1. Introduction
Breast cancer remains an important area of medical research due to its high incidence and mortality worldwide. Continued progress in this area is driven by the need to improve diagnostic methods, treatment options, and patient outcomes. Bibliometric analysis serves as a valuable tool for quantifying and evaluating research trends while providing insight into the growth and development of scientific knowledge over time. This study focuses on breast cancer research publications from 2014 to 2023, analysing data sourced from the Scopus database. The objectives include assessing publication growth, citation impact, document types, leading countries, preferred journals, and authorship patterns. By identifying these trends and patterns, the study aims to provide a comprehensive overview of the current state of breast cancer research and its evolution over the past decade. Such analysis is critical for researchers, policymakers, and funding agencies to understand the landscape of breast cancer research, identify gaps, and effectively allocate resources to areas with the most significant potential impacts.
2. Literature Review
[15]4 conducted a scientometric analysis of India’s AIDS/HIV research output from 1999 to 2008. The study assessed growth, global publication share, citation impact, and international collaboration. Using the Scopus database, they found that India ranked 12th globally in AIDS/HIV research, with a publication share of 2.07%, higher than Brazil but lower than China and South Africa. India’s research output growth rate was also higher than Brazil’s but lagged behind China and South Africa. However, India’s international collaboration and citation impact were lower than these countries. The study concluded that India needs to enhance research quality and output by increasing R&D investment, qualified manpower, international collaboration, and modernizing research infrastructure. Jhamb and Verma (2020)9 conducted a scientometric analysis of the research output of the Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research, and Education in Cancer (ACTREC) from 2003 to 2018. Using data from the Web of Science and R Studio, the study found that ACTREC’s research had a compound annual growth rate of 35.1% and an average of citations per paper. The analysis also highlighted ACTREC’s strong international collaborations, with an affinity value greater than 1. The most frequently used journals by ACTREC scientists were PLoS One and the International Journal of Cancer. Jamatia, K & Gayan, M. A.(2021)8 in his paper on The bibliometric analysis of PubMed-indexed research from 2020 to 2021 provided valuable insights into COVID-19 treatment modalities. The study identified 3,043 relevant documents, with a focus on vaccines and COVID-19 as key topics. The United States was the leading contributor, with Mahase E as the top author and the University of Maryland as the top organization. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) emerged as the most cited journal. The study highlights the need to include additional databases for a broader understanding of COVID-19 treatment research. [5]13 conducted a bibliometric analysis of research on COVID-19 treatment modalities published in PubMed-indexed journals from 2020 to 2021. The study focused on various treatments, including vaccines, oxygen supplementation, steroids, and antiviral drugs. A total of 3,043 documents were analyzed, with vaccines and COVID-19 being the most prominent topics. The United States led in research output, Mahase E was the top author, and the University of Maryland was the leading organization. BMJ (Clinical Research Ed.) was the most frequently cited journal. The study highlights the effectiveness of bibliometric analysis in providing deeper insights into COVID-19 treatments and suggests using additional databases for a more comprehensive understanding of the topic. R [11]14 conducted a scientometric analysis of trends in artificial intelligence (AI) research related to liver cancer, analyzing 3,950 publications from 1968 to August 2023. The study found a 12.7-fold increase in AI-related publications between 2013 and 2022, compared to a 1.7-fold increase in overall liver cancer publications. A significant shift in AI-related research trends occurred in 2019, with a consistent rise in publications over time. Radiology journals published the majority (53%) of these works, with the highest contributions from China, the US, and Germany. The most common research categories were medical image analysis for diagnosis, diagnostic or prognostic biomarker modeling and bioinformatics, and genomic or molecular analysis. Viswanathan, G. and Yugapriya, S, (2020) 15 conducted a bibliometric analysis of research on viral infections affecting the eyes, using publications indexed in the PUBMED database from 2000 to 2018. The study analyzed 6,613 publications, revealing a fluctuating trend in research productivity over the years. Coauthored works dominated, with Rouse, B.T. identified as the most prolific author. England led in research output, and the American Journal of Ophthalmology was the most preferred journal. The keyword "virology" was most frequently used. Despite significant annual publications, the growth in literature was not steady, with 344 publications in 2019, only slightly higher than 280 in 2000. The study suggests that more research is needed in densely populated countries to better manage viral eye diseases and improve healthcare.
3. Objective
To Analyse the publications growth on breast cancer research from 2014 to 2023.
To Study the average number of citations per article and the total citations per year.
