Submitted:
18 September 2024
Posted:
19 September 2024
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
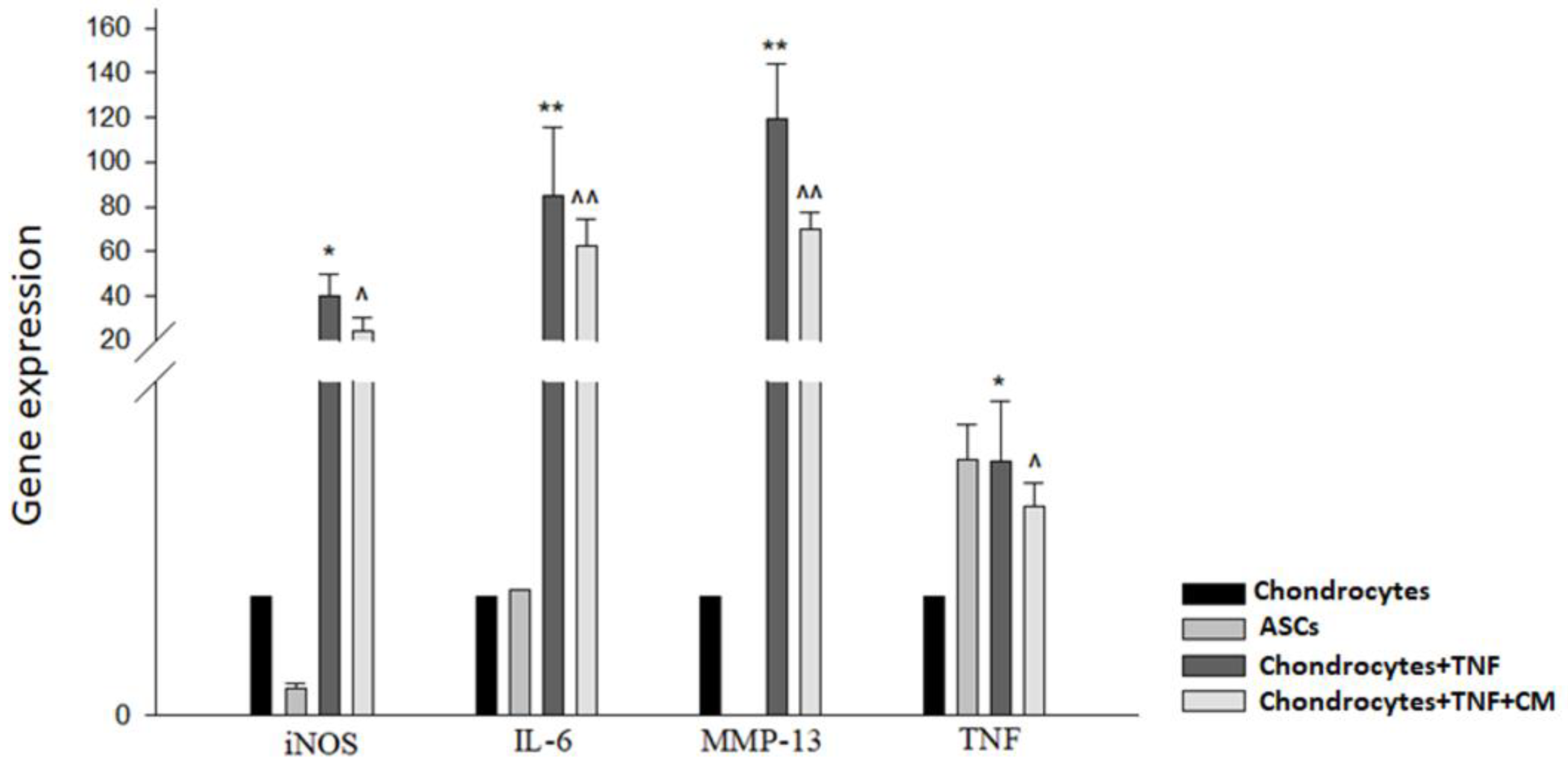
2.1. ASC-Derived Secretome Downregulates the Expression of iNOS, IL-6, MMP-13, and TNF
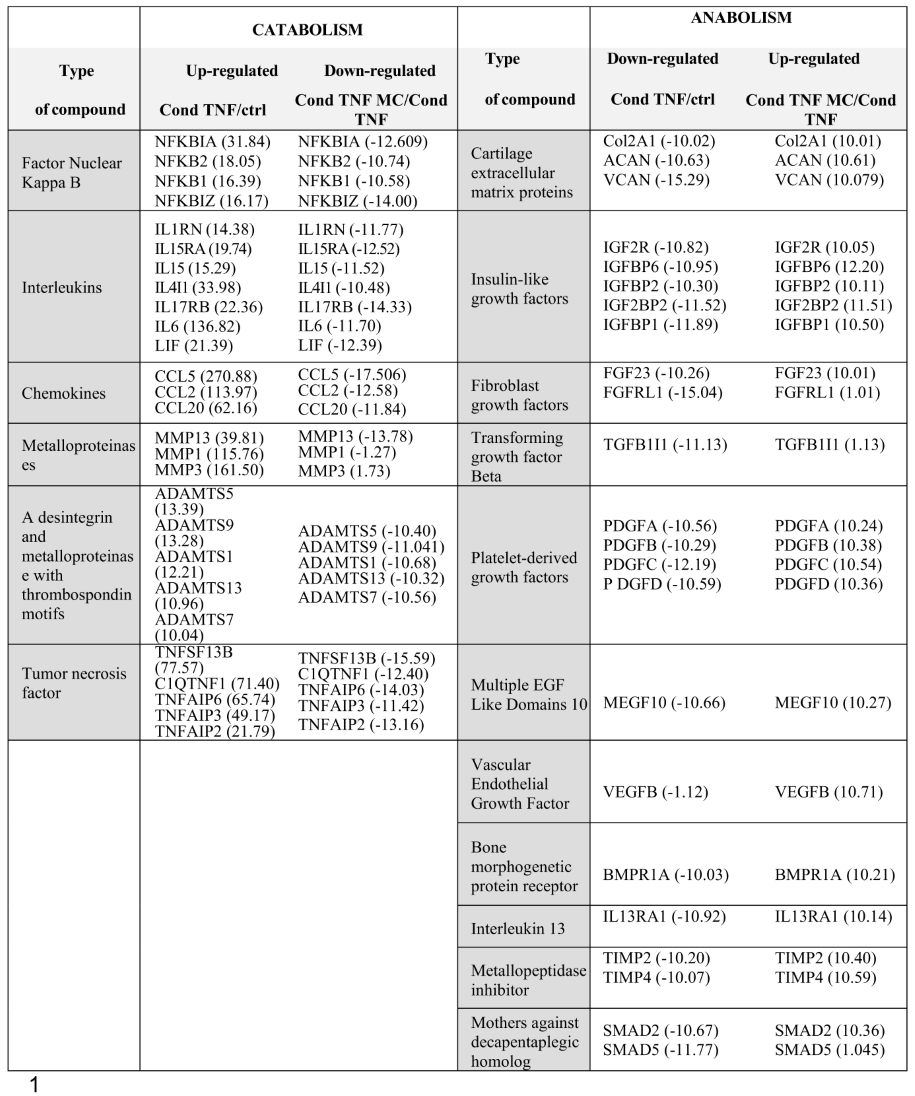
2.2. ASC-Derived Secretome Induces Downregulation of Catabolic Markers and Upregulation of Anabolic Markers
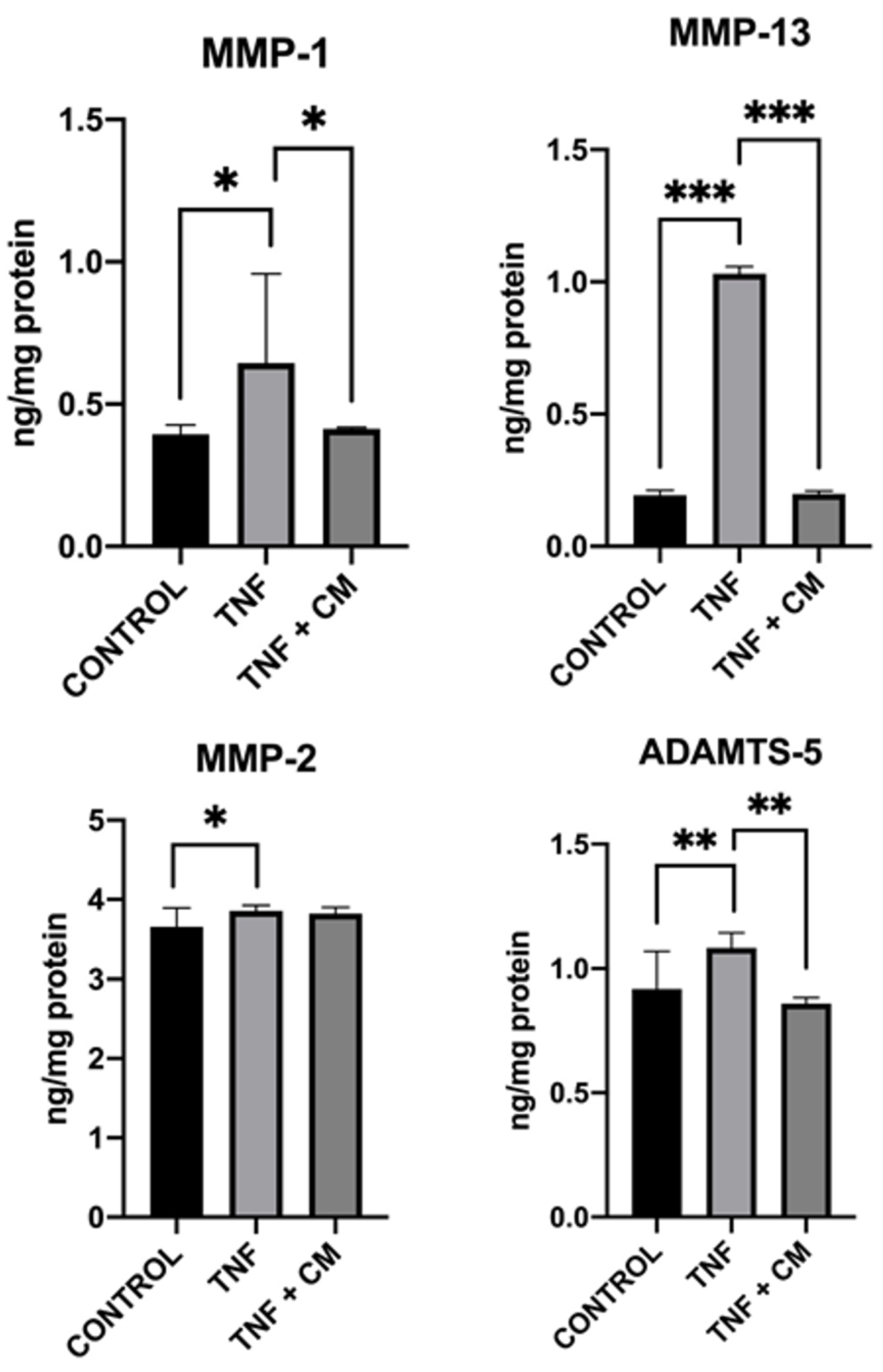
2.3. ASC-Derived Secretome Mitigates TNF-Induced MMP and ADAMTS-5 Activity
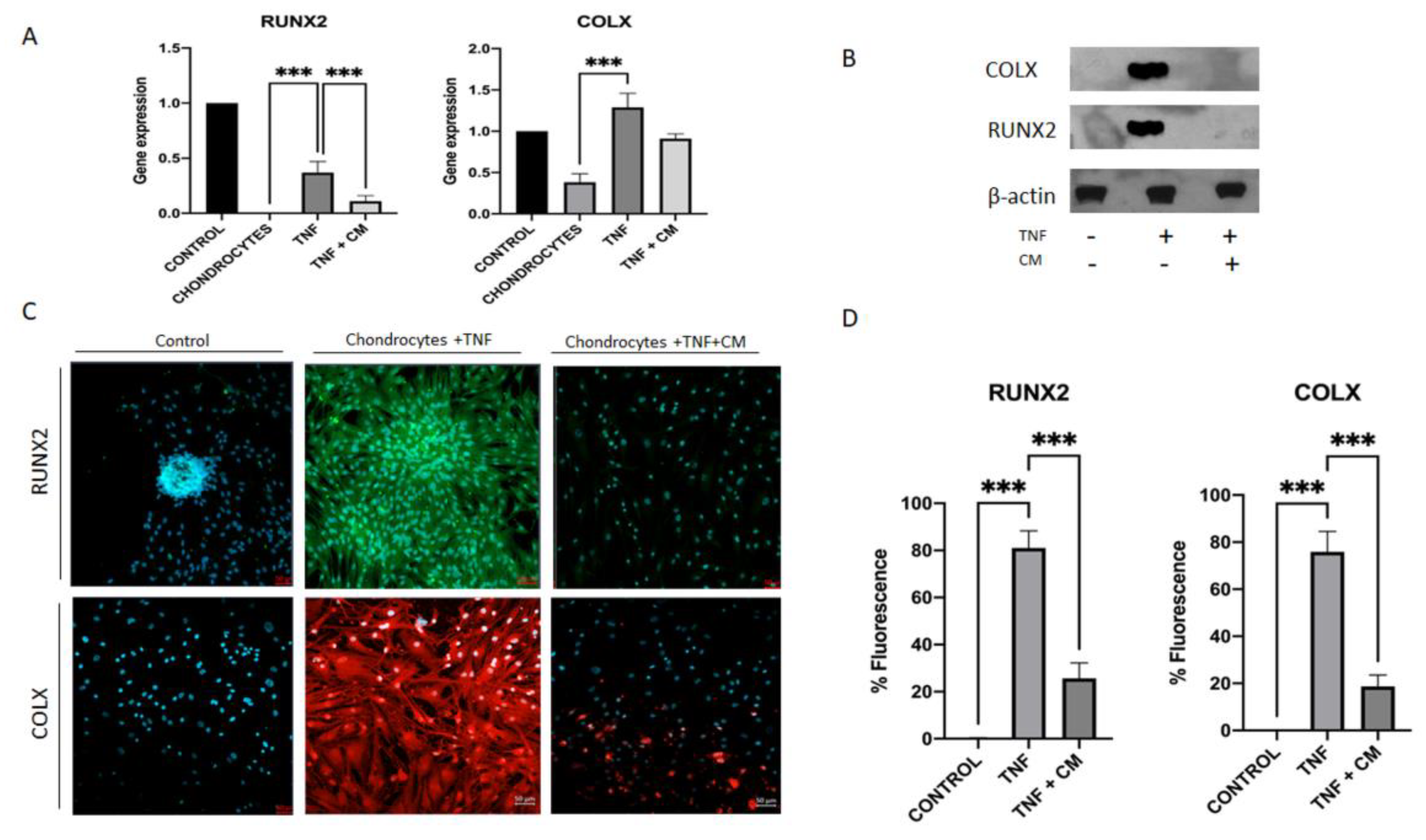
2.4. ASC-Derived Secretome Significantly Reduces Levels of Hypertrophy Markers in Inflamed Chondrocytes
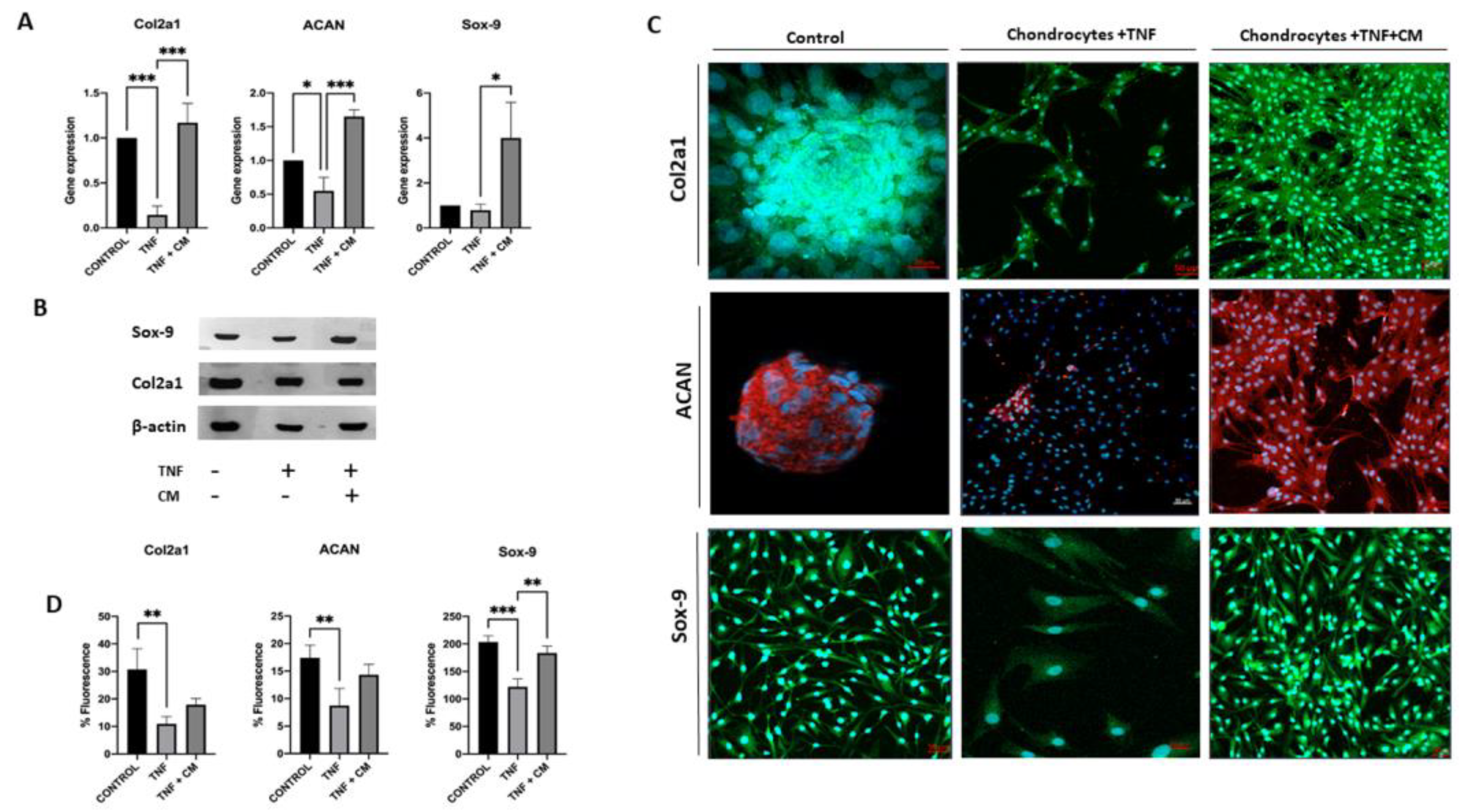
2.5. ASC-Derived Secretome Increases the Expression of Sox-9, Col2a1 and ACAN in TNF-Inflamed Chondrocytes
