies due to difficulties in obtaining consistent lung function data and symptom evaluation using validated scales.
This pilot study aims to overcome these limitations by identifying variables within EHR associated with asthma and COPD control and developing a predictive model to estimate the preclinical probability of poor control. This model would allow a focus on patients at higher risk, facilitating a proactive management and an optimization of primary care interventions.
Developing this model required redefining disease control as the probability of a patient experiencing an exacerbation: high probability indicates poor control, while low probability indicates good control. Although disease control is well-established for asthma [
28,
29,
30], no universally accepted definition exists for COPD [
31]. In our model, a “COPD exacerbation patient” is defined by GOLD and GesEPOC criteria: two or more moderate exacerbations or one severe exacerbation (hospitalization) in the past year. These guidelines prioritize exacerbation frequency and severity to identify high-risk patients and guide patient management [
26,
32], since frequent exacerbations correlate with worse prognosis and increased disease burden [
33,
34,
35,
36,
37].
Given challenges in performing spirometry in primary care and the limited use of peak flow meters, lung function data and validated symptom evaluations were excluded, as they are often not recorded. Instead, we included the use of short-acting beta-agonist (SABA) inhalers as an additional metric in our control model. SABA use correlates with exacerbation risk, with higher use linked to poorer disease control and increased symptoms [
38,
39,
40]. In patients without prior exacerbations, higher SABA use may indicate uncontrolled symptoms, potentially increasing the risk of future exacerbations.
Quantifying SABA inhaler canisters use in the previous year offers a practical and sensitive measure method of symptom control for both COPD and asthma. Recent studies support this as an indirect marker of disease control, as a valuable marker for assessing current symptoms and for predicting exacerbation risk [
41,
42]. The integration of this variable provides a comprehensive assessment of a patient’s condition, accounting for both acute events and symptom burden over time.
The criteria selected for this study—based on scientific evidence [
41,
42,
43,
44,
45,
46] and easily identifiable within the EHR—defined poor asthma control as either SABA use ≥3 canisters/year or ≥1 exacerbations/year [
41,
43,
44,
45]. For COPD, poor control was defined by SABA use ≥6 canisters/year, ≥2 moderate exacerbations/year, or ≥1 severe exacerbation/year (requiring hospital admission) [
42,
46]. Based on these criteria, these definitions were programmed into our database to automatically classify patients from Seville and Valencia as either well-controlled or poorly controlled, aiming for a streamlined approach in real-world clinical settings.
2.4. Statistical Analysis
Following the classification of each patient according to their disease control status (good or poor), a comprehensive statistical analysis was performed to evaluate the predictive value of each collected variable. The analysis was conducted using R software (version 4.34.2) [
47], with a statistical significance level set at 95% and an alpha error of 5%.
The data structure was explored using the inspectdf R package, and incomplete clinical variables were excluded from the analysis (e.g., variables with more than 50% missing data and categorical variables with fewer than two categories). The development of the predictive model followed a two-phase approach:
2.4.1. Phase 1
The association between each variable and the dichotomous outcome (good/poor disease control) was evaluated using appropriate statistical tests, such as the Chi-square test and Fisher’s Exact Test for dichotomous variables, and the Wilcoxon signed-rank test for continuous variables. To control for Type I error, a Benjamini-Hochberg correction was applied to the combined set of p-values from all tests. Additionally, Spearman’s correlation matrices were used to confirm significant associations between clinical variables and disease control.
2.4.2. Phase 2
Variables identified as statistically significant in Phase 1 (adjusted p-value < 0.05) were included in a binary logistic regression model, developed using the
glmnet R package. A backward stepwise procedure based on the Akaike Information Criterion – AIC
(stepAIC function from
MASS R package [
48]) was applied to identify the most parsimonious model, which was defined as the model with the lowest AIC, indicating an optimal balance between model complexity and goodness of fit.
The model’s performance was assessed using a confusion matrix and various classification metrics, including sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), accuracy rate, and their 95% confidence intervals. These metrics were calculated using the
confusionMatrix function from the
caret R package [
49], with both training and validation sets (80% and 20% of the original data, respectively) to ensure robust model performance and generalizability in real-world scenarios.
In order to develop a predictive model for identifying factors associated with poor control events in patients with asthma or COPD, we divided each sample into two subsets: a training set, comprising 80% of the data, and a validation set, containing the remaining 20%. The training set was used to train the model, allowing it to learn relevant patterns and relationships within the data to predict outcomes. This prevents overfitting by ensuring the model does not become overly specific to the training data. The validation set was then employed to evaluate the model’s performance on an independent subset of data not used during training, providing an unbiased assessment of its generalizability to new data. This partitioning strategy is standard in predictive modeling to ensure a robust evaluation of model performance and applicability in real-world scenarios.
2.5. Definition of minimal sample size for model validation
To determine the minimal sample size required for identifying predictive variables of disease control with a dichotomous outcome (based on European-level data, where the incidence of the least frequent category is 28% for asthma [
50,
51,
52] and 27.5% for COPD [
53]), and considering three independent variables, the following steps were taken:
2.5.1. Determination of the minimum number of events in the training set:
According to the “10 events per predictor variable” rule, the training set (80% of the original dataset) must include at least 10 events for each predictor variable to ensure stable model estimates. For three predictor variables, this necessitates a minimum of 30 events in the training set.
2.5.2. Calculation of the total sample size required
To ensure both the training and validation sets contain sufficient events, the total sample size was calculated to achieve a minimum of 10 events in the validation set (20% of the dataset). Solving the equations for asthma and COPD, we find: 0.2 · n · 0.28 ≥10 for asthma and 0.2 · n · 0,275 ≥10 for COPD. Resolving for both n: n ≥10 / (0.2 · 0.28) ≈ 179 for asthma and n ≥10 / (0.2 · 0.275) ≈ 182 for COPD.
2.5.3. Verification of the number of events in the training set
It was verified that the training set (80% of the original dataset) contains more than 30 events, meeting the required threshold: 0.8 · 179 · 0.28 ≈ 40.10 for asthma and 0.8 · 182 · 0.275 ≈ 40.04 for COPD. Both calculations exceed the requirement of having at least 30 events in the training set, thereby ensuring the stability of the model during fitting.
For a predictive model with three independent variables, a minimum sample size of approximately 179 for asthma and 182 for COPD is needed to ensure proper validation, fulfilling the “10 events per predictor variable” rule for the training set and providing at least 10 events in the validation set. However, the initial sample sizes do not meet these calculated thresholds, limiting the internal validity of the predictive models. Despite this, given the novelty and significance of the topic, the authors have chosen to proceed with this pilot study. While the sample sizes are suboptimal for robust validation, the findings from this exploratory analysis lay a valuable foundation for future studies with larger, adequately powered samples.
3. Results
3.1. Patient Characteristics
A total of 132 asthma patients and 110 COPD patients’ EHR data were included for the exploratory data analysis for the development of a putative predictive model of poor control disease.
The baseline patient characteristics can be found in
Table 1. Asthma patients were primarily located in Seville (75.8%), with the remainder from Valencia (24.2%). Conversely, COPD patients exhibited a more balanced geographic distribution between Seville (54.5%) and Valencia (45.5%). The age range for asthma patients extended from 18 to 78 years, with the most prevalent age group being 40 to 49 years. However, the age range for COPD patients was from 48 to 80 years.
Regarding disease severity, 9.1%, 1.5%, 29.5%, 38.6%, and 21.2% of asthma participants were at degrees 1, 2, 3, 4, and 5, respectively, according to classification of GEMA 5.4 [
25]. According to the 2024 GOLD classification, 16.4% of COPD patients were in group A, 40.0% in group B, and 43.6% in group E [
20]. The most prevalent pharmacological treatments for asthma and COPD are listed in the
Table 2.