To study the distribution of different types of documents (articles, reviews, book chapters, etc.) published in the field of breast cancer research.
To identify the leading countries in breast cancer research based on publication output and citation impact.
To Determine the most preferred journals for publishing breast cancer research.
To Study the patterns of authorship, including the number of authors per paper.
4. Methodology
The data for the present study is retrieved from the Scopus database by using the search strategy query “SRCTITLE ( "breast cancer" ) AND ( LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2014 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2015 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2016 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2017 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2018 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2019 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2020 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2021 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR, 2022 ) OR LIMIT-TO ( PUBYEAR , 2023 ) )” There was 12073 documents were retrieved during the year 2014-2023. The synonym was searched from Medline. For the research study Article, Review, Book Chapter, Letter, Erratum, Editorial, Note, Book, Conference Paper etc. MSExecl and Biblioshiny software were used for analysis and visualizing the collected data.
4.1. Data Analysis and Interpretation
5. Publication Growth
Summarizes breast cancer research publications over the past decade. Therewere a total of 12,073 publications, with the annual total increasing but with some fluctuations. The peak was in 2021 with 1,478 publications and the lowest in 2015 with 1,036. However, the average number of citations per article is decreasing. In 2014, articles averaged 32.49 citations, but by 2023 it had dropped to just 2.11. This decline suggests that older research gets cited more often over time, while newer studies don’t get enough time to get citations. Average citations per article (taking into account the year’s articles available) also decreased from 2.95 in 2014 to 1.05 in 2023, likely due to an overload of research topics or more competition for citations. A downward trend has been observed in total referrals each year, with the highest total in 2014 at 35,644 and the lowest at 2,643 in 2023. Reference years, indicating how long articles are available for reference, fell from 11 in 2014 to just 2 in 2023. Between 2014 and 2015, both publications and citations declined slightly. Between 2016 and 2017, publications increased, while citations per article declined slightly. From 2018 to 2019, publications continued to grow, but with lower average citations. Publications increased significantly in 2020, likely due to Covid-19 research, although average citations decreased. Finally, from 2022 to 2023, both publications and citations decreased, indicating that recent articles have not yet had a chance to collect many citations.
Table 1.
Publication Growth Research on Breast Cancer.
Table 1.
Publication Growth Research on Breast Cancer.
Y
ear |
Total
Publication |
MeanTCper-
Art |
MeanTCperYear |
Citable
Years |
Total
Citation |
| 2014 |
1097 |
32.49 |
2.95 |
11 |
35644 |
| 2015 |
1036 |
29.79 |
2.98 |
10 |
30867 |
| 2016 |
1042 |
26.03 |
2.89 |
9 |
27127 |
| 2017 |
1169 |
24.17 |
3.02 |
8 |
28256 |
| 2018 |
1194 |
23.95 |
3.42 |
7 |
28593 |
| 2019 |
1162 |
20.97 |
3.49 |
6 |
24367 |
| 2020 |
1319 |
14.25 |
2.85 |
5 |
18790 |
| 2021 |
1478 |
9.12 |
2.28 |
4 |
13479 |
| 2022 |
1321 |
5.3 |
1.77 |
3 |
7003 |
| 2023 |
1255 |
2.11 |
1.05 |
2 |
2643 |
| Total |
12073 |
|
|
|
216769 |
6. Document Wise Distribution
Shows that articles are the majority with a total of 8,864 publications and receive the most 171,705 citations, indicating their central role in the dissemination of research findings Reviews are the second most common document type with 1,396 publications and 41,237 citations, reflecting their importance in summarizing and synthesizing existing research. Although relatively few book chapters have a total of 911 publications and 656 citations, they have little citation impact compared to articles and reviews. Papers have moderate presence and citation impact, with 325 publications and citations, often providing brief reports or responses within the research community. Errata, with 261 publications and 233 citations, are published to correct errors in previous publications and have a relatively low citation count. 137 publications and editorial articles with 805 citations that provide opinions or commentary from journal editors have moderate citation impact. Notes are brief articles with 77 publications and 495 citations and have a low presence but moderate citation impact. Books, although sparse with 67 publications, contribute to the overall research output with 262 citations. Conference papers with a total of 27 publications and 439 citations arefew, but contribute to the dissemination of primary research findings with moderate citation impact. Retracted papers, although very few with 7 publications, still have 167 citations, indicating their initial impact before retraction. Small surveys with only 1 publication and 7 citations are extremely rare, with minimal citation impact.