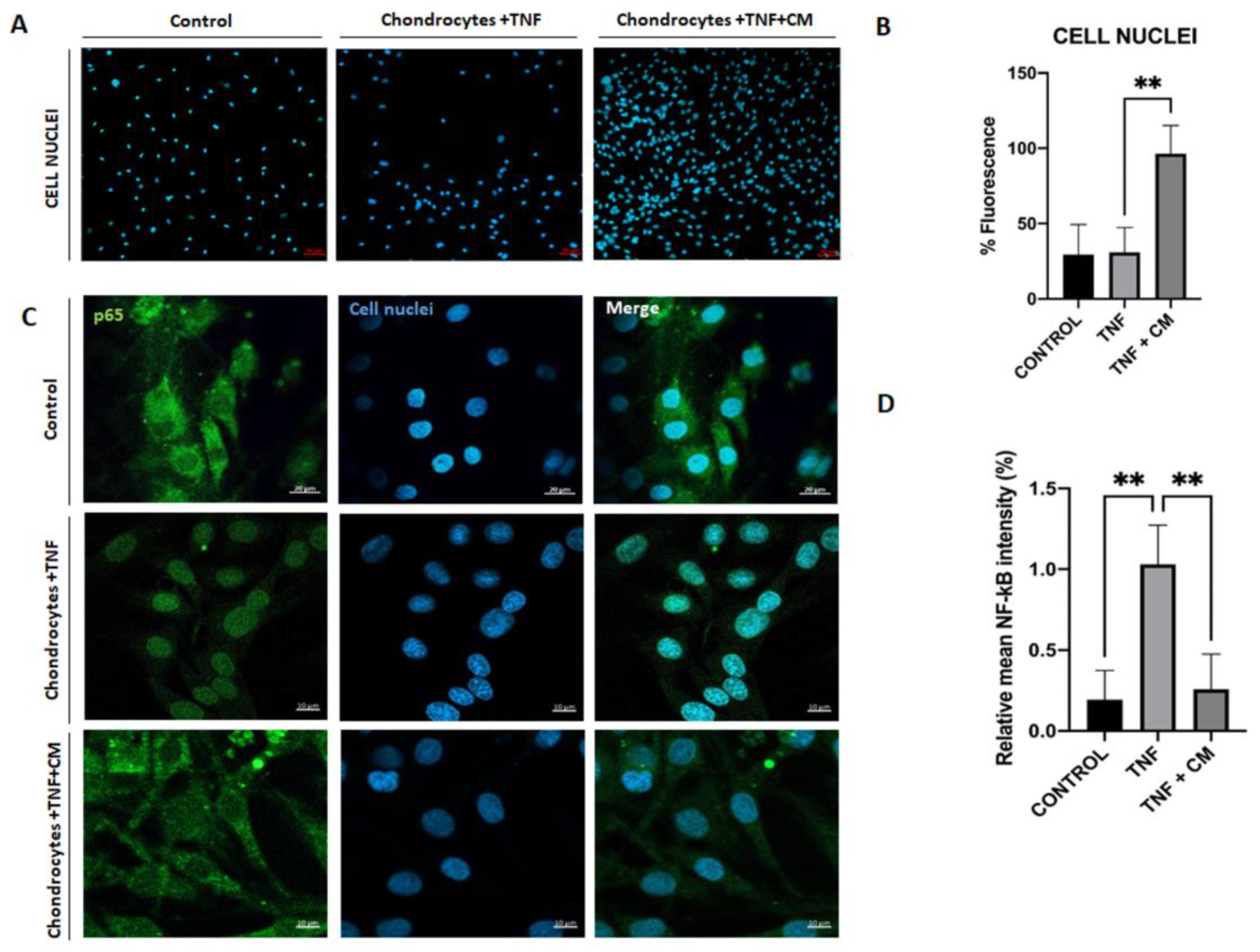
2.6. ASC-Derived Secretome Increases Chondrocyte Proliferation
2.7. ASC-Derived CM Inhibits NF-κB Translocation
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Biological Material
4.1.1. ASC and Chondrocyte Cultivation
4.2. Secretome or Conditioned Medium (CM) Collection
4.3. In-Vitro Model of Chondrocyte Inflammation
- Group 1 (non-inflamed chondrocytes): chondrocytes cultured in a mix of serum-free DMEM and 1% penicillin/streptomycin.
- Group 2 (ASC control samples): ASCs cultured in a mix of serum-free DMEM and 1% penicillin/streptomycin.
- Group 3 (TNF-inflamed chondrocytes): chondrocytes cultured in a mix of serum-free DMEM and 1% penicillin/streptomycin plus TNF (25 ng/mL).