In terms of the daily frequency of inhalations, we found significant differences between the treatment recommended for asthmatic patients and for patients with COPD. Asthma patients averaged 3 daily inhalations, with 15.9% using 1 inhalation daily, 34.1% using 4 inhalations, and 31.8% using 2 inhalations. COPD patients averaged 2.5 daily inhalations, with 43.6% using 1 inhalation daily, 23.6% using 4 inhalations, and 19.1% using 2 inhalations.
Both patient groups exhibited significant data gaps in the EHR. There was a significant amount of missing information regarding height (46.2% and 58.2%), weight (75.8% and 70.0%), body mass index (BMI) (78.0% and 72.7%), obesity diagnosis (72.7% and 61.8%), and smoking status (31.8% and 27.3%) in patients with asthma and COPD, respectively.
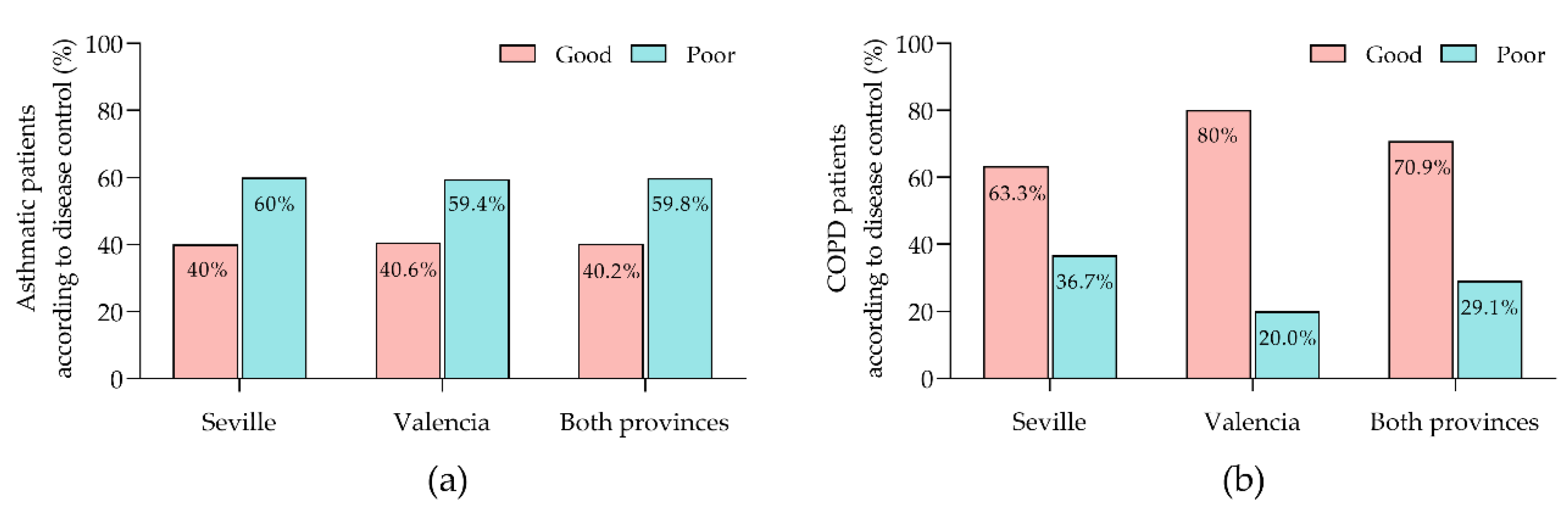
The degree of asthma control was comparable between the provinces: 40.0% of patients in Seville and 40.6% in Valencia exhibited good control, while 60.0% in Seville and 59.4% in Valencia had poor control, with no statistically significant differences between the provinces (
Figure 1a). In contrast, control of COPD revealed significant provincial disparities: 63.3% of patients in Seville achieved good control compared to 80.0% in Valencia, and poor control was observed in 36.7% of patients in Seville versus 20.0% in Valencia (
Figure 1b).
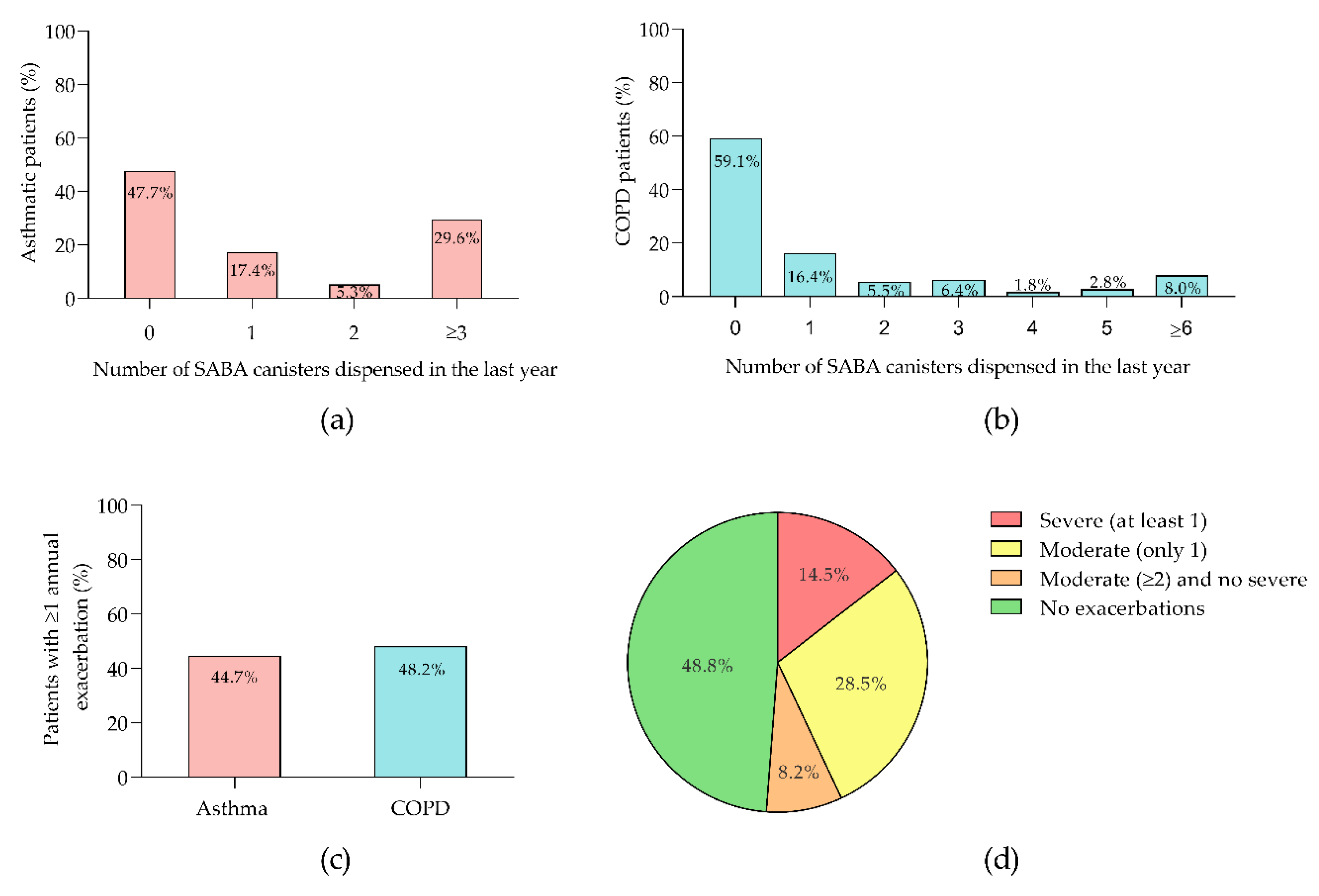
Analysis of SABA canister usage among asthmatic patients in the past year revealed that 47.7% used no canisters, 17.4% used one, 5.3% used two, and 29.6% used three or more (
Figure 2a). Of the 70 patients prescribed SABA, 4.3% received Terbutaline, while the rest were prescribed Salbutamol. For COPD patients, the distribution of canisters usage was 59.1% for zero, 16.4% for one, 5.5% for two, 6.4% for three, 1.8% for four, 2.8% for five, and 8.0% for six or more canisters (
Figure 2b). All 45 COPD patients who received SABA were prescribed Salbutamol. Annual exacerbation rates were 44.7% for asthma and 48.2% for COPD (
Figure 2c). In the COPD cohort, 18.9% of 90 exacerbations were severe. Among COPD patients, 14.5% had at least one severe exacerbation, 28.5% had two or more moderate exacerbations, 8.2% had one moderate exacerbation, and the remainder had no recorded exacerbations (
Figure 2d).