Table 2.
Document Wise Distribution.
Table 2.
Document Wise Distribution.
| DOCUMENT TYPE |
Total Publication |
Total Citation |
| Article |
8864 |
171705 |
| Review |
1396 |
41237 |
| Book Chapter |
911 |
656 |
| Letter |
325 |
783 |
| Erratum |
261 |
213 |
| Editorial |
137 |
805 |
| Note |
77 |
495 |
| Book |
67 |
262 |
| Conference Paper |
27 |
439 |
| Retracted |
7 |
167 |
| Short Survey |
1 |
7 |
| Total |
12073 |
216769 |
7. Geographic Collaboration
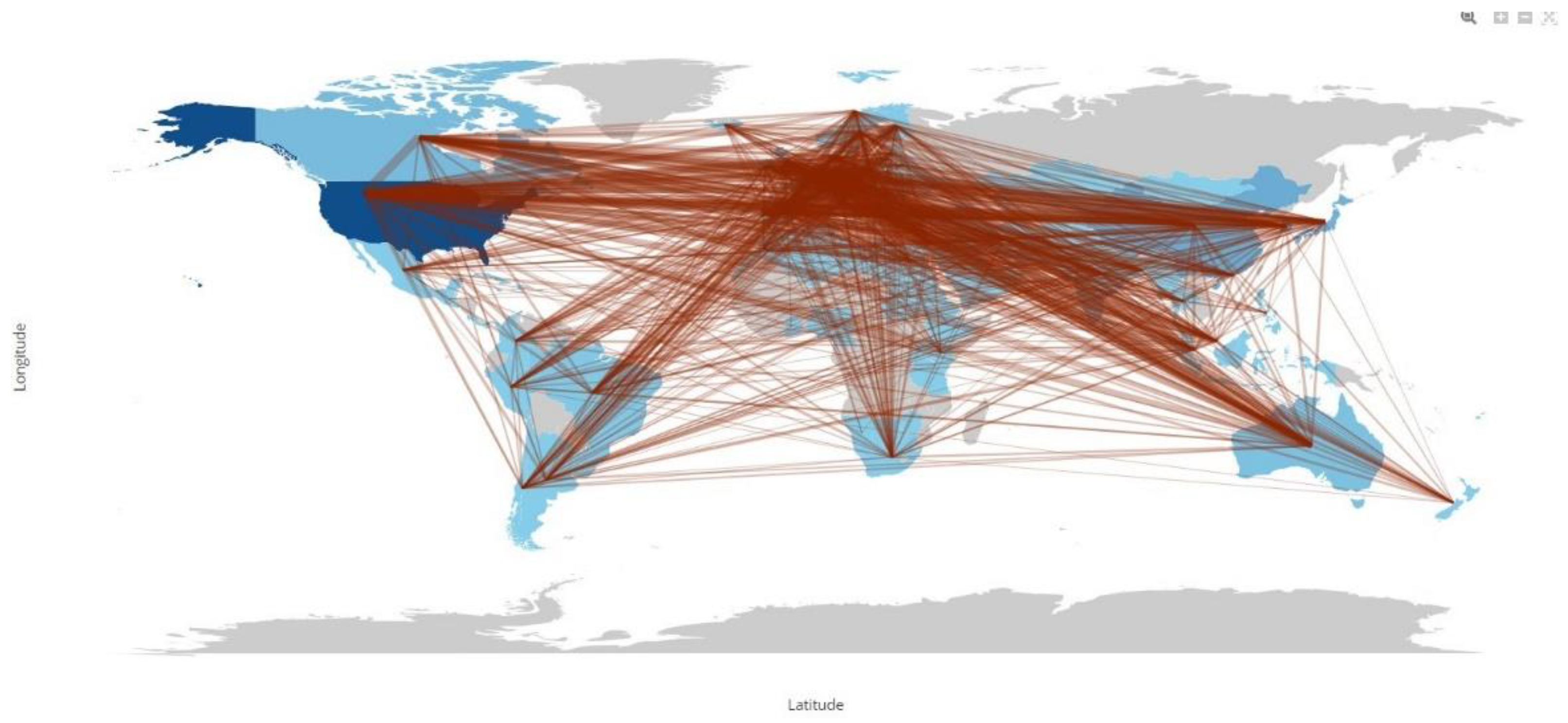
Shows the top 15 countries in breast cancer research. America leads with 4,903 publications and 71,092 citations, underlining its dominance. China and Japan followed with 1,122 publications and 15,746 citations, while Japan had 1,009 publications and 10,303 citations. In Europe, the U. K., Italy and Germany are significant contributors, although with fewer references, indicating less global impact. South Korea and Canada are emerging researchers, showing increasing production but still developing results. India and Spain are also active, with India publishing 382 and Spain 363 papers, both with relatively modest citations. Sweden and Belgium also contribute, albeit to a lesser extent. These figures reflect extensive international cooperation with different levels of influence and recognition.