- Group 4 (CM-treated TNF-inflamed chondrocytes): chondrocytes were treated with TNF (25 ng/mL) and conditioned medium-CM (50 μg/mL).
4.4.1. Quantitative Real-Time PCR (qPCR)
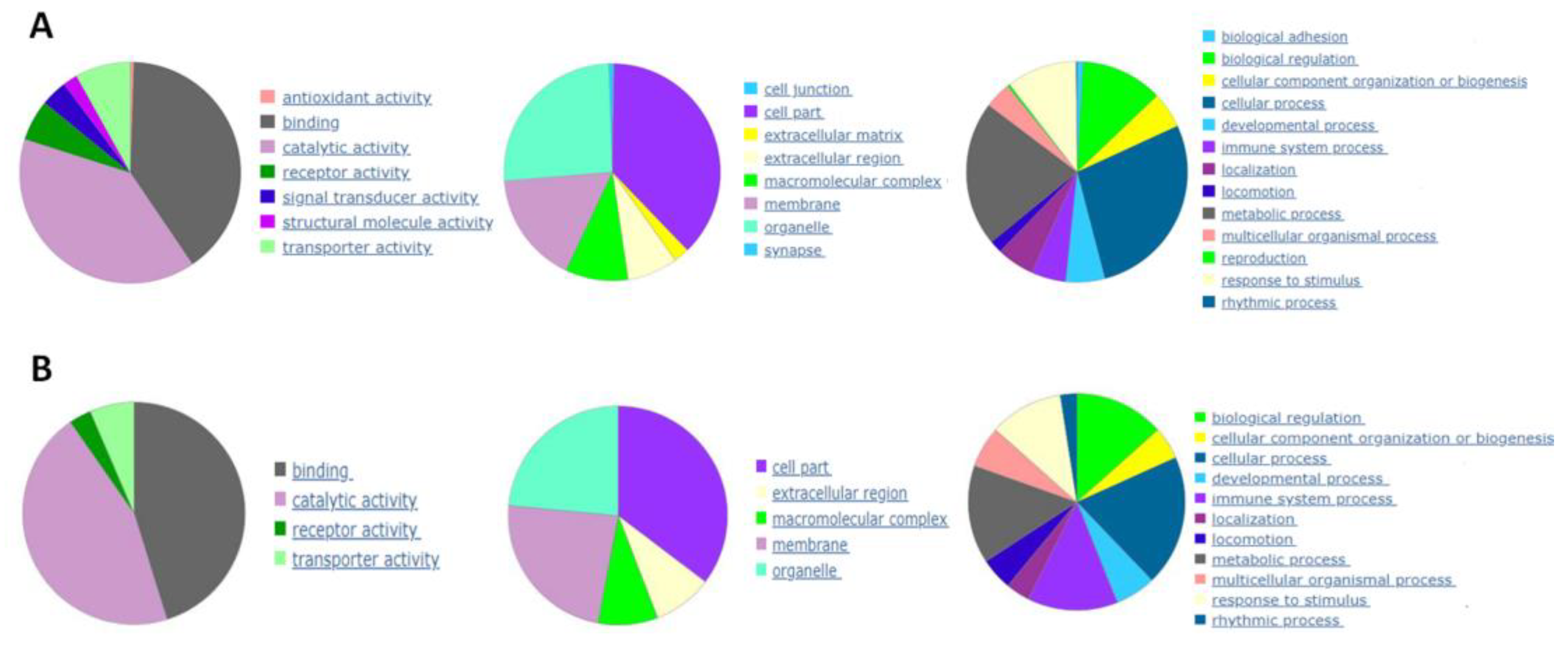
4.4.2. Microarray
4.5. Nuclear Factor Kappa B (NF-κB) Activity Assay
4.6. Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay (ELISA)
4.7. Protein Analysis
4.7.1. Total Protein Extraction and Quantification
4.7.2. Western Blotting Analysis
4.7.3. Confocal Microscopy
4.8. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cui, A.; Li, H.; Wang, D.; Zhong, J.; Chen, Y.; Lu, H. Global, Regional Prevalence, Incidence and Risk Factors of Knee Osteoarthritis in Population-Based