Based on these results, an analysis was conducted to identify the variables most strongly associated with the degree of asthma and COPD control.
3.2. Determination of Clinical Variables for Predict Poor Control of Asthma and COPD Disease
A Spearman’s correlation analysis was performed on patient data from EHR for both asthma and COPD to identify variables significantly associated with disease control, with results corrected using the Bonferroni method to minimize Type I errors. For both conditions, significant variables (adjusted p<0.05) included the number of SABA canisters prescribed annually, total number of SABA and SAMA canisters prescribed per year, number of annual exacerbations, number of respiratory-related consultations, number of annual prednisone courses, annual equivalent prednisone dose for lower respiratory tract problems (bronchitis or asthma attacks, in the case of asthma, or bronchitis or COPD exacerbations, in the case of COPD), number of annual antibiotic courses, and annual days of antibiotic use for lower respiratory tract problems. In addition, in the case of asthma, the type of SABA (none, Salbutamol, Terbutaline or both) was also included, and in the case of COPD, the annual number of severe exacerbations.
These correlations were validated with univariate analyses and statistical tests appropriate to each variable, followed by Bonferroni correction. Chi-square tests applied to dichotomous variables found statistical significance for the type of SABA, in the case of COPD, and the type of SAMA prescribed (none or Ipratropium Bromide; adjusted p<0.05), in both pathologies, while Fisher’s exact test confirmed significance for dichotomous variables with low representation. The Wilcoxon test showed significance for continuous variables, such as the number of SABA canisters prescribed the previous year, number of SAMA canisters prescribed the previous year, total number of SABA and SAMA canisters prescribed the previous year, number of exacerbations in the previous year, number of respiratory-related consultations attended in the previous year, number of prednisone courses prescribed in the previous year for lower respiratory tract problems, total equivalent dose of prednisone in the previous year, number of antibiotic courses prescribed for lower respiratory tract problems the previous year, and number of days of antibiotic use prescribed in the previous year.
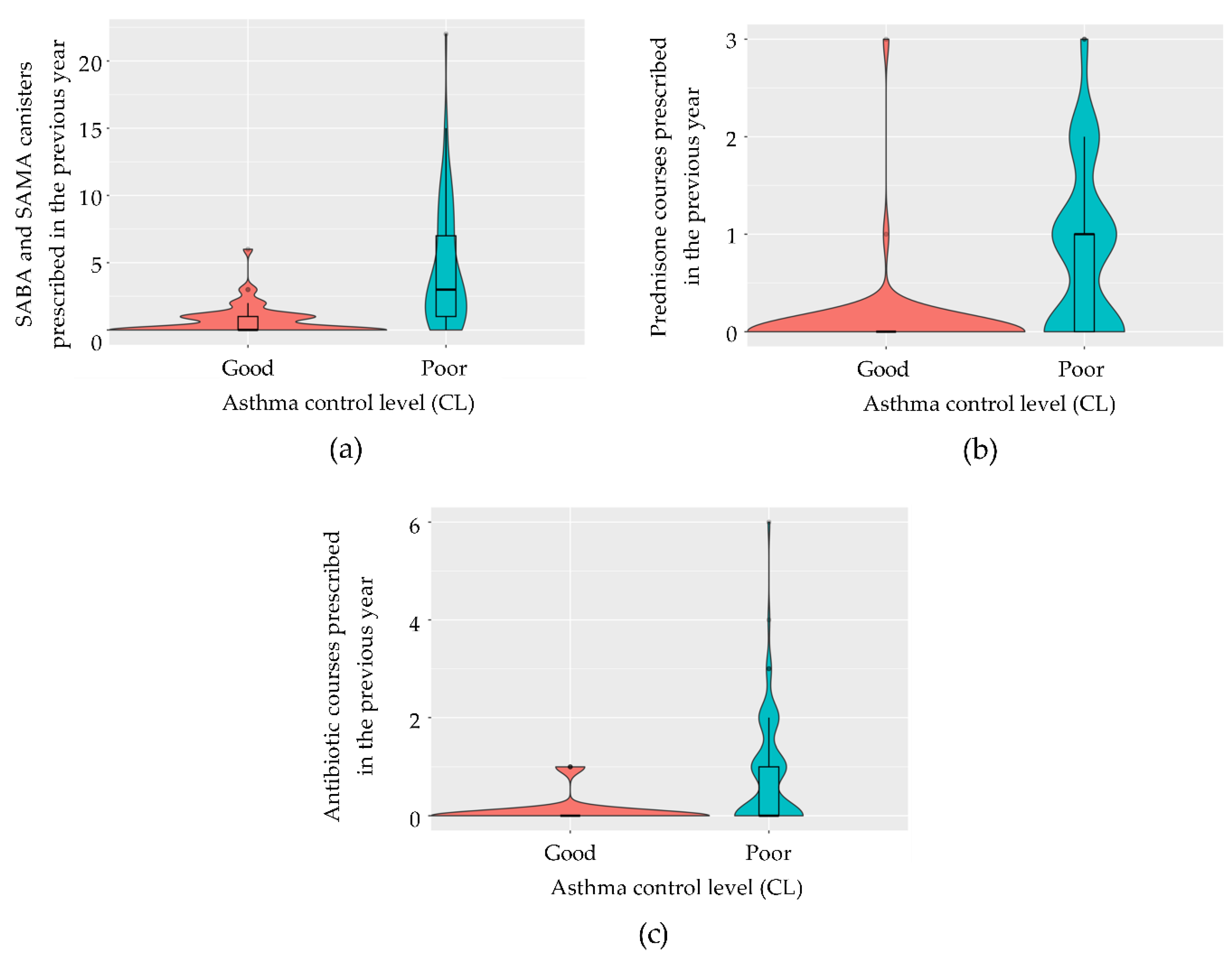
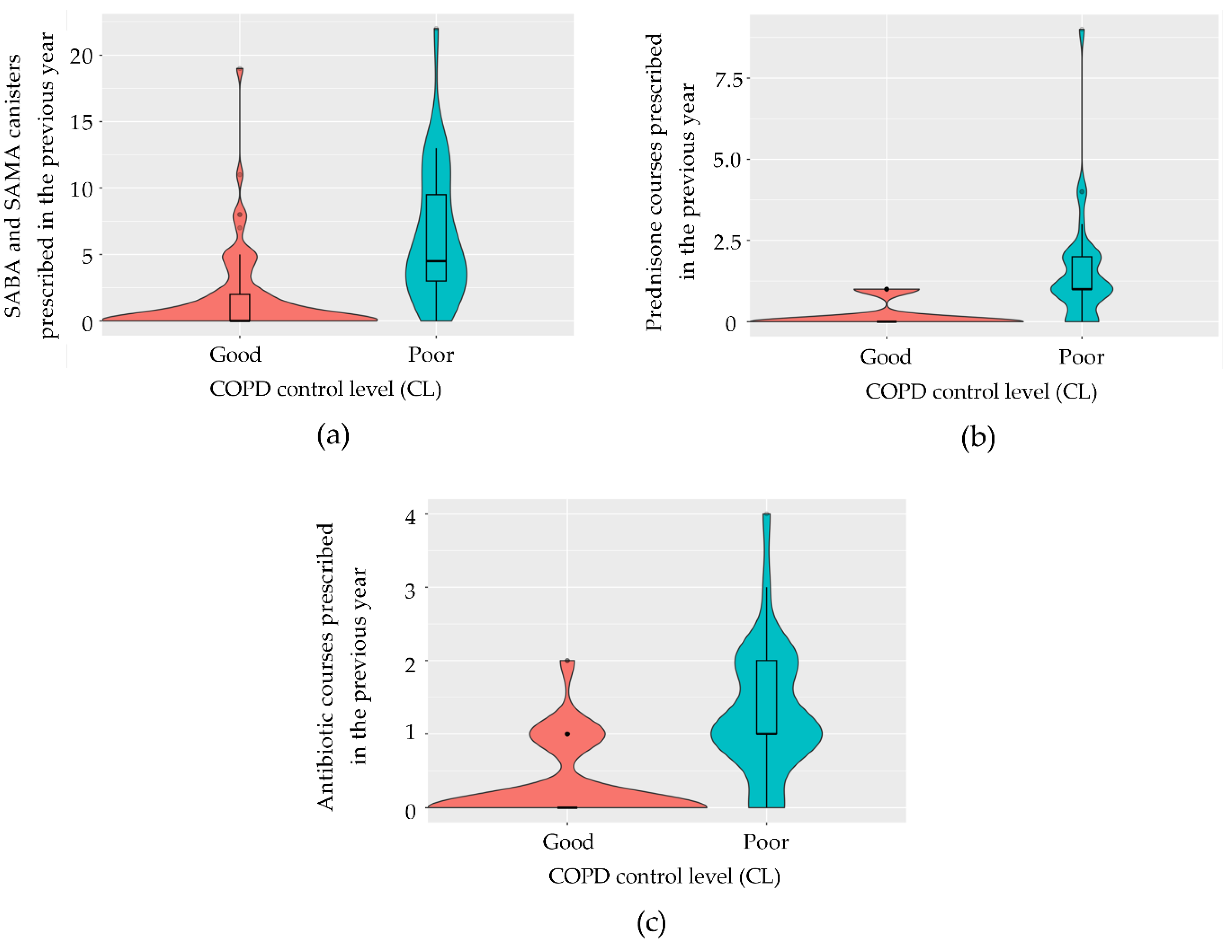
Variables used to define disease control were initially excluded from the model. Given that the calculation of variance-inflation factors (VIFs) on the model containing all pre-selected variables indicated the presence of multicollinearity, we employed a stepwise regression based on the AIC to evaluate the goodness-of-fit of the most simplified model, identified as the one with the lowest AIC value. For both diseases, the final models identified the total number of SABA and SAMA canisters prescribed in the previous year (
Figure 3a and
Figure 4a), the number of prednisone courses prescribed in the previous year (
Figure 3b and
Figure 4b), and the number of antibiotic courses prescribed for lower respiratory tract issues (
Figure 3c and
Figure 4c) as significant predictors. In asthma, the model achieved 88.5% accuracy (95% CI: 69.9–97.6), with 83.3% sensitivity, 92.9% specificity, and a kappa correlation coefficient of 76.7%. In COPD, the model achieved 86.4% accuracy (95% CI: 65.1–97.1), with 93.8% sensitivity, 66.7% specificity, and a kappa correlation coefficient of 63.7%. The predictive logistic regression coefficients for the identified variables in the model were presented in