8. Journal Preferred
Outlines the major journals in breast cancer research. Breast cancer research and treatment published by Springer in the Netherlands leads the way with 4,277 publications and an impact factor of 4.514, reflecting its broad and influential scope. U. S. A. Elsevier has a focus on clinical research, with 1,463 publications after clinical breast cancer and a low impact factor of 2.972. U. K. Breast cancer research from BioMed Central, ranked third with 1,419 publications and a high impact factor of 5.897. There are 1,141 breast cancer publications published by SpringerJapan but the impact factor is low at 2.746. U. K. N. of Nature Publishing Group in P. J. Breast cancer, while having fewer publications (636), has the highest impact factor of 8.189, indicating high-quality research. Other notable journals include Journal of Breast Cancer from South Korea (586 publications, 1.618 impact factor), Breast Cancer: Targets and Therapy from the UK (409 publications, 3.146 impact factor) and Current Breast Cancer Reports (379 publications, 2 impact factor) is Iran’s Archives of Breast
Table 3.
Top 15 countries collaborating.
Table 3.
Top 15 countries collaborating.
| Sr No |
Country |
Total Publication |
Total Citation |
| 1 |
United States |
4903 |
71092 |
| 2 |
China |
1122 |
15746 |
| 3 |
Japan |
1009 |
10303 |
| 4 |
United Kingdom |
940 |
10834 |
| 5 |
Italy |
769 |
7929 |
| 6 |
South Korea |
740 |
8494 |
| 7 |
Canada |
693 |
7636 |
| 8 |
Germany |
545 |
5702 |
| 9 |
Netherlands |
501 |
6936 |
| 10 |
Australia |
433 |
5201 |
| 11 |
France |
430 |
3763 |
| 12 |
India |
382 |
2057 |
| 13 |
Spain |
363 |
2851 |
| 14 |
Sweden |
311 |
3068 |
| 15 |
Belgium |
285 |
2542 |
Figure 1.
Countries’ Collaboration World Map.
Figure 1.
Countries’ Collaboration World Map.
Cancer has 238 publications with an impact factor of 0.789 and U. K. Sage Publications’ Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research has 234 publications with an impact factor of 1.676.
9. Broadford Law
Analysis of breast cancer research publications from 2014 to 2023, using Bradford’s law, journals are classified into three categories based on publication frequency. In zone 1 is the journal Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, which is the most influential with thehighest publication frequency of 4277 articles and a cumulative frequency of 4277. Zone 2 includes three journals: Clinical Breast Cancer (1463 articles), Breast Cancer Research (1419 articles) and Breast Cancer (1141 articles). These journals have collectively contributed 4023 articles with cumulative editions of 5740,7159 and 8300 respectively. Zone 3 includes six periodicals: N. P. J. Breast Cancer (636 articles), Breast Cancer Journal (586 articles), Breast Cancer: Targets and Treatments (409 articles), Current Breast Cancer Reports (379 articles), Breast Cancer Archives (238 articles) and Breast Cancer: Basic and Clinical Research (234 article). Together these journals contain 2840 articles, with a cumulative edition of 8936,9522,9931,10310,10548 and 10782 respectively. Bradford’s law divides periodicals into core and peripheral groups. Zone 1 has the highest volume of articles with a single journal, underscoring its central role in breast cancer research. Zone 2, with three periods, also plays an important role but to a lesser
Table 4.
Top 10 Journal Preferred.
Table 4.
Top 10 Journal Preferred.