Studies. EClinicalMedicine 2020, 29–30, 100587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Funck-Brentano, T.; Cohen-Solal, M. Subchondral Bone and Osteoarthritis. Curr. Opin. Rheumatol. 2015, 27, 420–426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, J.C.; Martel-Pelletier, J.; Pelletier, J.-P. The Role of Cytokines in Osteoarthritis Pathophysiology. Biorheology 2002, 39, 237–246. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tetlow, L.C.; Adlam, D.J.; Woolley, D.E. Matrix Metalloproteinase and Proinflammatory Cytokine Production by Chondrocytes of Human Osteoarthritic Cartilage: Associations with Degenerative Changes. Arthritis Rheum. 2001, 44, 585–594. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.; Ji, Q.; Wang, X.; Kang, L.; Fu, Y.; Yin, Y.; Li, Z.; Liu, Y.; Xu, X.; Wang, Y. SOX9 Is a Regulator of ADAMTSs-Induced Cartilage Degeneration at the Early Stage of Human Osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr. Cartil. 2015, 23, 2259–2268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mengshol, J.A.; Vincenti, M.P.; Coon, C.I.; Barchowsky, A.; Brinckerhoff, C.E. Interleukin-1 Induction of Collagenase 3 (Matrix Metalloproteinase 13) Gene Expression in Chondrocytes Requires P38, c-Jun N-Terminal Kinase, and Nuclear Factor ΚB: Differential Regulation of Collagenase 1 and Collagenase 3. Arthritis Rheum. 2000, 43, 801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldring, S.R.; Goldring, M.B. Bone and Cartilage in Osteoarthritis: Is What’s Best for One Good or Bad for the Other? Arthritis Res. Ther. 2010, 12, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Phillips KL, Chiverton N, Michael AL, Cole AA, Breakwell LM, Haddock G, Bunning RA, Cross AK, L. M.C. The Cytokine and Chemokine Expression Profile of Nucleus Pulposus Cells: Implications for Degeneration and Regeneration of the Intervertebral Disc. Biomaterials 2006, 12, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Attur, M.G.; Patel, I.R.; Patel, R.N.; Abramson, S.B.; Amin, A.R. Autocrine Production of IL-1 Beta by Human Osteoarthritis-Affected Cartilage and Differential Regulation of Endogenous Nitric Oxide, IL-6, Prostaglandin E2, and IL-8. Proc. Assoc. Am. Physicians 110, 65–72.