Table 3, for asthma, and in
Table 4, for COPD.
However, McNemar’s test showed no significant difference between the models’ error rates and reference classifiers (asthma: p=0.332, COPD: p=0.302), suggesting that larger sample sizes are needed to improve the robustness and predictive accuracy.
Predictive equations were developed for both conditions (Equation 1 for asthma and Equation 2 for COPD), where y represents the probability of poor control. If y<0.50, the patient is considered to have good control; if y>0.50, the patient is classified as having poor control, with y=0.50 being inconclusive.
3.2.1. Asthma Group Analysis
Equation 1. Predictive equation for poor control in asthma.
[SABA+SAMA]: the number of SABA+SAMA canisters prescribed in the last year.
[Prednisone_courses]: number of Prednisone courses prescribed in the last year due to bronchitis or asthma attacks.
[Antibiotic_courses]: number of antibiotic courses prescribed in the last year due to bronchitis or asthma attacks.
3.2.2. COPD Group Analysis
Equation 2. Predictive equation for poor control in COPD.
[SABA+SAMA]: number of SABA+SAMA canisters prescribed in the past year.
[Prednisone_courses]: number of prednisone courses prescribed in the past year due to bronchitis or COPD exacerbations.
[Antibiotic_courses]: number of antibiotic courses prescribed in the past year due to bronchitis or COPD exacerbations.
4. Discussion
The global aging population has led to an increase in chronic diseases, with asthma and COPD being major health problems in developed countries due to their high prevalence and associated healthcare costs [
54,
55]. As populations continue to age, the burden of these diseases is expected to rise, necessitating effective control strategies to mitigate their impact on patients’ lives. Despite existing pharmacological and non-pharmacological strategies, many patients with asthma and COPD experience poor disease control, largely due to suboptimal medical care and the significant workload in primary care settings [
12,
15,
56,
57,
58,
59,
60,
61,
62,
63,
64,
65,
66,
67,
68,
69,
70,
71]. Our study aimed to develop a predictive model to estimate the preclinical probability of poor disease control using data from EHR. This tool was designed to identify patients at higher risk without requiring in-person consultations, potentially alleviating the burden on primary care.
Just as the Seles priestesses of ancient Greece predicted people’s futures by listening to the wind rustling through the leaves of oak trees (known as Zeus trees) or the tinkling of bronze vessels hanging from their branches, we have sought to interpret the ‘signals’ captured in EHRs to predict the preclinical likelihood of poor disease control in patients with asthma or COPD. In analogy, we named our study Seleida, meaning “the Seles way”. This proactive approach allows for initial preclinical assessments, strategic prioritization of care, and improved clinical outcomes without overburdening primary care services [
72,
73]. While integrated care programs and pharmaceutical interventions have shown success in managing chronic patients by reducing exacerbations and hospitalizations [
74,
75,
76], our EHR-based model could offer a more efficient and scalable approach.