Rank
No
1 |
Name Of The Journal
Breast Cancer Research |
TP
4277 |
Publisher
Springer |
Coun-
try
Nether- |
Impact
Factor
4.514 |
| |
And Treatment |
|
|
lands |
|
| 2 |
Clinical Breast Cancer |
1463 |
Elsevier |
USA |
2.972 |
| 3 |
Breast Cancer Research |
1419 |
BioMed Central |
UK |
5.897 |
| 4 |
Breast Cancer |
1141 |
Springer Japan |
Japan |
2.746 |
| 5 |
Npj Breast Cancer |
636 |
Nature Publishing |
UK |
8.189 |
| |
|
|
Group |
|
|
| 6 |
Journal Of Breast Cancer |
586 |
Korean Breast Cancer |
South |
1.618 |
| |
|
|
Society |
Korea |
|
| 7 |
Breast Cancer: Targets |
409 |
Dove Medical Press |
UK |
3.146 |
| |
And Therapy |
|
|
|
|
| 8 |
Current Breast Cancer |
379 |
Springer |
USA |
2 |
| |
Reports |
|
|
|
|
| 9 |
Archives Of Breast Cancer |
238 |
Tabriz University of |
Iran |
0.789 |
| |
|
|
Medical Sciences |
|
|
| 10 |
Breast Cancer: Basic And |
234 |
SAGE Publications |
UK |
1.676 |
| |
Clinical Research |
|
|
|
|
Table 5.
Broadford Law.
Sr
No |
Name of the Journal |
Rank |
Freq |
cum-
Freq |
Zone |
| 1 |
BREAST CANCER RESEARCH AND |
1 |
4277 |
4277 |
Zone |
| |
TREATMENT |
|
|
|
1 |
| 2 |
CLINICAL BREAST CANCER |
2 |
1463 |
5740 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
2 |
| 3 |
BREAST CANCER RESEARCH |
3 |
1419 |
7159 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
2 |
| 4 |
BREAST CANCER |
4 |
1141 |
8300 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
2 |
| 5 |
NPJ BREAST CANCER |
5 |
636 |
8936 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
3 |
| 6 |
JOURNAL OF BREAST CANCER |
6 |
586 |
9522 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
3 |
| 7 |
BREAST CANCER: TARGETS AND THERAPY |
7 |
409 |
9931 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
3 |
| 8 |
CURRENT BREAST CANCER REPORTS |
8 |
379 |
10310 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
3 |
| 9 |
ARCHIVES OF BREAST CANCER |
9 |
238 |
10548 |
Zone |
| |
|
|
|
|
3 |
| 10 |
BREAST CANCER: BASIC AND CLINICAL |
10 |
234 |
10782 |
Zone |
| |
RESEARCH |
|
|
|
3 |
extent. Zone 3, with six journals, reflects the long tail of journals with low publication frequency, highlighting their more specialized roles. The distribution from Area 1 to Area 3 shows the concentration and spread of research articles, with a clear decrease in publication frequency as we move from core to peripheral journals. This distribution highlights the importance of some major journals in disseminating breast cancer research and the broader role of numerous specialized journals in the field.
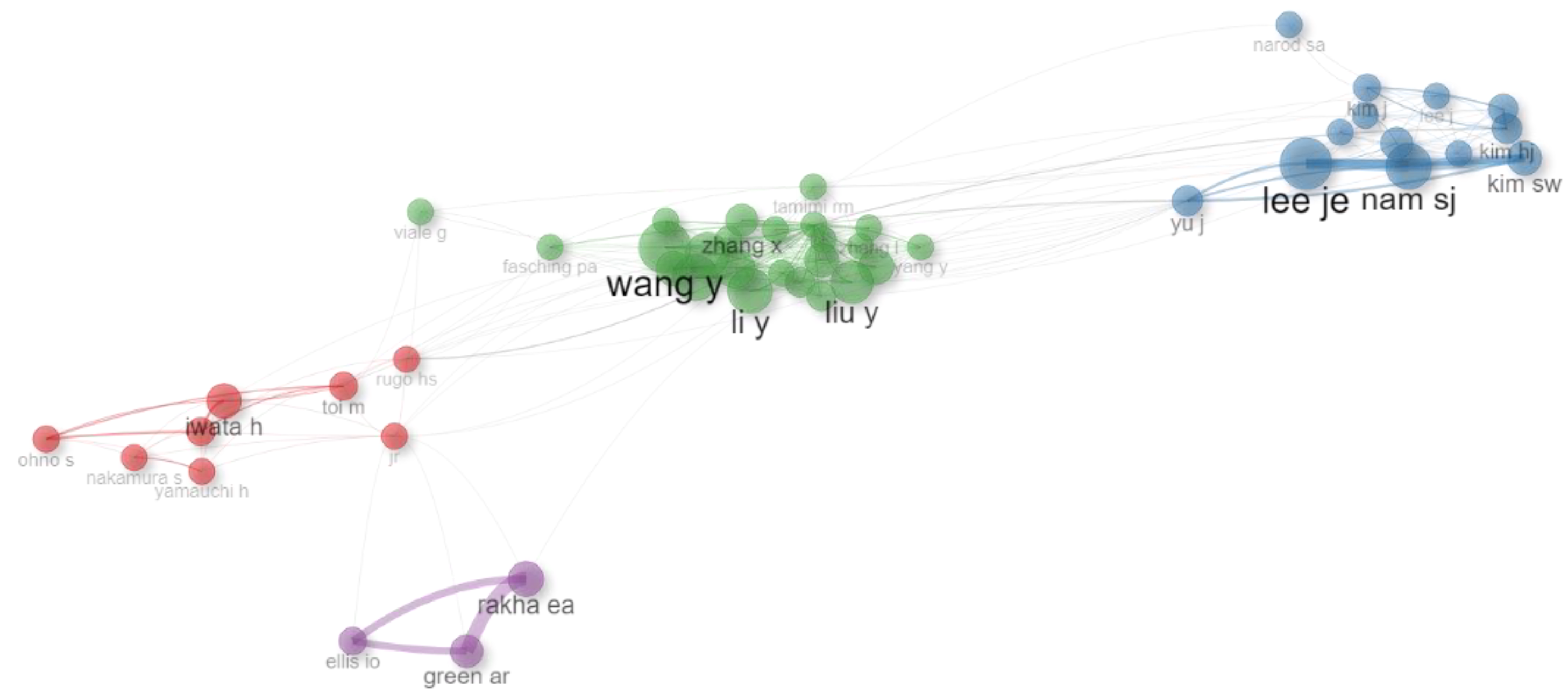
10. Author Productivity