- Clancy, R.M.; Amin, A.R.; Abramson, S.B. The Role of Nitric Oxide in Inflammation and Immunity. Arthritis Rheum. 1998, 41, 1141–1151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawasaki, Y.; Xu, Z.Z.; Wang, X.; Park, J.Y.; Zhuang, Z.Y.; Tan, P.H.; Gao, Y.J.; Roy, K.; Corfas, G.; Lo, E.H.; et al. Distinct Roles of Matrix Metalloproteases in the Early- and Late-Phase Development of Neuropathic Pain. Nat. Med. 2008, 14, 331–336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Orozco, L.; Munar, A.; Soler, R.; Alberca, M.; Soler, F.; Huguet, M.; Sentís, J.; Sánchez, A.; García-Sancho, J. Treatment of Knee Osteoarthritis With Autologous Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Transplant. J. 2013, 95, 1535–1541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kristjánsson, B.; Honsawek, S. Current Perspectives in Mesenchymal Stem Cell Therapies for Osteoarthritis. Stem Cells Int. 2014, 2014, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jung, Y.; Bauer, G.; Nolta, J.A. Concise Review: Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells: Progress toward Safe Clinical Products. Stem Cells 2012, 30, 42–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- L., P.K.; Kandoi, S.; Misra, R.; S., V.; K., R.; Verma, R.S. The Mesenchymal Stem Cell Secretome: A New Paradigm towards Cell-Free Therapeutic Mode in Regenerative Medicine. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2019, 46, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lavoie, J.R.; Rosu-Myles, M. Uncovering the Secretes of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Biochimie 2013, 95, 2212–2221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pawitan, J.A. Prospect of Stem Cell Conditioned Medium in Regenerative Medicine. Biomed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 965849. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- JM, W.; GK, S. LimmaGUI: A Graphical User Interface for Linear Modeling of Microarray Data. Bioinformatics 2004, 20, 3705–3706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- RC, G.; VJ, C.; DM, B.; B, B.; M, D.; S, D.; B, E.; L, G.; Y, G.; J, G.; et al. Bioconductor: Open Software Development for Computational Biology and Bioinformatics. Genome Biol. 2004, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- P, D.; WA, K.; SM, L. Lumi: A Pipeline for Processing Illumina Microarray. Bioinformatics 2008, 24, 1547–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the False Discovery Rate: A Practical and Powerful Approach to Multiple Testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- M, A.; CA, B.; JA, B.; D, B.; H, B.; JM, C.; AP, D.; K, D.; SS, D.; JT, E.; et al. Gene Ontology: Tool for the Unification of Biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liu, D.; Tadum, D.; Vithran, A.; Kwabena, B.R. CC Chemokines and Receptors in Osteoarthritis : New Insights and Potential Targets. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2023, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, M.; Sampson, E.R.; Jin, H.; Li, J.; Ke, Q.H.; Im, H.-J.; Chen, D. MMP13 Is a Critical Target Gene during the Progression of Osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, R5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Davidson, R.K.; Waters, J.G.; Kevorkian, L.; Darrah, C.; Cooper, A.; Donell, S.T.; Clark, I.M. Expression Profiling of Metalloproteinases and Their Inhibitors in Synovium and Cartilage. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2006, 8, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Huang, X.; Karperien, M.; Post, J.N. The Regulatory Role of Signaling Crosstalk in Hypertrophy of MSCs and Human Articular Chondrocytes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 19225–19247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’arrigo, D.; Roffi, A.; Cucchiarini, M.; Moretti, M.; Candrian, C.; Filardo, G. Secretome and Extracellular Vesicles as New Biological Therapies for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Liang, X.; Liao, S.; Wang, W.; Wang, J.; Li, X.; Ding, Y.; Liang, Y.; Gao, F.; Yang, M.; et al. Potent Paracrine Effects of Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Attenuate Doxorubicin-Induced Cardiomyopathy. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 11235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wojdasiewicz, P.; Poniatowski, Ł.A.; Szukiewicz, D. The Role of Inflammatory and Anti-Inflammatory Cytokines in the Pathogenesis of Osteoarthritis. Mediators Inflamm. 2014, 2014, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Gao, S.-G.; Zhang, F.-J.; Luo, W.; Xue, J.-X.; Lei, G.-H. Effects of Osteopontin on the Expression of IL-6 and IL-8 Inflammatory Factors in Human Knee Osteoarthritis Chondrocytes. Eur. Rev. Med. Pharmacol. Sci. 2014, 18, 3580–3586. [Google Scholar]
- Porée, B.; Kypriotou, M.; Chadjichristos, C.; Beauchef, G.; Renard, E.; Legendre, F.; Melin, M.; Gueret, S.; Hartmann, D.J.; Malléin-Gerin, F.; et al. Interleukin-6 (IL-6) and/or Soluble IL-6 Receptor down-Regulation of Human Type II Collagen Gene Expression in Articular Chondrocytes Requires a Decrease of Sp1. Sp3 Ratio and of the Binding Activity of Both Factors to the COL2A1 Promoter. J. Biol. Chem. 2008, 283, 4850–4865. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The Pro- and Anti-Inflammatory Properties of the Cytokine Interleukin-6; 2011; Vol. 1813, pp. 878–888;
- Gabay, C.; Lamacchia, C.; Palmer, G. IL-1 Pathways in Inflammation and Human Diseases. Nat. Rev. Rheumatol. 2010, 6, 232–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogerson, F.M.; Chung, Y.M.; Deutscher, M.E.; Last, K.; Fosang, A.J. Cytokine-Induced Increases in ADAMTS-4 Messenger RNA Expression Do Not Lead to Increased Aggrecanase Activity in ADAMTS-5-Deficient Mice. Arthritis Rheum. 2010, 62, 3365–3373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlos Rodrı́guez-Manzaneque, J.; Westling, J.; Thai, S.N.-M.; Luque, A.; Knauper, V.; Murphy, G.; Sandy, J.D.; Iruela-Arispe, M.L. ADAMTS1 Cleaves Aggrecan at Multiple Sites and Is Differentially Inhibited by Metalloproteinase Inhibitors. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2002, 293, 501–508. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Camassola, M.; de Macedo Braga, L.M.G.; Chagastelles, P.C.; Nardi, N.B. Methodology, Biology and Clinical Applications of Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells. In Methods in molecular biology (Clifton, N.J.); 2012; Vol. 879, pp. 491–504.