However, this pilot study has several limitations. First, as a pilot study, the limited sample size affects the statistical power of the findings, and results should therefore be interpreted with caution and not generalized to other populations. Second, our assumption that poor disease control in both asthma and COPD is primarily linked to exacerbations and excessive SABA use may not fully align with current guidelines, especially for COPD. Although our model was built on systematically defined, evidence-based criteria, these may differ from control definitions proposed by other authors. Additionally, the omission of symptom assessment and lung function measurements in asthma may overestimate the “good control” group while ensuring accurate classification of “poor control” patients. Third, due to the lack of a universally accepted definition of control in COPD, we adapted the asthma control concept to COPD, focusing on exacerbations and SABA use (≥6 canisters/year), as these criteria have been reliably used in similar contexts where more standardized tools like GesEPOC were not applicable [
19,
20,
21]. However, we acknowledge that this adaptation may introduce biases that warrant further exploration in future studies. Fourth, the issue of COPD patients who have had a single moderate exacerbation in the last year remains unresolved. Can these patients be considered fully controlled? In our opinion, they cannot, but this controversial issue warrants further discussion. Moreover, the variability in EHR data recording practices across different clinical settings may influence the generalizability of our model, indicating the need for standardized data entry protocols to optimize predictive accuracy.
Our study demonstrates that predictive models using EHR data can reliably estimate poor disease control in asthma and COPD, achieving high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity (88.5% and 86.4% accuracy; 83.3% and 93.8% sensitivity; 92.9% and 66.7% specificity for asthma and COPD, respectively). By prioritizing poorly controlled patients, healthcare resources can be managed more effectively, potentially reducing emergency visits, secondary care burdens, and associated costs. Given the limitations of current management strategies and the economic burden of uncontrolled chronic diseases [
77], our model offers a promising solution to improve patient outcomes and healthcare efficiency.
Regarding the internal validity of the study, the observed proportion of poorly controlled cases in the asthma sample was 40.2%, higher than the initially estimated 28%. This higher incidence results in a sufficient number of events in both training and validation sets, satisfying the “10 events per predictor variable” rule. Thus, despite not meeting the initial sample size requirements (see section 2.5), the observed data confirm the internal validity of the predictive model for asthma. For COPD, the observed incidence was 29.1%, slightly above the initial estimate of 27.5%. However, this increase is not enough to meet the minimum event requirement for internal validity due to sample size limitations. Nevertheless, the data from this study provide a closer approximation to real-world conditions, offering insights to inform future studies with larger, better-powered samples for further validation.
The COVID-19 pandemic underscored telemedicine’s potential as a complementary strategy in chronic disease management [
78]. Integrating our predictive model with telemedicine options could further enhance individualized care for asthma and COPD patients, reducing costs and healthcare burdens while maintaining care quality [
79,
80]. EHR-based predictive models have been effective in other contexts, such as Alzheimer’s disease and hypertension [
81,
82,
83,
84], and could drive personalized medicine in chronic respiratory disease management [
84].
The development of preclinical predictive tools enables short-, medium-, and long-term clinical strategies focused on reducing exacerbation rates by prioritizing high-risk patients. Integrating this tool into EHR systems would allow practitioners to conduct proactive assessments and optimize care.
Finally, we observed a significant data gap in EHR records for key variables like height, weight, and smoking status. This gap suggests a need for healthcare providers to ensure comprehensive data recording to support high-quality clinical practice.
This pilot study highlights the potential of EHR-based predictive models to improve early identification of patients at risk for poor asthma and COPD control. Despite limitations in sample size and control definitions, the findings offer valuable insights for future research and more robust model development. As telemedicine and EHR-based tools become integral to healthcare, the ability to proactively manage high-risk patients could revolutionize chronic respiratory disease care, easing healthcare burdens and enhancing outcomes. Future studies should validate these models in larger, more diverse cohorts and refine control criteria to align with evolving guidelines.
Integrating such predictive models into clinical practice could significantly advance chronic respiratory disease management. By enabling early and targeted interventions, these models can optimize patient care and resource use. With the growing emphasis on telemedicine and data-driven decisions, such tools are becoming essential for personalized and efficient care.
5. Conclusions
Effective predictive strategies are essential for improving patient outcomes and preventing disease progression. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first predictive model developed using real-world data from electronic medical records of asthma and COPD patients within the Spanish SNS database. The model’s high accuracy, sensitivity, and specificity make it a valuable tool for the early and precise identification of poorly controlled asthma and COPD patients in primary care, enabling proactive management without the need for in-person assessments. Following validation in broader clinical settings, primary care physicians could utilize the identified clinical variables—such as the number of SABA and SAMA inhaler canisters, prednisone courses, and antibiotic regimens in the past year—to prioritize the assessment of poorly controlled patients, conduct screenings, identify underlying causes, and adjust treatment to prevent future exacerbations.
However, the findings from this pilot study should not be yet generalizable to other populations. Future research should apply the model to a larger and more geographically diverse cohort and compare its predictions to standardized clinical assessments to validate its effectiveness. Successful validation could pave the way for integrating these predictive tools into clinical practice, potentially improving chronic disease management and optimizing healthcare resource allocation.
In conclusion, integrating real-world data-driven predictive models, such as ours, into clinical practice represents a significant advancement in chronic respiratory disease management. By leveraging electronic health record and telemedicine data, healthcare providers can make more informed and timely decisions, prioritize their interventions, and improve health outcomes for both patients and healthcare systems. As healthcare continues to embrace digital transformation, these predictive tools will become indispensable for delivering high-quality and personalized care that meets the changing needs of an aging global population.
Author Contributions
Both authors contributed equally to the conceptualization, methodology, and draft preparation through their scientific and medical expertise. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by EP Health Marketing, S.L.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Hospital Universitario Doctor Peset of Valencia (protocol code CEIm 132.22, date of approval 06 March 2023). The project was registered in the Portal de Ética de la Investigación Biomédica de Andalucía through the Sistema de Información de los Comités de Ética de la Investigación (protocol code 1140-N-23, date of approval 12 September 2023). The SEMERGEN research department gave its endorsement to the project (2023-00035, date of approval 06 June 2023).
Informed Consent Statement
Patient consent was waived due to the retrospective design of the study, which involved exclusively extracting anonymized data from EHR. No diagnostic tests were performed, no clinical interventions were conducted, and no modifications to patient management were made. Furthermore, no treatment recommendations were provided based on the extracted data. The study’s sole objective was to extract specific variables to develop a predictive model, with no implications for patient privacy or confidentiality. This waiver aligns with the ethical guidelines of the Research Ethics Committees consulted, which determined that the study posed minimal risk to patients and that obtaining individual informed consent was unnecessary.
Acknowledgments
Medical writing assistance was provided by EP Health Marketing, S.L., Spain and bioinformatic analysis by Lina Marcela Gallego-Paez. The authors thank Eva Trillo Calvo, family physician and current director of primary care of Sector II of Zaragoza at the Servicio Aragonés de Salud, for her support and collaboration at the beginning of this study.
Conflicts of Interest
Maya Viejo, J.D. has received research grants from AMGEN, AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, GSK, Menarini and Novartis. He is a member of the SEMERGEN and SEMG and he belongs to the SEMERGEN respiratory work group. Navarro i Ros, F.M. has received research grants from AstraZeneca, Boehringer Ingelheim, Chiesi, Esteve, Ferrer, GSK, Kern Parma, Lundbeck, MSD, Novartis, Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Sanofi and Viatris. He is a member of the SEMERGEN and he belongs to the SEMERGEN respiratory work group.
References
- Hacker, K. The Burden of Chronic Disease. Mayo Clin Proc Inn Qual Out 2024, 8, 112–119. [CrossRef]
- Ramli, A. Primary Care Access. Med Heal. Rev 2008, 1, 63–80.
- WHO Global Status Report on Noncommunicable Diseases 2014; 2014.