Reveals significant contributions from a small group of prolific authors. The top ten authors, led by WANG Y with 122 publications, dominate the field. Other notable contribu- tors include WANG X (104 articles) and LI Y (102 articles). The predominance of authors with similar surnames, especially common Chinese surnames like WANG, LI, and LIU, suggests a strong research output from Chinese institutions.
Table 6.
Top 10 Authors.
| Rank |
Authors |
Articles |
| 1 |
WANG Y |
122 |
| 2 |
WANG X |
104 |
| 3 |
LI Y |
102 |
| 4 |
LIU Y |
95 |
| 5 |
LI J |
94 |
| 6 |
LI X |
86 |
| 7 |
WANG J |
85 |
| 8 |
IWATA H |
82 |
| 9 |
ZHANG Y |
80 |
| 10 |
LEE JE |
79 |
11. Lotka’s Law
Table 7.
Lotka’s Law.
| Documents written |
N. of Authors |
Proportion of Authors |
| 1 |
31422 |
0.672 |
| 2 |
6899 |
0.148 |
| 3 |
2866 |
0.061 |
| 4 |
1633 |
0.035 |
| 5 |
938 |
0.02 |
| 6 |
598 |
0.013 |
| 7 |
438 |
0.009 |
| 8 |
315 |
0.007 |
| 9 |
260 |
0.006 |
| 10 |
231 |
005 |
Shows Lotka’s rule in breast cancer research, with 67.2% of authors (31,422) contributing to only one paper, indicating that most are occasional contributors. Authors who have written two papers are 14.8% (6,899) and those who have three papers are 6.1% (2,866). As the number of contributions increases, the percentage decreases, with only 0.5% (211 authors) having written ten research papers. This pattern, where some authors are extremely prolific while most contribute only sporadically, closely follows Lotka’s law, reflecting a certain scientific productivity. This underscores the balance between broad participation and the considerable influence of the prolific researchers in the field.
12. Authorship Pattern
Categorizes the number of authors involved in breast cancer research theses, highlighting the collaborative nature of the field. Single-authored research papers are rare, with only 631 examples, indicating that most research is done in groups. Papers by two and three authors are more common, with 967 and 961 chapters, respectively. The number of authors per paper generally increases and reaches six-authored papers (1,064 times). After six authors, there is a gradual decline, although collaboration remains significant with 529 papers involving twenty or more authors. Notably, a paper written by 448 researchers illustrates the massive collaborative effort and wide network in breast cancer research. The trend toward multi-authored papers reflects the complexity and interdisciplinary nature of breast cancer research, which requires expertise from diverse fields such as oncology, genetics, epidemiology, and bioinformatics. This collaborative approach increases the rigor and depth of research and contributes to more comprehensive and impactful findings.