- Lozito, T.P.; Jackson, W.M.; Nesti, L.J.; Tuan, R.S. Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells Generate a Distinct Pericellular Zone of MMP Activities via Binding of MMPs and Secretion of High Levels of TIMPs. Matrix Biol. 2014, 34, 132–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawston, T. Matrix Metalloproteinases and TIMPs: Properties and Implications for the Rheumatic Diseases. Mol. Med. Today 1998, 4, 130–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cawston, T.E.; Wilson, A.J. Understanding the Role of Tissue Degrading Enzymes and Their Inhibitors in Development and Disease. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Rheumatol. 2006, 20, 983–1002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rigoglou, S.; Papavassiliou, A.G. The NF-ΚB Signalling Pathway in Osteoarthritis. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2013, 45, 2580–2584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Liu, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, Q.; Liu, T.; Li, J. Mesenchymal Stem Cells-Derived Exosomes for Drug Delivery. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2021 121 2021, 12, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruderer, M.; Richards, R.G.; Alini, M.; Stoddart, M.J. Role and Regulation of Runx2 in Osteogenesis. Eur. Cells Mater. 2014, 28, 269–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haag, J.; Gebhard, P.M.; Aigner, T. SOX Gene Expression in Human Osteoarthritic Cartilage. Pathobiology 2008, 75, 195–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mariani, E.; Pulsatelli, L.; Facchini, A. Signaling Pathways in Cartilage Repair. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2014, 15, 8667–8698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishimura, R.; Hata, K.; Takahata, Y.; Murakami, T.; Nakamura, E.; Yagi, H. Regulation of Cartilage Development and Diseases by Transcription Factors. J. bone Metab. 2017, 24, 147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Huang, X.; Karperien, M.; Post, J.N.; Malemud, C.J.; Mobasheri, A. The Regulatory Role of Signaling Crosstalk in Hypertrophy of MSCs and Human Articular Chondrocytes. OPEN ACCESS Int. J. Mol. Sci 2015, 16, 19226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niada, S.; Giannasi, C.; Gomarasca, M.; Stanco, D.; Casati, S.; Brini, A.T. Adipose-Derived Stromal Cell Secretome Reduces TNFα-Induced Hypertrophy and Catabolic Markers in Primary Human Articular Chondrocytes. Stem Cell Res. 2019, 38, 101463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platas, J.; Guillén, M.I.; Del Caz, M.D.P.; Gomar, F.; Mirabet, V.; Alcaraz, M.J. Conditioned Media from Adipose-Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells Downregulate Degradative Mediators Induced by Interleukin-1 β in Osteoarthritic Chondrocytes. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casagrande, D.; Stains, J.P.; Murthi, A.M. Identification of Shoulder Osteoarthritis Biomarkers: Comparison between Shoulders with and without Osteoarthritis. J. shoulder Elb. Surg. 2015, 24, 382–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
 |
| Gen | NCBI RefSeq |
Forward/Reverse (5’-3’) | Tª melting ºC | Product size (bp) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ACT-β | NM_001101.3 | CCCTCCATCGTCCACCGCAAATGCT CTGCTGTCACCTTCACCGTTCCAGT |
59.7 58.0 |
131 |
| IL-6 | NM_000600.3 | ATAACCACCCCTGACCCAA CCATGCTACATTTGCCGAA |
74.4 72.5 |
169 |
| iNOS | NM_000625.4 | AACGTTGCTCCCCATCAAGCCCTT AGCAGCAAGTTCCATCTTTCACCCACT |
54.2 54.1 |
130 |
| MMP-13 | NM_002427.3 | CCAGAACTTCCCAACCGTATTGATGC TGCCTGTATCCTCAAAGTGAACAGC |
72.3 69.1 |
145 |
| TNF | NM_000594.3 | CCTGAAAACAACCCTCAGACGCCACA TCCTCGGCCAGCTCCACGTCCC |
77.9 79.3 |
155 |
| RUNX2 | NM_001024630.3 | AAGCTTGATGACTCTAAACC TCTGTAATCTGACTCTGTCC |
55.1 54.0 |
164 |
| COLX | NM_000006.12 | GCTAGTATCCTTGAACTTGG CCTTTACTCTTTATGGTGTAGG |
55.5 56.1 |
129 |
| Sox-9 | NM_000346.4 | AGTTTTGGGGGTTAACTTTG AAGCTTACCAAATGCTTCTC |
59.4 57.7 |
132 |
| ACAN | NM_001369268.1 | CTGCCCAACTACCCGGCCAT TGCGCCCTGTCAAAGTCGAG |
72.1 71.0 |
200 |
| Col2a1 | NM_001844.5 | CCCATCTGCCCAACTGACC CACCTTTGTCACCACGATCCC |
58.5 58.2 |
166 |
| Target protein | Dilution | Company |
|---|---|---|
| β-Actin | 1:5,000 | Merck® |
| Sox-9 | 1:1,000 | Cell Signaling® |
| RUNX2 | 1:1,000 | Cell Signaling® |
| Col2a1 | 1:1,000 | Cell Signaling® |
| COLX | 1:1,000 | Santa Cruz Biotechnology® |
| ACAN | 1:1,000 | Cell Signaling® |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