- Lee, L.K.; Ramakrishnan, K.; Safioti, G.; Ariely, R.; Schatz, M. Asthma Control Is Associated with Economic Outcomes, Work Productivity and Health-Related Quality of Life in Patients with Asthma. BMJ open Respir. Res. 2020, 7, e000534. [CrossRef]
- Miravitlles, M.; Soriano, J.B.; García-Río, F.; Muñoz, L.; Duran-Tauleria, E.; Sanchez, G.; Sobradillo, V.; Ancochea, J. Prevalence of COPD in Spain: Impact of Undiagnosed COPD on Quality of Life and Daily Life Activities. Thorax 2009, 64, 863–868. [CrossRef]
- Abdel-Aal, A.; Lisspers, K.; Williams, S.; Adab, P.; Adams, R.; Agarwal, D.; Barnard, A.; Bouloukaki, I.; van Boven, J.F.M.; Chavannes, N.; et al. Prioritising Primary Care Respiratory Research Needs: Results from the 2020 International Primary Care Respiratory Group (IPCRG) Global e-Delphi Exercise. npj Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2022, 32, 6. [CrossRef]
- Boers, E.; Barrett, M.; Su, J.G.; Benjafield, A. V.; Sinha, S.; Kaye, L.; Zar, H.J.; Vuong, V.; Tellez, D.; Gondalia, R.; et al. Global Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Through 2050. JAMA Netw. Open 2023, 6, E2346598. [CrossRef]
-
The Global Asthma Report Asthma Symptoms Controlled Symptoms Essential Asthma Medicines; 2022; Vol. 26; ISBN 9780473637033.
- Wang, H.; Ye, X.; Zhang, Y.; Ling, S. Global, Regional, and National Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease from 1990 to 2019. Front. Physiol. 2022, 13, 925132. [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.; Khan, A.A.; Seedat, A.; Heis, F.; Alkhatib, A.; Alrjoob, M.; Philip, L.; Weinwe, S.M.; Breener, K.R.; Fish, P. COPD Outcomes in Different Demographic Cohorts: A Reflection of 20 Years. Chest 2023, 164, A5031–A5032. [CrossRef]
- Safiri, S.; Carson-Chahhoud, K.; Noori, M.; Nejadghaderi, S.A.; Sullman, M.J.M.; Ahmadian Heris, J.; Ansarin, K.; Mansournia, M.A.; Collins, G.S.; Kolahi, A.-A.; et al. Burden of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease and Its Attributable Risk Factors in 204 Countries and Territories, 1990-2019: Results from the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019. BMJ 2022, 378, e069679. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, E.H. Management : What Will It Take To Improve. Eff. Clin. Pract. 1998, 1, 2–4.
- Sundaresan, A.S.; Schneider, G.; Reynolds, J.; Kirchner, H.L. Identifying Asthma Exacerbation-Related Emergency Department Visit Using Electronic Medical Record and Claims Data. Appl. Clin. Inform. 2018, 9, 528–540. [CrossRef]
- Barkley, S.; Marten, R.; Reynolds, T.; Kelley, E.; Dalil, S.; Swaminathan, S.; Ghaffar, A. Primary Health Care: Realizing the Vision. Bull. World Health Organ. 2020, 98, 727-727A.
- Anderson Rothman, A.; Wagner, E.H.; Showstack, J.A. Chronic Illness Management: What Is the Role of Primary Care? Ann. Intern. Med. 2003, 138, 256–261. [CrossRef]
- Reynolds, R.; Dennis, S.; Hasan, I.; Slewa, J.; Chen, W.; Tian, D.; Bobba, S.; Zwar, N. A Systematic Review of Chronic Disease Management Interventions in Primary Care. BMC Fam. Pract. 2018, 19, 11. [CrossRef]
- Hansen, J.; Groenewegen, P.P.; Boerma, W.G.W.; Kringos, D.S. Living In A Country With A Strong Primary Care System Is Beneficial To People With Chronic Conditions. Health Aff. (Millwood). 2015, 34, 1531–1537. [CrossRef]
- Price, D.; Fletcher, M.; Van Der Molen, T. Asthma Control and Management in 8,000 European Patients: The REcognise Asthma and LInk to Symptoms and Experience (REALISE) Survey. NPJ Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2014, 24, 14009. [CrossRef]
- Calle Rubio, M.; Rodriguez Hermosa, J.L.; de Torres, J.P.; Marín, J.M.; Martínez-González, C.; Fuster, A.; Cosío, B.G.; Peces-Barba, G.; Solanes, I.; Feu-Collado, N.; et al. COPD Clinical Control: Predictors and Long-Term Follow-up of the CHAIN Cohort. Respir. Res. 2021, 22, 36. [CrossRef]
- Miravitlles, M.; Sliwinski, P.; Rhee, C.K.; Costello, R.W.; Carter, V.; Tan, J.H.Y.; Lapperre, T.S.; Alcazar, B.; Gouder, C.; Esquinas, C.; et al. Changes in Control Status of COPD Over Time and Their Consequences: A Prospective International Study. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2021, 57, 122–129. [CrossRef]
- Alcazar-Navarrete, B.; Fuster, A.; García Sidro, P.; García Rivero, J.L.; Abascal-Bolado, B.; Pallarés-Sanmartín, A.; Márquez, E.; Valido-Morales, A.; Boldova Loscertales, A.; Callejas-Gonzalez, F.J.; et al. Relationship Between Clinical Control, Respiratory Symptoms and Quality of Life for Patients with COPD. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2020, 15, 2683–2693. [CrossRef]
- Carr, T.; Tkacz, J.; Chung, Y.; Ambrose, C.S.; Spahn, J.; Rane, P.; Wang, Y.; Lindsley, A.W.; Lewing, B.; Burnette, A. Gaps in Care Among Uncontrolled Severe Asthma Patients in the United States. J. allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2024, 12, 1775-1782.e2. [CrossRef]
- Agencia Española de Protección de Datos Guía Para Pacientes y Usuarios de La Sanidad. 2019, 1–15.
- Tapuria, A.; Porat, T.; Kalra, D.; Dsouza, G.; Xiaohui, S.; Curcin, V. Impact of Patient Access to Their Electronic Health Record: Systematic Review. Inform. Health Soc. Care 2021, 46, 192–204. [CrossRef]
-
GEMA 5.4. Spanish Guideline on the Management of Asthma; 2024; ISBN 9788419832566.
- Venkatesan, P. GOLD COPD Report: 2024 Update. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2024, 12, 15–16.
- Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Marzo, M.; Catalán, P.; Miralles, C.; Alcazar, B.; Miravitlles, M. Validation of Clinical Control in COPD as a New Tool for Optimizing Treatment. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 3719–3731 . [CrossRef]
- Racine, G.; Forget, A.; Moullec, G.; Jiao, T.; Blais, L.; Lemiere, C. Predictors of Asthma Control and Exacerbations: A Real-World Study. J. allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2021, 9, 2802-2811.e2 . [CrossRef]
- Olaguibel, J.M.; Quirce, S.; Juliá, B.; Fernández, C.; Fortuna, A.M.; Molina, J.; Plaza, V. Measurement of Asthma Control According to Global Initiative for Asthma Guidelines: A Comparison with the Asthma Control Questionnaire. Respir. Res. 2012, 13, 50. [CrossRef]
- Murphy, K.R.; Chipps, B.; Beuther, D.A.; Wise, R.A.; McCann, W.; Gilbert, I.; Eudicone, J.M.; Gandhi, H.N.; Harding, G.; Coyne, K.S.; et al. Development of the Asthma Impairment and Risk Questionnaire (AIRQ): A Composite Control Measure. J. allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2020, 8, 2263-2274.e5 . [CrossRef]
- Guimarães, M.; Bugalho, A.; Oliveira, A.S.; Moita, J.; Marques, A. COPD Control: Can a Consensus Be Found? Rev. Port. Pneumol. 2016, 22, 167–176. [CrossRef]
- Miravitlles, M.; Calle, M.; Molina, J.; Almagro, P.; Gómez, J.T.; Trigueros, J.A.; Cosío, B.G.; Casanova, C.; López-Campos, J.L.; Riesco, J.A.; et al. Spanish COPD Guidelines (GesEPOC) 2021: Updated Pharmacological Treatment of Stable COPD. Arch. Bronconeumol. 2022, 58, 69–81 . [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.R.; Han, M.L.K.; Singh, B.; Sharma, S.; Kaur, G.; de Nigris, E.; Holmgren, U.; Siddiqui, M.K. Prognostic Risk Factors for Moderate-to-Severe Exacerbations in Patients with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Literature Review. Respir. Res. 2022, 23, 213 . [CrossRef]
- Rothnie, K.J.; Müllerová, H.; Smeeth, L.; Quint, J.K. Natural History of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations in a General Practice-Based Population with Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2018, 198, 464–471 . [CrossRef]
- Anzueto, A. Impact of Exacerbations on Copd. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2010, 19, 113–118. [CrossRef]
- Rahman, A. Direct Costs of Acute Exacerbation of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disorder in Hospital Inpatient Setting : A Cross Sectional Study. Sarawak J. Pharm. 2023, 9, 1–4.
- Hurst, J.R.; Skolnik, N.; Hansen, G.J.; Anzueto, A.; Donaldson, G.C.; Dransfield, M.T.; Varghese, P. Understanding the Impact of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Exacerbations on Patient Health and Quality of Life. Eur. J. Intern. Med. 2020, 73, 1–6. [CrossRef]
- Gondalia, R.; Bender, B.G.; Theye, B.; Stempel, D.A. Higher Short-Acting Beta-Agonist Use Is Associated with Greater COPD Burden. Respir. Med. 2019, 158, 110–113. [CrossRef]
- Janson, C.; Menzies-Gow, A.; Nan, C.; Nuevo, J.; Papi, A.; Quint, J.K.; Quirce, S.; Vogelmeier, C.F. SABINA: An Overview of Short-Acting β(2)-Agonist Use in Asthma in European Countries. Adv. Ther. 2020, 37, 1124–1135. [CrossRef]
- Baron, A.J.; Flokstra-de Blok, B.M.J.; Kerstjens, H.A.M.; Koopmans-Klein, G.; Price, D.B.; Sellink, A.A.; Tsiligianni, I.; Kocks, J.W.H. High Use of SABAs Is Associated with Higher Exacerbation Rate in Dutch Patients with Asthma. J. Asthma Allergy 2021, 14, 851–861. [CrossRef]
- Nwaru, B.I.; Ekström, M.; Hasvold, P.; Wiklund, F.; Telg, G.; Janson, C. Overuse of Short-Acting β(2)-Agonists in Asthma Is Associated with Increased Risk of Exacerbation and Mortality: A Nationwide Cohort Study of the Global SABINA Programme. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 55, 1901872. [CrossRef]
- Janson, C.; Wiklund, F.; Telg, G.; Stratelis, G.; Sandelowsky, H. High Use of Short-Acting β(2)-Agonists in COPD Is Associated with an Increased Risk of Exacerbations and Mortality. ERJ open Res. 2023, 9. [CrossRef]
- Reddel, H.K.; Taylor, D.R.; Bateman, E.D.; Boulet, L.-P.; Boushey, H.A.; Busse, W.W.; Casale, T.B.; Chanez, P.; Enright, P.L.; Gibson, P.G.; et al. An Official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society Statement: Asthma Control and Exacerbations: Standardizing Endpoints for Clinical Asthma Trials and Clinical Practice. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2009, 180, 59–99. [CrossRef]
- Soremekun, S.; Heaney, L.G.; Skinner, D.; Bulathsinhala, L.; Carter, V.; Chaudhry, I.; Hosseini, N.; Eleangovan, N.; Murray, R.; Tran, T.N.; et al. Asthma Exacerbations Are Associated with a Decline in Lung Function: A Longitudinal Population-Based Study. Thorax 2023, 78, 643–652. [CrossRef]
- Matsunaga, K.; Hirano, T.; Oka, A.; Tanaka, A.; Kanai, K.; Kikuchi, T.; Hayata, A.; Akamatsu, H.; Akamatsu, K.; Koh, Y.; et al. Progression of Irreversible Airflow Limitation in Asthma: Correlation with Severe Exacerbations. J. allergy Clin. Immunol. Pract. 2015, 3, 759-64.e1. [CrossRef]
- Hurst, J.R.; Vestbo, J.; Anzueto, A.; Locantore, N.; Müllerova, H.; Tal-Singer, R.; Miller, B.; Lomas, D.A.; Agusti, A.; Macnee, W.; et al. Susceptibility to Exacerbation in Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010, 363, 1128–1138. [CrossRef]
- Computing, R.F. for S. The R Project for Statistical Computing Available online: https://www.r-project.org/.
- Venables, W.; Ripley, B. Modern Applied Statistics; 4th ed.; Springer, 2002.
- Kuhn, M. Building Predictive Models in R Using the Caret Package. J. Stat. Softw. 2008, 28, 1–26.
- Partridge, M.R.; van der Molen, T.; Myrseth, S.-E.; Busse, W.W. Attitudes and Actions of Asthma Patients on Regular Maintenance Therapy: The INSPIRE Study. BMC Pulm. Med. 2006, 6, 13. [CrossRef]
- Partridge, M.R. Examining the Unmet Need in Adults with Severe Asthma. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2007, 16, 67–72. [CrossRef]
- Papaioannou, A.I.; Kostikas, K.; Zervas, E.; Kolilekas, L.; Papiris, S.; Gaga, M. Control of Asthma in Real Life: Still a Valuable Goal? Eur. Respir. Rev. an Off. J. Eur. Respir. Soc. 2015, 24, 361–369. [CrossRef]
- Miravitlles, M.; Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Marzo, M.; Catalan Serra, P.; Miralles, C.; Alcázar, B.; Alcázar, B. Validation of an Assessment Tool for Control in Copd: Analysis of Clinical Variables. Int. J. Chron. Obstruct. Pulmon. Dis. 2018, 13, 3719–3731. [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Li, X. Editorial: Aging and Chronic Disease: Public Health Challenge and Education Reform. Front. Public Heal. 2023, 11, 1175898. [CrossRef]
- WHO World Report on Ageing and Health; 2015; ISBN 9781626239777.