Table 8.
Authorship Pattern.
Table 8.
Authorship Pattern.
Sr. No.
1 |
No of Authors
Single Author |
No. of Authors
631 |
| 2 |
Two Author |
967 |
| 3 |
Three Author |
961 |
| 4 |
Four Author |
922 |
| 5 |
Five Author |
1053 |
| 6 |
Six Author |
1064 |
| 7 |
Seven Author |
1027 |
| 8 |
Eight Author |
951 |
| 9 |
Nine Author |
826 |
| 10 |
Ten Author |
677 |
| 11 |
Eleven Author |
550 |
| 12 |
Twelve Author |
444 |
| 13 |
Thirteen Author |
328 |
| 14 |
Fourteen Author |
310 |
| 15 |
Fifteen Author |
227 |
| 16 |
Sixteen Author |
178 |
| 17 |
Seventeen Author |
140 |
| 18 |
Eighteen Author |
130 |
| 19 |
Nineteen Author |
106 |
| |
Twenty authors above |
529 |
Figure 2.
Authors Collaboration Network.
Figure 2.
Authors Collaboration Network.
13. Result, Finding & Discussion
The results indicate that although the number of publications in breast cancer research has generally increased over the past decade, the average number of citations per article has decreased. This trend may be due to a number of factors, including repetition of publications, changes in the focus of research, or the broader scientific publishing landscape. The data highlight the importance of time in the accumulation of references and suggest that recent publications should be monitored over the coming years to fully understand their impact.
This analysis shows that articles and reviews are the main document types in breast cancer research, both in terms of publication volume and citation impact. Other document types such as book chapters, letters and editorials also contribute significantly but to a lesser extent. The presence of errors and retracted papers underscores the ongoing process of scientific improvement and integrity. Overall, these data highlight the variety of formats through which breast cancer research is communicated and the varying levels of impact each format has on the academic community.
Country collaboration European countries collectively show strong participation, and Asian countries are emerging as important contributors. This analysis highlights the importance of international collaboration and the differential impact of research results in different regions.
The results of preferred journals highlight that breast cancer research is widely disseminated in various prestigious journals with different impact factors and publication volumes. N. P. J. Some journals, such as Breast Cancer and Breast Cancer Research, have higher impact factors, while other journals, such as Breast Cancer Research and Treatment, have higher publication volume factors, reflecting a balance between the quality and quantity of research dissemination. The geographical distribution of these journals highlights the global nature of breast cancer research, with significant contributions from the US, UK and other countries. This diversity in publication venues facilitates a comprehensive and collaborative approach to advancing breast cancer research.
An analysis based on Bradford’s law shows that breast cancer research is concentrated in a few core journals, with Breast Cancer Research and Treatment being the most prominent. A second tier of journals also plays an important role, including clinical breast cancer and breast cancer research, while a large number of journals contribute less frequently. This distribution is consistent with Bradford’s law, which suggests a small core of journals publishing most articles and a large number of journals with fewer publications. This information is important for researchers and librarians to identify key journals for breast cancer research and to make informed decisions about journal subscription and research dissemination strategies.
The dominance of a few prolific authors underscores the critical role of pioneering researchers in advancing breast cancer research. Consistency with Lotka’s law suggests that while many researchers contribute to the field, the bulk of publications come from a small core group. This distribution can affect collaboration patterns, funding allocations, and the dissemination of knowledge within the community. The collaborative nature of this scientific field, dominated by multi-authored research papers, reflects the reliance on teamwork and interdisciplinary collaboration to address the complexities of breast cancer.This trend is likely to continue, prompting innovative approaches and comprehensive studies that can significantly advance our understanding and treatment of breast cancer. An exceptional example of a paper with 448 authors symbolizes the extent of collaboration in the field, highlighting the collective efforts to combat this prevalent disease. Lotka’s law states that the majority of authors contribute only one paper, while a small number of highly productive researchers produce multiple publications. This distribution highlights the collaborative nature of breast cancer research, where many researchers contribute to a collective knowledge base. However, it also emphasizes the important role of prolific authors in advancing the field. Understanding these patterns can inform strategies to promote more comprehensive and effective contributions, ultimately increasing research outcomes in the fight against breast cancer.
14. Conclusions
This bibliographic analysis of breast cancer research from 2014 to 2023 highlights significant growth in the field, with more than 12,000 publications and significant citation impact. The US, China and Japan have emerged as leading contributors, showing strong research output and collaboration. The dominance of articles as the primary document type and the proliferation of multi-authored papers reflect the collaborative nature of contemporary breast cancer research. Major journals, such as Breast Cancer Research and Treatment and Clinical Breast Cancer, serve as important forums for the dissemination of research findings. Leading institutions, including Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center and Sungkyunkwan University School of Medicine, are instrumental in advancing the field. This study highlights the importance of international collaboration and the contribution of different document types to enriching breast cancer research. Future research should focus on emerging technologies, such as the impact of new diagnostic technologies and personalized medicine, to continue to improve patient outcomes. These 282 findings provide a fundamental understanding of the breast cancer research landscape, guide future investigations, and allocate resources to areas with the greatest potential for scientific and clinical progress.
References
- Dhawle, G.U.; Hase, V.L.; Dahibhate, N.B. Reference and information services in the digital era. Asian Journal of Multidisciplinary Studies 2014, 2, 18–25. [CrossRef]
- Ansari, S.; Yamaoka, Y. Helicobacter pylori infection, its laboratory diagnosis, and antimicrobial resistance: a perspective of clinical relevance. Clin. Microbiol. Rev 2022, 35, 25821–25821. [CrossRef]
- Ke, Y.; Tan, C.; Zhen, J.; Dong, W. Global status and trends of gastric cancer and gastric microbiota research: a bibliometric analysis. Frontiers in Microbiology 2024, 15, 1341012–1341012.
- Jamatia, K.; Gayan, M.A. A Scientometrics analysis of Ovarian Cancer Research during 2010 to 2019: with special reference to South Asian contribution. Library Philosophy and Practice 2021, pp. 5271–5271.
- Naseer, A.; Ali, S.M.; Ahmad.; I. Research Visualization of Different Treatment Modalities to Treat COVID-19 Infection: Bibliometric Analysis of PubMed Database. Library Philosophy and Practice 2021, pp. 5891–5891.
- Zhang, H.; Chen, Y.; Jiang, X.; Gu, Q.; Yao, J.; Wang, X.; Wu, J. Unveiling the landscape of cytokine research in glioma immunotherapy: a scientometrics analysis. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2024, 14, 1333124–1333124. [CrossRef]
- Viswanathan, V.; Govindarajan, R.; Yugapriya, S., 2020.
- Kulkarni, S. Reading Club: An Alternative Framework for Academic Enhancement. International Journal of Advance and Applied Research 2022, 10, 22–22.
- Hase, V.; Ahirarao, M. Scientific Productivity of KavayitriBahinabai Chaudhari North Maharashtra University,(KBCNMU) Jalgaon (India) A Scientometric Analysis. DOGO RANGSANG 2022, 12, 179–179.
- Hase, V.L.; Gaikwad, M.N.; Jadhav, Y.G. Online Databases Backbone for Teaching and Research. In Proceedings of the Library Philosophy and Practice, 2021.
- Rezaee-Zavareh, M.S.; Kim, N.; Yeo, Y.H.; Kim, H.; Lee, J.M.; Sirlin, C.B.; Yang, ..; D, J. Artificial intelligence in liver cancer research: a scientometrics analysis of trends and topics. Frontiers in Oncology 2024, 14, 1355454–1355454.
- Hase, V.; Gaikwad, M. Research Productivity of Rajarambapu Institute of Technology.Journal of Engineering Education Transformations 2024, 38. [CrossRef]
- Lin, X.; Yang, Q.; Zheng, D.; Tian, H.; Chen, L.; Wu, J.; Li, ..; Z. Scientometric analysis of lipid metabolism in breast neoplasm. Frontiers in Physiology 2023, 14, 2012–2021.
- Fan, X.; Qin, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, Z.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, J. Screening for gastric cancer in China: advances, challenges and visions. Chin. Journal of Cancer Research 2021, 33, 168–180. [CrossRef]
- Gupta, B.M.; Bala, A.; Kaur, H. Mapping of AIDS/HIV research in India: a scientometrics analysis of publications output during 1999-2008. Collnet Journal of Scientometrics and Information Management 2011, 5, 185–203. [CrossRef]
- Jhamb, G.; Verma, S. Research Output of Advanced Centre for Treatment, Research and Education in Cancer. A Scientometrics Analysis. IME Journal 2003, 14, 37–43. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).