- Razai, M.S.; Majeed, A. General Practice in England: The Current Crisis, Opportunities, and Challenges. J. Ambul. Care Manage. 2022, 45, 135–139. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.; Schwebel, D.C.; Hu, G. Physicians’ Workloads in China: 1998−2016. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2018, 15, 1649. [CrossRef]
- Helfrich, C.D.; Simonetti, J.A.; Clinton, W.L.; Wood, G.B.; Taylor, L.; Schectman, G.; Stark, R.; Rubenstein, L. V; Fihn, S.D.; Nelson, K.M. The Association of Team-Specific Workload and Staffing with Odds of Burnout Among VA Primary Care Team Members. J. Gen. Intern. Med. 2017, 32, 760–766. [CrossRef]
- Svedahl, E.R.; Pape, K.; Toch-Marquardt, M.; Skarshaug, L.J.; Kaspersen, S.-L.; Bjørngaard, J.H.; Austad, B. Increasing Workload in Norwegian General Practice - a Qualitative Study. BMC Fam. Pract. 2019, 20, 68. [CrossRef]
- Asher, M.I.; García-Marcos, L.; Pearce, N.E.; Strachan, D.P. Trends in Worldwide Asthma Prevalence. Eur. Respir. J. 2020, 56, 2002094. [CrossRef]
- Backman, H.; Räisänen, P.; Hedman, L.; Stridsman, C.; Andersson, M.; Lindberg, A.; Lundbäck, B.; Rönmark, E. Increased Prevalence of Allergic Asthma from 1996 to 2006 and Further to 2016-Results from Three Population Surveys. Clin. Exp. Allergy 2017, 47, 1426–1435. [CrossRef]
- Orozco-Beltrán, D.; Arriero-Marin, J.M.; Carratalá-Munuera, C.; Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Lopez-Pineda, A.; Gil-Guillén, V.F.; Quesada, J.A. Trends in Hospital Admissions for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease in Men and Women in Spain, 1998 to 2018. J. Clin. Med. 2021, 10, 1529. [CrossRef]
- Collaborators, G.C.R.D. Prevalence and Attributable Health Burden of Chronic Respiratory Diseases, 1990-2017: A Systematic Analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. Respir. Med. 2020, 8, 585–596. [CrossRef]
- Nibber, A.; Chisholm, A.; Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Alcazar, B.; Price, D.; Miravitlles, M. Validating the Concept of COPD Control: A Real-World Cohort Study from the United Kingdom. COPD 2017, 14, 504–512. [CrossRef]
- Miravitlles, M.; Sliwinski, P.; Rhee, C.K.; Costello, R.W.; Carter, V.; Tan, J.; Lapperre, T.S.; Alcazar, B.; Gouder, C.; Esquinas, C.; et al. Evaluation of Criteria for Clinical Control in a Prospective, International, Multicenter Study of Patients with COPD. Respir. Med. 2018, 136, 8–14. [CrossRef]
- Busse, W.W.; Kraft, M. Current Unmet Needs and Potential Solutions to Uncontrolled Asthma. Eur. Respir. Rev. 2022, 31, 210176. [CrossRef]
- Soler-Cataluña, J.J.; Huerta, A.; Almagro, P.; González-Segura, D.; Cosío, B.G. Lack of Clinical Control in COPD Patients Depending on the Target and the Therapeutic Option. Int. J. COPD 2023, 18, 1367–1376. [CrossRef]
- Megaritis, D.; Hume, E.; Chynkiamis, N.; Buckley, C.; Polhemus, A.M.; Watz, H.; Troosters, T.; Vogiatzis, I. Effects of Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Interventions on Physical Activity Outcomes in COPD: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. ERJ open Res. 2023, 9, 00409–02023. [CrossRef]
- Ur Rehman, A.; Hassali, M.; Abbas, S.; Ali, I.; Harun, S.N.; Muneswarao, J.; Hussain, R. Pharmacological and Non-Pharmacological Management of COPD; Limitations and Future Prospects: A Review of Current Literature. J. Public Health (Bangkok). 2020, 28, 357–366. [CrossRef]
- Schuers, M.; Chapron, A.; Guihard, H.; Bouchez, T.; Darmon, D. Impact of Non-Drug Therapies on Asthma Control: A Systematic Review of the Literature. Eur. J. Gen. Pract. 2019, 25, 65–76. [CrossRef]
- Clemente-Suárez, V.J.; Mielgo-Ayuso, J.; Ramos-Campo, D.J.; Beltran-Velasco, A.I.; Martínez-Guardado, I.; Navarro Jimenez, E.; Redondo-Flórez, L.; Yáñez-Sepúlveda, R.; Tornero-Aguilera, J.F. Basis of Preventive and Non-Pharmacological Interventions in Asthma. Front. public Heal. 2023, 11, 1172391. [CrossRef]
- Sandelowsky, H.; Weinreich, U.M.; Aarli, B.B.; Sundh, J.; Høines, K. COPD – Do the Right Thing. BMC Fam Pr. 2021, 22, 244.
- Levy, M.L.; Bacharier, L.B.; Bateman, E.; Boulet, L.P.; Brightling, C.; Buhl, R.; Brusselle, G.; Cruz, A.A.; Drazen, J.M.; Duijts, L.; et al. Key Recommendations for Primary Care from the 2022 Global Initiative for Asthma (GINA) Update. npj Prim. Care Respir. Med. 2023, 33, 7. [CrossRef]
- Kruis, A.L.; Smidt, N.; Assendelft, W.J.J.; Gussekloo, J.; Boland, M.R.S.; Rutten-van Mölken, M.; Chavannes, N.H. Cochrane Corner: Is Integrated Disease Management for Patients with COPD Effective? Thorax 2014, 69, 1053–1055. [CrossRef]
- Mehuys, E.; Van Bortel, L.; De Bolle, L.; Van Tongelen, I.; Annemans, L.; Remon, J.P.; Brusselle, G. Effectiveness of Pharmacist Intervention for Asthma Control Improvement. Eur. Respir. J. 2008, 31, 790–799. [CrossRef]
- Lee, T.C.; Shah, N.U.; Haack, A.; Baxter, S.L. Clinical Implementation of Predictive Models Embedded within Electronic Health Record Systems: A Systematic Review. Informatics 2020, 7, 25. [CrossRef]
- Duan, K.I.; Birger, M.; Au, D.H.; Spece, L.J.; Feemster, L.C.; Dieleman, J.L. Health Care Spending on Respiratory Diseases in the United States, 1996–2016. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2023, 207, 183–192. [CrossRef]
- Persaud, Y.K. Using Telemedicine to Care for the Asthma Patient. Curr. Allergy Asthma Rep. 2022, 22, 43–52. [CrossRef]
- McLean, S.; Nurmatov, U.; Liu, J.L.Y.; Pagliari, C.; Car, J.; Sheikh, A. Telehealthcare for Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Cochrane Review and Meta-Analysis. Br. J. Gen. Pract. 2012, 62, e739-49. [CrossRef]
- Jeminiwa, R.; Hohmann, L.; Qian, J.; Garza, K.; Hansen, R.; Fox, B.I. Impact of EHealth on Medication Adherence among Patients with Asthma: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Respir. Med. 2019, 149, 59–68. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y.; Hu, X. Healthcare Predictive Analytics for Disease Progression: A Longitudinal Data Fusion Approach. J. Intell. Inf. Syst. 2020, 55, 351–369. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Keeley, E.C.; Barrette, E.; Cooper-DeHoff, R.M.; Dhruva, S.S.; Gaffney, J.; Gamble, G.; Handke, B.; Huang, C.; Krumholz, H.; et al. Use of Electronic Health Records to Characterize Patients with Uncontrolled Hypertension in Two Large Health System Networks. Res Sq [Preprint] 2024, rs.3.rs-3943912.
- Zhao, J.; Henriksson, A.; Asker, L.; Boström, H. Predictive Modeling of Structured Electronic Health Records for Adverse Drug Event Detection. BMC Med. Inform. Decis. Mak. 2015, 15, S1. [CrossRef]
- Rajkomar, A.; Oren, E.; Chen, K.; Dai, A.M.; Hajaj, N.; Hardt, M.; Liu, P.J.; Liu, X.; Marcus, J.; Sun, M.; et al. Scalable and Accurate Deep Learning with Electronic Health Records. npj Digit. Med. 2018, 1, 18. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).